Found 764 results
Open Access
Article
14 May 2025Age Differences and Underlying Psychological Mechanisms in Short Video Use: From an Adult Lifespan Perspective
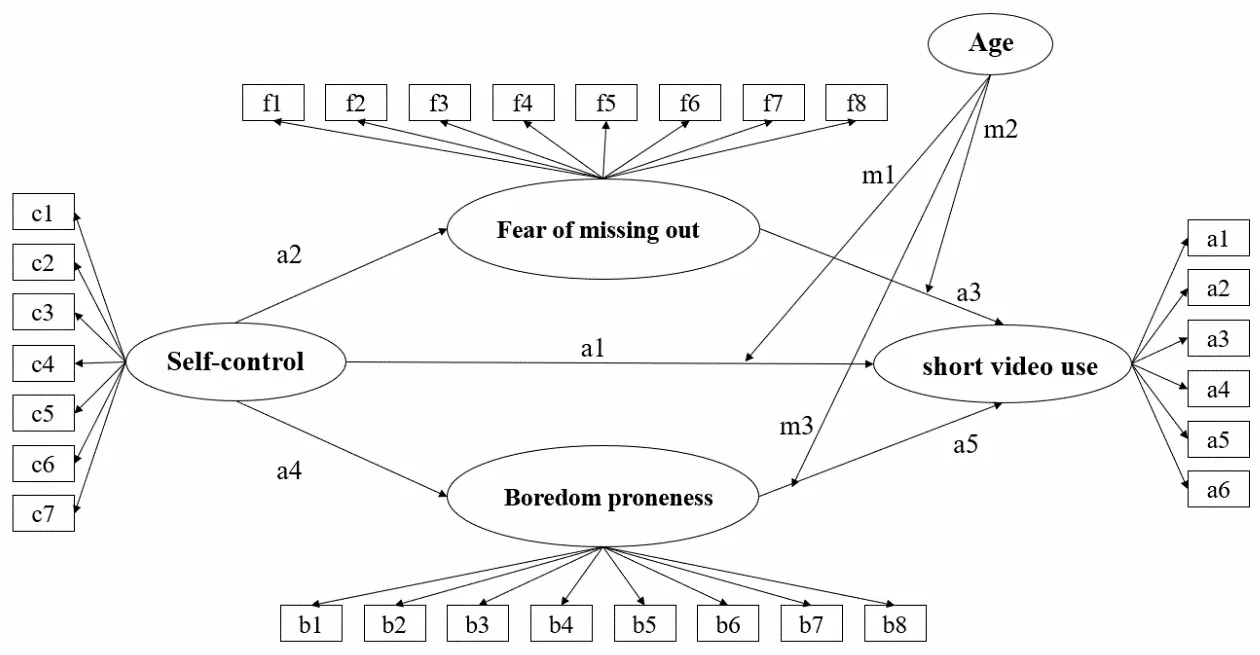
Short videos attract users across various age groups; however, studies focusing on single populations, such as adolescents, have limited the understanding of possible age-related changes and differences in short video use. The aim of this study was to examine age trends in short video use and to identify age differences in the psychological mechanisms underlying use behaviors. A total of 1006 adults aged 18–83 years participated in the study and completed a battery of assessments, including short video use, self-control, social motivation, and covariates. The results showed that age moderated the effects of boredom proneness and fear of missing out on short video use. Self-control was associated with people’s use behavior, and boredom proneness and fear of missing out mediated this association across age. Specifically, older adults’ use was more likely to be associated with alleviating boredom rather than fear of missing out, whereas both were associated with young adults’ use. Investigating these mechanisms may provide a better understanding of the factors that correlate with short video use and help target interventions to different age groups.
Open Access
Review
14 May 2025Current Status of Biological Production Using C2 Feedstocks
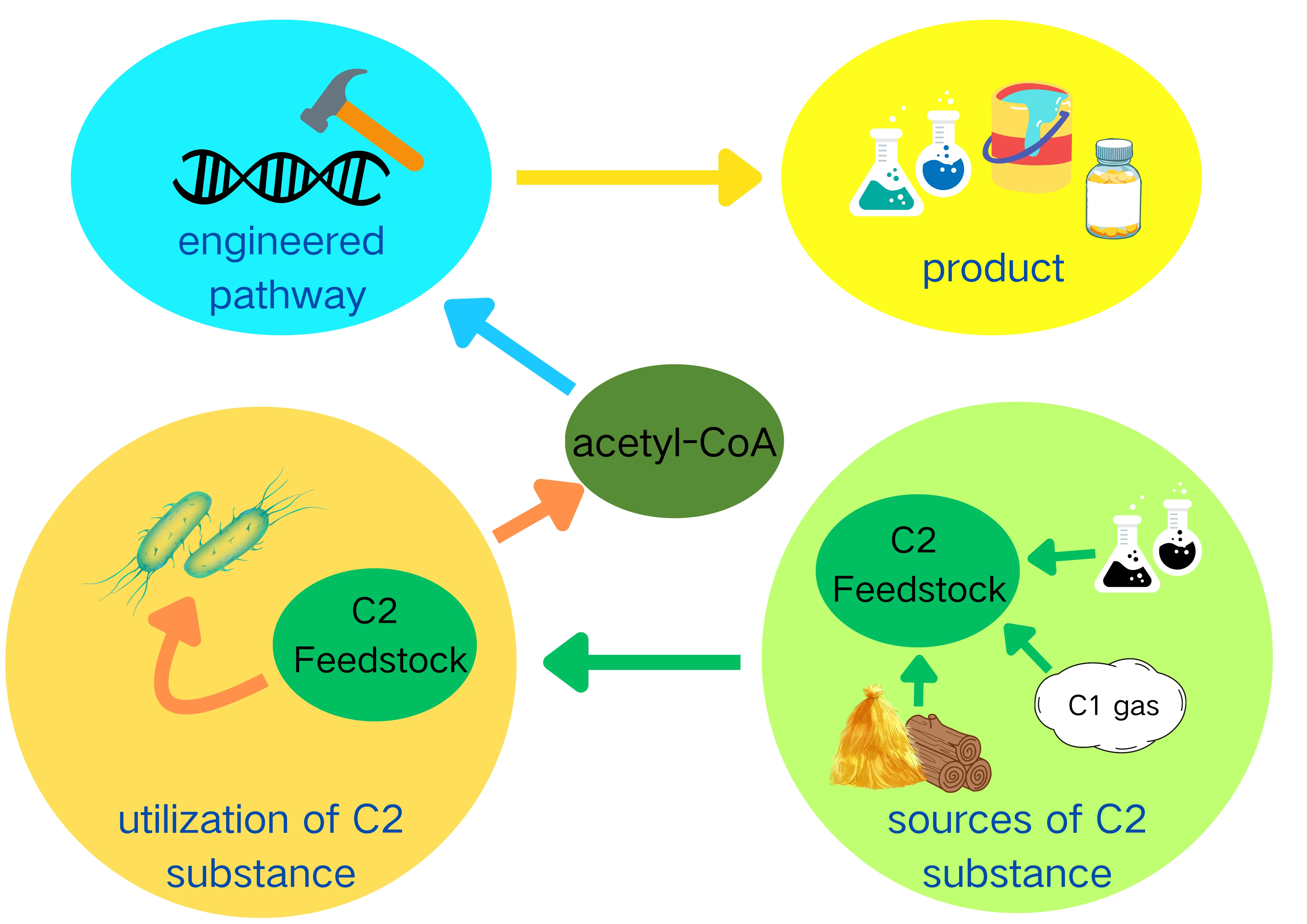
C2 feedstocks have emerged as promising carbon sources for the biological production of various value-added chemicals. Compared to the traditional C6/C5 sugars-contained/constituted feedstocks, C2 feedstocks have diverse and abundant sources, including non-food biomass, industrial by-products, and C1 gases. This diversification not only eliminates competition with human food demands but also aligns with environmental sustainability goals. Moreover, the metabolic route for C2 compounds to enter central carbon metabolism is more direct, which minimizes the carbon loss and enhances the efficiency of bio-based production processes. This review extensively analyzes three prominent C2 chemicals: ethylene glycol, ethanol, and acetate. After introducing the sources of those compounds, it details the metabolic pathways through which they are converted into acetyl-CoA in vivo. Several chemicals produced from these C2 feedstocks in fermentation are also exemplified. Furthermore, different perspectives are proposed to promote the efficient utilization of C2 feedstocks.
Open Access
Article
12 May 2025Drone Operation with Human Natural Movement
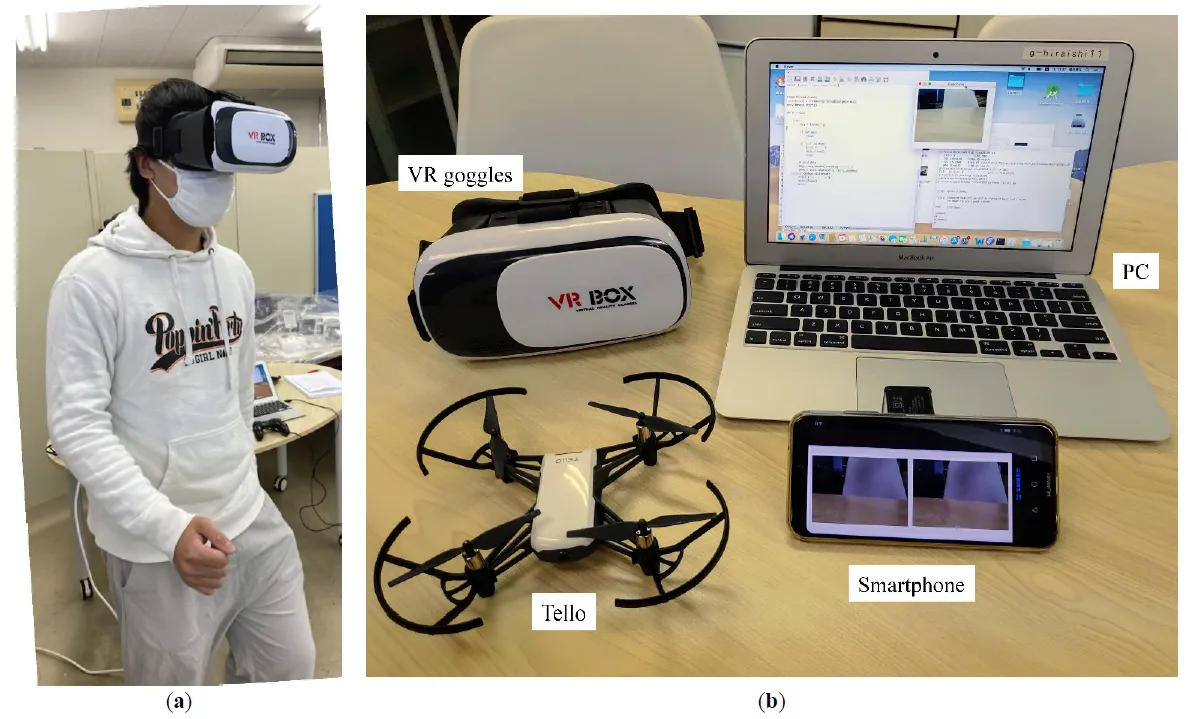
This study proposes a method for operating drones using natural human movements. The operator simply wears virtual reality (VR) goggles. An image from the drone camera was displayed on the goggles. When the operator changes the direction of his or her face, the drone changes the direction to match that of the operator. When the operator moves their head up or down, the drone rises or falls accordingly. When the operator walks in place, rather than walking, the drone moves forward. This allows the operator to control the drone as if they were walking in the air. Each of these movements was detected by the values of the acceleration and magnetic field sensors of the smartphone mounted on the VR goggles. A machine learning method was adopted to distinguish between walking and non-walking movements. Compared with operation via conventional remote control, it was observed that the remote controller performed better than the proposed approach in the early stages. However, when the participants familiarized themselves with the natural operation, these differences became relatively small. This study combined drones, VR, and machine learning. VR provides drone pilots with a sense of realism and immersion, whereas machine learning enables the use of natural movements.
Open Access
Article
09 May 2025Modeling and Assessing Economical Feasibilities for Waste to Energy Conversion/Incineration Process in Context of Municipal Solid Waste
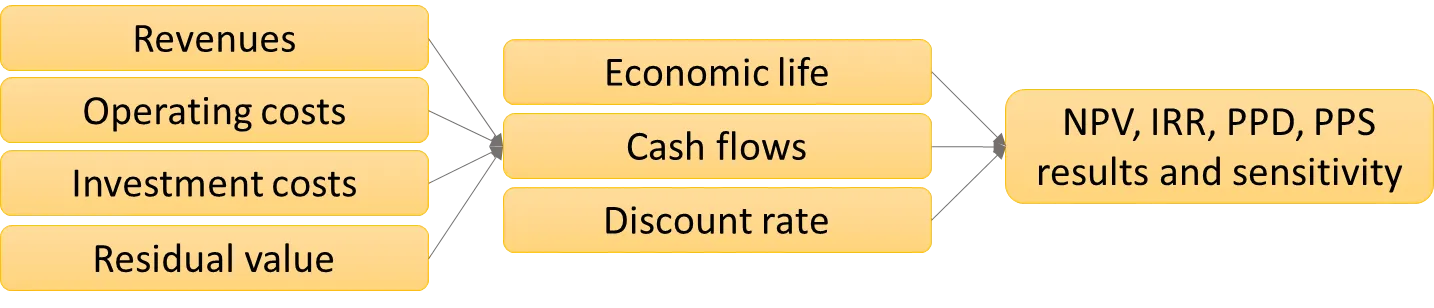
At the time of the study, most of the municipal waste, including solid municipal waste, in the city of St. Petersburg and in the connected larger Leningrad region is processed by landfilling. This sort of waste processing in open landfills causes environmental damage, uncontrollable landfill fires, bad and dangerous odors, nearby rivers/streams, groundwater pollution, CH4 and CO2 emissions, to mention a few. Additionally, landfilling is a waste of energy and material resources present in the content dumped into landfills. In this context, Waste-to-Energy (WtE) incineration is a process that we use to recover the energy the materials have back to usable form, which we use in the form of heat and electricity. Even though a lot of resources and energy are available in the (municipal solid) waste, it does not mean that recovering it would always make sense. Our study analyses and estimates the profitability of a WtE incineration plant(s) in the city of St. Petersburg and the connected Leningrad region. With the available data and following analysis, we have concluded that the WtE incineration is economically feasible in this specific region and city areas, given that the implementations follow more traditional (economically less expensive and easier) technical and process model solutions. As a note of results stability, it needs to be pointed out that the changes in estimates of gate fees, cost of electricity and heat, and so on do impact the economic feasibility a lot, and larger scale changes in the assumed revenues would have a high impact on the outcome of repeatability of the results.
Open Access
Article
08 May 2025Vulnerability Assessment of Food Crop Production and Climate Change: Implication for Agricultural Productivity and Development in Nigeria
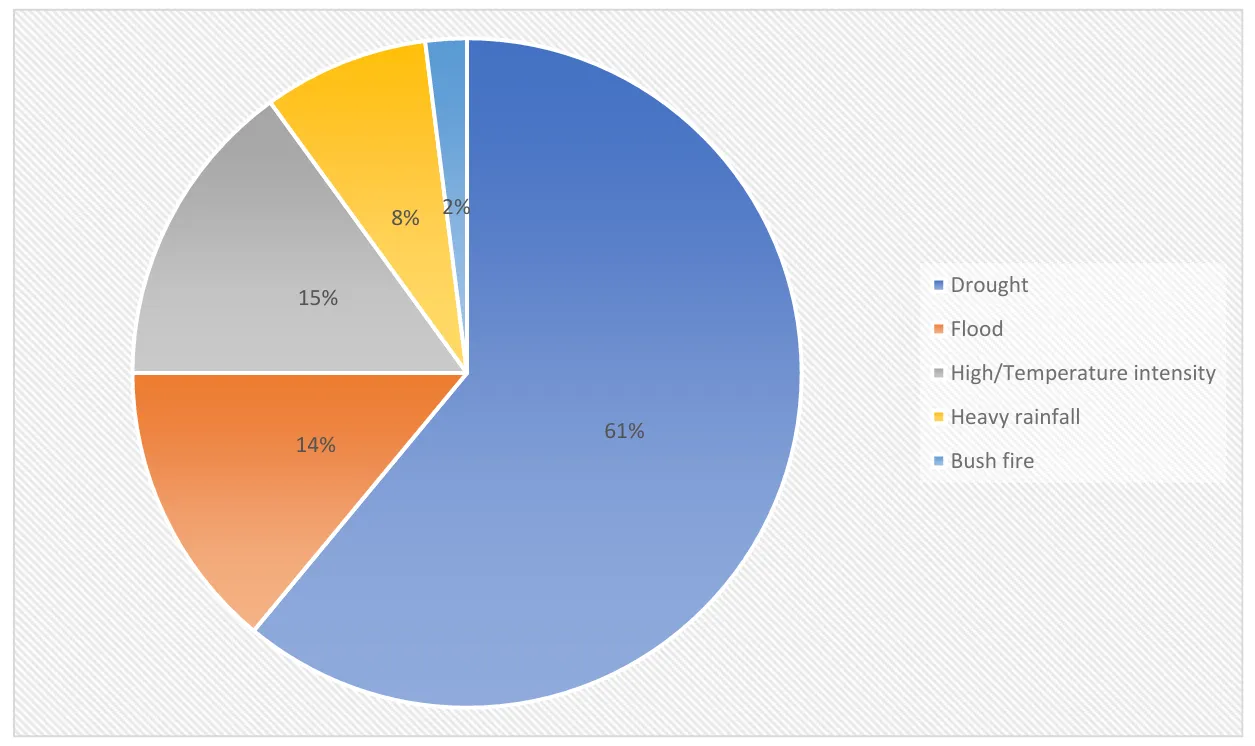
Climate change poses significant challenges to agriculture, particularly in developing nations like Nigeria, where the sector is highly dependent on vulnerable rain-fed farming systems. Extreme weather events such as prolonged droughts, erratic rainfall, flooding, and rising temperatures threaten agricultural productivity, food security, and rural livelihoods. This study examines the vulnerability of food crops to climate change, focusing on smallholder farmers’ perceptions and adaptation strategies. Using a multistage sampling technique, data were collected from 480 smallholder farmers across selected agro-ecological zones in Nigeria. The study employed descriptive statistics and a crop vulnerability scale to assess the susceptibility of key food crops—maize, cassava, sorghum, rice, millet, soybean, and yam—to climate extremes. Findings reveal that drought is the most critical climate-induced stressor affecting food crops, with maize and cassava exhibiting the highest vulnerability indices. Flooding also presents a substantial risk, particularly to maize, while temperature fluctuations have relatively less severe immediate impacts. The study highlights the importance of climate information dissemination, cooperative memberships, and extension services in enhancing farmers’ resilience. However, limited access to climate information remains a significant barrier to adaptation. Given the observed variability in crop vulnerability, it is recommended to implement targeted climate adaptation strategies such as drought-resistant crop varieties, improved drainage systems, and early warning mechanisms. This study underscores the urgent need for climate-smart agricultural policies and resilience-building measures to safeguard food production and rural livelihoods in Nigeria amid escalating climate change threats.
Open Access
Article
08 May 2025Nonlinear Optimal and Multi-Loop Flatness-Based Control for the 6-DOF Autonomous Bicopter
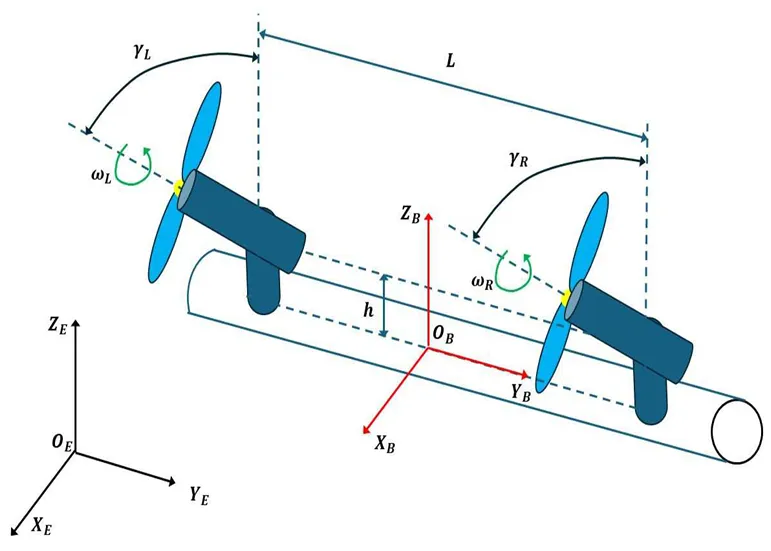
Bicopter UAVs can find use in several civilian and defence applications. In the present article a solution of the nonlinear optimal control problem of 6-DOF bicopters is first attempted using a novel nonlinear optimal control method. This method is characterized by computational simplicity, clear implementation stages and proven global stability properties. At a first stage, approximate linearization is performed on the dynamic model of the 6-DOF bicopter with the use of first-order Taylor series expansion and through the computation of the system’s Jacobian matrices. This linearization process is carried out at each sampling instance, around a temporary operating point. At a second stage, an H-infinity stabilizing controller is designed for the approximately linearized model of the 6-DOF bicopter. To find the feedback gains of the controller an algebraic Riccati equation is repetitively solved, at each time-step of the control method. Lyapunov stability analysis is used to prove the global stability properties of the control scheme. Next, the article examines a multi-loop flatness-based control method for the dynamic model of the 6-DOF bicopter. The drone’s dynamics is written in the form of two chained subsystems which are shown to be differentially flat. The state vector of the second subsystem becomes virtual control input to the first subsystem, while the control inputs of the first subsystem become setpoints for the second subsystem. Local controllers for the individual subsystems invert their dynamics. The global stability properties of the multi-loop flatness-based control scheme are also proven though Lyapunov analysis.
Open Access
Article
08 May 2025Evaluating Orthophoto Mosaic Accuracy Using RTK UAVs and AeroPoints 2 Ground Control Points: A User’s Perspective
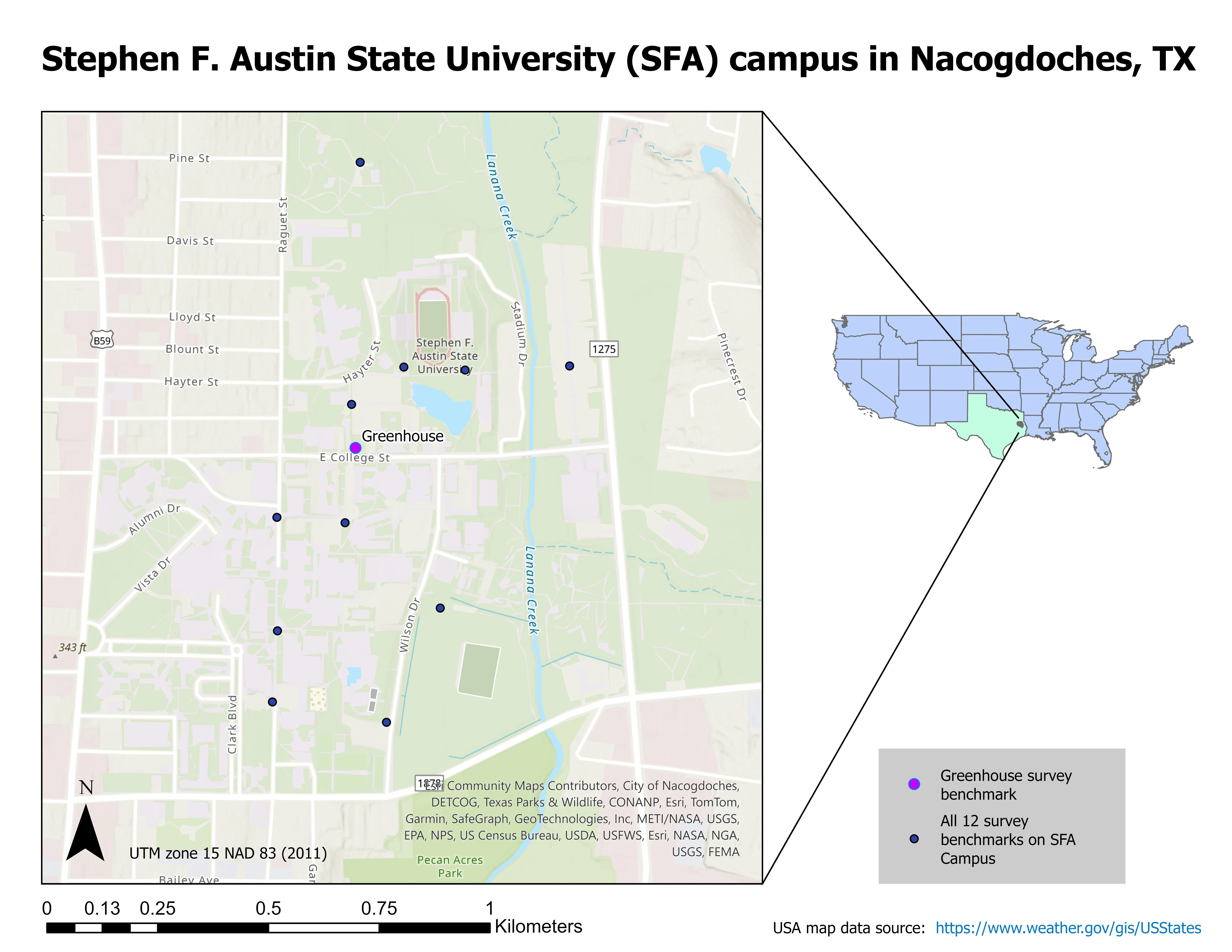
With the growing use of Real Time Kinematics (RTK) Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and advancements in ground control points (GCPs), assessing positional accuracy of UAV derived orthophoto mosaics is crucial. This study aimed to improve UAV aerial image accuracy for more reliable orthophoto mosaics by examining the positional accuracy of orthophoto mosaics derived with (1) an RTK UAV; and (2) an RTK UAV combined with AeroPoints 2 GCPs. We tested two GPS base station methods for the RTK UAV: self-determined and manually assigned coordinates. The manually assigned coordinates resulted in significantly lower root mean square error (RMSE = 0.0729 m) compared to the self-determined method (RMSE = 1.9762 m), indicating improved accuracy. For the AeroPoints 2 GCPs, we recorded coordinates from a central GCP at a known location and four additional GCPs placed in each cardinal direction. The AeroPoints 2 system showed lower RMSE at all points compared to the RTK, with the central GCP at 0.0136 m, indicating high accuracy. These findings suggest that while RTK UAVs improve accuracy with manual base station assignment, incorporating AeroPoints 2 GCPs provides consistently higher precision across multiple locations. The study highlights the potential of AeroPoints 2 GCPs and suggests further research opportunities to enhance RTK UAV accuracy in areas lacking GPS correctional networks.
Open Access
Review
06 May 2025Genetic Insights into Ancient Kinship and Human History: Methods, Applications, and Implications
Recent advances in ancient DNA analysis have transformed our understanding of kinship and underlying social structures in past populations. The application of next-generation sequencing technologies has enabled researchers to reconstruct the genetic makeup of ancient individuals with unprecedented precision, providing new insights into lineage, ancestry, and social organization. Ancient DNA evidence has revealed a wide range of kinship systems, including patrilineal and matrilineal descent, consanguineous marriages, female exogamy, and family-based burial practices. These findings underscore the complexity of human social relationships and the dynamic interactions between genetic inheritance, cultural traditions, and environmental factors in ancient societies. By examining case studies across different geographic and temporal contexts, this review highlights the transformative potential of ancient DNA in deciphering past human relationships. However, it also addresses key ethical concerns, including the importance of respecting cultural sensitivities and avoiding overly deterministic interpretations of genetic data. The integration of genetic evidence with archaeological and anthropological perspectives enables a more comprehensive reconstruction of ancient social systems, moving beyond simplistic genetic determinism to appreciate the intricate interconnections between biology, culture, and identity.

Open Access
Article
06 May 2025High-Efficiency Wireless Charging System for UAVs Based on PT-Symmetric Principle
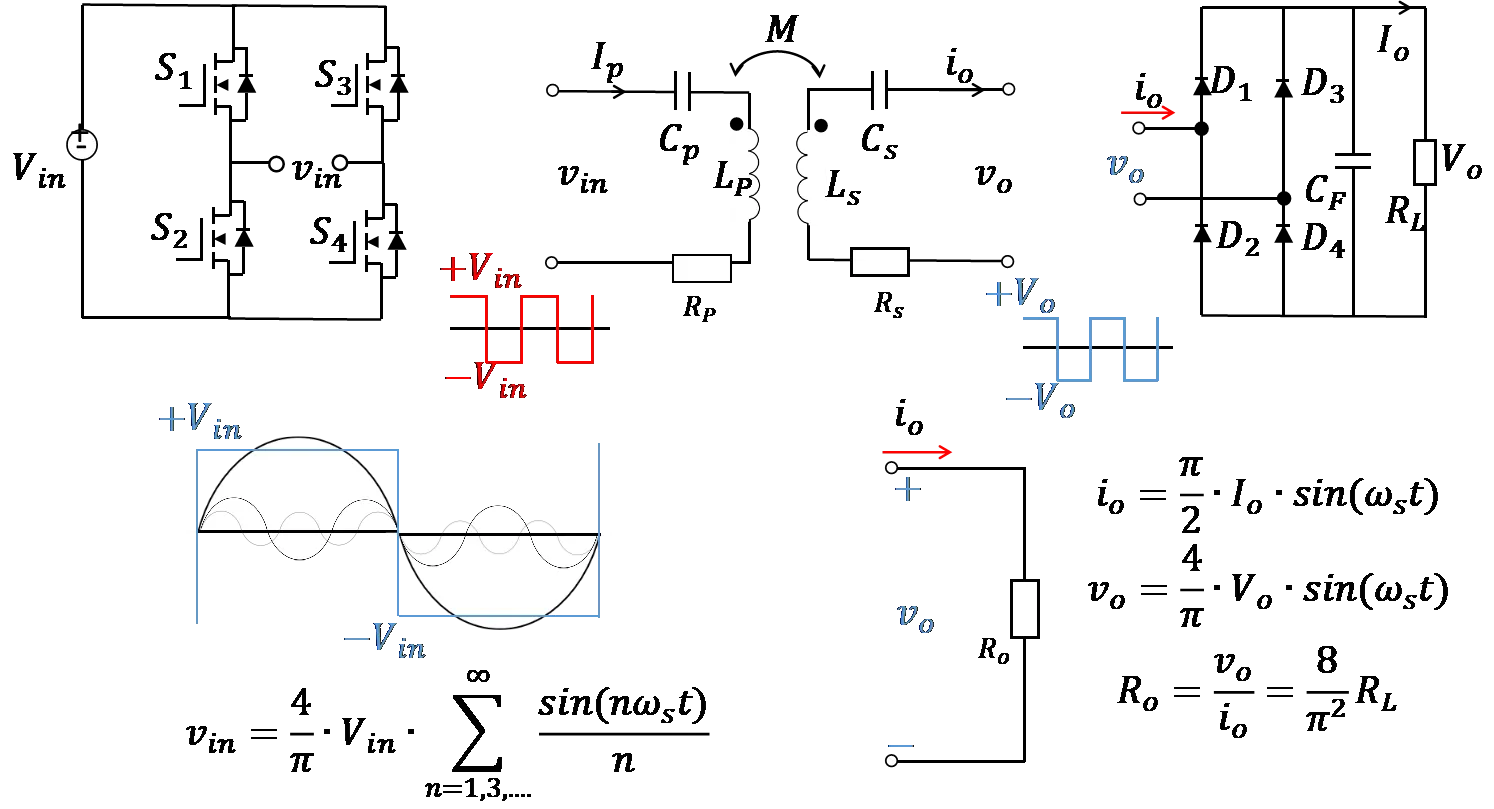
To address the limited endurance of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and the efficiency degradation and instability in traditional wireless charging systems, this study proposes a high-efficiency UAV wireless charging system based on the parity-time (PT) symmetric principle. A non-Hermitian coupled resonator model is established, incorporating a dynamic gain-loss balancing mechanism and real-time parameter feedback control to adaptively compensate for coupling coefficient fluctuations caused by UAV positional deviations, thereby maintaining PT-symmetric phase stability. The receiver coil adopts a planar air-core spiral structure and is integrated beneath the UAV landing gear to minimize interference with aircraft operations. Experimental results show a transmission efficiency of 90.2% at 65 W output power, with both power and efficiency remaining stable in the strong coupling region. The system demonstrates strong robustness against horizontal misalignment and eliminates the need for complex relay structures or high-precision alignment. This work not only provides a theoretical foundation for the application of PT-symmetry in wireless power transfer but also offers a novel technical pathway for enhancing UAV endurance.
Open Access
Editorial
30 April 2025