Human civilization threatens the life support functions generated by global ecosystems. Humanity must forge an ecological civilization to avoid collapse. We apply evolutionary theory to the human system, with an emphasis on the economy, to understand how we have arrived at our current predicament and to suggest paths forward. Neoliberal economic theory claims that within markets, the self-interested behavior of individuals and firms maximizes societal welfare, while some strands of evolutionary theory claim that selfish individuals will outcompete their selfish conspecifics. Yet, cooperation is ubiquitous. Humans have become more interdependent than ever. We present a theoretical argument that the structure of the global economy is best explained by multilevel selection (MLS)—an evolutionary process wherein competitive individuals outcompete cooperative individuals within groups, while cooperative groups outperform competitive groups. MLS helps explain why both cooperation and selfishness co-exist, with cooperation the most adaptive social behavior at higher-scales. We conclude that achieving an ecological civilization will not only require cooperation at the global scale, but also the forging of a new relationship between humans and the rest of nature, akin to the relationship between a human cell and the human body.

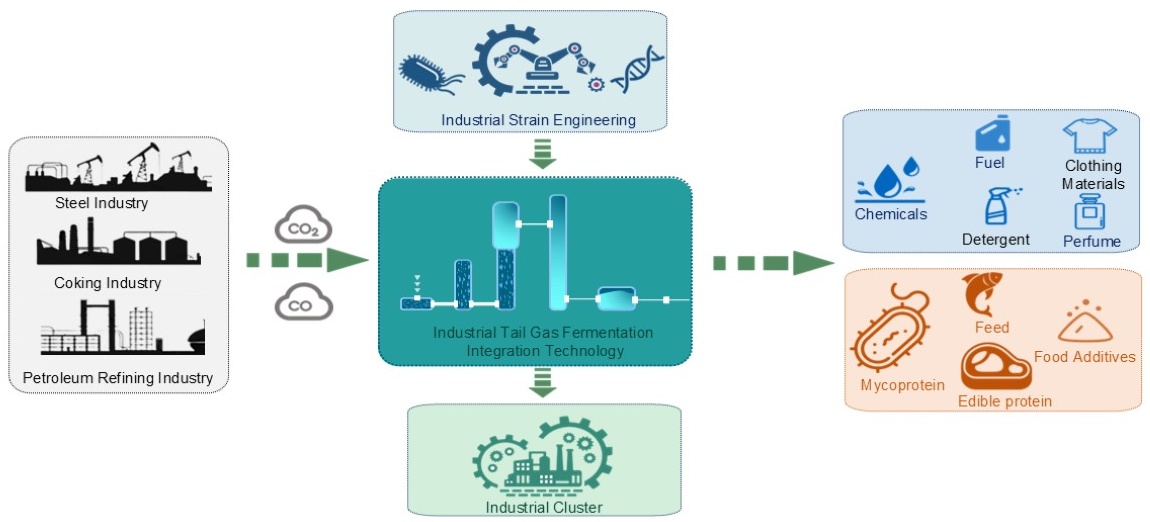
In the context of the global carbon neutrality strategy, syngas fermentation technology has emerged as a research hotspot in biomanufacturing because it can recover and convert industrial exhaust gas. Relying on the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway in acetogens, this technology converts gaseous substrates, such as CO and CO2, into high-value-added chemicals. However, bottlenecks including low gas-liquid mass-transfer efficiency and challenges with scale-up, severely limit its industrialization. The review focuses on core research-level topics, including the key enzymatic mechanisms of acetogens, metabolic regulation strategies, and high-throughput strain construction technologies; systematically analyzes the feed gas pretreatment process, design principles of large-scale reactors, fermentation process optimization, efficient product separation and purification technologies, and full-process integration at the process level; and summarizes techno-economic analysis and global policy support for industrial application. Finally, it thoroughly analyzes the core challenges of this technology across core mechanisms, engineering operations, economic markets, and industrial chain coordination, and outlines the future development direction of the technology. By systematically collating the syngas fermentation technology system and its industrialization bottlenecks, this review provides references for its industrialization. It is positioned to boost the economic viability and industrial appeal of the CCUS system, acting as a pivotal engine for advancing deep industrial decarbonization and fostering emerging green industries.
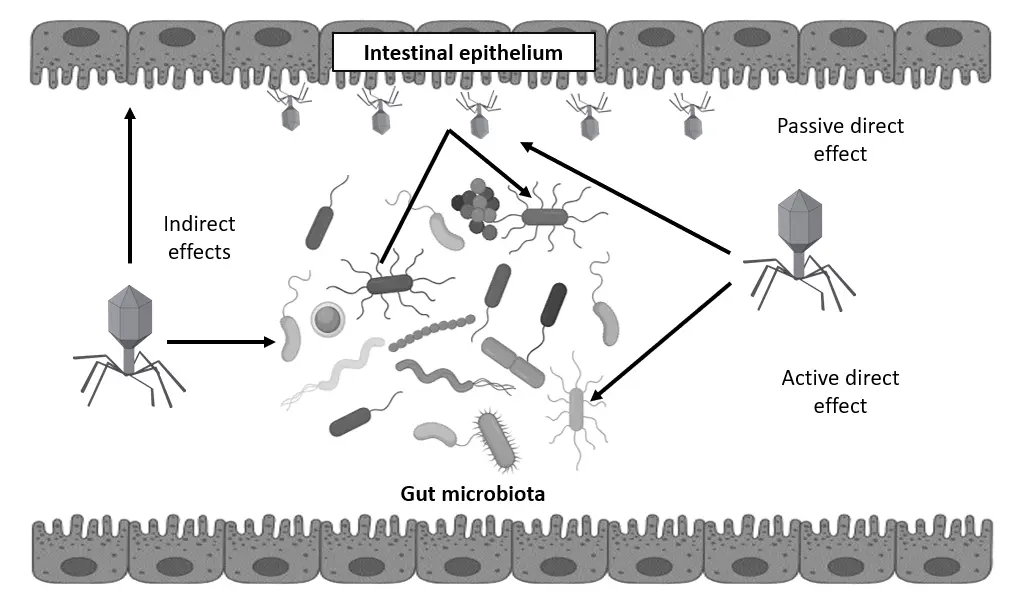
Bacteriophages are abundant viruses that naturally inhabit the human gastrointestinal tract, interacting closely with bacterial communities. While their therapeutic potential against bacterial infections has been recognized, clinical evidence remains limited. Here, we review recent randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled human trials evaluating oral bacteriophage administration for gastrointestinal applications, including treatment of bacterial diarrhea and supplementation in individuals with mild gastrointestinal distress. These studies demonstrate that phage therapy is safe and well-tolerated, with minimal impact on overall gut microbiota composition. There is also some evidence of reduced target bacterial populations and symptom improvement during prolonged use. Additionally, combining phages with probiotics shows promise in enhancing gastrointestinal health. These findings suggest bacteriophages may serve as safe adjuncts or supplements for maintaining gut health and preventing infections, warranting further investigation into their mechanisms and long-term effects within the human microbiome.
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) remains indispensable for high-precision machining of advanced and hard-to-machine materials; however, its broader industrial adoption is constrained by high energy consumption, unstable discharge behavior, dielectric degradation, and limited integration of sustainable and intelligent manufacturing strategies. Although existing reviews address micro-EDM and environmentally benign EDM individually, a consolidated and critical synthesis linking discharge physics, sustainability bottlenecks, and intelligent process control has remained limited. This review systematically analyzes highly cited and recent studies (2020–2024) indexed in Scopus and Web of Science, focusing on micro-EDM, green dielectric systems, hybrid-assisted EDM, and intelligent EDM technologies. The synthesized literature identifies key bottlenecks, including deterioration of the inter-electrode environment, inefficient debris evacuation, dielectric decomposition, and the absence of standardized sustainability performance metrics. The analysis reveals a clear convergence toward hybrid-assisted, sustainability-driven EDM strategies, in which coupled plasma–thermal–chemical interactions govern material removal and surface integrity rather than purely thermal effects. Comparative findings indicate that ultrasonic assistance is most effective for micro-scale and brittle materials, magnetic field assistance enhances plasma stability in conductive metallic systems, and biodegradable or water-based dielectrics significantly reduce environmental impact while maintaining acceptable machining performance. Furthermore, intelligent EDM approaches integrating sensor-based monitoring, AI-assisted optimization, and digital-twin frameworks show strong potential for adaptive control, although industrial deployment remains limited by sensing robustness and system integration challenges. Overall, this review proposes a structured roadmap for transitioning EDM toward intelligent, energy-efficient, and sustainable industrial manufacturing.

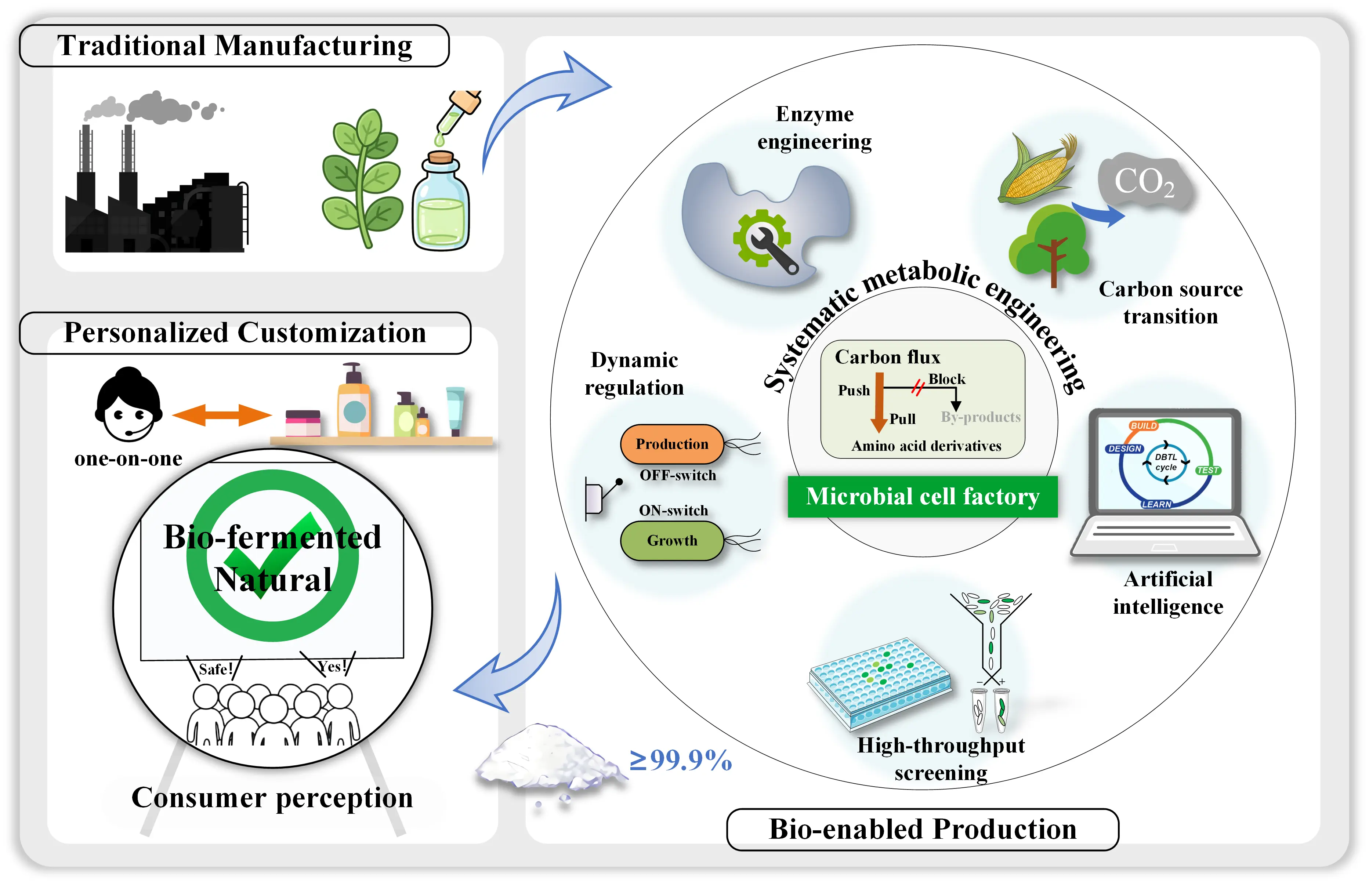
The cosmetics industry is undergoing a historic transition from natural extraction to precision biomanufacturing. Amino acid derivatives, as a kind of core functional cosmetic ingredient, have witnessed synthetic biology–based production technologies overcome traditional bottlenecks in efficiency and cost. In this Perspective, grounded in recent advances in the construction of amino acid derivative cell factories, we propose the core trends for the future development of cosmetic ingredients: enzyme engineering, dynamic metabolic control, and irrational strategies are converging to enable both functional customization and production intelligence. Star molecules such as ergothioneine, spermidine, and bioactive peptides are poised to redefine the boundaries of anti-aging efficacy, while AI-driven R&D paradigms offer broad prospects but must still overcome cost, regulatory, and consumer perception barriers. We emphasize that only by establishing an integrated “efficient synthesis–precise delivery–validated activity” end-to-end chain can cosmetic ingredients move from laboratory to market, achieving an industrial leap from chemical addition to biological empowerment.