Artiles
Open Access
Review
15 January 2026Renal Aging and Fibrosis in the Elderly: Frontiers in Non-Invasive Assessment
Today’s society has gradually entered an aging phase, and among the elderly population, the risk of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is significantly increased. Renal fibrosis is the key pathological mechanism for the development of chronic kidney disease to end-stage renal disease. With the increase in age, the phenomenon of glomerular sclerosis and interstitial fibrosis in aging kidneys gradually aggravates, and the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) decreases, further affecting renal function. Fibrosis not only accelerates the loss of renal function but also significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, which seriously affects the quality of life and life expectancy of patients. This paper reviews the relevant literature and discusses the characteristics of an aging kidney and the diagnostic methods for renal fibrosis.

Open Access
Article
15 January 2026The Role of Empathy in Resource Control Strategy Selection and Social Dominance in Early Childhood
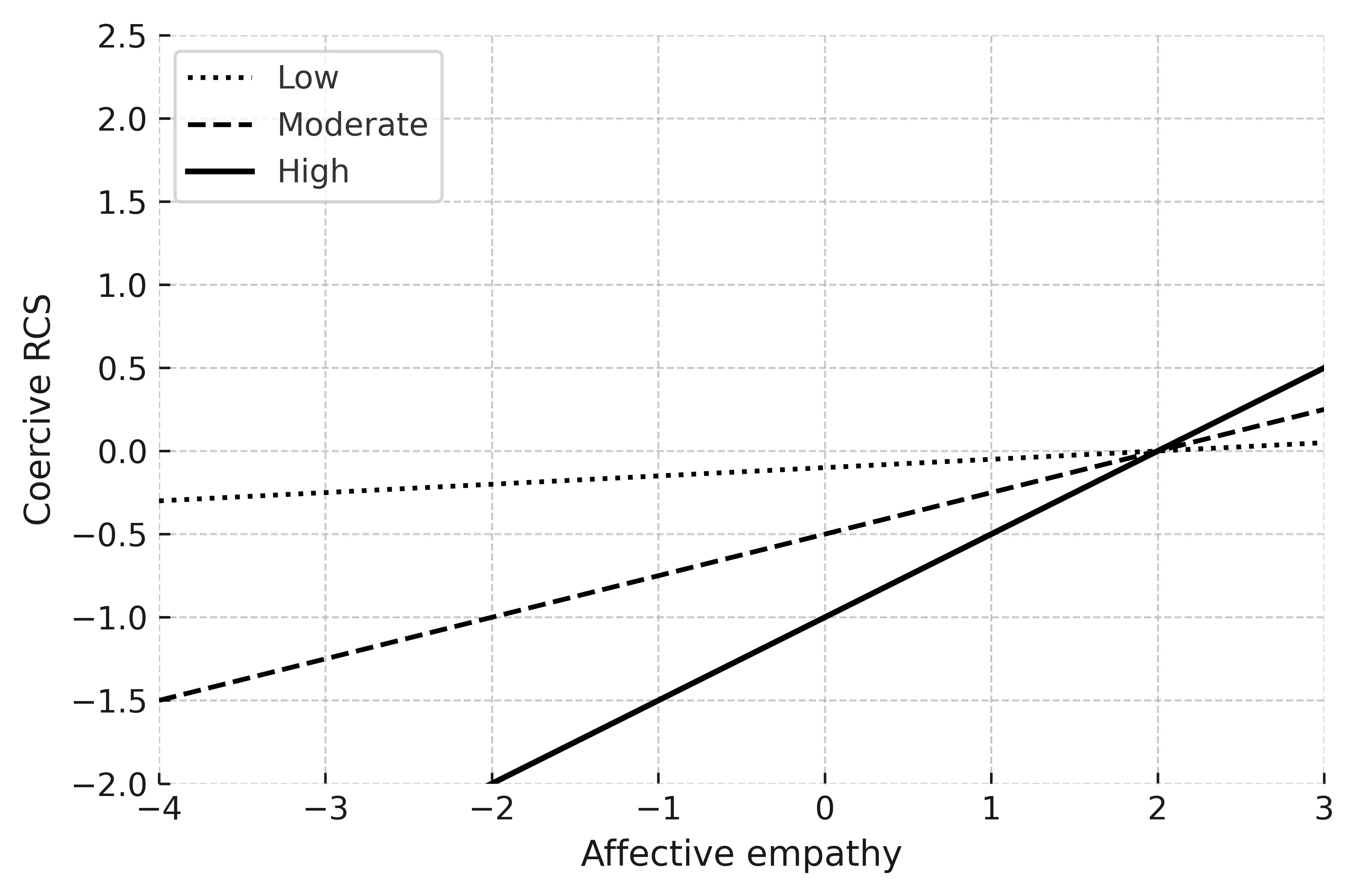
This cross-sectional study examined the associations between affective and cognitive empathy, resource control strategies (RCS), resource control success, and social dominance in preschool children, within the framework of resource control theory. Ninety-two children (ages 4–5) completed assessments of empathy, while teachers rated their prosocial and aggressive behaviors, prosocial and coercive RCS, resource control success, and social dominance. Hierarchical regression analyses indicated that prosocial resource control strategies uniquely predicted children’s resource control success, whereas social dominance, examined as a distinct social status outcome, was explained by a combination of prosocial and coercive strategies, general prosocial behavior, and resource control success. Affective empathy was positively related to both types of RCS, while cognitive empathy moderated the link between affective empathy and coercive RCS. These findings highlight the dual potential of empathy in early peer relations, suggesting that empathy may facilitate both cooperative and coercive tactics in the pursuit of social influence. The findings also underscore the need to distinguish between behavioral strategies, their effectiveness, and broader social status outcomes when examining early social dominance. Implications for interventions that cultivate constructive applications of empathy are discussed.
Open Access
Article
15 January 2026Does the Implementation of Rights of Nature Enhance Nature Conservation in Practice?
The debate surrounding Rights of Nature has been ongoing for some time, with many different concepts being put forward. Some consider them to be extremely effective, others useless or even counterproductive. The paper begins by summarising the complex debate and presents different approaches to categorising the debate. Based on those approaches, simplified categories for the various concepts for Rights of Nature are proposed: animal rights, rights for nature as a whole, and rights for non-animal natural entities, with a possible further distinction between rights for ecosystems and other natural entities. Subsequently, the paper goes on to study the effect of legally recognising Rights of Nature and finds that in South America, nations that recognise Rights of Nature perform slightly better in terms of Ecosystem Vitality and public awareness of environmental risks. While further research is needed, those results indicate that Rights of Nature may be a modest catalyst for conservation efforts.

Open Access
Article
14 January 2026Large-Scale Language Model Assisted Construction of Multi-Source Heterogeneous Knowledge Graphs for Marine Renewable Energy
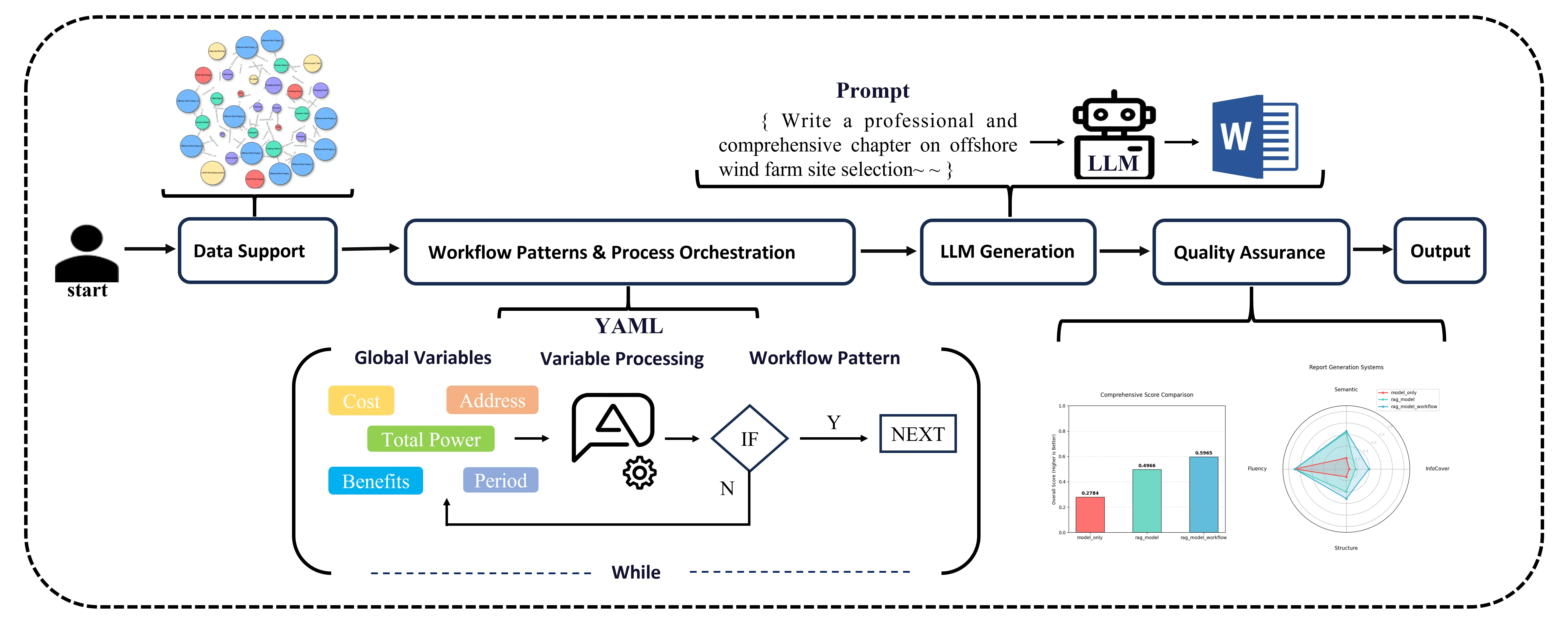
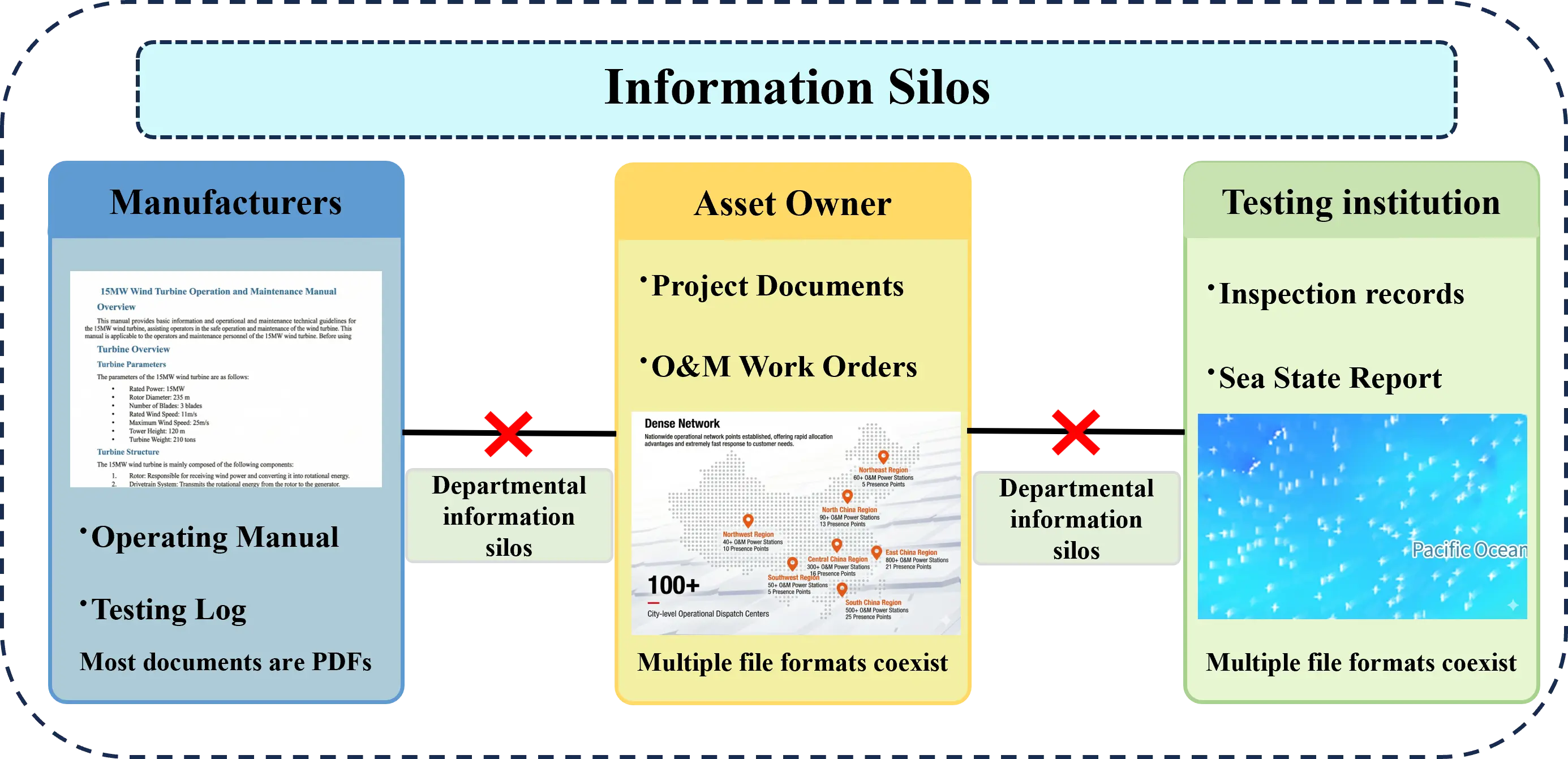
Marine renewable energy systems, particularly offshore wind and photovoltaic (PV) installations, generate large volumes of heterogeneous maintenance texts. However, the resulting knowledge remains fragmented due to dispersed sources, diverse formats, and domain-specific terminology. To address these challenges, this study proposes a large-scale language model assisted methodology for constructing a multi-source heterogeneous knowledge graph for intelligent operation and maintenance (O&M). The method integrates unified document preprocessing, domain-oriented prompt engineering, large-scale language model–based entity and relation extraction, and multi-level entity normalization. It systematically transforms unstructured documents (e.g., standards, procedures, manuals, inspection records, and environmental reports) into structured triples, enabling the construction of a dynamically evolving O&M knowledge graph. A rigorous ablation study on real-world offshore wind and PV datasets demonstrates that the proposed workflow exhibits exceptional robustness against OCR noise (e.g., scanned artifacts, stamps, and signatures) and substantially improves extraction volume, accuracy, and coverage compared with traditional methods. In particular, combining high-quality preprocessing and optimized prompts yields the most reliable and semantically coherent results. The study provides a practical technical pathway for automated knowledge management in marine renewable energy and offers a foundation for future applications in intelligent diagnostics, predictive maintenance, and digital-twin systems.
Open Access
Article
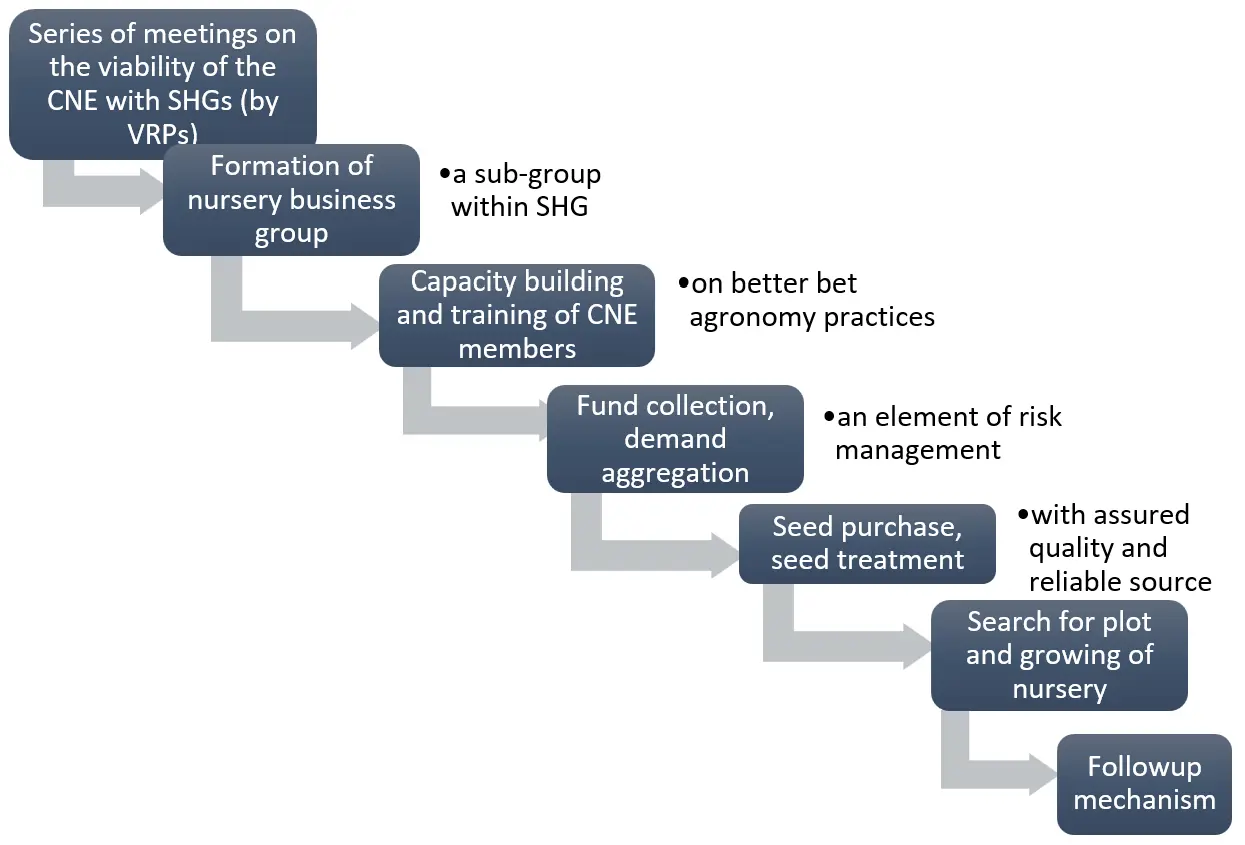
13 January 2026Small Is Big: Making Difference in Lives of Small and Marginal Farmers with Focus on Women Through Rice Nursery Entrepreneurship
With increasing climate stress and monsoon variability, it becomes imperative to design and plan innovations catering to the needs of small and marginalized farmers in rice farming. This requires interventions to encourage farmers to adopt better management practices in their fields, using cost-saving technologies. Along with technology innovation improving yields, strategy promoting inclusion is equally important to address the gender gap existing in rice farming for equitable development. Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia has initiated one such innovation known as Rice Nursery Enterprise (RNE), led by small and marginal farmers in the state of Bihar, India. This very innovation adopted a livelihood centric approach, reaching out to farmers through strategic partnerships with community-based organization, research universities, government agencies, private players, and Bihar Rural Livelihood Promotion Society, popularly known as JEEVIKA. In order to understand the process, characteristics, and feasibility of rice nursery entrepreneurship (RNE), a field study was organized with both men and women farmers in the state of Bihar. It was found that RNE helps both women and men farmers to set up a coping mechanism tackling monsoon variability with the availability of timely seedlings and generating additional income in their household through the service economy. Importantly, when women farmers are strategically mainstreamed with informed choices to lead through Self Help Groups (SHGs), it was found that, along with added income and coping variable monsoon, they are increasingly establishing their identity as farmers at both the household and community level.
Open Access
Review
12 January 2026The Anti-Fibrotic Potential of GLP-1 and GIP Receptor Agonists in Chronic Inflammatory Disorders: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Horizons
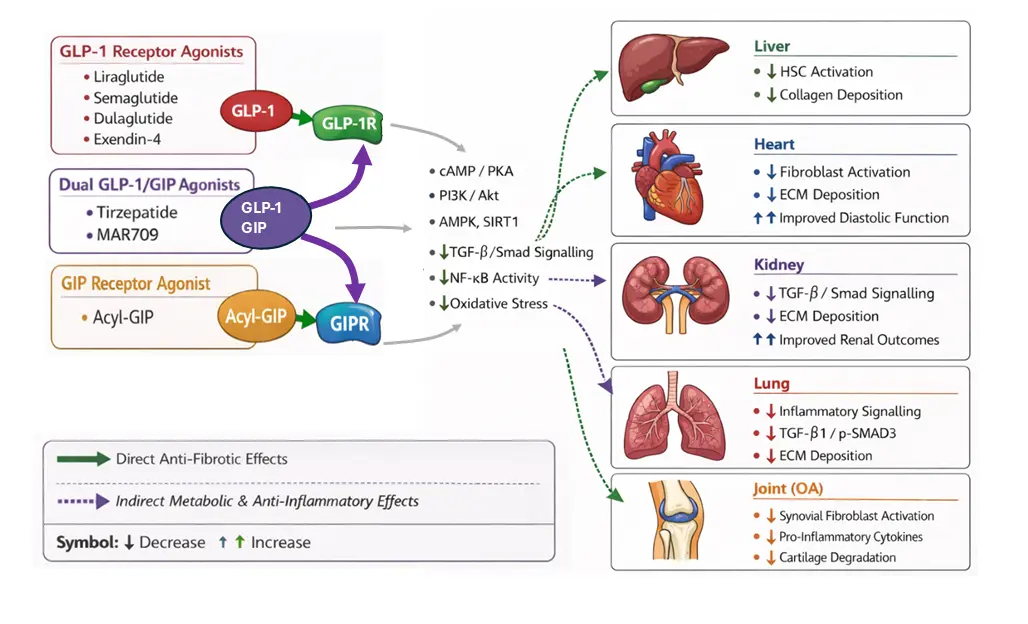
Fibrosis, characterised by the excessive deposition of extracellular matrix via activated fibroblasts, is a pathological feature of several chronic inflammatory disorders, which collectively contribute significantly to global morbidity and mortality. Despite this, current anti-fibrotic therapies are of limited efficacy. However, incretin-based therapies, primarily glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, are now emerging as candidate drugs for modulating fibrotic signalling pathways. This review synthesises the growing body of preclinical and clinical evidence that incretin receptor agonists exert direct and indirect anti-fibrotic effects. We detail the molecular mechanisms and survey the promising data across hepatic, cardiac, renal, lung, and joint tissues, which underscore the potential for repurposing of this drug class as a therapeutic strategy for fibro-inflammatory conditions.
Open Access
Article
09 January 2026Corrosion Behaviors of Aluminate Coatings on Mg Alloy AE44
Chromate-based corrosion protection, such as that on aluminum (Al), magnesium (Mg), titanium (Ti), and other alloys, has often been used with some success. Considering the pollution problem associated with chrome, it is necessary to search for an alternative process to conventional chromate coating technology. Plasma electrolytic oxidation processing (PEO) is an emerging, environmentally friendly surface engineering technique. The study in this article was to utilize the PEO technology to deposit aluminate coatings on magnesium alloy AE44 for corrosion protection. Potentiodynamic polarization measurements and electrochemical impedance tests were performed to investigate corrosion behaviors of coated and uncoated AE44 alloy samples immersed in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. The surfaces of coated and uncoated samples before and after corrosion tests were observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). SEM and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) and X-ray diffractometry (XRD) were used to study the effect of PEO coatings on the surface morphology change of the alloy in association to their corrosion behaviors. The differences in corrosion behaviors under different electrical parameters of aluminate-based coatings on Mg alloy AE44 were elucidated through potentiodynamic polarization measurements, complemented by SEM and EDS analysis.
Open Access
Review
09 January 2026Recent Progress in Organically Modified Silica and Self-Matting Polymers for Coating Applications
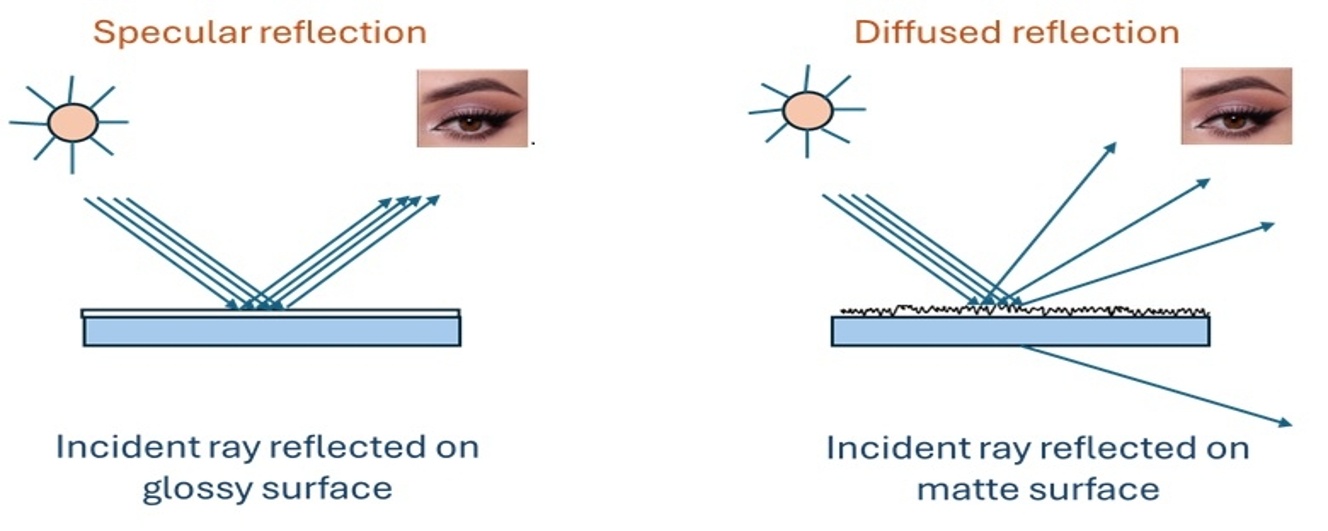
The conventional way of reducing the gloss of coating is to use matting agents such as silica, wax, and fillers. The demerits of these matting agents are sedimentation, poor compatibility, and deterioration of mechanical properties over time. Recent advances in organically modified matting agents and self-matting polymers have addressed these limitations by enabling uniform matte finishes without compromising film integrity. Organically modified silica, functionalized with silane or acrylate moieties, has been shown to deliver lower gloss values in the range of 5–14 gloss units at 60°, in contrast to the typically observed >70 gloss units for conventional high-gloss coatings. Similarly, self-matting polymers, particularly waterborne polyurethane (WBPU) and acrylate dispersions, achieve matte effects through intrinsic micro-roughness during film formation. The gloss value achieved with self-matting acrylic resin synthesized using hydrolyzable silane functionality is 6.3 units at 60°. This review emphasizes distinct techniques for organic modifications of matting agents, synthetic approaches for self-matting polymeric architectures, and their applications in the fields of decorative coatings, industrial coatings, and wood coatings.
Open Access
Review
08 January 2026Synthetic Biology-Inspired Biocontainment Strategies of Therapeutic Genetically Engineered Bacteria
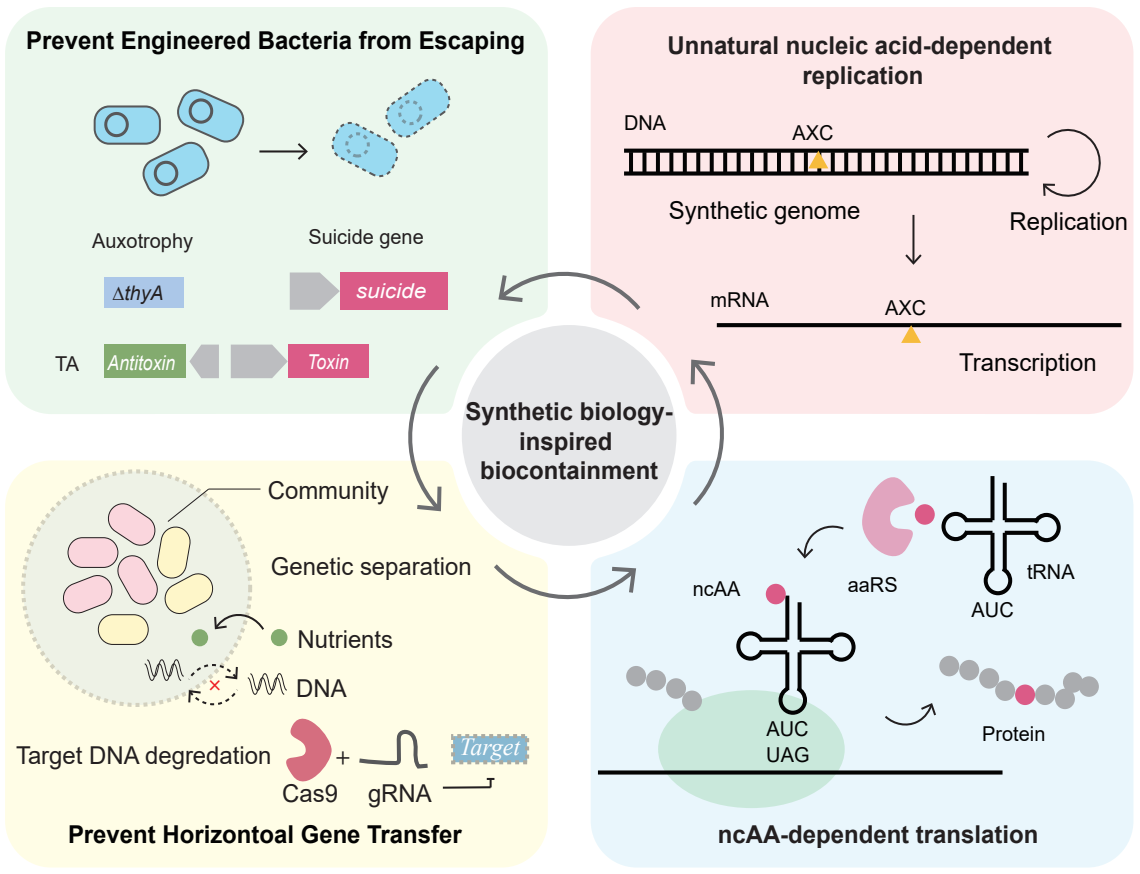
With the rapid expansion of synthetic gene technologies and engineered bacteria for disease diagnosis or therapy, biosafety concerns have intensified. Substantial efforts have therefore been directed toward developing biocontainment systems that prevent the unintended release of engineered microorganisms and the horizontal transfer of synthetic genetic elements into natural ecosystems. Recent advances in synthetic biology have yielded a diverse suite of biocontainment strategies, including engineered biosafety genetic circuits, genetic isolation approaches, targeted degradation of genetic material, and physical encapsulation of microbial chassis. Furthermore, the incorporation of unnatural nucleic acids and noncanonical amino acid-based orthogonal replication, transcription, and translation systems has markedly improved the robustness and orthogonality of these containment platforms. In this review, we summarize the latest developments in biocontainment strategies for genetically engineered bacteria and discuss how these innovations may address current and emerging biosafety challenges.
Open Access
Article
08 January 2026A Large-Scale Language Model Based System for Automated Generation of Offshore Wind Power Feasibility Study Reports
Driven by global energy transition goals, the large-scale development of offshore wind power imposes rigid requirements for professionalism, standardization, and timeliness on feasibility study reports (FSR). Traditional manual compilation and existing automated methods fail to meet these requirements due to interdisciplinary complexity, poor process controllability, and insufficient domain adaptation. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a configurable and interpretable offshore wind FSR generation system built on a three-tier framework that encompasses “data support, process orchestration, and quality assurance”. The system integrates a YAML-based workflow architecture, multi-level prompt engineering, and a comprehensive evaluation system. Notably, the introduced “Cyclic Aggregation Mode” enables the iterative generation and logical summarization of multi-subproject data, effectively distinguishing this system from traditional linear text generation models. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed “Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) + Large-scale Language Model (LLM) + Workflow” system outperforms baseline models with key metrics including semantic consistency (0.6592), information coverage (0.3908), structural compliance (0.5123), and an overall score (0.5965). Ablation studies validate the independent contributions of the RAG and Workflow components, thereby establishing the “RAG + LLM + Workflow” paradigm for intelligent professional document generation. This work addresses core challenges related to controllability, accuracy, and interpretability in high-stakes decision-making scenarios while providing a reusable technical pathway for the automated feasibility demonstration of offshore wind power projects.