Found 301 results
Open Access
Article
16 December 2025Toluene or Formaldehyde Removal by Photocatalysis and Adsorption Using Hybrid Optical Fiber Textiles Containing Activated Carbon and/or TiO2
Indoor air treatment has become a significant concern in recent years. The aim of this study is to investigate the effectiveness of coupling adsorption and photocatalysis for the removal of toluene and formaldehyde, especially in the presence of optical fiber textile. First, we examine the adsorption properties of various commercial activated carbon (AC) filters, as well as different amounts of AC deposited on optical fiber textiles, and assess the impact of titanium dioxide (TiO2) on the adsorption performance. In the second phase, we compare the photocatalytic degradation of toluene and formaldehyde under different irradiance levels. Finally, we analyze the impact of three AC-TiO2 combinations: separate filters, TiO2 deposited on AC-impregnated fiber optic textiles, and TiO2 partially deposited on AC filters. The results led us to test a new photocatalytic and adsorbent material, including heating wires and optical fibers.

Open Access
Article
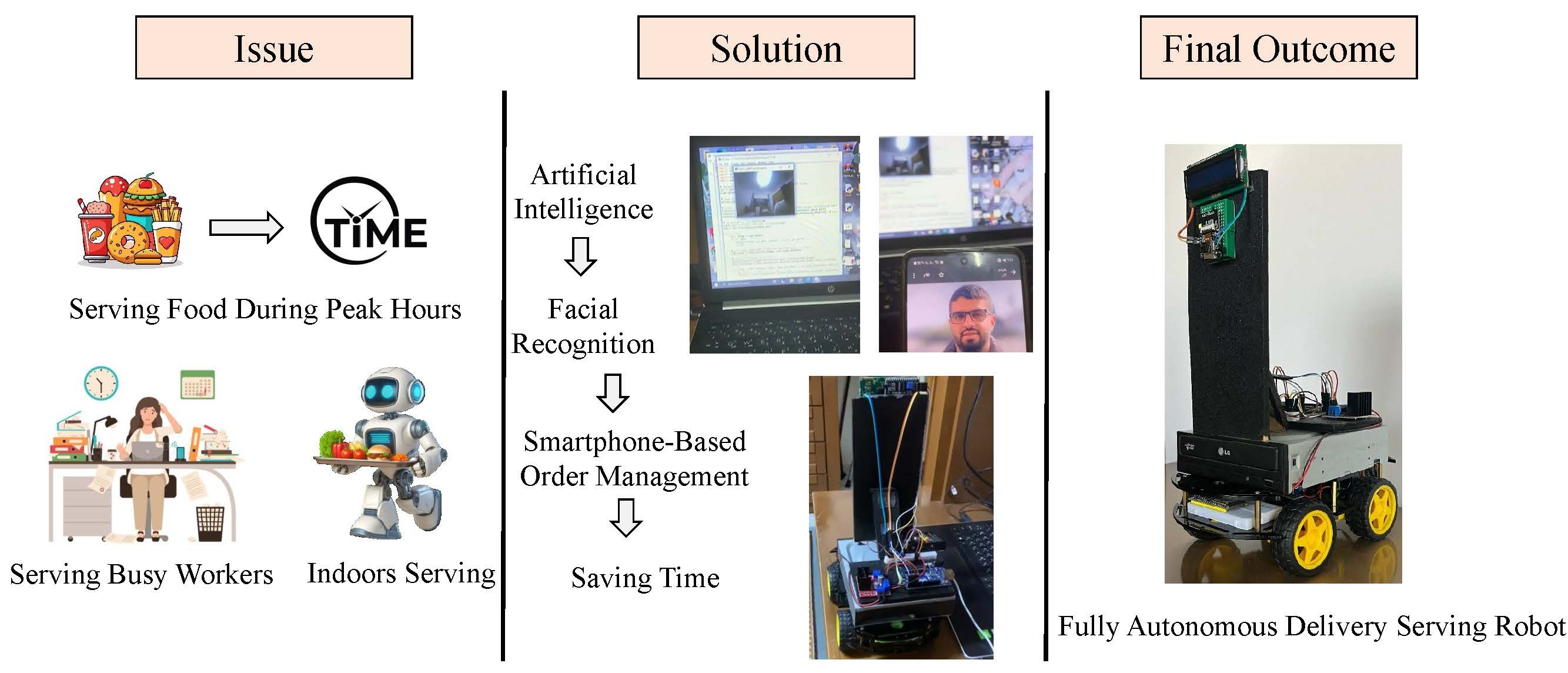
16 December 2025Design and Implementation of an Autonomous Smart Food Delivery Robot for Commercial Environments
The integration of robotics into service environments is transforming how labor-intensive tasks are managed, particularly during peak hours with staff shortages and long wait times. This research presents a fully autonomous, modular food-delivery robot designed to enhance operational efficiency and improve service experience. The system combines artificial intelligence, facial recognition, smartphone-based order management, Arduino, ESP32, ESP32-CAM, and Python to navigate indoor environments and deliver food directly to recipients, supported by a secure handover mechanism. Experimental results indicate that the robot performs waiter-like delivery reliably, maintaining mobility and structural integrity across various surfaces by using lightweight materials and motors that have been optimized. Through the use of a motion coordination algorithm, responsive navigation can be achieved, while a simple user interface can be operated by anyone with minimal training. According to these results, automation reduces the need for manual labor, increases the speed of service, and ensures consistency in the delivery process. Additionally, the system provides a practical framework for future research and potential applications beyond food delivery, such as surveillance, environmental monitoring, and disaster response. Future work will focus on scaling for real-world deployment and integration advanced AI navigation to enhance autonomy, adaptability, and overall operational performance.
Open Access
Review
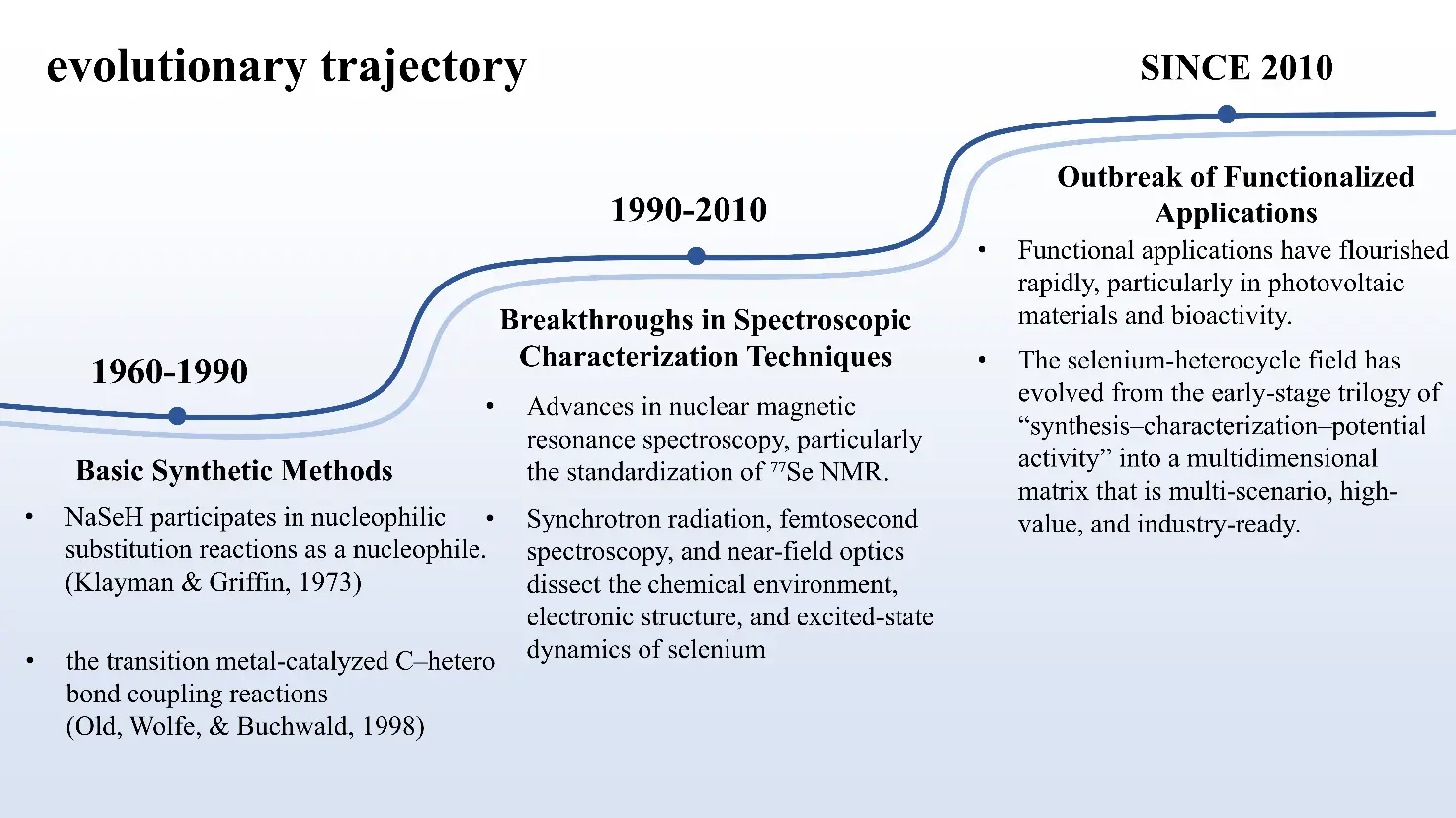
15 December 2025Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization Techniques, and Functional Applications of Selenium Heterocycles
The paper reviews the unique chemical properties of selenium, focusing on selenium-containing heterocycles and organoselenium chemistry. The present study undertakes a critical examination of synthetic strategies, ranging from classical nucleophilic selenation and transition-metal catalysis to emerging photo-redox and electrochemical approaches. The text goes on to highlight advanced characterisation techniques, with particular reference to the combination of 77Se NMR spectroscopy with DFT calculations and single-crystal X-ray diffraction for structural elucidation. The functional applications of these compounds are the subject of extensive discussion, including their role in enhancing the performance of sustainable organic photovoltaic (OPV) materials for renewable energy conversion, and their potential in biomedicine as TrxR inhibitors for cancer therapy and as photosensitizers in antibacterial applications. The present study places particular emphasis on the contribution of selenium-containing heterocycles to improving the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of solar devices. Finally, the review outlines future research directions and common challenges in this field, such as enhancing the sustainability of catalytic processes and addressing biosafety concerns associated with selenium-based reagents.
Open Access
Article
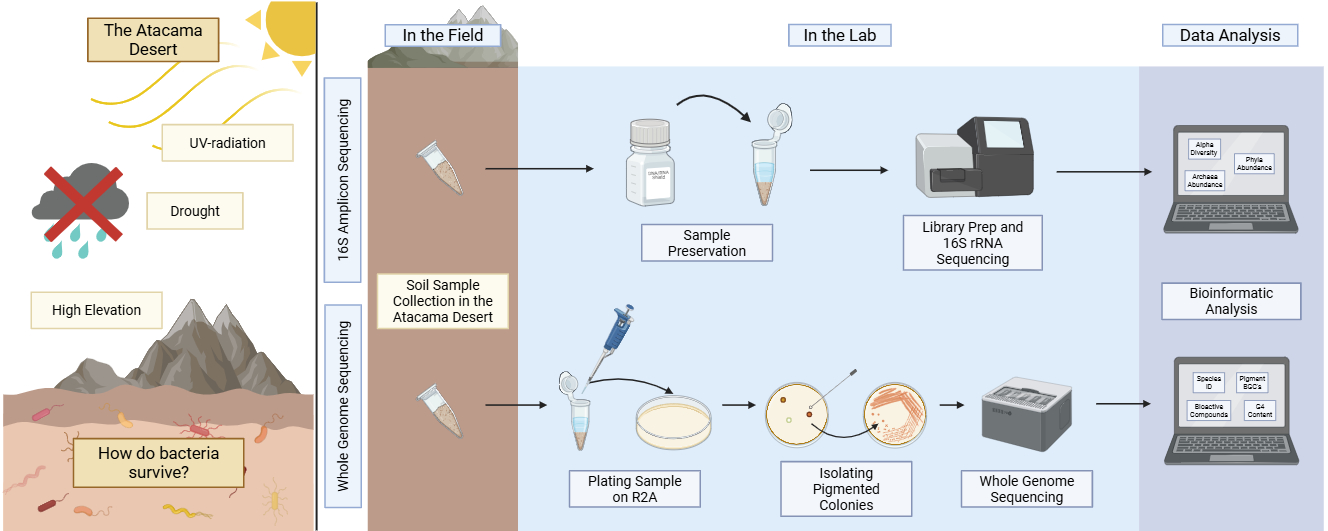
12 December 2025Understanding the Genetic Diversity of Bacteria Isolated from Across the Atacama Desert
Despite being one of the driest and harshest deserts on Earth, the Atacama Desert is home to a variety of bacterial life. Microorganisms that reside here may have developed adaptations to help them survive this unique environment. In this study, we used bioinformatic and genetic methods to assess the abundance of phyla that are present in this environment and focus on the types of adaptations individual bacteria have obtained. To assess bacterial diversity, we used 16S rRNA sequencing on soil samples and determined the relative composition of different phyla and archaea at sixteen locations. The whole genome sequence genome of eight selected pigmented bacteria was also performed. We found that all strains we sequenced are predicted to produce bioactive compounds. We focused on stress-tolerance capabilities, including pigment production pathways, biofilm-related genes, antibiotic production, and genome stability. We also found that the pigments that these bacteria produce have antioxidant, iron, and ion chelating, and/or antibiotic properties. This characterization allows us to assess adaptive strategies of bacteria, which is important in the fields of agriculture, biotechnology, and health.
Open Access
Review
12 December 2025Review of Ground Insulation Resistance Detection Methods for Photovoltaic (PV) Systems
With the rapid growth of PV systems, accurate detection of insulation resistance in PV inverters has become increasingly crucial to ensure system safety and operational stability. This paper presents a systematic review of current ground insulation resistance detection methods for PV systems. First, the operating principles of various insulation resistance detection schemes are reviewed. Furthermore, the performance of these methods is evaluated based on several key metrics. Additionally, various fault locating techniques are examined. Overall, this paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements in insulation resistance detection for PV systems.

Open Access
Article
09 December 2025Mechanical Characterization of Ship Building Grade A Steel by Rapid Cooling in Different Liquid Media
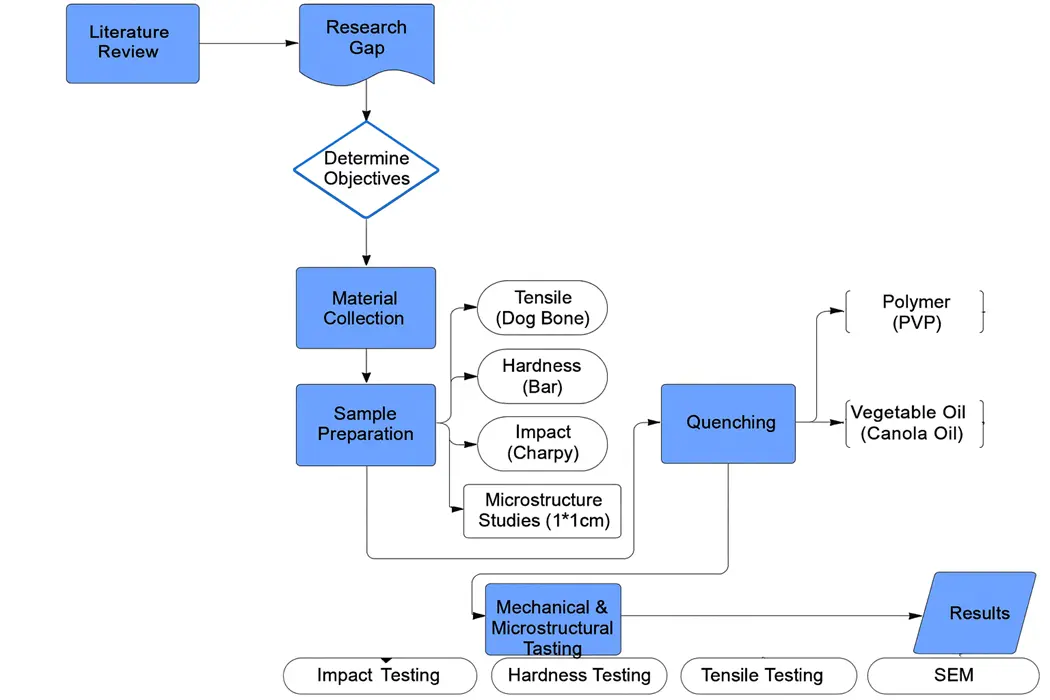
Steel is an essential component used to build marine vessels due to its endurance of the sea’s harsh conditions, including corrosion and dynamic stresses, therefore, different grades of mild steel are used in shipbuilding. It provides the strength, ductility, and weldability necessary for structural integrity, consisting of carbon, manganese, etc., as alloying elements. In this research, different quenching media were employed to assess variations in mechanical properties. This process ultimately triggered alterations in the microstructure of the steel. Two types of media, such as vegetable oil (Canola) and Polyvinylpyrrolidone polymer (PVP), were studied in comparison with simple heat-treated steel. Mechanical characterization comprised of tensile testing, hardness and impact testing to evaluate major changes in strength and ductility. Furthermore, a microscope was used to interpret the microstructure. To guarantee consistency in testing, samples were prepared in accordance with ASTM guidelines. The yield strength of as-received steel was increased from 298 MPa to 358 MPa and 370 MPa because of rapid cooling action in PVP and oil, respectively. A significant increase in Ultimate tensile strength was achieved due to the variety of quenching media; however, ductility was seriously compromised because of the excessive hardness of the material. Impact energy analysis revealed a notable reduction, which is linked with degradation in toughness.
Open Access
Article
09 December 2025Demethylation of Lignin from Rice-Straw Biorefinery: An Integrated Chemical and Biochemical Approach
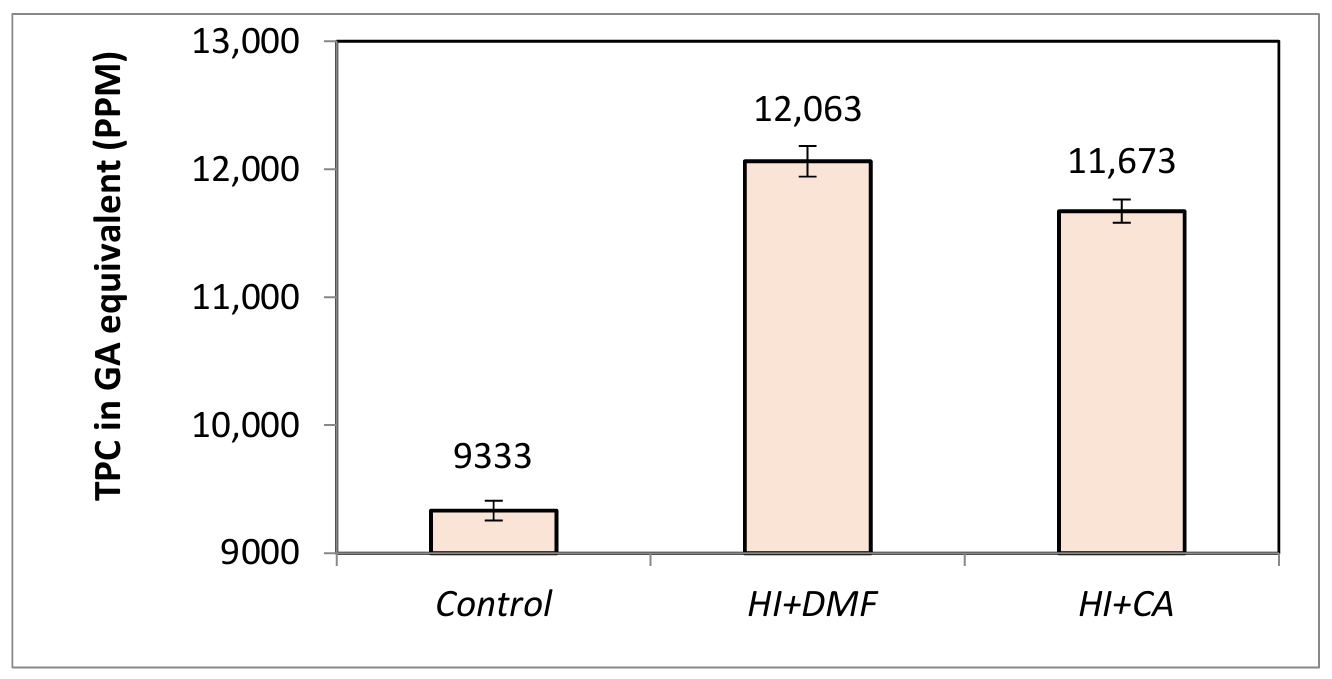
The efficiency of lignocellulosic biorefineries is limited because of the high recalcitrance and low reactivity of lignin. The reactivity of lignin can be enhanced through various chemical and biochemical approaches. Demethylation is one of the methods that improve the availability of phenolic hydroxyl groups in lignin, thereby enhancing its reactivity and application in sustainable adhesives. The goal of this study is to integrate microbial and chemical approaches to aid in the demethylation of lignin. Towards that end, lignin was first extracted and purified from the rice straw biorefinery solid residue obtained post ethanol fermentation. This rice straw lignin was then subjected to chemical and microbial demethylation. For microbial demethylation under alkaline conditions, Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas fluorescens were employed, while demethylation under neutral conditions was conducted using Trametes versicolor. Integrated treatment using Pseudomonas putida followed by hydrogen iodide yielded an increase in the phenolic hydroxyl content by approximately 39–43%. Demethylation using chemical methods and biological methods alone provided approximately 18–27% increases in phenolic hydroxyl content, respectively. Furthermore, to assess the physical and chemical properties of demethylated lignin, FT-IR, TGA, and morphological analytical tools were employed.
Open Access
Review
08 December 2025Advances in the Biosynthesis and Application of Sialyllactose
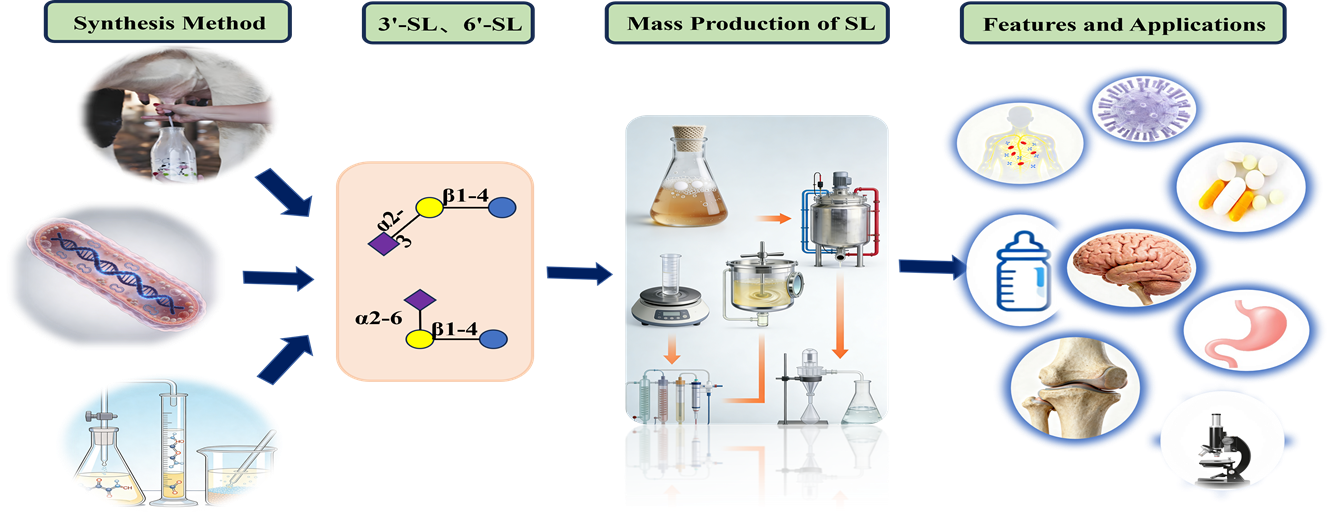
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), the third most abundant solid component in human milk after lactose and lipids, are recognized as crucial prebiotics that support infant gut health and immune development. Salivary HMOs account for approximately 13% of the total HMOs molar ratio, with 3′-sialyllactose (3′-SL) and 6′-sialyllactose (6′-SL) accounting for approximately 2% and 6%, respectively. Sialyllactose (SL) exhibits a range of notable physiological functions, including prebiotic activity, antiviral properties, prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis, immunomodulatory effects, and enhancement of brain development and cognition. Both 3′-SL and 6′-SL have been approved as “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS) by the U.S. FDA and are increasingly incorporated into infant formula. Currently, the biosynthesis of SL is mainly efficiently produced through engineered microorganisms. However, face bottlenecks: low yields, complex downstream processing, and prohibitive costs. Recent advances in synthetic biology and metabolic engineering offer promising avenues to overcome these barriers. This review introduces the synthesis methods, functions, and applications of SL, as well as conducting safety evaluation and regulatory status analysis. We hope this article will enhance understanding of the challenges encountered in the synthetic biology production and application of SL.
Open Access
Article
08 December 2025Public Participation in Ecological Civilization Construction in Urumqi: A Case Study of a Rapidly Expanding Arid Metropolis in Northwestern China
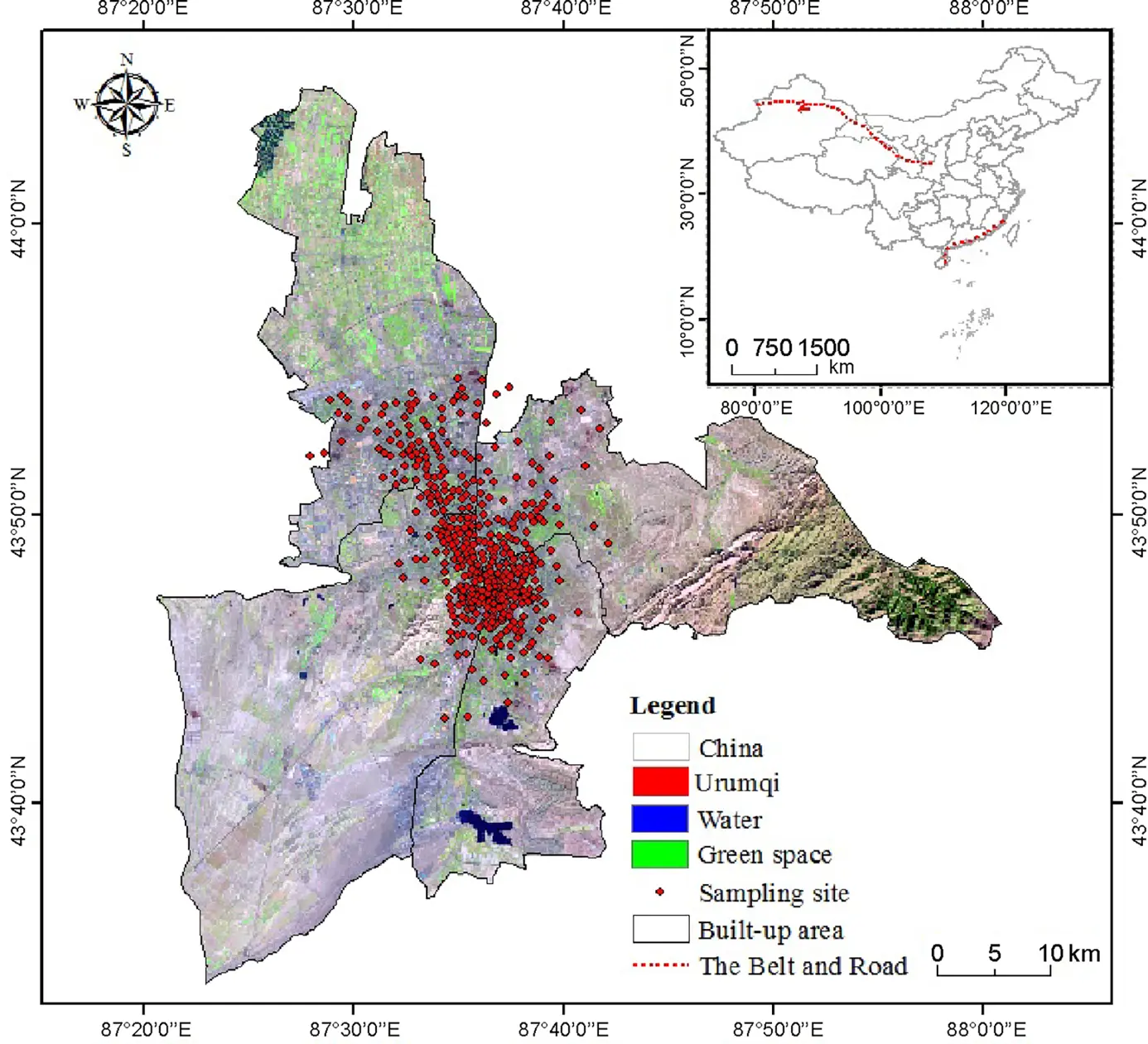
Public participation in ecological civilization construction is a critical pathway for advancing ecological urban design. This study examines residents’ perceptions, satisfaction, and participation in the construction of ecological civilization in Urumqi, northwestern China. Drawing on 1012 questionnaires, this empirical study investigates factors influencing public participation in the construction of ecological civilization. The findings indicate that residents exhibited a strong subjective awareness of public participation in ecological civilization construction (mean score = 4.66), yet ecological cognition (2.75) and participation confidence (2.97) were relatively weak and require further improvement. Satisfaction levels were relatively higher for green status (2.51) and information transparency (2.41), whereas overall satisfaction remained modest, with water resources (1.81) and waste management (1.99) emerging as key concerns. Residents demonstrated a moderate willingness to contribute financially and primarily engaged in low-cost, habitual ecological practices. Significant differences were observed across socio-demographic variables (p < 0.05). Uncivil behaviors and natural pressures were observed as visible obstacles. Strong government leadership, active public engagement, and effective media communication contribute to advancing ecological civilization construction. These results provide valuable insights for promoting ecological civilization construction in northwestern China.
Open Access
Article
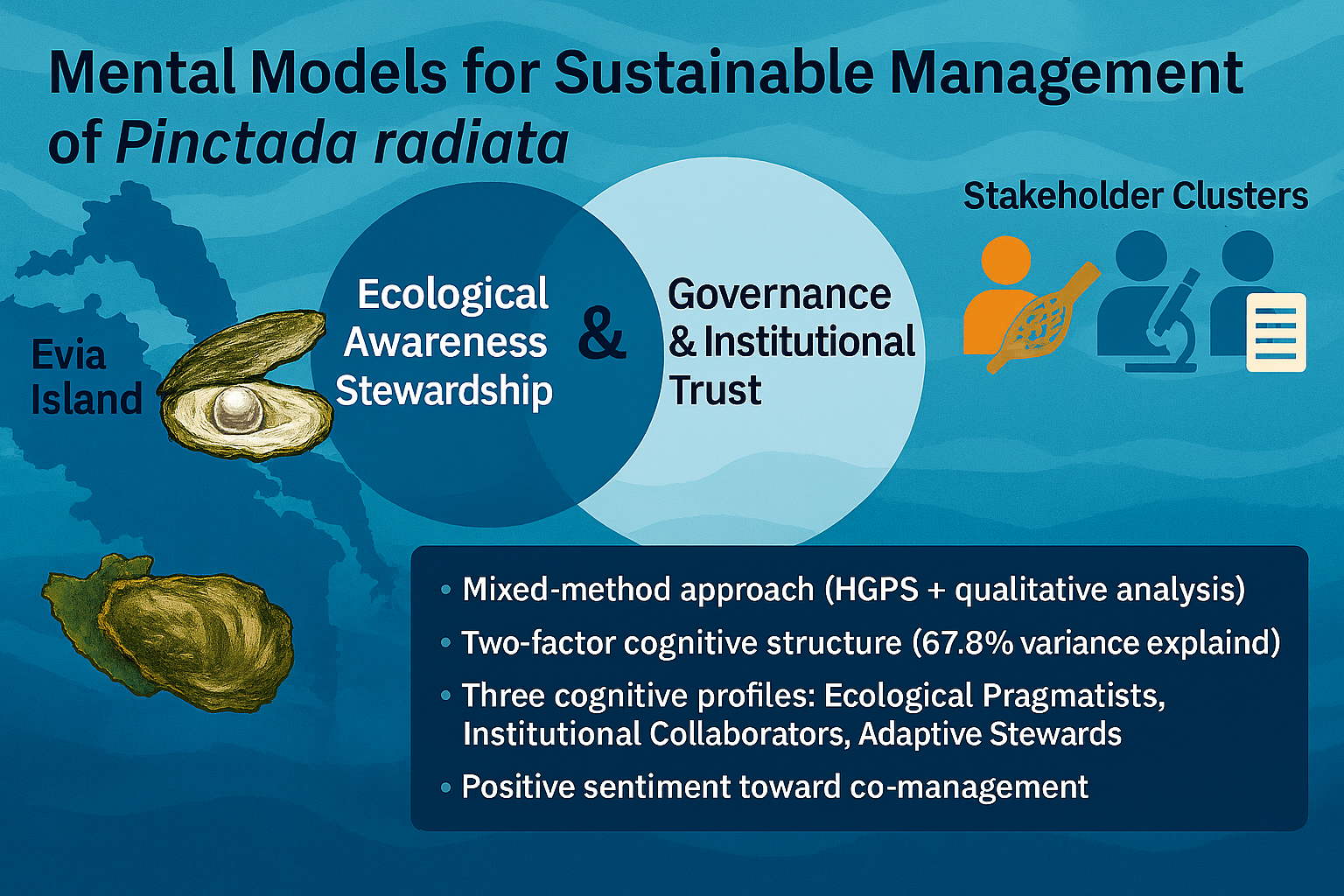
04 December 2025Stakeholder Mental Models for Sustainable Management of the Invasive Pearl Oyster Pinctada radiata in the Eastern Mediterranean
Sustainable management of marine and coastal systems depends not only on ecological dynamics but also on the ways stakeholders perceive and interpret them. This study investigates how fishers, scientists, and government officials understand and frame the management of the Indo-Pacific pearl oyster Pinctada radiata, a non-native yet economically valuable species established around Evia Island, Greece. Using a mixed-methods approach (N = 80), we combined an eleven-item Hydro-ecological Governance Perception Scale (HGPS) with open-ended responses to explore cognitive patterns and governance perspectives. Sampling adequacy was satisfactory (KMO = 0.74; Bartlett’s χ2(55) = 350.41, p < 0.001) and factor analysis revealed two interrelated dimensions explaining 67.8% of total variance (α = 0.84; ω = 0.86; CR = 0.82). Although Kruskal–Wallis tests showed no statistically significant differences among groups (p > 0.05), hierarchical clustering distinguished three partially overlapping cognitive profiles: Ecological Pragmatists, Institutional Collaborators, and Adaptive Stewards (Silhouette = 0.45; CH = 150.23; DBI = 0.75). Thematic and sentiment analyses underscored the importance of collaboration, transparency, and education (mean sentiment = 0.58). The findings demonstrate how cognitive diversity can improve hydro-ecological resilience and the sustainability of coastal governance when it is mobilized through co-management and participatory monitoring.