Artiles
Open Access
Article
12 November 2025Topological Optimization for Environmental Sustainability in Civil Engineering Structures Design
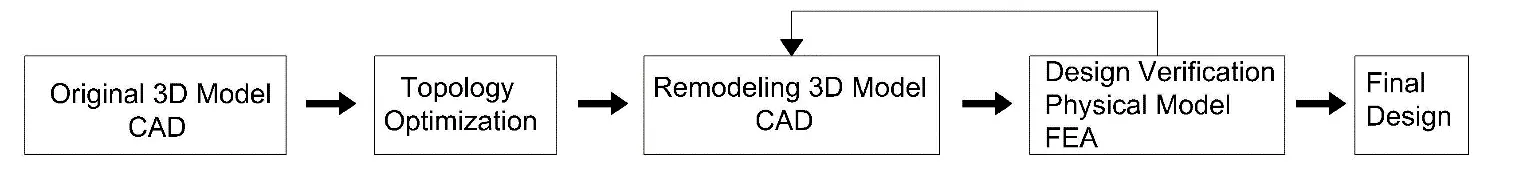
The increasing demand for sustainable and cost-efficient construction highlights the need to minimize material consumption in civil engineering structures without compromising safety or performance. This study investigates the optimization of steel purlin cross-sections in metal buildings as a means to enhance structural efficiency and environmental sustainability. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and the Solid Isotropic Material with Penalization (SIMP) method were employed to identify optimal material distributions and evaluate the effects of varying cross-section geometries. Both rectangular and IPE purlin sections were analyzed under realistic loading conditions to compare stress, deformation, and weight performance before and after optimization. The results demonstrate that substantial reductions in material mass, up to approximately 25–30%, can be achieved while maintaining nearly identical stress and displacement responses. These findings confirm that structural optimization effectively reduces both construction costs and environmental impact. The study concludes by recommending the adoption of topology and cross-section optimization techniques in the design of steel structures, particularly in public projects, to promote resource efficiency and sustainable construction practices.
Open Access
Article
10 November 2025Gendered Mismatches in the Business Support System in Rural Sweden
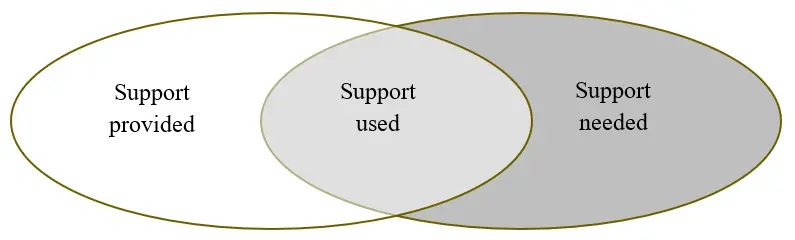
Rural women often start enterprises in sectors that are vital for long-term rural sustainability, but these organizations run the risk of not being properly recognized by public rural development support systems. In this paper, we ask whether existing business support measures meet the needs of rural women entrepreneurs, and if not, what can be improved? Our data consists of recorded interviews with twenty women entrepreneurs from the rural regions of southern Sweden. We asked how they perceive the business support that is provided, used, and needed. We found a gendered mismatch between the forms of public support provided and the support needed by women entrepreneurs in rural areas. The analysis reveals that current business support initiatives often overlook social, cultural, and environmental innovations and enterprises that do not prioritise economic growth as their primary objective, despite their importance for rural viability and development. We argue for a shift towards valuing alternative growth models, broadening eligibility criteria, and simplifying access to funding. As key players in this context, public funds should support long-term sustainability. By embracing the proposed changes, the business support system can be better aligned with the realities of rural entrepreneurship, contributing more meaningfully to rural development and gender equality.
Open Access
Case Report
10 November 2025Non-Fallot Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome in Fetuses: Key Insights for Prenatal Diagnosis and Postnatal Care
Absent pulmonary valve syndrome (APVS) is a rare cardiac malformation that is almost always associated with a Fallot-type ventricular septal defect (VSD). More rarely, it can occur with an intact ventricular septum or muscular VSD. The limited number of observations reported in the medical literature affects the quality of prenatal counselling given to the families concerned. We report 3 new cases of APVS without Fallot-type VSD, with 1 case associated with a muscular VSD, and have carried out a review of the literature on this rare malformation. Two of the fetuses had hydrops fetalis and one of these two had intra-uterine death. A 16p13.11 microduplication transmitted by the father was found in one fetus whose post-natal evolution was favorable following surgical ligation of an aneurysmal ductus arteriosus. A newborn with hydrops fetalis had a favorable outcome after spontaneous closure of the ductus arteriosus on the third day of life. Unlike Fallot-type APVS, non-Fallot type APVS is characterized antenatally by the constant presence of a large ductus arteriosus, the absence of aneurysmal pulmonary branches, a high frequency of chromosomal anomalies, but the absence of 22q11 micro deletion. After birth, early closure of the ductus may be indicated in cases of significant heart failure.

Open Access
Review
07 November 2025Value Engineering in the Era of Industry 4.0: From Gap Analysis to Research Methodologies and Strategic Framework
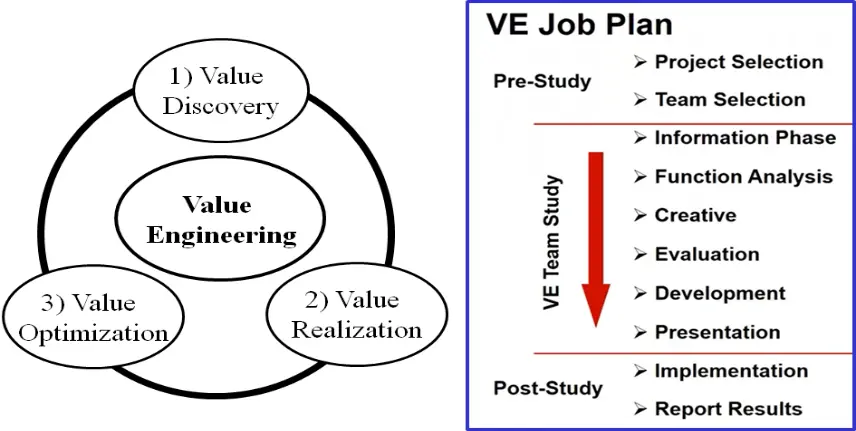
Traditional Value Engineering (VE) has long focused on optimizing the function-to-cost ratio but faces limitations in digitalized industrial contexts. Conventional VE lacks integration with advanced technologies, empirical validation in smart environments, and alignment with sustainability and circular economy objectives. The emergence of Industry 4.0—driven by cyber-physical systems, IoT, big data analytics, digital twins, and artificial intelligence—has transformed industrial ecosystems, necessitating a redefinition of VE practices. This study employs a systematic literature review and structured gap analysis to examine the evolution, applications, and challenges of VE across manufacturing, construction, supply chain, and service sectors. The analysis identifies three key deficiencies in conventional VE: (i) absence of integrated digital frameworks, (ii) limited empirical validation in smart environments, and (iii) weak incorporation of sustainability and circular economy principles. To address these gaps, Value Engineering 4.0 (VE 4.0) is proposed as a function-driven, data-intelligent, and human-centric methodology. It is structured around a six-component strategic framework: (1) digital foundations for technological readiness and organizational alignment; (2) smart VE processes leveraging AI, IoT, and advanced analytics for predictive, connected decision-making; (3) an enhanced Job Plan integrating AR/VR, NLP, and blockchain for improved speed, accuracy, and lifecycle alignment; (4) a phased implementation roadmap; (5) real-time DMAIC integration for continuous optimization; and (6) enablers covering leadership, skills, infrastructure, and cybersecurity. VE 4.0 provides both a research agenda and a practical roadmap, enabling organizations to innovate, enhance resilience, and achieve sustainable competitiveness in Industry 4.0 ecosystems.
Open Access
Perspective
07 November 2025A Critical Analysis of Kinetic Models in Photocatalysis and Some Necessary Improvements
A brief critical analysis of kinetic models is presented, particularly the quadratic model (QM), highlighting their strengths and weaknesses. A generalized quadratic model (GQM) is proposed that can accommodate the experimental observation that the degradation rate is non-zero in the limit of zero substrate concentration. The limits of this model are outlined by comparison with a more extended kinetic scheme.

Open Access
Article
07 November 2025Parking Space Detection Using a Machine Learning-Enhanced Unmanned Aerial Vehicle in a Virtual Environment
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have increased in popularity for several diverse applications over the past few years. Parking, especially in crowded parking lots, can be very time-consuming, as a driver must manually search for vacant spaces among many occupied ones. In this work, reinforcement learning—a category of machine learning in which an agent receives inputs from the environment while outputting actions in order to maximize reward—was utilized in tandem with AirSim, a drone simulator developed by Microsoft, to automate a virtual UAV’s movement. A convolutional neural network (CNN) was then utilized to detect both vacant and filled parking spots, which achieved 98% recall and 93% accuracy. Unreal Engine was used to create a custom environment that resembled a parking lot, and the virtual drone was trained using a Deep Q-Network (DQN). The DQN achieved a mean reward of 394.5 in training and 460.4 in evaluation. A pre-trained CNN integrated with the DQN enables the real-time classification of vacant/occupied parking spaces from drone imagery. Results validate the effectiveness of combining reinforcement learning navigation with CNN image classification, demonstrating deployment-ready performance for real-world congested parking applications.

Open Access
Article
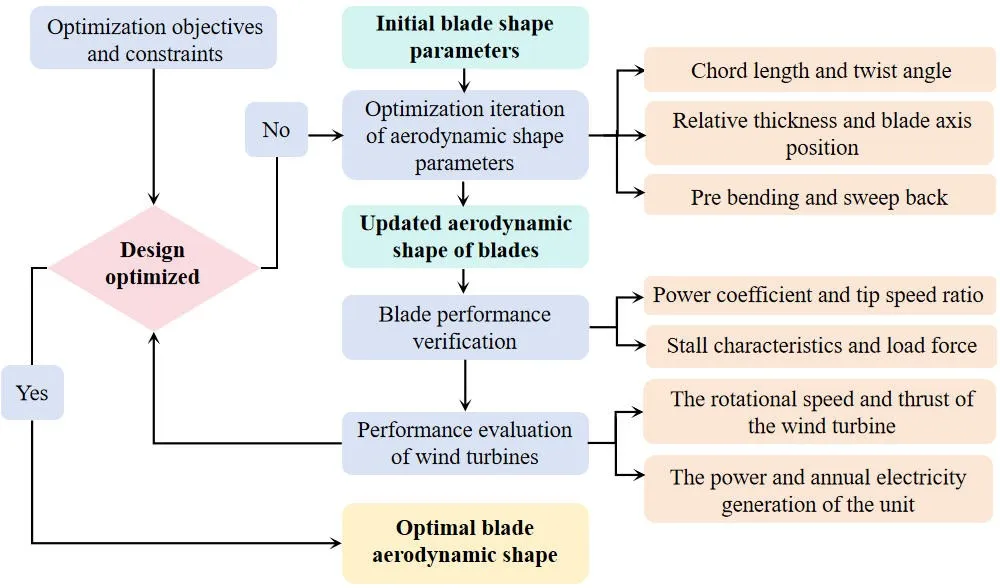
06 November 2025Application of Blades Aerodynamic Optimization Design Platform Based on the Performance of Offshore Wind Turbines
Optimizing aerodynamic performance with low loads is a core objective in high-power wind turbine blade design. This study develops a blade aerodynamic optimization design platform based on the performance of a wind turbine. By applying automated design principles, the platform rapidly iterates to obtain blade profiles that meet turbine development requirements, significantly improving design efficiency and reliability. Key findings include That Optimizing chord length and relative thickness distributions substantially contribute to enhancing power generation while reducing load levels. Relative thickness and twist angle distributions are critical parameters influencing stall characteristics during blade operation. Superior aerodynamic performance notably increases annual rated power generation hours but simultaneously elevates blade thrust and root loads. Among the evaluated designs meeting turbine specifications, the #436 blade achieves a maximum power coefficient of 0.4679 while maintaining low ultimate and fatigue loads. Furthermore, when paired with the wind turbine, its rated wind speed reaches 10.9 m/s, and its annual rated power generation hours under various inflow wind speed conditions all meet the turbine system’s development requirements. Consequently, the #436 blade demonstrates exceptional system compatibility, making the 8.5 MW turbine equipped with this blade highly competitive in the market.
Open Access
Article
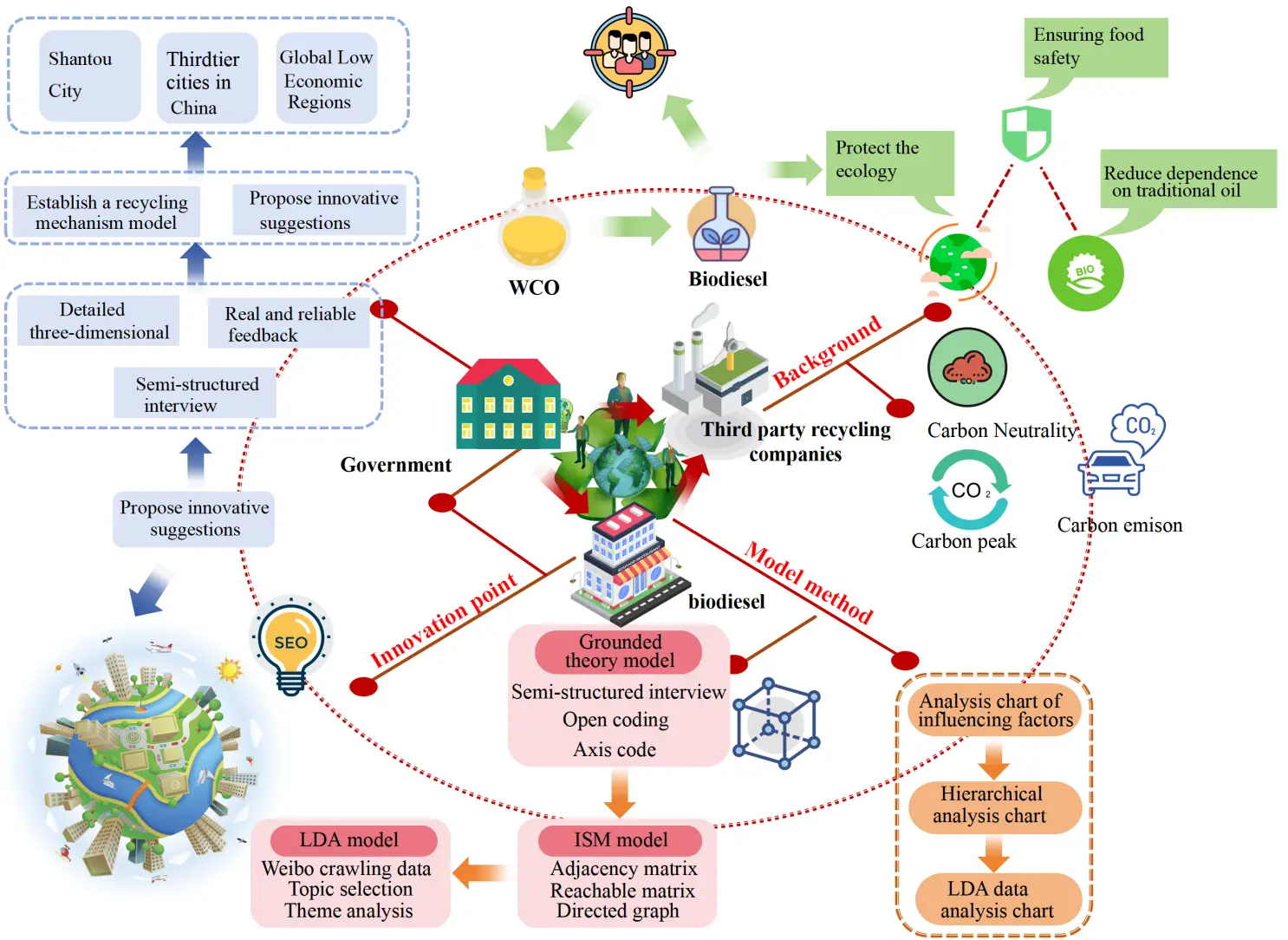
06 November 2025Sustainable Recycling Mechanisms for Waste Cooking Oil in China’s Third-Tier Cities: Evidence from Restaurant Practices
The conversion of waste cooking oil (WCO) into biodiesel is a key strategy for advancing energy sustainability, particularly within China’s rapidly expanding restaurant industry. In third-tier cities such as Shantou, Guangdong Province, WCO collection faces unique challenges. Through in-depth interviews with 20 restaurant operators, this study identifies multiple barriers to effective WCO management, including an aging population, underdeveloped local economies, limited technological infrastructure, and unequal access to educational opportunities, all of which hinder the adoption of advanced filtration systems and broader environmental sustainability initiatives. Moreover, the non-standardized operations of third-party WCO collection services, coupled with space constraints in small restaurant kitchens, further exacerbate inefficiencies in recovery processes. To address these challenges, this study develops a comprehensive framework for WCO collection that is adaptable to regions with similar socio-economic conditions. Integrating grounded theory, Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM), and Latent Dirichlet Allocation, the framework fills critical gaps in existing research. The analysis reveals that government financial incentives occupy the foundational layer of the ISM hierarchy and serve as a key driver of recycling behavior among restaurant operators; educational attainment enhances awareness and compliance but is moderated by structural constraints; and trust in third-party recyclers exerts a relatively limited influence. Correspondingly, H1 receives qualitative support, H2 is partially supported, and H3 gains only limited support. Building on these findings, the study proposes a multi-stakeholder governance framework that includes a “community-school-family” education system, an intelligent third-party management platform, and a government-led industrial chain to promote the formation of a closed-loop circular economy. The results demonstrate that the proposed framework not only offers actionable policy recommendations but also facilitates the adoption of sustainable practices and deepens the understanding of socio-economic and operational factors affecting WCO management, thereby providing strong support for energy and environmental sustainability.
Open Access
Review
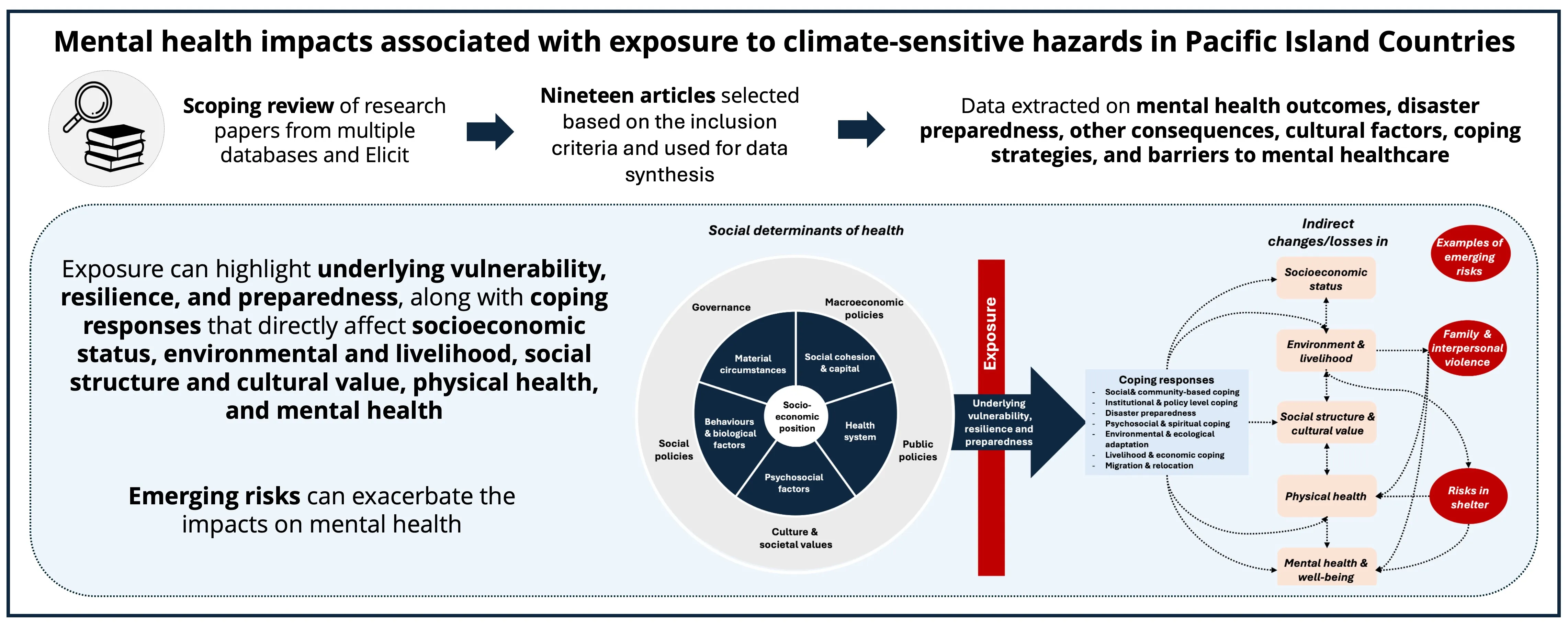
05 November 2025Mental Health Impacts Associated with Exposure to Climate-Sensitive Hazards in Pacific Island Countries: A Scoping Review
Pacific Island Countries (PICs) face some of the most severe health risks from climate change, with associated mental health impacts that remain under-recognized. This scoping review synthesizes peer-reviewed literature published by February 2025 to examine the mental health consequences of exposure to climate-related hazards across 22 PICs. The search identified 193 studies, 19 of which were included in the review. Most studies employed qualitative or mixed methods, focusing on storms, droughts, sea-level rise, planned relocation, and environmental changes. Reported mental health outcomes included increased depression, anxiety, grief, and distress, often linked to direct exposure and secondary effects such as displacement, resource insecurity, and social disruption. Risk and protective factors were identified, emphasizing broader social, cultural, spiritual, and environmental influences that mediate the relationships between climate-sensitive hazard exposures and mental health outcomes in PICs. Cultural mediators such as traditional knowledge, land connection, and community cohesion shaped both vulnerability and resilience. Common coping strategies included relocation, community-based support, and leadership-driven actions. However, access to mental healthcare remained limited due to a shortage of trained professionals, stigma, and preference for traditional healing methods. To address these challenges, it is essential to integrate mental health into national public health frameworks, enhance disaster preparedness, increase access to mental health services, and conduct context-specific research.
Open Access
Communication
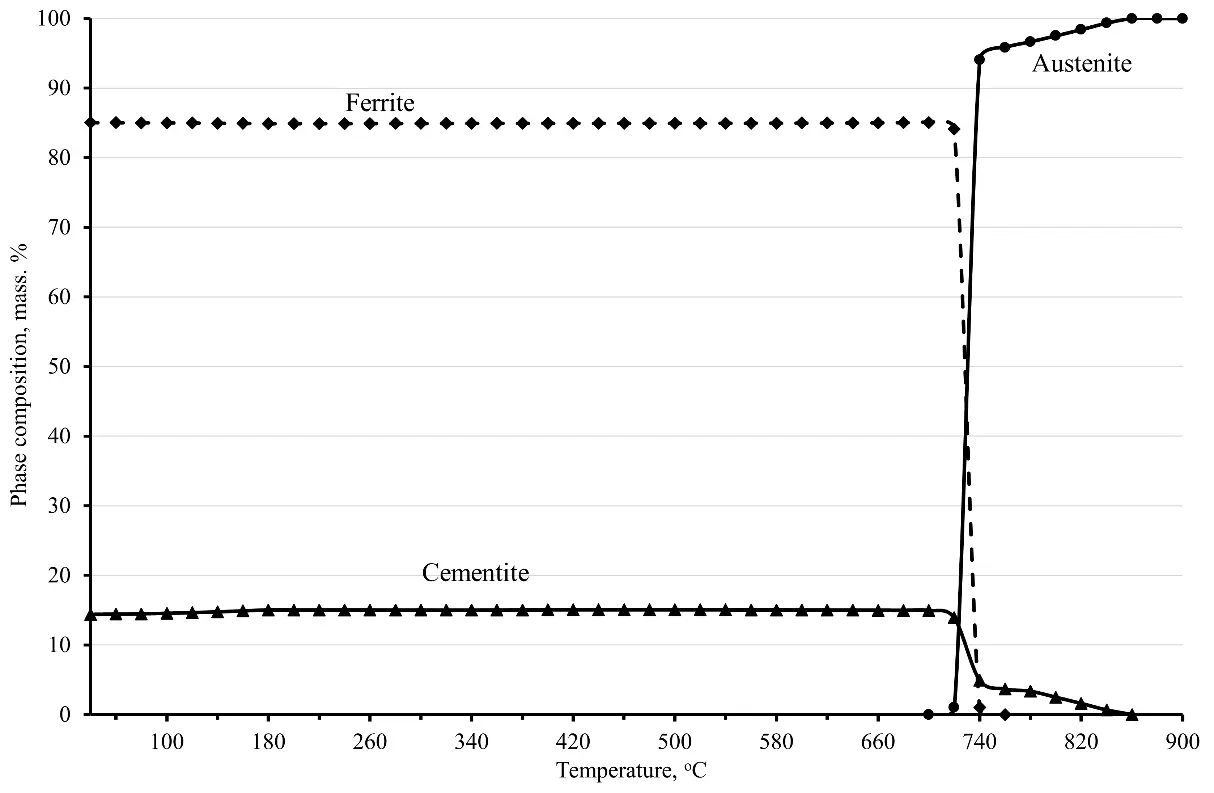
05 November 2025Computer Simulation of the Heat Treatment of Knitting Needles
The article discusses the main steels that are used to make needles for knitting machines. Based on an analysis of literature data, needles for knitting machines are primarily made of high-carbon steel, the main alloying elements of which are carbon in an amount of about 1.0 wt. %, silicon (0.3–0.5 wt. %), manganese (0.55–0.75% by weight), and chromium (about 0.4% by weight). In addition, these steels may contain microalloying additives, such as niobium in an amount of about 0.010% by weight. The publicly available computer model has been expanded to simulate the heat treatment of new materials for knitting machine needles. Using the developed computer model, the optimal structural and phase composition of the knitting needle material is established, which confirms its performance characteristics. It is shown that computer simulation of heat treatment modes makes it possible to conduct computer simulations of heat treatment modes with good accuracy and evaluate the effect of optimizing heat treatment parameters to obtain the best properties. Based on the results of computer modeling, one or more promising heat treatment modes can be selected, which can ultimately have a positive effect on the quality and service life of knitting needles.