Found 301 results
Open Access
Article
14 August 2025A Smart Kinetic Double-Skin Window System for Enhancing Natural Ventilation in Sustainable Buildings
This study presents the design and performance evaluation of a smart kinetic double-skin window system designed to enhance natural ventilation in buildings, especially those limited to single-sided airflow. The system dynamically adjusts external blade angles in response to real-time wind conditions, using environmental sensors and automated control to optimise airflow distribution and energy performance. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations were conducted for two blade configurations (7° and 15°) under varying wind speeds and directions. Results show that the 15° configuration enhances airflow reach and achieves up to 40% higher air change rates (ACH) compared to the 7°, making it more suitable for high-demand ventilation scenarios. In contrast, The 7° configuration produces lower but more uniform airflow, which is more appropriate for occupant comfort in residential or office environments. Detailed analysis of velocity fields, pressure distributions, and airflow paths confirms that the system effectively adapts to wind direction, maintaining balanced ventilation through integrated airflow channels. The simulations were validated against experimental data, achieving a Close correlation. While thermal and buoyancy effects were not included, future work will extend the model to hybrid ventilation scenarios. The proposed system demonstrates significant potential for sustainable ventilation applications in new and retrofitted building envelopes.
Open Access
Article
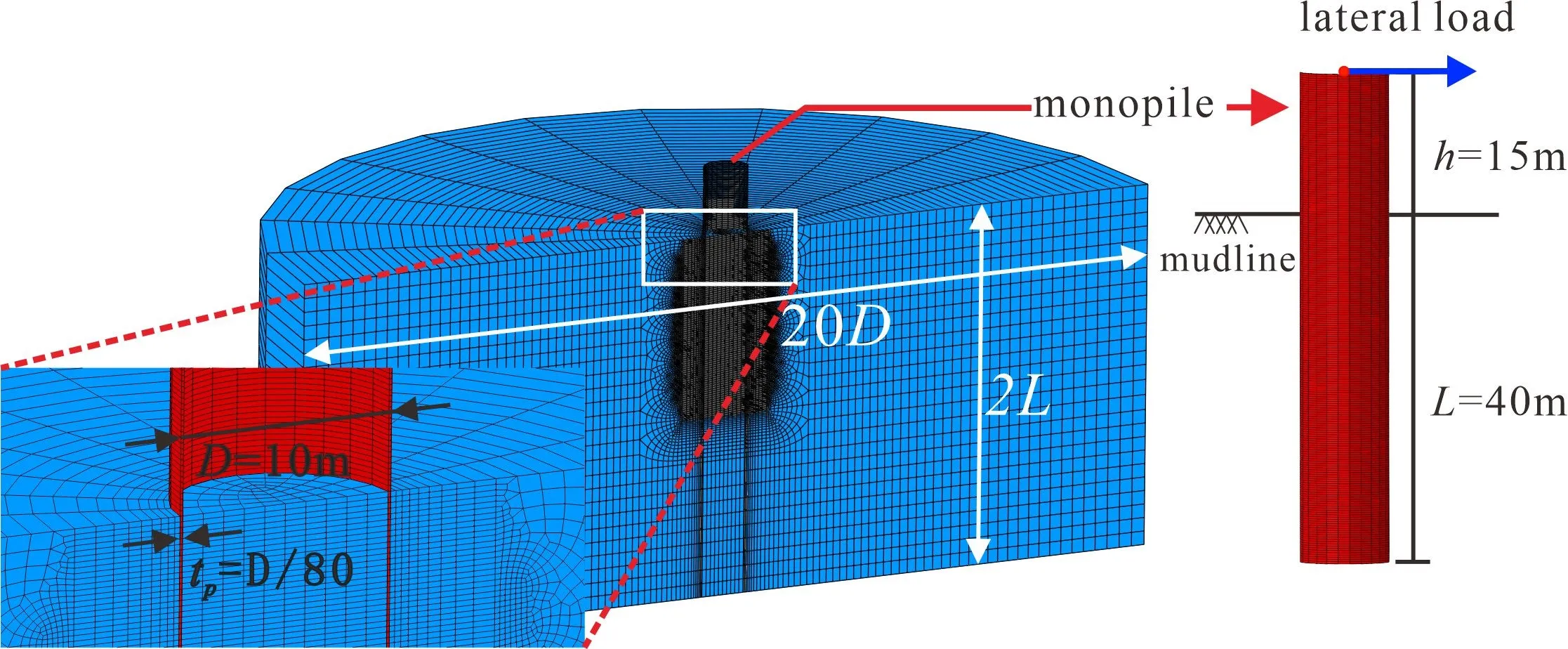
13 August 2025Influence of Pile Diameter on Lateral Load Behavior and Failure Mechanisms of Large-Diameter Monopiles
Increasing monopile diameter significantly alters lateral load response, and traditional design methods have already demonstrated limitations, while the influence mechanism of the diameter effect is still not in consensus. Using the three-dimensional finite element simulation, which is validated against centrifuge test results, the influence mechanism of the diameter effect is analyzed, and the related failure modes are also examined. It is found that the lateral bearing capacity of the monopile increases significantly with increasing pile diameter. The interaction of the soil plug and soil around the pile can enhance the nonlinear characteristics of the lateral load-displacement response. As the pile diameter increases, the deformation response of the pile evolves from flexible through semi-rigid to rigid behavior, and distinct failure modes are also developed. With the increase of pile diameter, the depth range of the wedge failure zone for flexible piles increases gradually, whereas for rigid piles, the depth range remains essentially unchanged, but the radius of the rotational failure zone significantly expands. The depth range of the full flow failure zone of semi-rigid piles progressively shrinks with the reduction in pile bending deformation. Failure modes can significantly affect the initial stiffness of the p-y curve. The initial stiffness exhibits the dependence on the pile diameter, embedment depth, and failure mode simultaneously.
Open Access
Case Report
11 August 2025Transition to Hydrogen Aviation: A 2030–2050 Scenario Performance Analysis for an Airline
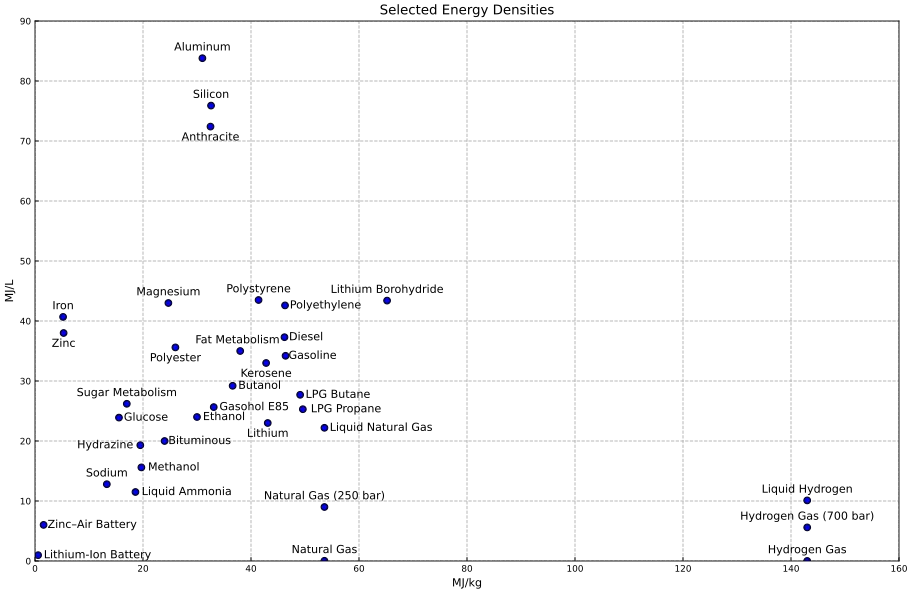
This study presents a realistic hypothetical scenario-based analysis of an airline’s transition from kerosene to hydrogen propulsion between 2030 and 2050, under a Techno-Economic Environmental Risk Assessment (TERA) framework. Two scenarios are modelled: a baseline fleet scenario using only conventional CMRT and CLRT aircraft, and a hydrogen transition scenario that introduces hydrogen-powered Airbus ZEROe and HVLMR aircraft starting in 2035. Using detailed aircraft (Orion from Cranfield) and jet engine (TURBOMATCH from Cranfield) performance simulations across 85 global routes, fuel consumption, energy demand, emissions, and operating costs are assessed. Strategic hydrogen hubs at London Heathrow and Neom Bay enable network feasibility for aircraft with limited range. Key findings show that the hydrogen scenario reduces total fuel mass consumption by approximately 28%, due to hydrogen’s high specific energy, and cuts CO2 emissions by 49%, assuming green hydrogen usage. However, it also results in a 9.6% increase in energy demand and ~15–20% higher cumulative operating costs, driven by greater depreciation, maintenance, and fuel price premiums. While the hydrogen transition introduces higher upfront and operational costs, it offers long-term environmental benefits and compliance with net-zero aviation goals. The study concludes that hydrogen aviation holds strategic promise but faces significant technical challenges, particularly due to the immaturity of hydrogen storage and propulsion systems. Realising this potential will require coordinated investment in infrastructure, policy support, and adaptive route planning.
Open Access
Communication
05 August 2025Autoimmune Adverse Events Following Immunization
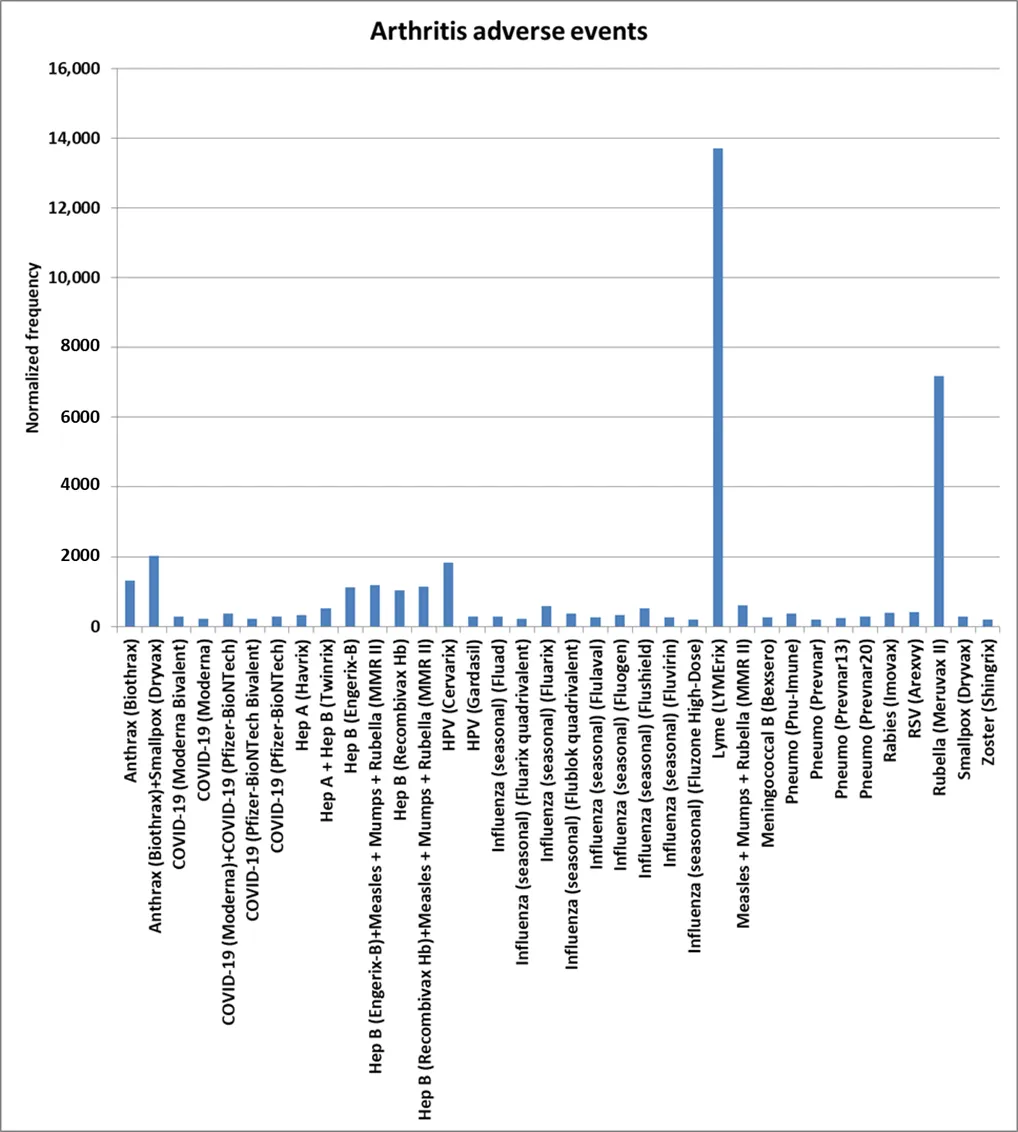
Adverse events (AEs) following immunization can include autoimmune AEs for some vaccines and combinations. This study retrospectively examines autoimmune AEs to detect safety signals for vaccines and concomitantly administered vaccines in the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) database. This study focuses on which vaccines were administered or coadministered for retrospective analysis of analyzed autoimmune AEs. Observed results include multiple autoimmune AE safety signals: human papillomavirus (HPV) Cervarix, HPV Gardasil, hepatitis (Hep) A + Hep B (Twinrix), Lyme disease (LYMErix), coadministered COVID-19 Moderna + Pfizer-BioNTech, Hep B (Engerix-B), and others. Identified arthritis AE safety signals include Lyme disease (LYMErix), rubella (Meruvax II), HPV (Cervarix), Anthrax (Biothrax) + Smallpox (Dryvax), and more. Coadministered DTaP + HepB + IPV (Pediarix) + Hib (Pedvaxhib) + Pneumococcal (Prevnar13) + Rotavirus (Rotarix) may be exhibiting synergy AE rate for eczema AEs. Thirty five influenza vaccines were observed with Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) AE safety signals, plus additional safety signals for multiple other vaccines. influenza (H1N1 monovalent) (GSK) exhibits a very high rate for narcolepsy AEs.
Open Access
Article
29 July 2025Air Conditioning Heat Exchanger Intelligent Production Line: Design Methodologies and Applications
As a key component in modern building environmental control systems, the production quality and performance of multi-split central air conditioning systems directly influence the comfort, energy efficiency, and operational stability of buildings. However, the current manufacturing process primarily relies on a combination of traditional manual labor and automated equipment, resulting in low efficiency, high energy consumption, and limited automation. This paper first presents an optimized design for an intelligent manufacturing production line for multi-split central air conditioning heat exchangers to address these issues. It details the design of key systems for the intelligent production line and ensures continuous production and processing. Additionally, the paper analyzes the production process of the intelligent manufacturing line, with particular emphasis on the mechanism of the heat exchanger tube expansion process. Furthermore, it designs the fixture structure of the transfer robot for each process in the production line and discusses the principles of workpiece positioning and clamping. Utilizing technologies such as sensor networks, PLC, and industrial Ethernet, the system completes the closed-loop process of perception, transmission, analysis, decision-making, and execution within the production line, enabling transparency, fault predictability, and automated management. The results show that the intelligent assembly production line has significantly improved the assembly efficiency, achieving a 300% increase in the daily production capacity of a single line. While enabling the continuous and intelligent production of multi-split central air conditioning heat exchangers.
Open Access
Article
28 July 2025Investigating Touch DNA Success Rates in Vehicle Sites for Hit-and-Run Casework
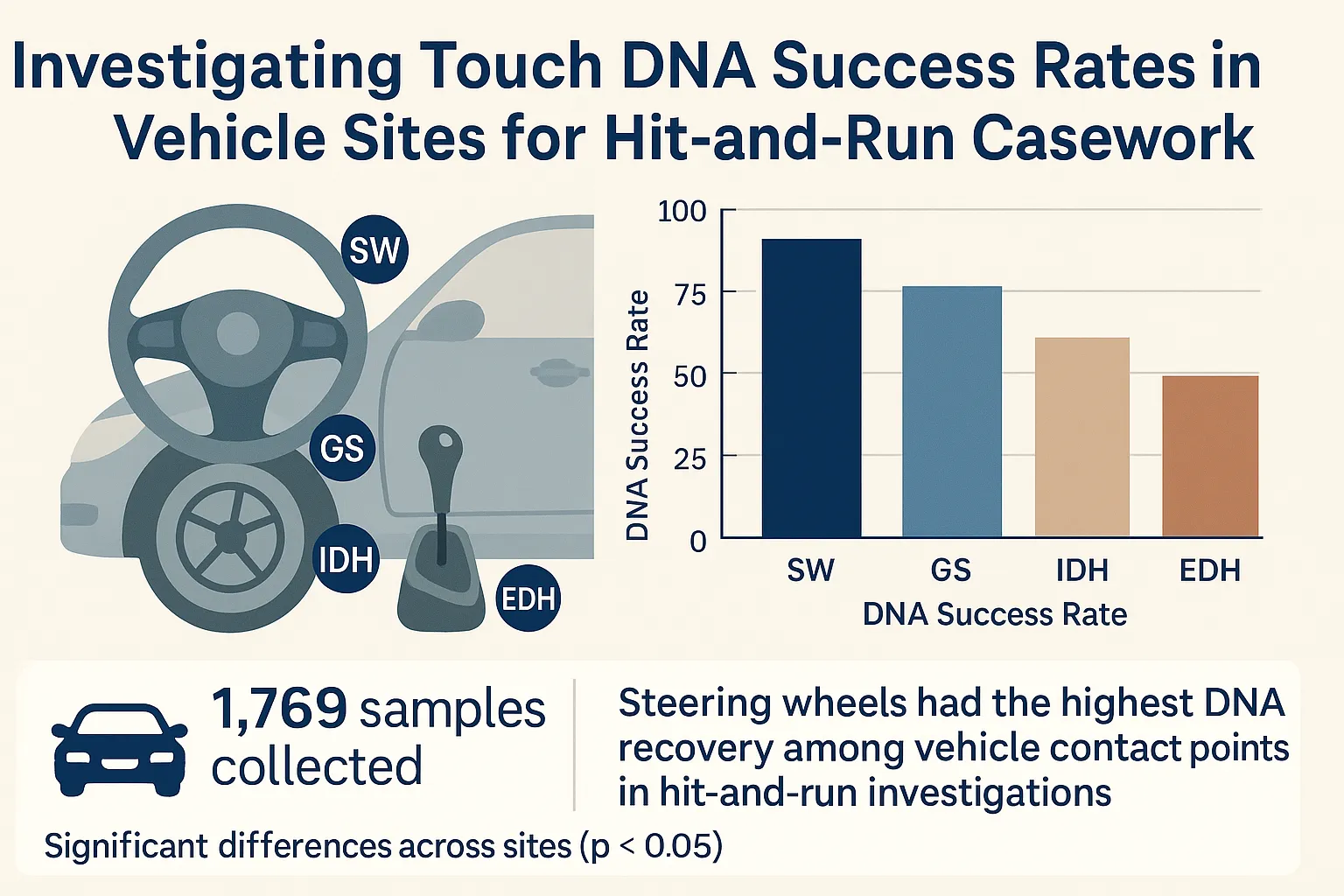
This study evaluated the effectiveness of Touch DNA recovery from four key vehicle contact points—steering wheel (SW), gear shift (GS), interior door handle (IDH), and exterior door handle (EDH)—in the context of hit-and-run forensic casework. 1769 samples were collected from 359 vehicles processed between 2020 and 2023. Statistically significant differences were observed in the quantity and quality of DNA recovered across these sites (p < 0.05). The steering wheel yielded the highest DNA success rates, followed by the gear shift, whereas the exterior and interior door handles demonstrated substantially lower recovery efficiency. These findings underscore the critical role of strategic sampling site selection in maximizing evidentiary outcomes. The results support prioritizing the steering wheel and gear shift as primary targets for DNA collection in vehicle-based investigations. The study highlights the practical utility of Touch DNA in linking individuals to vehicular crimes and calls for further research into alternative sampling techniques and contamination control measures to optimize forensic DNA recovery protocols in real-world hit-and-run scenarios.
Open Access
Article
21 July 2025The Intergovernmental Networks of Ecological Protection Policies Issuing Entities in the Source Region of the Yangtze River: A Case Study of Qinghai Province
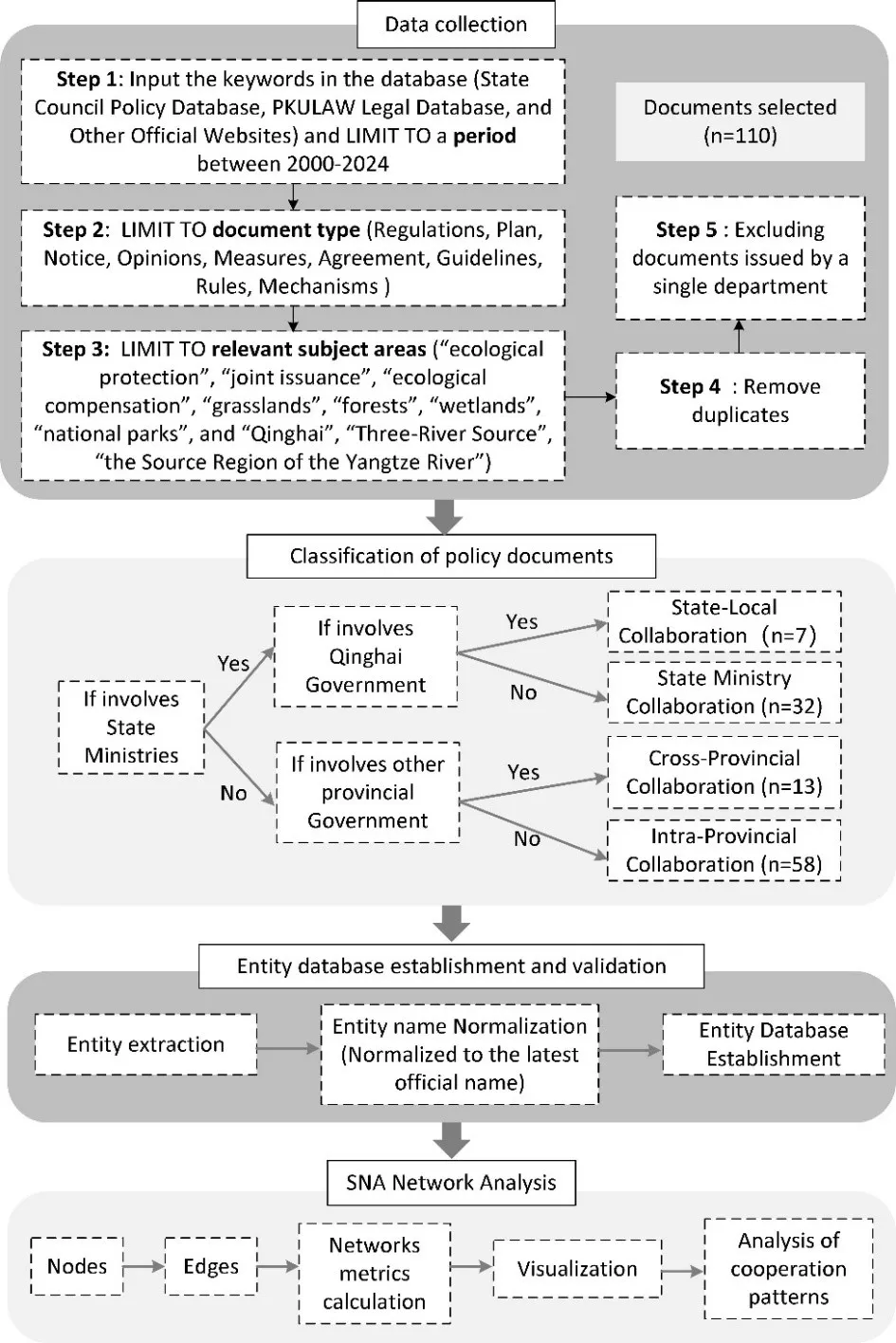
Ecological conservation and governance play key roles in constructing an ecological civilization society, while intergovernmental cooperation provides new perspectives for cross-regional ecological governance. We employed a social network analysis (SNA) method to examine 110 published ecological policies from 2000 to 2024 in the Source Region of the Yangtze River (SRYR). The study has three key findings. Firstly, intergovernmental collaborative policies on ecological protection showed an upward trend, with intra-provincial collaborations within Qinghai Province being the most frequent. Secondly, four collaboration models were demonstrated, namely: national ministries, national and provincial, cross-provincial and intra–provincial collaborations. National agencies and Qinghai provincial agencies collaboratively set objectives, which Qinghai operationalizes with incentive-constraint measures. Then, the targeted guidelines were launched by national and provincial authorities. Afterward, cross–provincial agreements and mechanisms facilitate joint actions. Thirdly, we revealed the hierarchical structures, including a national network, two central-local sub-networks, three-tier inter-provincial partnerships, and four regional sub-clusters. Core actors include national ministries that coordinate cross-departmental efforts. The Qinghai provincial government serves as a central-local hub. It maintains strong transboundary ties with Aba and Ganzi Prefectures of Sichuan Province. Provincial departments such as ecology and environment, forestry and grasslands, and finance lead intra-provincial collaborations. These findings offer new insights for integrating multi-level governance in ecological protection and ecological civilization construction.
Open Access
Article
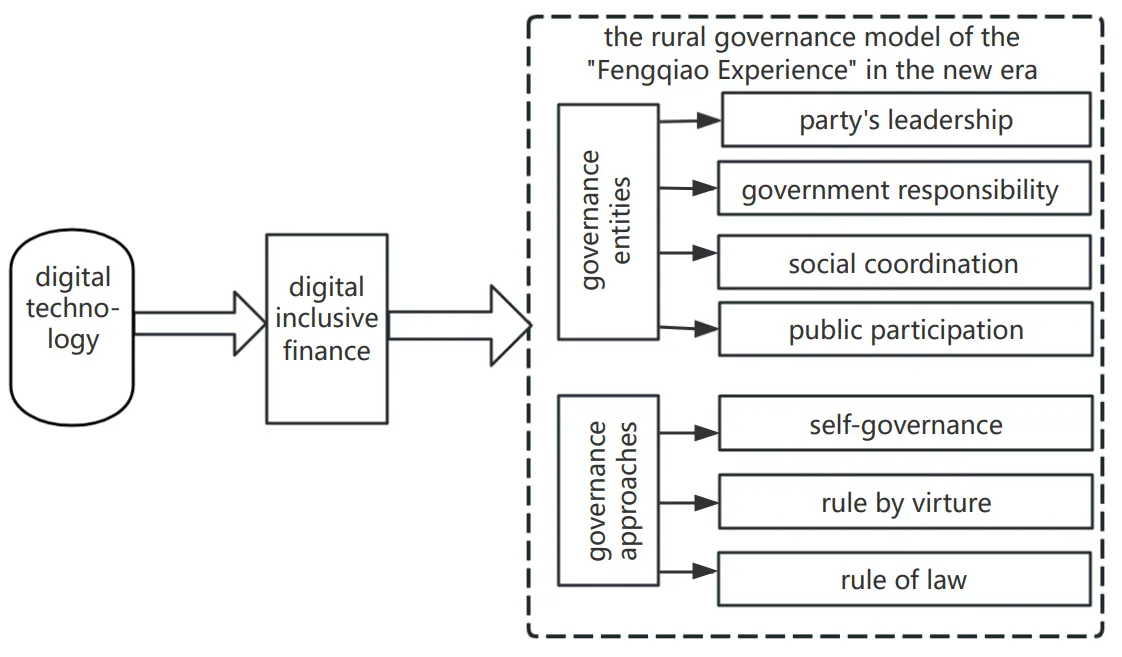
15 July 2025Exploring the Sustainable Path of Rural Governance: An Empirical Study on Digital Technology Empowering the “Fengqiao Experience” Model in the New Era
Understanding digital technology and digital inclusive finance in rural governance is key to exploring the sustainable development path of rural governance in China. This study constructs a multidimensional index evaluation system for the “Fengqiao Experience” rural governance model in the new era, measures the model’s rural governance level in 30 provinces in China (2011–2022), and empirically assesses digital technology’s impact on rural governance and its mechanism. The results are as follows: (1) During the sample survey period, the rural governance level of digital technology and “Fengqiao Experience” in 30 provinces in China has improved year by year. (2) Benchmark returns to reality and digital technology significantly promotes the improvement of rural governance levels, which remains valid after using GLS, replacing core explanatory variables, excluding the impact of the epidemic, and excluding municipalities directly under the central government. (3) Digital inclusive finance plays an intermediary role in the digital technology process, enabling rural governance. (4) Digital technology’s impact on rural governance has significant spatial spillover characteristics. Such technology helps improve the level of rural governance both locally and in surrounding areas. This study contributes to the understanding of the mechanism, effect, and regional differences of digital technology-enabled rural governance.
Open Access
Review
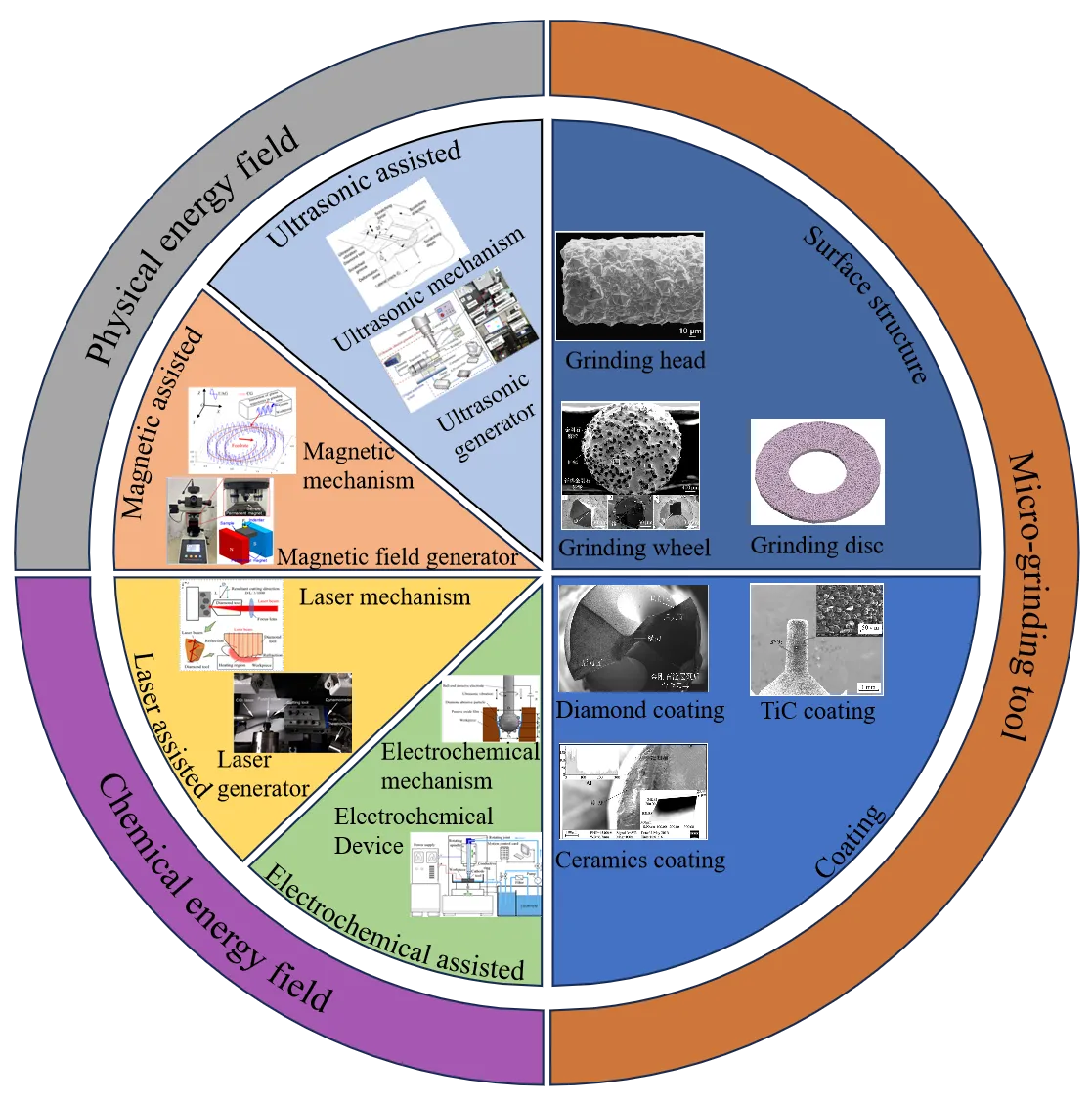
09 July 2025Muti-Energy Field-Assisted Grinding of Hard and Brittle Materials: Tools, Equipment and Mechanisms
Hard, brittle and difficult-to-machine materials are prone to surface cracks, subsurface damage and other defects in the traditional grinding process, accompanied by low processing efficiency and severe tool wear. As a new type of processing technology, energy field-assisted grinding provides a new approach for the efficient and high-quality processing of hard and brittle materials. This paper reviews the latest research progress of muti-energy field-assisted grinding from aspects such as the types and selection of grinding tools, processing equipment and physical-chemical coupled mechanisms. Firstly, micro-grinding tools are classified based on different surface structures and coating materials, with the aim to enhance processing efficiency, improve the surface quality and geometric accuracy of workpieces, and reduce tool wear. Secondly, the processing mechanisms, parameter selection and current difficulties faced by four energy field-assisted grinding methods, including laser-assisted grinding, electrochemical-assisted grinding, magnetic-assisted grinding and ultrasonic field-assisted grinding, are discussed under both chemical and physical effects. Thirdly, different equipment and auxiliary devices developed for energy field-assisted grinding have been introduced, providing reliable platforms for the distribution design and efficient regulation of the energy field. Finally, the cutting-edge progress, main challenges and development trends of energy field-assisted grinding are prospected, illustrating the great potential of this technology in fields such as aerospace, electronics, and optical components.
Open Access
Article
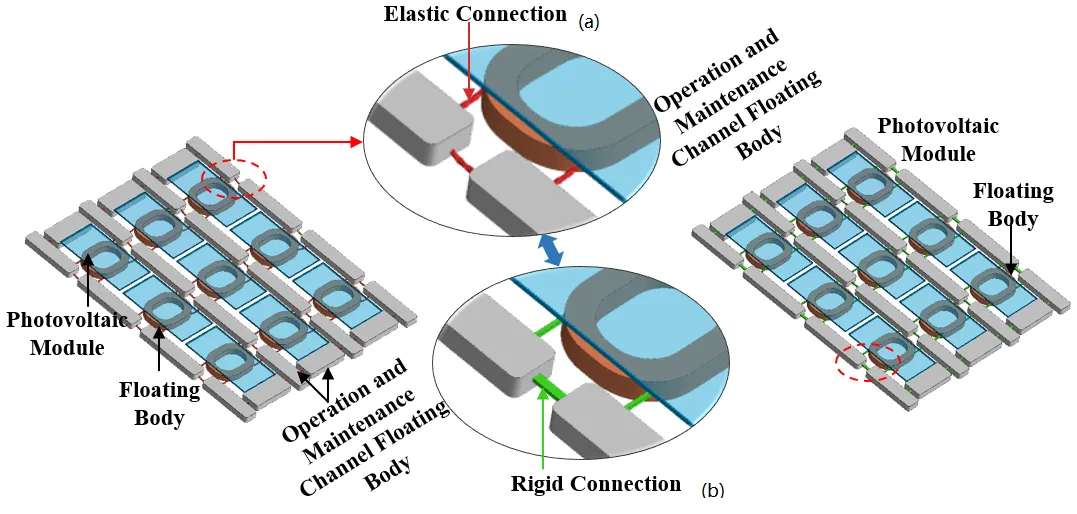
30 June 2025Hydrodynamic Analysis of Offshore Floating Photovoltaic Structure with Elastic Connection
Offshore Floating Photovoltaic structure (OFPV) represents a promising solar energy technology characterized by high conversion efficiency and suitability for large-scale deployment. However, the safety and economic synergy problems of floating structures restrict the industrialization and large-scale development of OFPV. We propose a novel OFPV with elastic connection and modularizable HDPE float blocks. The numerical wave tank is established by the turbulence model in FLOE-3D, based on the Navier-Stokes equations. Hydrodynamic analysis of the OFPV is conducted by using the Generalized Mode-Order (GMO) approach. Furthermore, the dynamic responses and mooring loads of the OFPV with elastic and rigid connections are compared. The results show that the average pressure of the photovoltaic support structure with the elastic connection is positively correlated with the wave height. The tension value of the elastic cable is higher at the outermost peak tension. The OFPV with the elastic connection structure has more obvious advantages in extreme wave state conditions than the rigid connection. This study provides theoretical support for the design and engineering application of OFPV.