Artiles
Open Access
Article
03 February 2026Rebuilding Community Cohesion in Migrant-Sending Villages: A Theory-of-Change Model for Social Work and Public Policy in Depopulating Rural Romania
Rural out-migration has become one of the most significant drivers of social and institutional fragility in contemporary Europe, particularly in peripheral and migrant-sending regions. Beyond demographic decline, sustained mobility generates care drain, school disengagement, elderly isolation, and erosion of interpersonal and institutional trust, ultimately leading to community fragmentation. While existing research has extensively documented these effects, far less attention has been given to how they can be systematically reversed through coordinated public policy and social intervention. This paper proposes a governance-ready Theory of Change that integrates social capital theory, social disorganization, rural migration studies, and cohesion-oriented social policy into a unified framework for restoring community cohesion in migrant-sending rural areas. The model specifies how multi-sectoral policy inputs, spanning social work, education, local government, civil society, and EU cohesion instruments, activate bonding, bridging, and linking forms of social capital, generating measurable improvements in school engagement, community participation, intergenerational solidarity, return-migrant reintegration, and institutional trust. Through two complementary visual models, a linear recovery pathway and a self-reinforcing cohesion cycle, the paper demonstrates how social recovery becomes cumulative and resilient once critical relational and institutional thresholds are reached. The proposed framework advances rural development scholarship by shifting the focus from managing migration impacts to governing social regeneration, offering a transferable policy architecture for strengthening cohesion, resilience, and sustainable development in mobility-affected rural regions.

Open Access
Perspective
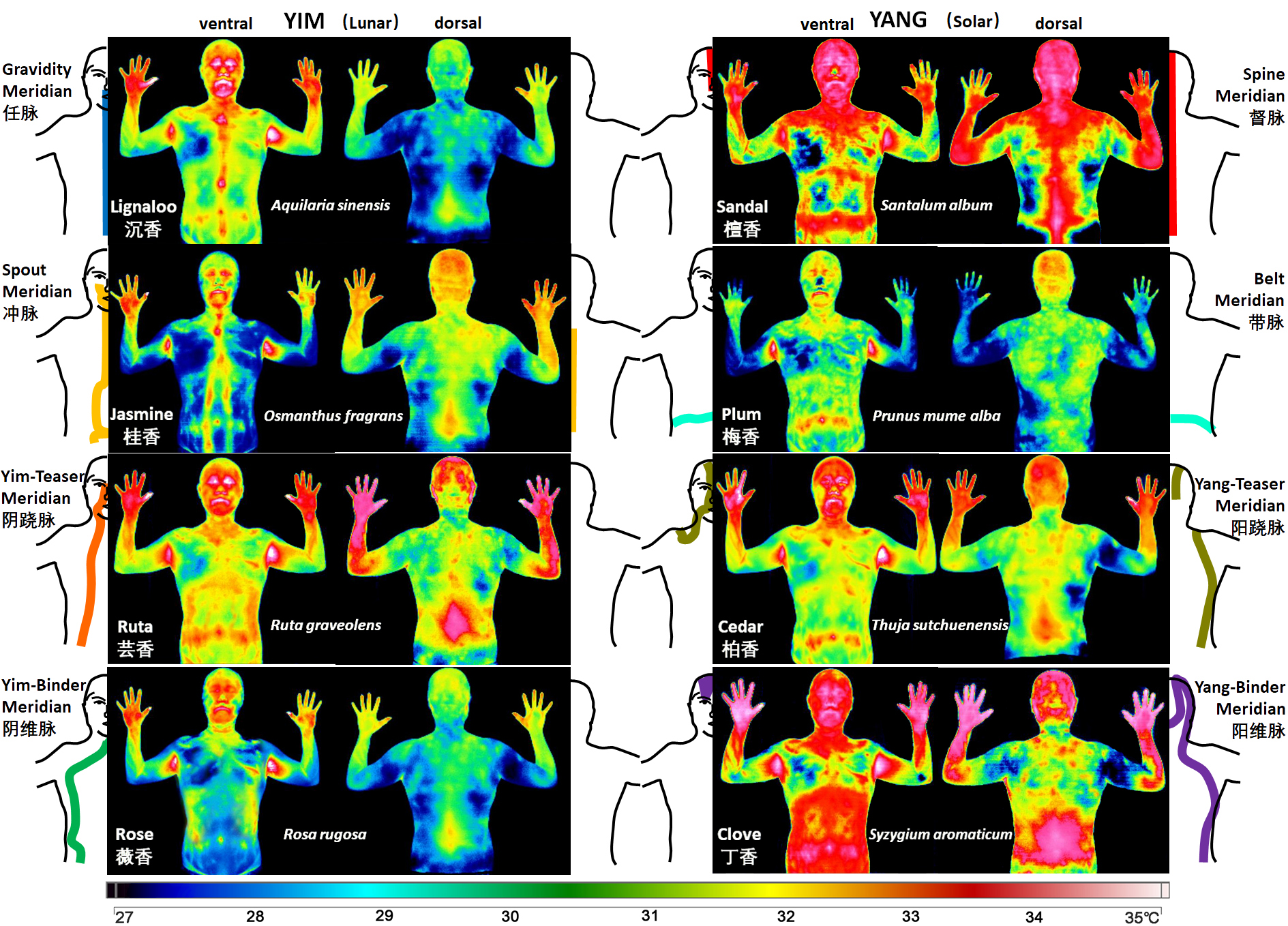
03 February 2026Regularity of Human Body Temperature Change Induced by Various Aromatic Smokes
Aromatherapy is a widely used clinical complementary therapy. Incense therapy, as one of the primary methods of aromatherapy, releases volatile aromatic compounds that rapidly interact with the human body. To explore its potential mechanisms, we collected 123 common natural aromatherapy fragrances and employed infrared thermography to record human surface temperature changes after smoke inhalation. The results showed that most incense samples could induce localized temperature increases, exhibiting eight stable and distinct heating patterns. These patterns show a phenomenological correspondence with the eight extra meridians described in traditional Chinese medicine. This phenomenon suggests that natural incense smoke may induce meridian-specific warming effects, which may provide thermographic evidence for the meridian hypothesis while also offering new perspectives for modern aromatherapy research.

Open Access
Article
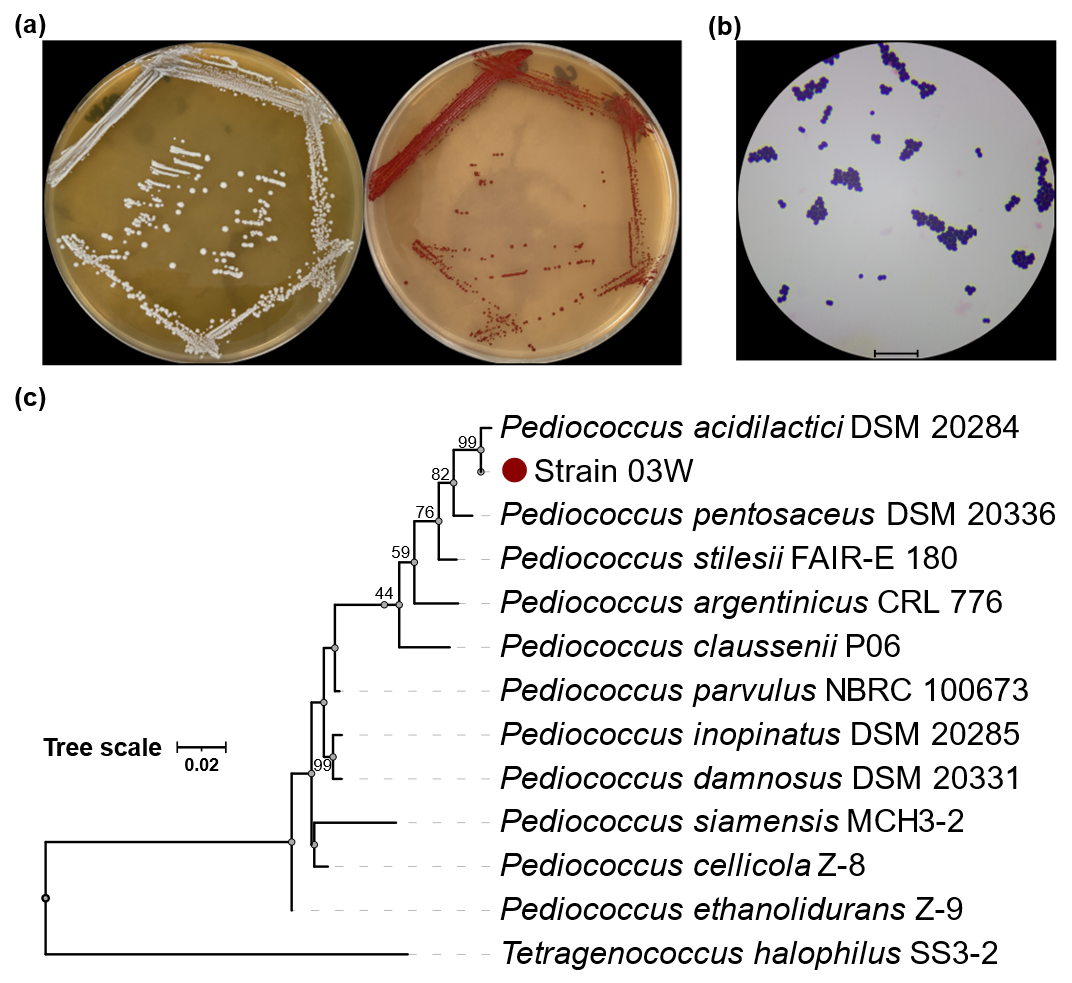
02 February 2026Transcriptomic Insights into Selenite Response and Biotransformation in a Novel Selenium-Enriching Lactic Acid Bacterium
Many microorganisms are capable of surviving selenium (Se)-rich environments and efficiently transforming inorganic Se into organic Se, enabling them to act as a potent biocatalyst for the synthesis of organic Se. Here, we isolated a novel selenium-enriching lactic acid bacterium, Pediococcus acidilactici 03W, from the selenium-rich soil. The growth experiment showed that glucose is the optimal carbon source for P. acidilactici 03W when grown in 1000 µg·mL−1 sodium selenite at pH 6. RNA-seq analysis revealed that a total of 761 genes exhibited altered expression in response to selenite exposure. Downregulation of the phosphate transporter operon (pstA/B/C) and TauE/SafE-type exporters signaled a flux-throttling program that curtailed transmembrane anion flow—limiting high-affinity phosphate uptake and modulating sulfur/selenite export—thereby aligning net anion influx with the cell’s available reductive capacity. In contrast, the expression of the key genes responsible for NAD(P)H or FMN-dependent oxidoreductases and thiol-based redox systems (e.g., trxA/B, tpx, gor, and garB) was induced, together with cysteine desulfurases and sulfurtransferases, supporting the enzymatic reduction of selenite. Interestingly, Fe–S cluster assembly genes (e.g., sufU) were suppressed (not induced), suggesting a shift away from de novo Fe–S biogenesis toward sulfur–selenium transfer and detoxification under oxidative stress. Also, some key genes involved in central carbon metabolism, including the glycolytic pathway (e.g., pfkA) and the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) (e.g., zwf), were downregulated, which is consistent with reallocating resources from rapid growth to redox homeostasis. Collectively, selenium assimilation in P. acidilactici 03W proceeds through anion transport, enzymatic reduction to Se0 or H2Se, and incorporation into seleno-amino acids (selenocysteine and selenomethionine). Our findings provide a basis for microbial selenium transformation and highlight the potential of P. acidilactici 03W for developing selenium-enriched probiotic foods.
Open Access
Article
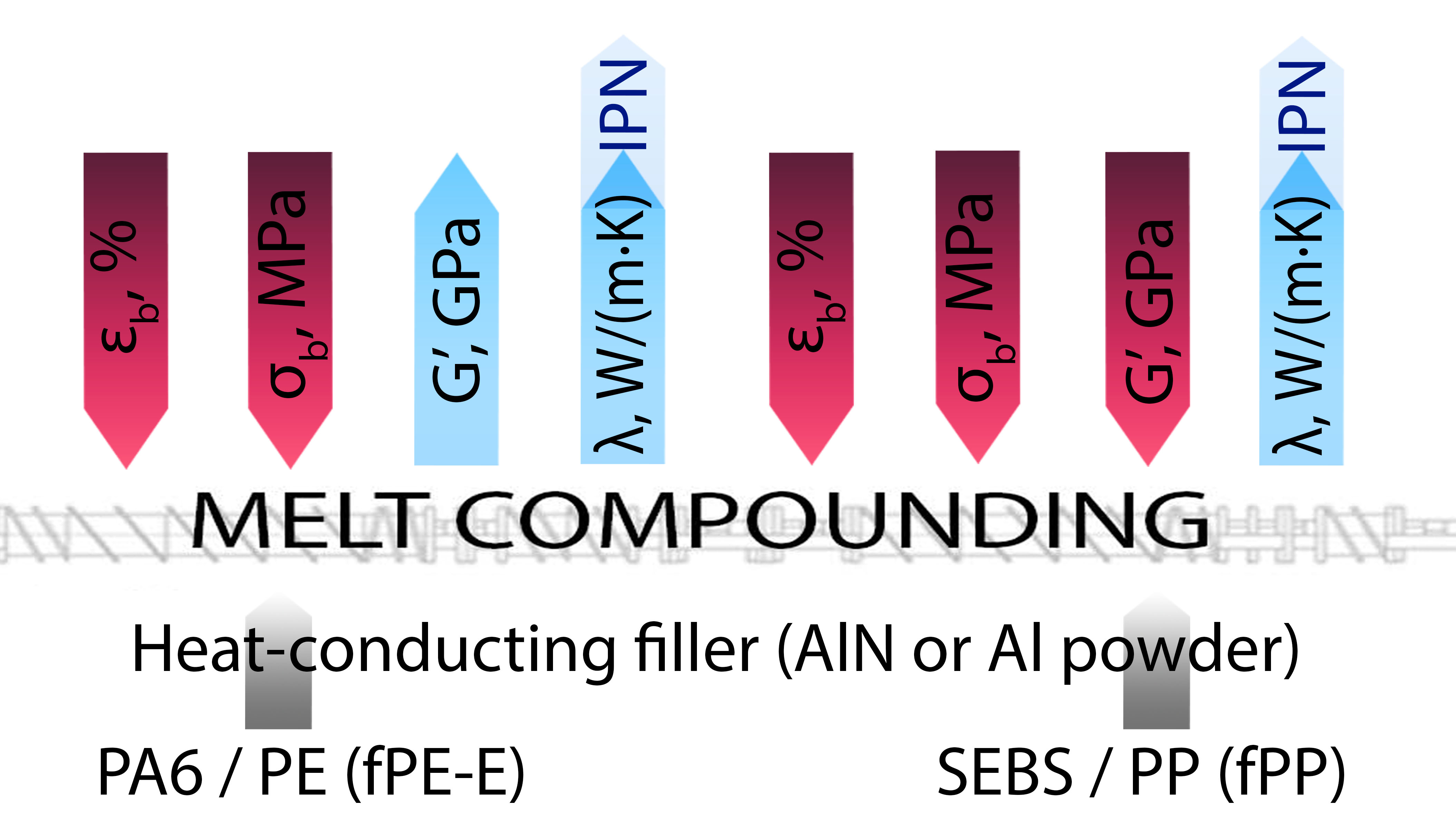
02 February 2026Effect of Aluminum and Aluminum Nitride on Some Thermophysical Properties of Polyamide 6/High-Density Polyethylene and Styrene-Ethylene-Butadiene-Styrene/Polypropylene Blends
The structure and physical-mechanical properties of non-compatibilized and compatibilized blends of polyethylene with polyamide 6 and polypropylene with styrene-ethylene-butadiene-styrene, containing heat-conducting modifiers (aluminum and aluminum nitride) in their composition, were studied. Data were obtained on the influence of the ratio of polymer components in the blend and the functionalization of one of them, as well as the type of heat-conducting filler, on the mechanical and dynamic mechanical properties of composites and their thermal conductivity. Using SEM, no selective distribution of aluminum and aluminum nitride in the two-component polymer matrix was found when composites were obtained by extrusion compounding. It was found that the reinforcing effect of the filler (change in shear modulus) is largely determined by the presence of a polar polymer in the blend matrix. Both heat-conducting modifiers affect the position of the glass transition temperature maxima of the polymers used. The prospect of creating an interpenetrating polymer network structure to achieve additional thermal conductivity gain while maintaining the proportion of the conductive modifier is demonstrated.
Open Access
Article
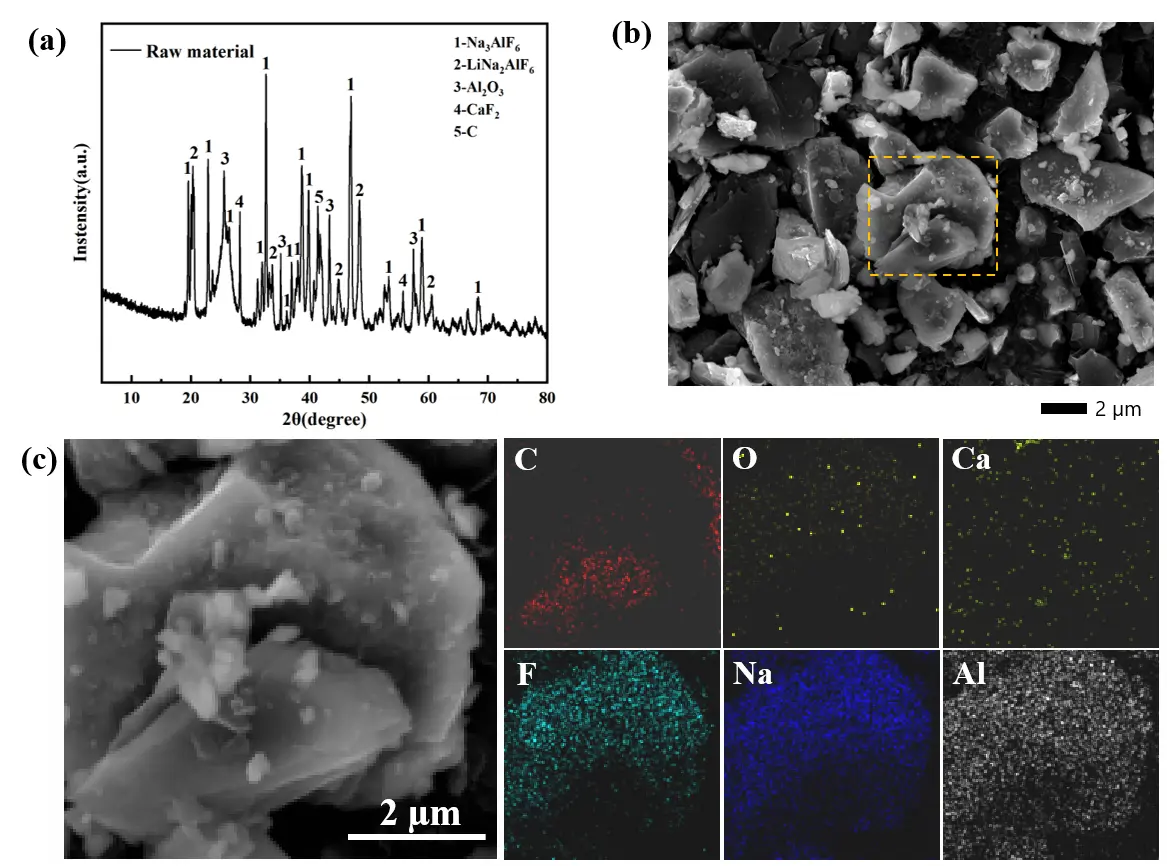
02 February 2026Alkaline Leaching Lithium from Spent Carbon Anode and Coupling of Extraction-Carbonization for Cryolite Regeneration
This paper proposes an integrated coupling process of alkali leaching, HBTA-TOPO synergistic extraction, and carbonation for the resource utilization of spent carbon anode (SCA), a typical lithium-bearing industrial solid waste from electrolytic aluminum production, whose lithium content exceeds the ore grade. Compared with conventional acid leaching methods, the adopted alkaline leaching approach features mild reaction conditions, low equipment corrosion risk, and eliminates the volatilization of toxic hydrogen fluoride (HF) gas, thus showing prominent environmental safety advantages. Under the optimal alkaline leaching conditions (NaOH concentration of 10 mol/L, reaction temperature of 90 °C, liquid-to-solid ratio of 10:1, and reaction time of 120 min), the maximum Li+ leaching rate reaches 89.46%. As the leaching process proceeds, lithium in the carbon slag rapidly migrates to the alkaline leaching solution. The Na–Al–F bonds of cryolite (Na3AlF6) and lithium cryolite (Na2LiAlF6) present in the SCA gradually break, and soluble ions such as Na+, Li+, Al3+, and F− enter the solution. High-concentration Na+ reacts with free F− to form sodium fluoride (NaF), which adheres to the SCA, leading to an increase in the sodium-aluminum ratio (Na/Al) of the SCA. The HBTA-TOPO synergistic extraction system is proposed for the extraction and enrichment of lithium in the lithium alkaline leaching solution, and the extraction residue is used to repair and regenerate cryolite. The extraction efficiency of Li+ reaches and the yield of cryolite reaches 81.54% and 76.54%. The molecular ratio of sodium fluoride to aluminum fluoride in synthetic cryolite products is relatively high. This integrated process realizes the efficient recovery of lithium and the high-value regeneration of cryolite from SCA, providing a sustainable technical route for the clean utilization of electrolytic aluminum solid waste. This integrated closed-loop process realizes the simultaneous recovery of lithium and high-value regeneration of cryolite from SCA, which not only mitigates the environmental pollution caused by SCA stacking and the scarcity of lithium resources, but also provides a sustainable technical route for the clean and high-value utilization of electrolytic aluminum solid waste.
Open Access
Article
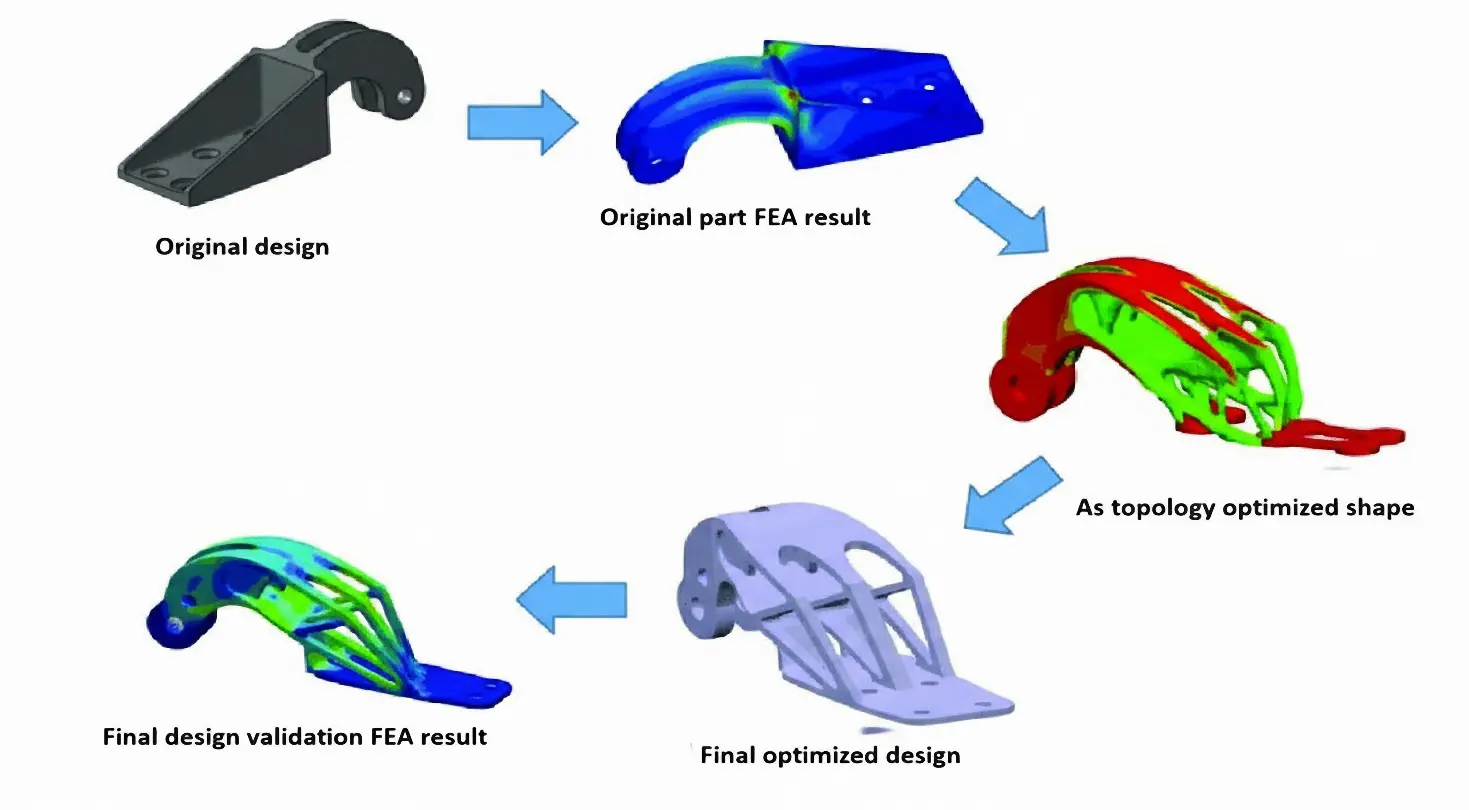
02 February 2026Topology Optimization for Drone Structure: Comprehensive Workflow Including Conceptual Modeling, Components Preparation and Additive Manufacturing
Payload drones are often limited more by frame weight than by motor power. This work aims to design, optimize, and validate a flat octocopter frame with eight independently driven rotors arranged symmetrically on separate arms. The drone frame design in SOLIDWORKS uses Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and topology optimization to remove material from low-stress regions while keeping the main load paths intact. The final design cuts the frame mass by 37.3% compared to the baseline model and reduces the 3D printing time by about five hours using a Creality K1C printer with Polylactic Acid (PLA) filament. These changes increase the available thrust-to-weight margin for payload without exceeding the allowable stress or deformation limits of the material. The electronic components also identified compatible flight controllers, ESCs, motors, and radio systems to show that the proposed frame can be integrated into a complete multirotor platform. Overall, this work demonstrates a practical approach to designing lighter octocopter frames that are easier to 3D print and can be used more effectively for delivery and inspection missions.
Open Access
Article
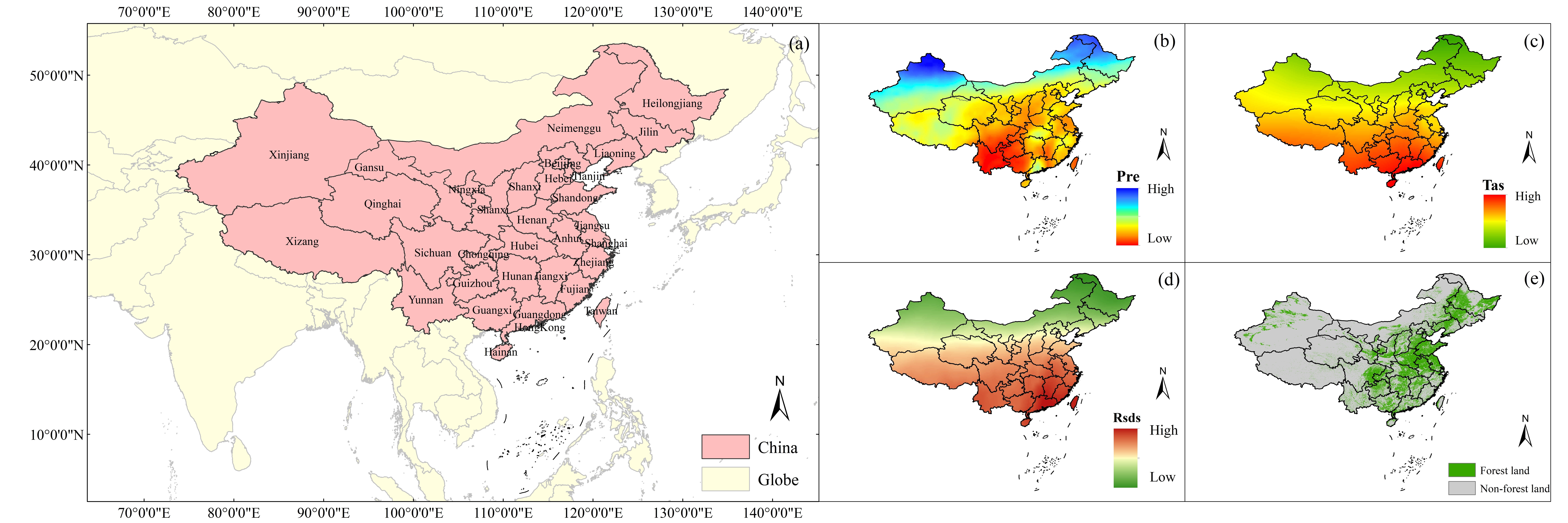
30 January 2026Forecasting Forest Product Yields in China Based on a Random Forest Model: Interaction Between Climate Change and Socio-Economic Factors
This study presents a comprehensive projection of China’s forest product yield dynamics (encompassing commodity timber and logs) through 2100, employing an innovative integration of machine learning and economic modeling. We developed a hybrid analytical framework combining random forest algorithms with Cobb-Douglas production functions to assess multi-dimensional drivers, including climatic variables, socio-economic indicators, and demographic trends. Our multi-model validation demonstrated strong predictive performance (R2 are 0.86 and 0.92), particularly in quantifying climate-production interactions, with sensitivity analysis identifying surface downward shortwave radiation (RSDS), population density (POP), and mean annual temperature (MAT) as dominant predictors explaining 68% of yield variance. Future yields exhibited significant spatial and temporal variations under different SSP scenarios, especially under SSP126, where yields were more stable, and under SSP245 and SSP370, where yields showed a moderate increasing trend. The SSP585 shows higher fluctuations and a decreasing trend in yields due to climate change. Geospatial modeling uncovered critical regional disparities, suggesting potential production migration from traditional southern bases to north-eastern/northwestern frontiers under climate stress. The southern subtropical belt emerged as particularly vulnerable to thermal extremes and precipitation variability, while northern regions demonstrated greater climate resilience but require substantial silvicultural adaptation. These results provide a scientific basis for developing more precise forest management policies and sustainable development strategies to help meet the challenges posed by future demand for forest products and climate change.
Open Access
Article
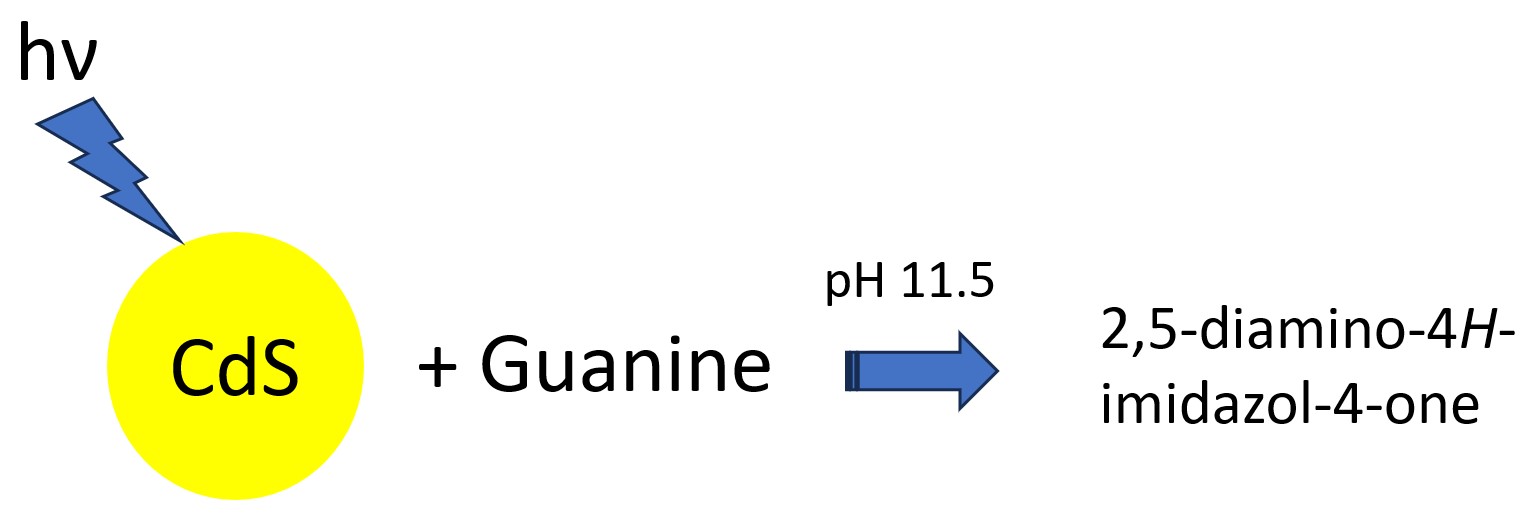
30 January 2026Photocatalytic Transformation of Guanine Using Colloidal CdS Nanoparticles
Investigations into the photoinduced reactions of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) bases are important for human health. Herein, we have synthesized colloidal CdS nanoparticles by a method reported in the literature. The mean particle diameter of the semiconductor was about 55 nm. The colloidal CdS particles were used as a photocatalyst to investigate the organic transformation of guanine (2-amino-6-oxopurine). The products of the semiconductor-induced reaction were analyzed by liquid chromatography-mass chromatography (LC-MS) measurements. The solitary product of the photocatalytic reaction of guanine was revealed as 2,5-diamino-4H-imidazol-4-one. The likely reaction pathway for the formation of the product has been presented. To our understanding, the present work is the first account on the mechanistic aspects of the semiconductor-induced photocatalytic reaction of guanine.
Open Access
Article
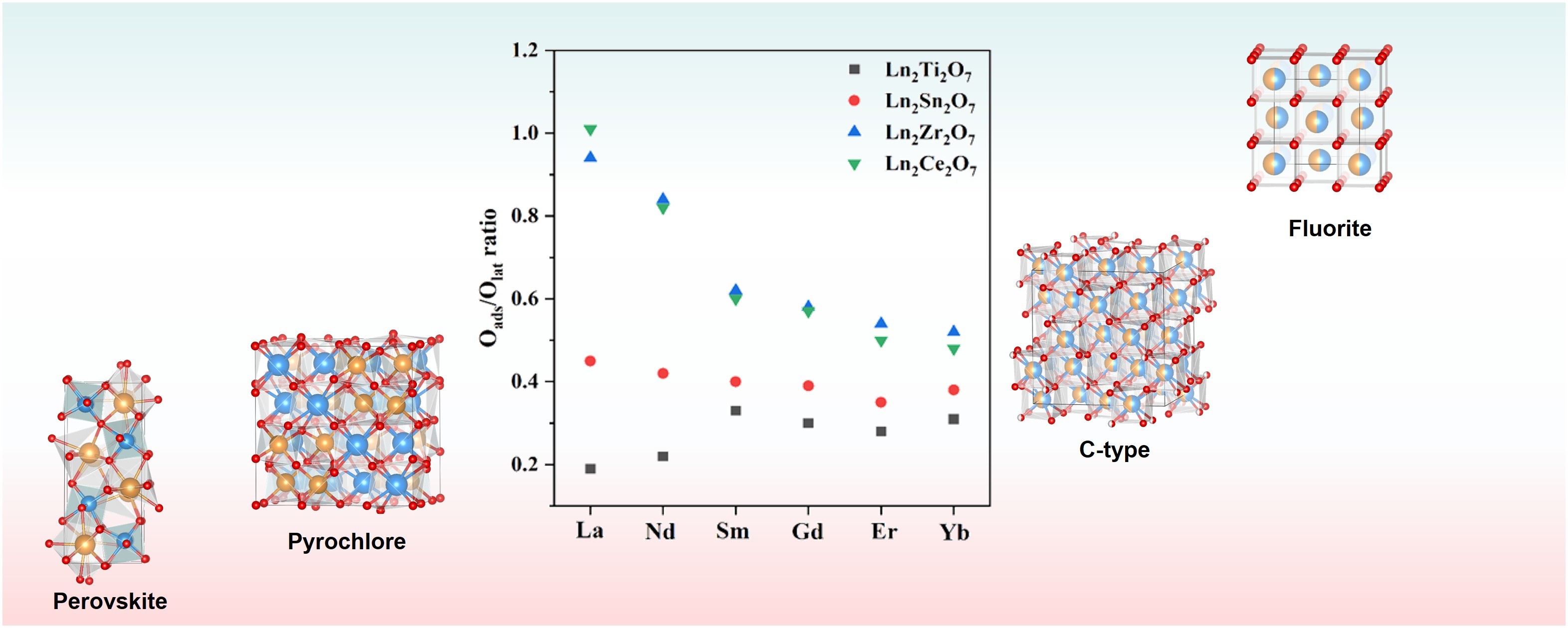
29 January 2026A Comprehensive Study on the Phase Structure, Surface Properties, and Active Oxygen Species of A2B2O7 Composite Oxides
A2B2O7 complex oxides have a great potential to be used in high-temperature catalytic processes. Herein, a series of A2B2O7 (A = La, Nd, Sm, Gd, Er, Yb; B = Ti, Sn, Zr, Ce) compounds with all four kinds of typical sub-crystalline phases were synthesized to study their bulk and surface properties. FTIR spectroscopy was adopted as a novel method in this study to identify distinctively these phases. Whereas, it cannot be used to distinguish the subtle structure difference between disordered and ordered pyrochlores, nor that between the disordered defect fluorite and the rare earth. To discriminate these exquisite phase differences, XPS spectra must be supplementarily used. Specifically, it was discovered that the coordination numbers of the A- and B-site cations are the key factor affecting their binding energies. Furthermore, the electronegativity of the A- and B-site elements significantly influences the binding energy of surface lattice oxygen, reflecting their electrophilic and nucleophilic properties, which can thus be used to effectively identify the sub-crystalline phase. The oxygen vacancy concentration of different sub-crystalline phases is the primary factor controlling the amount of surface chemisorbed oxygen species on A2B2O7 compounds, with superoxide anions (O2−) identified as the major species.
Open Access
Article
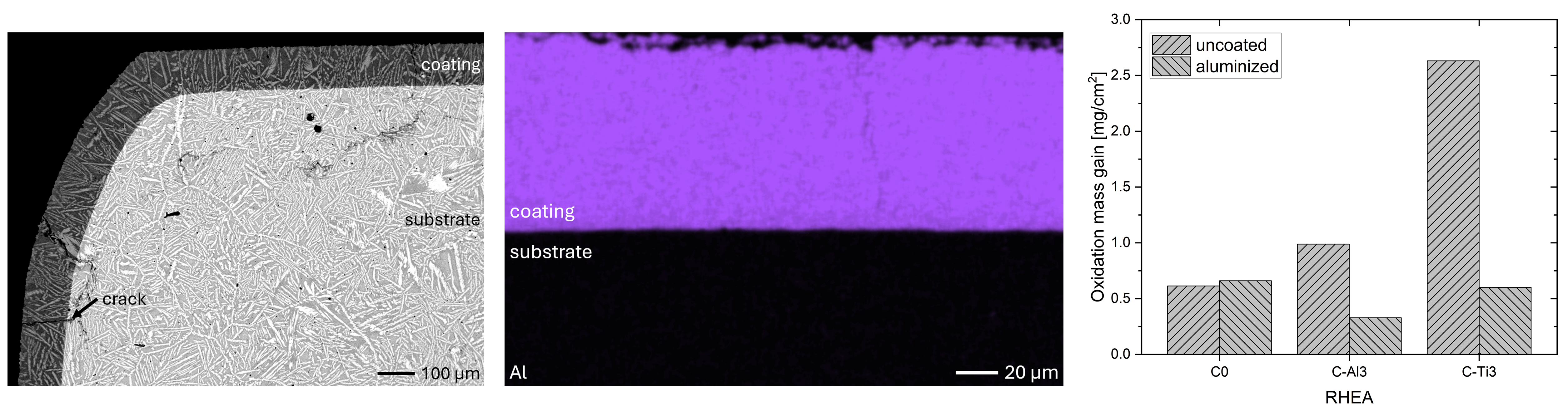
28 January 2026Enhanced High-Temperature Oxidation Resistance of Refractory High-Entropy Alloys Al-Cr-Mo-Ta-Ti by Aluminizing Using Pack Cementation
Refractory high-entropy alloys (RHEAs) show promising properties for applications as structural materials in high-temperature applications, such as high solidus temperature and high strength. Improving their density, oxidation resistance, and room temperature ductility are still the aims of research in alloy development. In this study, Al-rich diffusion coatings by pack cementation are developed for three different alloys in the system Al-Cr-Mo-Ta-Ti in order to improve their high-temperature oxidation resistance. Equimolar AlCrMoTaTi, Al-rich Al3CrMoTaTi, and Ti-rich AlCrMoTaTi3 are synthesized by vacuum arc melting with subsequent milling to powder, consolidation to bulk material by field-assisted sintering technology/spark plasma sintering (FAST/SPS), and homogenization heat treatment. The applied aluminizing coatings are investigated by gravimetry, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD). Experimental analyses are supplemented by CALPHAD simulations. Compact, uniform, and adhesive Al-rich diffusion coatings are produced on all three substrate RHEAs and exhibit single-layered D022 Al3(Cr,Mo,Ta,Ti) intermetallic compound analogous to Al3Ti in the binary Al-Ti system. Isothermal oxidation at 1000 °C for 48 h in ambient air results in the formation of 1–2 µm thin protective single-layered alumina scale—in contrast to multi-layered oxide scales in uncoated condition—and mass gains as low as binary Al3Ti and Ni-based superalloys.