Artiles
Open Access
Article
08 December 2025Public Participation in Ecological Civilization Construction in Urumqi: A Case Study of a Rapidly Expanding Arid Metropolis in Northwestern China
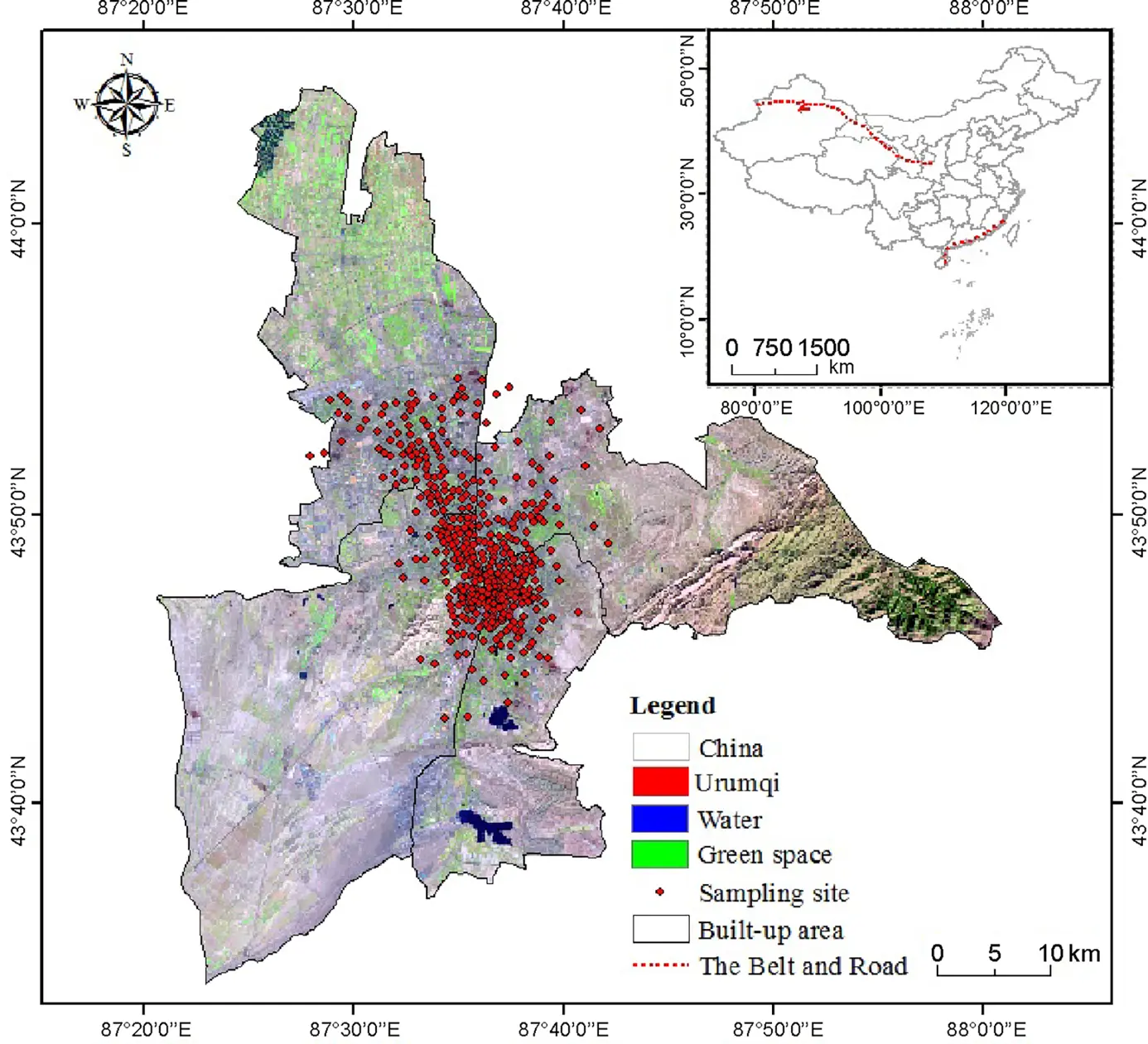
Public participation in ecological civilization construction is a critical pathway for advancing ecological urban design. This study examines residents’ perceptions, satisfaction, and participation in the construction of ecological civilization in Urumqi, northwestern China. Drawing on 1012 questionnaires, this empirical study investigates factors influencing public participation in the construction of ecological civilization. The findings indicate that residents exhibited a strong subjective awareness of public participation in ecological civilization construction (mean score = 4.66), yet ecological cognition (2.75) and participation confidence (2.97) were relatively weak and require further improvement. Satisfaction levels were relatively higher for green status (2.51) and information transparency (2.41), whereas overall satisfaction remained modest, with water resources (1.81) and waste management (1.99) emerging as key concerns. Residents demonstrated a moderate willingness to contribute financially and primarily engaged in low-cost, habitual ecological practices. Significant differences were observed across socio-demographic variables (p < 0.05). Uncivil behaviors and natural pressures were observed as visible obstacles. Strong government leadership, active public engagement, and effective media communication contribute to advancing ecological civilization construction. These results provide valuable insights for promoting ecological civilization construction in northwestern China.
Open Access
Article
05 December 2025Long-Term Creep Performance of Ferritic SOC Interconnect Steel
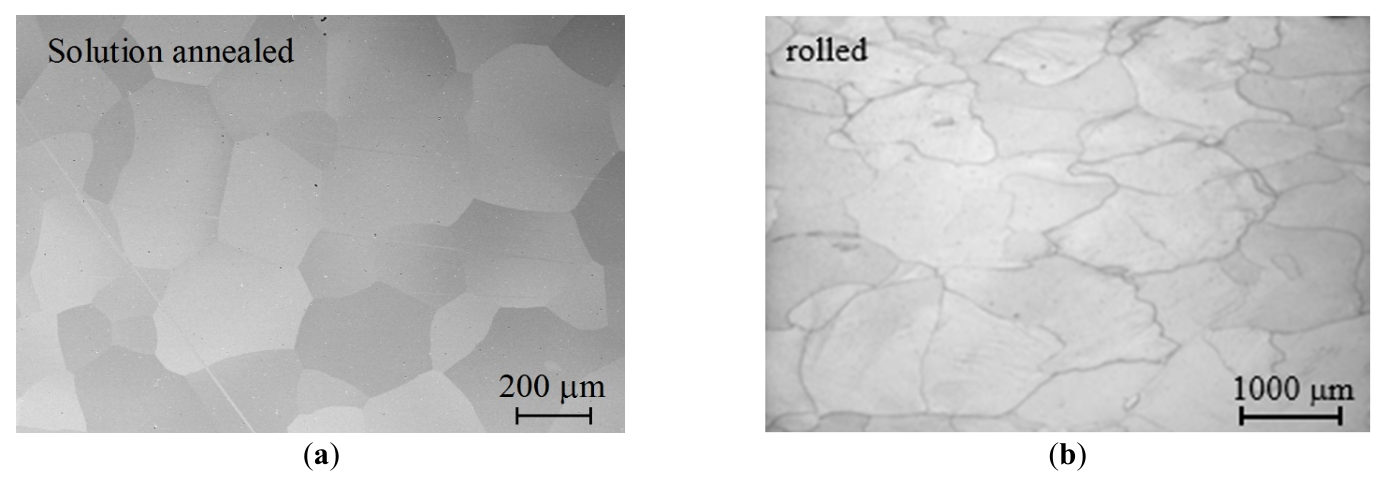
Crofer® 22 H is a well-known commercial ferritic stainless steel for the construction of SOC interconnect plates. Its performance under creep loading conditions in the temperature range from 700 to 800 °C was evaluated against a pre-commercial trial steel to signify the impact of thermomechanical treatment history on long-term creep response. While the commercial grade prevailed in solution treated, i.e., low dislocation density, state, the trial steel was put into creep service in a deformed, i.e., high dislocation density, condition. Dislocations do play a major role in the early stages of the nucleation of strengthening Laves phase precipitates, and for this reason, sensitively impact the creep response of the materials in the primary stage of creep, which even affects the following (limited) secondary stage and especially the transition into the creep life dominating tertiary creep stage.
Open Access
Article
05 December 2025Stopping Rules for Two-Sigma Structural Monophyly in Morphology-Based High-Resolution Phylogenetics
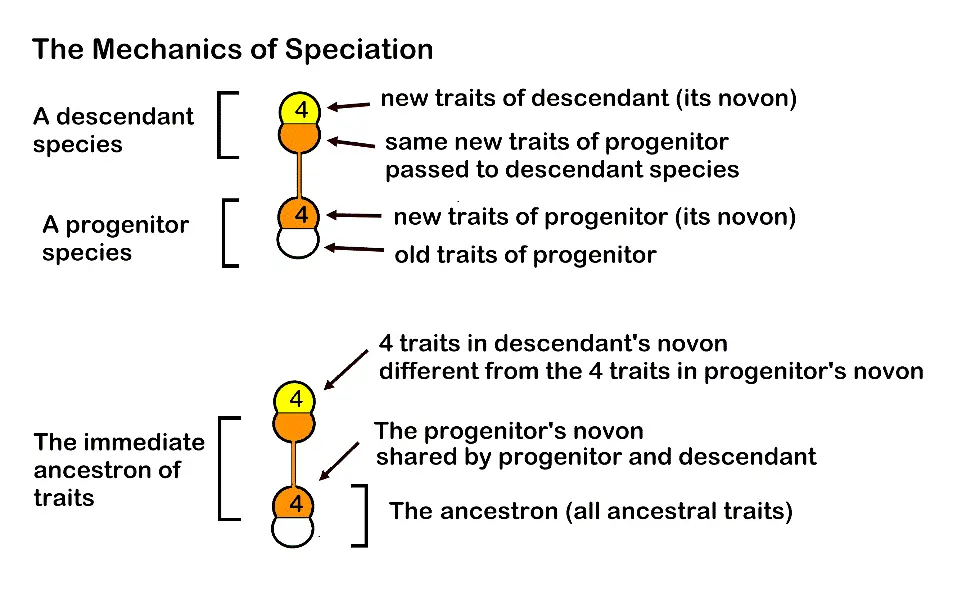
Stopping rules for sampling designs are critical for limiting the effort needed to obtain adequate or significant data, and in many cases for conservation of the species sampled. Such rules are commonly based on pre-determined criteria or a lack of new information as sampling continues. Structural monophyly analysis of minimally monophyletic groups of one ancestral species and a few immediate ancestral species uses a series of steps, each step with a statistical evaluation that helps produce a concise model. Demonstration of two-sigma exclusion of uncertainty is a new stopping rule requirement. The full series of analytic steps has not previously been consolidated in one publication.
Open Access
Article
04 December 2025Stakeholder Mental Models for Sustainable Management of the Invasive Pearl Oyster Pinctada radiata in the Eastern Mediterranean
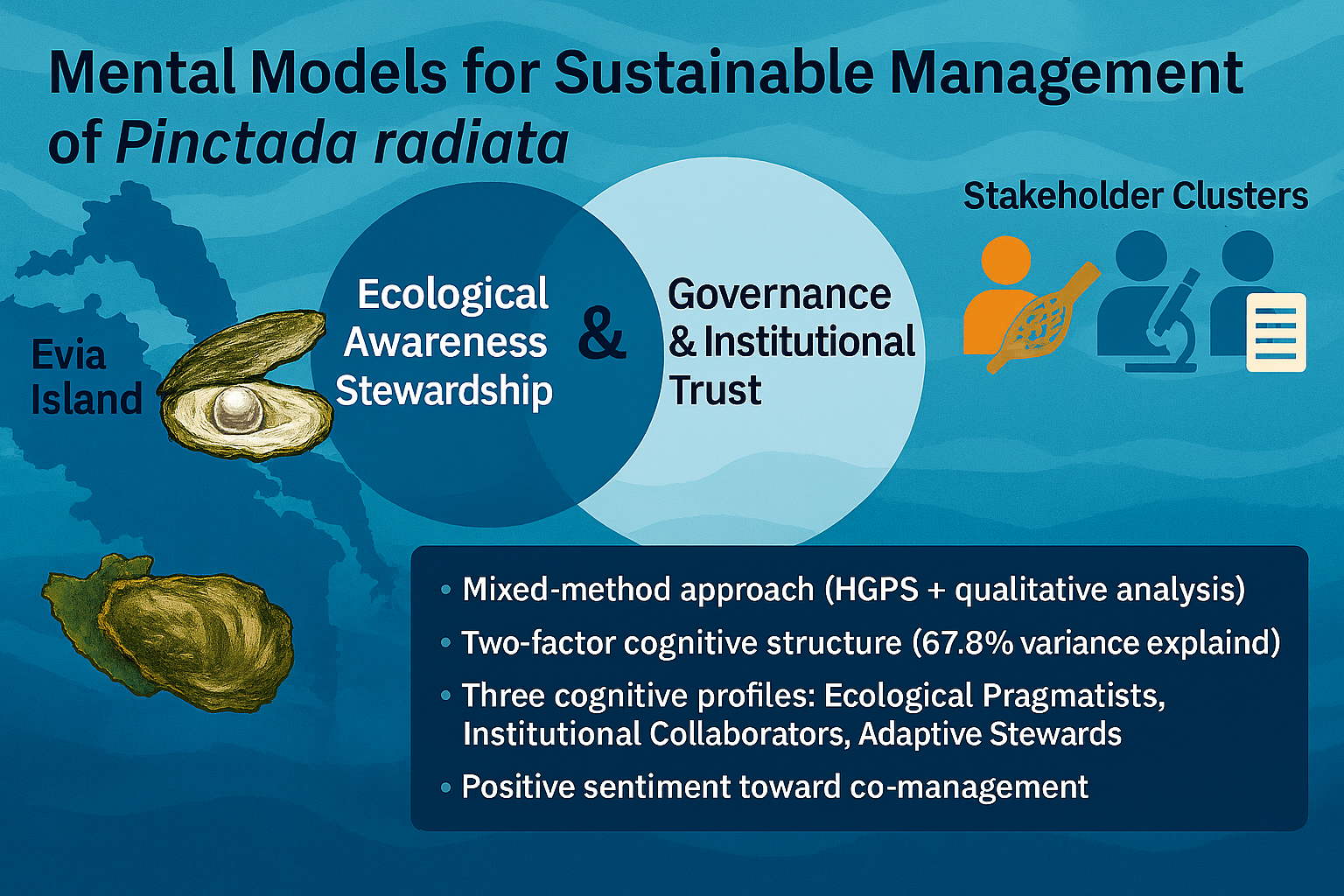
Sustainable management of marine and coastal systems depends not only on ecological dynamics but also on the ways stakeholders perceive and interpret them. This study investigates how fishers, scientists, and government officials understand and frame the management of the Indo-Pacific pearl oyster Pinctada radiata, a non-native yet economically valuable species established around Evia Island, Greece. Using a mixed-methods approach (N = 80), we combined an eleven-item Hydro-ecological Governance Perception Scale (HGPS) with open-ended responses to explore cognitive patterns and governance perspectives. Sampling adequacy was satisfactory (KMO = 0.74; Bartlett’s χ2(55) = 350.41, p < 0.001) and factor analysis revealed two interrelated dimensions explaining 67.8% of total variance (α = 0.84; ω = 0.86; CR = 0.82). Although Kruskal–Wallis tests showed no statistically significant differences among groups (p > 0.05), hierarchical clustering distinguished three partially overlapping cognitive profiles: Ecological Pragmatists, Institutional Collaborators, and Adaptive Stewards (Silhouette = 0.45; CH = 150.23; DBI = 0.75). Thematic and sentiment analyses underscored the importance of collaboration, transparency, and education (mean sentiment = 0.58). The findings demonstrate how cognitive diversity can improve hydro-ecological resilience and the sustainability of coastal governance when it is mobilized through co-management and participatory monitoring.
Open Access
Article
02 December 2025The Role of Electric Vehicles in Environmental Transformation-Goal Towards a Pollution-Free Climate
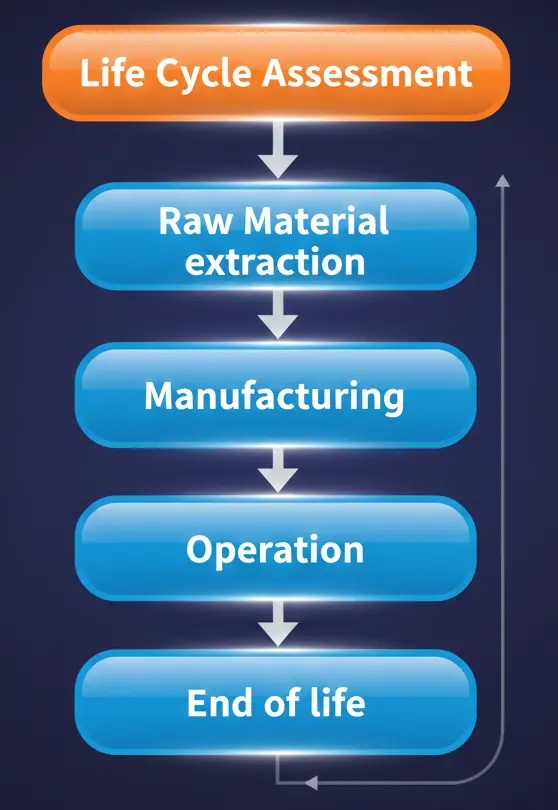
Government agencies have worked tirelessly to minimize the effects of pollution. This problem is pretty dominant in developing countries like Pakistan. The world is facing a severe problem in the form of pollution and the greenhouse effect in recent years. At present, cities like Karachi and Lahore are facing a very high index of Air pollution caused by vehicular emissions. In this framework, the current research proposes an optimized design of student electric vehicles to attenuate environmental pollution. Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, which means no toxic gases. A Carbon Footprint Analysis is conducted in the proposed study to measure the effect of greenhouse gases over the various phases of a vehicle’s life. To simulate the long-term impacts of electric vehicles on the environment, Agent-based Modelling is performed. It mainly includes the analysis of technological advancements in battery recycling. The idea of the student electric vehicle is based on several key points, including the use of an AGS (Automatic Gear System) and Self-Driving mode, to make it easier for students to navigate. Further, a sensing mechanism is developed for predictive maintenance and diagnostics. Hence, the proposed idea of student electric vehicles may be a game-changer for the students by providing them with a safe and pollution-free environment. The analysis shows that EVs like those proposed by students will reduce life cycle emissions by upto 71 percent as compared to ICE.
Open Access
Article
01 December 2025Preparation, Characterization and Performance Assessment of Metal Complexes of Curcuma longa Extract as Sensitizers for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
The dye extract of Curcuma longa (turmeric), which is very rich in curcumin, was chemically modified by complexation reaction with Zn2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+ ions to enhance its stability, electron transfer and photovoltaic performance. The dye and complexes were characterized by Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-Vis) absorption and Fourier Transform Infra-Red (FTIR) spectroscopy of potential chromophores and functional groups. The spectral data obtained indicated that the curcuminoid ligands were successfully coordinated with the metal centers, resulting in red-shifted absorption bands from beyond 460 nm and C=O vibrational frequency decreasing below 1650 cm−1. Complexation reaction resulted in improved photochemical response and enhanced light-harvesting potential. When compared, the solar cells fabricated with titanium dioxide (TiO2) photoanodes sensitized by the complexes afforded improvement in the magnitude of short-circuit current density as well as power conversion efficiency compared to the devices sensitized with the crude extract. Among the three complexes, the Zn-complex afforded the highest efficiency (1.20%), attributed to favourable electronic coupling and reduced recombination losses. Computational studies conducted through quantum chemical calculations based on the curcumin structure supported the experimental findings. The findings from this study demonstrate that metal ions-natural dye complexes have potential for application as low-cost, eco-friendly and sustainable sensitizers, thereby opening a novel horizon in green photovoltaic technologies.
Open Access
Article
28 November 2025Sustainable Bioplastic Using Lignin Extracted from Neolamarckia cadamba Bark by Deep Eutectic Solvent
Lignin, a highly complex and abundant biopolymer, forms an integral part of plant cell walls and represents a promising resource for sustainable industrial applications. Lignin has recently gained attention due to its potential use in biofuels, bioplastics, adhesives, and antioxidant formulations. This paper focuses on lignin extraction from Neolamarckia cadamba bark by deep eutectic solvent (DES) composed of thymol and menthol. Extracted lignin and starch (extracted from Colocasia esculenta roots) were used for the synthesis of bioplastic. The extracted lignin was characterized through multiple analytical techniques, including UV-V is spectroscopy, FTIR, and visual staining with safranin. Bioplastic was characterized for thermal resistance, absorbance, and solubility. The moisture content was obtained as 29.59%, water solubility as 72.61% with almost completely (98%) biodegradable. The work contributes to valorising environmental biomass and enhancing the industrial relevance of lignin. Furthermore, it aligns with the sustainable development goals by transforming bio-waste into valuable bioproducts, such as bioplastics, biochemicals, bioadsorbents, etc. The outcomes of this research may serve as a foundation for future studies in lignin-based material innovation and biorefinery integration.
Open Access
Article
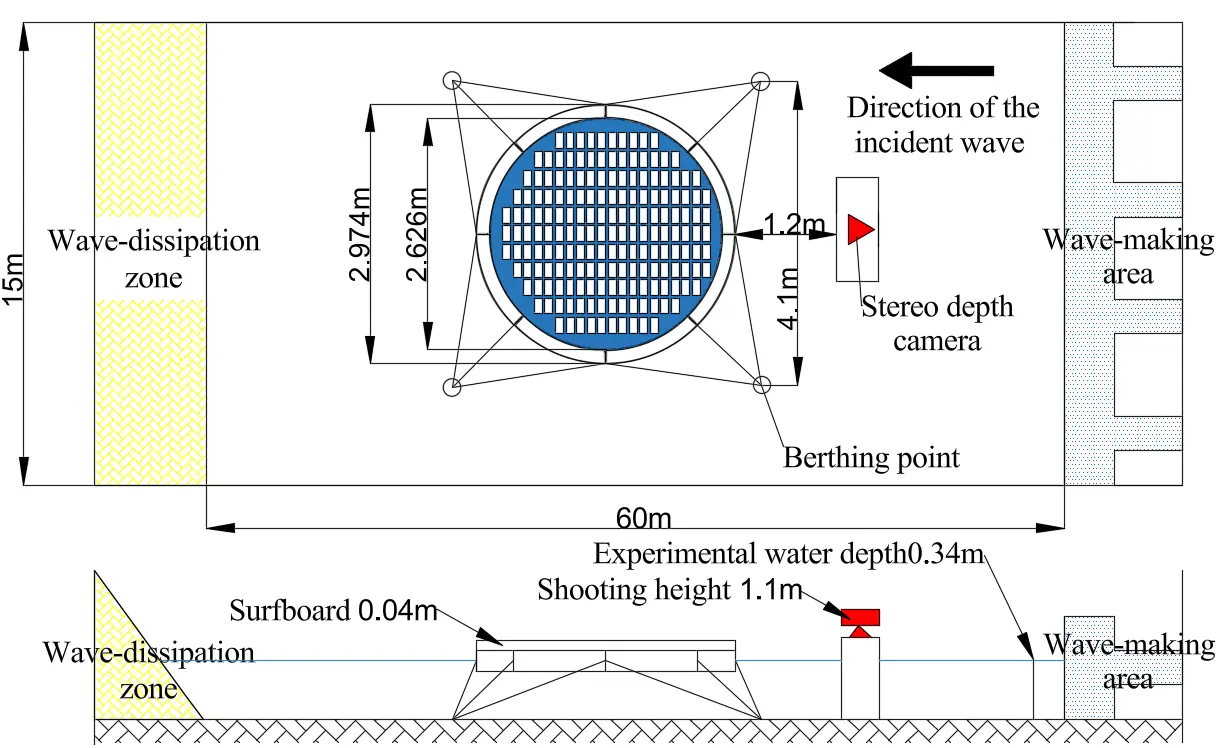
28 November 2025Binocular Camera-Based Depth Recognition for Motion Monitoring and Response Analysis of Flexible Floating Structures for Offshore Photovoltaics
Driven by the global goal of carbon neutrality, offshore floating photovoltaic (OFPV) technology has become a primary focus of photovoltaic research. In particular, flexible thin-film structures have become a central focus of research in sustainable energy development. It offers numerous advantages, including light weight, low cost, and strong adaptability to the marine environment. However, traditional experimental methods still face challenges in accurately capturing the motion response of flexible thin films. To address this issue, this study proposes a motion measurement and monitoring framework based on binocular vision. The framework is validated using gyroscope data, and the results demonstrate its high accuracy and real-time performance. The research team conducted experiments on a flexible floating photovoltaic structure in a wave flume, applying the proposed framework to monitor its motion response under wave excitation. The experimental results show that wave height and wave period have significant effects on the acceleration response of the thin film: higher wave heights lead to notably greater accelerations, whereas longer wave periods result in a gradual decrease in acceleration. Overall, the proposed framework provides reliable technical support for the design optimization and safety assessment of flexible thin-film FPV structures.
Open Access
Article
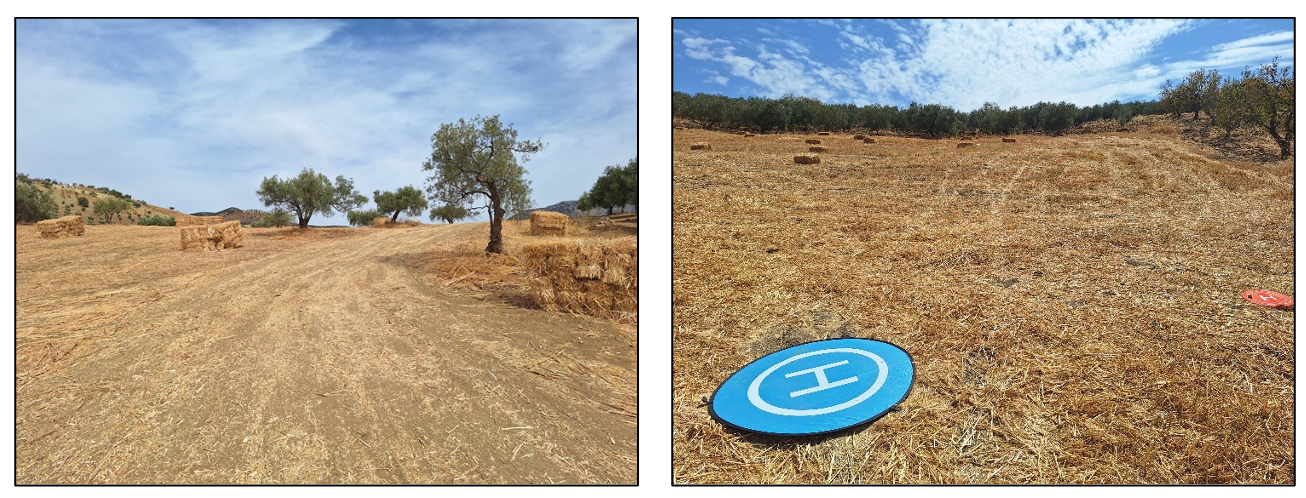
27 November 2025The Limits of RGB-Based Vegetation Indexes under Canopy Degradation: Insights from UAV Monitoring of Harvested Cereal Fields
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) equipped with RGB cameras are increasingly used as low-cost tools for crop monitoring, offering a range of vegetation indexes in the visible spectral range. These indexes have often been reported to correlate with other multispectral indexes such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) during active growth stages. However, still efforts should be done about their performance under conditions of canopy degradation. In this study, UAV flights were conducted over a cereal field immediately after harvest, when the canopy consisted mostly of bare soil and dry residues. RGB-based indexes were calculated from the orthomosaic, normalized to a [0–1] scale, and compared to NDVI derived from a multispectral sensor. Data preprocessing included ground control point (GCP) georeferencing, removal of NoData pixels, and raster alignment. Results revealed very weak correlations between RGB indexes and NDVI (Pearson r < 0.15), with Visible Atmospherically Resistant Index (VARI) showing almost no variability across the field. Although the Leaf Index (GLI), yielded the lowest error values, all RGB indexes failed to reproduce the variability of NDVI under post-harvest conditions. These findings highlight a critical methodological limitation: RGB indexes are unsuitable for vegetation monitoring when canopy cover is severely reduced. While they remain useful during active growth, their reliability diminishes in degraded or post-harvest scenarios, thereby limiting their application in assessing abiotic stress in cereals.

Open Access
Article
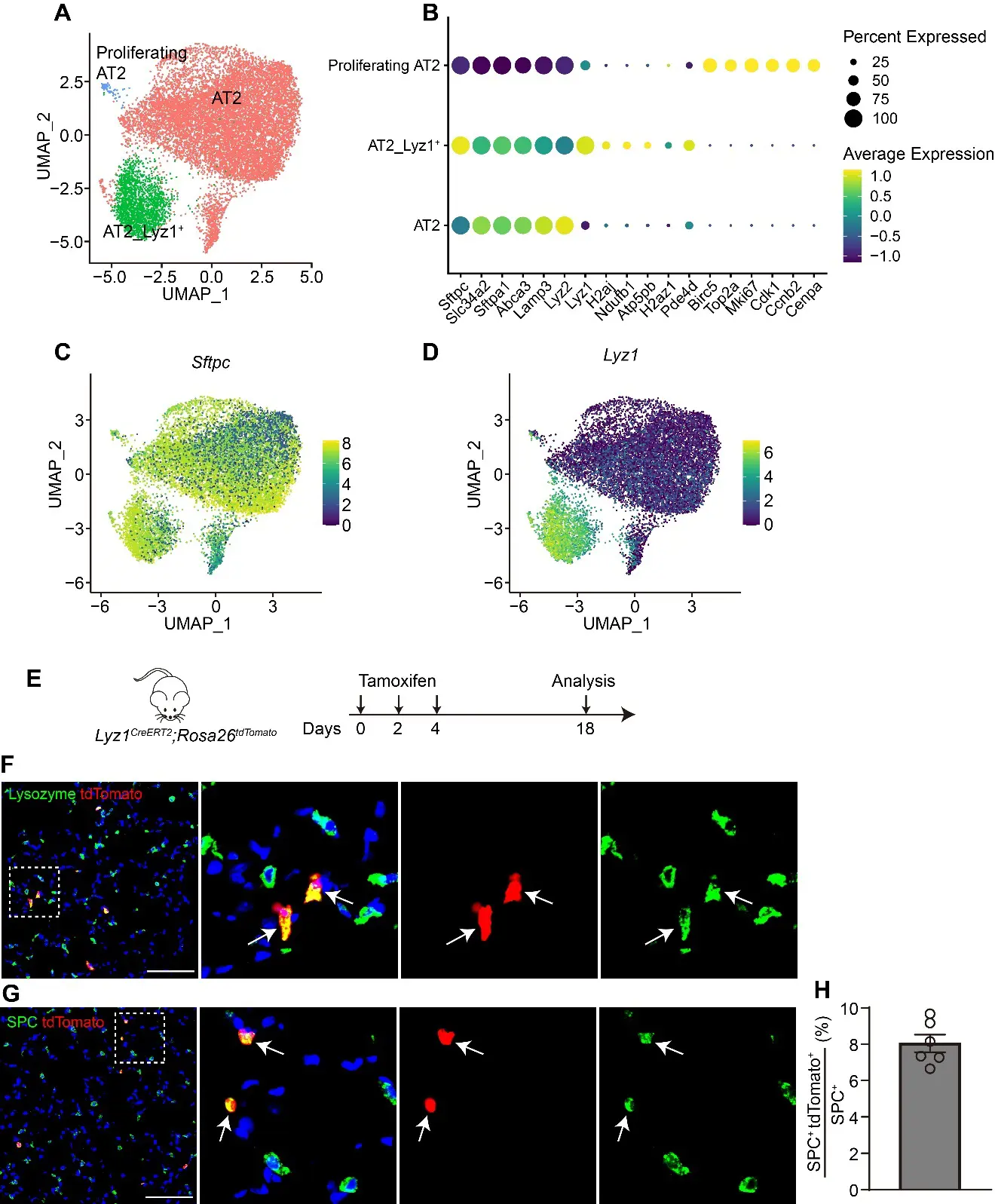
27 November 2025Lyz1-Expressing Alveolar Type II Cells Contribute to Lung Regeneration
The alveolar units, composed of alveolar epithelial type II cells (AT2) and type I cells (AT1), are essential for efficient gas exchange. While AT2 cells are known to play critical roles in alveolar homeostasis and regeneration, the contribution of heterogeneous AT2 cells to lung repair remains poorly understood. Here, we identified a distinct AT2 subpopulation that exclusively expressed Lysozyme 1 (Lyz1) through single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) analyses. Cell fate mapping revealed that the Lyz1CreERT2 mouse strain specifically labeled Lyz1-expressing AT2 cells in vivo at homeostasis. Following lung injury, Lyz1+ AT2 cells expanded and contributed to alveolar regeneration by generating both self-renewing AT2 cells and differentiating AT1 cells. We further observed the emergence of de novo Lyz1-expressing cells in the airways after lung injury. Additionally, Lyz1+ AT2 cells displayed significantly enhanced proliferative capacity compared with general bulk AT2 cells in 3D organoid cultures. These findings define Lyz1+ AT2 cells as a previously unrecognized progenitor population, expanding the paradigm of alveolar regeneration and providing insight into how epithelial diversity supports lung regeneration.