Artiles
Open Access
Review
24 February 2026Technological Innovation in Syngas Fermentation and Prospects for Industrial Application
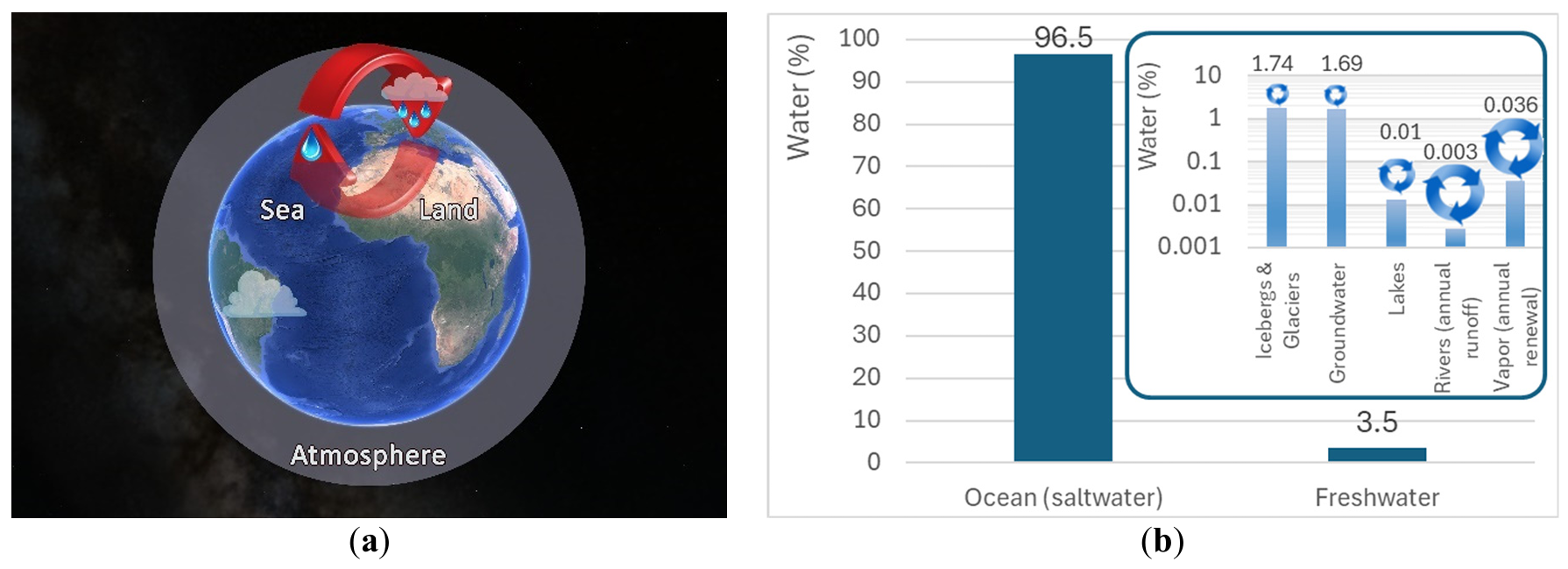
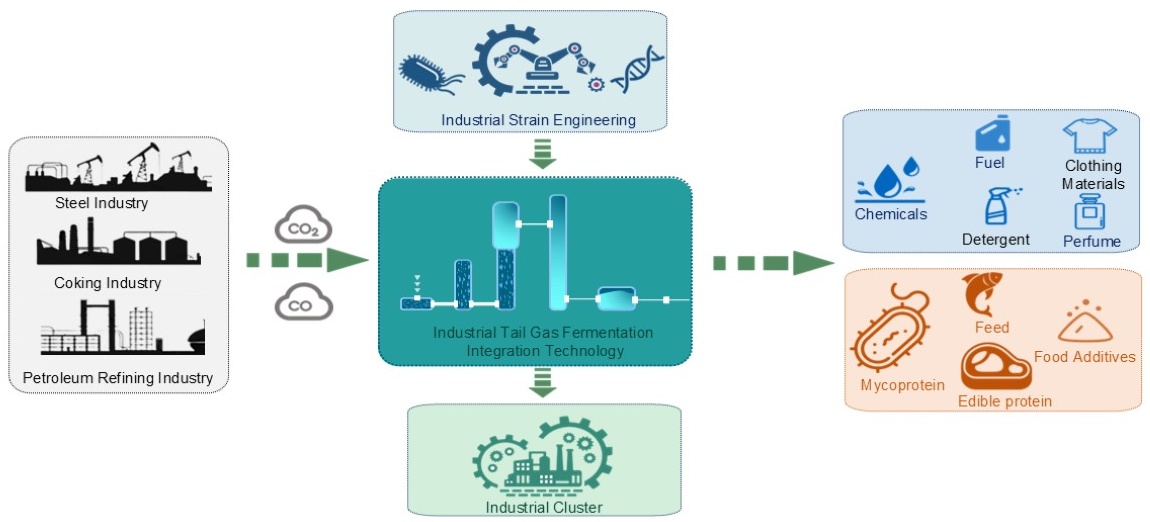
In the context of the global carbon neutrality strategy, syngas fermentation technology has emerged as a research hotspot in biomanufacturing because it can recover and convert industrial exhaust gas. Relying on the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway in acetogens, this technology converts gaseous substrates, such as CO and CO2, into high-value-added chemicals. However, bottlenecks including low gas-liquid mass-transfer efficiency and challenges with scale-up, severely limit its industrialization. The review focuses on core research-level topics, including the key enzymatic mechanisms of acetogens, metabolic regulation strategies, and high-throughput strain construction technologies; systematically analyzes the feed gas pretreatment process, design principles of large-scale reactors, fermentation process optimization, efficient product separation and purification technologies, and full-process integration at the process level; and summarizes techno-economic analysis and global policy support for industrial application. Finally, it thoroughly analyzes the core challenges of this technology across core mechanisms, engineering operations, economic markets, and industrial chain coordination, and outlines the future development direction of the technology. By systematically collating the syngas fermentation technology system and its industrialization bottlenecks, this review provides references for its industrialization. It is positioned to boost the economic viability and industrial appeal of the CCUS system, acting as a pivotal engine for advancing deep industrial decarbonization and fostering emerging green industries.
Open Access
Review
24 February 2026Bacteriophages in Human Gastrointestinal Health Applications
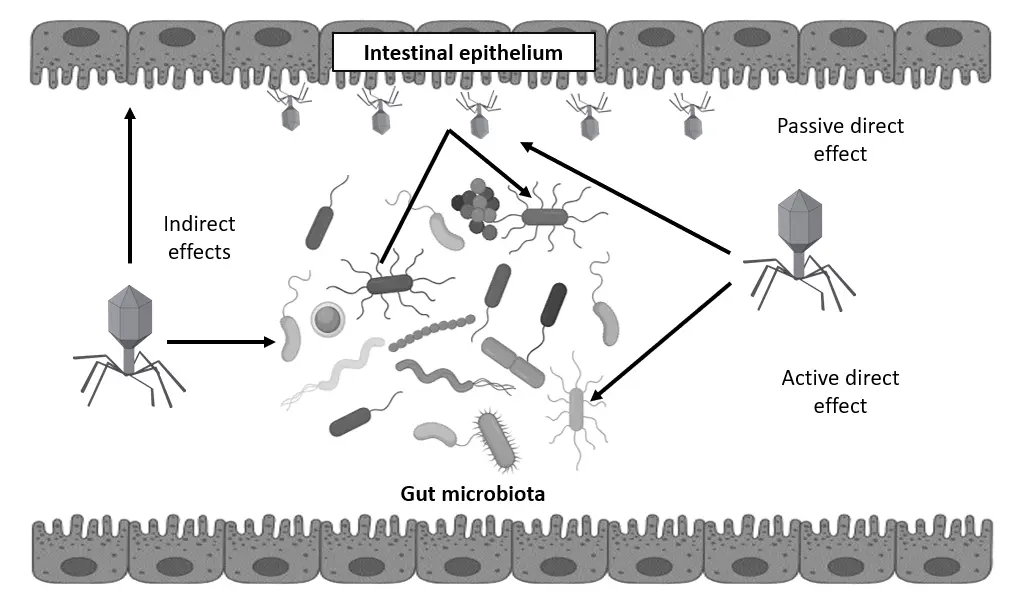
Bacteriophages are abundant viruses that naturally inhabit the human gastrointestinal tract, interacting closely with bacterial communities. While their therapeutic potential against bacterial infections has been recognized, clinical evidence remains limited. Here, we review recent randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled human trials evaluating oral bacteriophage administration for gastrointestinal applications, including treatment of bacterial diarrhea and supplementation in individuals with mild gastrointestinal distress. These studies demonstrate that phage therapy is safe and well-tolerated, with minimal impact on overall gut microbiota composition. There is also some evidence of reduced target bacterial populations and symptom improvement during prolonged use. Additionally, combining phages with probiotics shows promise in enhancing gastrointestinal health. These findings suggest bacteriophages may serve as safe adjuncts or supplements for maintaining gut health and preventing infections, warranting further investigation into their mechanisms and long-term effects within the human microbiome.
Open Access
Review
24 February 2026A Critical Review on Recent Advances and Sustainability Challenges in EDM of Advanced Materials
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) remains indispensable for high-precision machining of advanced and hard-to-machine materials; however, its broader industrial adoption is constrained by high energy consumption, unstable discharge behavior, dielectric degradation, and limited integration of sustainable and intelligent manufacturing strategies. Although existing reviews address micro-EDM and environmentally benign EDM individually, a consolidated and critical synthesis linking discharge physics, sustainability bottlenecks, and intelligent process control has remained limited. This review systematically analyzes highly cited and recent studies (2020–2024) indexed in Scopus and Web of Science, focusing on micro-EDM, green dielectric systems, hybrid-assisted EDM, and intelligent EDM technologies. The synthesized literature identifies key bottlenecks, including deterioration of the inter-electrode environment, inefficient debris evacuation, dielectric decomposition, and the absence of standardized sustainability performance metrics. The analysis reveals a clear convergence toward hybrid-assisted, sustainability-driven EDM strategies, in which coupled plasma–thermal–chemical interactions govern material removal and surface integrity rather than purely thermal effects. Comparative findings indicate that ultrasonic assistance is most effective for micro-scale and brittle materials, magnetic field assistance enhances plasma stability in conductive metallic systems, and biodegradable or water-based dielectrics significantly reduce environmental impact while maintaining acceptable machining performance. Furthermore, intelligent EDM approaches integrating sensor-based monitoring, AI-assisted optimization, and digital-twin frameworks show strong potential for adaptive control, although industrial deployment remains limited by sensing robustness and system integration challenges. Overall, this review proposes a structured roadmap for transitioning EDM toward intelligent, energy-efficient, and sustainable industrial manufacturing.

Open Access
Perspective
24 February 2026Synthetic Biology–Driven Innovation in the Production of Cosmetic Ingredients: From Natural Mimicry to Precision Creation
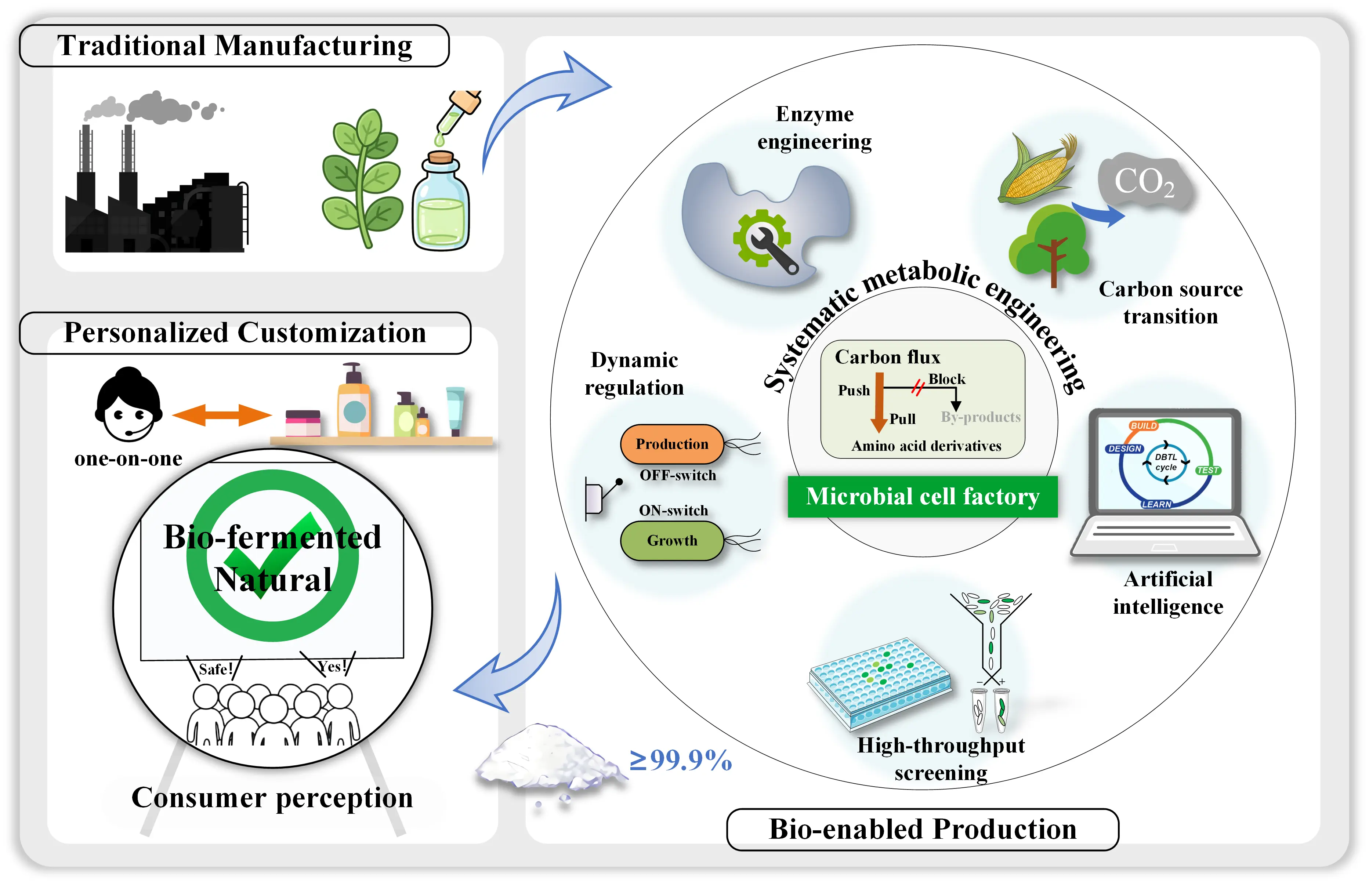
The cosmetics industry is undergoing a historic transition from natural extraction to precision biomanufacturing. Amino acid derivatives, as a kind of core functional cosmetic ingredient, have witnessed synthetic biology–based production technologies overcome traditional bottlenecks in efficiency and cost. In this Perspective, grounded in recent advances in the construction of amino acid derivative cell factories, we propose the core trends for the future development of cosmetic ingredients: enzyme engineering, dynamic metabolic control, and irrational strategies are converging to enable both functional customization and production intelligence. Star molecules such as ergothioneine, spermidine, and bioactive peptides are poised to redefine the boundaries of anti-aging efficacy, while AI-driven R&D paradigms offer broad prospects but must still overcome cost, regulatory, and consumer perception barriers. We emphasize that only by establishing an integrated “efficient synthesis–precise delivery–validated activity” end-to-end chain can cosmetic ingredients move from laboratory to market, achieving an industrial leap from chemical addition to biological empowerment.
Open Access
Article
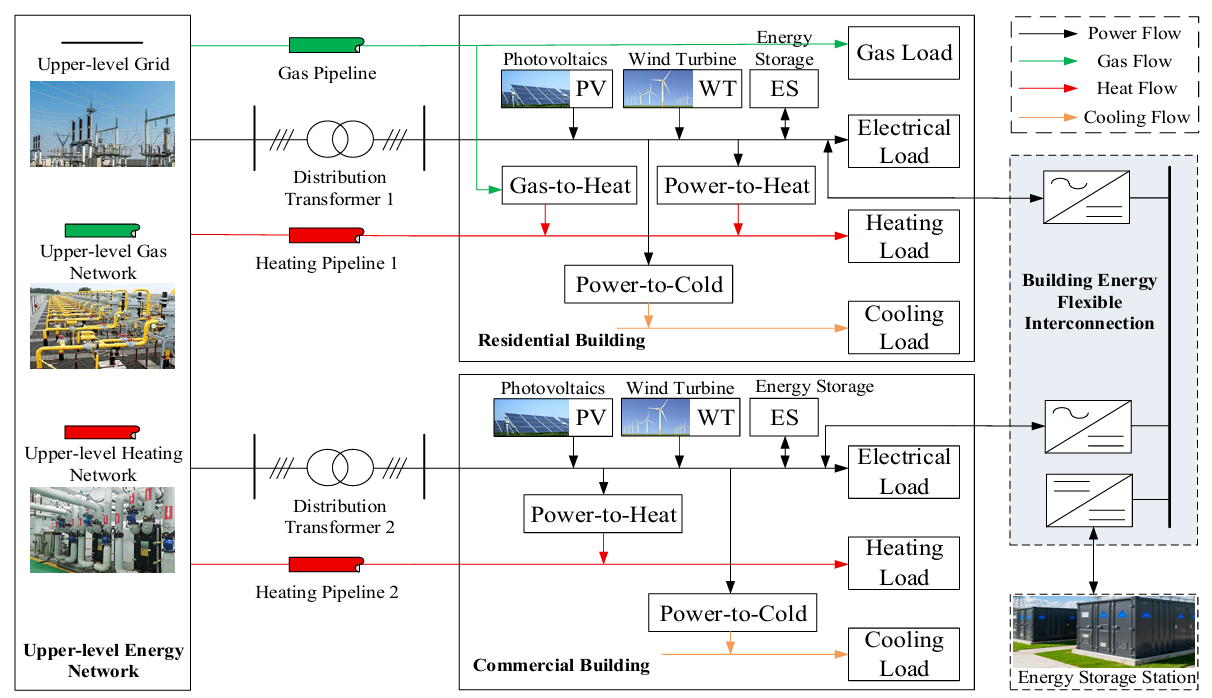
24 February 2026Bi-Level Optimal Configuration of Multi-Building Flexible Interconnected Energy Systems Considering Multi-Energy Complementarity
Flexible interconnection among different building types holds significant importance for integrating distributed energy resources, mitigating regional load peak-valley differences, and enhancing the local consumption capacity of renewable energy. Addressing the issue of insufficient multi-energy synergy in multi-building clusters, this paper proposes a bi-level optimal configuration method for flexible interconnected energy systems that accounts for multi-energy complementarity. By constructing a comprehensive multi-energy flow model encompassing all elements of source, network, load, storage, and conversion, a bi-level optimization framework is established. The upper level aims to minimize total lifecycle cost and carbon emissions, while the lower level targets maximizing the renewable energy self-consumption rate and minimizing daily operational cost. An improved NSGA-II algorithm integrating Lévy flight and a good point set is employed for an efficient solution. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed scheme can achieve cross-spatiotemporal energy transfer and multi-energy collaborative optimization. In a typical summer day scenario, the system’s renewable energy self-consumption rate increased to 96.20%, operational cost was reduced by 8.83%, and carbon emissions decreased by 10.18%, validating the effectiveness and superiority of the method in improving energy utilization efficiency and supporting the low-carbon and economic transition of regional building systems. The outcomes of this study can provide theoretical support and engineering reference for the low-carbon, economical, and efficient planning of multi-building energy systems.
Open Access
Article
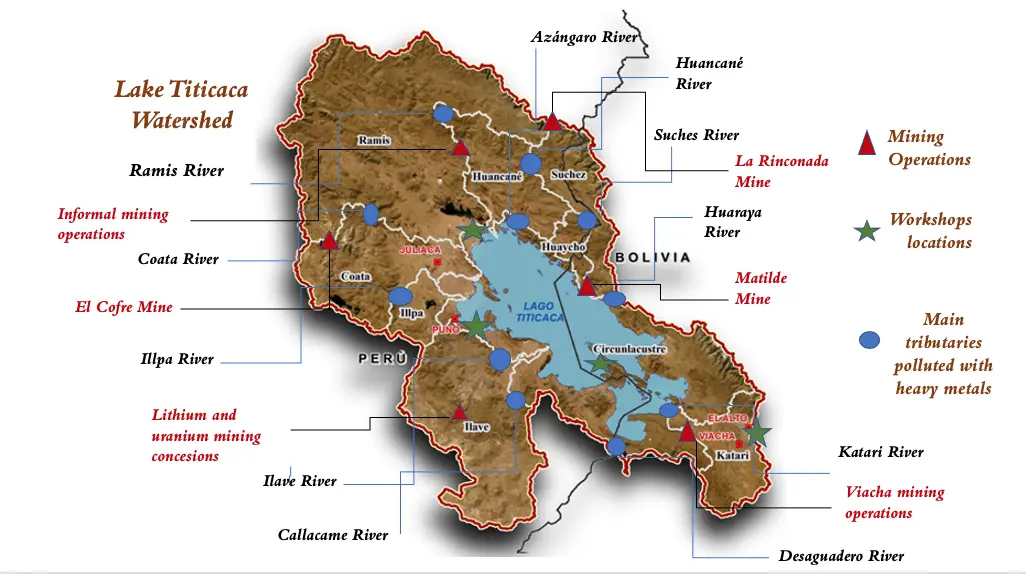
06 February 2026Dialogue of Water Stories as a Methodology: Storytelling Water Struggles and Embracing Resonance in Lake Titicaca
This article presents conceptual and methodological reflections that have emerged from a participatory action research project in the binational Lake Titicaca region. The ecosystem faces critical degradation due to mining contamination and untreated wastewater, which has led to the establishment of a series of local initiatives, as the recent recognition of the lake as a rights holder in Peru. In this spectrum, the research sought to bolster local defense initiatives by facilitating internal spaces for dialogue and co-production of knowledge, and by exploring avenues for strengthening collective strategies to transform water-related conflicts. Central to this study is the “Dialogue of Water Stories”, a community-based methodological proposal that integrates theoretical and practical components of dialoguing and storytelling. The findings demonstrate that this methodology effectively articulates the discussion of conflicts, unpacking several perspectives from multiple stakeholders. In this case, this led to the revelation of a plurality of community water values and historical care practices—particularly those upheld by women—while generating resonance for regional water defense. The article proposes the “Dialogue of Water Stories” as a transformative methodological approach to narrating water struggles and inspiring socio-environmental change.
Open Access
Communication
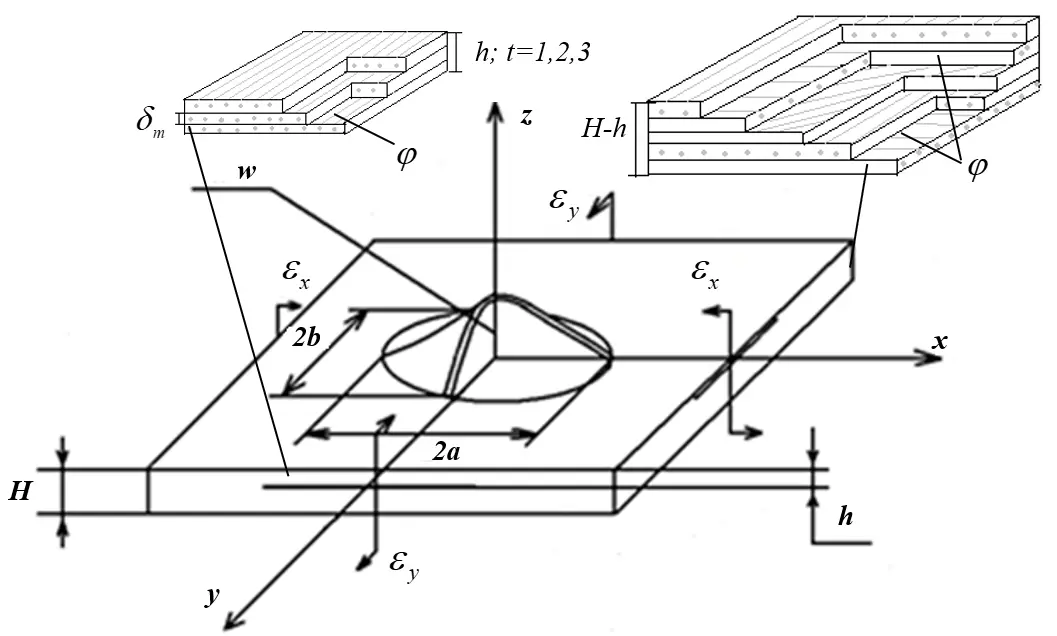
06 February 2026Buckling and Post-Buckling Behavior of the Delaminated Composite Plates
Multilayer composite materials, having high specific strength and rigidity, are sensitive to interlayer defects. The problem of interlayer laminations in a composite plate subjected to a plane compressive load is studied using a new analytical structure previously developed by the authors. Elastic characteristics of a multilayer package of thin lamination, including the elastic characteristics of separate layers, depending on modulus of elasticity, shear modulus, Poisson’s ratio, and angle of orientation of fibers of the unidirectional layer, are determined. Ratios are obtained for the unidirectional composite material that reflect the contribution of each component (fiber, matrix) in proportion to its volume fraction, according to the so-called “mixture rule”. This work examines the behavior after the loss of stability of an elliptical defect in a composite plate. Only the local bulging of the delamination type defect was considered. The difference between this work and others lies in the fact that the application of the developed method, based on the energy approach, makes it possible to obtain explicit analytical expressions for quantities characterizing the critical load and describing the supercritical behavior of the detached part. The energy method is generalized to the case of analyzing the stability of defects in a non-linear formulation. The value of the critical load was obtained, and the analysis of the supercritical deformation of the defect was made.
Open Access
Article
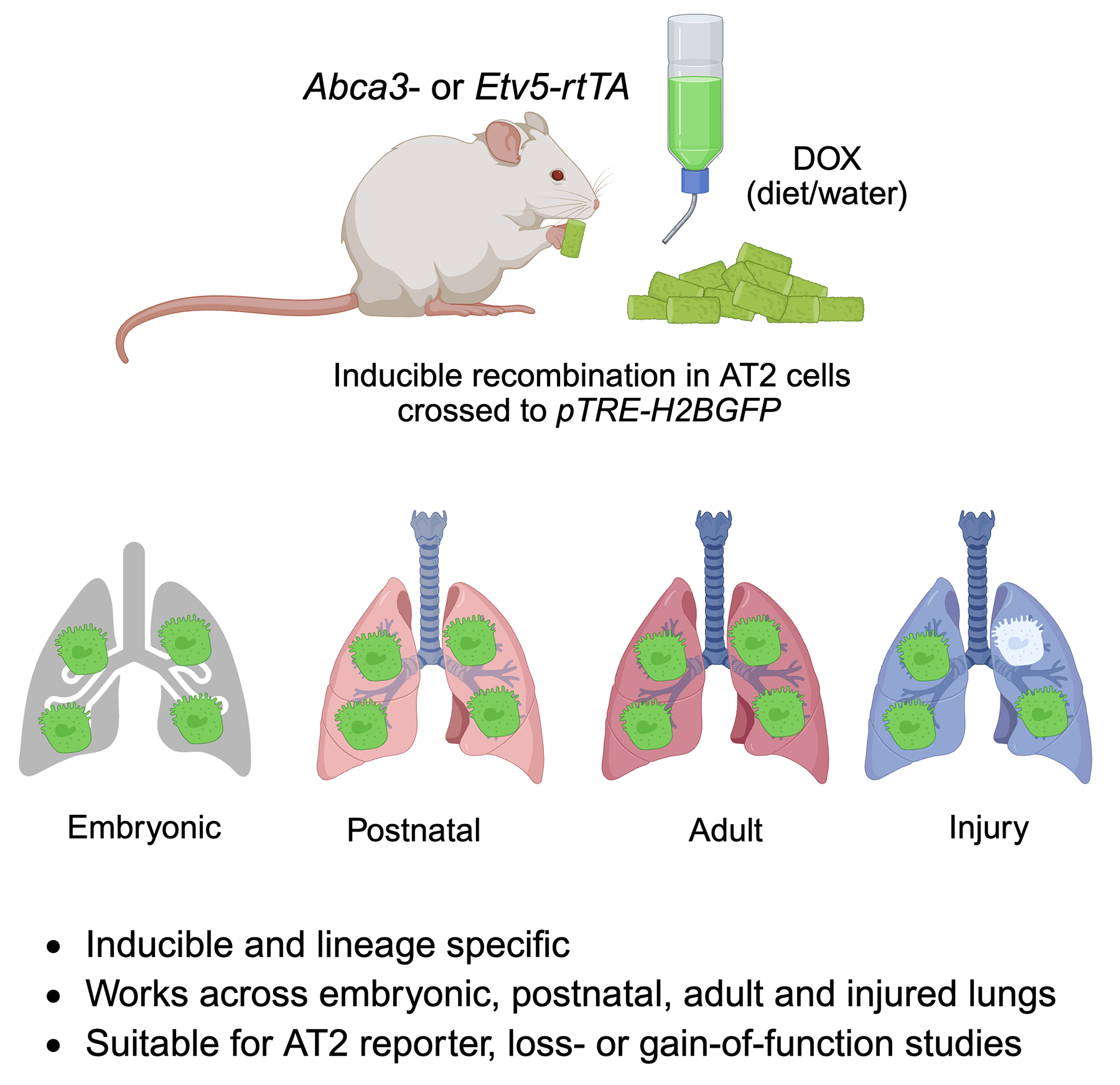
06 February 2026Genetic Strategies for Labeling AT2 Cells in Murine Lung via Abca3 and Etv5-Driven Reporters
Precise labeling of alveolar type 2 (AT2) cells is essential for elucidating lung development and injury responses. In this study, we evaluated Abca3 and Etv5-based genetic strategies for labeling AT2 cells in murine models. Using targeted genetic approaches, we generated Abca3-rtTA and Etv5-rtTA knock-in mouse lines and crossed them with pTRE-H2BGFP to create inducible reporter models driven by Abca3 or Etv5. Labeling specificity and efficiency were assessed by flow cytometry and co-immunostaining. Our results show that both Abca3 and Etv5 strategies faithfully label AT2 cells across developmental stages and following lung injury. Comprehensive analyses confirmed the high specificity and efficiency of labeling. These Abca3- and Etv5-driven systems offer robust tools for investigating AT2 cell biology and pathology and may serve as effective drivers for tetO-mediated gene knockout or overexpression studies specifically in AT2 cells in mouse models.
Open Access
Commentary
06 February 2026Novel Therapeutic Targets of Endothelial Inflammation in Acute Lung Injury and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
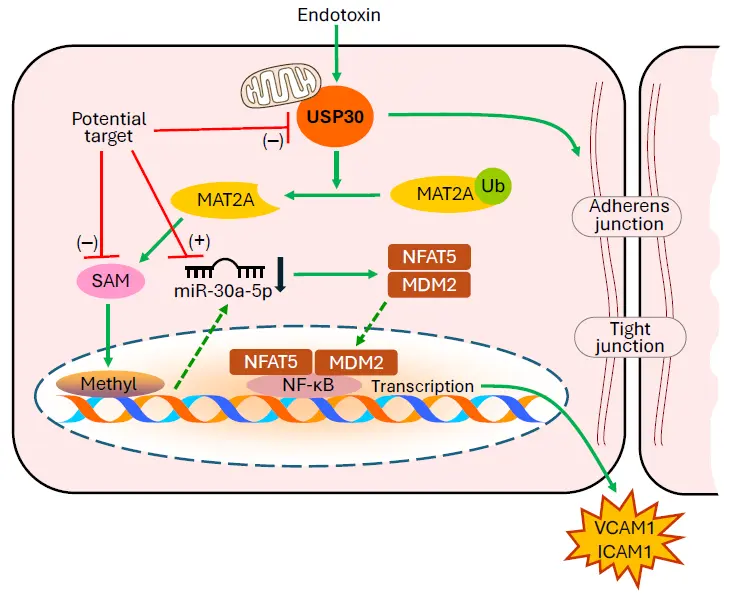
Lung microvascular endothelial inflammation and barrier dysfunction play critical roles in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury (ALI)/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Despite recent scientific advances, the mortality of ALI/ARDS is still extremely high because the molecular mechanisms involved in ALI/ARDS remain unclear. In a recent issue of the journal Advanced Science, Baoyinna and colleagues reported that deubiquitinase USP30 induces lung microvascular inflammation and endothelial barrier disruption through the S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) cycle, DNA methylation, and miR-30a-5p down-regulation in ALI/ARDS. Their findings provide a strong rationale for targeting microRNAs, S-adenosylmethionine, DNA methylation, and deubiquitinating enzymes as potential therapeutic strategies for the treatment of ALI/ARDS.
Open Access
Article
05 February 2026Geospatial Analysis of Energy Requirements for Supplying Desalinated Seawater to the Greek Territory
Greece confronts intensifying water scarcity driven by population growth, urbanization, tourism, and climate variability, despite its extensive coastline. Traditional sources are strained, with agriculture consuming ~80% of withdrawals (surface water ~38%, groundwater ~62%). Desalination, predominantly reverse osmosis (RO), offers a mature solution, already meeting 30–95% of domestic needs in Aegean islands, but its energy intensity challenge sustainability within the water–energy–food nexus. This study presents a geospatial framework to assess energy requirements for a hypothetical scenario in which seawater desalination fully supplies domestic water demand in Greece. High-resolution GIS data, WorldPop population grids, and hydrological networks enable estimation of daily demand (173 L/capita/day) and energy decomposition: desalination (SEC = 5 kWh/m3 SWRO), elevation pumping plus residual pressure (15 m head), and frictional losses. The hypothetical pipelines follow reverse natural drainage paths for realistic routing. Results highlight substantial spatial disparities: inland cities face significantly higher and more uniform energy costs (Ioannina: mean dynamic head 8.3 kWh/m3, ~43% higher than the coastal reference of Athens at 5.8 kWh/m3), driven by elevation and distance; coastal centres show lower means but greater variability (Athens: highest total ~3.35 GWh/day). In summary, fully supplying domestic water demand via desalination would necessitate an additional ~8% of the country’s total electricity consumption. Findings affirm desalination’s potential for coastal/island supply while revealing energy barriers inland.