Found 469 results
Open Access
Article
17 October 2025Enhancing Ablation Resistance of C/C-HfC-SiC Composites by In-Situ Growth of HfC Nanowires
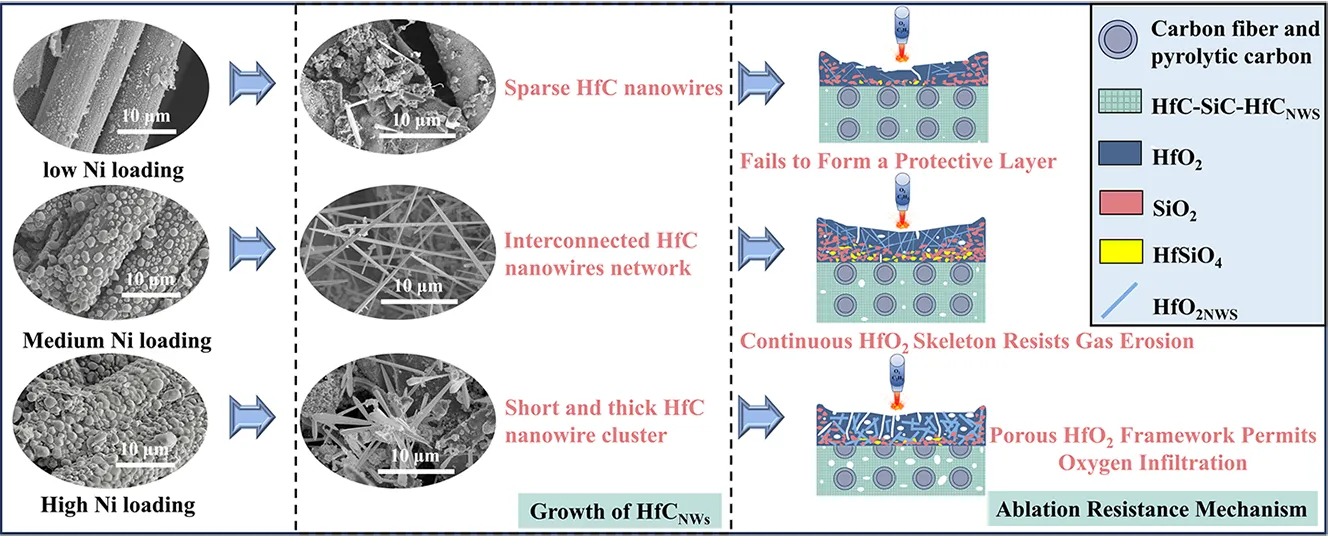
C/C-HfC-SiC composites are promising ablation-resistant ultra-high temperature thermal protection materials. To further enhance their performance in extreme thermal environments, the introduction of HfC nanowires (HfCNWs) into the composite has been identified as an effective strategy. The quantity and morphology of the introduced HfCNWs significantly influence the ablation resistance of the composites. In this study, by controlling the concentration of Ni salt during the hydrothermal synthesis process, the loading amount of Ni catalysts on the surface of carbon fibers was regulated, thereby achieving control over the quantity and structure of HfCNWs in the C/C-HfC-SiC composites. It was found that a low Ni loading facilitates the growth of sparse and slender HfCNWs. As the Ni loading increases, the number of HfCNWs rises, gradually evolving into a high-density, multi-oriented network structure. However, excessive Ni tends to induce short, thick, and clustered growth of the nanowires. Based on this, three types of HfCNWs-modified C/C-HfC-SiC composites were prepared using the polymer impregnation and pyrolysis (PIP) process. The quantity and diameter of the HfCNWs significantly affect the ablation resistance of the composites. Among them, the composite prepared with a 4.38 wt% Ni loading exhibited excellent ablation resistance, with mass and linear ablation rates of 0.47 mg·s−1·cm−2 and 5.50 μm·s−1, respectively. The performance improvement is attributed to the formation of a continuous HfO2 skeletal structure after the oxidation of an appropriate amount of HfCNWs. This continuous HfO2 skeleton significantly enhances the ability of the oxide layer to resist high-speed gas flow erosion and oxygen penetration. This study can provide support for the design of HfCNWs-reinforced C/C-HfC-SiC composites and promote their engineering application in the field of aerospace thermal protection.
Open Access
Article
17 October 2025Bioenergy Technology and Carbon Intensity in U.S. and China: Threshold Roles of Capital Accumulation, Education and Inequality
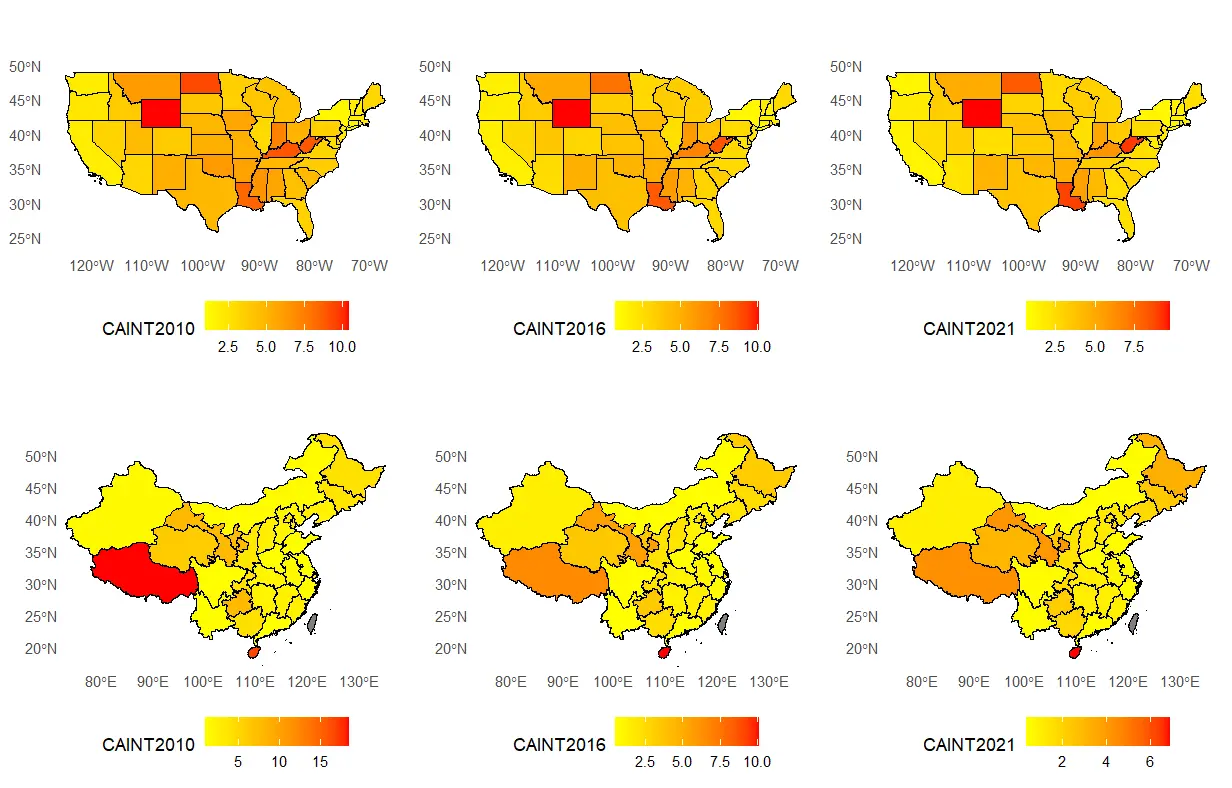
Bioenergy technology holds significant promise for reducing carbon intensity and fostering sustainable development, yet its impact remains unclear. This article employs both a panel threshold model and a random forest model, analyzing data from the primary administrative regions in the United States and China to explore the threshold effects and regional heterogeneity of bioenergy technology on carbon intensity, where the bioenergy technology is measured using patent data. In the United States, the impact of bioenergy technology on carbon intensity initially shows a positive effect, which later turns negative as per capita capital stock increases. The technology’s inhibitory effect strengthens with higher levels of education but becomes insignificant as the Gini coefficient rises. In China, increasing per capita capital stock shifts the impact of bioenergy technology from negative to insignificant, while higher education levels enhance its inhibitory effect. The Gini coefficient, however, does not significantly affect the impact of technology. Additionally, these threshold effects exhibit notable regional variations. The study provides cross-country evidence of how institutional and structural conditions shape the carbon mitigation effects of bioenergy technology, offering practical insights for policies that combine trade facilitation, education, and inequality reduction with low-carbon energy transitions.
Open Access
Meeting Report
16 October 2025
Open Access
Article
14 October 2025Electrical Characterization, Optical Micrographs, and the Compositional Analyses of Al-Glass/C-Glass Composites
This report shows the resistance (r) of Carbon-Glass composites and the Current/Voltage (I-V) characterization of Al-Glass composites. The optical micrographs and elemental determination of Carbon-Glass and Al-Glass are in this record. The effects of pressure and the influence of particle size on the electrical properties of these composites are included. The sample area, thickness range, and particle size are respectively 34.0 × 35.0 mm2, 20.8–22.10 mm, and 100 µm. The constituents of the same particle size were made into solids by applying a pressure of 30 MPa. The results obtained from examinations showed that the composition of Al in glass, compaction pressure, and particle size significantly influenced the resistance and the electrical I-V relationship of the compacted materials. The electrical properties of samples are within the range of 10–50% weight of Al in composites, and 0–100% weight of carbon in composites. The resistance of Carbon-Glass is sinusoidal with Mega Ohms values. The current variation of Al-Glass composites is also a sine wave in the I-V display, which is between 0 and 10 µA. The Current-Voltage notation is with sinusoidal resolution for Al-Glass composites. The voltage range is from −0.5 V to 1.0 V.
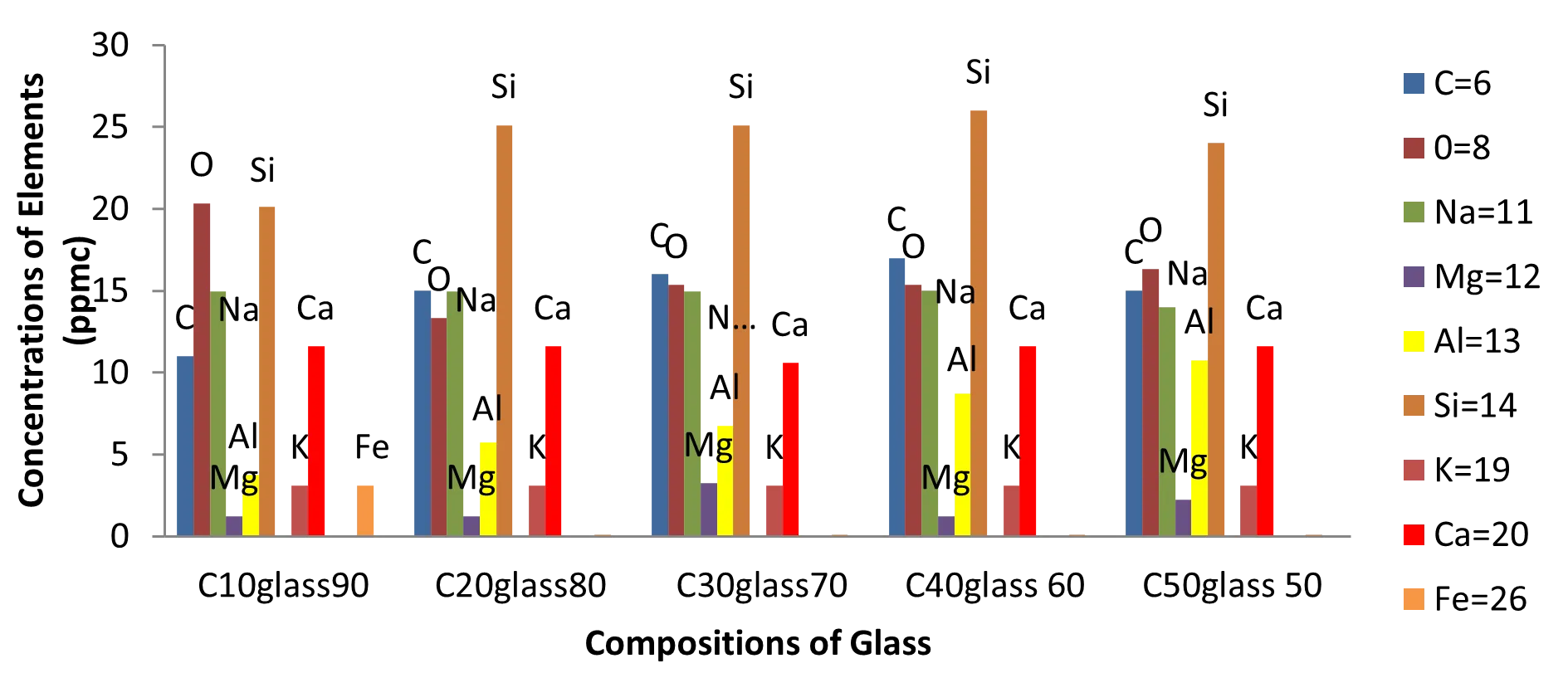
Open Access
Article
11 October 2025Catalytic Potential of Green-Synthesized Iron Nanoparticles from Psidium guajava for 4-Nitrophenol Reduction
This study presents a sustainable approach for the green synthesis of iron nanoparticles (Fe(NPs)) using an aqueous extract of Psidium guajava (guava leaves) as a reducing and stabilizing agent. The FeNPs were applied in the catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. To minimize the use of sodium borohydride (NaBH4), different volumetric ratios of plant extract and NaBH4 were tested. The influence of these ratios on the physicochemical and morphological properties of the FeNPs was evaluated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM/EDS), high-resolution field-emission SEM (HR-FESEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and N₂ physisorption. Increasing the proportion of plant extract led to reduced crystallinity, larger particle sizes, and lower surface areas. Despite these changes, using up to 40% extract improved catalytic performance, achieving over 90% reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Ecotoxicological assessments confirmed the biocompatibility of the FeNPs, the effective neutralization of 4-nitrophenol toxicity post-reduction, and highlighted the inherent toxicity of NaBH4. These findings demonstrate the potential of Psidium guajava-mediated FeNPs as eco-friendly catalysts for pollutant reduction, combining efficiency with reduced environmental impact.
Open Access
Article
10 October 2025Guidance and Control System for an Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle as a Wingman
This study focuses on designing and testing a formation guidance system for a UCAV as a wingman to an F-16 fighter jet. A critical assessment of the UCAV autopilot revealed areas for improvement, which were addressed to refine the stable foundation of the autopilot for implementing the guidance system. This system uses PID controllers to minimise the along-track, cross-track, and vertical-track errors during standard manoeuvres. The system performed exceptionally well in the vertical (z) direction but showed robustness challenges in the along-track (x) and cross-track (y) directions under wind disturbances. A notable outcome was the identification of a novel mathematical relationship between the along-track offset command and its gains, offering a pathway for advanced formation systems. These findings pave the way for future enhancements in diverse formation operations.

Open Access
Article
10 October 2025Immunoprofiling of Alcohol-Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells Reveals Mechanisms of Immune Evasion through NK/T Lymphocyte Checkpoint Signaling
Chronic alcohol consumption induces the pathogenic activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSC) and their conversion into proliferative myofibroblasts (Myo), which together constitute a disease hub in alcohol-associated liver disease (AALD). While natural killer (NK) lymphocytes efficiently target early activated HSC and ameliorate liver fibrosis in mouse models of diet- and alcohol-induced liver disease, late-activated HSC evade immune surveillance. To gain insight into evasive resistance mechanisms, we profiled the expression of immunoregulatory ligands by HSC and showed that HSC dynamically express CD80, a B7-family ligand that suppresses NK and T cell responses. Using a mouse model of acute-on-chronic alcohol consumption, we show that combined blockade of the CTLA-4//TIGIT/PD-1 inhibitory checkpoints overcomes this resistance mechanism, promoting the selective elimination of activated HSC (aHSC)/Myo, yet fails to diminish fibrosis or ameliorate liver function. Single-cell transcriptome profiling of liver non-parenchymal cells revealed that checkpoint blockade promotes hepatic infiltration of pro-fibrotic Th1 and Th17 T cell subpopulations, while decreasing immunosuppressive Treg. Strikingly, antibody-directed engagement of the PD-1 and TIGIT checkpoints also fails to reduce fibrosis or improve liver function. Thus, selective targeting of aHSC/Myo may be necessary to achieve significant therapeutic benefit.
Open Access
Case Report
09 October 2025A Case Report of Telehealth Assessment for Adolescent Anxiety, Depression and COVID-Related Grief
Rates of anxiety and depression in children and adolescents have steadily risen over the past decade, and the arrival of COVID-19 exacerbated existing psychological problems for many youth. In the context of these increased rates and the pandemic lockdown, telepsychology, including virtual assessment, evolved as a cornerstone of mental health practice. There are salient benefits to telepsychology, most notably its convenience and accessibility, which have contributed to its expanded application across different types of problems and populations. At the same time, it can pose challenges in acquiring a comprehensive picture of client functioning. This article presents a case study of an adolescent with combined anxiety and depression who was referred for teletherapy during COVID-19, with an emphasis on the assessment intake. Results from a multi-method approach to the assessment are provided along with a brief discussion of treatment and future implications for the practice of telepsychology with youth and families.

Open Access
Review
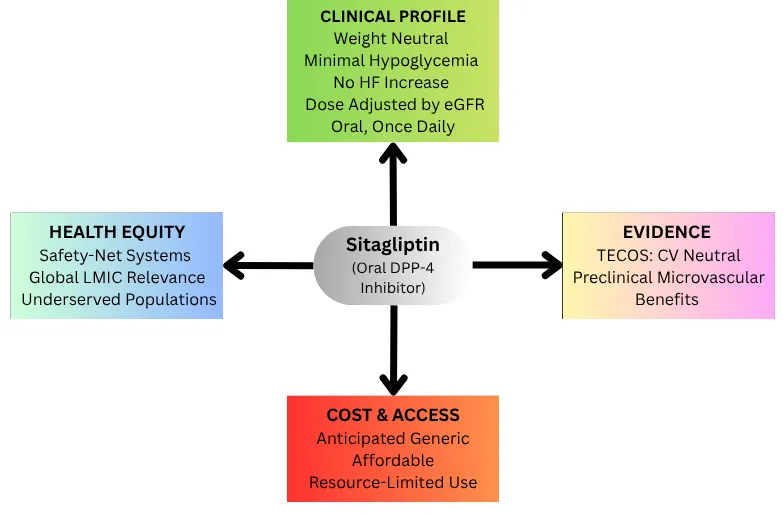
09 October 2025Sitagliptin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease: A Public Health and Health Equity Perspective
Type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease are interrelated conditions that disproportionately affect underserved populations, with compounded risk in communities facing systemic barriers to care. This review synthesizes clinical trial evidence, preclinical research, and public health perspectives to evaluate sitagliptin’s pharmacologic profile, safety, and potential vascular effects, particularly in resource-limited settings. Sitagliptin, the first FDA-approved oral DPP-4 inhibitor, demonstrates weight neutrality, minimal hypoglycemia risk, and renal dosing flexibility. Large cardiovascular outcomes trials confirm cardiovascular neutrality, while preclinical and animal studies suggest possible microvascular benefits. Despite superior cardiovascular outcomes with newer agents like GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors, sitagliptin remains a practical option for patients who cannot access or tolerate these therapies, supported by oral dosing, low side-effect burden, and anticipated generic availability in the US. Its continued value is evident in U.S. safety-net systems such as federally qualified health centers (FQHCs), and globally in low- and middle-income countries where newer drugs remain unaffordable. Achieving meaningful public health impact will require pairing pharmacologic safety with structural access improvements, including expanded insurance coverage, protection of safety-net drug pricing programs, culturally tailored interventions, and inclusive research practices. Sitagliptin illustrates a broader principle in chronic disease care: even safe therapies cannot close disparities until equitable access.
Open Access
Review
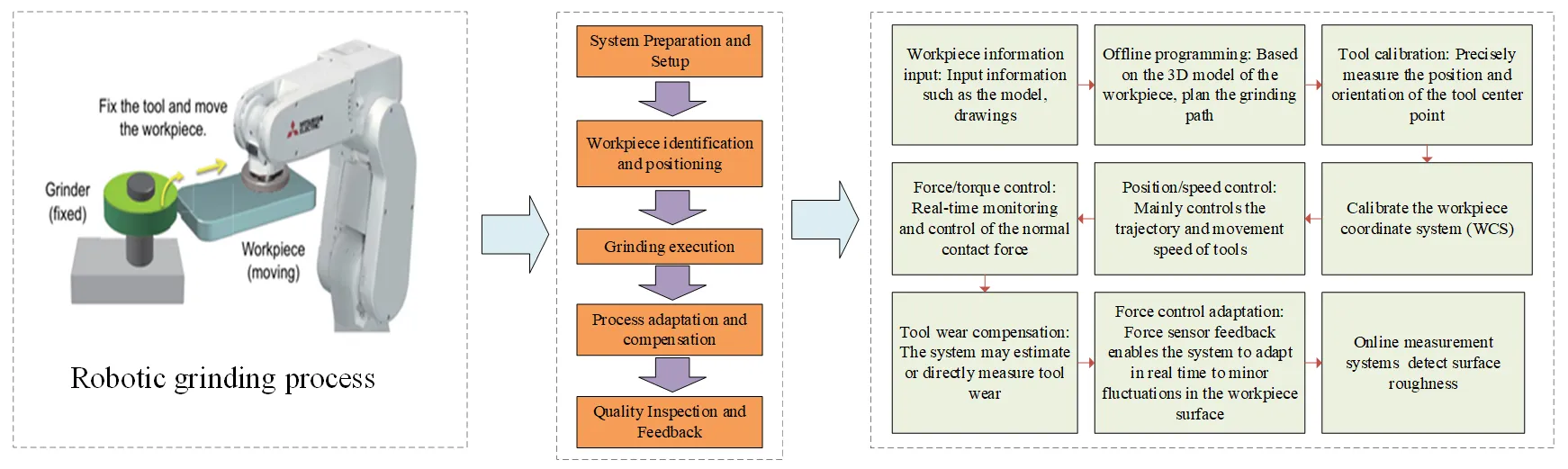
29 September 2025Robot Grinding: From Frontier Hotspots to Key Technologies and Applications
Robot grinding technology has shown broad application prospects in the field of machining complex curved parts due to its high flexibility, strong adaptability, and high automation. However, industrial robots are generally only suitable for rough machining, and for semi-finishing and finishing, improving the machining accuracy of robots and the surface quality of parts is a key issue. This paper summarizes the current research status of robot grinding and provides a reference for realizing robot precision grinding. At present, the research on robot grinding technology mainly focuses on robot pose control, force/position hybrid control strategy, intelligent machining path planning, vibration suppression technology, compliance control, and so on, aiming at solving the key bottleneck problems such as low machining accuracy, large grinding force fluctuation and poor surface quality consistency caused by insufficient robot stiffness. Firstly, the development history of the robot grinding system and the research status of process technology are summarized systematically. Secondly, the analysis focuses on grinding path planning, programming technology, and robot compliance force control technology. Finally, the current status of optimization research in robot grinding technology is summarized. The overarching purpose of this paper is to provide a systematic analysis and a comprehensive reference framework, aiming to address the core challenges hindering the achievement of high-precision, consistent surface quality in robotic grinding manufacturing. Based on the summarized state-of-the-art, robot grinding technology development trend is also predicted.