Dissimilar Joining of 316L and A131 Steel by Shield Metal Arc and Tungsten Inert Gas Welding to Evaluate Bending and Tensile Behavior
Received: 07 October 2025 Revised: 14 October 2025 Accepted: 18 November 2025 Published: 25 November 2025
© 2025 The authors. This is an open access article under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
1. Introduction
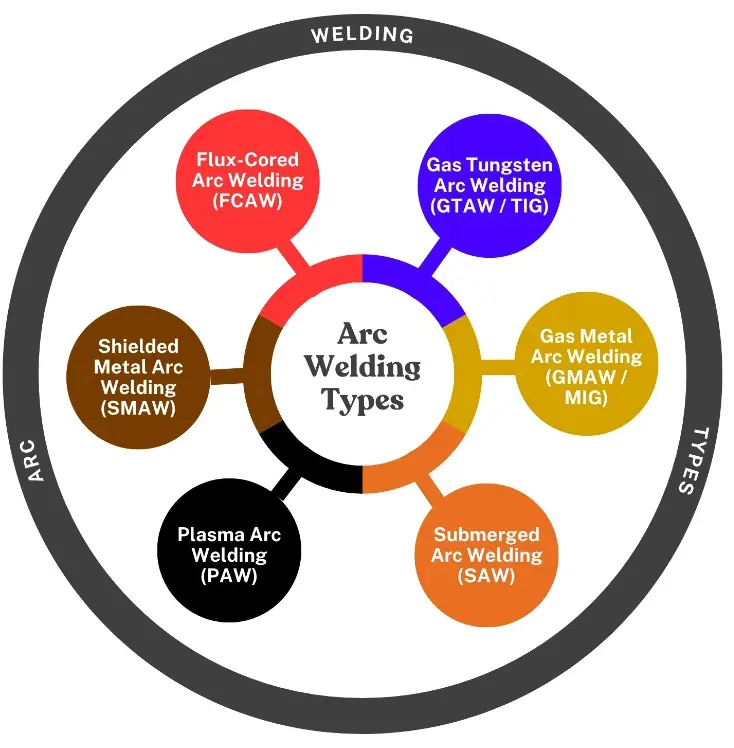
Fusion welding is considered the most significant and accessible process for joining materials by melting the edges and surfaces, with versatile applications in the automotive and construction industries for fabrication. The heat required for melting in fusion welding processes can be provided by various sources, such as electric arcs, gas flames, and high-energy beams [1]. However, the electric arc welding process is the widely utilized joining category of fusion welding, which encompasses Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG), Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW/MIG) [2,3], Submerged Arc Welding (SAW), Plasma Arc Welding (PAW), or Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) graphically illustrated in Figure 1.
Each of the aforementioned types of electric arc welding possesses distinct advantages and specific applications. For example, GTAW employs a non-consumable tungsten electrode with argon or helium as a shielding gas, and it is renowned for producing high-quality welds, particularly in aluminum alloys and stainless steels [4,5]. In contrast, GMAW is a semi-automatic or automatic process that utilizes a continuously fed wire electrode, with shielding gas delivered through the welding gun to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination. SMAW, on the other hand, offers notable advantages such as versatility, ease of use across various metals and positions, and cost-effectiveness, as it requires minimal equipment and uses self-shielded electrodes that eliminate the need for an external gas supply [6,7,8].
Welding dissimilar metals poses greater challenges than welding similar metals due to variations in their physical and chemical properties. Nonetheless, such joints are increasingly utilized in industries such as chemical processing, oil and gas, shipbuilding, and railways, providing sufficient strength and cost-effective solutions [9]. Among the various welding techniques, TIG welding is often preferred for dissimilar-metal joining because it produces high-quality, stable welds. However, the success of TIG welding largely depends on selecting appropriate welding procedures. In dissimilar-metal welding, choosing the proper filler material and welding method is one of the most critical factors. Recent research has focused on this area, exploring different welding techniques and material combinations [10]. In this regard, Ata et al. [11] examined the mechanical properties of ASTM A131 (Grade AH) steel joints fabricated using SAW, MIG, and PAW welding methods. Their findings indicated that welds produced by SAW and PAW had higher strength than those produced by MIG. Likewise, Mishra et al. [12] investigated the dissimilar welding of stainless steels (grades 202, 304, 310, and 316) with mild steel using TIG and MIG processes. They analyzed the percentage dilution and tensile strength of the dissimilar joints. They concluded that TIG-welded joints demonstrated superior physical and mechanical properties compared to those produced by the MIG process.
Based on dissimilar steel welding, Çelik et al. [13] conducted a study on joining 316L stainless steel and A106 carbon steel using TIG and SMAW processes, employing different welding parameters and electrodes, including 309L and Inconel 82 (ERNiCr-3). Consequently, the weldability of stainless and carbon steels using different filler metals was examined to evaluate their effects on mechanical properties. The findings indicated that welding with E309L stainless steel produced superior results compared to Inconel 182. On the other hand, Hajiannia et al. [14] investigated the mechanical properties of a dissimilar joint between AISI 347 austenitic stainless steel and ASTM A335 low-alloy steel via TIG welding, using two different filler metals (i.e., ER309L and ERNiCr-3). It was shown that the ERNiCr-3 filler was a better choice for dissimilar joining of 347 austenitic stainless steel to A335 low-alloy steel. Furthermore, Mamat et al. [15] conducted a study on dissimilar joining of 316L stainless steel to low-carbon steel via GTAW with ER316L and GMAW with ER309L welding electrodes, respectively. It was found that the welded samples using ER316L filler metal exhibited slightly higher yield and tensile strengths than those welded with ER309L.
Moreover, different types of stainless steel are reported in the literature to exhibit dissimilar weld joint behavior with variations in welding electrode [16,17]. Tandon et al. [18] reported the joining of 201 and 316L austenitic stainless steels using various filler electrodes, including 316L, 309L, and 309LMo, to produce dissimilar welds. The study investigated their microstructural evolution and mechanical properties. In addition, Pahlawan et al. [19] investigated dissimilar metal welding of 316L stainless steel and ST41 steel using the SMAW process, focusing on the effects of electrode types, specifically E309L and E6013. Tembhurkar et al. [20] conducted an experimental study on the dissimilar welding of 316L austenitic and 430 ferritic stainless steels using the GTAW process, both with fillers (ER316L and ER309L) and without fillers (autogenous). The mechanical properties were evaluated, revealing that the autogenous weld exhibited higher hardness compared to the ER316L and ER309L filler welds.
Careful selection of base materials, fillers, and electrodes is an essential parameter in dissimilar joining, as these factors have been emphasized in numerous studies focused on optimizing welding performance [21,22]. Based on this, R. Ramachandran et al. [23] studied the GTAW joining of austenitic stainless steel (316L), analyzing the effects of current, voltage, and gas flow rate to achieve optimal weld quality, mechanical properties, and minimal HAZ. The results identified an optimal parameter range for TIG welding of SS316L. Choudhury et al. [24] investigated TIG welding conditions to maximize the ultimate and breaking loads of weld specimens, considering current, gas flow rate, and filler rod diameter as key input parameters. However, modern joining methods such as laser welding, electron beam welding (EBW), and friction stir welding (FSW) are increasingly used to minimize the formation of a broad HAZ [25,26]. FSW is particularly popular today because it enables solid-state joining without high heat input [27], thereby improving strength and ductility by reducing distortion and residual stresses. The microstructure of FSW joints generally remains stable, except in the weld zone, where severe plastic deformation occurs during the initial weld and subsequent repair cycles [28,29].
In the shipbuilding (SB) industry, transition joints are commonly used to connect dissimilar metals, such as joining an aluminum or stainless steel (SS) superstructure to a mild steel (MS) lower deck. However, these transition joints are costly, making it essential to explore alternatives that can eliminate their use. This experimental study focuses on joining SB-grade steel with SS-316 to evaluate the feasibility of direct welding. A comparative analysis was conducted using TIG and SMAW to assess the tensile and bending strength of the welded joints. For each welding method, two different filler electrodes were employed to determine the most suitable combination for achieving superior mechanical properties, which are critical for shipbuilding applications. The evaluation criteria for optimal dissimilar-metal welds between SS-316L and SB-grade A131 steels included ultimate tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, and bending strength.
2. Experimental Methodology
2.1. Specimen Preparation
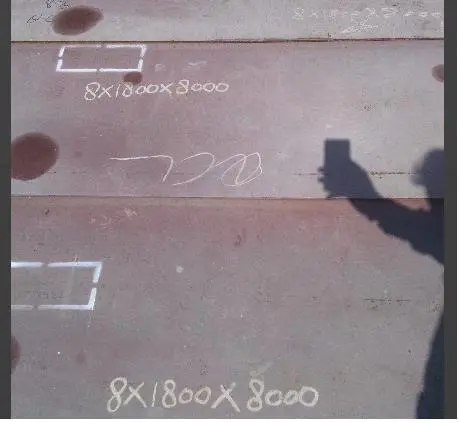
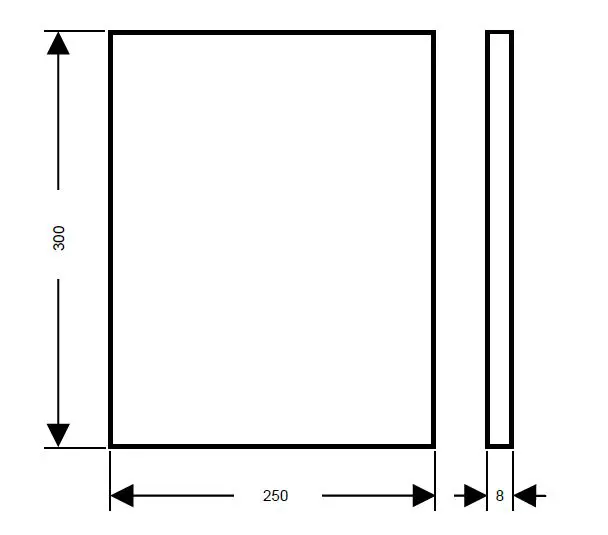
The first practical phase of this experiment involved arranging SB-grade plates. The corrosion-free plates used in this study are shown in Figure 2a. SS-316 and A131-AH plates of 8 mm thickness were procured for the experiment. The plates were cut using a CNC air plasma cutter to meet the minimum dimensions for a tensile specimen, as recommended by ASME, as shown in Figure 2b.
 |
 |
(a) |
(b) |
Figure 2. (a) Arrangement of shipbuilding grade plates, (b) Initail dimensions of individual steel plates (mm).
Cutting of Plates and Groove Development
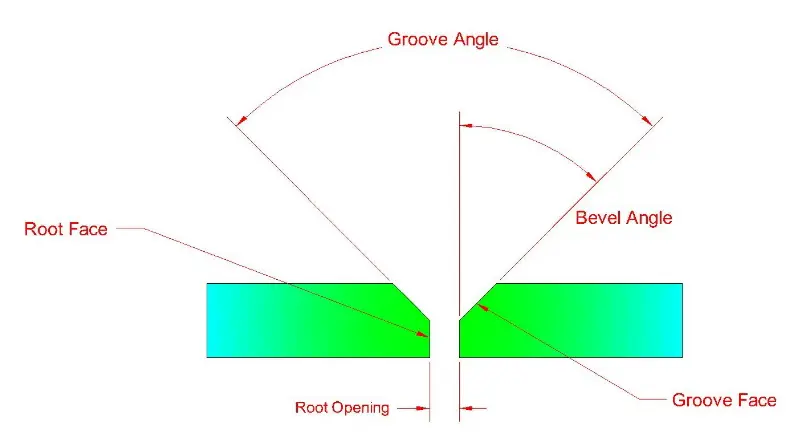
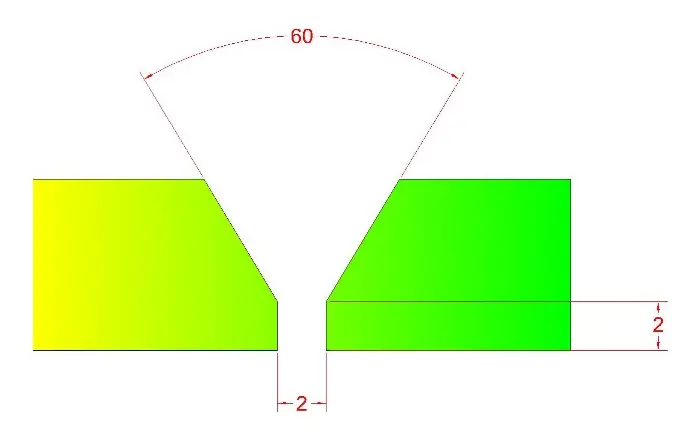
The plates were then cut from the middle to make arrangements for dissimilar steels. According to standards, welding plates with a thickness of 1/4-inch or greater should be prepared by beveling their edges or by J-, U-, or V-grooving, of which one is most applicable [30,31]. The details of the V-groove joint are shown in Figure 3, which illustrates the deep (full-penetration) joint and provides sufficient clearance for the electrode. Groove face lies at the bevel angle from the root face, as shown in Figure 4a, whereas Figure 4b depicts the sample arrangement on the welding platen for TIG and SMAW operations.
 |
 |
(a) |
(b) |
Figure 4. (a) Groove developed for the experiment, (b) arrangement of plates for TIG and SMAW operation execution.
Table 1 presents the mechanical properties of SS316L and A131-AH grade steels, as reported in the literature, following tensile and hardness testing. Base material properties are essential for comparing variations in welded joints, because joint strength depends entirely on several other factors.
Table 1. Base Material Mechanical Properties.
|
Material Type |
Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) |
Yield Strength (MPa) |
Hardness Brinell |
|---|---|---|---|
|
SS 316L |
512 |
207 |
150 |
|
A131-AH |
480 |
387 |
198 |
2.2. Welding Arrangement
Two welding machines were used in this study: one for SMAW and the other for TIG welding. First, the specimens were welded by TIG using ER308L and ER309L filler rods, and the next set was welded by SMAW using E308-16 and E309-16 electrodes. There are different parameters involved in these two types of welding processes that affect their application across various materials and environments. The main TIG and SMAW welding parameters used in this experiment, along with the corresponding filler rods, are listed in Table 2.
Table 2. Parameters of TIG and SMAW Welding.
|
Process |
Filler Rod |
Diameter (mm) |
Ampere Range |
Shielding Gas |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1st Pass |
2nd Pass |
3rd Pass |
||||
|
TIG (GTAW) |
ER 308L |
2.4 mm |
80 |
90 |
115 |
100% Argon |
|
TIG (GTAW) |
ER 309L |
2.4 mm |
80 |
90 |
115 |
100% Argon |
|
SMAW |
E 308-16 |
3.2 mm |
60 |
75 |
85 |
100% Argon |
|
SMAW |
E 309-16 |
3.2 mm |
60 |
75 |
85 |
100% Argon |
2.3. Tensile and Bending Test Specimens Extractions
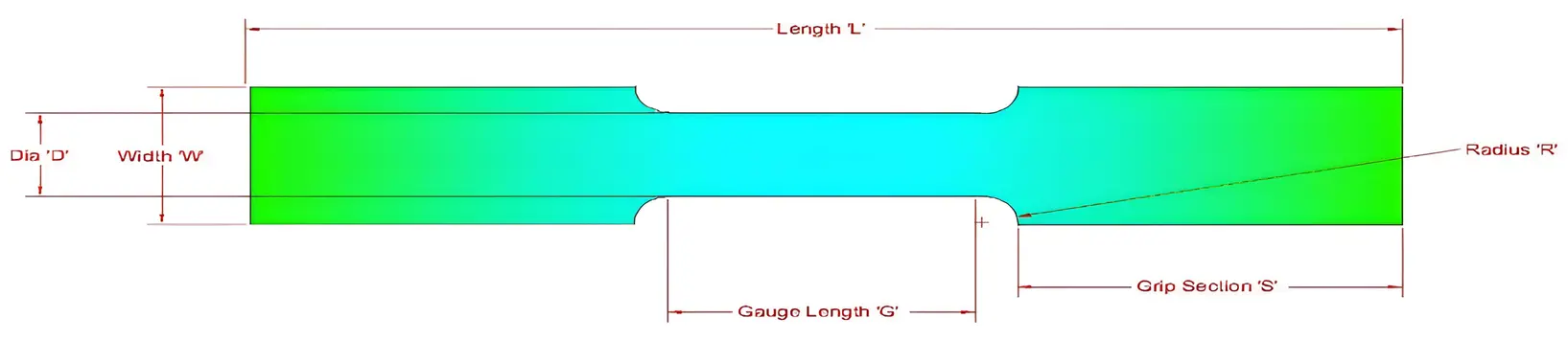
Test specimens are to be prepared in such a way that they are not subjected to any significant straining or heating, which might alter the properties of the material. Figure 5 represents four welded sample plates, which were later machined to determine the mechanical properties of all four welded plates. The tensile test measures key mechanical properties, including yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, elongation, and reduction of area. The graphical illustration of the tensile specimen and the actual extracted samples are shown in Figure 6a and Figure 6b, respectively. However, the dimensional details are provided in Table 3.
 |
|
(a) |
 |
|
(b) |
Figure 6. (a) Tensile specimen details, (b) Extracted tensile specimens from the welded plate.
Table 3. Dimensions of the tensile testing sample.
|
Length |
L |
300 mm |
|
Width of Grip |
W |
50 mm |
|
Diameter/Width of Gauge |
D |
25 mm |
|
Radius |
R |
25 mm |
|
Gauge length |
G |
35 mm |
|
Thickness |
T |
8 mm |
The weld runs transverse to the specimen’s longitudinal axis, which is bent so that the face surface becomes the convex side during testing. The extracted transverse face-bend specimen and its dimensions are shown in Figure 7.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Tensile Testing Results
The mechanical properties of dissimilar SMAW and TIG-welded stainless steel welds were evaluated after tensile testing. As investigated [31,32], the microstructure of SS-316 base metal consists of austenite and banded delta ferrite, whereas other research suggests that A131 base metal contains needle-like ferrite and pearlite phase structure [33].
It was observed that the UTS and yield strength of SMAW E308-16 weld metal were the highest among the other electrodes, which can be explained by the more uniform mixing of the austenitic phase in the weld with the base metal at the fusion zone, or by the absence of cracks or pores in the fusion zone [34]. Also, the average elongation for the E308-16 electrode was higher than that of all other electrodes, which may be due to the coarser grain size of the weld metal [35,36].
The UTS of specimens SMAW welded with E308-16 and E309-16 electrodes were 595.85 and 557.05 MPa, respectively, as shown in Table 4 and Table 5. In contrast, the average UTS of specimens TIG-welded with ER308L and ER309L filler rods was estimated at 562 and 556 MPa, respectively. The average UTS of the SMAW (E308-16 electrode) welded specimen was found to be 6.96% greater than that of the SMAW (E309-16 electrode) welded specimen. The average UTS of the TIG (ER308L filler rod) welded specimen was calculated to be 1.07% greater than that of the TIG (ER309L filler rod) welded specimen. SMAW (E308-16 electrode) welded specimen showed 1.86% increase in average yield strength compared with SMAW (E309-16 electrode) welded specimen, whereas TIG (ER308L filler rod) welded specimen showed 3.36% increase in average yield strength compared with TIG (ER309L filler rod) welded specimen. A slight increase of about 7.14% in average percent elongation of SMAW (E308-16 electrode) welded specimen compared with SMAW (E309-16 electrode) welded specimen was observed; however, TIG ER308L filler rod, welded specimen showed an increase in average percent elongation of about 2.75% compared with TIG (ER309L filler rod) welded specimen. Table 6 and Table 7 present tensile test data for all TIG-welded samples for comparative analysis.
The average UTS of SMAW E309-16 weld metal was lower than that of TIG ER308-L weld metal, which may be due to pores formed by entrapped gases in the liquid phase during solidification. The average yield strength of E309-16 weld metal was found to be greater than that of TIG weld metals, which may be due to the high carbon content (0.08%) in SMAW electrodes. However, the average elongations of these two were found to be equal, indicating the presence of internal defects in the E309-16 weld metal. It was also found that the fracture occurred at the HAZ to base metal direction for the case of both SMAW electrodes, and this ensures the high strength of the weld metal.
Figure 8 indicates the location of the fracture in the case of ER308-L and ER309-L, which were recognized at the weld zones due to greater stress concentration in these areas and significant residual stresses or internal flaws. The average yield strengths and elongations for both TIG-welded samples were the lowest, suggesting segregation.
Table 4. Average Tensile Test Results of SMAW E308-16 Electrode.
|
Tensile Sample E308-16 |
UTS (N/mm2) |
Average UTS (N/mm2) |
Yield Strength (N/mm2) |
Average Yield Strength (N/mm2) |
% Elongation |
Average % Elongation |
Fracture Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TS1 |
593.7 |
595.85 |
457.4 |
457.45 |
30 |
30 |
HAZ to BM |
|
TS2 |
598 |
457.5 |
30 |
HAZ to BM |
Table 5. Average Tensile Test Results of SMAW E309-16 Electrode.
|
Tensile Sample E309-16 |
UTS (N/mm2) |
Average UTS (N/mm2) |
Yield Strength (N/mm2) |
Average Yield Strength (N/mm2) |
% Elongation |
Average % Elongation |
Fracture Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TS1 |
555.8 |
557.05 |
421.6 |
422.75 |
28 |
28 |
HAZ to BM |
|
TS2 |
558.3 |
423.9 |
28 |
HAZ to BM |
Table 6. Average Tensile Test Results of TIG ER308-L Wire.
|
Tensile Sample ER308-L |
UTS (N/mm2) |
Average UTS (N/mm2) |
Yield Strength (N/mm2) |
Average Yield Strength (N/mm2) |
% Elongation |
Average % Elongation |
Fracture Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TS1 |
556 |
562 |
411 |
415 |
28 |
28 |
Weld |
|
TS2 |
568 |
419 |
28 |
Weld |
Table 7. Average Tensile Tests Results of TIG ER309-L Wire.
|
Tensile Sample ER309-L |
UTS (N/mm2) |
Average UTS (N/mm2) |
Yield Strength (N/mm2) |
Average Yield Strength (N/mm2) |
% Elongation |
Average % Elongation |
Fracture Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TS1 |
554 |
556 |
393 |
401.5 |
27.5 |
27.25 |
Weld |
|
TS2 |
558 |
410 |
27 |
Weld |
3.2. Face Bend Test Results
Three-point bending tests were performed on specimens using the UTM, and the specimens were subjected to 180° bending. By visual inspection, no crack openings were observed in the weld bead region and at the weld-base metal junction after face bend tests. Figure 9 shows the sample after the bending test. The tests revealed the bending strengths of the specimens for 180° bending; these are listed in Table 8.
The average bending strength of the TIG-welded specimen using ER 308-L filler rod was found to be the greatest among all (i.e., 167.5 N/mm2). The average bending strength of the SMAW, E309-16 electrode, welded specimen was found to be 11.03% greater than that of the SMAW, E308-16 electrode, welded specimen. In contrast, the TIG (ER308L filler rod) welded specimen showed an increase in average bending strength of about 3.71% compared with the average bending strength of the TIG (ER309L filler rod) welded specimen. This can be explained by the presence of impurities/phases oriented in a way that resists the applied moment, as all specimens showed approximately equal average percent elongation. Another reason for this high average bending strength could be the presence of residual stresses, which might be against the resisting moment. The lower average bending strength in SMAW welding compared with TIG welding may be due to the absence of these residual stresses or to the presence of pores/internal cracks [37,38,39,40]. The composition of the filler material, the abutting metals, and the welding condition can also affect the bending strength of the weld. Figure 10 compares the average UTS values for different weld configurations.
Table 8. Bending strengths of welds for 180° bending.
|
SMAW (E308-16) |
Specimen 1 |
146 N/mm2 |
|
Specimen 2 |
135 N/mm2 |
|
|
SMAW (E309-16) |
Specimen 1 |
155 N/mm2 |
|
Specimen 2 |
157 N/mm2 |
|
|
TIG (ER 308-L) |
Specimen 1 |
166 N/mm2 |
|
Specimen 2 |
169 N/mm2 |
|
|
TIG (ER 309-L) |
Specimen 1 |
155 N/mm2 |
|
Specimen 2 |
168 N/mm2 |
4. Conclusions
This study was conducted to evaluate the impact of different welding methods on the tensile and bending strengths of dissimilar joints used in shipbuilding steel to replace transition joints.
- i.
-
The average tensile strength of dissimilar joints welded using electrode E308-16 in the SMAW process was 594.5 N/mm2, which is higher than that obtained using E309-16 (557.5 N/mm2). This improvement in tensile properties can be attributed to the better flow characteristics of the former electrode and the formation of a more homogenized weld joint.
- ii.
-
The tensile strength of the joint produced by SMAW was slightly higher than that of the TIG-welded joint. This difference may be due to the higher hardness induced by a broader HAZ and the presence of non-uniform residual stresses. In TIG-welded samples, the weld zone exhibited relatively lower strength because of limited reinforcement and less homogenization of the weld metal. Consequently, TIG joints failed during tensile testing, with the fracture occurring within the weld region.
- iii.
-
The average bending strength of TIG-welded joints was higher than that of SMAW joints, which can be attributed to the narrower HAZ in TIG welding that enhances bending performance. In contrast, a wider HAZ in SMAW joints concentrates bending stresses due to its directional nature.
- iv.
-
Overall, the experimental results indicate that SMAW joints exhibit superior tensile strength, whereas TIG joints demonstrate better bending performance.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to provide special thanks to all the team members for providing support in the testing.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A. and F.R.; Methodology, M.A. and F.R.; Validation, M.A., F.R. and A.S.; Formal Analysis, F.R. and A.S.; Investigation, M.A., F.R. and A.S.; Data Curation, F.R., M.M. and M.S.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, M.A., F.R., M.M. and M.S.; Writing-Review & Editing, M.A., M.M. and M.S.; Visualization, F.R. and M.M.; Supervision, M.A.; Project Administration, M.A.
Ethics Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
-
Guia-Hernandez LA, Ochoa-Palacios RM, Costa PS, Altamirano-Guerrero G, Resendiz-Hernandez PJ, Facusseh-Valerio CA. Underwater welding: Evaluation of the structural characteristics of the fusion zone generated in an A36 structural steel welded by FCAW-S. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2025, 137, 5247–5265. doi:10.1007/s00170-025-15461-7. [Google Scholar]
-
Hewett P. The particle size distribution, density, and specific surface area of welding fumes from SMAW and GMAW mild and stainless steel consumables. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1995, 56, 128–135. doi:10.1080/15428119591017150. [Google Scholar]
-
Haider SF, Quazi MM, Bhatti J, Bashir MN, Ali I. Effect of Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) parameters on mechanical properties of low-carbon, mild and stainless-steel welded joints: A review. J. Adv. Technol. Eng. Res. 2019, 5, 191–198. doi:10.20474/jater-5.5.1. [Google Scholar]
-
Muzamil M, Wu J, Samiuddin M, Majeed A, Zhang Z. The response of heat-treatable filler on non-heat-treatable aluminum alloy substrate against age hardening cycle for intelligent development of surface welded joints using TIG welding process. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 229. doi:10.1007/s40430-019-1731-x. [Google Scholar]
-
Shah LH, Ishak M. Review of research progress on aluminum–steel dissimilar welding. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 29, 928–933. doi:10.1080/10426914.2014.880461. [Google Scholar]
-
Shazad A, Astif M, Uzair M, Zaidi AA. Evaluation of preheating impact on weld residual stresses in AH-36 steel using finite element analysis. Mem. Investig. En Ing. 2024, 225–243. doi:10.36561/ING.26.14. [Google Scholar]
-
Alkahla I, Pervaiz S. Sustainability assessment of shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) process. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017, Volume 244, No. 1, p. 012001. [Google Scholar]
-
Zumelzu E, Sepulveda J, Ibarra M. Influence of microstructure on the mechanical behaviour of welded 316L SS joints. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1999, 94, 36–40. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(98)00450-6. [Google Scholar]
-
Edy DL, Wahyudi BA. Analysis of Wire Feeder Speed and Gas Flow Rate on the Mechanical Properties of SS316 Metal GMAW Welding. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Research Symposium on Advanced Engineering and Vocational Education (IRSAEVE), Malang, Indonesia, 1 September 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 19–23. [Google Scholar]
-
Kumar AS, Sharma SK, Shukla AK. Microstructural, mechanical, and thermal analysis of SS316L weldment for marine engineering application. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024, 33, 13502–13515. doi:10.1007/s11665-023-08906-1. [Google Scholar]
-
Ata F, Calık A, Ucar N. Investigation on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ASTM A131 steel manufactured by different welding methods. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2022, 22, 32–40. doi:10.2478/adms-2022-0017. [Google Scholar]
-
Mishra RR, Tiwari VK, Rajesha S. A study of tensile strength of MIG and TIG welded dissimilar joints of mild steel and stainless steel. Int. J. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 3, 23–32. doi:10.14810/ijamse.2014.3203. [Google Scholar]
-
Çelik ETŞ, Çelik BE, Talaş Ş. Weldability study of dissimilar joints of A312 TP316L and A106 Gr. B steels using GTAW and SMAW with ER309L, ER309L-15, INCONEL 82 and INCONEL 182 electrodes. Türk Doğa ve Fen Dergisi 2022, 13, 41–48. doi:10.46810/tdfd.1496947. [Google Scholar]
-
Hajiannia I, Shamanian M, Kasiri M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI 347 stainless steel/A335 low alloy steel dissimilar joint produced by gas tungsten arc welding. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 566–573. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2013.03.029. [Google Scholar]
-
Mamat MF, Hamzah E, Ibrahim Z, Majid RA, Bahador A. Effect of filler metals on the microstructures and mechanical properties of dissimilar low carbon steel and 316L stainless steel welded joints. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Wollerau, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 819, pp. 57–62. [Google Scholar]
-
Kumar R, Sirohi S. Comparative Evaluation of Ni-Based Electrodes for Shielded Metal Arc Dissimilar Welding of P91 and AISI 310 Steels: Microstructure and Mechanical Performance. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, doi:10.1007/s11665-025-11732-2. [Google Scholar]
-
Mahajan S, Chhibber R. Investigations on dissimilar welding of P91/SS304L using Nickel-based electrodes. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2020, 35, 1010–1023. doi:10.1080/10426914.2020.1755041. [Google Scholar]
-
Tandon V, Patil AP, Kowshik S. Impact of filler electrodes on welding properties of dissimilar welded 316L/201 austenitic stainless steels. Eng. Proc. 2023, 59, 90. doi:10.3390/engproc2023059090. [Google Scholar]
-
Pahlawan IA, Arifin AA, Marliana E, Irawan H. Effect of welding electrode variation on dissimilar metal weld of 316L stainless steel and steel ST41. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1010, p. 012001. [Google Scholar]
-
Tembhurkar C, Kataria R, Ambade S, Verma J, Sharma A, Sarkar S. Effect of fillers and autogenous welding on dissimilar welded 316L austenitic and 430 ferritic stainless steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 1444–1453. doi:10.1007/s11665-020-05395-4. [Google Scholar]
-
Shazad A, Uzair M. Impact of quenching medium on tensile properties and hardness of 15CDV6 TIG welded joints. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2025, 66, 701–707. doi:10.1007/s11041-025-01106-9. [Google Scholar]
-
Muzamil M, Wu J, Akhtar M, Azher K, Majeed A, Zhang Z, et al. Nanoparticle-induced control (MWCNTs–TiO2) on grain size and tensile strength response and multi-response optimization on TIG welded joints. Trans. Can. Soc. Mech. Eng. 2022, 46, 626–638. doi:10.1139/tcsme-2021-0210. [Google Scholar]
-
Ramachandran R. Analysis and experimental investigations of weld characteristics for a TIG welding with SS316L. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. (IJAER) 2015, 10, 2454–1796. [Google Scholar]
-
Choudhury N, Bandyopadhyay A, Rudrapati R. Design optimization of process parameters for TIG welding based on Taguchi method. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2014, 2, 12–16. doi:10.14741/ijcet/spl.2.2014.03. [Google Scholar]
-
Ghari H, Taherizadeh A, Sadeghian B, Sadeghi B, Cavaliere P. Metallurgical characteristics of aluminum–steel joints manufactured by rotary friction welding: A review and statistical analysis. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 2520–2550. doi:10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.03.089. [Google Scholar]
-
Sadeghi B, Shamanian M, Ashrafizadeh F, Cavaliere P, Rizzo A. Friction stir processing of spark plasma sintered aluminum matrix composites with bimodal micro- and nano-sized reinforcing Al2O3 particles. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 32, 412–424. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.03.013. [Google Scholar]
-
Liu FC, Hovanski Y, Miles MP, Sorensen CD, Nelson TW. A review of friction stir welding of steels: Tool, material flow, microstructure, and properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 39–57. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2017.10.024. [Google Scholar]
-
Laska A, Sadeghi B, Sadeghian B, Taherizadeh A, Szkodo M, Cavaliere P. Temperature evolution, material flow, and resulting mechanical properties as a function of tool geometry during friction stir welding of AA6082. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 10655–10668. doi:10.1007/s11665-023-08671-1. [Google Scholar]
-
Shazad A, Muzamil M, Ali J, Adil S, Latif A, Khan SY. Influence of Dual Soaking Durations and Variable Tool Feed Rates on Tensile Behavior of Friction Stir Welded Aluminum 2219. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Wollerau, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 1164, pp. 15–25. [Google Scholar]
-
Sahin M. Joining of stainless-steel and aluminium materials by friction welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 41, 487–497. doi:10.1007/s00170-008-1492-7. [Google Scholar]
-
Üstündağ Ö, Bakir N, Gook S, Gumenyuk A, Rethmeier M. Hybrid laser-arc welding of laser- and plasma-cut 20-mm-thick structural steels. Weld. World 2022, 66, 507–514. doi:10.1007/s40194-022-01255-y. [Google Scholar]
-
Liu D, Wang W, Zha X, Guo R, Jiao H, Zhao L. Effects of groove on the microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar steel welded joints by using high-entropy filler metals. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 13, 173–183. doi:10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.04.060. [Google Scholar]
-
Wan Y, Jiang W, Li H. Cold bending effect on residual stress, microstructure and mechanical properties of Type 316L stainless steel welded joint. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 117, 104825. doi:10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.104825. [Google Scholar]
-
Zhou X, Zhao H, Liu F, Yang B, Chen B, Tan C. Influence of energy ratio on microstructure and mechanical properties in the transition zone of hybrid laser-MIG welded AH36/316L dissimilar joints. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 4487–4501. doi:10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.10.046. [Google Scholar]
-
Mostafanejad A, Iranmanesh M, Zarebidaki A. An experimental study on stress corrosion behavior of A131/A and A131/AH32 low carbon steels in simulated seawater. Ocean Eng. 2019, 188, 10620. doi:10.1016/j.oceaneng.2019.106204. [Google Scholar]
-
Ibrahim IR, Khedr M, Mahmoud TS, Abdel-Aleem HA, Hamada A. Study on the mechanical performance of dissimilar butt joints between low Ni medium-Mn and Ni-Cr austenitic stainless steels processed by gas tungsten arc welding. Metals 2021, 11, 1439. doi:10.3390/met11091439. [Google Scholar]
-
He Y, Xing Z. Investigations on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of SUS 304 austenitic stainless steel welded joints by pulsed current gas tungsten arc welding. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 088001. doi:10.1088/2053-1591/ab1b85. [Google Scholar]
-
Rafiei M, Mostaan H. The effect of filler metal and butter layer on microstructural and mechanical properties of pure Cu to AISI304 stainless steel dissimilar joint. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2019, 233, 1894–1905. doi:10.1177/1464420718796042. [Google Scholar]
-
Kumar DS, Srikar P. A review on comparison of mechanical properties of dissimilar steels welded by TIG and MIG. In E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2020; Volume 184, p. 01030. [Google Scholar]
-
Alwan AH. Modeling of bending properties of stainless steel 304 sheets welded by tungsten inert gas welding process. Al-Khwarizmi Eng. J. 2019, 15, 10–22. doi:10.22153/kej.2019.09.003. [Google Scholar]