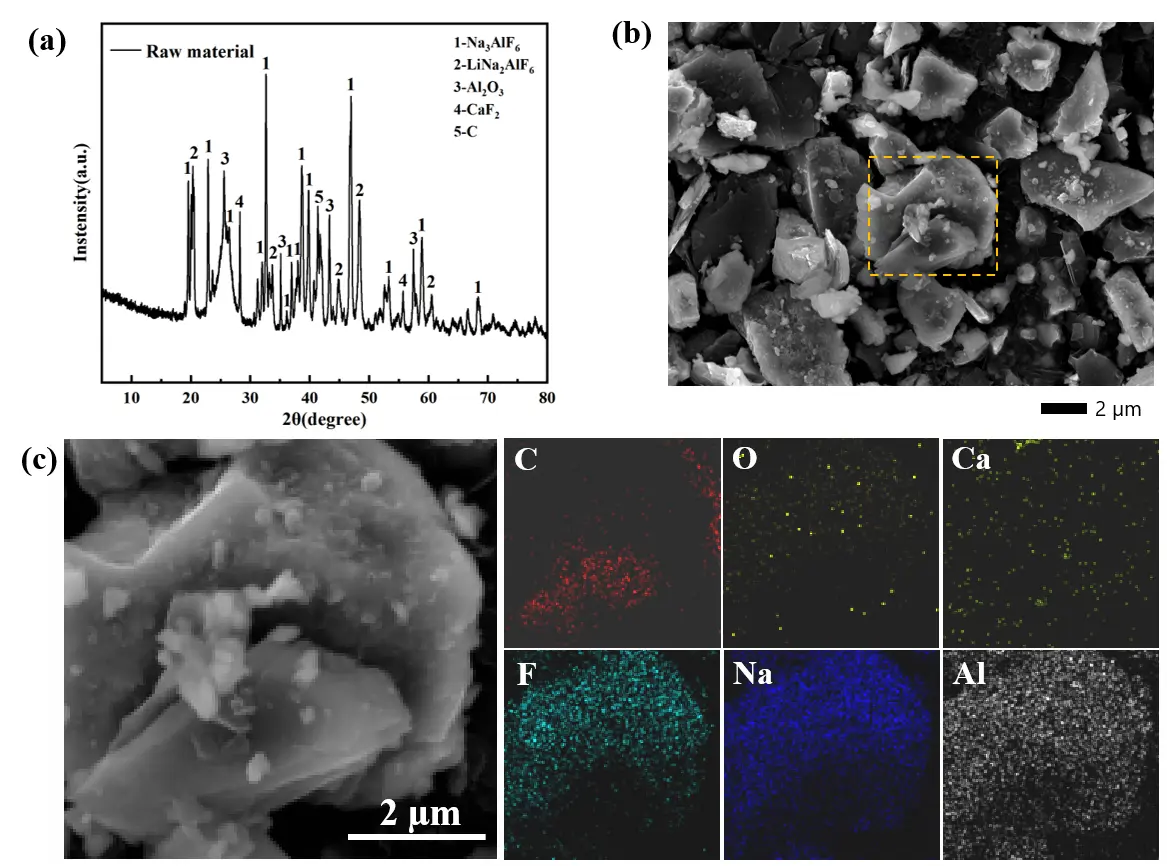
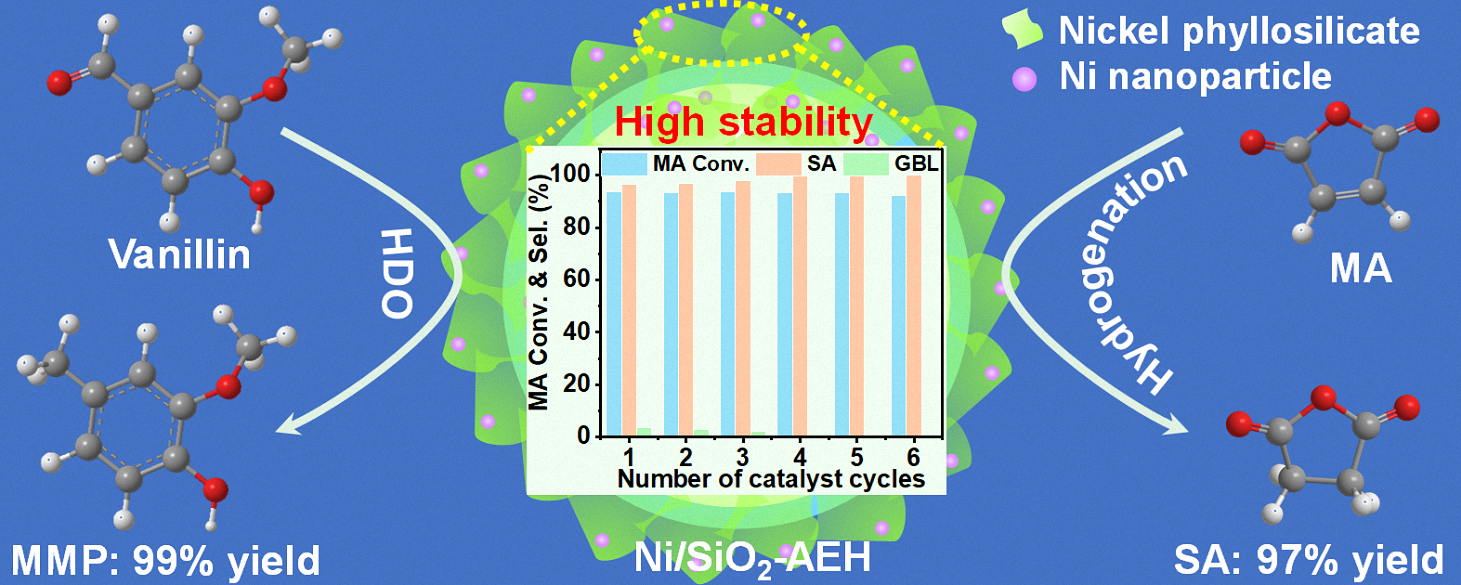
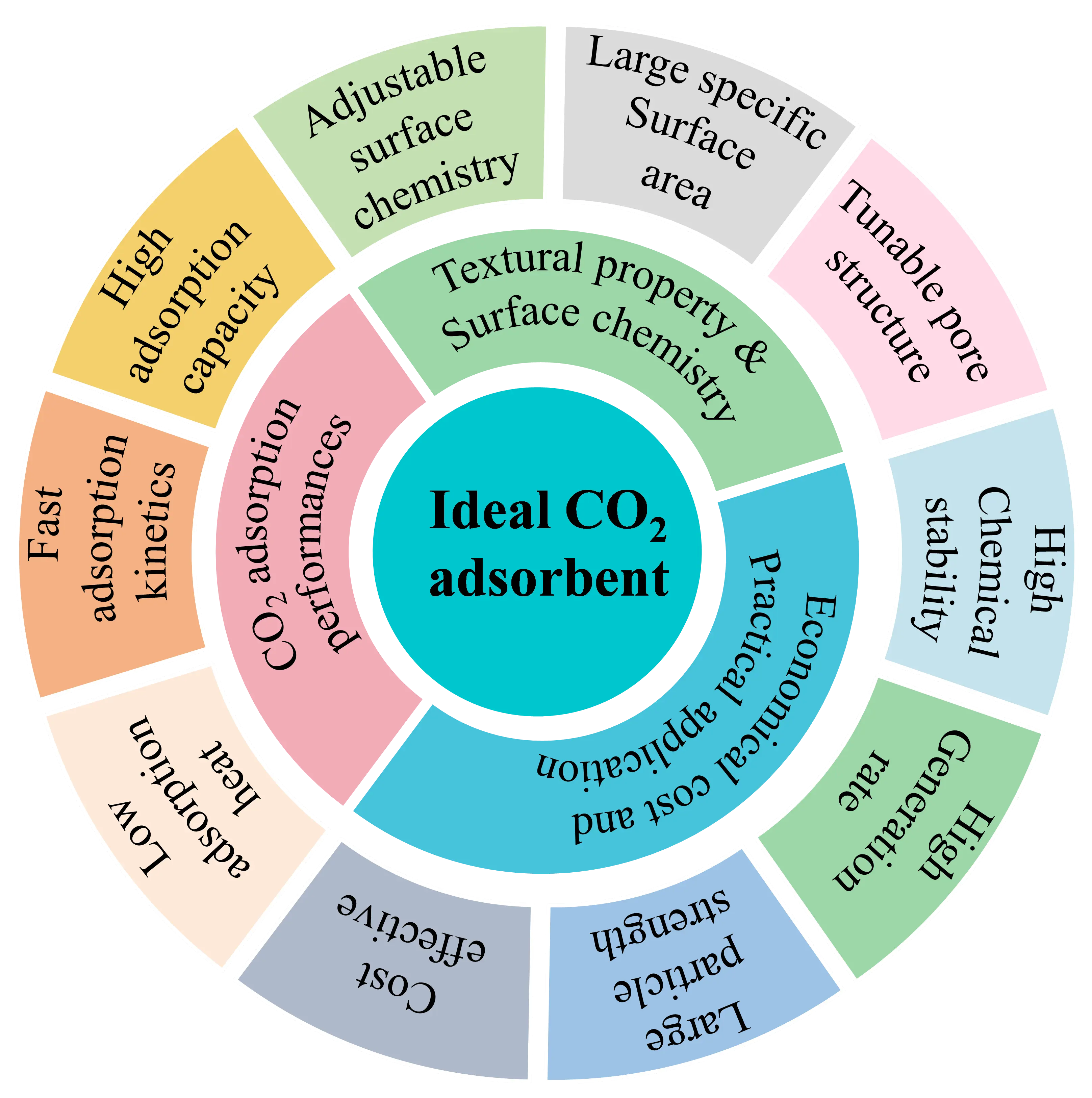
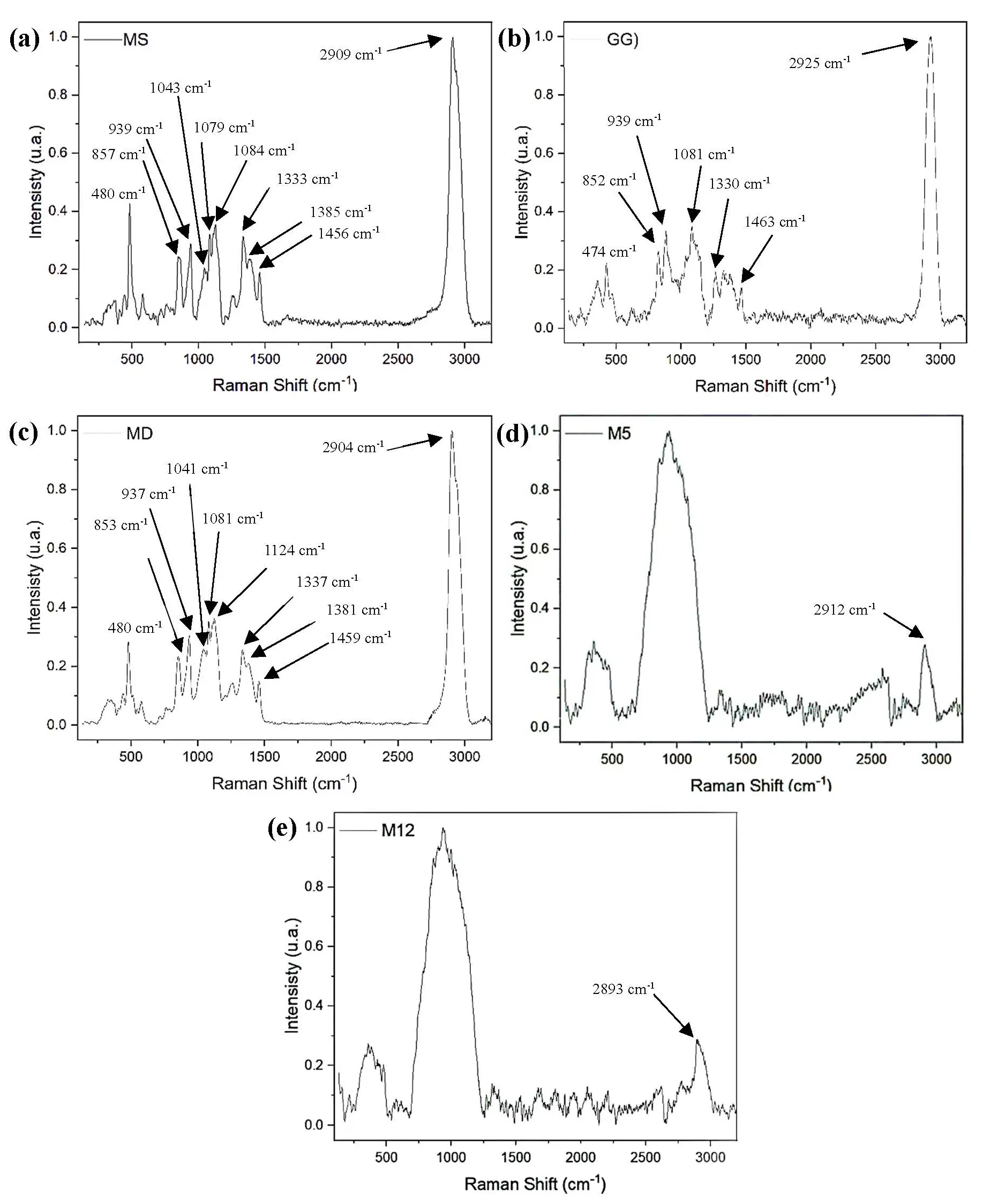
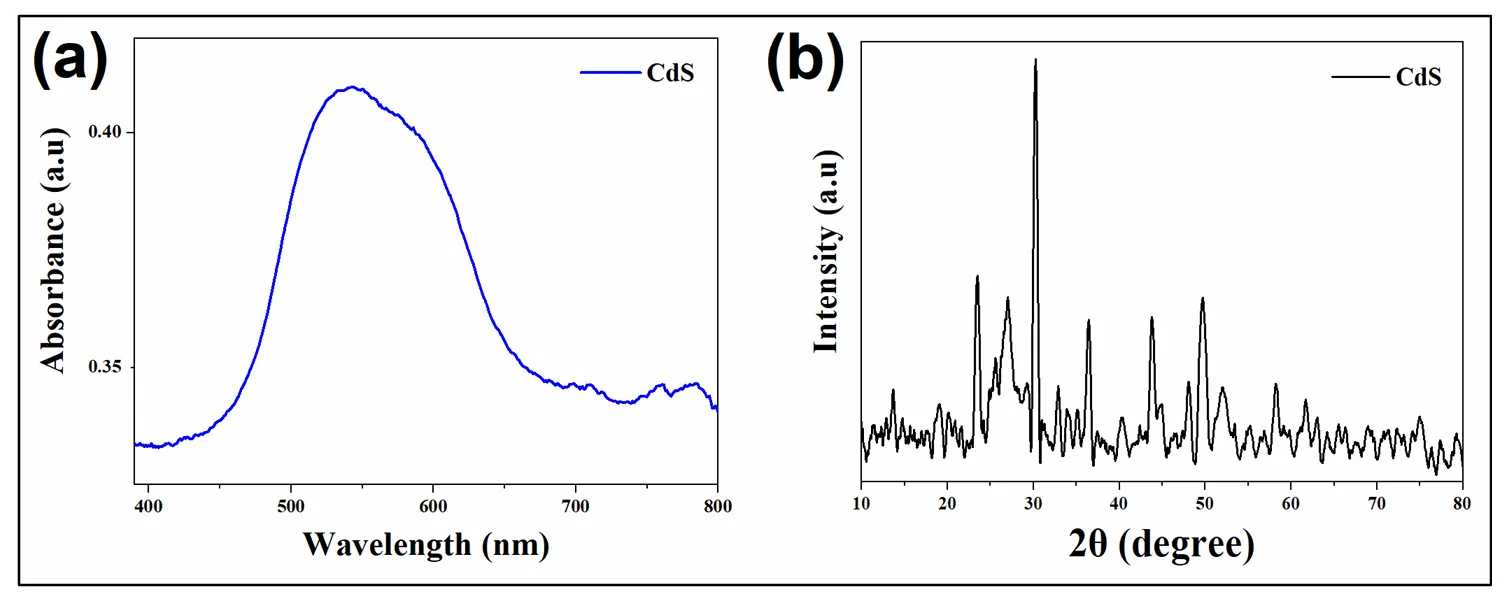
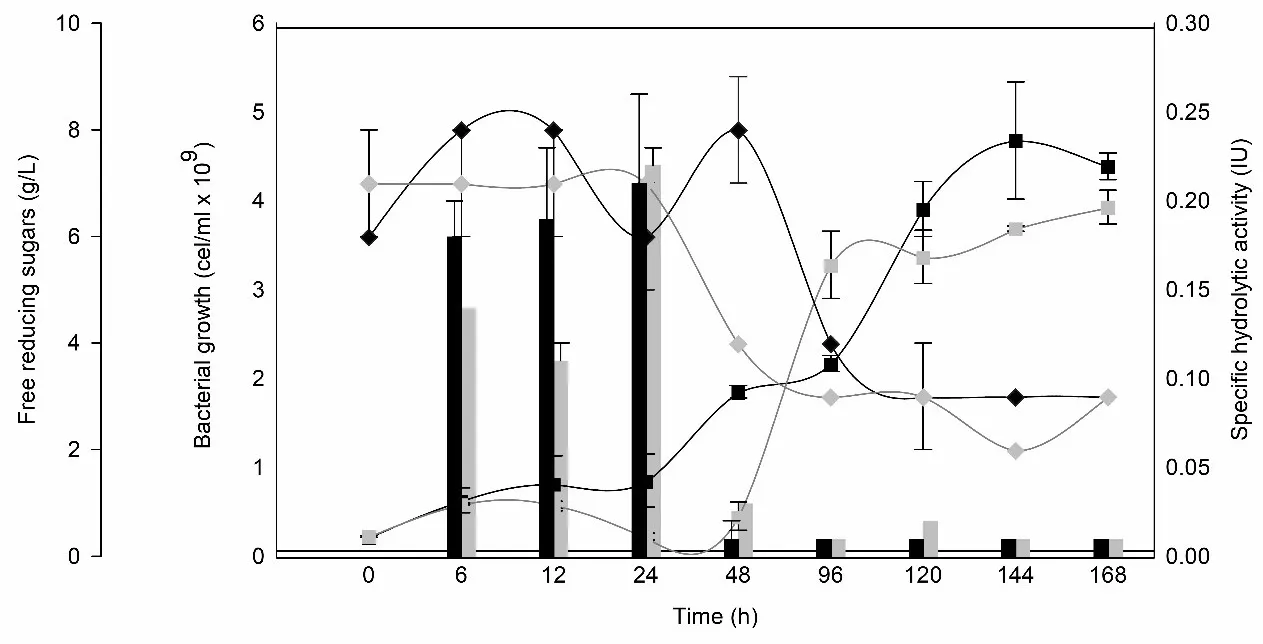
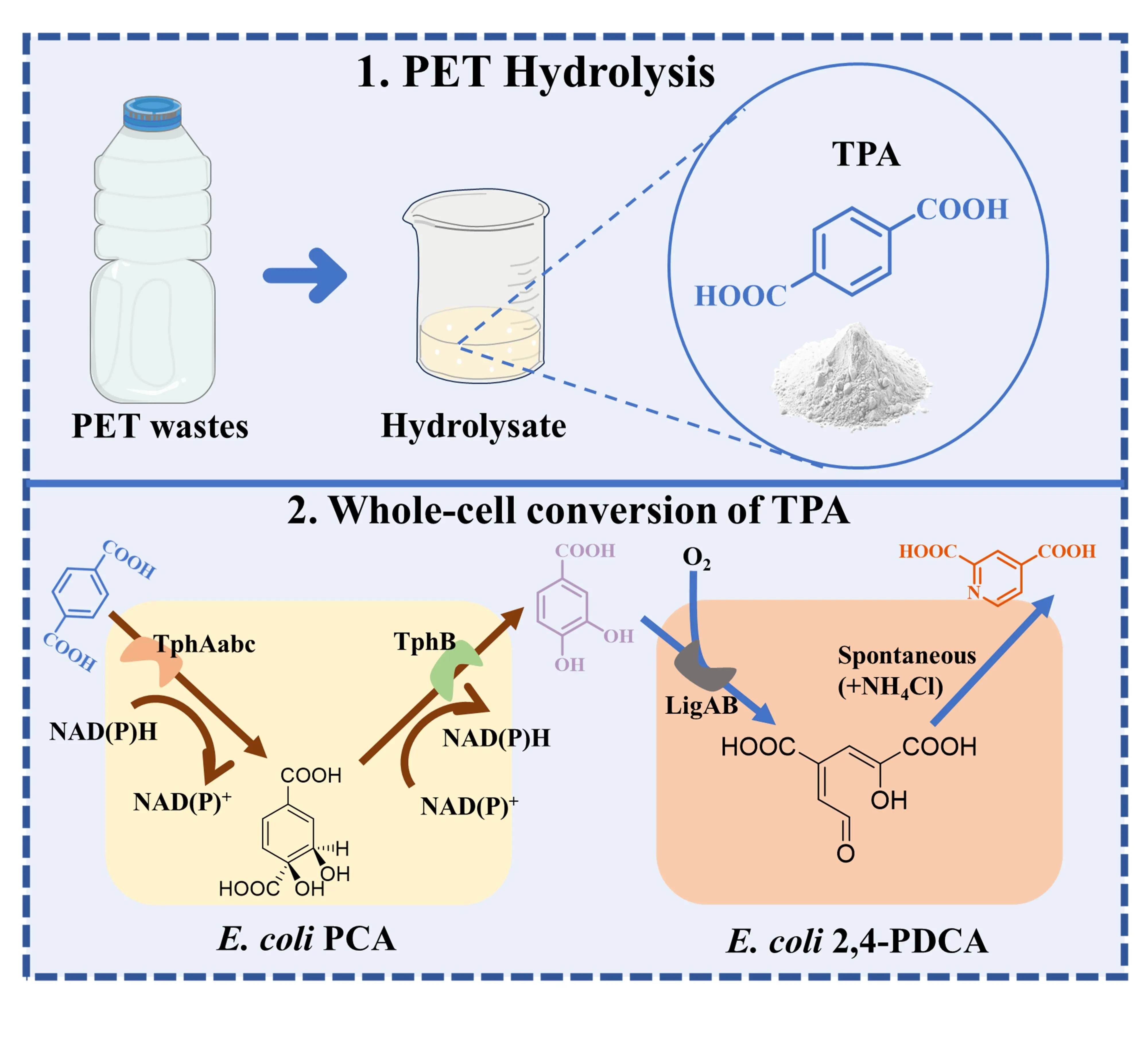
Escalating
atmospheric CO2 levels and the consequent climate crisis have become
urgent imperatives for advancing efficient carbon capture technologies. Porous
carbon adsorbents stand out as a leading candidate in this field, owing to
their inherently high specific surface areas, tailorable pore architectures,
and cost advantages over conventional solid adsorbents. This review focuses on
recent progress in the rational engineering of porous carbons for boosted CO2 capture performance, with a particular emphasis on three complementary
modification pathways: pore structure refinement, surface functional group
regulation, and metal oxide incorporation. We begin by clarifying the distinct
mechanisms of CO2 physisorption and chemisorption on carbonaceous
surfaces, while also elucidating how key operating parameters (temperature,
pressure) and real-world flue gas components (e.g., water vapor, SO2)
modulate adsorption behavior. Critical evaluation is then given to strategies
for enhancing three core performance metrics—CO2 uptake capacity,
selectivity over N2, and cyclic stability—including the construction
of sub-nanometer micropores (<0.8 nm) for efficient low-pressure CO2 capture, the introduction of nitrogen- and oxygen-containing moieties to
strengthen dipole–quadrupole interactions with CO2 molecules, and
the loading of alkaline metal oxides (e.g., MgO, CaO) to enable reversible
chemisorption, which is especially beneficial under humid conditions. Finally,
we outline the key challenges that hinder the practical application of porous
carbon adsorbents, such as the design of hierarchical pores for both high
uptake and fast mass transfer, the precise control of heteroatom doping sites
and concentrations, and the mitigation of competitive adsorption in complex
multicomponent flue gases. Corresponding future research priorities are also
proposed, with a focus on scalable and sustainable synthesis routes using
biomass or waste precursors. Ultimately, this review seeks to provide targeted
insights for the rational design of high-performance porous carbon adsorbents,
thereby accelerating their deployment in sustainable CO2 capture
systems.
 Open Access
Open Access