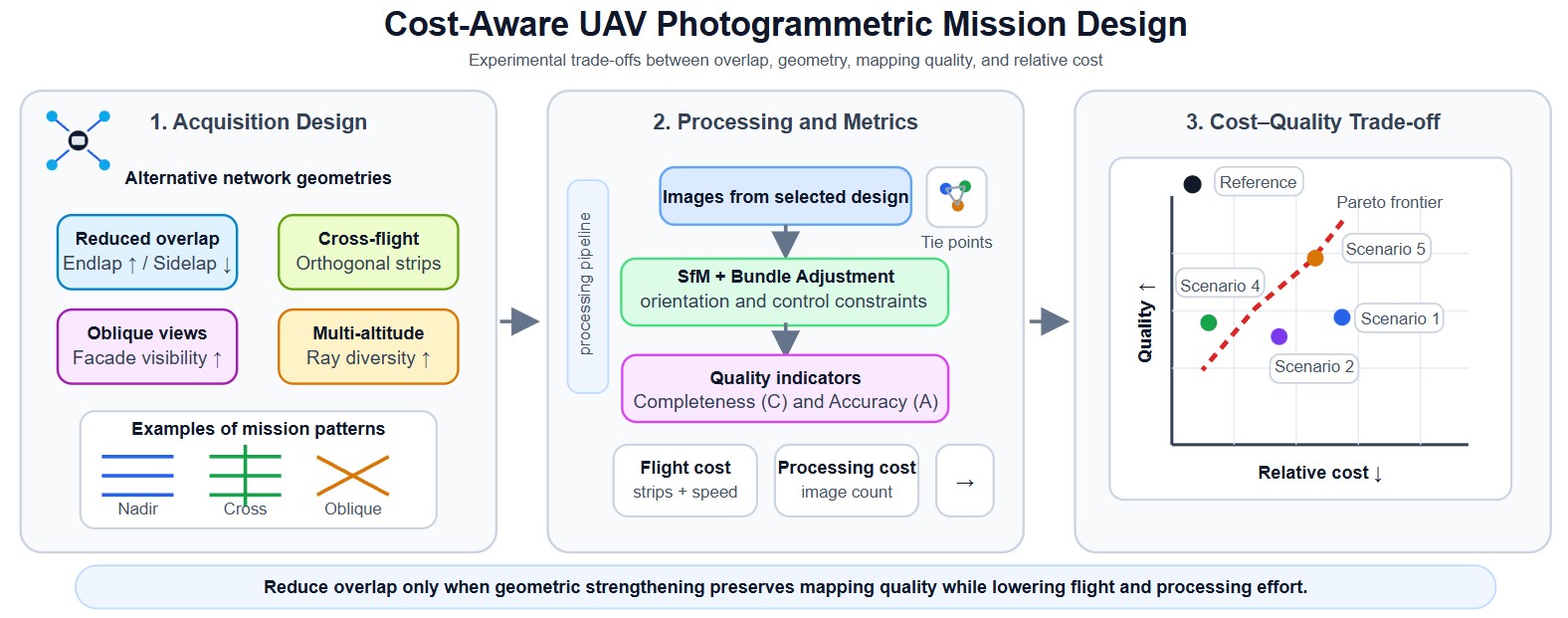
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) photogrammetry enables high-resolution mapping and 3D reconstruction, yet operational and processing costs often scale rapidly with conservative mission designs (e.g., high overlap and redundant geometries). This paper presents an experimentally validated, cost-aware network-design study that quantifies cost–quality trade-offs in urban UAV photogrammetry. Five mission strategies—reduced sidelap with increased endlap, cross-flight compensation, partial high-overlap calibration, multi-altitude acquisition, and oblique cross-flight integration—are evaluated using a controlled experimental campaign over two urban test areas (2 × 20 ha), comprising 98 test blocks with overlaps ranging from 60% to 95%, sidelap from 20% to 80%, image counts from 70 to 2961, 7 check points, 15–17 ground control points, and GSD values between 2.6 cm and 4.6 cm, including nadir, oblique, cross-flight, and multi-altitude imagery. Each configuration is assessed using three indicators: (i) cost (flight and processing cost proxies), (ii) completeness, quantified by the number of reconstructed tie points, and (iii) accuracy, defined as a combined image–ground error at check points. Results show that cost reductions of over 50% in both flight and processing proxies can be achieved under the tested conditions while maintaining checkpoint accuracy comparable to a high-overlap reference configuration, provided that reduced overlap is compensated by stronger network geometry (e.g., cross-flight and/or oblique views). The analysis highlights product-dependent recommendations: vector map (MAP) generation can remain reliable even with very low sidelap (down to approximately 20%) when supported by adequate longitudinal overlap, whereas ortho-image mosaic (OIM) production requires at least moderate overlap in both directions (typically ≥60% endlap and sidelap) to ensure radiometric and geometric consistency. In contrast, dense 3D mesh reconstruction demands substantially stronger network geometry, including cross-flight and oblique imagery in addition to nadir views, with overlap levels exceeding 60% and preferably approaching 80%. These findings provide practical mission-planning guidelines that support efficient autonomous and semi-autonomous UAV mapping workflows.
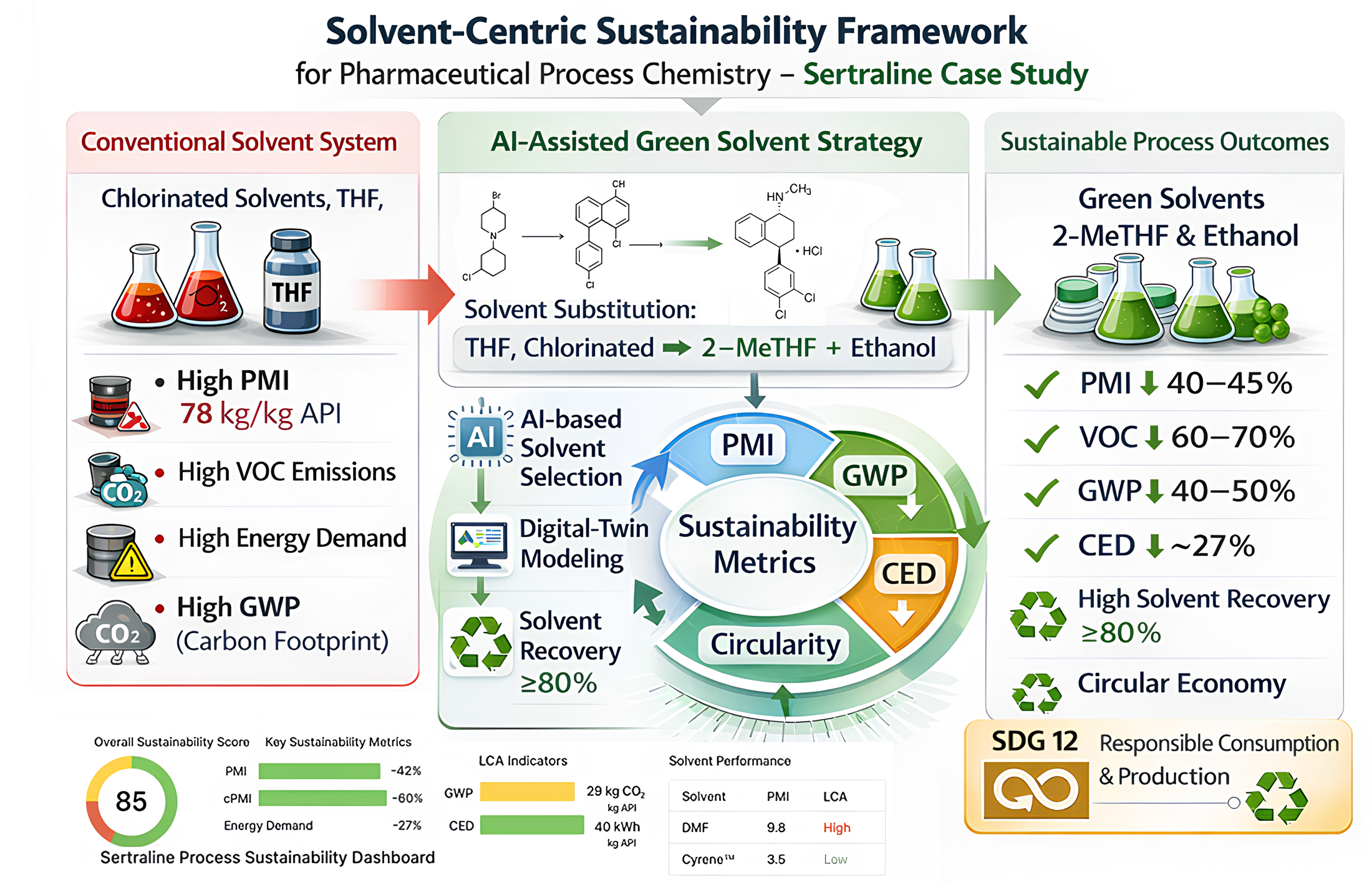
Solvents dominate mass input, energy demand, and environmental impact in pharmaceutical manufacturing, yet solvent selection and recovery are often evaluated using fragmented or non-comparable metrics. Here, we present a solvent-centric sustainability framework that integrates mass-based indicators with life-cycle and energy metrics to enable transparent comparison of conventional and redesigned solvent systems. The framework harmonizes Process Mass Intensity (PMI), circular PMI (cPMI), Global Warming Potential (GWP), and Cumulative Energy Demand (CED) within consistent cradle-to-gate system boundaries, supported by literature-derived data, machine-learning (ML) models, and digital-twin–based sustainability assessment tools. The methodology is demonstrated using Sertraline as a representative solvent-intensive active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). A simplified, literature-based synthesis route contextualizes solvent use across key reaction and isolation steps. Targeted solvent substitutions—most notably replacement of tetrahydrofuran, chlorinated solvents, and dipolar aprotic media with 2-methyltetrahydrofuran and ethanol-based systems—are evaluated alongside enhanced solvent recovery and catalytic hydrogenation. Relative to the solvent-dominant subsequence of the synthesis (PMI ≈ 78 kg·kg−1 API), for which detailed solvent mass-balance data are available, the redesigned solvent strategy reduces PMI to approximately 45 kg·kg−1 API, achieves a cPMI of 6–10 at ≥80% solvent recovery, and consistently decreases GWP and CED. By explicitly mapping solvent redesign outcomes to the 12 Principles of Green Chemistry, this study demonstrates how solvent-focused interventions, supported by predictive digital tools with excellent agreement between modelled and empirical trends, can deliver substantial sustainability improvements without modifying the underlying synthetic route or relying on proprietary process data. While not intended as an industrial benchmark, the Sertraline case study illustrates how harmonized metrics, life-cycle thinking, and AI-enabled digital assessment can support evidence-based solvent selection and sustainability-oriented process development in API manufacturing.
This study investigates the need for the adoption of modern handloom tools, including jacquard and warping drums, and evaluates their impact on income generation, production efficiency, market reach, and women’s empowerment in rural areas of Udalguri District, Assam. A purposive sampling method was used to survey 50 households in total. The findings reveal that the jacquard and warping drums significantly reduced the time required for weaving, mitigating weather dependence and improving productivity. Consequently, beneficiaries reported increased income, leading to independent entrepreneurship. The marketing strategies employed included direct market linkage through Civil Society Organizations (CSOs), participation, and connection with buyers to expand market access. Types of products included Silk and Cotton, and most of the products were sold in local markets. Training initiatives have been conducted to enhance product quality and design diversity. Weavers, who previously worked with limited designs, have now adopted innovative patterns to boost product demand. The study underscores the pivotal role of CSOs in hand-holding support, development of marketing linkage, tracking systems, and development of community resource persons (CRPs) through cluster-based training programs. The modern handloom tools play a transformative role in enhancing productivity, income, and market access, while simultaneously empowering women and strengthening rural economies.

Elucidation of the mechanism of multielectron transfer reactions, such as photocatalytic water oxidation and oxygen reduction, is essential for achieving high efficiency in the utilization of sustainable solar energy. Herein, we demonstrate that photocatalytic oxygen reduction on platinum-loaded tungsten(VI) oxide (Pt/WO3) photocatalyst proceeds predominantly by two-electron transfer pathway under conventional light-intensity conditions. Light intensity-dependence analyses of the acetic acid decomposition reaction revealed the role of the Pt co-catalyst in enhancing overall quantum efficiency. We also report for the first time that the reaction can be initiated even on bare WO3, in addition to Pt, under extremely high light-intensity conditions.

The paper aims to contribute to planning decisions, policies, strategies, and management of inland areas affected by a protected natural area in the Campania region (Italy). Inland and rural areas, often affected by depopulation and economic decline, can and must be a crucial resource in the ecological transition. At a time when urbanisation is expected to increase, the bioeconomy offers a way to repopulate rural areas, promoting a transition to a more sustainable and inclusive production model and making the best use of the resources already present in the area. A significant example of the circular bioeconomy in action is the Campania region, which has been designated as a hub for a series of European projects currently underway that aim to integrate innovation, sustainability, and social inclusion. In this context, the area chosen is Roccamonfina, a volcanic area that has been inactive for thousands of years, with forests at the top and very fertile foothills. The area, which is part of the province of Caserta, one of the five provinces of the Campania Region (Italy), is characterised by a sparse human presence and by abandonment, in which local communities alone are unable to create conditions for sustainable development. The methodological approach starts from an analysis of the territory and gives priority to landscape, environmental, socio-economic, productive, and cultural characteristics, using a SWOT analysis. This approach aims to define policy scenarios to promote conditions for sustainable development. The results achieved in the study are designed to be scalable to similar areas.