Artiles
Open Access
Article
28 February 2026Photocatalyzed Thiocarbamylation of Alkenyl Radicals via Thiophene Salts
In recent years, visible-light-induced transformations have taken a central role in driving forward the progress of modern organic synthesis. Despite the abundance of synthetic strategies enabling access to aryl- and alkyl-centered radicals, the exploitation of photochemistry to generate highly reactive alkenyl radicals has remained notably underdeveloped. Herein, we report a sustainable strategy for generating alkenyl radicals based on a photocatalytic single-electron transfer process. Through systematic optimization of conditions such as photocatalysts, light sources, and additives, we confirmed that radical reactions can efficiently occur under metal-free conditions using styrenylthiophene salt as radical donors, thiuram derivatives as radical acceptors, and 4CzIPN (1,2,3,5-tetrakis(carbazol-9-yl)-4,6-dicyanobenzene) as the photocatalyst. This method is operationally simple, environmentally friendly, and does not require the addition of precious metal reagents, providing a novel strategy for the methodology of alkenyl radical generation.

Open Access
Article
28 February 2026Unveiling the Dynamics: How Does the Digital Economy Influence the Development of New-Type Urbanization in China
Digital economy is a vital driving engine for new-type urbanization and continues to promote the regional economy. In this study, it adopts the entropy weight method is adopted to measure the digital economy and new-type urbanization in 31 provinces in China from 2011 to 2021, and conducts an in-depth analysis on the relationship between them. The conclusions are: Digital economy has a significant role in promoting new-type urbanization and is regionally heterogeneous, especially the impact in eastern region; Moreover, through the mediating mechanisms analysis, it indicates that industrial structure and innovation level are important paths to promote new-type urbanization. Along with the increase of R&D intensity, the promotion effect shows a non-linear characteristic of “increasing marginal effect”. In light of this, the following countermeasures are put forward to strengthen digital economy’s impetus for new-type urbanization: promote the gradient development of digital technologies and innovate digital economy application scenarios to fuel new-type urbanization; establish a novel digital-industrial integration model and capitalize on the fundamental role of industrial transformation in new-type urbanization; and refine the innovation system and fully realize the marginal incremental effect of R&D intensity once it crosses the threshold.

Open Access
Article
28 February 2026Euclid sUAV Handling Qualities Evaluation Through Flight Simulation, Using Cooper-Harper Handing Qualities Rating Scale
This article briefly presents the design steps, from the conceptual design up to flight simulation of the Euclid 3D printed small Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (sUAV). The use of valid tools and proper methodology implementation is essential throughout this entire path to render the aircraft’s kinematics properly in the flight simulator. The primary object of study in this article is the Euclid sUAV handling qualities evaluation through flight simulation, using Cooper-Harper Handing Qualities Rating Scale. A novel methodology consisting of eighteen flight tests is presented, each one evaluating a certain flight procedure. For each procedure, performing instructions are provided. This methodology can be used either as is, or modified, to evaluate the handling qualities of similar sUAV’s. Furthermore, a full video of the procedure is given for validation and replication purposes. The results from the application of the 18-step procedure for the Euclid sUAV, indicated that all scores fluctuated in the (1–3) score region. These score region is translated as satisfactory handling qualities, without improvement needed to the system, according to Cooper-Harper Handing Qualities Rating Scale.

Open Access
Article
26 February 2026Associations of Oppositional Defiant Disorder, Irritability, and Headstrong Dimensions with Other Psychological Disorders in Adolescents
The current study aimed to use both multiple regression analyses (MRA) and latent regression analysis (LRA) to examine unique and suppression effects of DSM-5 oppositional defiant disorder irritability and headstrong dimensions with common DSM-5 internalizing (Generalized Anxiety Disorder, Persistent Depressive Disorder, Separation Anxiety Disorder, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder, and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder), externalizing (ADHD, and Conduct Disorder), neurodevelopmental (Specific Reading Disorder, Autism Spectrum Disorder, Language Disorder, and Speech Sound Disorder) and eating disorders (Anorexia Nervosa, and Bulimia Nervosa) among clinic-referred adolescents. Parents of 1877 adolescents [boys = 1089, girls = 788; age range = 11 to 17 years] provided ratings of their adolescents’ ODD symptoms and the symptoms for the other 14 disorders. The MRA findings indicated that, generally, internalizing disorders, autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and eating disorders were associated positively and uniquely with the irritability dimension, and externalizing disorders were associated positively and uniquely with the headstrong dimension. With the exception of autism spectrum disorder, the other neurodevelopmental disorders showed little or no associations with irritability or headstrong dimensions. There was little evidence of suppression effects. The LRA findings for unique associations were generally comparable with the MRA findings, except that there was strong evidence for the headstrong dimension suppressing the unique associations involving irritability, and irritability suppressing the unique associations involving the headstrong dimension. These findings raise the possibility that both irritability and headstrong may be transdiagnostic, having a dominant influence on the comorbidity of internalizing (and possibly eating disorders) and externalizing disorders, respectively. To date, there has been little discussion on headstrong being a major transdiagnostic factor for externalizing disorders. Further theoretical, methodological. and clinical implications of the findings are discussed.

Open Access
Review
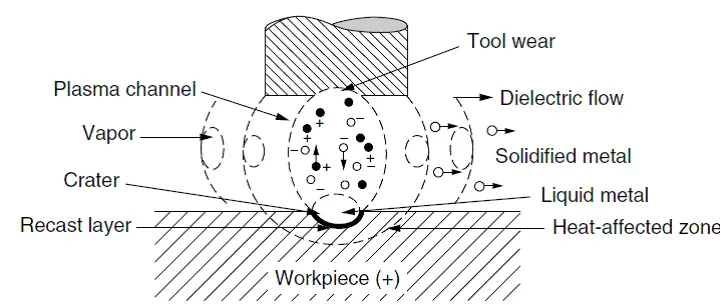
26 February 2026Electro-Discharge Machining Advanced Materials under Low Frequency Vibrations: Modeling, Application, and Outlook
The material removal in Electro-Discharge Machining (EDM) occurs through the generation of high temperatures caused by intense electrical discharges, leading to the melting and vaporization of the workpiece and tool electrode. The ejected molten material solidifies in the dielectric liquid, forming debris that can significantly affect process accuracy, efficiency, productivity, and machinability if not effectively removed from the machining zone. The utilization of Low Frequency (LF) vibration (typically <1 kHz) to assist debris evacuation during Micro-EDM (µEDM) and EDM processes has emerged as a feasible solution. Moreover, the integration of powder into the dielectric medium (Powder mixed EDM, PMEDM) along with LF vibration presents an interactive approach to further enhance process performance. Despite its promise, the field lacks a unified understanding of LFV-EDM’s underlying mechanisms, systematic optimization frameworks, and clear pathways for industrial integration. This paper presents a comprehensive overview of research focusing on the influence of process parameters on key performance indicators such as Material Removal Rate (MRR), Electrode Wear Rate (EWR), surface roughness (Ra), and geometric accuracy in LF vibration-assisted µEDM and EDM. Various optimization methodologies, including statistical modeling, finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and advanced techniques like Taguchi and artificial neural networks (ANN) employed in this field are extensively reviewed. Critical analysis of contradictory findings and material-specific responses is included. The review concludes with identified research gaps and prioritized future directions, including hybrid processes, advanced powder materials, and AI-driven optimization for LF- assisted µEDM and EDM processes. This work provides researchers with a consolidated knowledge base, a critical perspective on current limitations, and a prioritized agenda for future innovation, ultimately bridging the gap between laboratory research and scalable industrial application.
Open Access
Article
25 February 2026Analysis of Grinding Mechanics and Improved Force Model in Ultrasonic Assisted Grinding Cf/SiC Composites
Grinding is a key precision machining method for achieving high surface quality and dimensional accuracy in carbon fiber reinforced silicon carbide ceramic matrix composites (Cf/SiC). Ultrasonic vibration-assisted grinding (UVAG), with its high-frequency intermittent loading characteristics, offers a novel approach to regulating the dynamic removal behavior of heterogeneous materials. This study firstly analyzed the material removal mechanism of abrasive particles based on abrasive geometry and kinematics. On this basis, mechanical models are developed for a single abrasive grain across three removal stages: ductile removal, ductile-to-brittle transition, and brittle removal. These are further extended into a grinding force prediction model by integrating the effects of multiple abrasive grains and process correction factors during ultrasonic-assisted grinding. Finally, the model is validated through UVAG experiments. Results show that under an ultrasonic frequency of 20 kHz and amplitude of 5 μm, the predicted grinding forces match the experimental values with a high degree of accuracy (98.98%). This grinding force model provides theoretical support and process guidance for high-performance, low-damage precision machining of Cf/SiC composites.
Open Access
Article
25 February 2026Ecological Application of UAVs for Monitoring and Eliminating Oil Product Spills on the Sea Surface
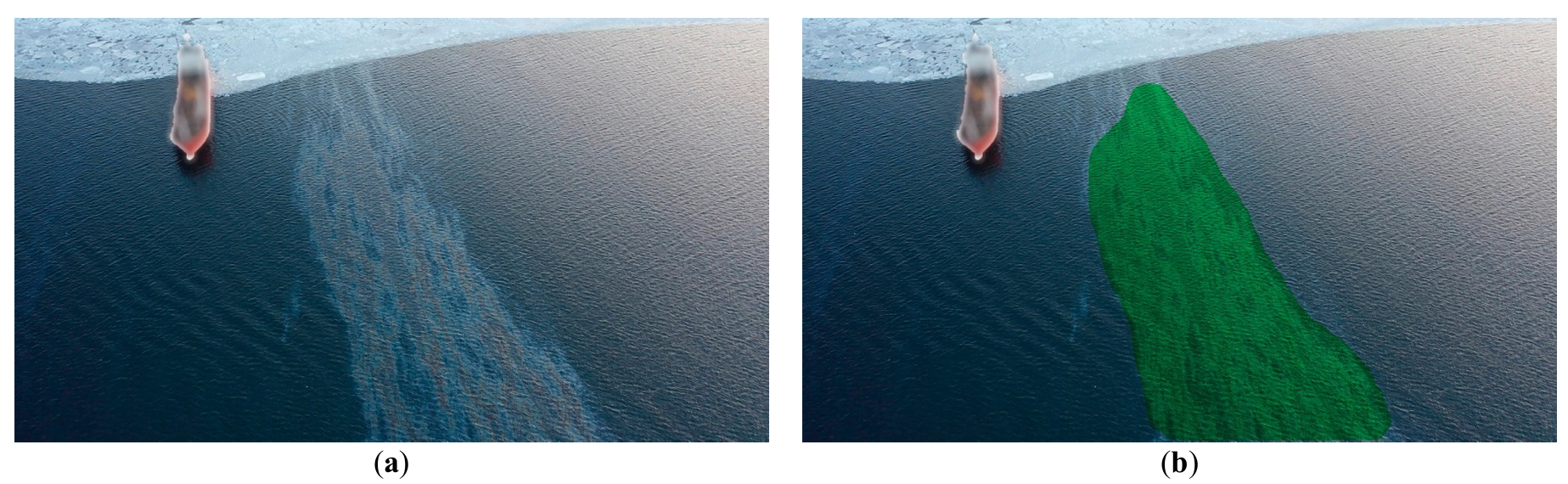
The objective of marine ecological safety necessitates the development of comprehensive, integrated strategies for oil spill management, encompassing advanced monitoring and effective remediation. This paper introduces and validates a novel integrated methodology and conceptual framework for autonomous marine environmental safety. The core of this framework lies in the merging of AI-assisted monitoring capabilities with a multi-agent Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) system for targeted dispersant delivery. UAV systems, within this methodology, function as a cost-effective and readily deployable operational platform. The study details the primary development stages of the methodology-driven system and presents empirical results from in-situ field trials. The framework leverages artificial intelligence (AI) tools developed and validated for slick monitoring, which execute primary segmentation for spill detection and subsequent secondary segmentation to categorize the slick into thickness uniformity maps. Datasets of actual marine oil slick imagery were compiled to facilitate robust deep learning of the underlying neural network architectures. The study explores scientific feasibility, specifically employing Laser-Induced Fluorescence (LIF) spectroscopy to classify oil product grades and assess the ecological impact of various remediation agents on local phytoplankton communities. This integrated method for spill response is underpinned by successful field validation results. The full methodology was tested during actual oil spill incidents in the waters of Peter the Great Bay from 2019 to 2024. The article presents experimental validation of a new concept and methodology of integrated environmental safety of marine areas by a multi-agent UAV system in the event of oil product spills.

Open Access
Article
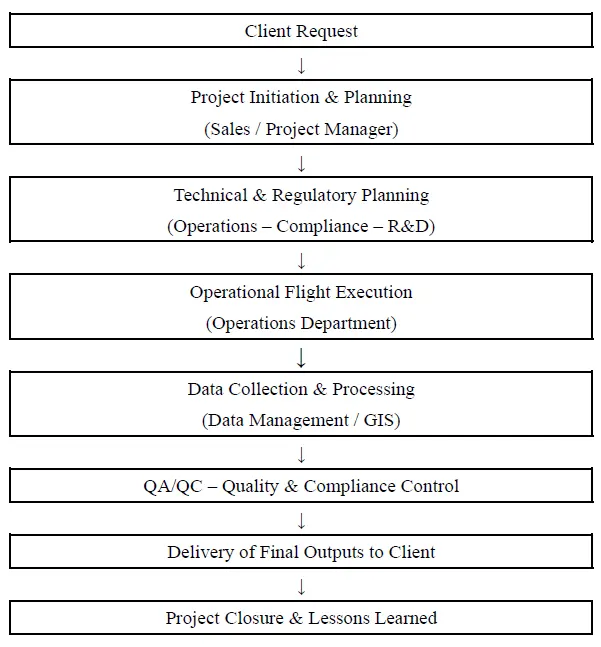
25 February 2026Evaluating UAS Integration into Geoinformatics: An Operational, Regulatory and Policy Analysis in Greek Geoinformatics Service Providers
The rapid evolution of geoinformatics technologies, particularly through the adoption of Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS), has brought significant changes to the collection, processing, and analysis of spatial data. UAS are increasingly integrated into Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing, and spatial analysis, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in applications such as precision agriculture and infrastructure management. However, limited empirical research has examined the consequences of their integration for operational efficiency, regulatory compliance, and related management practices in the Greek context. This study evaluates how UAS integration into the operations of Greek geoinformatics firms enhances efficiency and supports compliance with Greek and European regulatory frameworks. A qualitative multi-case study methodology is employed across five Greek geoinformatics service providers, and data are collected through semi-structured interviews and secondary sources. Findings indicate that UAS integration improves the quality of spatial data, reduces data collection costs, and facilitates regulatory compliance of these firms. Finally, the study highlights the emergence of optimal operational management policies of UAS including standardized end-to-end workflows, clear role allocation and compliance responsibilities, systematic QA/QC procedures, proactive regulatory monitoring (PDRA/SORA readiness), which strengthen and promote innovative geoinformatics technologies.
Open Access
Article
25 February 2026Optimizing SI Engine Performance and Emissions with Gasoline-Ethanol and Gasoline-Methanol Blends
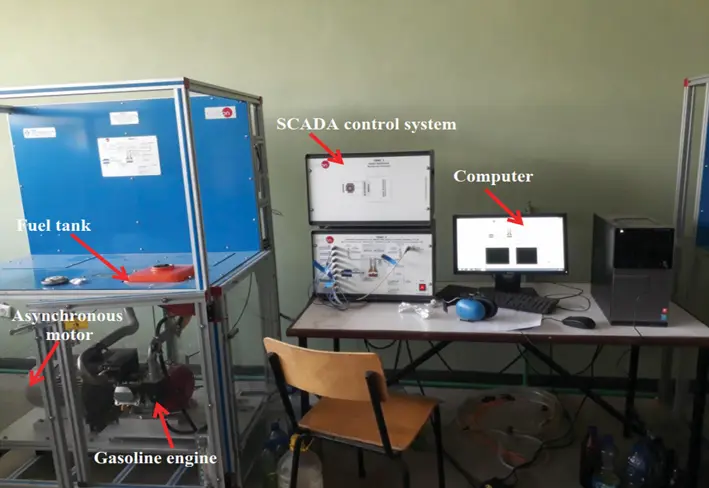
Although fossil fuels are the primary source of energy in the world, their greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants provide serious environmental problems. This study uses a gasoline blend with ethanol and methanol to examine the emissions and performance of a spark ignition (SI) engine. An experimental design focused on engine input factors such as load and fuel blends. Brake-specific fuel consumption (BSFC), brake thermal efficiency (BTE), and emissions of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) were examined about these parameters using Taguchi’s L16 orthogonal array and ANOVA via Minitab 18. The results show that 80% engine load and a 15% blend for both ethanol and methanol provide the best engine performance, greatly lowering BSFC and raising BTE. Notably, 20% engine load and 15% blend result in the lowest CO emissions, whilst 20% load and 0% blend result in the lowest NOx emissions. Also, 20% load and 15% blend result in the lowest HC emissions. This study highlights the potential of alternative fuel blends to improve engine efficiency and reduce hazardous emissions.

Open Access
Article
25 February 2026Evolutionary and Economic Foundations for an Ecological Civilization
Human civilization threatens the life support functions generated by global ecosystems. Humanity must forge an ecological civilization to avoid collapse. We apply evolutionary theory to the human system, with an emphasis on the economy, to understand how we have arrived at our current predicament and to suggest paths forward. Neoliberal economic theory claims that within markets, the self-interested behavior of individuals and firms maximizes societal welfare, while some strands of evolutionary theory claim that selfish individuals will outcompete their selfish conspecifics. Yet, cooperation is ubiquitous. Humans have become more interdependent than ever. We present a theoretical argument that the structure of the global economy is best explained by multilevel selection (MLS)—an evolutionary process wherein competitive individuals outcompete cooperative individuals within groups, while cooperative groups outperform competitive groups. MLS helps explain why both cooperation and selfishness co-exist, with cooperation the most adaptive social behavior at higher-scales. We conclude that achieving an ecological civilization will not only require cooperation at the global scale, but also the forging of a new relationship between humans and the rest of nature, akin to the relationship between a human cell and the human body.
