Found 469 results
Open Access
Review
20 November 2025Vibrational Spectroscopy in Forensic Science: A New Frontier for Biopharmaceutical Drug Authentication
The global proliferation of counterfeit biologic medicines poses a growing threat to public health and pharmaceutical integrity. Traditional laboratory-based methods for verifying drug authenticity are often time-consuming, costly, and impractical for real-time or field-based applications. This paper explores the emerging potential of infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopy for forensic detection and authentication of biologics. While these technologies are currently underutilised in forensic science, advancements in instrumentation and data analysis are rapidly enhancing their sensitivity, portability, and usability. Focusing on protein- and peptide-based therapeutics, the paper reviews the principles and applications of IR and Raman spectroscopy, highlighting their ability to detect structural and compositional differences between authentic and counterfeit biologic drugs. The discussion emphasises the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between forensic and biopharmaceutical sciences. As counterfeiters become more sophisticated, the integration of non-destructive spectroscopic tools into forensic workflows offers a promising path toward the rapid and reliable screening of biologic drugs in both field and laboratory settings.

Open Access
Article
19 November 2025Effects of Platform Motions on Dynamic Responses in a Floating Offshore Wind Turbine Blade
Floating offshore wind turbines (FOWTs) offer great potential for harnessing deep-sea wind energy. This study examines the effects of six-degree-of-freedom (6-DOF) platform motions on the dynamic structural responses of a FOWT blade by comparing its performance with a fixed-bottom system. Integrated aero-hydro-servo-elastic simulations for a 5-MW spar-type FOWT were conducted under various design load cases. Results indicate that the floating tower’s first-order natural frequency was about 29% higher than that of the fixed-bottom tower. Platform motions markedly influenced blade flapwise and torsional responses, with the effect intensifying under larger waves. For instance, as the significant wave height increased from 1.70 m to 9.90 m, the differences in peak response between the floating and fixed-bottom systems grew from 0.104 m to 0.363 m for blade-tip flapwise deflection, from 528.1 kN·m to 1817.4 kN·m for the root flapwise bending moment, and from 5.02 kN·m to 18.73 kN·m for the root torsional moment. In contrast, blade edgewise responses showed negligible changes, with peak deflection differences below 0.05 m. Blade loads were more sensitive to wave conditions, while platform motion magnitudes were more affected by wind. These findings offer insights into the load characteristics and structural design of FOWT blades.
Open Access
Article
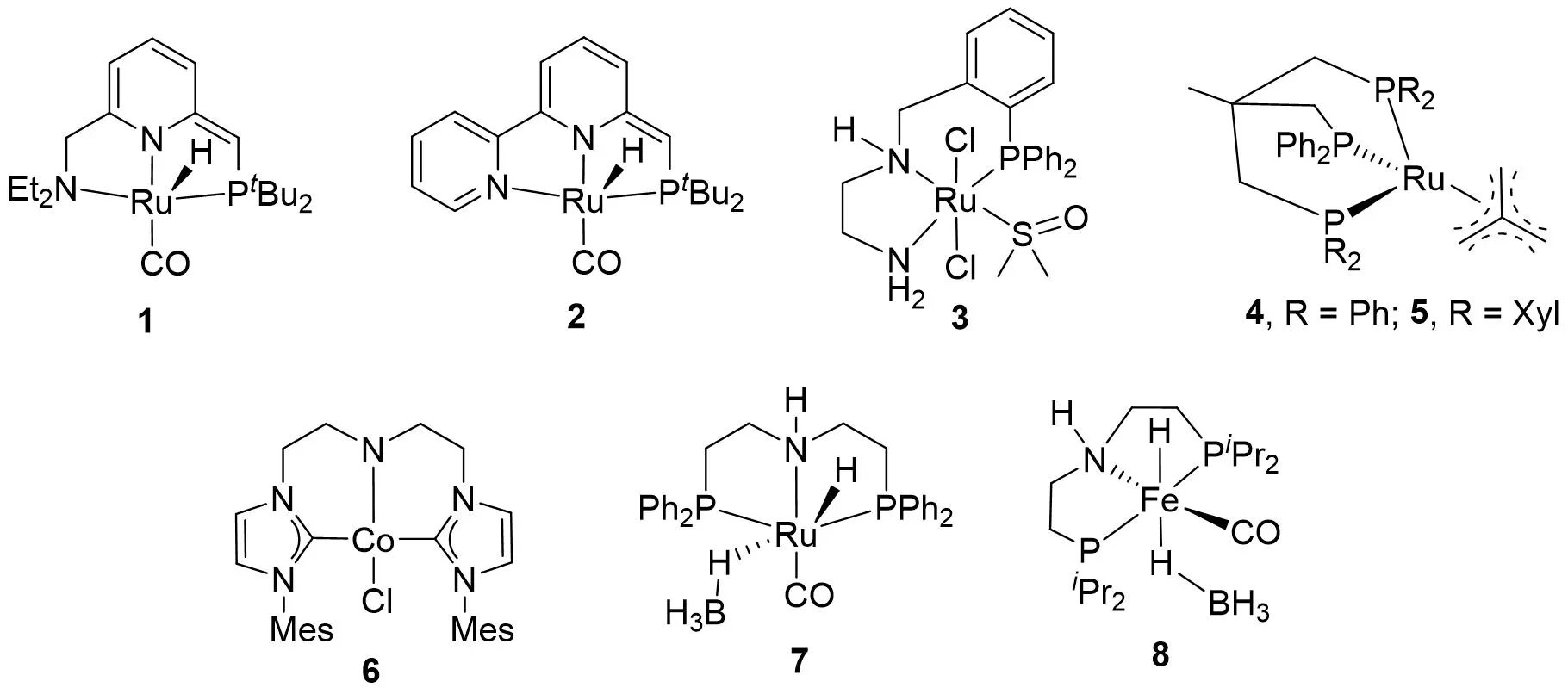
19 November 2025Hydrogenative Depolymerization of Polyesters Catalyzed by a PN3-Ruthenium Complex Using Both H2 and EtOH as Hydrogen Sources
Selective hydrogenative depolymerization of polyesters to diols is regarded as a promising strategy for plastics upcycling. However, many catalysts documented in literature still involve harsh reaction conditions, such as high temperature and high H2 pressure. In this work, we present a PN3-ruthenium complex catalyzed polyesters upcycling into various highly value-added diols under mild reaction conditions using H2 as a hydrogen source. It is worth noting that PLA depolymerizes into 1,2-propanediol under 1 MPa hydrogen pressure at ambient temperature within 2 h; the conditions are much milder than those of previous reports. Aromatic polyester PET degradation needs harsher reaction conditions (80 °C, 4 MPa, 3 h). The different reaction conditions enable direct separation of the degradation products of PLA and PET mixture via sequential depolymerization, as well as mixing them with polyolefins (PE, PP, PS). More strikingly, this catalyst is also effective for the catalytic hydrogenation of polyesters in the presence of ethanol to afford various diols, avoiding the use of harsh reaction conditions and an expensive autoclave.
Open Access
Article
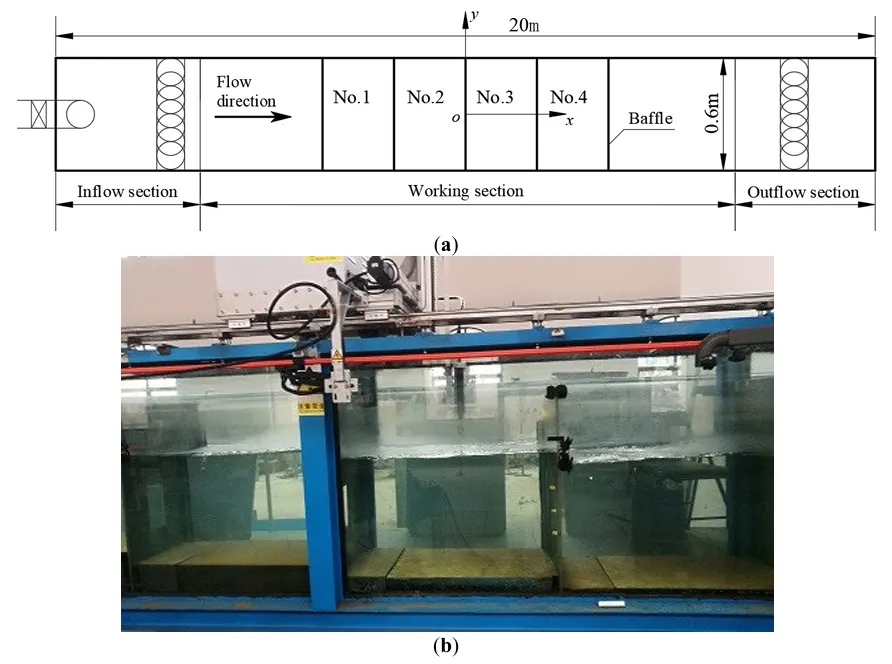
18 November 2025Turbulent Characteristics in an Egg-Shaped Orifice Fishway and a Comparison with a Rectangular Orifice
A fishway can assist fish species in overcoming barriers to migration, which depends on the eco-hydraulic characteristics of the fishway. Based on the tail fish benefiting when at the rear of a school than when at the front, and taking into account most anadromous fish species being characterized by egg-shaped morphology, the turbulent characteristics of an egg-shaped orifice fishway were experimentally studied in a fishway flume, a comparison with a rectangular orifice fishway with the same aspect ratio was made. The results showed that the maximum longitudinal velocity for the egg-shaped orifice decays faster than that for the rectangular one, the longitudinal velocity profile exhibits two peak values, while the corresponding velocity distribution for the rectangular orifice only reveals one peak, peak values of turbulence intensity on the different horizontal plane of egg-shaped orifice occur in the orifice edges, the larger turbulence intensities still exists in the central besides the edges for the rectangular orifice, Reynolds stress reaches peak value at the orifice edges, Auto-correlation coefficient of longitudinal velocity within orifice region is of small amplitude and short period relative to the outside the orifice region, microscale eddies within the orifice region were larger than those outside, mean scale of eddy is of larger variation and shorter period, and develops outside the orifice region, frequency-spectrum of velocity fluctuation exhibits dominant frequency in the low-frequency domain.
Open Access
Article
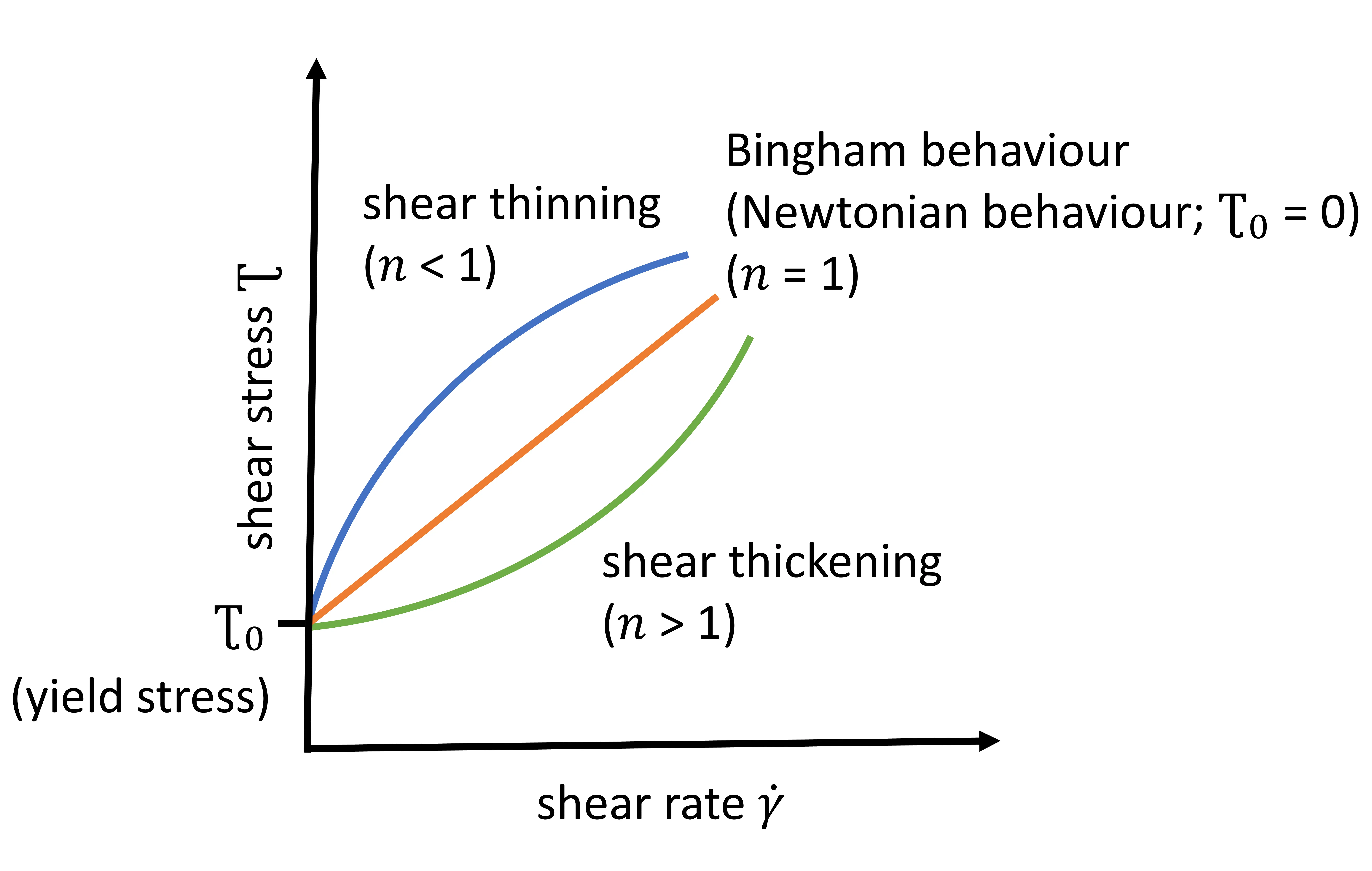
18 November 2025Effects of Changing the Specific Surface Area in the Ceramic Matrix of CAC-Containing Refractory Castables on the Rheology and Processing
Besides the coarse and medium grain size distribution, the matrix components play a central role in the performance of refractory castables. Practical experience shows that the particle size distribution (PSD) and the specific surface area (SSA) of the ceramic matrix significantly influence processing, setting, and sintering behaviour. However, there is a lack of systematic studies on how changes in PSD or SSA affect castable properties. This study aims to address this gap by varying ceramic matrices to create model refractory castables with different matrix surface areas. Three dispersing agents with different mechanisms (electrosteric and steric) were used at graded concentrations. Results show that the SSA of the ceramic matrix has a significant influence on the rheological behaviour of refractory castables. A low SSA leads to shear thickening behaviour, a (very) low relative yield stress, and a high slump‑flow. Castables with an intermediate SSA and a multimodal composition show Bingham behaviour with a moderate relative yield stress and low relative viscosity, whereas a high SSA leads to shear thinning behaviour with a (very) high relative yield stress, (very) high relative viscosity, and a low slump-flow. Measurements of the dynamic viscosity of matrix suspensions at very low shear rates correlate with the rheological behaviour of fully composed refractory castables. Regression analysis using the Herschel‑Bulkley model successfully captures the observed qualitative relationships.
Open Access
Review
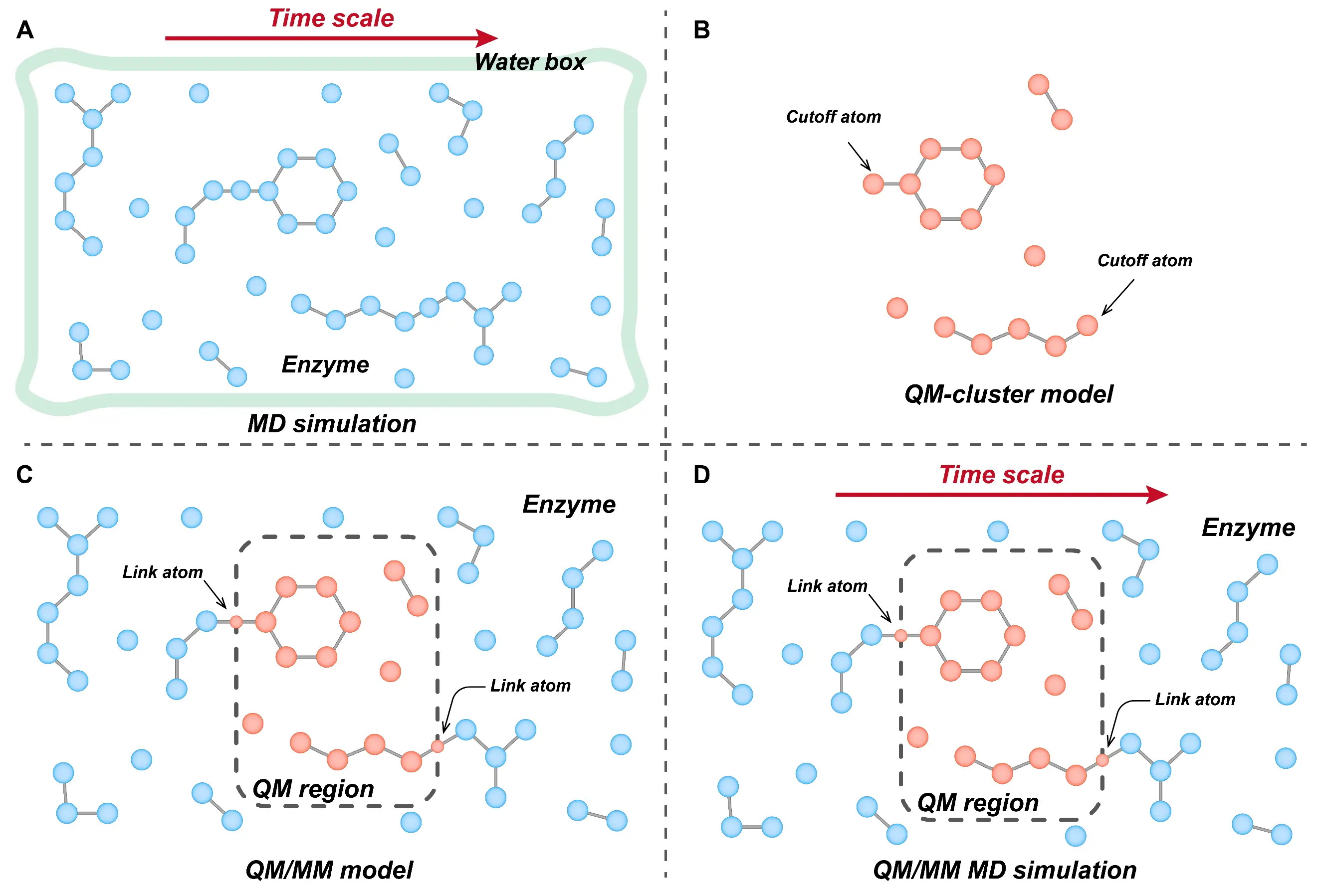
17 November 2025Enzyme-Mediated Carbon Dioxide Fixation: Catalytic Mechanisms and Computational Insights
Carbon conversion technologies that transform carbon dioxide (CO2) into high-value chemicals are pivotal for achieving sustainability. Among these, enzyme-mediated CO2 fixation has recently gained increasing attention as a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional chemical methods, which typically require harsh conditions and impose significant environmental costs. Recent advances in computer-aided techniques have greatly facilitated the mechanistic understanding of CO2-fixing enzymes and accelerated the development of enzyme-catalyzed carboxylation strategies. This review highlights recent progress in enzyme-mediated CO2 fixation by categorizing key enzymes into four classes based on their cofactor or metal ion requirements: cofactor-independent enzymes, metal-dependent enzymes, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAD(P)H)-dependent enzymes, and prenylated flavin mononucleotide (prFMN)-dependent enzymes. We outline the basic principles and applications of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and quantum mechanical (QM) calculations, which serve as essential tools for investigating enzyme conformational dynamics and reaction mechanisms. Through representative case studies, we demonstrate how computational analyses uncover catalytic features that enhance CO2 conversion efficiency. These insights underscore the critical role of computer-aided approaches in guiding the rational design and optimization of biocatalysts, thereby advancing the application of enzyme-based systems for CO2 fixation.
Open Access
Article
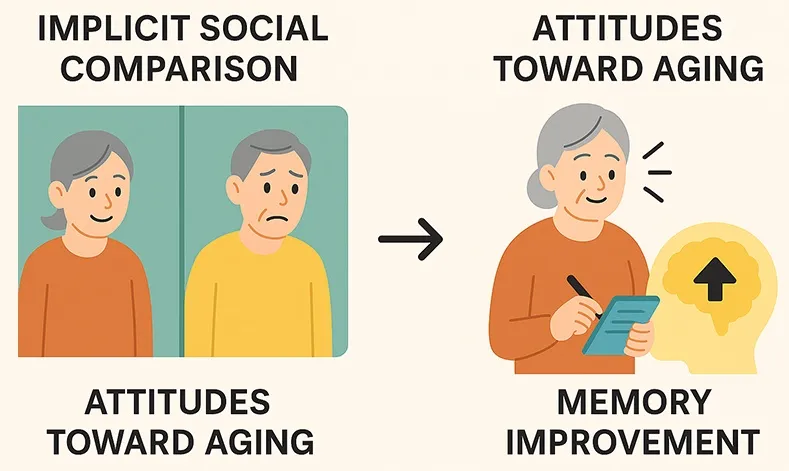
17 November 2025Implicit Social Comparison: An Effective Approach to Promote Positive Attitudes Toward Aging Among Older Adults
Previous studies have consistently demonstrated that positive attitudes toward aging are associated with better psychological well-being and cognitive performance among older adults. Building upon these findings, the present study focused on memory improvement as a direct indicator of cognitive benefit derived from more positive self-perceptions of aging. Specifically, we examined whether an implicit social comparison manipulation could enhance older adults’ memory performance by altering their attitudes toward aging. A total of 161 community-dwelling older adults (M = 66.88 years) were randomly assigned to one of five conditions: Better-self (downward comparison), Worse-self (upward comparison), Equal-good, Equal-bad, and Control. In four experimental conditions, an adopted directed-thinking task was used to activate attitudes toward one’s own and peers’ aging in different combinations, implicitly triggering upward or downward social comparisons. Attitude toward own aging (ATOA), attitude toward peers’ aging (ATPA), self-superiority (ATOA–ATPA), and memory performance were assessed before and after the manipulation. Results showed that significant changes in self-superiority were found only under the two contrast conditions. Specifically, self-superiority increased in the Better-self group and decreased in the Worse-self group. Moreover, the Better-self group demonstrated greater memory gains than the Control and Worse-self groups. These findings suggest that implicit downward comparison can serve as an effective, non-defensive strategy to strengthen older adults’ self-perceptions of aging and to produce short-term improvements in memory. The study extends prior research on social comparison in old age by linking its psychological and cognitive effects within a single experimental framework.
Open Access
Article
17 November 2025The Reconstruction of China’s Land-Based Marine Pollution Governance under the Concept of “Rights of Nature”
Under the concept of “Rights of Nature”, the governance of land-based marine pollution in China faces unprecedented opportunities and challenges. Traditional governance paradigms are predominantly anthropocentric, treating the ocean as a resource to be utilized. From this perspective, governance measures for the prevention and control of land-based marine pollution primarily rely on administrative management and end-of-pipe treatments. Within this context, “Rights of Nature” provide a new pathway for marine ecological protection. However, promoting a shift in land-based marine pollution governance from the traditional anthropocentric view to an eco-centrism under the “Rights of Nature” concept is by no means an instantaneous process, and it must proceed gradually and systematically. Currently, China’s institutional framework for preventing and controlling land-based marine pollution remains dominated by the anthropocentric paradigm. Furthermore, it encounters multiple difficulties across many key areas, including the legal system, law enforcement mechanisms, relief mechanisms, and public participation. Issues such as poor coordination within the legal framework, fragmented law enforcement, lagging legislation related to ecological restoration, and insufficient public participation significantly constrain the effectiveness of land-based marine pollution governance. Given the fundamental differences between anthropocentrism and “Rights of Nature”, directly introducing this concept would likely have a substantial impact on China’s existing legal framework. Therefore, at the current stage, China could first incorporate the proposition from the “Rights of Nature” concept that nature possesses “intrinsic value independent of human use or perception”. This involves weakening the perception of the ocean as a mere appendage to human activities, recognizing and respecting the unique value of the ocean as a living entity and ecosystem at a conceptual level, and gradually forming a set of nature-friendly governance paradigms for land-based marine pollution that respect the intrinsic value of nature. This approach can ultimately drive transformative practices in China’s land-based marine pollution governance.

Open Access
Article
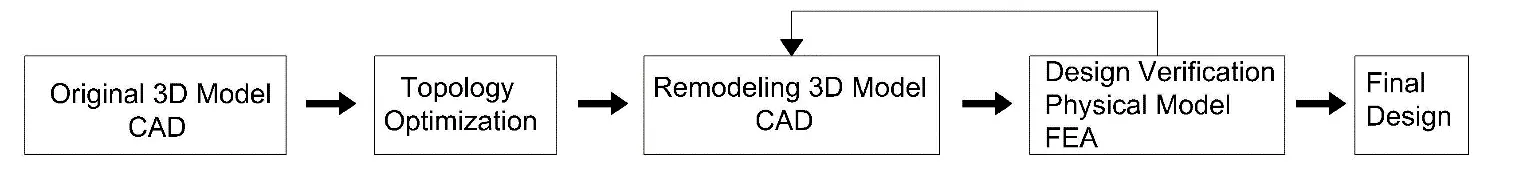
12 November 2025Topological Optimization for Environmental Sustainability in Civil Engineering Structures Design
The increasing demand for sustainable and cost-efficient construction highlights the need to minimize material consumption in civil engineering structures without compromising safety or performance. This study investigates the optimization of steel purlin cross-sections in metal buildings as a means to enhance structural efficiency and environmental sustainability. Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and the Solid Isotropic Material with Penalization (SIMP) method were employed to identify optimal material distributions and evaluate the effects of varying cross-section geometries. Both rectangular and IPE purlin sections were analyzed under realistic loading conditions to compare stress, deformation, and weight performance before and after optimization. The results demonstrate that substantial reductions in material mass, up to approximately 25–30%, can be achieved while maintaining nearly identical stress and displacement responses. These findings confirm that structural optimization effectively reduces both construction costs and environmental impact. The study concludes by recommending the adoption of topology and cross-section optimization techniques in the design of steel structures, particularly in public projects, to promote resource efficiency and sustainable construction practices.
Open Access
Article
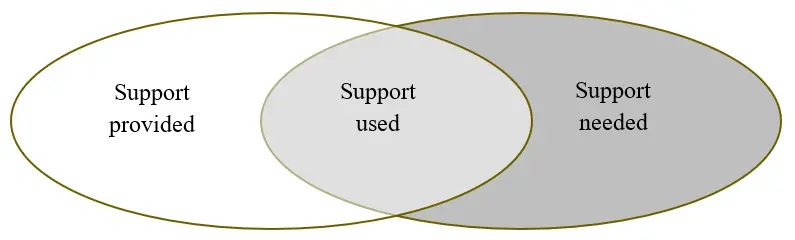
10 November 2025Gendered Mismatches in the Business Support System in Rural Sweden
Rural women often start enterprises in sectors that are vital for long-term rural sustainability, but these organizations run the risk of not being properly recognized by public rural development support systems. In this paper, we ask whether existing business support measures meet the needs of rural women entrepreneurs, and if not, what can be improved? Our data consists of recorded interviews with twenty women entrepreneurs from the rural regions of southern Sweden. We asked how they perceive the business support that is provided, used, and needed. We found a gendered mismatch between the forms of public support provided and the support needed by women entrepreneurs in rural areas. The analysis reveals that current business support initiatives often overlook social, cultural, and environmental innovations and enterprises that do not prioritise economic growth as their primary objective, despite their importance for rural viability and development. We argue for a shift towards valuing alternative growth models, broadening eligibility criteria, and simplifying access to funding. As key players in this context, public funds should support long-term sustainability. By embracing the proposed changes, the business support system can be better aligned with the realities of rural entrepreneurship, contributing more meaningfully to rural development and gender equality.