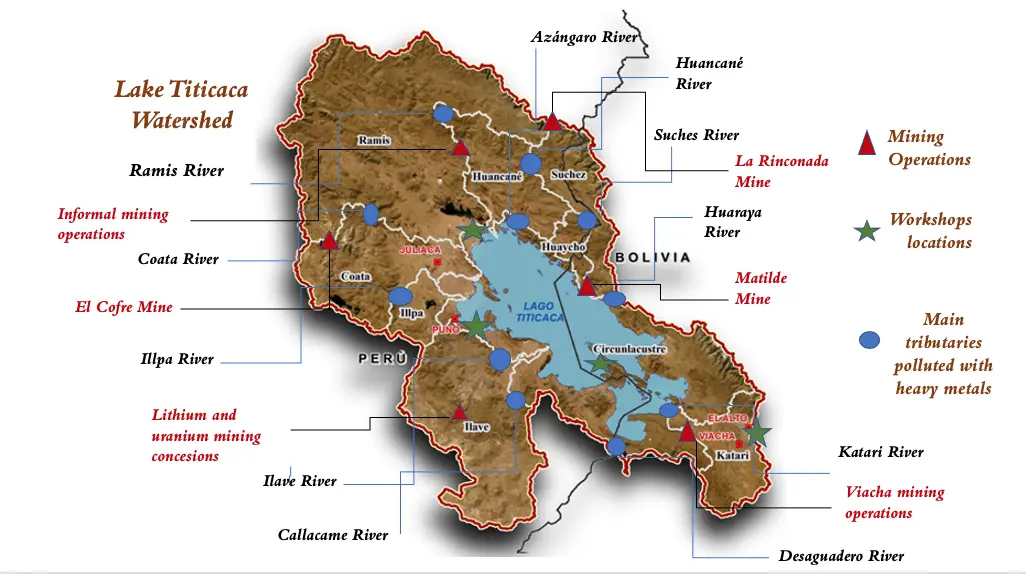
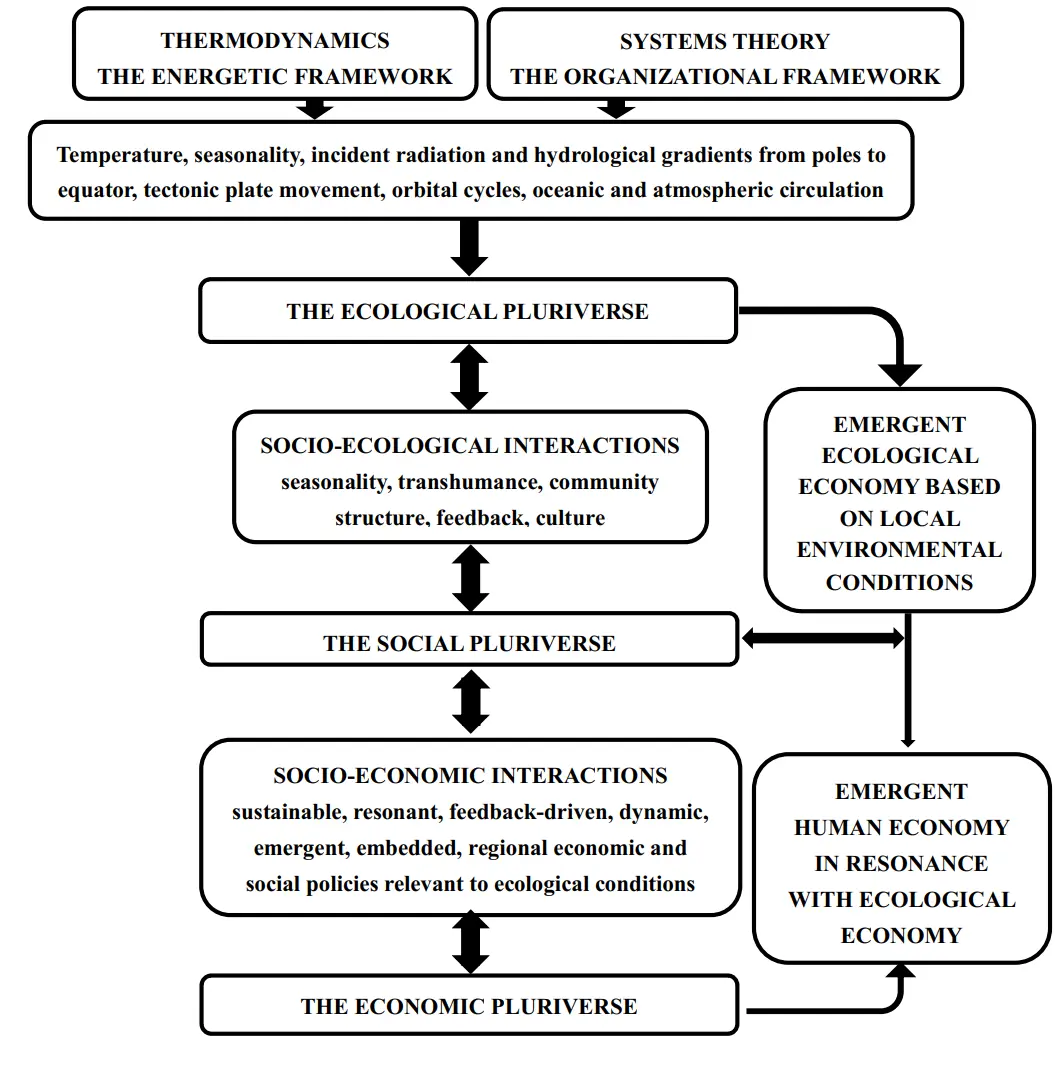
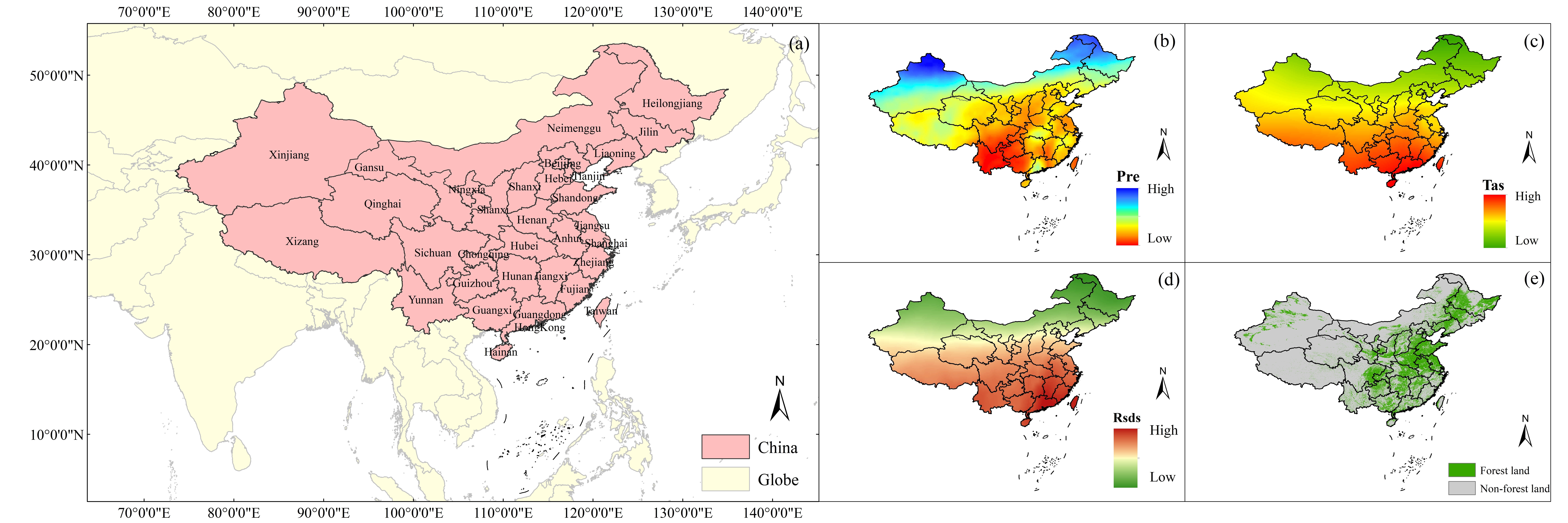
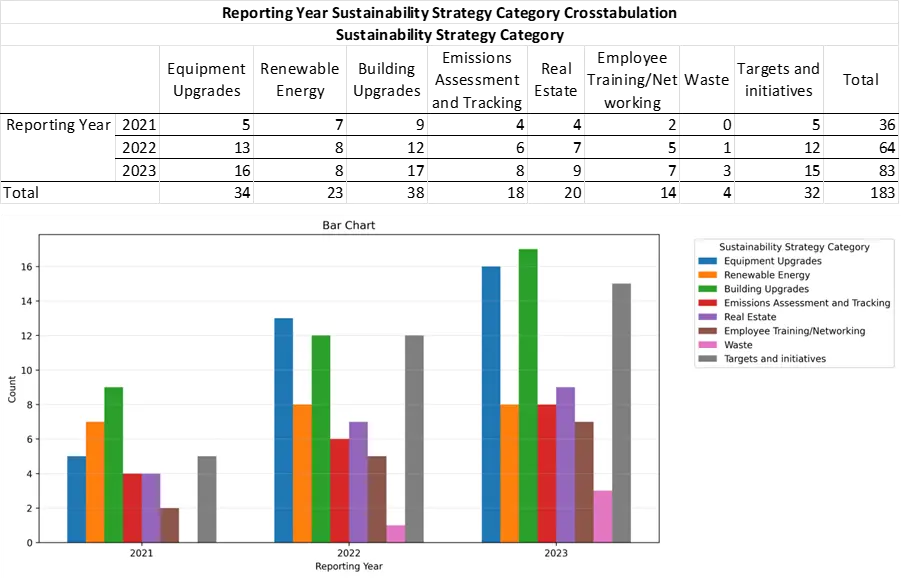
In 2007, a report to the 17th National People’s Congress in Beijing introduced the concept of Ecological Civilization (EC) (Shēngtài Wénmíng 生态文明) to the official lexicon of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). With origins in the state discourse of the Soviet Union of the 1980s, the term gained new forms of traction in China and abroad as it drew from ecological Marxism, constructive postmodernism, and process philosophy to propose a new technic of statecraft and international cooperation for the development of long-term, global ecological justice and sustainability. In 2012, the constitution of the People’s Republic of China enshrined the goals of EC as a primary national objective, promulgating specific policies on environmental management, green technology, and ideological development. Although some critics view EC discourse as the epitome of authoritarian environmentalism, others cite the PRC’s remarkable strides in developing green technologies and assuming leadership in international treaty negotiations, such as the COP 15, as evidence that the CCP is taking on a new role in global environmental leadership. Beyond the immediate concerns of EC’s performative dimensions, rigorous analysis of EC as a discursive political strategy is critical for understanding its potential for opening spaces of unprecedented international cooperation on planetary environmental governance. While skepticism is in order, facile reductions of the scope of Shēngtài Wénmíng discourse to mere propaganda designed to disguise authoritarian environmentalism marks a dangerous foreclosure on what could very well emerge as a workable vision of international cooperation to solve ecological and social crises arising from the global climate emergency, the Sixth Mass Extinction, and severe regional disparities in resource access. Strong EC theory and practice ascribe transcendent value to the earth’s biogeochemical systems as the very oikos (οίκος)—the ecological home within which human economy and infrastructure engage with more-than-human forces constitutive of “nature” to co-create our shared terrestrial world. Within this highly variegated terrestrial ecology, with its multiplicity of biomes, human and more-than-human potentials can be realized for mutual benefit—the essential condition for sustainability. Given these considerations, to dismiss PE discourse in summary fashion constitutes a grave mistake and an act of bad faith. This analysis reconceptualizes the oikos as deeply similar to the East Asian philosophical concept of Tiānxià (天下) and, concomitantly, equates the Western conception of cosmos (σύμπαν) with the Daoist and Confucian concept of (Tiān天).This vision of wealth and common property embodied in the global biospheric commons grounds, reproduces, and inflects the human terrestrial condition. The mechanism for achieving global EC involves the overcoming of the fundamental contradictions between classical paradigms of industrial development and emerging conceptions of ecological resilience, by fast-tracking ecological development at all terrestrial scales on a foundation of unprecedented international cooperation and social justice. This includes the treatment of scarce mineral resources, which are required to meet the growing global demand for green technologies and mitigate the disastrous effects of global climate change, as common pool resources. EC comprises a radical and crucial reconfiguration of geopolitical theory and practice based on a new ecological ethics for the Anthropocene Epoch. This readjustment of international relations to meet actually existing global crises cannot be realized without a concomitant and symmetrical system of demilitarization based on the transfer of resources, materiel, personnel, expertise, and security policy out of the global military-industrial complex, which centers on monocentric geographic realms (East Asia, North America, the EU, South Asia, and Russia) and a series of shifting alliances the G-7, NATO, the UN. The United States and China currently enjoy an unprecedented degree of prominence and agency on the world stage. They must, for that very reason, play leading roles in global demilitarization. The most effective means of insuring multilateral involvement in this process, and the protocol with the largest peace dividends, is called Global Green Demilitarization. This article provides the philosophical, ethical, and political groundwork to replace destructive practices of resource competition with diplomatic processes leading to international, multilateral, and global Ecological Civilization. The road will be long and perhaps the way will be arduous, but the rewards will exceed the difficulties, consisting, as they will, of a thriving planet and a dynamic, peaceful, and equitable civilization in the 21st century and for the remainder of the third millennium.
 Open Access
Open Access