Found 764 results
Open Access
Article
25 November 2025Self-Determination of Adolescents with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities in China: Evidence from Students and Teachers
Self-determination is closely associated with individuals’ autonomy and independence and is crucial for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities. This study investigated the self-determination of adolescents with intellectual and developmental disabilities in China. Using the AIR Self-Determination Scale, data were collected from 116 students and 29 corresponding special education teachers. Findings indicated that the adolescent with intellectual and developmental disabilities had a moderate level of self-determination. However, teachers consistently rated students’ self-determination lower than students’ self-rating. Students’ self-evaluations of their self-determination were significantly influenced by geographic location, age, and disability severity, and teacher evaluations were affected by students’ age and disability severity, as well as teachers’ teaching experience and subject area. The study revealed that teachers face notable challenges in their conceptual understanding and pedagogical implementation of self-determination instruction. Based on these findings, recommendations are proposed across four domains: parents, teachers, schools, and broader society.

Open Access
Article
25 November 2025Dissimilar Joining of 316L and A131 Steel by Shield Metal Arc and Tungsten Inert Gas Welding to Evaluate Bending and Tensile Behavior
In this paper, the effect of filler metal and type of welding on the strength and ductility of dissimilar welding of two different grades of stainless steel was investigated. One of the benefits of stainless steel is its corrosion resistance, which is often necessary for equipment longevity in these facilities. During shipbuilding, as required, stainless steel 316L needs to be welded to the shipbuilding-grade carbon steel A131. In these applications, welding between the two should demonstrate superior strength during vessel construction. To provide a clear illustration, experimental work was needed to allow a careful selection of the joining procedure and filler metal or electrode. The current research work includes a comparative experimental analysis of dissimilar-metal welding (SS-316L & A131 steel). The reasons for choosing these two materials are their greater corrosion resistance and high strength in humid environments. Furthermore, two different welding methods (SMAW & TIG) with varying filler metals were employed in the experiment. The ultimate tensile strength and yield strength of the SMAW welds using E308-16 filler metal were the highest among all, while the TIG welds with ER308L showed superior bending strength. Observations suggest that SMAW with the E308-16 electrode exhibits superior tensile strength, while TIG joints with ER 308L filler provide better bending strength for the welding of SS-316L and shipbuilding (SB) grade A131 steels.
Open Access
Article
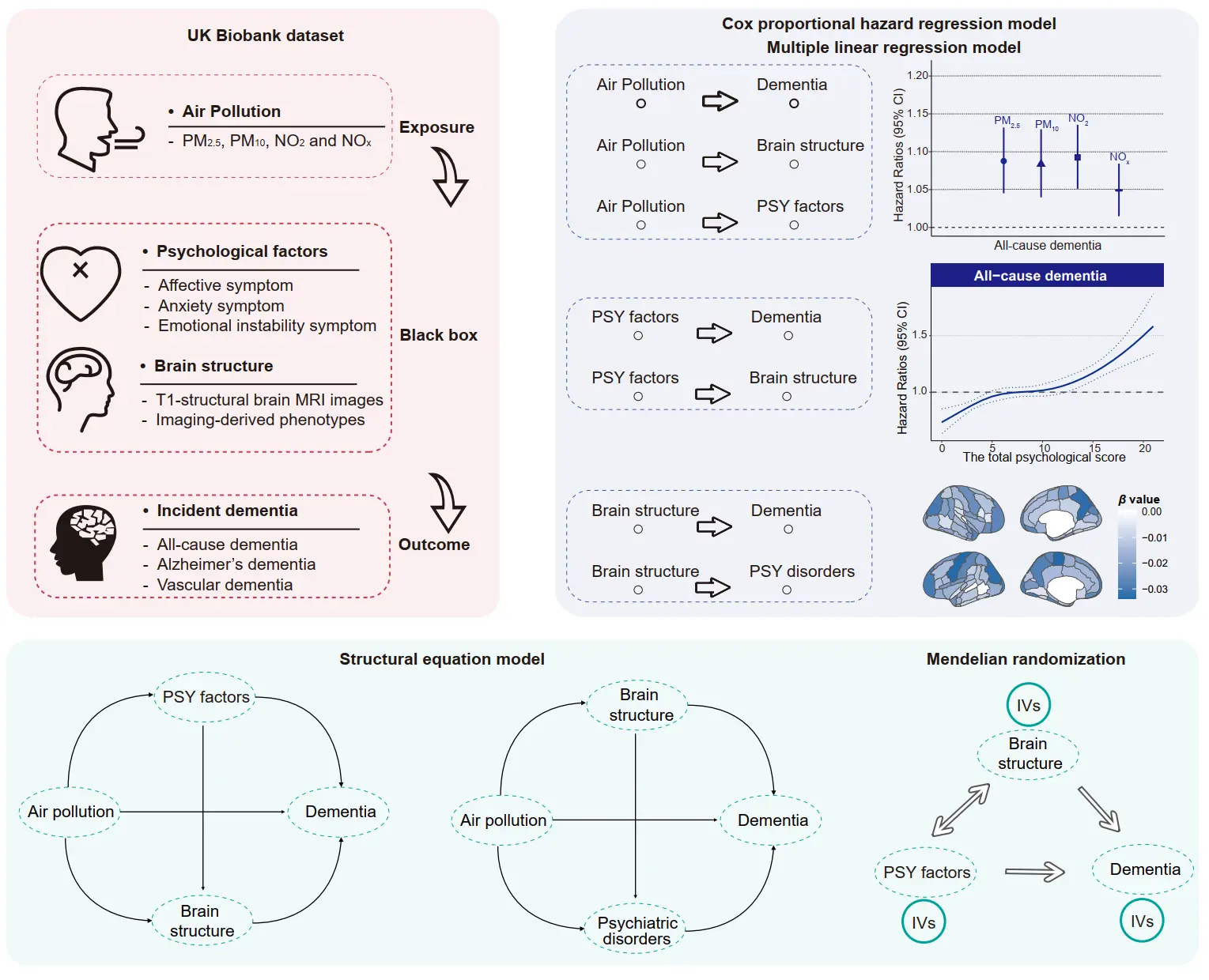
25 November 2025Ambient Air Pollution Exposure Influences Dementia through the Bidirectional Pathways of Psychological Factors and Brain Structure
Exposure to air pollution contributes to increased dementia risk, which may be mediated through its impact on psychological and brain structural changes. However, the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. We analyzed data from the UK Biobank of 263,095 participants aged 40 years and older. We examined the association between air pollution and incident dementia using Cox proportional hazard regression models. Mediation analysis was performed to explore the mediating roles of psychological and brain structural factors on these associations. Structural equation model (SEM) and bidirectional Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses were further employed to explore the potential pathways involving psychological factors and brain structure in this relationship. During an over 13-year follow-up, a total of 3039 dementia cases were identified. We observed significant associations between air pollution and dementia, with each interquartile range (IQR) increase in air pollution associated with a 5~9% increased risk of dementia. We observed that both psychological and brain structural factors mediated the air pollution-dementia association, particularly loneliness, social isolation, lack of enthusiasm, and reductions in volumes of the amygdala, hippocampus, temporal pole, and frontal pole, with mediation proportions ranging from 4.23% to 11.11%. SEM and MR analyses revealed bidirectional pathways linking air pollution exposure to dementia through psychological factors and brain structural changes: (1) air pollution → psychological disturbances → brain structural damage → dementia; (2) air pollution → brain structural damage → psychiatric disorders → dementia. These findings elucidate the interplay between psychological well-being and neuroanatomical integrity in mediating the neurocognitive impacts of air pollution, offering insights for targeted interventions to mitigate dementia risk associated with environmental exposures.
Open Access
Article
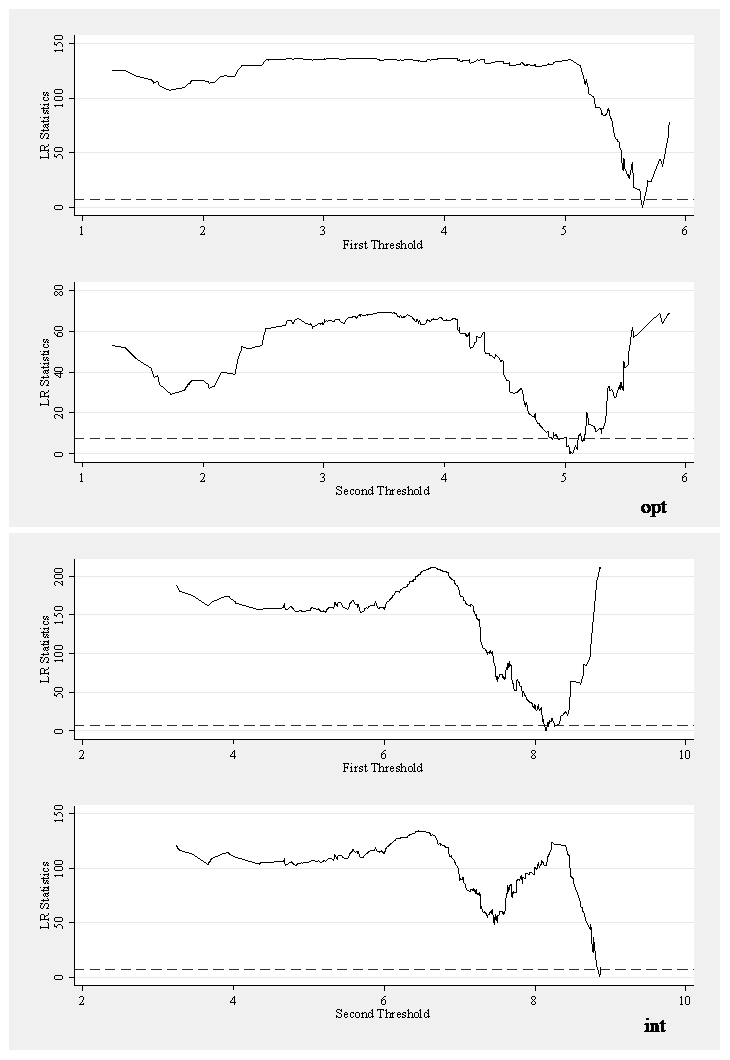
25 November 2025The Impact of Digital Infrastructure on Economic Resilience: Evidence from the Four Major Regions of China
Amid accelerating global structural changes and China’s transition to the digital-driven fourth industrial revolution, this paper examines the impact of digital infrastructure on economic resilience by clustering China’s 31 provinces into the four major economic regions during 2008–2022. Through the application of the Threshold Regression Model, Mediation Effect Model, and GTWR Model, the analysis reveals that digital infrastructure exhibits a threshold effect in enhancing economic resilience, with significant increasing marginal returns beyond specific scale thresholds. Regional heterogeneity is pronounced: the eastern region demonstrates amplified nonlinear benefits, while the northeast exhibits diminishing returns after crossing the threshold. Industrial diversification is an effective way for digital infrastructure to build resilience. The effects of industrial specialization, however, vary by region: it strengthens resilience in the east, weakens it in the central region, and shows no statistically significant impact in the western and northeastern regions. The findings provide empirical evidence for regionalized policymaking during technological paradigm shifts, highlighting the need to consider both digital infrastructure scale thresholds and industrial structure dynamics in economic resilience strategies.
Open Access
Article
24 November 2025Bridging the Urban-Rural Divide: How Urban Agriculture Enhances Food Security in High-Urbanized Regions in Guangdong, China
The COVID-19 pandemic starkly exposed vulnerabilities in global food supply chains, highlighting the critical need for resilient, localized alternatives to ensure urban food security. Urban agriculture (UA), which we define as all agricultural output occurring in cities with an urbanization rate exceeding 85%, emerges as a pivotal strategy to mitigate such risks by shortening supply chains, particularly for perishable goods like vegetables and fruits. This study investigates the underexplored role of UA in Guangdong Province, China—a region characterized by rapid urbanization, high population density, and economic dynamism- to assess its contribution to food self-sufficiency. Leveraging a novel classification framework, we categorize Guangdong’s 21 prefecture-level cities into two groups based on an 85% urbanization threshold (2017–2022), distinguishing high-degree urbanized cities (e.g., Shenzhen, Guangzhou) from others. Using panel data, we analyze spatial-temporal patterns in grain, vegetable, and fruit self-sufficiency through geospatial and statistical methods. Key findings reveal pronounced disparities: high-degree urbanized cities exhibit critically low grain self-sufficiency, relying heavily on external supplies, while non-urbanized regions achieve exceptional surpluses. Conversely, vegetables and fruits demonstrate a center-periphery gradient, with peri-urban zones bridging the gap between urban cores and rural surplus hubs. Despite incremental gains in UA productivity, urban yields lag behind non-urban areas for grains and vegetables, though fruit production shows convergence, underscoring UA’s niche potential. These results highlight the indispensability of non-urban regions in sustaining provincial food security while emphasizing UA’s role in fresher, faster urban supply chains. We propose actionable policies, including: (1) integrating farmland protection redlines with UA incentives (e.g., vertical farming subsidies, peri-urban logistics optimization); (2) scaling technology-driven UA (controlled-environment agriculture, digital platforms); and (3) reducing post-harvest losses through urban-centric infrastructure. Our findings advance the discourse on crisis-resilient food systems, offering a replicable framework for high-density regions globally.
Open Access
Article
21 November 2025Effect of Support Preparation Method on the Performance of Ni/SrTiO3 Catalysts for Dry Reforming of Methane
Dry reforming of methane (DRM) offers an efficient route to simultaneously convert CH4 and CO2 into synthesis gas (H2/CO), a key intermediate to produce fuels and valuable chemicals. Ni-based catalysts are regarded as the most promising candidates due to their high activity and low cost; however, their stability remains a major obstacle under the DRM conditions. Perovskite-type oxides such as SrTiO3 possess high thermal stability, tunable composition, and strong metal-support interactions, making them ideal to enhance the dispersion and durability of Ni species. In this study, Ni/SrTiO3 catalysts were synthesized via co-precipitation (CP), hydrothermal (HT), and sol-gel (SG) methods, and were comprehensively characterized before and after the reaction. The characterizations revealed that all samples preserved the perovskite framework after reduction and reaction. Among them, Ni/HT-STO and Ni/SG-STO exhibited larger surface areas (18.8 and 13.9 m2·g−1) and higher initial CH4 conversions (66.3% and 68.9%) than Ni/CP-STO (44.8%). However, Ni/HT-STO underwent rapid deactivation, with CH4 conversion decreasing to 21.2% after 60 h due to severe carbon accumulation (12.4 wt%) and notable Ni particle growth. In contrast, the sol-gel derived Ni/SG-STO maintained a higher activity (25.6% after 60 h) with moderate carbon deposition (9.2 wt%) and showed the smallest Ni particle growth of only 2.64 nm (from 14.91 to 17.55 nm), compared with 4.29 nm for Ni/CP-STO (25.83 to 30.12 nm) and 6.08 nm for Ni/HT-STO (27.12 to 33.20 nm). Temperature-programmed surface reaction (TPSR) analysis further revealed that Ni/SG-STO exhibited a more balanced CH4 activation and CO2 dissociation, enabling efficient carbon-oxygen coupling and inhibiting graphitic carbon formation. Overall, these results demonstrate that the sol-gel method effectively enhances the anti-sintering and anti-coking performance of Ni/SrTiO3 catalysts.

Open Access
Review
20 November 2025Vibrational Spectroscopy in Forensic Science: A New Frontier for Biopharmaceutical Drug Authentication
The global proliferation of counterfeit biologic medicines poses a growing threat to public health and pharmaceutical integrity. Traditional laboratory-based methods for verifying drug authenticity are often time-consuming, costly, and impractical for real-time or field-based applications. This paper explores the emerging potential of infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopy for forensic detection and authentication of biologics. While these technologies are currently underutilised in forensic science, advancements in instrumentation and data analysis are rapidly enhancing their sensitivity, portability, and usability. Focusing on protein- and peptide-based therapeutics, the paper reviews the principles and applications of IR and Raman spectroscopy, highlighting their ability to detect structural and compositional differences between authentic and counterfeit biologic drugs. The discussion emphasises the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between forensic and biopharmaceutical sciences. As counterfeiters become more sophisticated, the integration of non-destructive spectroscopic tools into forensic workflows offers a promising path toward the rapid and reliable screening of biologic drugs in both field and laboratory settings.

Open Access
Article
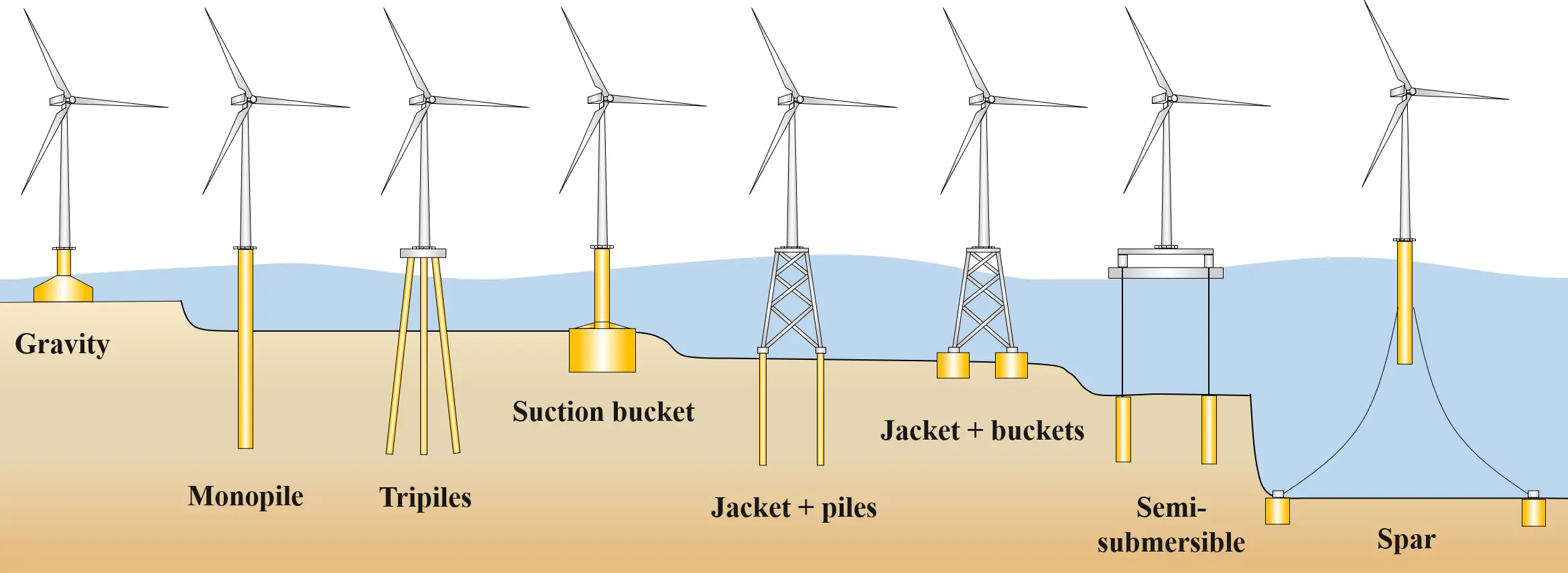
19 November 2025Effects of Platform Motions on Dynamic Responses in a Floating Offshore Wind Turbine Blade
Floating offshore wind turbines (FOWTs) offer great potential for harnessing deep-sea wind energy. This study examines the effects of six-degree-of-freedom (6-DOF) platform motions on the dynamic structural responses of a FOWT blade by comparing its performance with a fixed-bottom system. Integrated aero-hydro-servo-elastic simulations for a 5-MW spar-type FOWT were conducted under various design load cases. Results indicate that the floating tower’s first-order natural frequency was about 29% higher than that of the fixed-bottom tower. Platform motions markedly influenced blade flapwise and torsional responses, with the effect intensifying under larger waves. For instance, as the significant wave height increased from 1.70 m to 9.90 m, the differences in peak response between the floating and fixed-bottom systems grew from 0.104 m to 0.363 m for blade-tip flapwise deflection, from 528.1 kN·m to 1817.4 kN·m for the root flapwise bending moment, and from 5.02 kN·m to 18.73 kN·m for the root torsional moment. In contrast, blade edgewise responses showed negligible changes, with peak deflection differences below 0.05 m. Blade loads were more sensitive to wave conditions, while platform motion magnitudes were more affected by wind. These findings offer insights into the load characteristics and structural design of FOWT blades.
Open Access
Editorial
19 November 2025Patient Safety Matters with Use of Propofol in Critically Ill Patients
Despite its tendency to produce hypotension, propofol is used widely to induce general anesthesia and to facilitate endotracheal intubation in critically ill patients. Both dose reduction and routine co-administration of vasopressors have been used to offset this unfavorable hemodynamic effect in this subset of individuals. There are potential problems associated with each of these corrective measures, however, and criticism of other intravenous hypnotics used for this purpose—particularly etomidate—may be unwarranted. Choice of the appropriate pharmacology to induce anesthesia to assist with intubation should likely be based on individual clinical assessment, together with an understanding of the drug profile and realistic adverse effects.
Open Access
Article
19 November 2025Hydrogenative Depolymerization of Polyesters Catalyzed by a PN3-Ruthenium Complex Using Both H2 and EtOH as Hydrogen Sources
Selective hydrogenative depolymerization of polyesters to diols is regarded as a promising strategy for plastics upcycling. However, many catalysts documented in literature still involve harsh reaction conditions, such as high temperature and high H2 pressure. In this work, we present a PN3-ruthenium complex catalyzed polyesters upcycling into various highly value-added diols under mild reaction conditions using H2 as a hydrogen source. It is worth noting that PLA depolymerizes into 1,2-propanediol under 1 MPa hydrogen pressure at ambient temperature within 2 h; the conditions are much milder than those of previous reports. Aromatic polyester PET degradation needs harsher reaction conditions (80 °C, 4 MPa, 3 h). The different reaction conditions enable direct separation of the degradation products of PLA and PET mixture via sequential depolymerization, as well as mixing them with polyolefins (PE, PP, PS). More strikingly, this catalyst is also effective for the catalytic hydrogenation of polyesters in the presence of ethanol to afford various diols, avoiding the use of harsh reaction conditions and an expensive autoclave.