Artiles
Open Access
Article
26 June 2025Testing Photogrammetry in Assessing Health of Houston Toads (Bufo [=Anaxyrus] houstonensis)
The Houston toad (Bufo [=Anaxyrus] houstonensis) is an endangered amphibian species that occupies a small range in Texas, USA. Despite recent increases in juvenile detections, obtaining data is limited by a narrow temporal window of juvenile emergence. This necessitates the rapid collection of ecological data. Because of this, we seek to test the quality of image-based measurements as an alternative to assessing the body condition of Houston toads. We used caliper- and image-based measurements of wild-caught adult toads and captive-bred juveniles, while recording handling time for each method with the juveniles. We compared scaled mass indices (SMI) and residuals from ordinary least squares regressions (OLS) between methods and life stages. Handling time of juvenile toads was significantly lower (p < 0.0001) for the image-based trial than the caliper-based trial. While SMI values violated key assumptions for a valid Condition index (CI), OLS condition index values did not. OLS condition values from the image-based trial were also not statistically significantly different to those from the caliper-based trial. These observations suggest that our image-based measurement technique is a valuable alternative to gaining morphometric data, and that applying this data to an OLS residual index is a more appropriate approach to monitoring individual- and population-level health in Houston toads.

Open Access
Article
25 June 2025Time Is Lung: Inpatient Transbronchial Lung Cryobiopsy Decreases Wait Time to Treatment Initiation for Newly Diagnosed Interstitial Lung Disease
Although performing lung biopsies on hospitalized patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) has risk, initial studies have shown transbronchial lung cryobiopsy (TBLC) may be safely performed in this patient group. Data evaluating the value of this intervention in establishing a diagnosis and impacting management is lacking. We present a comparison of TBLC for inpatients and outpatients and provide data on the impact on medical therapy initiation and wait times from consultation to biopsy and treatment. Demographic data, pulmonary function values, chest imaging patterns, procedural information, diagnosis, and medical therapy changes, defined as medication initiation, adjustment, or cessation guided by TBLC results, were recorded from enrolled patients with newly identified ILD. Changes in medical therapy were the primary outcome. Time from consultation to biopsy and treatment was the secondary outcome. Fifty-four (54) patients (40 outpatient, 14 inpatient) were included. Inpatients underwent biopsy 2.5 ± 4.4 days after consultation compared to 15.5 ± 16.1 days for outpatients (p < 0.001). Medical therapy changes occurred 10.3 ± 7.9 days after biopsy for inpatients compared to 34.6 ± 37.0 days for outpatients (p < 0.001). There were no significant differences in medical therapy changes between the groups (p = 0.45). Our initial study suggests that performing TBLC on inpatients with newly identified ILD decreases wait times to treatment initiation and diagnosis. Efforts to understand the impact of a decreased wait time on ILD prognosis, including the development of progressive disease or fibrosis, symptom evolution, and quality of life, require further evaluation.
Open Access
Article
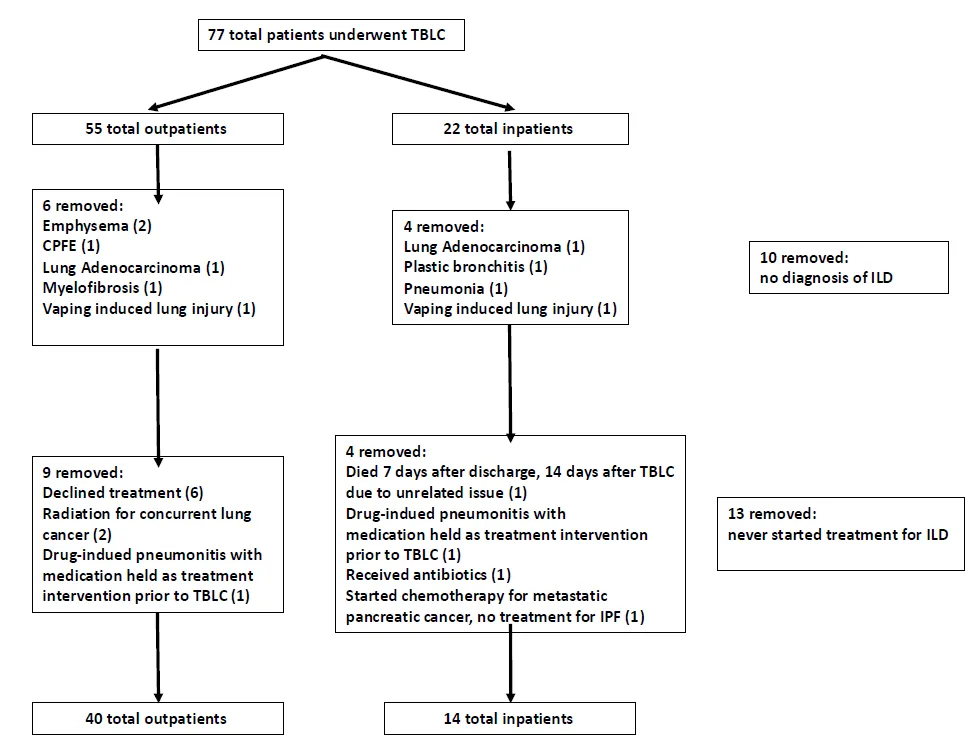
25 June 2025Fermentation of Wild Hydrolytic Bacteria Isolated from Opuntia ficus-indica, and Its Effect on Flow Behavior of Cladodes Flour Culture Media
The aim of this study was to evaluate the fermentation dynamics of two wild hydrolytic microorganisms and their effect on the flow behavior of a culture medium formulated with Opuntia ficus-indica cladode flour. Identified Acinetobacter pitti and Bacillus subtilis presented maximum values of specific hydrolytic activity (SHA) at 24 h of growth (0.21 ± 0.05 and 0.22 ± 0.01 IU, respectively). The apparent viscosity of cladode flour medium (CFM) measured by applying shear rates (66.7 s−1–0.003 s−1) in suspensions (20%) showed a significant decrease (60%) as a function of bacterial growth progressed. After fermentation, the CFM exhibited pseudoplastic (shear-thinning) behavior, which was linked to the enzymatic degradation of polysaccharides. The use of crude extracellular enzyme extracts from these wild bacteria effectively reduced medium viscosity by breaking down the plant matrix. These findings highlight the hydrolytic potential of native strains in modifying the rheological properties of cactus-based culture media, offering a low-cost alternative for biomass pretreatment and valorization in future biotechnological applications.
Open Access
Article
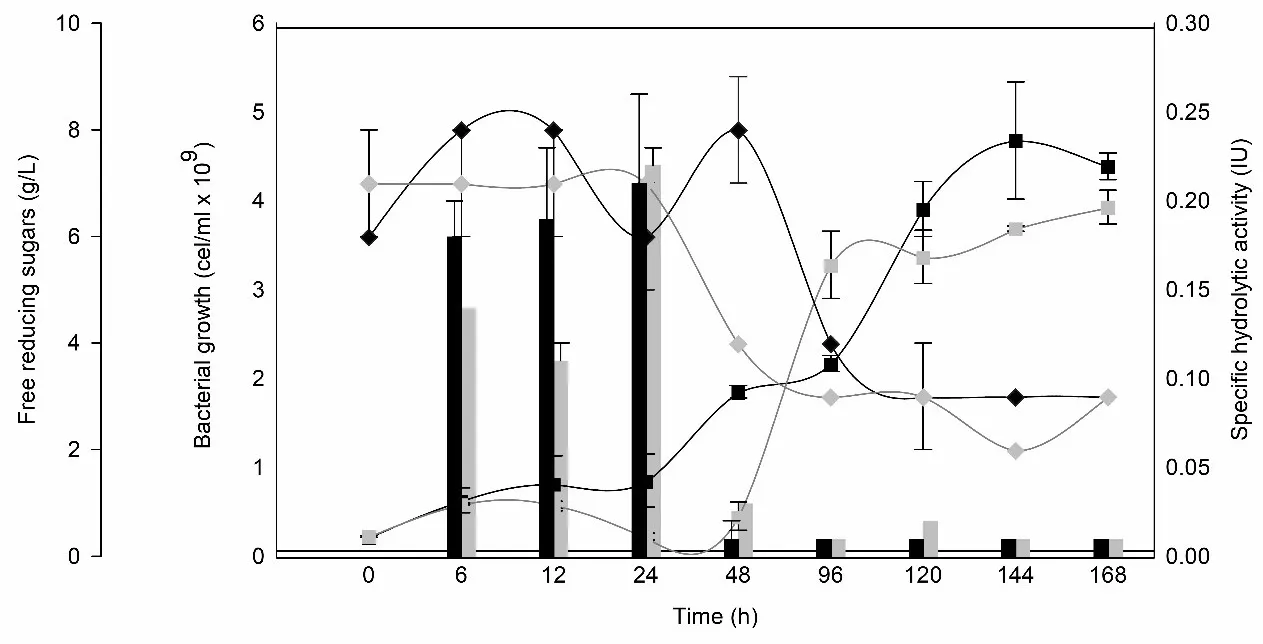
25 June 2025Synthesis and Characterization of Micron-Sized Spherical Calcium Carbonate Regulated by Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose
Spherical calcium carbonate particles were prepared with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) as an addition agent by using a double decomposition reaction. We studied the effects of the additional amount of CMC on the morphology and crystal forms of calcium carbonate. The morphology and size of the product were characterized by using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). We found that with the continuous increase of the additional amount of CMC, the number of prepared spherical calcium carbonate particles gradually increases. When the additional amount of CMC is 50% of the mass of calcium carbonate generated by the reaction, all calcium carbonate becomes micron-scale spherical calcium carbonate particles. The method can be used for the preparation of spherical calcium carbonate. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used to test the crystal form of calcium carbonate prepared by adding different qualities of CMC. It has been found that both calcite type and vaterite type calcium carbonate exist, but with the increase of the additional amount of CMC, the number of fingerprint peaks and amplitude deviated from the baseline increased gradually. These results show that the proportion of amorphous calcium carbonate is significantly increased as the additional amount of CMC increases. The study provides a reference for exploring the preparation conditions of calcium carbonate microcapsules and the mechanism of crystal form transformation.
Open Access
Article
24 June 2025Modelling of Thermodynamic and Transport Properties of R452B Refrigerant with Low GWP
Accurate and reliable estimation of the thermodynamic and transport properties of refrigerants is of paramount importance for the effective design and optimization of refrigeration cycles. In the context of growing environmental concerns, there is a pressing need to transition towards more environmentally benign refrigeration systems and applications. This imperative has driven the search for alternative refrigerants with reduced environmental impact. The refrigerant R452B has emerged as a promising candidate, particularly as a suitable replacement for R410A, due to its favorable thermodynamic characteristics and significantly lower Global Warming Potential (GWP). This research addresses the critical need for precise property data by developing mathematical models for key thermodynamic and transport properties of the R452B refrigerant. Specifically, the study focuses on modelling enthalpy, entropy, specific volume, thermal conductivity, viscosity, and thermal diffusivity. These properties are fundamental to understanding the behavior of the refrigerant within refrigeration systems and are essential for accurate system design and performance prediction. To achieve this modelling objective, the genetic expression programming (GEP) methodology, a powerful evolutionary algorithm capable of automatically generating complex mathematical expressions, was employed. GEP was selected for its ability to discover intricate relationships between variables and to produce explicit equations that can be readily implemented. The accuracy and reliability of the developed GEP models were rigorously evaluated. The coefficient of determination (R2) for the predicted thermodynamic and transport properties across a range of temperatures was found to be between 97% and 99%. This high degree of accuracy demonstrates the robustness and predictive power of the generated equations. The strong correlation between the model predictions and the actual property values indicates that these equations are sufficiently sensitive and accurate to be used with confidence in engineering calculations and simulations. The newly developed mathematical models offer a valuable tool for engineers and researchers working with R452B. These models provide a means to accurately estimate the thermodynamic and transport properties of this refrigerant without the need for complex and time-consuming experimental measurements or computationally intensive simulations. By providing dependable equations, this study facilitates more efficient and accurate design, analysis, and optimization of refrigeration systems utilizing the R452B refrigerant.
Open Access
Review
24 June 2025Obesity-Associated Chronic Inflammation: A Protective Mechanism against Type 2 Diabetes
Chronic inflammation is widely considered a risk factor for T2DM by inducing insulin resistance, but all attempts to translate the concept into clinical therapies have failed in the past 30 years. Anti-inflammatory medicines, including anti-TNF-α antibody (Etanercept), anti-IL1 antibody (Anakinra), anti-IL6 (Ziltivekimab), and NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor (Colchicine) have excellent activities in the control of inflammation in arthritis. They reduced inflammation in T2DM patients in the clinical trials, but none improved insulin sensitivity. Some of them exhibited a mild and transient activity in the control of blood glucose, but the activities were related to the improvement of insulin secretion by β-cells. The failure may be related to followings: over-interpretation of TNF-α activity; ignoring the role of anti-inflammatory cytokines; differences between mice and humans. However, the species difference cannot fully explain the failure as these therapies did not work in the animal models as well. Moreover, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) show that T2DM is not associated with proinflammatory cytokine genes, including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and CCL2(MCP1). More studies suggest that inflammation has beneficial activities in the mobilization of energy stores and promotion of energy expenditure to prevent energy surplus, a risk factor of obesity-associated T2DM. Inflammatory cytokines induce lipolysis, thermogenesis, and satiety. In this regard, the inflammatory response is a compensatory event to obesity-associated stress with beneficial effects on energy metabolism. It is time to reconsider inflammation activity in obesity for protective activities.
Open Access
Article
23 June 2025Asset Management Excellence: A Roadmap for Integrating Lean Six Sigma and ISO 55001 to Achieve Operational Excellence
Asset Management Excellence (AME) has become essential for sustaining operational efficiency and long-term competitiveness in today’s digitally driven and increasingly complex industrial landscape. This study introduces an integrated roadmap that aligns Lean Six Sigma (LSS)—specifically the DMAIC methodology—with ISO 55001 standards to enhance asset reliability, optimize lifecycle performance, and support continuous improvement. The proposed model embeds principles such as lifecycle value optimization, risk-based decision-making, and sustainability. It leverages proven tools, including Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), Root Cause Analysis (RCA), Statistical Process Control (SPC), predictive maintenance, and real-time monitoring to enable proactive, data-driven asset management. This integration supports efficiency, reduces variability, and extends asset life. Performance is measured through key indicators such as Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), and lifecycle cost-efficiency. These metrics enable organizations to monitor progress, validate improvements, and ensure alignment with strategic objectives. The study also addresses common implementation challenges across financial, organizational, workforce, technological, and structural domains. It proposes targeted mitigation strategies, including phased implementation, cost-benefit analyses, stakeholder engagement, digital readiness assessments, and capacity-building programs to enhance adoption and long-term sustainability. While conceptual, the roadmap offers a practical, scalable approach to embedding LSS within asset management systems. It fosters a transition from reactive to proactive practices, enhancing resilience, sustainability, and strategic value. Future research will validate the framework through sector-specific case studies and pilot implementations.
Open Access
Article
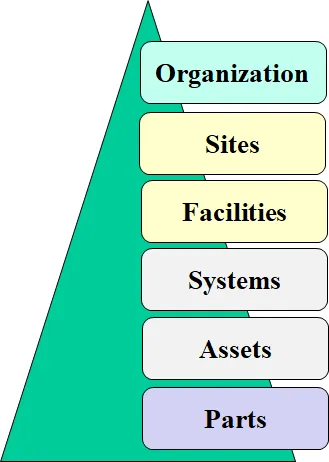
23 June 2025A Structured Framework for Formalized and Quantitative Handwriting Examination
The demand for a formalized and transparent approach to handwriting assessment has long been recognized within forensic and legal contexts. A structured methodology not only reduces interpretative subjectivity but also enables quantifiable measurement and ensures greater consistency in evaluations. This article presents a practical framework that models the degree of similarity between handwriting samples—texts and signatures—through a two-stage process: feature-based evaluation and congruence analysis. Both stages produce quantitative markers that are integrated into a unified similarity score, forming the foundation for more complex comparisons involving multiple questions and known texts. The proposed procedure, which is the major result of the paper, is not merely theoretical; it has been applied in real forensic casework, yielding preliminary statistical outcomes. In particular, it demonstrates the discriminative power of different handwriting features. The paper also discusses future directions for development, with a focus on the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance specific components of the assessment process.
Open Access
Article
23 June 2025A Systematic Review of Clean Cooking and to Whom Does the Clean Cooking Agenda Belong? Empirical Evidence from East African Community
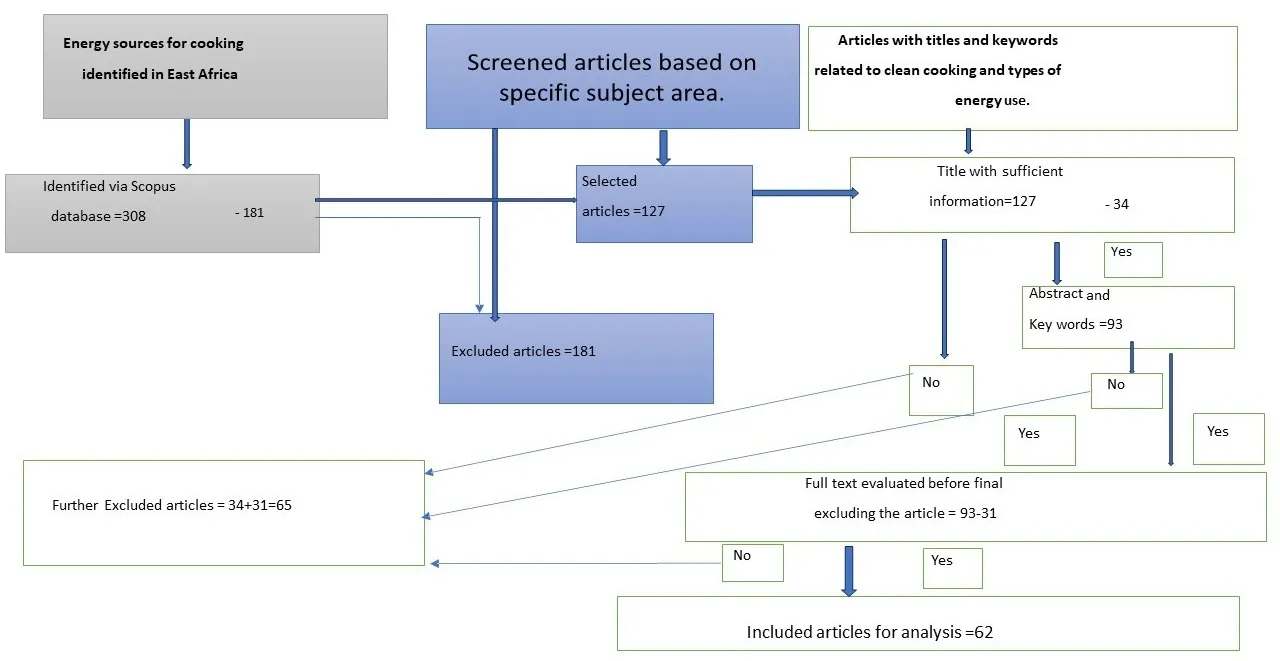
Today, about three billion people, including those in Tanzania, still cook using traditional methods and solid fuels. This practice, which primarily affects women and children who cook in many developing nations, contributes to serious health risks and forest degradation. Every year, household air pollution is responsible for over 34.4 million preventable deaths worldwide, with about 346,600 of those deaths occurring in East African Community and the Nile Basin. Even though switching to clean cooking technologies is a global health priority, adoption is still low in the East African community, and little is known about the factors influencing this change. To determine the factors driving East Africa’s energy transition to clean cooking, this study conducts a systematic review and looks at the history of the research agenda. A total of 308 articles were found using the Scopus database; 62 of these were chosen for analysis based on important search terms such as solar, biogas, firewood, charcoal, LPG, and electric stoves. Even though traditional fuels continue to be the most commonly used in the regions, the empirical analysis showed a focus on clean cooking technologies like electricity, improved cookstoves, and LPG. The clean cooking agenda appears to be primarily externally driven by European and USA researchers, which may have an impact on local adoption and relevance. It is noteworthy that authors from outside the region constituted 63.6 percent of publications on clean cooking in the East African Community.
Open Access
Article
20 June 2025Optimization of Powder Distribution and Feeding Efficiency Using an Annular Powder-Feeding Nozzle: A Numerical and Experimental Study
The quality of spherical powders required in plasma spheroidization is particularly important to advanced manufacturing, such as additive manufacturing and thermal spray coatings. Traditional powder feeding systems, such as radial and coaxial nozzles, often suffer from suboptimal powder distribution, low powder capture efficiency, and poor control of particle trajectories. These issues deteriorate spheroidization quality and material efficiency. We propose here an innovative annular powder-feeding plasma torch for these challenges and to optimize the powder-feeding dynamics. The novel nozzle consists of a tangential powder feeding mechanism and a concentric conical structure that provides uniform powder distribution and minimizes plasma jet interference. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations and Discrete Phase Modeling (DPM), combined with a literature review, are used to study such as throat size and convergent-divergent profiles of nozzles for gas-powder interactions. Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) powder was used for the experimental validation of the annular nozzle; the annular nozzle was found to outperform traditional nozzles in this application with a powder capture efficiency of 75%, a deposition efficiency of 92%, and a spheroidization efficiency of 85%; 85% of the particles had a circularity index >0.9. These results indicate that powder distribution uniformity, deposition efficiency, as well as spheroidization quality are greatly improved than those from conventional plasma spheroidization systems, demonstrating the potential for better process performance for plasma spheroidization. These findings demonstrate the relevance of the optimized annular nozzle in the field of high-value material manufacturing as it yields increased coating quality and minimized material wastage.