Found 764 results
Open Access
Review
11 December 2025CRISPR-Armed Phages: Design, Mechanisms, Applications, and Prospects in Precision Microbiome Engineering
The dysregulation of microbial communities poses severe threats to host health and ecological stability, yet traditional microbiome modulation strategies lack specificity and often exacerbate dysbiosis. The CRISPR-Cas system offers unprecedented potential for targeted microbiome regulation due to its sequence-specific nucleic acid recognition and cleavage capabilities, but its translation is hindered by inefficient and non-specific delivery. As natural bacterial predators with inherent host specificity, bacteriophages have emerged as ideal carriers to address this delivery bottleneck. The development of CRISPR-armed phages combines the targeted delivery of phages and the precision editing advantages of CRISPR-Cas systems. This review systematically elaborates on the design and mechanism of CRISPR-armed phages for microbiome engineering. CRISPR-Cas systems were classified on the basis of their structural and functional characteristics, as well as their regulatory effects, in detail after phage delivery. The engineering strategies of integrative and non-integrative phage vectors were then discussed, followed by their applications in ecological regulation and genetic regulation of the microbiome. The current limitations were finally analyzed, such as narrow phage host range, bacterial phage resistance, and low editing efficiency. This review provides a comprehensive theoretical framework to promote the development of CRISPR-armed phages, aiming to advance precision microbiome engineering for human health.
Open Access
Review
10 December 2025Intracellular Chloride Channels: A Rising Target in Lung Disease Research
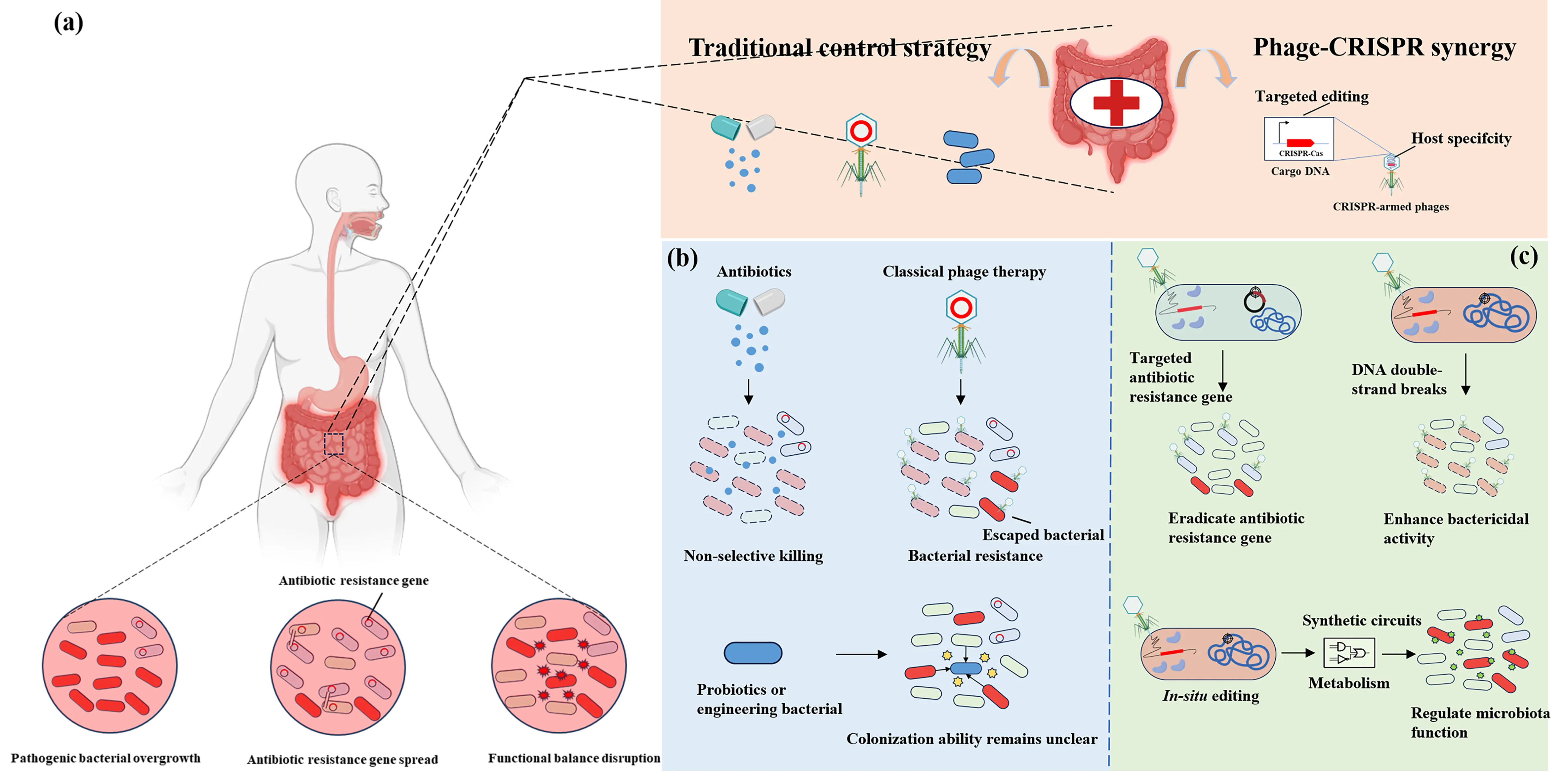
Chloride intracellular ion channels (CLICs) represent a relatively underexplored class of chloride channels and are included in a research initiative that focuses on druggable genes that have not been well studied yet. As a unique family, CLICs exist in membrane and soluble forms and play a role in regulating chloride flux and modulating various aspects of cellular biology. To date, six mammalian CLICs have been cloned and characterized at molecular and physiological levels. The respiratory system, responsible for gas exchange between the atmosphere and the human body, has recently been shown to express CLICs with functional relevance in lung pathophysiology, including lung carcinoma, inflammation, and endothelial dysfunction. Notably, the expression patterns of CLIC isoforms in lung cell types are distinct. Among them, CLIC1, CLIC3, and CLIC4 have been investigated more extensively, particularly in the context of lung cancer, inflammatory diseases, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. A deeper understanding of the role of CLICs in regulating lung cellular function may pave the way for developing novel therapeutic strategies to treat pulmonary disorders. In this review, we summarize the expression and functional roles of CLICs in lung pathophysiology, with particular emphasis on CLIC1, CLIC3, and CLIC4.
Open Access
Article
09 December 2025A Comprehensive Survey of Deep Reinforcement Learning Techniques for Soft Mobile Robots
Soft robotics has emerged as a promising direction for enabling safe, adaptive, and energy-efficient interactions with unstructured environments due to its inherent compliance. Recently, Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has become a powerful tool for autonomous behavior generation in soft robots, surpassing limitations of classical model-based control. However, despite rapid growth of publications in this domain, there is still a lack of systematic comparative surveys that clarify how different DRL approaches have been used for soft mobile robots, what types of tasks they address, and what performance evaluation criteria have been used. In this article, we review and classify existing works in DRL-enabled soft robotics, focusing particularly on soft mobile systems, and present a structured synthesis of contributions, algorithms, training strategies, and real-world applications. Unlike previous reviews that discuss soft robotics or DRL separately, this paper explicitly provides cross-comparison across DRL paradigms and soft robot tasks, enabling researchers to identify suitable DRL approaches for different soft mobile robotic behaviors. Finally, major challenges and promising future directions are proposed to advance this interdisciplinary research area.
Open Access
Article
09 December 2025Mechanical Characterization of Ship Building Grade A Steel by Rapid Cooling in Different Liquid Media
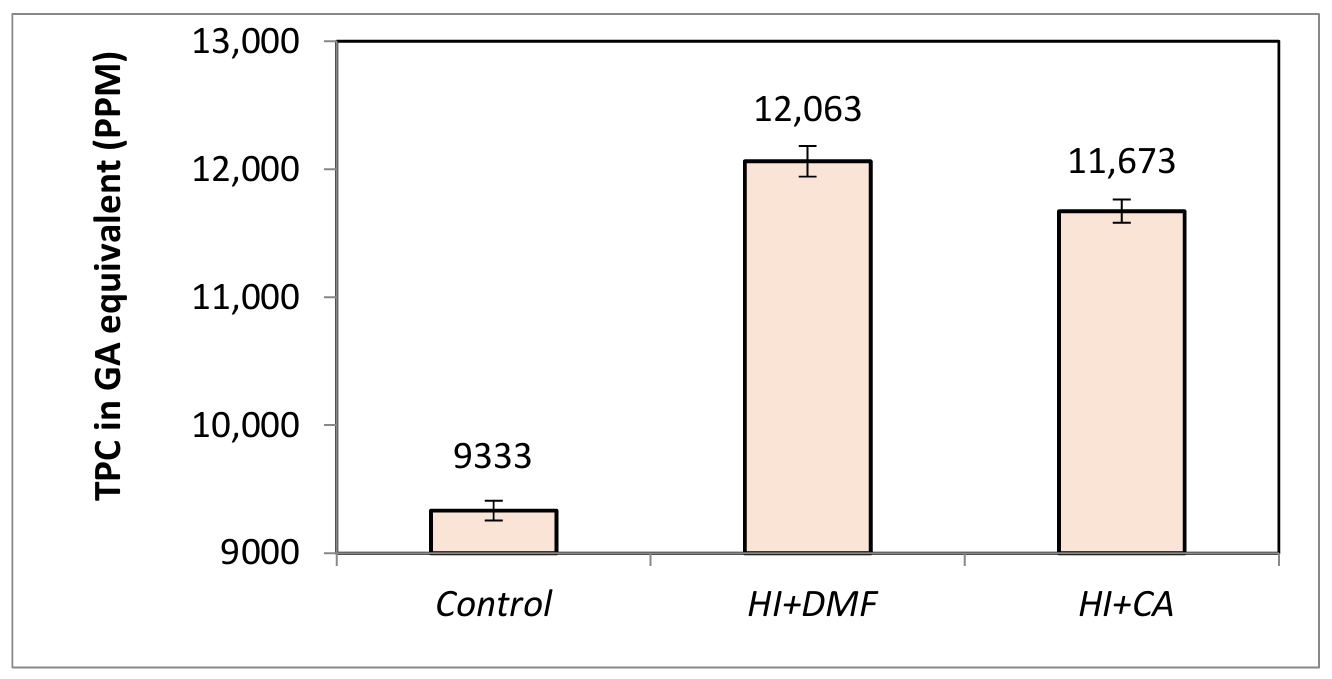
Steel is an essential component used to build marine vessels due to its endurance of the sea’s harsh conditions, including corrosion and dynamic stresses, therefore, different grades of mild steel are used in shipbuilding. It provides the strength, ductility, and weldability necessary for structural integrity, consisting of carbon, manganese, etc., as alloying elements. In this research, different quenching media were employed to assess variations in mechanical properties. This process ultimately triggered alterations in the microstructure of the steel. Two types of media, such as vegetable oil (Canola) and Polyvinylpyrrolidone polymer (PVP), were studied in comparison with simple heat-treated steel. Mechanical characterization comprised of tensile testing, hardness and impact testing to evaluate major changes in strength and ductility. Furthermore, a microscope was used to interpret the microstructure. To guarantee consistency in testing, samples were prepared in accordance with ASTM guidelines. The yield strength of as-received steel was increased from 298 MPa to 358 MPa and 370 MPa because of rapid cooling action in PVP and oil, respectively. A significant increase in Ultimate tensile strength was achieved due to the variety of quenching media; however, ductility was seriously compromised because of the excessive hardness of the material. Impact energy analysis revealed a notable reduction, which is linked with degradation in toughness.
Open Access
Article
09 December 2025Demethylation of Lignin from Rice-Straw Biorefinery: An Integrated Chemical and Biochemical Approach
The efficiency of lignocellulosic biorefineries is limited because of the high recalcitrance and low reactivity of lignin. The reactivity of lignin can be enhanced through various chemical and biochemical approaches. Demethylation is one of the methods that improve the availability of phenolic hydroxyl groups in lignin, thereby enhancing its reactivity and application in sustainable adhesives. The goal of this study is to integrate microbial and chemical approaches to aid in the demethylation of lignin. Towards that end, lignin was first extracted and purified from the rice straw biorefinery solid residue obtained post ethanol fermentation. This rice straw lignin was then subjected to chemical and microbial demethylation. For microbial demethylation under alkaline conditions, Pseudomonas putida and Pseudomonas fluorescens were employed, while demethylation under neutral conditions was conducted using Trametes versicolor. Integrated treatment using Pseudomonas putida followed by hydrogen iodide yielded an increase in the phenolic hydroxyl content by approximately 39–43%. Demethylation using chemical methods and biological methods alone provided approximately 18–27% increases in phenolic hydroxyl content, respectively. Furthermore, to assess the physical and chemical properties of demethylated lignin, FT-IR, TGA, and morphological analytical tools were employed.
Open Access
Article
09 December 2025Defiant Doctorates: Reshaping the Social, Cultural and Intellectual Value of the Doctorate in Regional Universities
Universities are ranked and clustered into ‘like-minded’ institutions. Regional universities—as an adjective and noun or a compound noun—are defined via location, rather than academic standards, teaching innovation, research rigour, or the use of innovative technology. Through the ‘regional’ labelling, they are marked and separated as different from, and implicitly less than, urban and metropolitan institutions, which carry the excitement of urbanity, encompassing Virilian speed and prestigious alumni. This differentiation has consequences for grants, funding, academic staff attrition, and leadership. But what happens to PhD students at regional universities? Where is their voice? How are their views recognized, codified, and understood? Written between an experienced supervisor and a PhD student, this paper offers a different pathway through the regional graduate programme, offering a different lens to re-vision regional higher education, beyond cliches of partnerships and collaborations. As a theoretical and conceptual paper, it creates and holds space for PhD students in a revisioning of regional universities.
Open Access
Article
08 December 2025Short-Form Video Application Use and Self-Rated Health among Older Adults: The Mediating Role of Perceived Social Support and the Moderating Role of Media Literacy
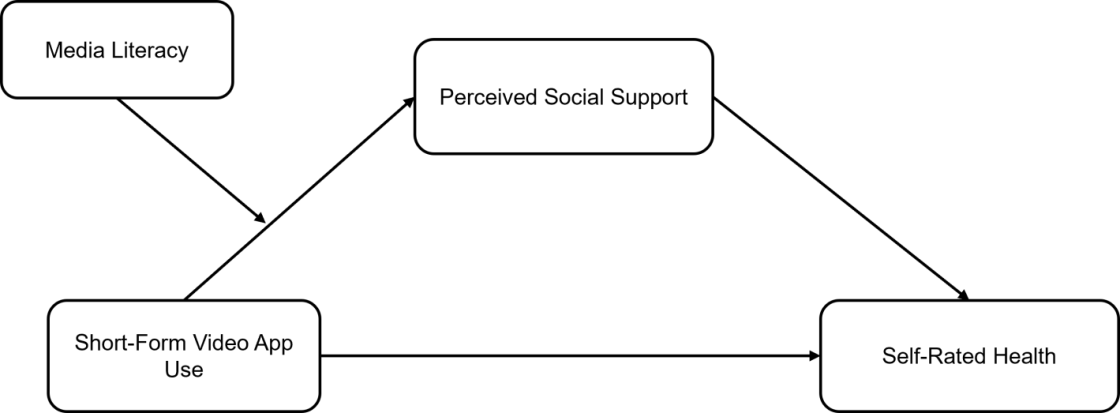
Although short-form video applications (apps) are increasingly popular among older adults, little research has investigated the relationship between their use of such apps and health outcomes. The present study aims to investigate this relationship while examining the mediating role of perceived social support and the moderating role of media literacy. Three hundred and nineteen older adults completed our questionnaire. The results showed that short-form video app use was positively associated with self-rated health among older adults, and this association was mediated by perceived social support. Moreover, the positive association between short-form video app use and perceived social support was observed in older adults with lower (but not higher) levels of media literacy. Future interventions aimed at promoting the health and well-being of older adults (especially those with lower media literacy) should consider teaching participants to use short-form video apps appropriately.
Open Access
Review
08 December 2025Advances in the Biosynthesis and Application of Sialyllactose
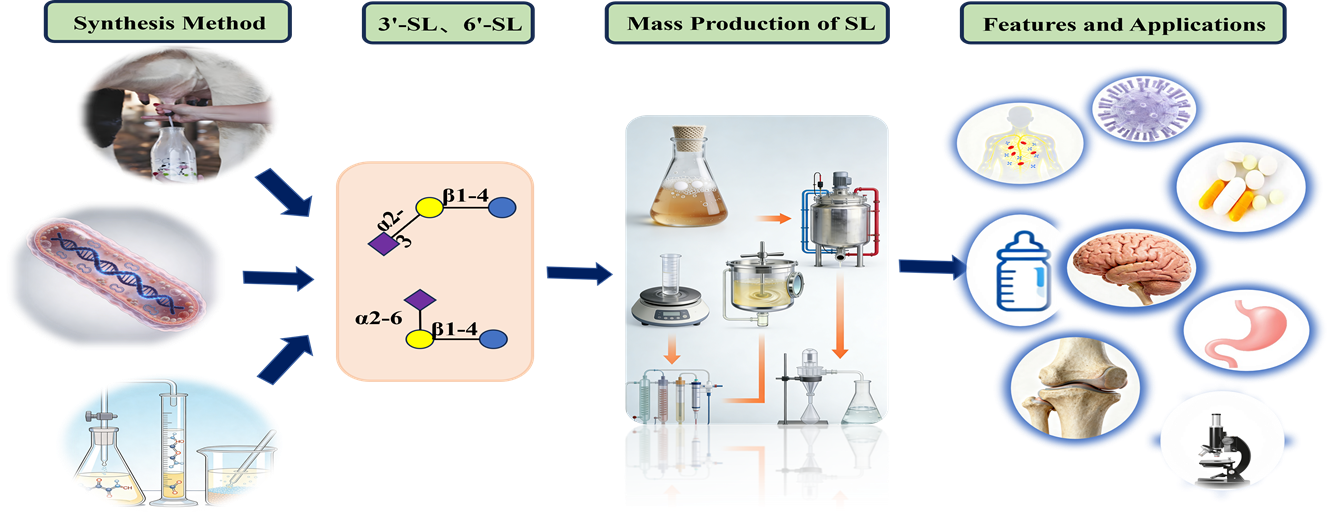
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs), the third most abundant solid component in human milk after lactose and lipids, are recognized as crucial prebiotics that support infant gut health and immune development. Salivary HMOs account for approximately 13% of the total HMOs molar ratio, with 3′-sialyllactose (3′-SL) and 6′-sialyllactose (6′-SL) accounting for approximately 2% and 6%, respectively. Sialyllactose (SL) exhibits a range of notable physiological functions, including prebiotic activity, antiviral properties, prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis, immunomodulatory effects, and enhancement of brain development and cognition. Both 3′-SL and 6′-SL have been approved as “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS) by the U.S. FDA and are increasingly incorporated into infant formula. Currently, the biosynthesis of SL is mainly efficiently produced through engineered microorganisms. However, face bottlenecks: low yields, complex downstream processing, and prohibitive costs. Recent advances in synthetic biology and metabolic engineering offer promising avenues to overcome these barriers. This review introduces the synthesis methods, functions, and applications of SL, as well as conducting safety evaluation and regulatory status analysis. We hope this article will enhance understanding of the challenges encountered in the synthetic biology production and application of SL.
Open Access
Article
08 December 2025Public Participation in Ecological Civilization Construction in Urumqi: A Case Study of a Rapidly Expanding Arid Metropolis in Northwestern China
Public participation in ecological civilization construction is a critical pathway for advancing ecological urban design. This study examines residents’ perceptions, satisfaction, and participation in the construction of ecological civilization in Urumqi, northwestern China. Drawing on 1012 questionnaires, this empirical study investigates factors influencing public participation in the construction of ecological civilization. The findings indicate that residents exhibited a strong subjective awareness of public participation in ecological civilization construction (mean score = 4.66), yet ecological cognition (2.75) and participation confidence (2.97) were relatively weak and require further improvement. Satisfaction levels were relatively higher for green status (2.51) and information transparency (2.41), whereas overall satisfaction remained modest, with water resources (1.81) and waste management (1.99) emerging as key concerns. Residents demonstrated a moderate willingness to contribute financially and primarily engaged in low-cost, habitual ecological practices. Significant differences were observed across socio-demographic variables (p < 0.05). Uncivil behaviors and natural pressures were observed as visible obstacles. Strong government leadership, active public engagement, and effective media communication contribute to advancing ecological civilization construction. These results provide valuable insights for promoting ecological civilization construction in northwestern China.
Open Access
Article
05 December 2025Long-Term Creep Performance of Ferritic SOC Interconnect Steel
Crofer® 22 H is a well-known commercial ferritic stainless steel for the construction of SOC interconnect plates. Its performance under creep loading conditions in the temperature range from 700 to 800 °C was evaluated against a pre-commercial trial steel to signify the impact of thermomechanical treatment history on long-term creep response. While the commercial grade prevailed in solution treated, i.e., low dislocation density, state, the trial steel was put into creep service in a deformed, i.e., high dislocation density, condition. Dislocations do play a major role in the early stages of the nucleation of strengthening Laves phase precipitates, and for this reason, sensitively impact the creep response of the materials in the primary stage of creep, which even affects the following (limited) secondary stage and especially the transition into the creep life dominating tertiary creep stage.