Open Access
Article
09 May 2025Modeling and Assessing Economical Feasibilities for Waste to Energy Conversion/Incineration Process in Context of Municipal Solid Waste
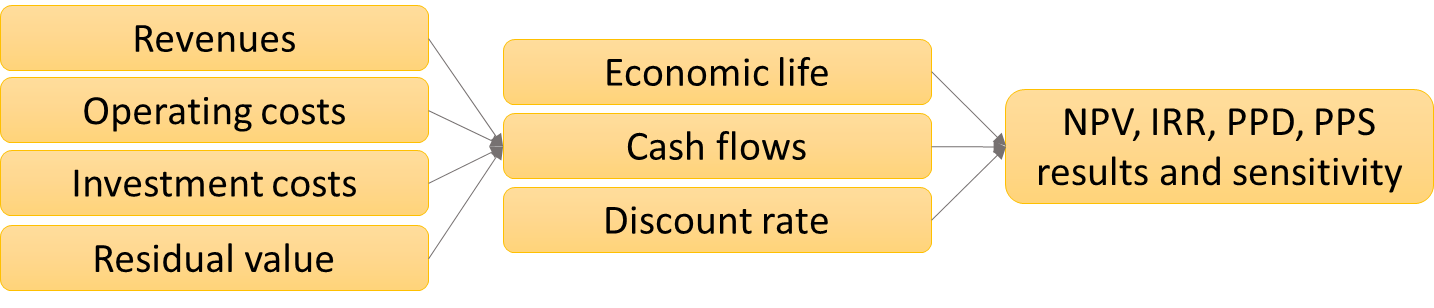
At the time of the study, most of the municipal waste, including solid municipal waste, in the city of St. Petersburg and in the connected larger Leningrad region is processed by landfilling. This sort of waste processing in open landfills causes environmental damage, uncontrollable landfill fires, bad and dangerous odors, nearby rivers/streams, groundwater pollution, CH4 and CO2 emissions, to mention a few. Additionally, landfilling is a waste of energy and material resources present in the content dumped into landfills. In this context, Waste-to-Energy (WtE) incineration is a process that we use to recover the energy the materials have back to usable form, which we use in the form of heat and electricity. Even though a lot of resources and energy are available in the (municipal solid) waste, it does not mean that recovering it would always make sense. Our study analyses and estimates the profitability of a WtE incineration plant(s) in the city of St. Petersburg and the connected Leningrad region. With the available data and following analysis, we have concluded that the WtE incineration is economically feasible in this specific region and city areas, given that the implementations follow more traditional (economically less expensive and easier) technical and process model solutions. As a note of results stability, it needs to be pointed out that the changes in estimates of gate fees, cost of electricity and heat, and so on do impact the economic feasibility a lot, and larger scale changes in the assumed revenues would have a high impact on the outcome of repeatability of the results.
Open Access
Article
28 May 2025Mechanisms of Machine Vision Feature Recognition and Quality Prediction Models in Intelligent Production Line for Broiler Carcasses
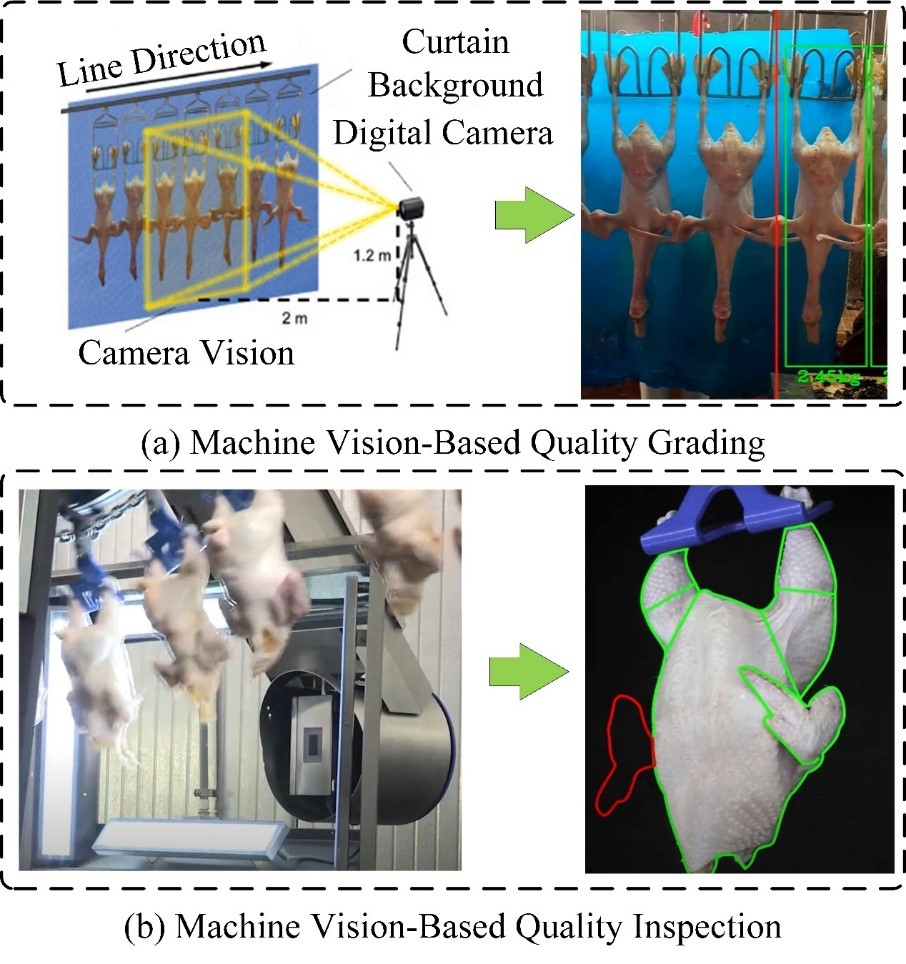
With global broiler production reaching 103 million tons in 2024—a 1.5% increase over 2023—the poultry industry continues to grow rapidly. However, traditional broiler segmentation methods struggle to meet modern demands for speed, precision, and adaptability. First, this study proposes an improved lightweight image segmentation algorithm based on YOLOv8-seg and integrates the Segment Anything Model (SAM) for semi-automatic annotation, achieving precise mask segmentation of broiler parts. Subsequently, Key geometric features (e.g., area, perimeter, axes) were extracted using image processing techniques, with enhancements from HSV color transformation, convex hull optimization, and ellipse fitting. Furthermore, Image calibration was applied to convert pixel data to physical dimensions, enabling real-sample validation. Using these features, multiple regression models—including CNNs—were developed for carcass quality prediction. Finally, by analyzing the broiler segmentation process, machine vision techniques were effectively integrated with quality grading algorithms and applied to intelligent broiler segmentation production lines, providing technical support for the intelligent and efficient processing of poultry products. The improved YOLOv8-seg model achieved mAP@0.5:box scores of 99.2% and 99.4%, and the CNN model achieved R2 values of 0.974 (training) and 0.953 (validation). Compared to traditional systems, the intelligent broiler cutting line reduced failure rates by 11.38% and improved operational efficiency by over 3%, offering a reliable solution for automated poultry processing.
Open Access
Article
05 June 2025Enhancing Product Development Excellence through Quality Management Tools: A Comprehensive Review and Integrated Conceptual Framework
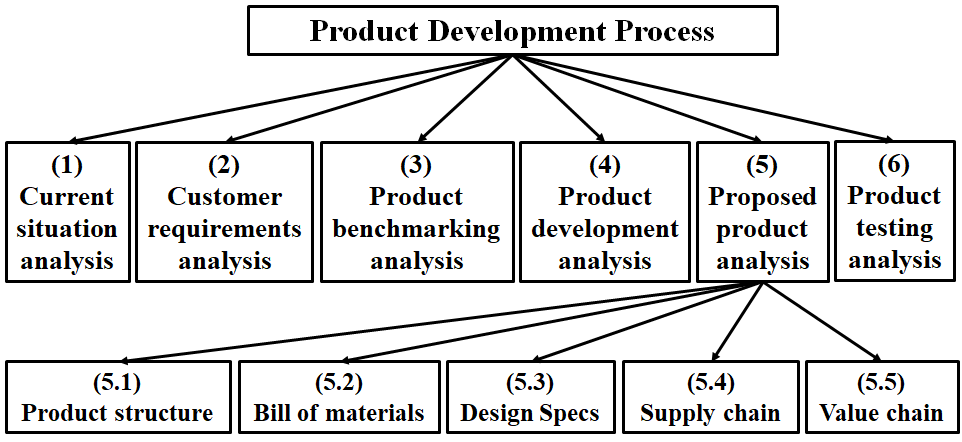
In today’s rapidly evolving and highly competitive global markets, achieving product development excellence is critical for organizations striving for sustained growth and customer-centric innovation. This study highlights the integral role of key quality management tools in enhancing product development processes, reducing defects, and driving continuous improvement. It presents a robust methodology that strategically combines Quality Function Deployment (QFD), Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), and the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) framework to significantly improve the quality, reliability, and efficiency of product development efforts. Built on core principles of customer-centricity, innovation, cross-functional collaboration, continuous improvement, and risk-based thinking, the methodology emphasizes capturing the Voice of the Customer (VoC) and identifying Critical-to-Quality (CTQ) attributes to align product outcomes with customer expectations and business objectives. Utilizing the DMAIC framework, the organization systematically drives process optimization and innovation throughout the product lifecycle Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are established to track efficiency, quality, customer satisfaction, and time-to-market, while Agile methodologies enhance flexibility, speed, and responsiveness. The study further identifies organizational, technical, cultural, and managerial barriers to product development excellence and proposes targeted strategies to address them and ensure sustainable success. This integrated framework fosters a culture of innovation and continuous learning, enabling organizations to anticipate challenges, manage risks, and consistently deliver superior product development outcomes. While currently conceptual, the framework is slated for empirical validation through case studies, pilot projects, and simulations to verify its practical applicability across diverse development contexts.
Open Access
Article
18 June 2025CO2 Emissions Comparisons on Cementous Sustainable Flooring Options: Modeling and Evaluation
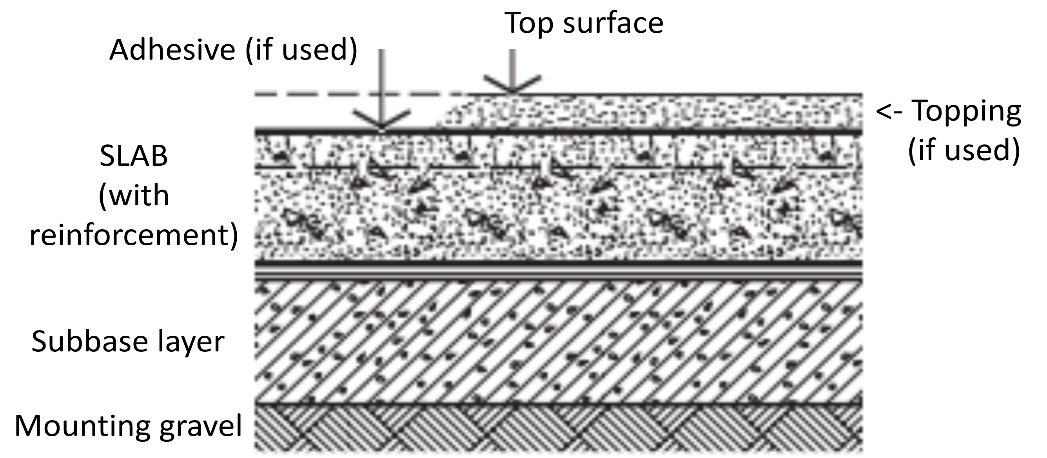
CO2 and greenhouse gas emissions have become a major environmental issue worldwide, and emissions have spiked faster than most could ever imagine. The issues have made it crucial to find financially feasible and long-term, use-efficient solutions that fulfill industrial needs. As society so much depends on the current industry outputs, we need to reduce emissions coming from those industrial facilities and premises where people shop and buy services and assets on a daily basis. These emissions need to be reduced on a global scale, and here, concrete as a building material comes into play as one of the most used materials, especially on industrial floors. A typical solution is a sturdy base slab with a use case-specific coating on it. The base slab is expected to last the whole life of the building, whereas the coating might be considered consumable and refurbished/fixed as a maintenance job many times before the building itself is demolished. In heavy use cases, the maintenance cycle might be fast, which reduces the usable time of the building and generates downtimes for business. The coating decisions have a major impact on the building’s lifetime emissions, which is the key focus of this study, too. Bad decisions can introduce unnecessary microplastics and nano dust particles to work environments and also generate restructuring needs of the operational activities. In the worst case, operations have to be shut down. Luckily, there are options, and emissions can be reduced in many ways. By using long-term and durable cementitious mix-based dry shake coatings, one can reduce top coating-based emissions, and by decreasing the amount of used reinforcement components in the base slab, an extra positive impact can be achieved. With a base slab, also more environmentally friendly low-carbon cement formulations can be considered, like fly ash or GGBS (ground granulated blast furnace slag) based formulas, which we discuss in detail and analyses traditional options compared to modern CEM3a and CEM3b versions. For the top coating, emissions are generated in the construction and maintenance phases. To find different options with cross implications on lifetime emissions, our study analyzes CO2 emissions sources for several concrete mixes, which are then paired with floor-top coatings based on Cementous mix or epoxy coating. We have pinpointed the potential for reducing the building’s floor-based lifetime CO2 emissions. The analysis is based on the impacts of the base slab and floor coating selection combinations. As a de facto comparison element, we used a 100 percent virgin Portland cement-based mix. The Portland cement was compared to CEM3a and CEM3b mixes. On the top surface of the floor, traditional epoxy base floor coating was compared to a modern dry shake-based option. In the analysis, the dry-shake-based floor showed major benefits. Emissions were drastically reduced, fewer maintenance downtimes were needed, and the general life expectancy was a lot longer for the dry shake option.
Open Access
Article
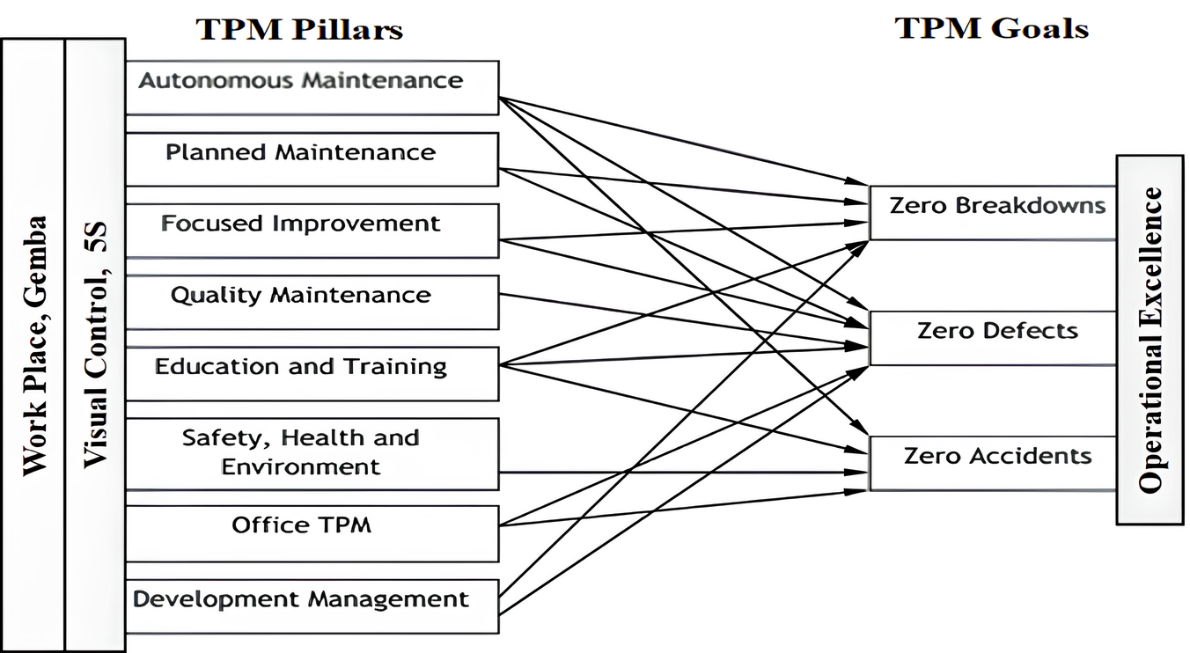
19 June 2025Advancing Total Productive Maintenance in Smart Manufacturing: From Methodology to Implementation
The rapid advancement of Industry 4.0 technologies has catalyzed the development of intelligent tools and methodologies to enhance operational efficiency, reliability, and productivity across modern industrial enterprises. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), a foundational approach in manufacturing, traditionally improves equipment reliability, reduces downtime, and drives continuous improvement through proactive employee involvement. However, in the context of Smart Manufacturing, traditional TPM reveals significant limitations—chiefly its reliance on manual data collection, reactive maintenance, and limited real-time insight. This paper explores TPM’s evolution, key innovations, and cross-industry applications while highlighting challenges in adopting Industry 4.0 technologies. It proposes a comprehensive TPM 4.0 framework integrating Lean Six Sigma’s DMAIC methodology with advanced digital tools for systematic failure mode classification, risk-based maintenance prioritization, and real-time performance optimization. Leveraging IIoT-enabled condition monitoring, Digital Twin simulations, and machine learning-driven predictive analytics, the framework supports real-time anomaly detection, cognitive diagnostics, and adaptive maintenance planning—substantially improving Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), cost efficiency, and system resilience. Additionally, federated learning promotes scalable, privacy-preserving AI collaboration, while blockchain enhances data security and transparency, mitigating cybersecurity risks. By merging traditional TPM with AI-driven automation and digital sustainability, TPM 4.0 establishes a foundation for self-optimizing, cyber-resilient maintenance ecosystems, accelerating the transition to autonomous manufacturing. Although conceptual, this framework offers a practical roadmap for smart manufacturing transformation, with future validation planned through case studies and pilot projects.
Open Access
Article
23 June 2025Asset Management Excellence: A Roadmap for Integrating Lean Six Sigma and ISO 55001 to Achieve Operational Excellence
Asset Management Excellence (AME) has become essential for sustaining operational efficiency and long-term competitiveness in today’s digitally driven and increasingly complex industrial landscape. This study introduces an integrated roadmap that aligns Lean Six Sigma (LSS)—specifically the DMAIC methodology—with ISO 55001 standards to enhance asset reliability, optimize lifecycle performance, and support continuous improvement. The proposed model embeds principles such as lifecycle value optimization, risk-based decision-making, and sustainability. It leverages proven tools, including Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), Root Cause Analysis (RCA), Statistical Process Control (SPC), predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring to enable proactive, data-driven asset management. This integration supports efficiency, reduces variability, and extends asset life. Performance is measured through key indicators such as Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), and lifecycle cost-efficiency. These metrics enable organizations to monitor progress, validate improvements, and ensure alignment with strategic objectives. The study also addresses common implementation challenges across financial, organizational, workforce, technological, and structural domains. It proposes targeted mitigation strategies, including phased implementation, cost-benefit analyses, stakeholder engagement, digital readiness assessments, and capacity-building programs to enhance adoption and long-term sustainability. While conceptual, the roadmap offers a practical, scalable approach to embedding LSS within asset management systems. It fosters a transition from reactive to proactive practices, enhancing resilience, sustainability, and strategic value. Future research will validate the framework through sector-specific case studies and pilot implementations.
Open Access
Article
08 July 2025Repurposed Ovens for Space Heating Following Global Catastrophic Infrastructure Loss: Methods and Efficiency Calculations
Global catastrophic infrastructure loss (GCIL) would disrupt energy supply networks, prohibiting heating in houses reliant on electricity or piped natural gas. In such situations, buildings in cold climates would require alternative heating methods, as space heating is critical to survival. This work assesses the viability of converting household appliances to wood-burning stoves and the scalability of such conversions in the event of a catastrophe. A standard residential electrical oven was converted to a wood-burning stove, using tools and materials likely to be readily available following GCIL, and tested by burning a total of 9.1 kg of pine wood and kindling. The conversion was successful, with an average useful heat output of 2.6 kW, showing the viability of ovens as wood-burning stoves for space heating. It is expected that such conversions could be completed in under one day, given sufficient availability of tools, materials, and labour. Global supplies of ovens, tools, materials, and fuel are expected to be sufficient for widespread conversion of ovens to wood-burning stoves, assuming international collaboration. However, international collaboration may be limited following GCIL, so countries should develop individual response plans accounting for this limitation, and knowledge should be disseminated ahead of time, or backup communication systems put in place.
Open Access
Review
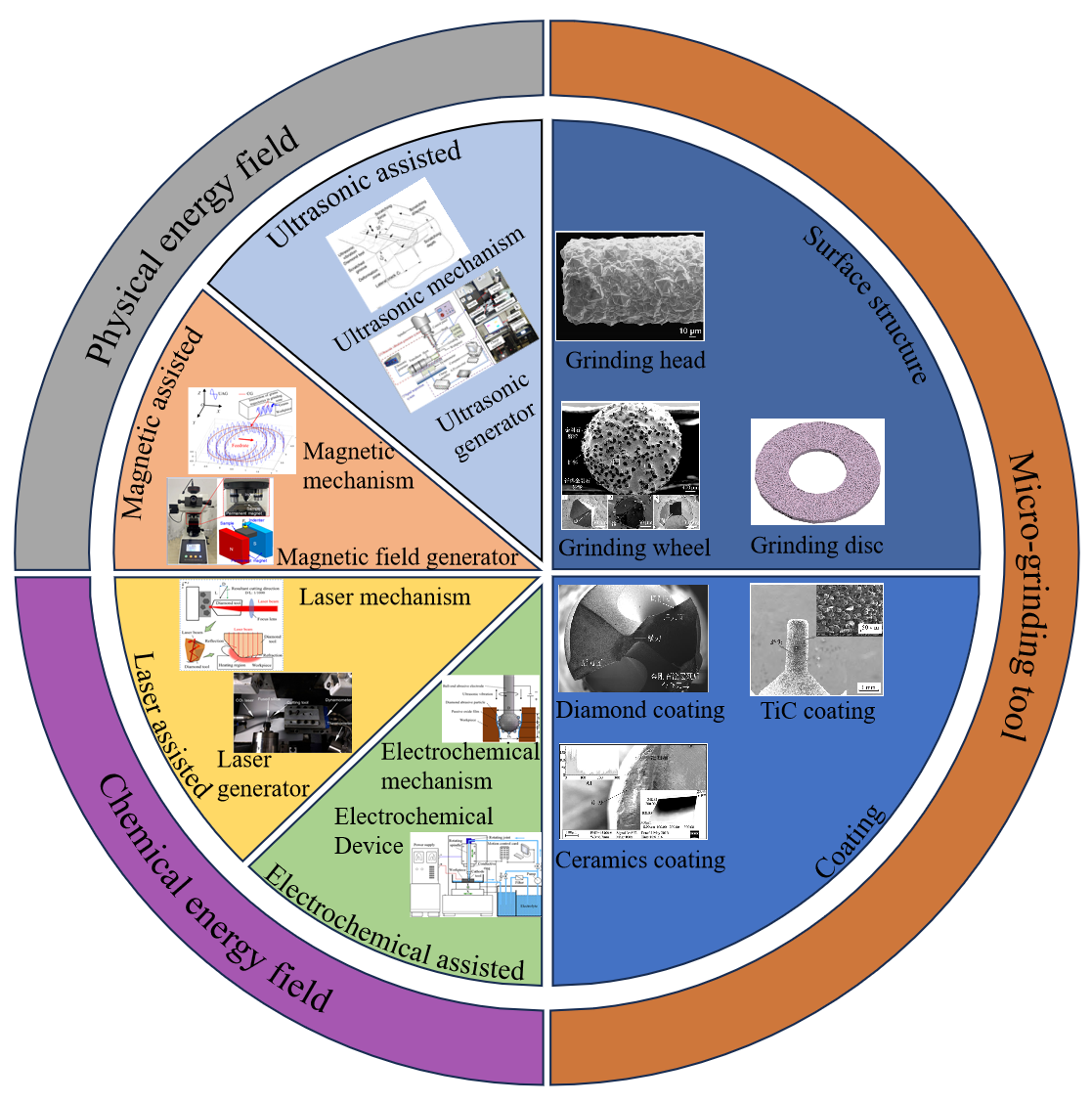
09 July 2025Muti-Energy Field-Assisted Grinding of Hard and Brittle Materials: Tools, Equipment and Mechanisms
Hard, brittle and difficult-to-machine materials are prone to surface cracks, subsurface damage and other defects in the traditional grinding process, accompanied by low processing efficiency and severe tool wear. As a new type of processing technology, energy field-assisted grinding provides a new approach for the efficient and high-quality processing of hard and brittle materials. This paper reviews the latest research progress of muti-energy field-assisted grinding from aspects such as the types and selection of grinding tools, processing equipment and physical-chemical coupled mechanisms. Firstly, micro-grinding tools are classified based on different surface structures and coating materials, with the aim to enhance processing efficiency, improve the surface quality and geometric accuracy of workpieces, and reduce tool wear. Secondly, the processing mechanisms, parameter selection and current difficulties faced by four energy field-assisted grinding methods, including laser-assisted grinding, electrochemical-assisted grinding, magnetic-assisted grinding and ultrasonic field-assisted grinding, are discussed under both chemical and physical effects. Thirdly, different equipment and auxiliary devices developed for energy field-assisted grinding have been introduced, providing reliable platforms for the distribution design and efficient regulation of the energy field. Finally, the cutting-edge progress, main challenges and development trends of energy field-assisted grinding are prospected, illustrating the great potential of this technology in fields such as aerospace, electronics, and optical components.
Open Access
Article
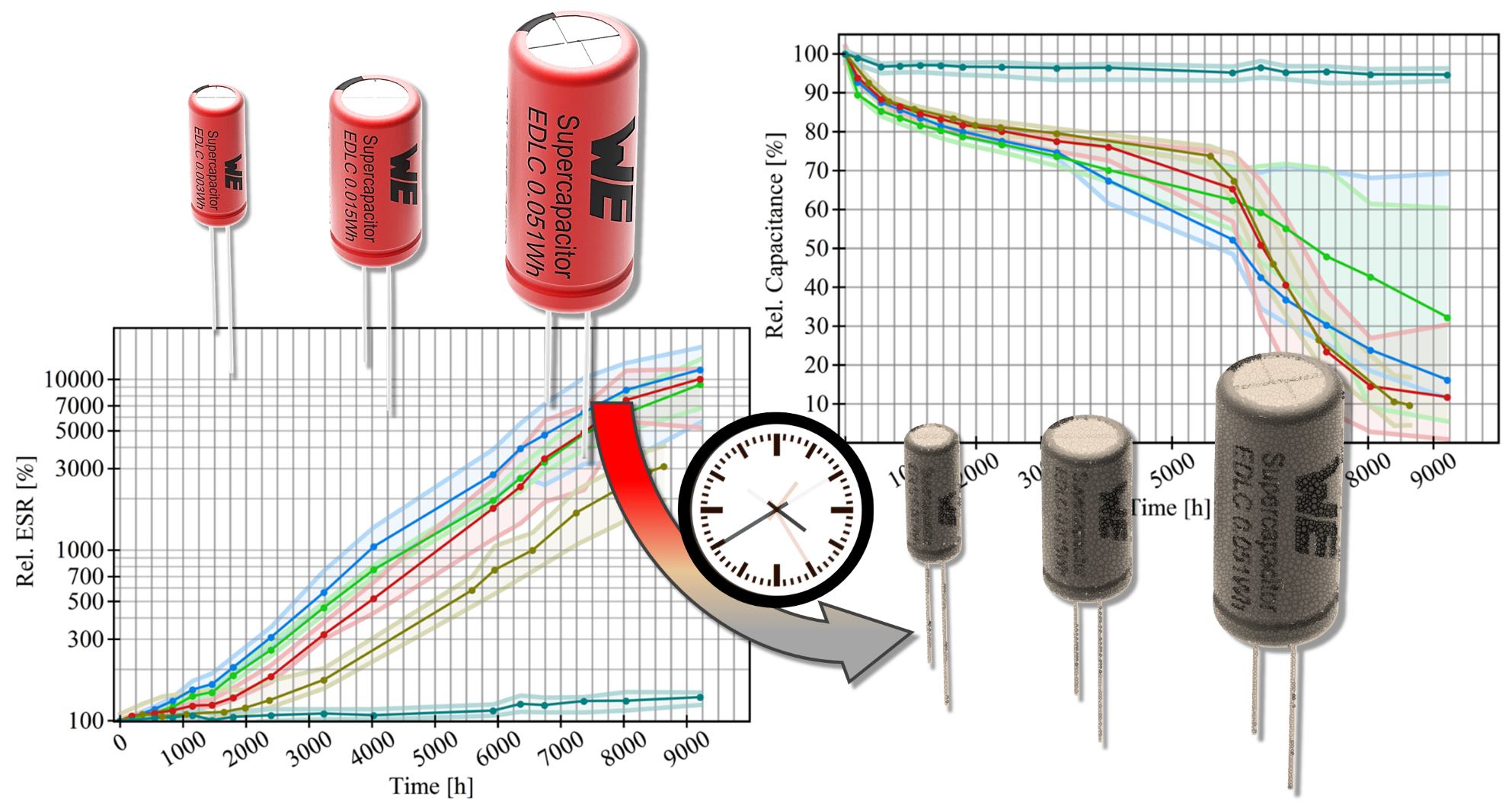
23 July 2025Evaluation and Modeling of Long-Term Endurance Measurement on Electric Double Layer Capacitors to Increase Reliability of Lifetime Predictions
Sustainability in the electrical industry and product reliability are fundamentally dependent on product lifetime predictions. Long-term DC voltage endurance measurements at two different temperatures on various commercial electric double-layer capacitors are presented, discussed, and used to develop a deterioration model suitable for estimating lifetime. Capacitors were tested under constant voltage for approximately 1 year at 65 °C and about 4 years at room temperature. To describe the deterioration in terms of capacitance and the equivalent series resistance, a phenomenological model is proposed and tested against measurements taken at room temperature. The proposed model is based on a general exponential relation with a time-dependent deterioration rate. The model is tested against long-term measurements with constant and time-dependent temperature acceleration factors. Analysis of capacitance and equivalent series resistance measurements shows a time or deterioration dependence in the temperature acceleration factor and different phases of deterioration.
Open Access
Article
29 July 2025Air Conditioning Heat Exchanger Intelligent Production Line: Design Methodologies and Applications
As a key component in modern building environmental control systems, the production quality and performance of multi-split central air conditioning systems directly influence the comfort, energy efficiency, and operational stability of buildings. However, the current manufacturing process primarily relies on a combination of traditional manual labor and automated equipment, resulting in low efficiency, high energy consumption, and limited automation. This paper first presents an optimized design for an intelligent manufacturing production line for multi-split central air conditioning heat exchangers to address these issues. It details the design of key systems for the intelligent production line and ensures continuous production and processing. Additionally, the paper analyzes the production process of the intelligent manufacturing line, with particular emphasis on the mechanism of the heat exchanger tube expansion process. Furthermore, it designs the fixture structure of the transfer robot for each process in the production line and discusses the principles of workpiece positioning and clamping. Utilizing technologies such as sensor networks, PLC, and industrial Ethernet, the system completes the closed-loop process of perception, transmission, analysis, decision-making, and execution within the production line, enabling transparency, fault predictability, and automated management. The results show that the intelligent assembly production line has significantly improved the assembly efficiency, achieving a 300% increase in the daily production capacity of a single line. While enabling the continuous and intelligent production of multi-split central air conditioning heat exchangers.
Open Access
Article
08 August 2025Rolling Bearing Health Indicator: From Design to Modeling and Evaluation
As a key component of industrial machinery, accurate prediction of the degradation trend of rolling bearings is crucial for equipment safety. However, traditional health indicator (HI) extraction methods often suffer from feature redundancy, and prediction models lack the ability to capture spatial dimension features, leading to significant prediction errors. To address these issues, 16 time-frequency domain features were first extracted, and a new HI was constructed by combining the Gaussian Process latent variable model (GPLVM) for non-linear feature fusion and exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA) for smoothing. Additionally, a spatial-temporal convolutional long short-term memory network (ST-CNet) was proposed, which integrates a 3-layer CLSTM, fully connected layers, and batch normalization to effectively capture local and long-term spatiotemporal dependencies. Case studies on IMS bearing datasets show that the constructed HI accurately describes the degradation process, and ST-CNet achieves superior performance with lower MAE and RMSE compared to existing methods.
Open Access
Article
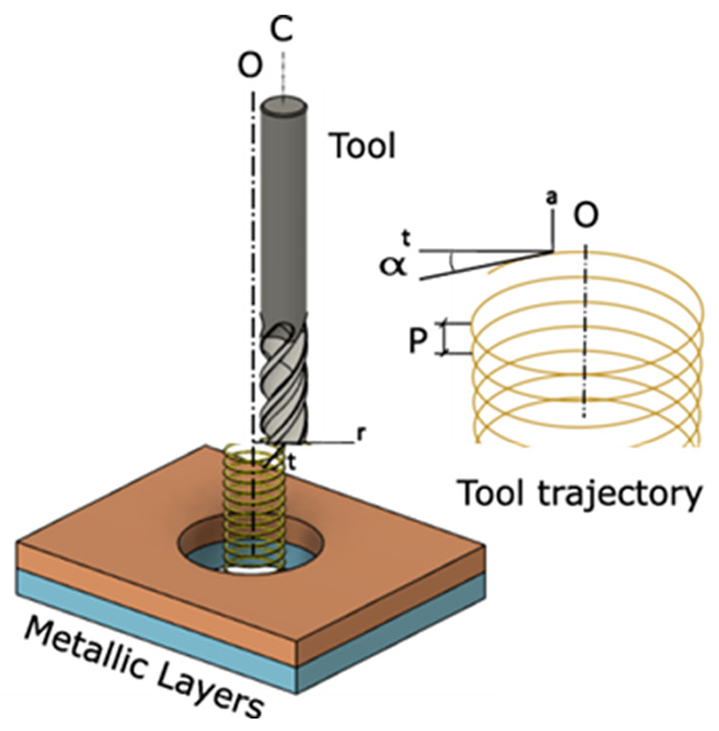
19 September 2025Cutting Power Model for Material Identification during Helical Milling of Aerospace Stacks
Smart factories increasingly rely on real-time data to optimize manufacturing, yet machining operations, particularly in aerospace stack drilling, still face challenges such as low productivity and accelerated tool wear. While advanced CNC machines already capture rich process data, its full potential for real-time decision-making remains underexplored. This work introduces a novel approach that leverages machine learning (ML) to identify material layers and optimize cutting conditions during drilling (helical milling) of aluminum–titanium stacks. Unlike prior methods that require additional sensors or complex instrumentation, our approach uniquely utilizes only spindle power signals from the CNC machine. Data maps consisting of cutting coefficients are used to train ML models to reliably predict material transitions across multiple layers under a range of cutting conditions. The results demonstrate appropriate material identification in comparison to experiments, enabling significant improvements in the hole-making of aerospace stacks. This study contributes a scalable, sensor-free, and non-intrusive framework for smart machining, establishing a practical pathway for process optimization in aerospace manufacturing without disrupting existing shop-floor setups.
Open Access
Review
29 September 2025Robot Grinding: From Frontier Hotspots to Key Technologies and Applications
Robot grinding technology has shown broad application prospects in the field of machining complex curved parts due to its high flexibility, strong adaptability, and high automation. However, industrial robots are generally only suitable for rough machining, and for semi-finishing and finishing, improving the machining accuracy of robots and the surface quality of parts is a key issue. This paper summarizes the current research status of robot grinding and provides a reference for realizing robot precision grinding. At present, the research on robot grinding technology mainly focuses on robot pose control, force/position hybrid control strategy, intelligent machining path planning, vibration suppression technology, compliance control, and so on, aiming at solving the key bottleneck problems such as low machining accuracy, large grinding force fluctuation and poor surface quality consistency caused by insufficient robot stiffness. Firstly, the development history of the robot grinding system and the research status of process technology are summarized systematically. Secondly, the analysis focuses on grinding path planning, programming technology, and robot compliance force control technology. Finally, the current status of optimization research in robot grinding technology is summarized. The overarching purpose of this paper is to provide a systematic analysis and a comprehensive reference framework, aiming to address the core challenges hindering the achievement of high-precision, consistent surface quality in robotic grinding manufacturing. Based on the summarized state-of-the-art, robot grinding technology development trend is also predicted.
Open Access
Article
29 September 2025Multivariant Time-Series Forecasting Methodology for Product Demand Using Deep Learning and Large Language Models
Accurate demand Soothsaying is a crucial element in force chain operation and business planning. Traditional statistical ways don’t consider the nonlinear, dynamic, and interdependent nature of variables that drive product demand, including deal history, prices, seasonality, elevations, request changes, and profitable pointers. This design presents a sophisticated soothsaying frame for guidance from an artificial intelligence system, integrating soothsaying using deep literacy models together with large language models(LLMs), that can negotiate both accurate soothsaying and give practicable intelligence. The deep literacy infrastructures used in this study include Long Short Term Memory(LSTM), Reopened intermittent Units(GRU), and other Motor models for timeseries soothsaying, which optimize temporal dependences and the complex cross-variable relations. To further increase interpretability of the vaticinations, LLMs are useful agents to convert the specialized cast affair into a completely automated and enhanced mortal-readable textbook and reports to develop intelligence for decision timber. Prophetic modeling and naturally generated reporting lead to better delicacy and practicable intelligence for their businesses. This intelligence empowers businesses to create better procurement processes, improve inventory management, and develop more resilient supply chains relevant to today’s business environment.