Artiles
Open Access
Article
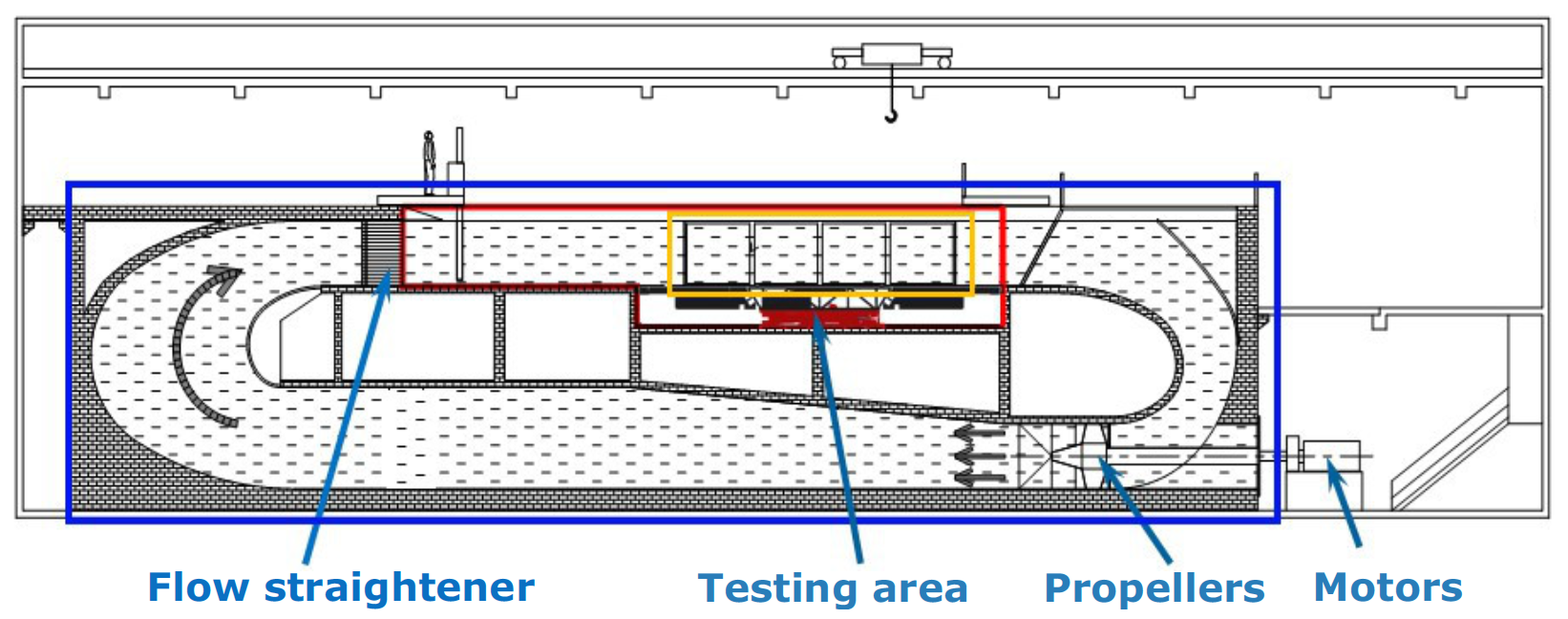
23 December 2025Wave Effects on Large-Scale Turbulent Flow Structures Propagating in the Water Column
Tidal flow often contains large-scale turbulent flow structures mainly caused by bathymetric variations or offshore marine structures. Understanding how waves interact with these structures is crucial for ocean sciences, as they influence vertical mixing, energy transfer, and dissipation. In this work, two flow configurations with current and waves are studied in a flume tank using Particle Image Velocimetry measurements: waves propagate either following or opposing the current and interact with convected flow structures. Compared to current-only cases, the mean velocity is slightly impacted, but the mean velocity gradient increases for waves propagating with the current. Turbulent Kinetic Energy increases regardless of wave direction and its production is also affected by the wave’s propagation direction. The integral length scale and flow Gaussianity are the most affected flow parameters. For waves propagating against the current, the Probability Density Functions of fluctuating velocity fields exhibit a bimodal representation, largely deviating from a Gaussian curve. Preliminary quadrant analysis reveals that waves significantly influence flow organisation, especially when they propagate against the current. These observations are valuable for applications such as defining tidal turbine farm areas, improving turbine performance estimation, and assessing structural fatigue.
Open Access
Review
22 December 2025Text Mining Approaches for Protein Function Annotation: Challenges and Opportunities
Understanding protein functions is essential for advancing quantitative synthetic biology, which applies quantitative and systems approaches to understand how biological functions emerge from building blocks, thereby guiding the rational design of complex living systems. Apart from a few model organisms, most species contain many proteins with unverified functions, highlighting the need for accurate, automated protein function annotation methods. Recent advances in protein bioinformatics, particularly in predicting structures and functions, have been driven by artificial intelligence (AI), especially deep learning models. Top-performing methods in the Critical Assessment of Function Annotation (CAFA) challenge have leveraged large language models to perform text mining-based protein function prediction, extracting features from scientific literature or using template proteins with similar descriptions in the literature. Despite these advances, several challenges remain. Current predictors often depend on PubMed abstracts curated by UniProt, leading to redundancy with manual annotations and to the overlooking of uncurated or full-text literature that contains richer functional evidence. Few systems automatically classify literature types or assess their relevance, limiting precision and interpretability. Benchmarking remains difficult due to the absence of unbiased gold standards, making it hard to evaluate true predictive capability. Furthermore, integrating heterogeneous evidence—from text, sequences, and structural or network data—presents additional challenges for model harmonization. This review not only summarizes current methods and limitations but also highlights strategies to improve text mining-based protein function annotation using recent AI developments. Overall, this work aims to guide the development of next-generation tools for more accurate and comprehensive protein function predictions.
Open Access
Communication
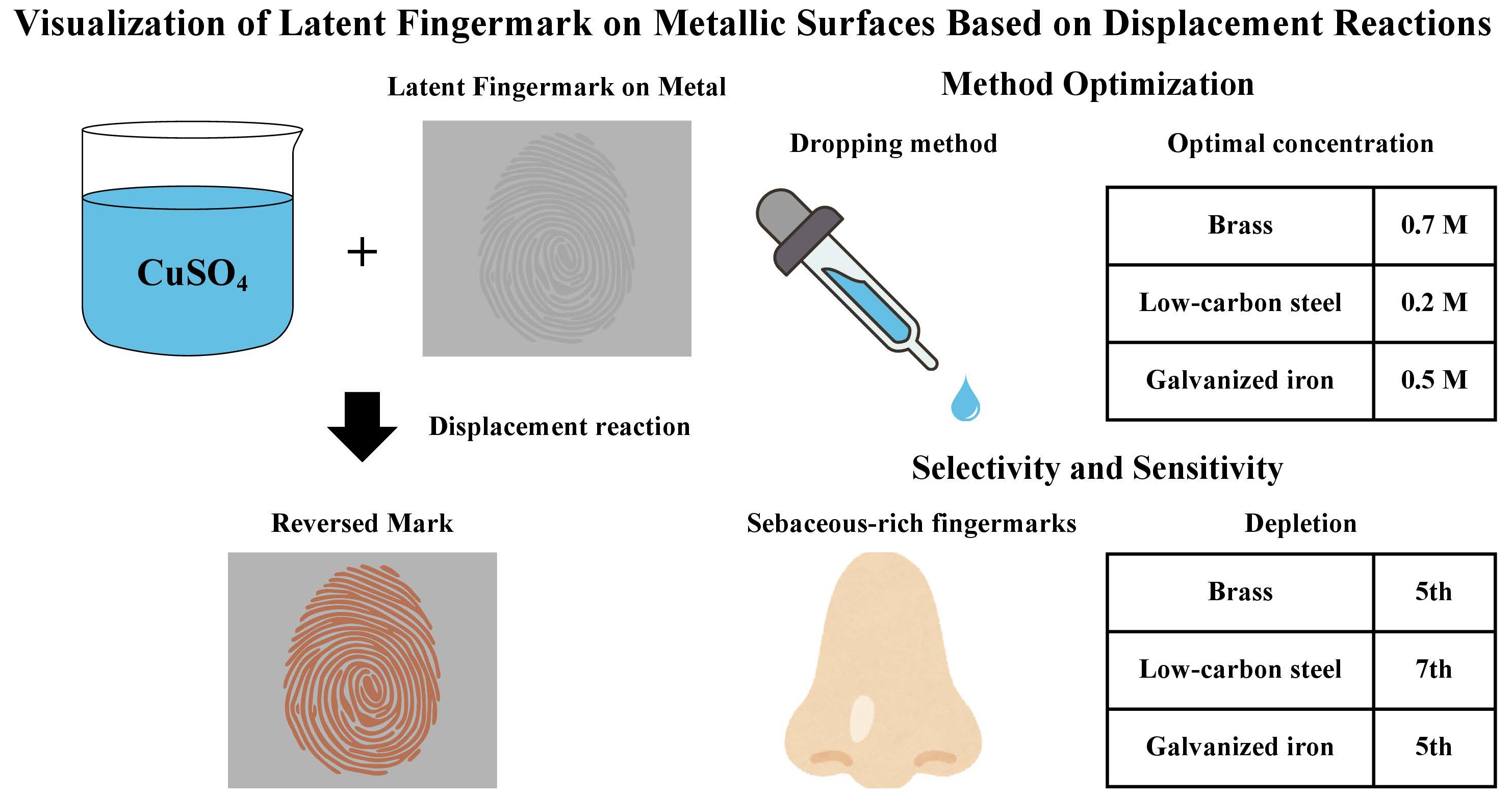
19 December 2025Visualization of Latent Fingermark on Metallic Surfaces Based on Displacement Reactions
Fingermarks are frequently left on metal surfaces such as kitchen utensils, door handles, or elevator buttons in crime scenes. They are crucial forensic evidence to identify individuals and link them to crimes. Fingermark development on metal surfaces targets either the fingermark residues or the substrate. This study aimed to develop a rapid fingermark development method based on displacement reactions between copper (II) sulphate and various types of metal substrates, such as brass, galvanized iron, and low-carbon steel. Immersion of the metal substrate was more effective in fingermark visualization than applying the solution using a dropper. The optimized concentrations of copper (II) sulphate solution for fingermark visualization were found to be 0.7 M for brass, 0.5 M for galvanized iron, and 0.2 M for low-carbon steel. Sebaceous-rich fingermarks were visualized after the 5th depletion on brass and galvanized iron, and even after the 7th depletion on low-carbon steel. Further improvement is required before incorporating the application of copper (II) sulphate onto metal substrates to visualize fingermarks in real crime cases, due to the destructive nature of substrate submersion.
Open Access
Letter
19 December 2025
Open Access
Review
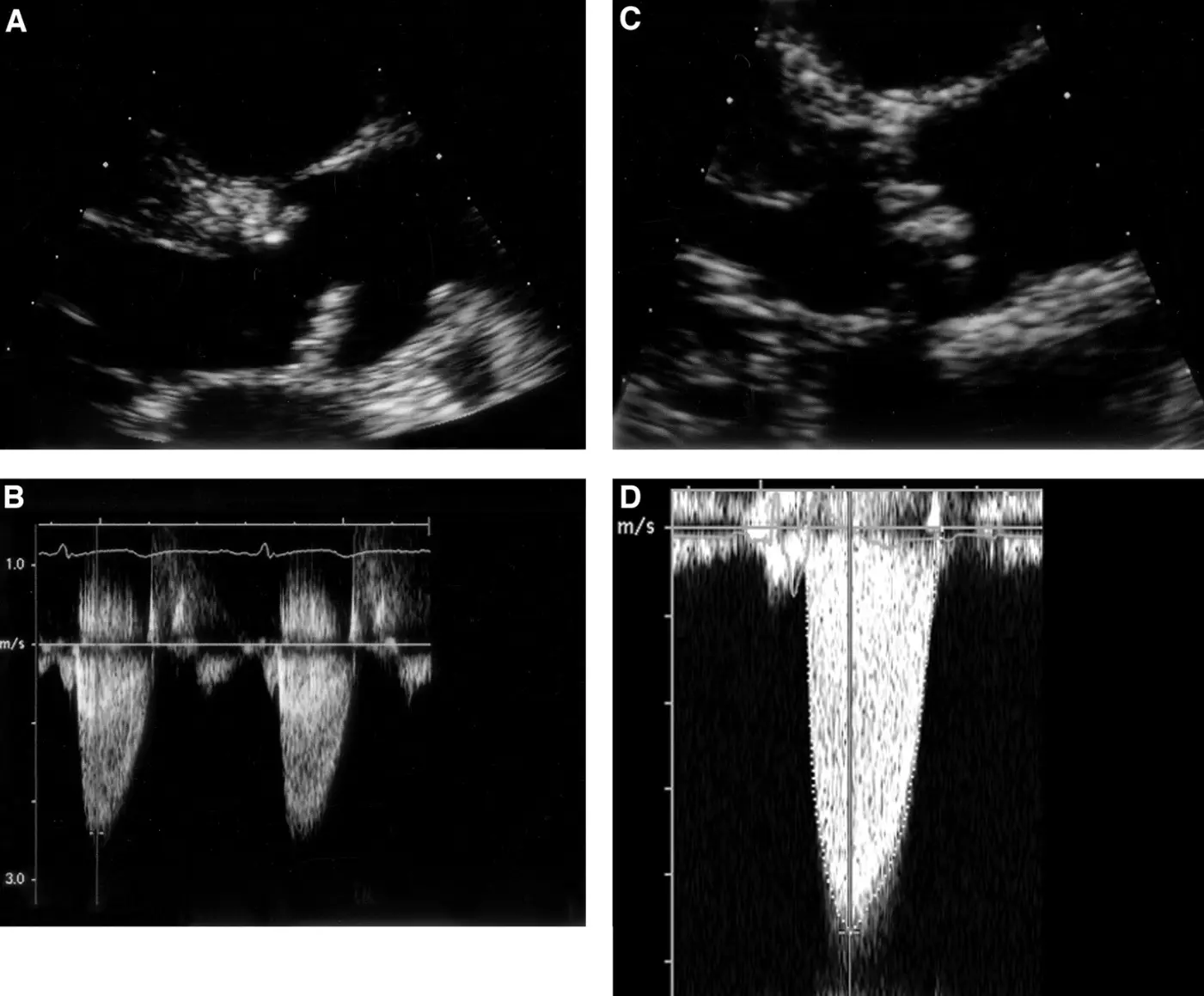
19 December 2025Contemporary Multimodality Imaging Evaluation in Native Aortic Stenosis
Aortic stenosis (AS) is the most prevalent valvular heart disease in developed nations, with increasing incidence driven by population aging. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial, as timely intervention significantly improves outcomes. Contemporary imaging plays a central role in the assessment of AS, enabling precise evaluation of valve anatomy, disease severity, left ventricular remodeling, and procedural planning. Transthoracic echocardiography remains the first-line modality, providing essential hemodynamic and structural data. However, limitations in cases of low-flow states, discordant grading, and atypical presentations necessitate adjunctive tools. Transesophageal echocardiography enhances visualization of valve morphology and annular dimensions, particularly for pre-procedural assessment. Cardiac computed tomography (CT) has emerged as a cornerstone in transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) planning, offering unparalleled spatial resolution for annular sizing, coronary height measurement, and vascular access evaluation. Meanwhile, cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) provides robust quantification of ventricular volumes, fibrosis, and myocardial strain, serving as a prognostic marker in asymptomatic and borderline cases. The integration of multimodality imaging offers a comprehensive framework, addressing diagnostic ambiguities and guiding individualized management strategies. This review highlights current advances, clinical applications, and future directions in multimodality imaging for AS, emphasizing its pivotal role in optimizing patient selection, risk stratification, and procedural outcomes.
Open Access
Review
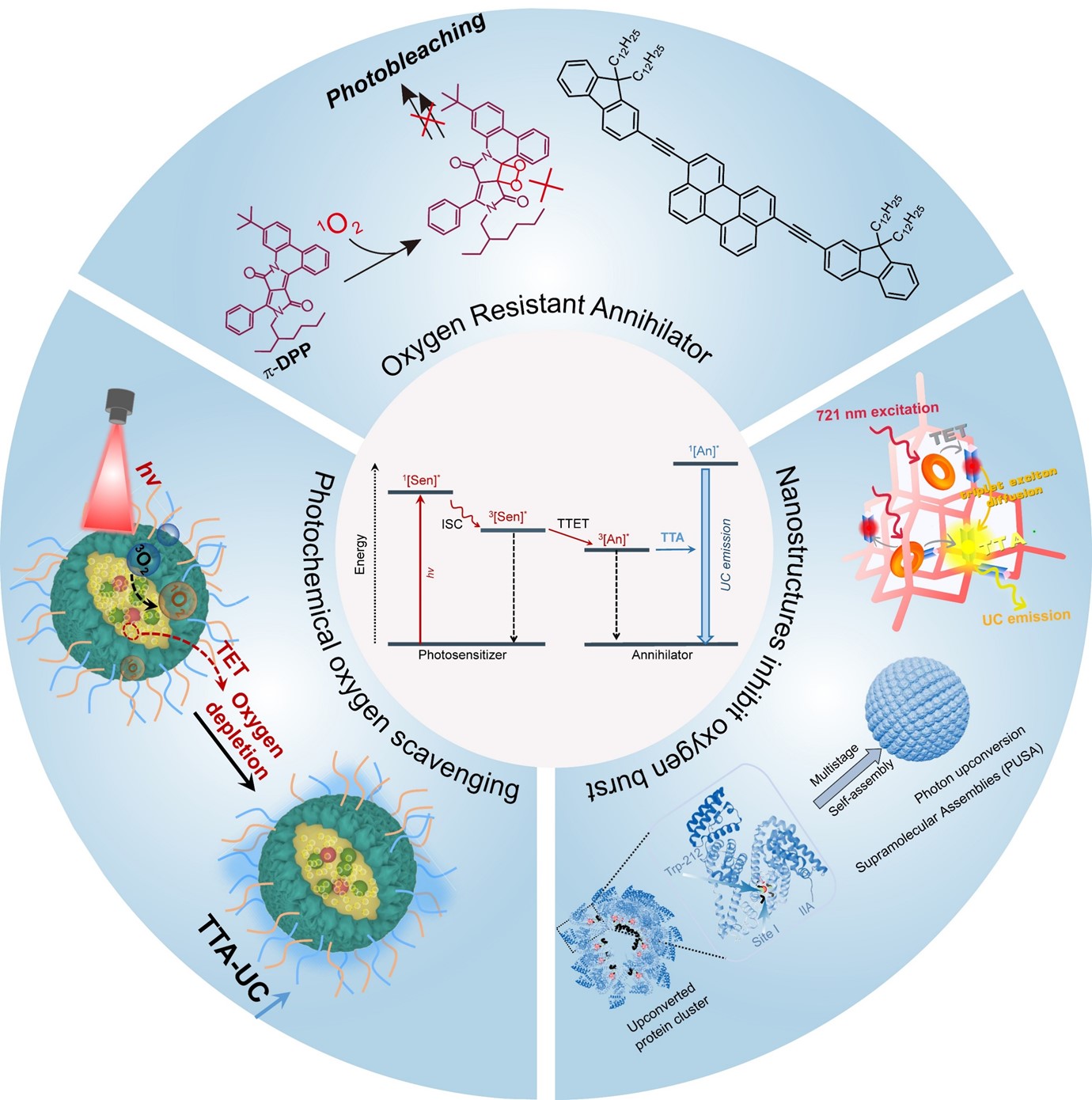
18 December 2025Construction and Applications of Efficient, Oxygen-Tolerant Triplet-Triplet Annihilation Upconversion Materials
Triplet–triplet annihilation upconversion (TTA-UC) is an emerging class of photonic upconversion materials notable for low excitation power thresholds, high upconversion quantum yields, and tunable absorption and emission profiles. These unique features give TTA-UC materials significant potential across diverse fields such as chemistry, biology, and materials science. A typical TTA-UC system consists of sensitizers and annihilators, functioning through a sequence where the sensitizer absorbs photons and transfers triplet energy to the annihilator via triplet–triplet energy transfer, followed by triplet–triplet annihilation (TTA) that emits higher-energy photons. Because TTA-UC materials can be excited by long-wavelength light, they overcome the limitations in penetration depth of conventional fluorescence technologies, showing great promise for applications such as deep-tissue imaging, targeted photodynamic therapy, and precise optogenetic modulation. However, molecular oxygen causes non-radiative decay pathways that severely quench upconversion efficiency, posing a major challenge for practical use. Over the past decade, researchers have developed various innovative strategies to counteract oxygen-induced quenching. This review systematically summarizes key scientific approaches to creating high-performance, oxygen-tolerant TTA-UC materials, with a focus on their underlying mechanisms. First, we discuss molecular engineering strategies involving electron-deficient groups and conformational control to improve the photostability of TTA-UC chromophores. Second, we describe the fabrication of oxygen-resistant TTA-UC nanoparticles using reductive oil droplets as soft templates. Finally, we discuss nanostructure-mediated optimization of intermolecular triplet energy transfer dynamics to enhance oxygen resilience. A critical evaluation of the advantages and limitations of each approach is provided. Additionally, we highlight key challenges, including improving the upconversion efficiency of near-infrared-responsive TTA-UC, developing novel nanoparticle fabrication methods, and refining surface bioconjugation chemistry. We conclude by exploring prospects for integrating TTA-UC with synthetic biology techniques to design biosynthetic upconversion proteins, potentially establishing upconversion luminescence as a vital tool in fundamental life science research and accelerating its application in diverse biomedical fields.
Open Access
Review
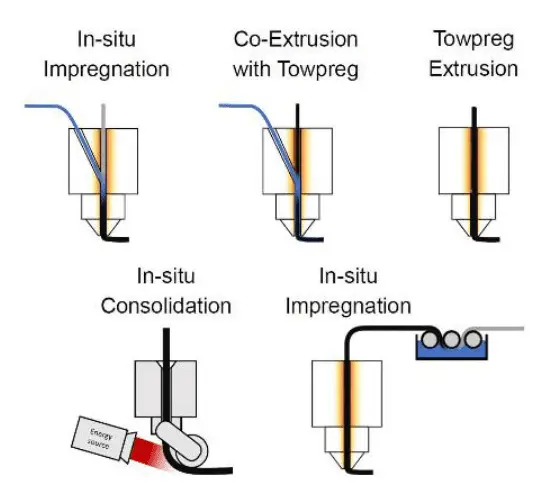
16 December 20253D-Printed Continuous Fiber Composites: An Overview of Materials, Systems and Processes
3D-printed composites represent a cutting-edge advancement in additive manufacturing, offering the ability to fabricate high-strength, lightweight structures by embedding continuous fibers within a single deposition process. This innovative approach significantly enhances the mechanical performance of printed parts compared to traditional polymer-based 3D printing. In this article, we present a structured review of recent developments in 3D-printed composite technologies. The discussion is organized into three key areas: (i) the types and properties of continuous fibers used in 3D printing, (ii) the underlying mechanisms and systems that enable fiber deposition, and (iii) emerging strategies involving commingled materials that integrate reinforcement and matrix components at the filament level. This review aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state and future directions of continuous fiber-reinforced additive manufacturing.
Open Access
Article
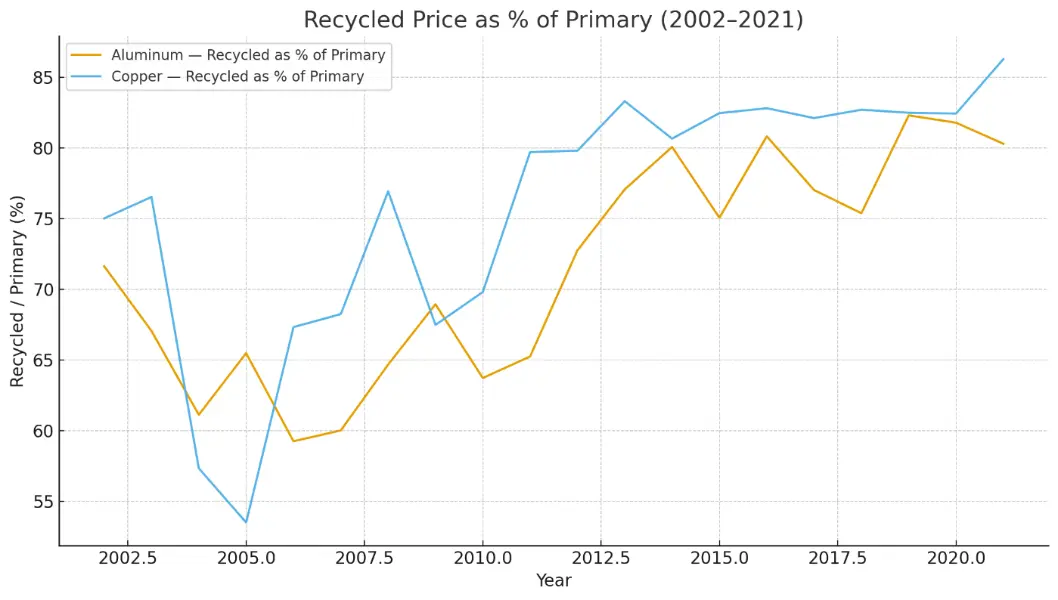
16 December 2025The Jevons Paradox and Vernon’s Product Life Cycle: Evidence from Primary–Secondary Price Differentials in Copper and Aluminium (2002–2021) with 2024–2025 Market Context
This study examines how efficiency improvements associated with Jevons’ Paradox and product-system maturation, as described by Vernon’s Product Life Cycle (PLC), jointly influence the long-term pricing relationship between primary and recycled copper and aluminium. Using author-provided nominal annual USD price series for 2002–2021, the analysis derives descriptive indicators most notably the recycled-to-primary (R/P) price ratio to characterize structural shifts consistent with PLC-driven secondary integration. Recent market conditions in 2024–2025, including tight physical availability, low inventories, regional premia, and recurrent episodes of backwardation, are incorporated as qualitative context without merging with the historical dataset. Results indicate a sustained narrowing of R/P discounts for both metals by 2021. The combined Jevons–PLC interpretation suggests that efficiency-driven service expansion and supply-side tightness increase the relative value of secondary material, supporting long-term convergence between primary and recycled streams.
Open Access
Article
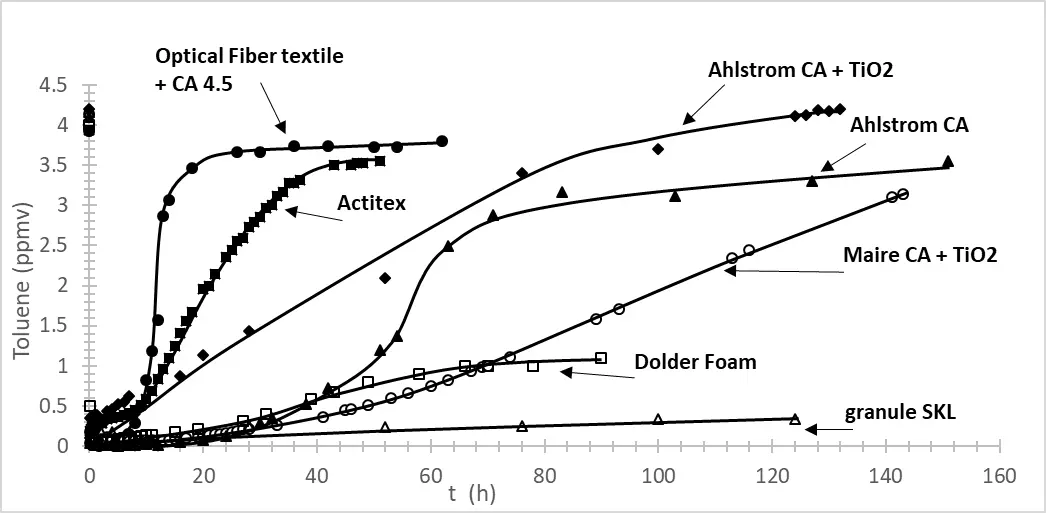
16 December 2025Toluene or Formaldehyde Removal by Photocatalysis and Adsorption Using Hybrid Optical Fiber Textiles Containing Activated Carbon and/or TiO2
Indoor air treatment has become a significant concern in recent years. The aim of this study is to investigate the effectiveness of coupling adsorption and photocatalysis for the removal of toluene and formaldehyde, especially in the presence of optical fiber textile. First, we examine the adsorption properties of various commercial activated carbon (AC) filters, as well as different amounts of AC deposited on optical fiber textiles, and assess the impact of titanium dioxide (TiO2) on the adsorption performance. In the second phase, we compare the photocatalytic degradation of toluene and formaldehyde under different irradiance levels. Finally, we analyze the impact of three AC-TiO2 combinations: separate filters, TiO2 deposited on AC-impregnated fiber optic textiles, and TiO2 partially deposited on AC filters. The results led us to test a new photocatalytic and adsorbent material, including heating wires and optical fibers.
Open Access
Article
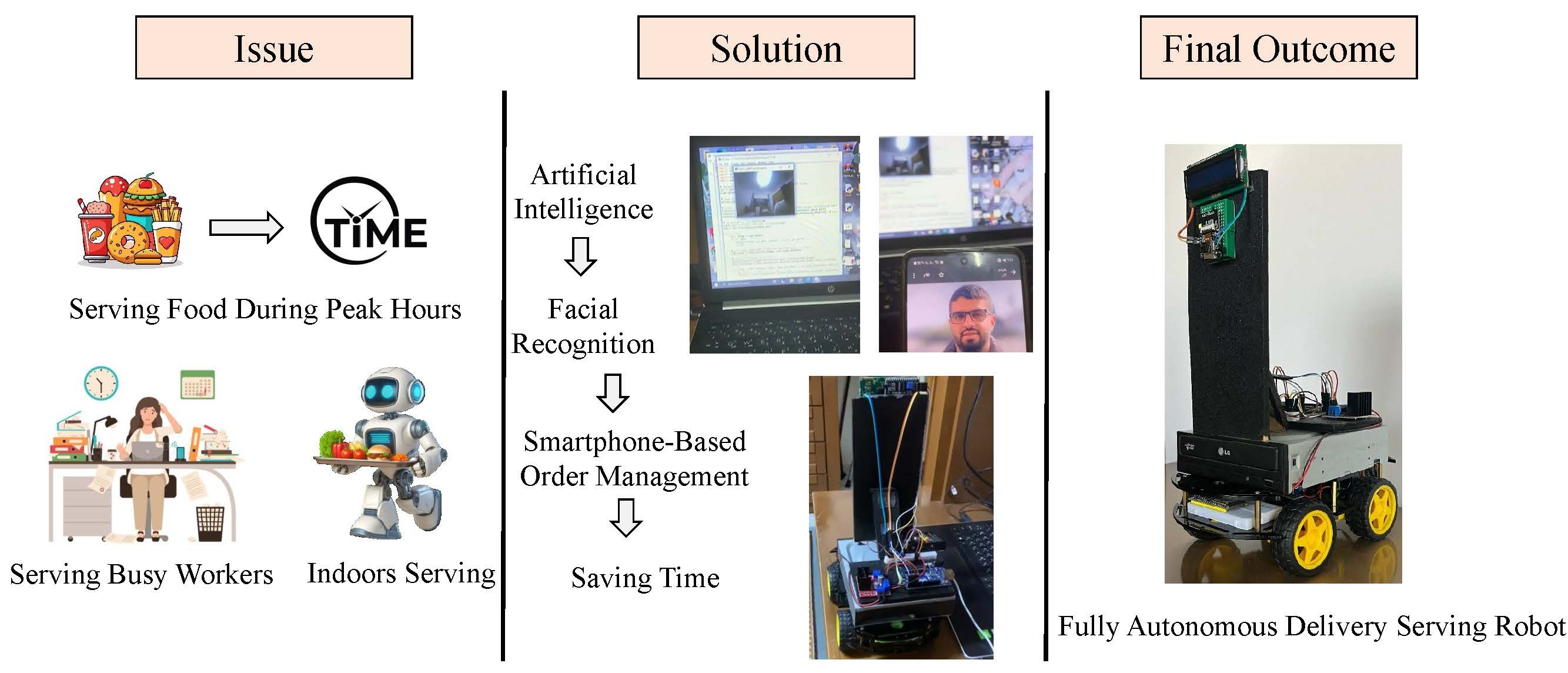
16 December 2025Design and Implementation of an Autonomous Smart Food Delivery Robot for Commercial Environments
The integration of robotics into service environments is transforming how labor-intensive tasks are managed, particularly during peak hours with staff shortages and long wait times. This research presents a fully autonomous, modular food-delivery robot designed to enhance operational efficiency and improve service experience. The system combines artificial intelligence, facial recognition, smartphone-based order management, Arduino, ESP32, ESP32-CAM, and Python to navigate indoor environments and deliver food directly to recipients, supported by a secure handover mechanism. Experimental results indicate that the robot performs waiter-like delivery reliably, maintaining mobility and structural integrity across various surfaces by using lightweight materials and motors that have been optimized. Through the use of a motion coordination algorithm, responsive navigation can be achieved, while a simple user interface can be operated by anyone with minimal training. According to these results, automation reduces the need for manual labor, increases the speed of service, and ensures consistency in the delivery process. Additionally, the system provides a practical framework for future research and potential applications beyond food delivery, such as surveillance, environmental monitoring, and disaster response. Future work will focus on scaling for real-world deployment and integration advanced AI navigation to enhance autonomy, adaptability, and overall operational performance.