Artiles
Open Access
Article
10 June 2025Influence of Surface Waves—Von Karman Street Interaction on Bottom Sediments Transport in the Vicinity of a Wind Turbine Mast: Experimental and Theoretical Study
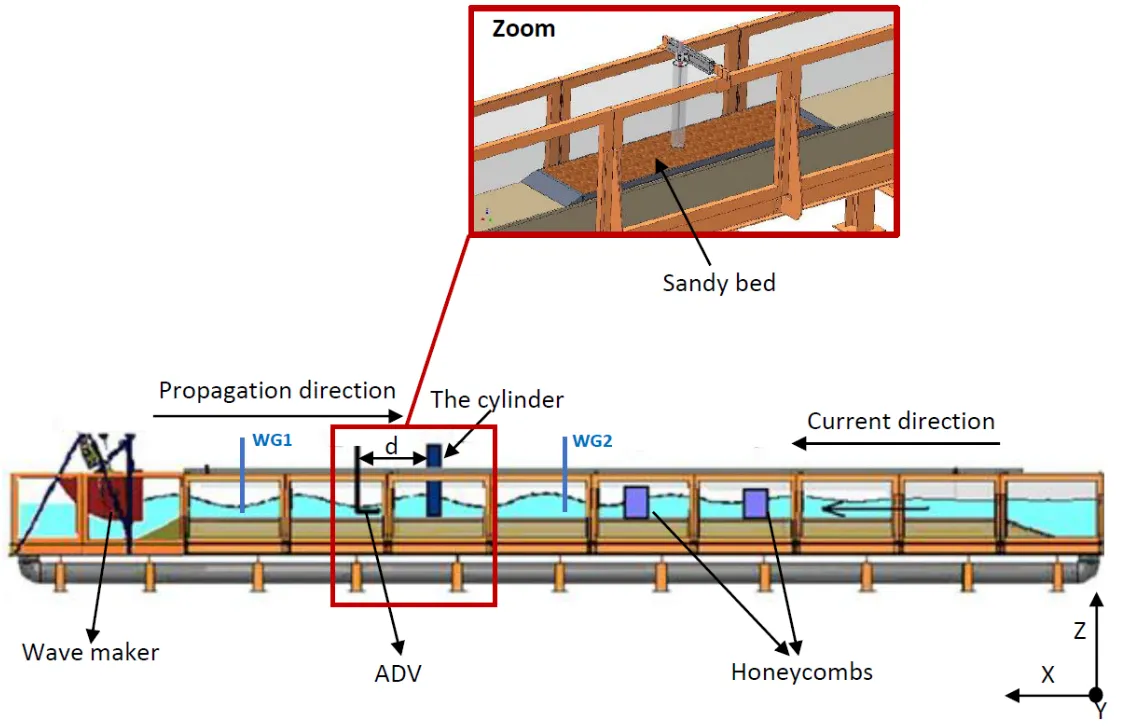
Cylindrical structures used in offshore energy production systems are subjected to various stresses and loads (waves and currents). Understanding the interactions between these cylindrical structures and bedforms is critical, as rapid changes in the bathymetry can expose and damage pile foundations and cables. The impact of a vertical cylinder on a sandy sedimentary bottom subjected to hydrodynamic currents and surface waves is experimentally and theoretically studied. Tests were carried out at the wave flume where patterns are produced. It is observed that patterns emerge due to a subcritical instability at the water-sand interface at the bottom. The characteristics of these patterns can be explained using the Swift-Hohenberg equation. Finally, the experimental results will be applied to the numerical model using the Swift-Hohenberg equation.
Open Access
Case Report
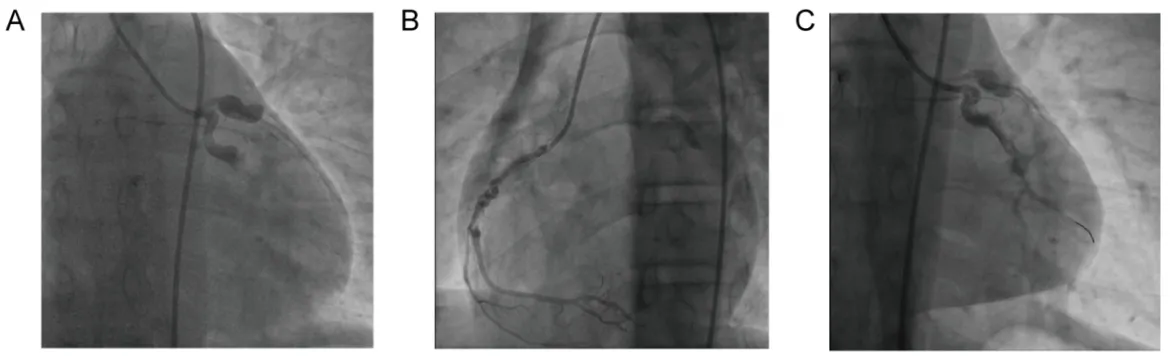
09 June 2025Acute Myocardial Infarction with Multiple Giant Coronary Artery Aneurysms in a Juvenile with Kawasaki Disease
Coronary artery aneurysm (CAA), the most risky late complication of Kawasaki disease (KD), is associated with severe adverse cardiac events, such as acute myocardial infarction (AMI), in young patients. Herein, we describe a 16-year-old boy who suffered from occasional angina attack after a recent myocardial infarction due to multiple giant CAAs during the asymptomatic period of KD. Coronary angiography (CAG) revealed multiple large CAAs of about 9 mm in diameter at the left anterior descending artery (LAD) and more than 12 mm at the left circumflex coronary artery (LCX). To optimize the management and reduce the morbidity and mortality of giant CAAs, it is imperative to consider antecedent KD at the earliest possible stage, particularly in young patients with angina pectoris or AMI but lacking traditional risk factors for atherosclerosis. Long-term follow-up with an electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, or coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) is essential and should not be overlooked. In addition, this case highlights the great significance of working out a more comprehensive and effective management strategy for such KD juveniles, including drugs, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or even surgery.
Open Access
Article
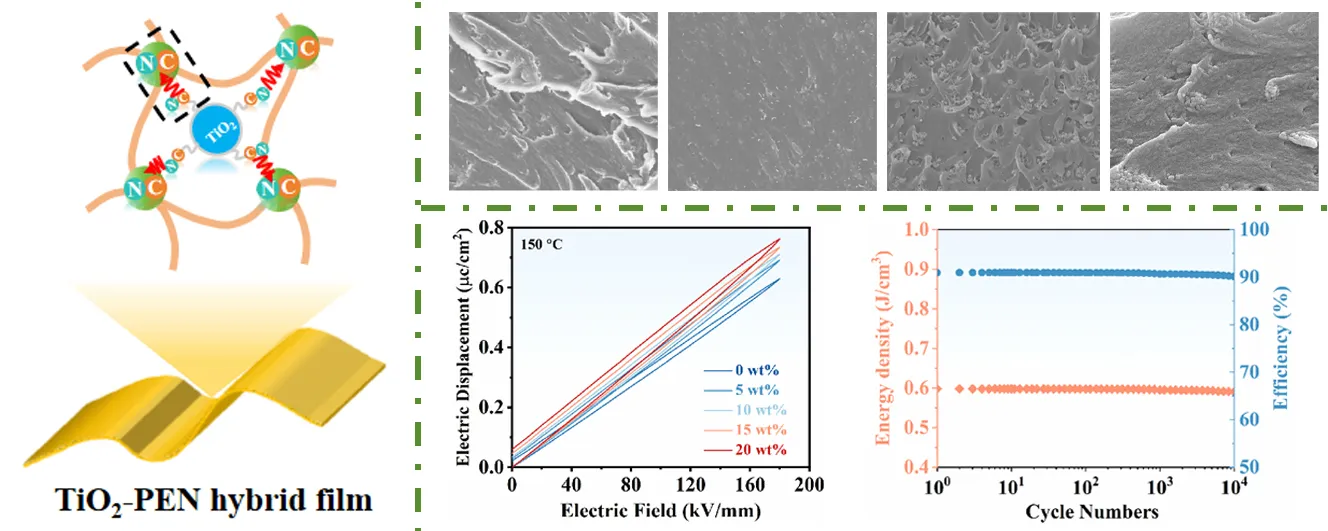
09 June 2025High-Temperature Dielectric Energy Storage Materials Fabricated by Crosslinking Titanium Dioxide and Polyarylene Ether Nitrile
Dielectric materials have broad application prospects in the field of high-temperature electronic power systems. Up to now, high-temperature dielectric materials are mainly prepared by using high glass transition temperature (Tg) polymers. However, the incompatibility between polymers and fillers, which are incorporated for high energy density, leads to soaring dielectric losses at high temperatures, resulting in a nosedive of discharged energy density (Ud) and efficiency (η). In this paper, we report the fabrication of high-temperature dielectric materials via the self-crosslinking of phthalonitriles from phthalonitriles modified titanium dioxide (TiO2-2CN) and phthalonitriles terminated polyarylene ether nitrile (PEN-2CN). TiO2-2CN is firstly synthesized and characterized, then incorporated into PEN-2CN to prepare TiO2/PEN nanocomposites, which transform into TiO2-PEN hybrids afterwards. The fabricated TiO2-PEN hybrids are confirmed by the change of SEM sectional morphology, as well as the increase of their Tg and thermal decomposition temperature (Td). With the addition of TiO2-2CN, both the Tg, Td, and Ud of TiO2/PEN nanocomposites are improved. In addition, due to the formation of covalent bonds within TiO2-PEN, the hybrids exhibit excellent high-temperature dielectric energy storage performance. Specifically, at 150 °C, the Ud of 10 wt% TiO2-PEN is 0.60 J/cm−3, which is over 95% of that at RT. Moreover, η is greater than 90% and remains unchanged after 10,000 charge and discharge cycles. This method used for preparing TiO2-PEN hybrids through a self-crosslinking reaction of phthalonitriles provides a new approach for preparing high-temperature dielectric materials.
Open Access
Article
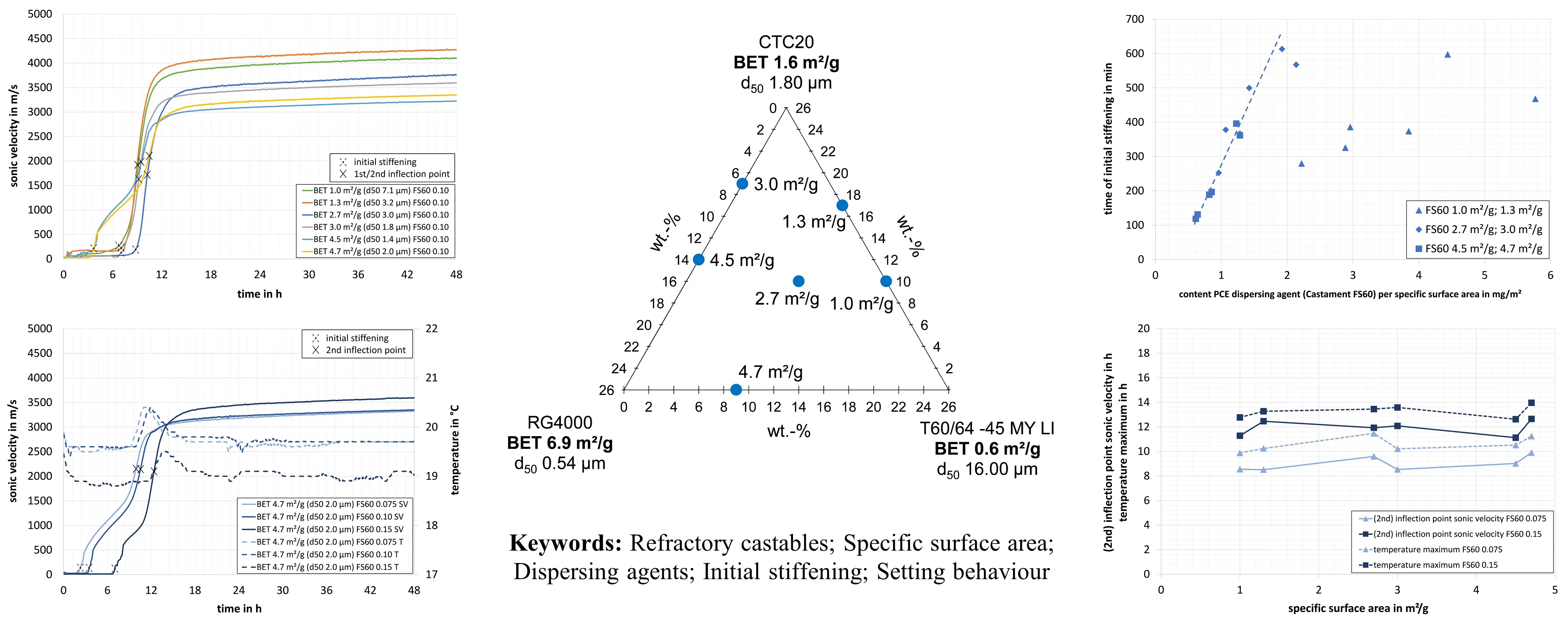
06 June 2025Effects of Changing the Specific Surface Area in the Ceramic Matrix of CAC-Containing Refractory Castables on the Initial Stiffening and Setting Behaviour
Besides the coarse and medium grain size distribution, the matrix components play a central role in the performance of refractory castables. Practical experience shows that the particle size distribution (PSD) and the specific surface area of the ceramic matrix significantly influence processing, setting, and sintering behaviour. However, there is a lack of systematic studies on how PSD or specific surface area changes affect castable properties. This study aims to address this gap by varying ceramic matrices to create refractory model castables with different matrix surface areas. Three dispersing agents with different mechanisms (electrosteric and steric) were used at graded concentrations. Results show that castables with higher specific surface areas (using (very) finely ground and highly sintered alumina raw materials with high specific surface areas) and different dispersing agents and their concentrations show substantial differences in the initial stiffening and setting behaviour. Higher specific surface areas of the matrix result in an earlier first stiffening, while adding more dispersing agents leads to delayed stiffening. The refractory model castables’ first stiffening and hydration range (with a simultaneous temperature maximum) vary considerably depending on the dispersing agent used and its concentration, caused by completely different mechanisms.
Open Access
Communication
06 June 2025Preparation and Characterization of Dibenzyldieneacetone Loaded Microparticles for Therapeutic Purposes
Among the known chalcones, dibenzyldieneacetone is an organic molecule that was synthesized in this study and encapsulated into the Ethyl cellulose matrix by solvent evaporation technique. Microencapsulation aims to shield the core material from environmental influences (like light, humidity, temperature, and oxygen), extend its shelf life, and enhance the product’s quality. The microsphere size distribution was determined using an optical microscope. The synthesis product, as well as the particles, were characterized by ultraviolet-visible, infrared, and XRD. This study allowed us to identify particle morphology, encapsulation rate, and particle size distribution.

Open Access
Article
05 June 2025Enhancing Product Development Excellence through Quality Management Tools: A Comprehensive Review and Integrated Conceptual Framework
In today’s rapidly evolving and highly competitive global markets, achieving product development excellence is critical for organizations striving for sustained growth and customer-centric innovation. This study highlights the integral role of key quality management tools in enhancing product development processes, reducing defects, and driving continuous improvement. It presents a robust methodology that strategically combines Quality Function Deployment (QFD), Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), and the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) framework to significantly improve the quality, reliability, and efficiency of product development efforts. Built on core principles of customer-centricity, innovation, cross-functional collaboration, continuous improvement, and risk-based thinking, the methodology emphasizes capturing the Voice of the Customer (VoC) and identifying Critical-to-Quality (CTQ) attributes to align product outcomes with customer expectations and business objectives. Utilizing the DMAIC framework, the organization systematically drives process optimization and innovation throughout the product lifecycle Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are established to track efficiency, quality, customer satisfaction, and time-to-market, while Agile methodologies enhance flexibility, speed, and responsiveness. The study further identifies organizational, technical, cultural, and managerial barriers to product development excellence and proposes targeted strategies to address them and ensure sustainable success. This integrated framework fosters a culture of innovation and continuous learning, enabling organizations to anticipate challenges, manage risks, and consistently deliver superior product development outcomes. While currently conceptual, the framework is slated for empirical validation through case studies, pilot projects, and simulations to verify its practical applicability across diverse development contexts.

Open Access
Article
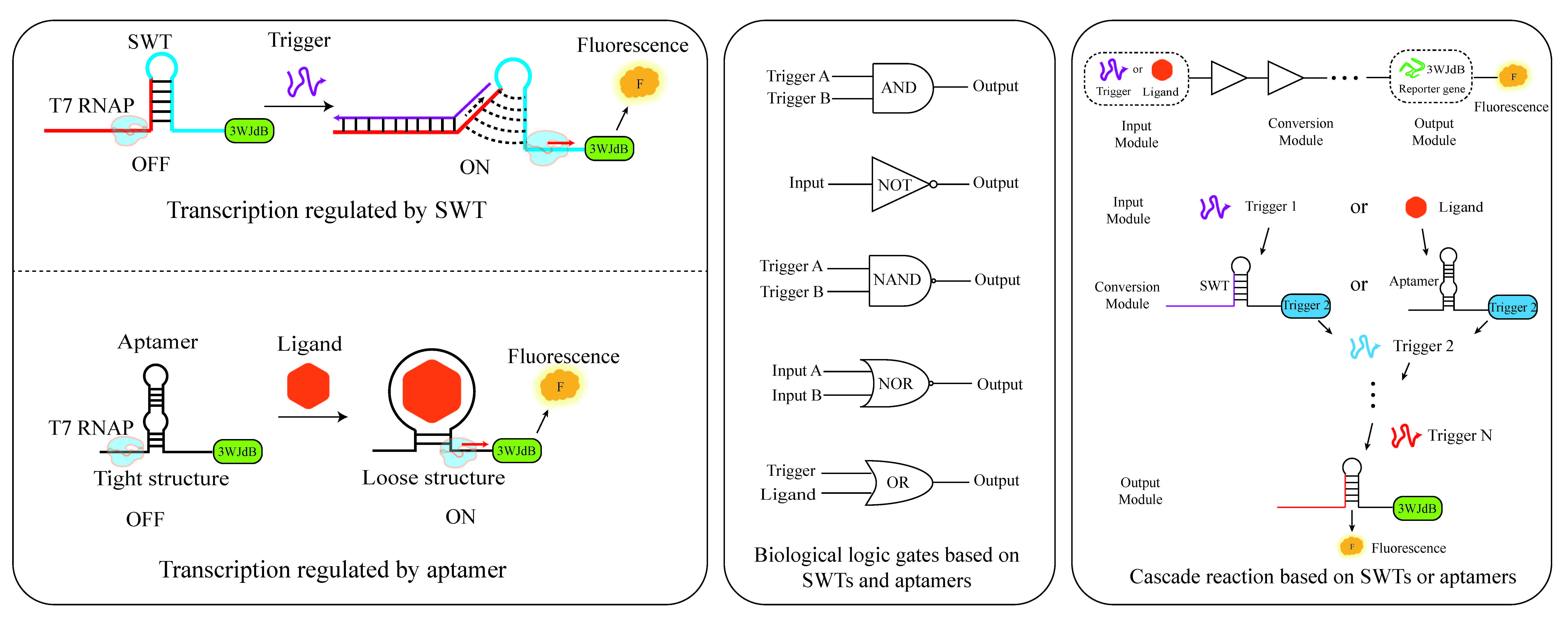
04 June 2025Modular Transcriptional Regulation Using Switchable Transcription Terminators and Aptamers: Design and Optimization in Synthetic Biology
Transcriptional regulation is a key step in gene expression control. While transcription factor-based regulation has been widely used and offers robust control over gene expression, it can sometimes face challenges such as achieving high specificity, rapid dynamic responses, and fine-tuned regulatory precision, which have motivated the exploration of alternative regulatory strategies. With the development of synthetic biology, novel genetic elements such as Switchable Transcription Terminators (SWT) and aptamers provide more flexible and programmable strategies for transcriptional regulation. However, the independent regulatory capabilities of these two types of elements and their combined regulatory mechanisms still require further investigation. In this study, based on an in vitro transcription system, we systematically explored the transcriptional regulation potential of SWT and aptamers. We innovatively combined these two elements to construct a modular gene expression regulation system. First, we screened and optimized a series of SWTs, obtaining high-performance SWTs with low leakage expression and high ON/OFF ratios. These were further validated for reproducibility of their regulatory performance in E. coli. Next, we constructed multi-level cascading circuits using SWTs, successfully extending the system to six levels and building four types of biological logic gates based on SWT in vitro: AND gate, NOT gate, NAND gate, and NOR gate. Furthermore, based on a previously identified thrombin aptamer capable of transcriptional regulation, we confirmed that ligand binding significantly promoted gene transcription. Finally, we integrate switchable transcription terminators (SWTs) and aptamers to create a modular, ligand-responsive system. We combined aptamers with SWTs to construct heterologous input logic gates, successfully improving the precision and dynamic range of regulation. Compared to the individual regulation of SWT and aptamer, the Aptamer-SWT synergistic regulation enhanced transcription activation by up to 3.3-fold and 7.84-fold, respectively. Additionally, we co-utilized these two genetic elements to construct heterologous input AND and OR gates in vitro. This study expands the strategies for gene expression regulation and provides new elements and theoretical support for efficient, programmable transcriptional regulation in synthetic biology. This system holds potential for biosensing, gene circuit design, and nucleic acid therapy applications.
Open Access
Article
03 June 2025Ecosystem Service Importance, Contributions, and Trends: Perspectives from Farmers in the Mountains of Nepal
Understanding farmers’ perceptions of local ecosystem services is crucial for developing effective ecosystem management strategies and policy interventions to improve the overall welfare of residents. Although there is widespread recognition of the linkages between ecosystem services and human well-being, empirical studies examining farmers’ perceptions and contributions to local ecosystem services, particularly at the micro level in mountainous regions, remain limited. To address these knowledge gaps, we conducted an empirical study employing focus group discussions (n = 6), key informant interviews (n = 12), and household surveys (n = 370) in Mid-Marsyangdi watershed, Lamjung, Nepal. The study revealed that farmers perceive high dependency on regulating followed by provisioning, supporting, and cultural ecosystem services such as freshwater, nutrient cycling, water regulation and purification, timber production, livestock fodder, and natural hazard regulation. Their contributions are notably high in managing freshwater, nutrient cycling, and timber production. Farmers’ practices like forest conservation, agroforestry, inter-cropping, terracing, terrace improvement, multi-year cropping, and organic composting enhance ecosystem services. A significant discrepancy exists between perceived importance and actual contribution, particularly in water regulation, purification, and wild edible food, highlighting areas needing greater attention. The study showed a significant difference (p < 0.001) between perceived importance and contribution across all ecosystem services, with perceived importance consistently higher. Further, a study showed the influence of socio-demographic variables on the farmers’ perception. These findings can inform more effective policy-making for farmer welfare, mountain development, and environmental management.

Open Access
Article
03 June 2025Optimization of High Energy Radiation-Induced Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole Using Response Surface Methodology
Ionizing irradiation is an emerging technology for the removal of toxic pollutants, such as antibiotics, in water and wastewater. In this study, gamma radiation-induced degradation of sulfamethoxazole (SMX) was optimized using response surface methodology (RSM) based on a Box-Behnken design. LC-MS analysis identified nine intermediate products (M1–M9), elucidating a dual oxidative-reductive degradation mechanism driven by hydroxyl radicals (•OH) and hydrated electrons (eaq⁻). These intermediates, characterized by hydroxylation, sulfonamide bond cleavage, and aromatic ring fragmentation, aligned with pathways distinct from conventional chlorination systems, underscoring the absence of toxic halogenated byproducts. According to experimental data, The study revealed that absorbed dose (0.2–2.0 kGy) and initial SMX concentration (5–40 mg/L) critically governed SMX degradation efficiency, achieving >99% removal under optimized conditions (≥1.2 kGy for 5–10 mg/L SMX). The robust RSM model (R2 = 0.9931) and experimental validation (±2% error) demonstrated the method’s reliability in reconciling nonlinear dose-concentration interactions as well as providing an effective approach to parameter optimization, offering practical insights for enhancing the treatment efficiency of antibiotic-containing wastewater.

Open Access
Review
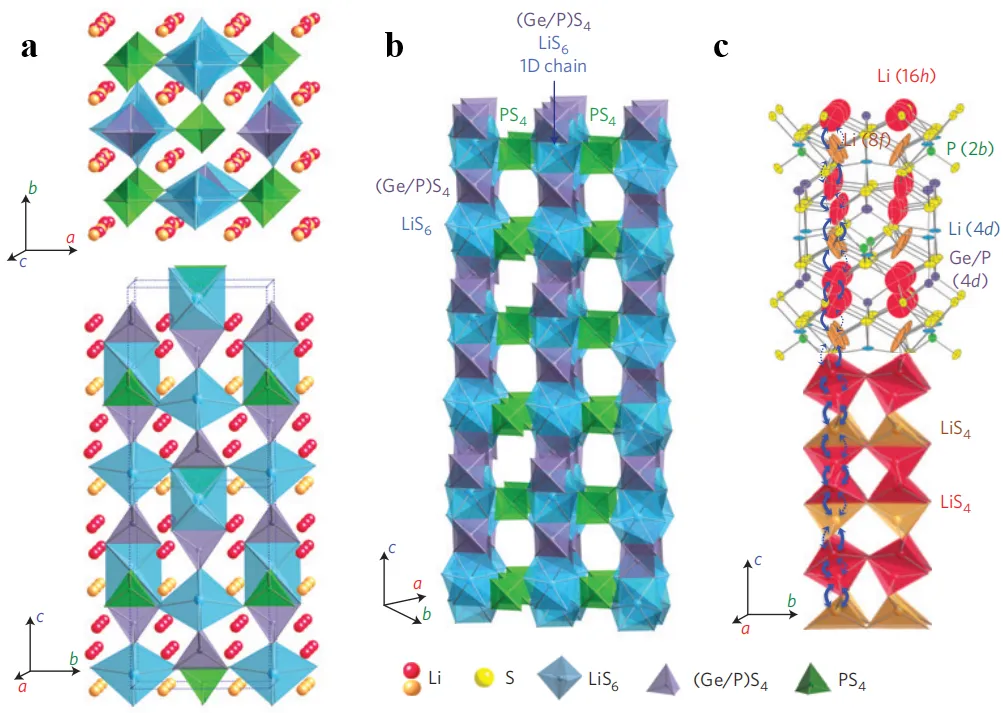
03 June 2025Progress in Theoretical Calculation and Simulation of Sulfide Solid Electrolytes and Their Application in All-Solid-State Batteries
Along with the development of electric vehicles and electronic devices, all-solid-state batteries (ASSBs) have become the next-generation energy storage batteries, owing to their safety and chemical stability. Sulfide Solid Electrolytes (SSEs) are deemed to be crucial materials for ASSBs because of their ultrahigh ionic conductivity (10−3–10−2 S cm−1), but are still plagued by the narrow electrochemical window and poor interfacial stability. In this paper, we summarize our systematic research progress on sulfide SSEs from the view of how theoretical calculations and simulations play a crucial role in material design. First-principles calculation gives evidence of the structure’s stability and ion migration mechanism for electrolytes, MD and AIMD simulations provide insights for the dynamic diffusion behavior and the interface reaction mechanism. High-throughput screening and machine learning have accelerated new electrolyte designs. Scientists discovered Li10GeP2S12 and explored ion dynamics in a crystal lattice of that material. There are also material interface phenomena such as space charge layers and chemical breakdown. These problems can be managed by developing and tuning appropriate computational models to steer material doping and protective layer design. In this paper, we demonstrate that the combination of computer simulations and real experiments is valuable.