Found 469 results
Open Access
Review
22 August 2025The Recyclability of Wind Turbine Blade Material, Manufacturing Process, and Recycling Technology
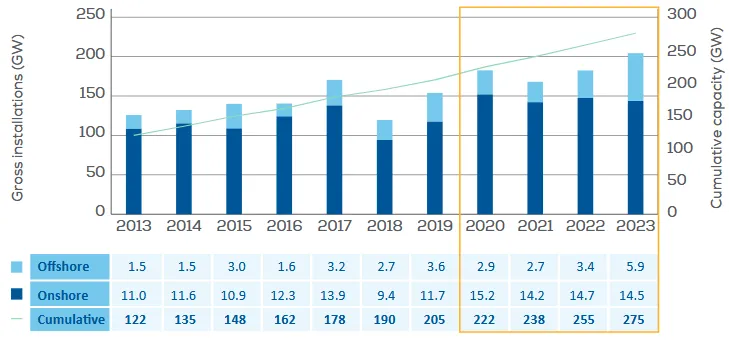
As wind energy continues to be deployed at a significantly increasing rate, the number of decommissioned wind turbines is expected to increase accordingly. To improve material efficiency, a large amount of waste requires appropriate identification and recycling, particularly the composite materials used in wind turbine blades (WTB). This study focuses on two life cycle stages, manufacturing and the decommissioning stage, which contribute most to the waste generation of WTB. This study investigates the material efficiency factors in WTB and organises fragmental information in manufacturing waste management, focusing on the recycling factor and quantifying the recyclability of wind turbine blade material regarding the different recycling technologies. This study fills the gap in existing research by evaluating recycling methods for specified carbon fibre-reinforced polymers (CFRPs) and glass fibre-reinforced polymers (GFRPs) using a revised recyclability index. Additionally, innovative sustainable materials and recent composite recycling studies have also been incorporated into the quantification and evaluation to update the current progress. The current source of WTB post-production waste, the corresponding disposal method, and opportunities were also reviewed and identified. The findings quantified recyclability and revealed that the recyclability of WTB materials varies significantly depending on the specific composite type and the recycling method employed. Furthermore, the calculated recyclability, combined with other factors such as global warming potential (GWP), cost, and technology readiness level (TRL), is discussed, along with the potential for improving material efficiency by selecting future material recycling technology and effective manufacturing waste management.
Open Access
Opinion
22 August 2025Are Probiotics a Panacea for All Diseases? A Scientific Opinion
Probiotics have gained widespread attention for their potential health benefits, particularly in promoting gut health and modulating the immune system. This article critically examines whether probiotics can be a universal remedy for all diseases, as often claimed in scientific literature and popular media. The objective is to evaluate the current scientific evidence regarding the efficacy of probiotics in preventing and treating various medical conditions, including gastrointestinal disorders, metabolic syndromes, allergies, and mental health issues. While some studies suggest promising outcomes in specific contexts, the evidence remains inconsistent and often limited to specific strains and conditions. Importantly, this review highlights that probiotics are not a one-size-fits-all solution and their effects can vary widely depending on individual physiology, dosage, and microbial composition. The article also addresses safety concerns, regulatory challenges, and the need for more rigorous, large-scale clinical trials. By analyzing existing data and expert opinions, this work aims to separate fact from hype and provide a balanced perspective on probiotics’ true potential and limitations in modern medicine.

Open Access
Case Report
22 August 2025Root Cause Identification of Vibration and Wear Due to Strainer Obstruction in Hydrocarbon Processing Compressors
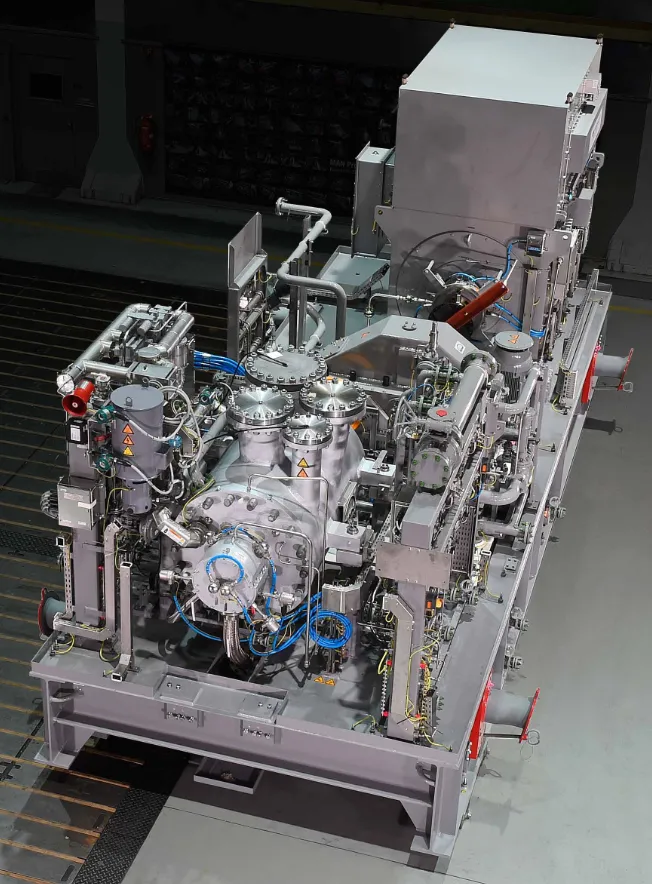
This study examines the root causes of vibration and wear in centrifugal compressors, particularly emphasising strainer obstruction in hydrocarbon processing environments. Strainer fouling is primarily driven by deposits from inlet gas compositions and deviations in operating conditions, which restrict flow, increase vibration, and accelerate component degradation. A combined methodology was applied to investigate these issues, including baroscopic inspection of compressor internals, chemical analysis of deposited materials, and evaluation of operational records against design specifications. Maintenance histories and strainer cleaning frequencies were also reviewed to establish links between performance decline and operating practices. The findings show that chemical cleaning is the most effective and cost-efficient solution, outperforming high-pressure water jet cleaning and full compressor overhauls by minimising downtime, restoring flow dynamics, and improving mechanical stability. Successful implementation across multiple compressors confirmed its scalability and reliability. This research validates chemical cleaning as a preferred maintenance strategy, delivering significant operational and economic benefits while extending compressor service life.
Open Access
Review
20 August 2025On the Utility of Nailfold Capillaroscopy in Detecting the Effects of Fibrinaloid Microclots in Diseases Involving Blood Stasis
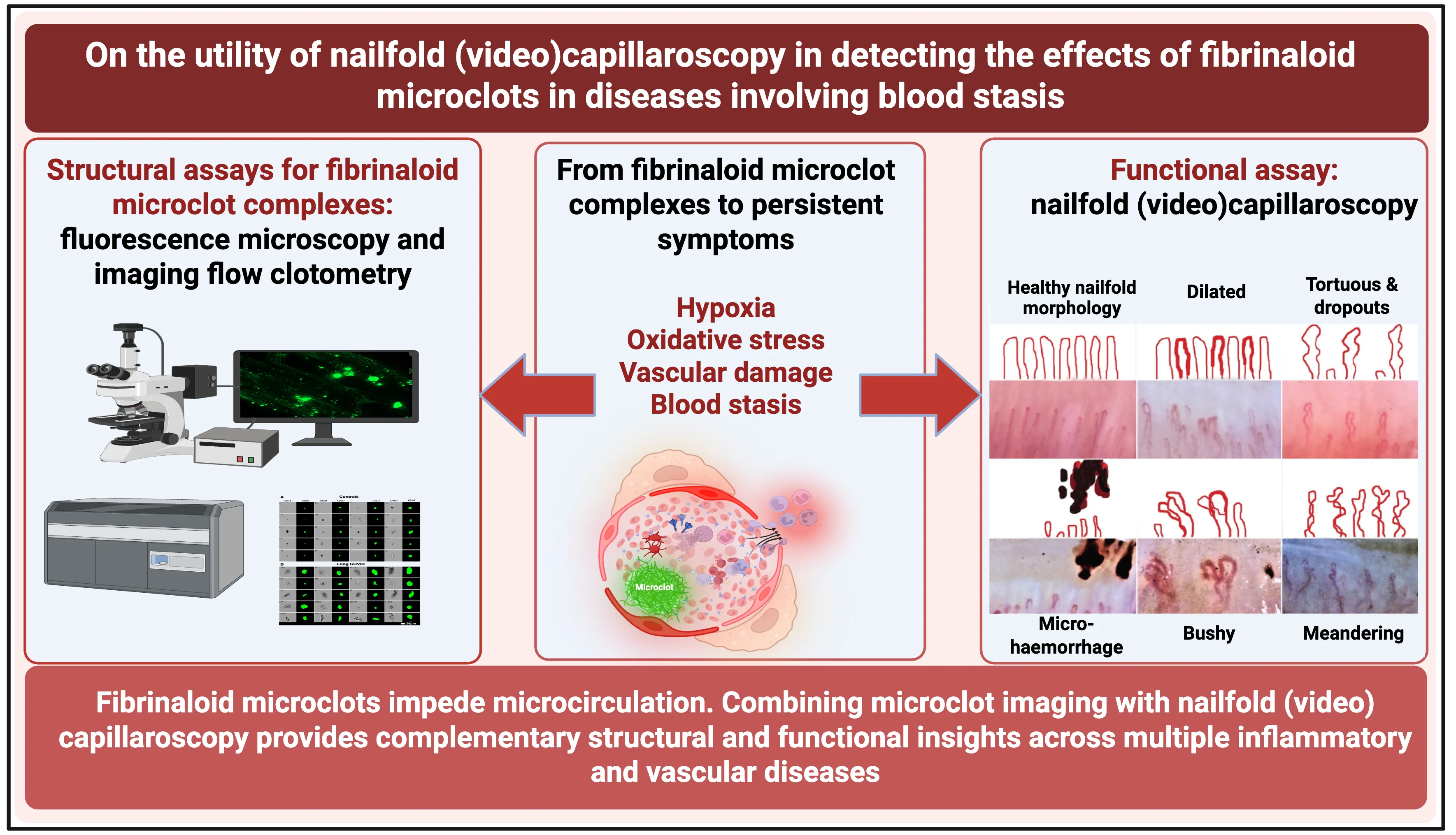
A variety of chronic, inflammatory vascular and autoimmune diseases are accompanied by fibrinaloid microclots. Such diseases reflect endothelial dysfunction and may be detected using a ‘structural’ assay in the form of the fluorescence microscopic or flow ‘clotometry’ analysis of suitably stained platelet-poor plasma. Their amyloid nature and the presence of anti-fibrinolytic molecules therein make the fibrinaloid microclots comparatively resistant to the normal processes of clot degradation. By inhibiting the free flow of blood, the many effects of fibrinaloid microclots include those causing hypoxia, oxidative stress, and ‘blood stasis’ in the microcirculation. Nailfold capillaroscopy is an established observational technique (with both ‘structural’ and ‘functional’ elements) for assessing the microcirculation, and it is thus of interest to establish whether it too demonstrates changes when these syndromes are diagnosed. All diseases in which both methods have been applied show both the presence of fibrinaloid microclots and changes in capillary properties, indicating the complementary value of the structural and functional assays. This also suggests the potential value of nailfold capillaroscopy in a variety of other diseases involving coagulopathies or a deficient microcirculation, which has been little studied to date.
Open Access
Article
20 August 2025Mitochondrial Lon Peptidase 1 Controls Diaphragm and Lung Development in a Context-Dependent Manner
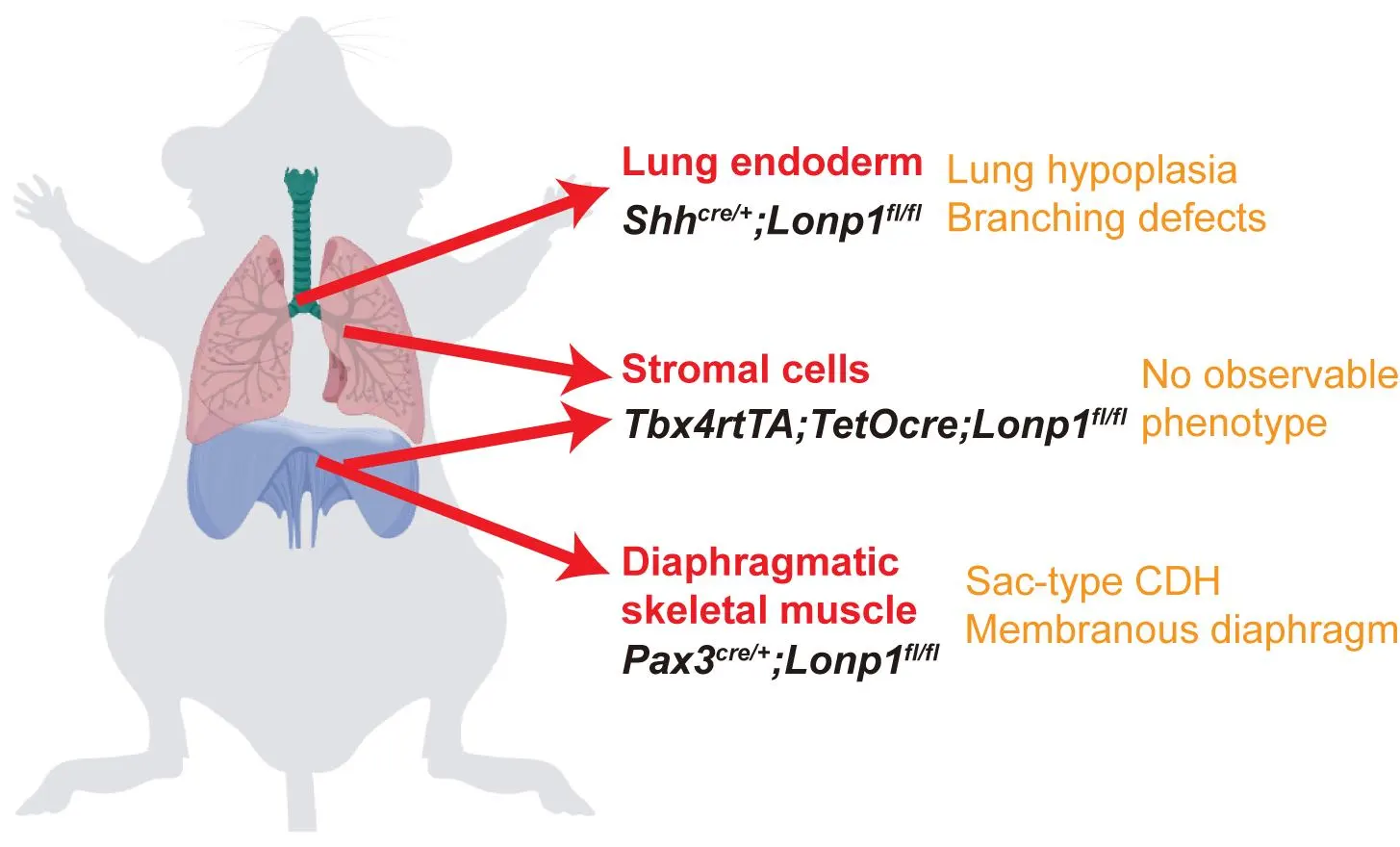
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH) is a rare neonatal disorder causing diaphragmatic defects and cardiopulmonary hypoplasia, traditionally attributed to mechanical compression from organ herniation. However, emerging evidence suggests genetic mutations may independently impair lung development, prompting debate over CDH etiology. Here, we investigated the requirement of mitochondrial function guarded by LON peptidase 1 (Lonp1), a CDH risk gene, in either diaphragm or lung development. Lonp1 loss in skeletal muscles of the diaphragm led to its thinning and membranization, recapitulating the pathology of sac-type CDH. On the other hand, lung-specific inactivation caused severe hypoplasia with defective branching morphogenesis, independent of diaphragm anomalies. Molecularly, Lonp1 disruption dysregulated key transcription factors and signaling pathways known to be critical for early lung development. Our findings here revealed that mitochondrial defects contribute to the pathogenesis of CDH in an organ and cell type specific manner, opening new avenues for drug and therapeutic development.
Open Access
Article
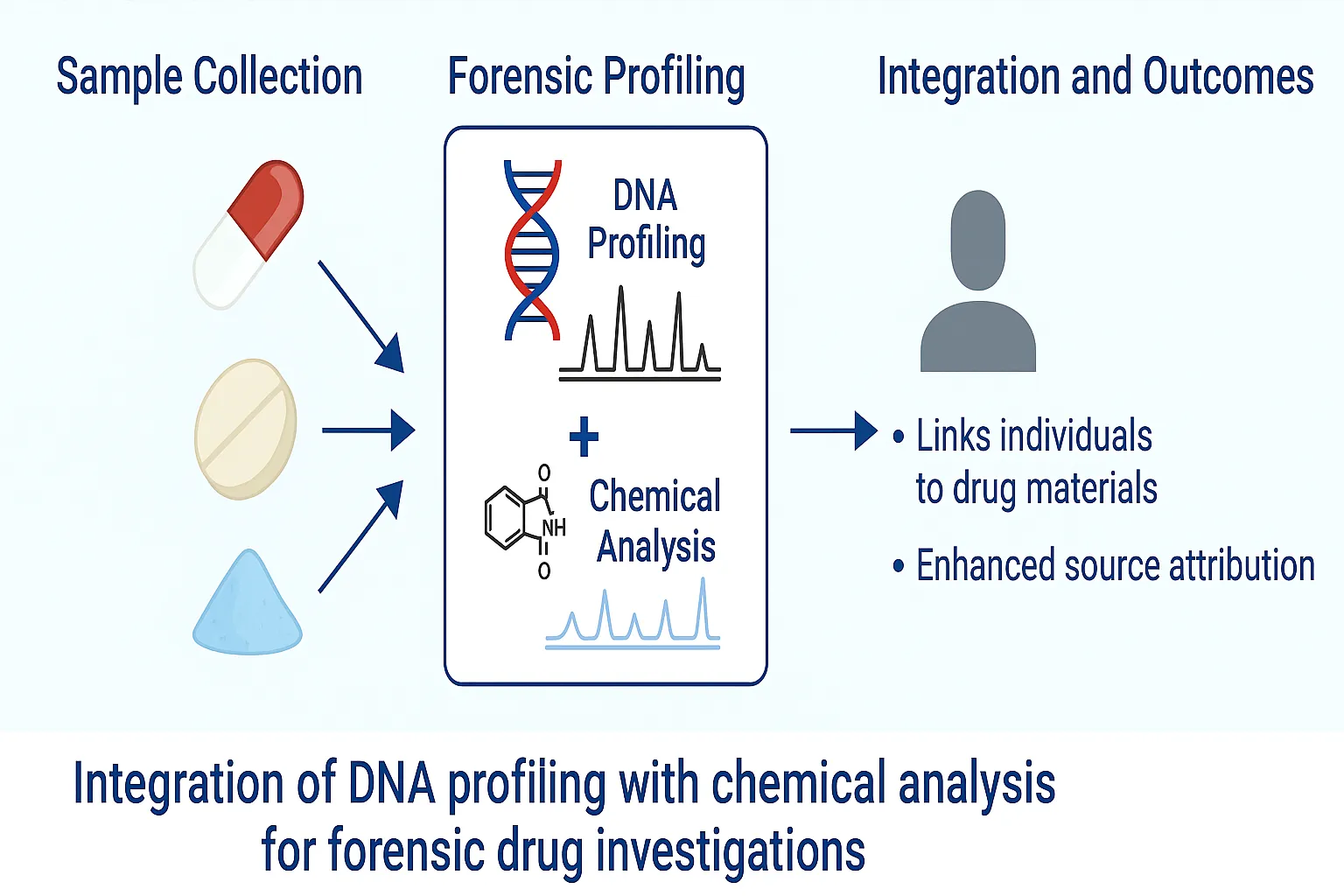
15 August 2025Integrating DNA and Chemical Profiling to Trace Illicit Drug Manufacture and Distribution
Illicit drug materials represent a valuable but underutilized source of forensic intelligence. While chemical profiling is routinely used to trace drug composition and origin, the recovery of trace DNA offers the potential to link these substances directly to individuals involved in their manufacture and distribution. This study evaluates the forensic utility of integrating DNA profiling with chemical analysis to improve source attribution across different drug formulations. Pharmaceutical-grade simulants in the form of capsules, tablets, and powders were handled by volunteers under controlled deposition scenarios. DNA was recovered using moistened cotton swabs, extracted via automated silica-based workflows, and analyzed using STR profiling. In parallel, chemical fingerprints were generated through GC-MS and LC-MS, with sample classification based on retention time and mass spectral data. Capsules yielded the highest DNA recovery (median: 310 pg), followed by tablets (230 pg) and powders (18 pg), with single-source STR profiles obtained in over 85% of capsule and tablet cases. Chemical profiling achieved 85% accuracy for capsules, 78% for tablets, and 65% for powders. When integrated, the combined approach significantly outperformed individual methods, achieving classification accuracies of 97% for capsules, 85% for tablets, and 72% for powders (p < 0.01). These findings demonstrate the enhanced evidentiary value of dual profiling, particularly in cases involving degraded or limited DNA. The proposed framework supports a more comprehensive forensic strategy, enabling biological and chemical linkage of drug materials to persons of interest and manufacturing sources. This integrative approach offers critical advantages for law enforcement and prosecution in disrupting drug trafficking networks.
Open Access
Article
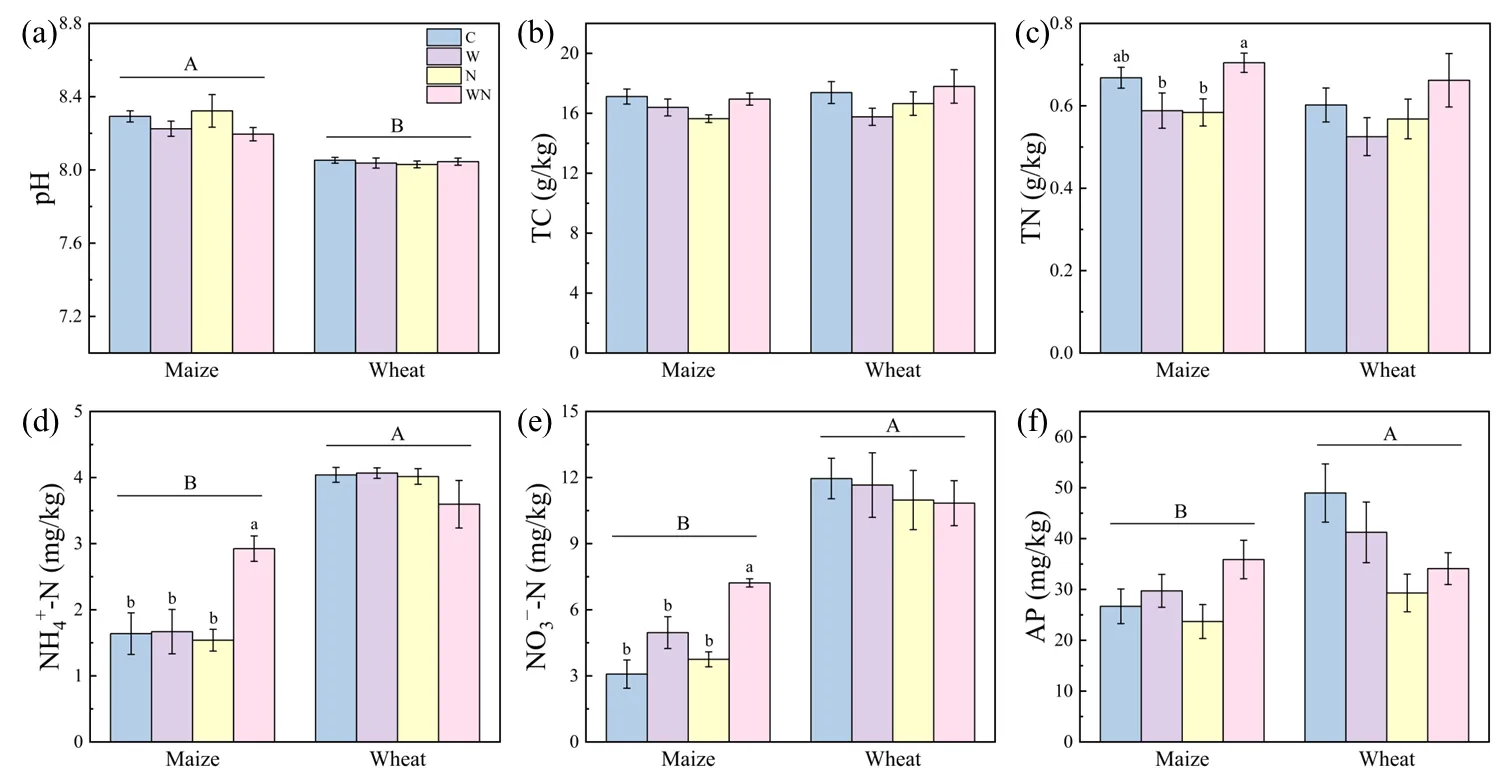
14 August 2025Wood Chips Ameliorate the Negative Effects of LDPE Microplastic on Wheat Growth and Soil Microbial Community
As an emerging pollutant, microplastics (MPs) pose a potential risk to ecosystem health due to recycling technology’s limitations and long-term durability. Wood chip amendments can enhance the holding capacity of water and nutrients and improve the soil structure and quality of terrestrial ecosystems. However, the effects of wood chip amendments on MPs-contaminated soil-plant systems are still unclear. In this experiment, we employed a combination of field experiments, soil and plant measurements, molecular techniques (DNA extraction and sequencing), and advanced statistical analyses. A comprehensive assessment was conducted on the effects of Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) MPs on soil properties, wheat growth, and soil microbial communities, and the potential of wood chips as a mitigating agent was also evaluated. The results indicated that wood chips improved soil nutrient content, enhanced the activity of enzymes related to carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycling, and promoted crop growth, all of which were negatively affected by LDPE. The effect of MPs on fungi was greater than that on bacterial communities, and adding wood chips could improve the α-diversity of fungal communities rather than bacteria. LDPE may increase the abundance of pathotrophic fungal groups, such as Stachybotrys and Alternaria. However, certain pathotrophic groups have been found to potentially facilitate the degradation of LDPE-MPs. LDPE reduced the symbiotroph groups and increased the competitiveness and complexity of the community in the microbial co-occurrence network. LDPE treatment inhibited the N-cycling bacteria group, while adding wood chips could promote most of the N-cycling bacteria groups. Wood chips increased saprotroph groups such as Trichoderma, which are able to degrade plastics. Wood chips emerge as a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution to improve soil quality and mitigate the negative impacts of microplastics on crop growth.
Open Access
Article
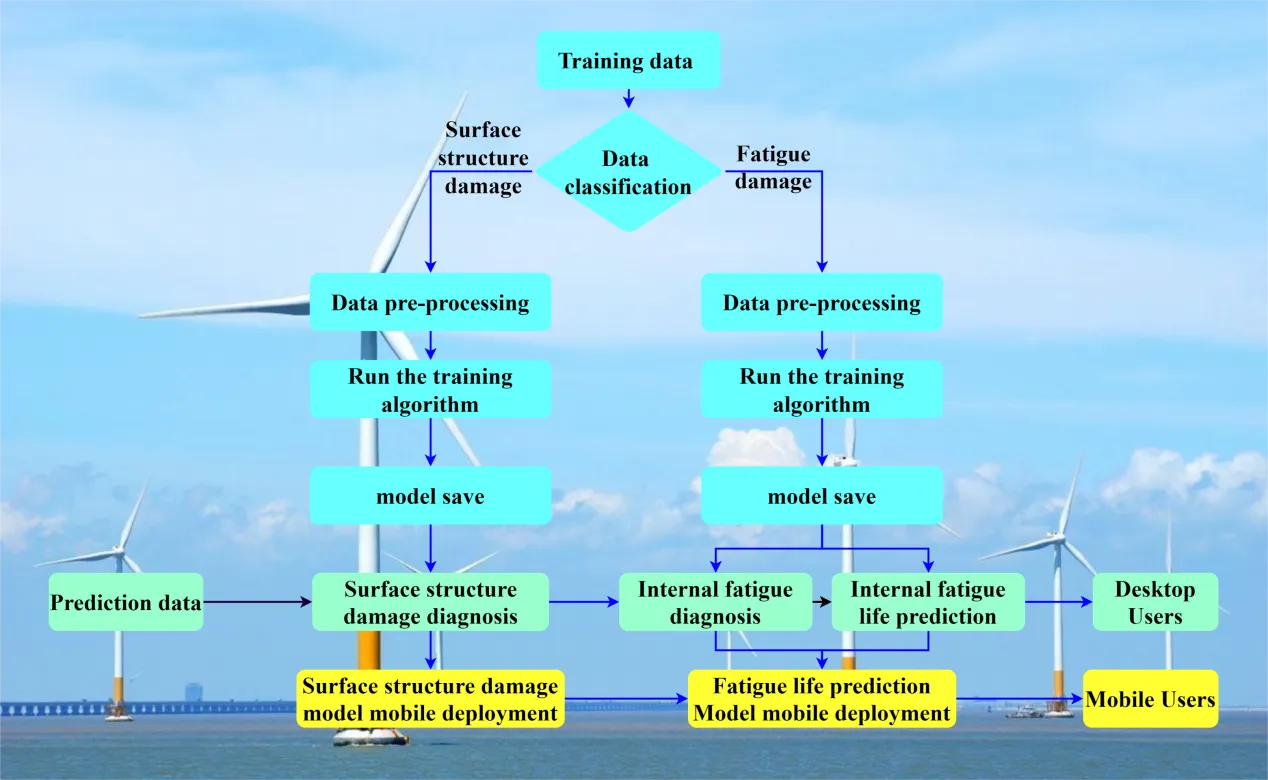
14 August 2025Advanced Study on Structural Health Diagnosis and Maintenance for Floating Wind Turbines Using Computer Vision
Global offshore wind capacity has now surpassed 50 GW and is projected to reach 264 GW by 2050, highlighting the pivotal role of floating wind in the future of clean energy. Given the complexity of marine environments, intelligent diagnostics for floating turbines are crucial for improving operational efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring robust and sustainable energy production. This paper presents a structural damage detection framework for floating wind turbines, integrating computer vision with advanced artificial intelligence technologies. First, a dataset is constructed through industry collaboration and open-source collection. Then, to optimise the YOLOv7 algorithm, SE attention mechanisms and WISE-IoU loss functions are incorporated, which significantly enhance the accuracy of surface damage detection. Experimental results indicate that the mAP (mean Average Precision) increases from 82.44% to 86.24% compared to the original YOLOv7. Finally, a deployment approach and an example are provided to use the diagnostic framework as a portable application. This enables real–time on–site analysis, enhances detection timeliness, and reduces maintenance costs. It allows for immediate issue identification and adaptation to diverse environments.
Open Access
Article
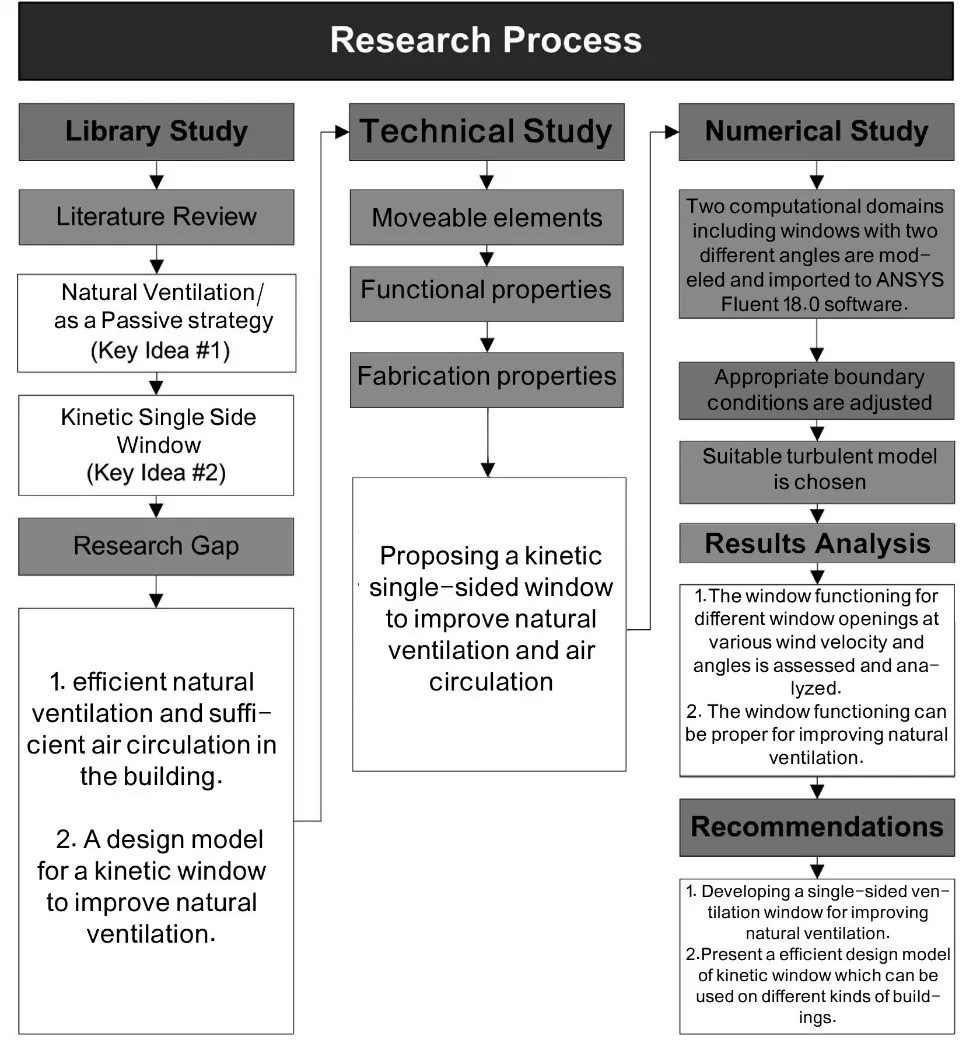
14 August 2025A Smart Kinetic Double-Skin Window System for Enhancing Natural Ventilation in Sustainable Buildings
This study presents the design and performance evaluation of a smart kinetic double-skin window system designed to enhance natural ventilation in buildings, especially those limited to single-sided airflow. The system dynamically adjusts external blade angles in response to real-time wind conditions, using environmental sensors and automated control to optimise airflow distribution and energy performance. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations were conducted for two blade configurations (7° and 15°) under varying wind speeds and directions. Results show that the 15° configuration enhances airflow reach and achieves up to 40% higher air change rates (ACH) compared to the 7°, making it more suitable for high-demand ventilation scenarios. In contrast, The 7° configuration produces lower but more uniform airflow, which is more appropriate for occupant comfort in residential or office environments. Detailed analysis of velocity fields, pressure distributions, and airflow paths confirms that the system effectively adapts to wind direction, maintaining balanced ventilation through integrated airflow channels. The simulations were validated against experimental data, achieving a Close correlation. While thermal and buoyancy effects were not included, future work will extend the model to hybrid ventilation scenarios. The proposed system demonstrates significant potential for sustainable ventilation applications in new and retrofitted building envelopes.
Open Access
Review
13 August 2025Allowing Space for Nature: Rewilding to Heal the Earth
The term “rewilding” often elicits strong emotions, especially as presented in the media. Thus, anger is provoked that farmers will be forced to waste precious cropland, letting it return to the wild, or from fear that dangerous animals will be released into the urban environment. With equal fervour, others, taking an approving view, comprise the growing movement of guerrilla rewilders, secretly breeding butterflies, birds and beavers, and illegally releasing them (e.g., “beaver bombing”) across the countryside. In truth, rewilding is a complex and widely encompassing proposition, which can be considered as a strategy within the natural climate solutions (NCS) [nature based solutions (NBS)] approach, aimed to restore and enhance wetlands, grasslands, forests, agricultural lands, seascapes etc. While exact definitions may vary, a key feature is that (after some initial support) it minimises the level of human intervention/management in a given region, instead encouraging natural processes to take the lead and self-manage, in the restoration, shaping and enhancement of natural ecosystems and of critical ecosystem functions. The resilience of such ecosystems should also be considered, especially in regard to how the impacts of a changing climate may prevail upon them. Rewilding is informed by science, traditional ecological knowledge (TEK), and other local (indigenous) knowledge. It is a long-term process with dynamic changes occurring over time, and rather than focussing on reaching a fixed endpoint, provides a continuous journey of letting nature’s processes unfold. This can lead to increased biodiversity, amelioration of and resistance to climate change, and the provision of ecosystem services, benefitting both nature and people, including economic opportunities for local and indigenous communities, along with improved overall health and well-being. Despite its manifold and clear benefits, rewilding (along with other NCS) is not a pancea for all our troubles, many of which are rooted in the systemic issue of human ecological overshoot, and it is this that must be addressed to begin fixing the current global polycrisis.
