Found 301 results
Open Access
Article
26 November 2024Utilization of High Intensity Statins in Patients Hospitalized for Myocardial Infarction
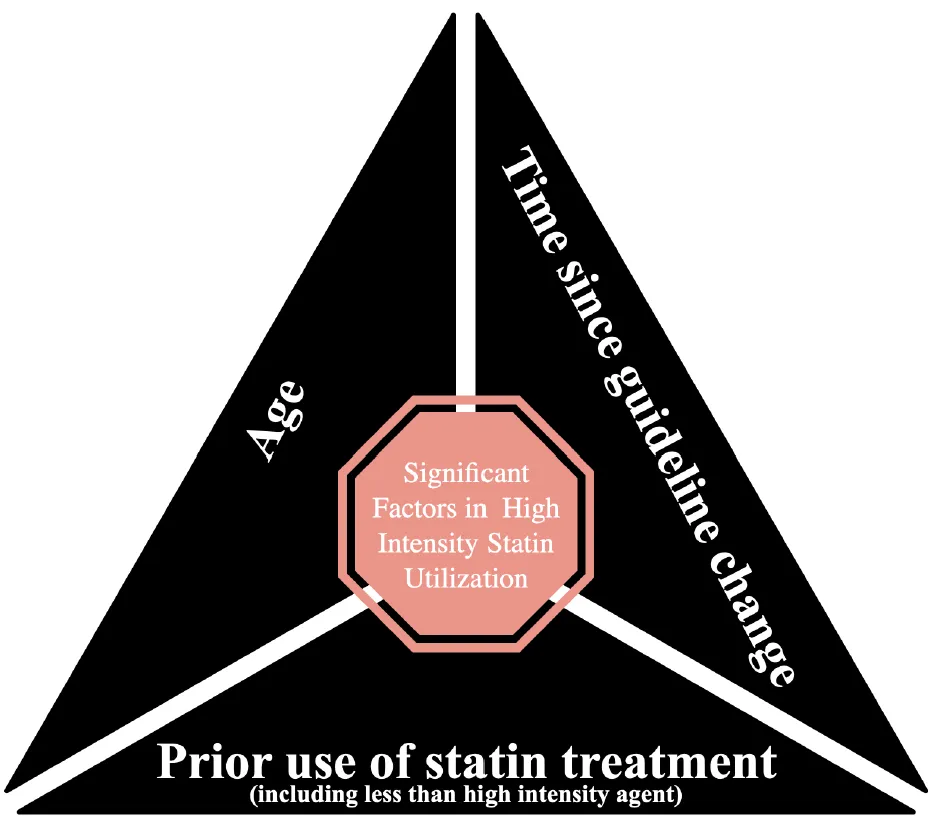
High intensity statin (HIS) therapy decreases LDL cholesterol and risk of recurrent cardiovascular events after acute myocardial infarction (MI). Recognizing the therapeutic significance of HIS, the ACC/AHA cholesterol treatment guidelines have recommended HIS for all patients following acute MI since 2013.The authors sought to define factors that result in continued underutilization and limited adherence to HIS among individuals post MI. This is a retrospective observational analysis of patients who had a diagnosis of MI between 2013 and 2018 at a single, large academic medical center. There was a significant increase in HIS prescriptions upon discharge after MI following, versus prior to 2013. Within the first year of guideline change (2013–2014), only 35.3% of patients with MI were discharged on a HIS compared to 80.1% in 2018. There was no significant difference between race or gender regarding HIS utilization. However, older age predicted a lower likelihood of being appropriately discharged on HIS. The use of statin therapy prior to hospitalization decreased the probability of being appropriately up titrated to HIS on discharge. Strikingly, HIS use was associated with a reduction in the 30-day readmission rate (4.7% versus 6.8%). Increased age was associated with lower rates of HIS use, which could stem from prior statin exposure uncovering titrational statin intolerance prior to the index event, a process that would be much less likely in younger patients, who tend to be statin naive. Although HIS have historically been underutilized in Blacks, this was not observed in the current study. Individuals discharged on HIS had lower readmission rates; while confounding factors separate from a pure treatment effect of HIS attenuating readmission rate may be represented, this remains a key finding underscoring the benefits of statin therapy in lowering societal burden of cardiovascular disease and associated costs.
Open Access
Communication
21 November 2024Trade-offs in Encapsulation Efficiency and Drug Release: A Multi-Objective Optimization Approach
Multi-objective optimization (MOO) techniques are crucial in addressing complex engineering problems with conflicting objectives, particularly in pharmaceutical applications. This study focuses on optimizing a biodegradable micro-polymeric carrier system for drug delivery, specifically maximizing the encapsulation efficiency and drug release of Candesartan Cilexetil antihypertensive drug. Achieving a balance between these two goals is essential, as higher encapsulation efficiency ensures adequate drug loading. In contrast, optimal drug release rates are critical for maintaining bioavailability and achieving therapeutic efficacy. Using response surface models to formulate the problem definition, five prominent MOO algorithms were employed: NSGA-III, MOEAD, RVEA, C-TAEA, and AGE-MOEA. The optimization process aimed to generate Pareto fronts representing compromise solutions between encapsulation efficiency and drug release. The results revealed inherent conflicts between objectives: increasing encapsulation efficiency often came at the cost of reducing the drug release rate. Evaluation of MOO algorithms using performance metrics such as hypervolume, generational distance, inverted generational distance, spacing, maximum spread, and spread metric provided insights into their strengths and weaknesses. Among the evaluated algorithms, NSGA-III emerged as the top performer, achieving a Weighted Sum Method (WSM) score of 82.0776, followed closely by MOEAD with a WSM score of 80.8869. RVEA, C-TAEA, and AGE-MOEA also demonstrated competitive formulation quality, albeit with slightly lower WSM scores. In conclusion, the study underscores the importance of MOO techniques in optimizing pharmaceutical formulations, providing valuable insights for decision-makers in selecting optimal formulations.

Open Access
Review
15 November 2024Intelligent Manufacturing Factory: A Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research Hotspots and Progress
Intelligent factories provide flexible and adaptive production processes, offering significant competitive advantages to manufacturers and are widely studied in industrial production. Information technology is recognized as a key factor influencing the production efficiency and intelligence of Intelligent factories. However, current research has primarily focused on the operational processes of intelligent factories, with limited analysis of information technology. To address this gap, this paper conducts a bibliometric analysis of information technology in intelligent factories, along with a review of its development and applications. Firstly, the data collection and visualization methods of bibliometrics are introduced. Secondly, bibliometric analyses are performed using platforms such as VOSviewer and Scimago to investigate co-authorship, co-citation, and contributions from countries and institutions in the field of information technology for intelligent factories. Finally, a framework for information technology in intelligent factories is established, summarizing its development in terms of information acquisition, transmission, processing, management, and control. This paper aims to assist scholars in understanding the development trends of intelligent factory technology and enhancing the informatization level of intelligent factories.
Open Access
Article
14 November 2024Hardness-Porosity-Grain Size Interrelationship in Conventionally Sintered 3 mol% Yttria Stabilized Zirconia
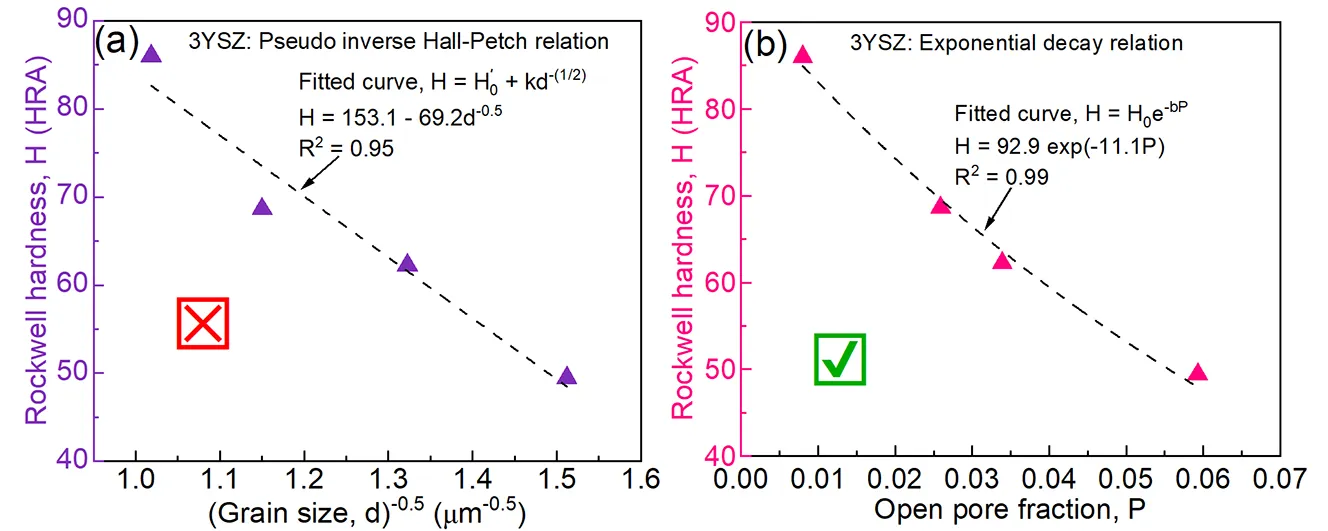
Considerable research has been done in the past on expensive, <50 nm particle size 3 mol% yttria-stabilized zirconia (3YSZ) using advanced sintering techniques. However, insights are still needed to reveal which factors among grain size and porosity, when both are changing simultaneously, more strongly control the hardness of conventionally sintered, relatively coarse, 250 nm 3YSZ powder, which can be used to make large industrial engineering ceramic parts at a lower cost. This investigation showed that elevating the sintering temperature from 1500 °C to 1650 °C increased the Rockwell hardness from 49.4 HRA to 86.0 HRA, which was concomitant with an increase in grain size and bulk density. A pseudo-inverse Hall-Petch relationship between hardness and grain size was observed given by H (in HRA) = 153.1 − 69.2/$$\small\sqrt{(\mathrm{grain}\,\mathrm{size})}$$ with a somewhat low R2 of 0.95, which was mainly due to the porosity being an additional important variable. Compared to grain size, the impact of open pore fraction (P) on hardness was stronger, inferred from a higher R2 of 0.99 while fitting the data into the well-known exponential decay equation, H = 92.9 exp(−11.1P). Finally, it was observed that the 3YSZ conventionally sintered at 1650 °C for 2 h had 0.8% open porosity, 6.08 g/cm3 bulk density, 960 nm grain size and consisted of only tetragonal ZrO2.
Open Access
Article
11 November 2024Rural Local Government Institutional Sustainability Programs and Plans in Cascadia: A Comparative Analysis
This research provides a comparative analysis of institutional sustainability programs in small and rural communities across British Columbia, Oregon, and Washington. The study reveals significant regional differences in the adoption of sustainability initiatives, with Oregon consistently leading in the implementation of various programs such as grant writing, conflict resolution, and e-government. The analysis identifies key factors influencing program adoption, including population growth, economic stability, and remoteness. Communities experiencing significant population growth and financial stability are more likely to adopt multiple sustainability programs, while remoteness and economic challenges, such as inflation, act as barriers. The study underscores the importance of regional context and local conditions in shaping the sustainability efforts of rural communities.

Open Access
Article
04 November 2024Diversity and Meta-Analysis of Microbial Differential Abundance in Nasal Metatranscriptomic Profiles of Asthma
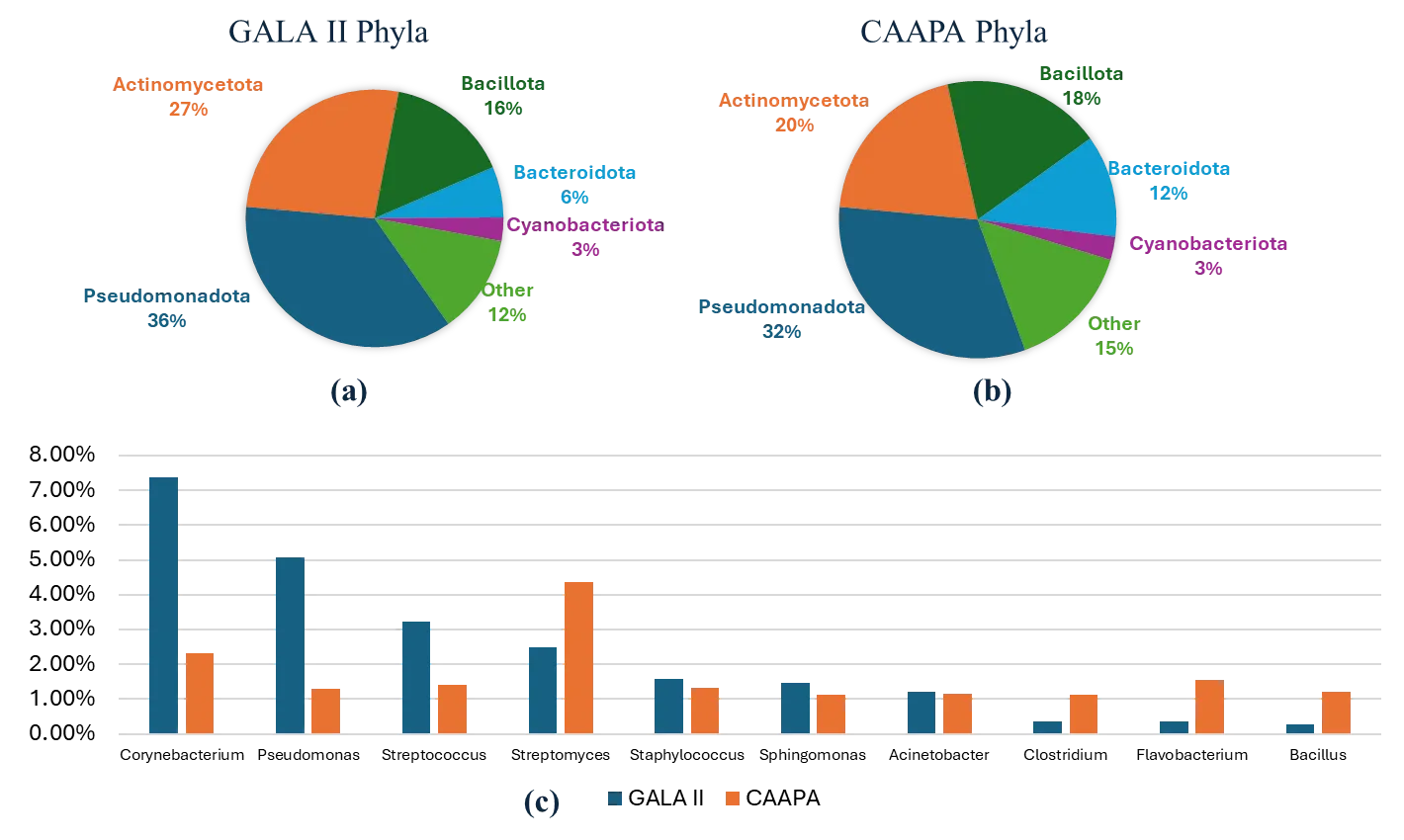
Asthma affects millions worldwide and involves complex genetic, immunological, and environmental factors. The nasal microbiome is increasingly recognized for its role in asthma development, but inconsistent results and small sample sizes have limited a clear understanding. We aimed to clarify the nasal microbiome’s role in asthma using large datasets and meta-transcriptomic analysis. RNA-seq data was analyzed from two large public studies: GALA II (694 children of Puerto Rican heritage; 441 asthmatics, 253 controls) and CAAPA (562 individuals of African ancestry; 265 asthmatics, 297 controls). After quality control and host read removal, microbial reads were annotated using Kraken2. α and β diversity analyses compared microbial diversity between asthmatic and control groups. Differential abundance analysis was conducted separately, controlling for age and sex, with results combined via meta-analysis. We found that asthmatic patients exhibited significantly higher α diversity indices (Shannon, Berger-Parker, Inverse Simpson, Fisher’s) in nasal microbiota compared to controls in GALA II, with similar trends in CAAPA. β diversity analysis showed significant differences in microbial composition in GALA II data. Differential abundance analysis identified 20 species in GALA II and 9 species in CAAPA significantly associated with asthma. Meta-analysis revealed 11 species significantly associated with asthma, including Mycobacterium_tuberculosis. Our study demonstrates increased nasal microbiome α diversity in asthmatic patients and identifies specific microbial species associated with asthma risk. These findings enhance understanding of asthma pathogenesis from the nasal microbiome perspective and may inform future research and therapeutic strategies.
Open Access
Article
01 November 2024Alkaline Modified Coir and Unmodified Hemp Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Based Composite for Automotive Application
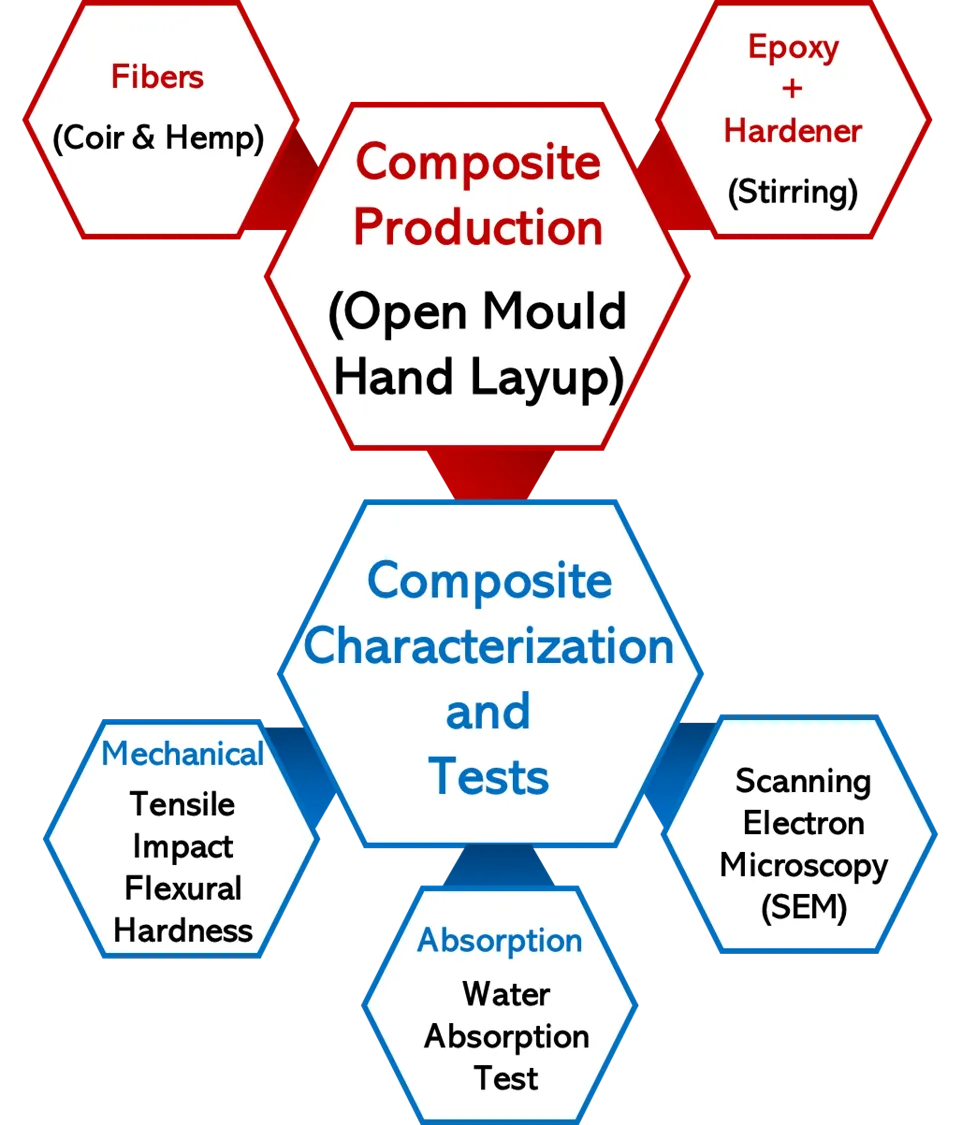
The growing demand for sustainable materials in the automotive industry has prompted research into natural fiber-reinforced composites. To reduce carbon footprints and enhance product sustainability, the sectors increasingly focus on renewable and biodegradable materials. Composites made from natural fibers, such as coir and hemp, offer a promising solution for creating lightweight, high-performance components with a reduced environmental impact.In this study, an experimental investigation was conducted to examine the impact of single and hybrid and treated and untreated fibers, on the properties of epoxy-based composites. Untreated hemp fiber with treated Coir fiber was used for the research. The composites were fabricated through the open mould hand lay-up technique. Samples were prepared by randomly dispersing the fibers in the epoxy matrix before pouring them into the respective moulds prepared according to ASTM standards. Tensile, impact, and hardness tests were conducted on the cured samples to determine their mechanical properties, while a scanning electron microscope was used to evaluate the fractured surface. Water absorption tendencies were also determined. The results showed that the sample denoted as 5CF wt.% had the best property combination with tensile strength (32.4 MPa), tensile modulus (11.9 GPa), flexural strength (167.0 MPa), and impact strength (46.8 kJ/mm2). It was discovered that hemp fiber-based composites were not enhanced properly due to lack of fiber surface modifications. Though optimum results were obtained from treated coir fiber-based single/distinct composite, untreated hemp fiber was discovered to aid some flexural modulus and hardness properties in the hybrid composite based on the best results obtained in its distinct-based composite. Therefore, untreated hemp fiber can be used in hybrid form with treated coir fiber where one of the fibers is scarce or when fiber surface medication is difficult to achieve. Thus, the results showed that 5CH-based composites are the most suitable composition for automotive components development where high-mechanical properties are essential.
Open Access
Article
29 October 2024Experimental Study on Cold Plasma Jet (CPJ) Assisted Micro-Milling of 30CrMnSiNi2A
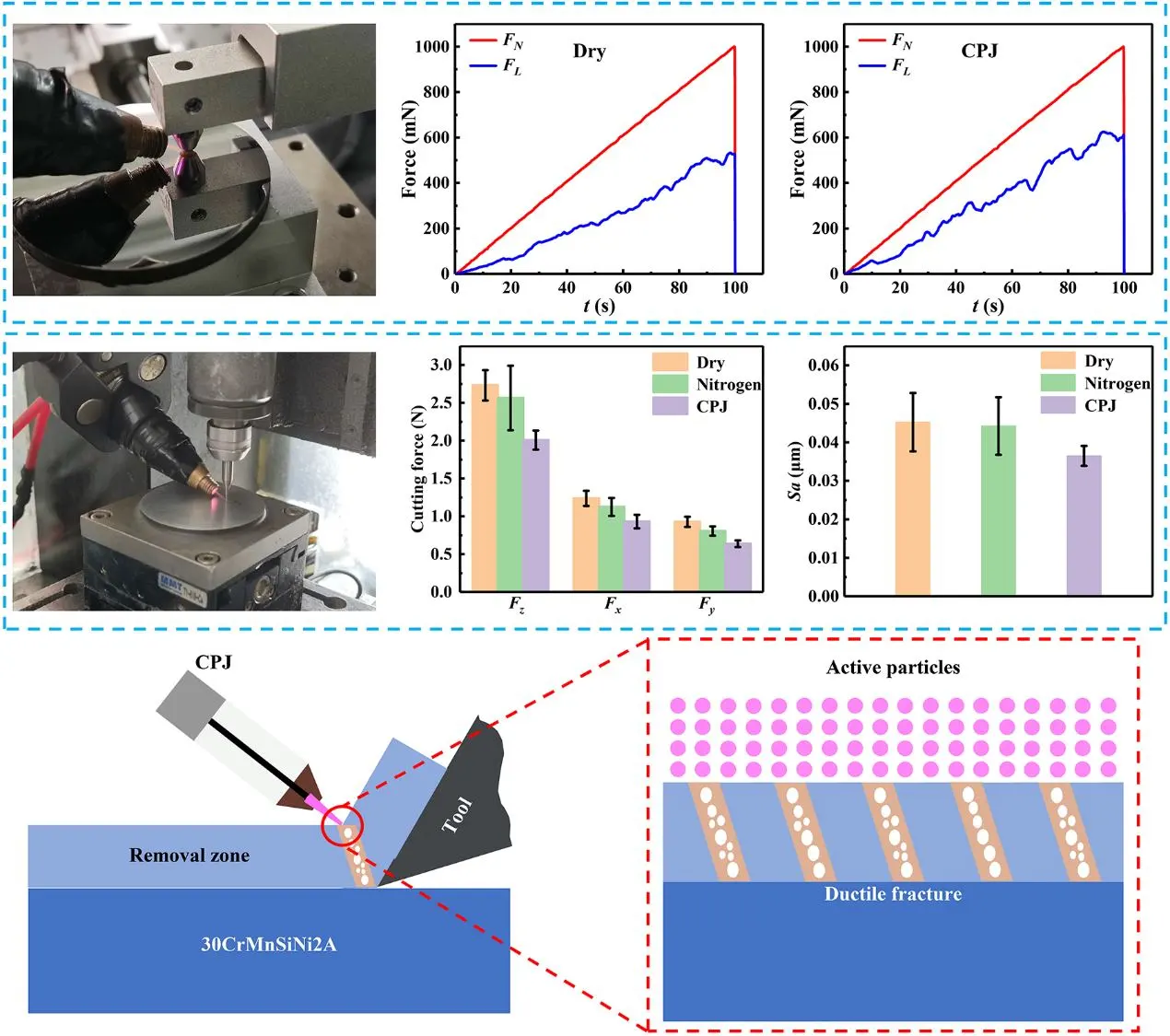
As a typical high-performance alloy, the excellent mechanical properties and stringent processing requirements of 30CrMnSiNi2A high-strength steel pose great challenges to high-quality and efficient processing. Currently, researchers have proposed methods such as improving cutting tool performance, minimal quantity lubrication (MQL), and applying external energy field to assist processing. However, due to the unregulated material properties, the further improvement of surface quality is limited, and there are problems of phase change and thermal damage in laser processing. Cold plasma jet (CPJ) is rich in active particles and has a low macroscopic temperature. It can effectively regulate material properties without causing serious surface damage. Therefore, a new 30CrMnSiNi2A machining approach adopting CPJ is proposed to improve the cutting process. The mechanism of its action on material properties and cutting process is revealed based on single-grain diamond scratching tests and micro-milling tests. The results show that CPJ can promote material fracture and improve material removal efficiency. The material removal efficiency R at 400 mN is increased from 0.433 before treatment to 0.895. Under the optimal processing parameters (feed speed Vf = 800 μm/s, spindle speed n = 40,000 rpm, and milling depth ap = 5 μm), compared with dry micro-milling, the cutting forces Fz, Fx and Fy in CPJ-assisted micro-milling are reduced by 26.5%, 24.8% and 31.3%, respectively. The surface roughness Sa is reduced by 19.3%, and the phenomena of plastic flow and burr are suppressed. The CPJ-assisted machining process proposed in this paper can regulate the material properties to improve the cutting process without causing serious damage to the material, providing a new approach for achieving high-quality and efficient processing of 30CrMnSiNi2A.
Open Access
Article
25 October 2024Supply Chain of Grey-Blue Hydrogen from Natural Gas: A Study on Energy Efficiency and Emissions of Processes
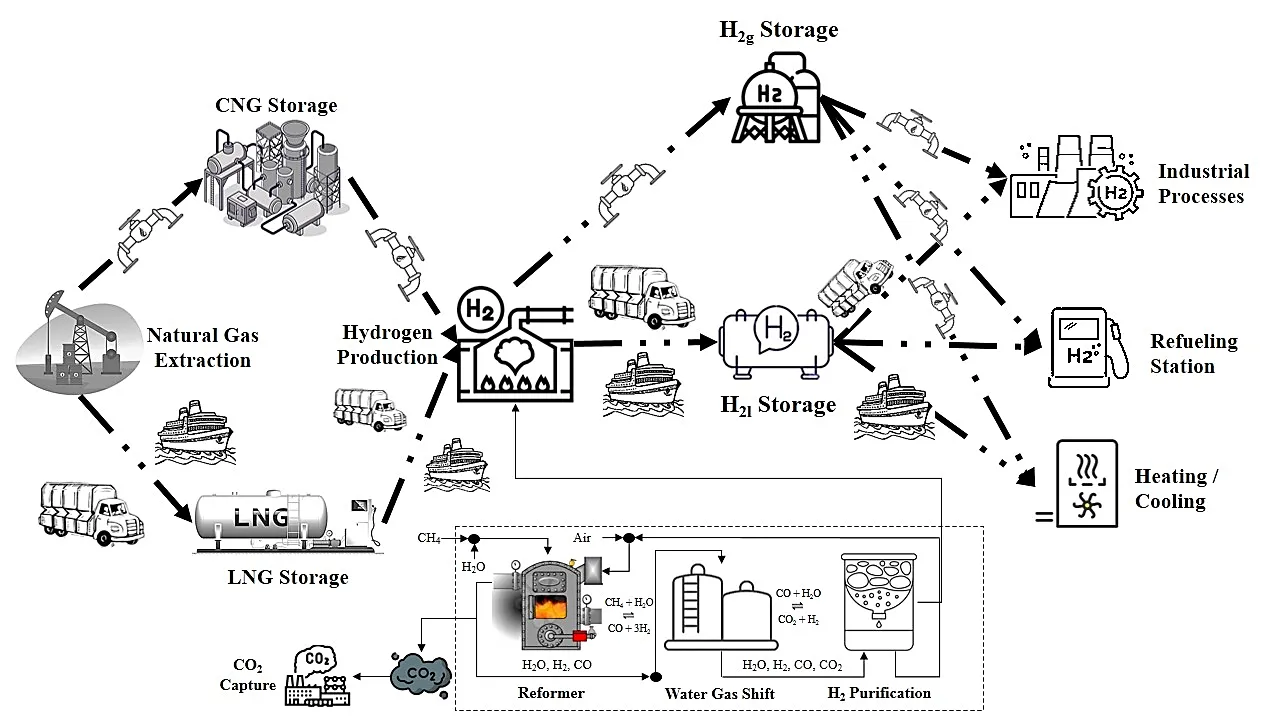
Hydrogen energy offers a significant potential for reducing carbon emissions and integrating clean energy across sectors such as heavy-duty vehicles, energy-intensive industries, and building heating. This study analyzes the energy efficiency and emissions of grey and blue hydrogen supply chains, identifying key issues such as high energy consumption and losses in transportation, steam methane reforming, and liquid hydrogen storage. Truck transportation emerges as the highest emitter, with emissions ranging from 0.140 to 0.150 kg CO2e per kg of hydrogen. Using a bi-objective Dijkstra Algorithm, the study identifies the most energy-emissions-efficient pathways and reveals a trade-off between energy efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions. Grey hydrogen shows higher energy efficiency (38.0%) but higher emissions (0.1689 kg CO2e per kg of hydrogen). In contrast, with 60% and 90% carbon capture and storage, blue hydrogen has slightly lower energy efficiencies (37.5% and 36.9%) but reduced emissions (0.1564 and 0.1514 kg CO2e per kg of hydrogen). Liquefied natural gas and hydrogen offer high energy efficiency but increase emissions, while compressed natural gas and hydrogen slightly reduce efficiency but nearly halve emissions. Hence, compressed options are preferable for an energy-emissions-efficient shortest path.
Open Access
Review
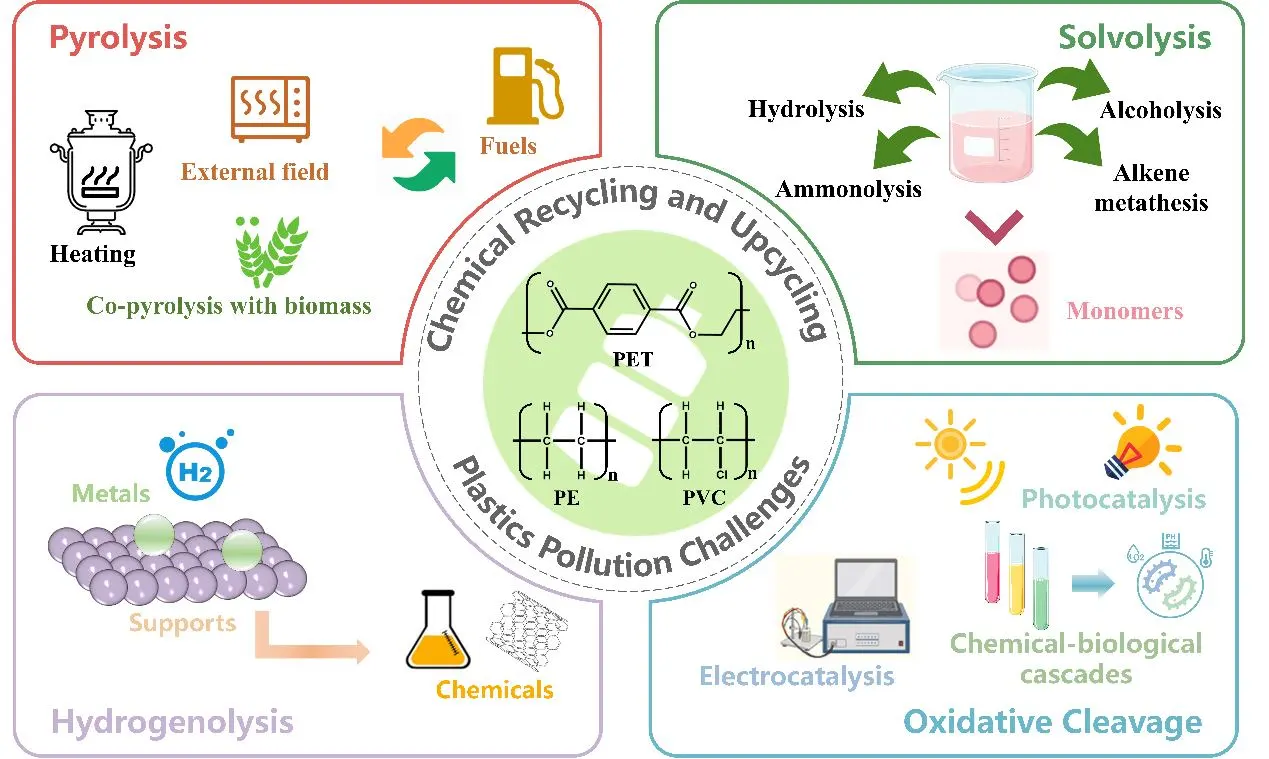
23 October 2024Chemical Recycling and Upcycling of Waste Plastics: A Review
The indiscriminate disposal of plastic waste represents a significant environmental hazard. Conventional remediation techniques, such as landfilling and incineration, also encounter limitations and are unable to adequately address the pollution issue. Chemical recycling and upcycling represent an effective method for the degradation of plastics into oligomers and subsequent transformation into other product substances. This review provides an overview of the various chemical treatment methods currently in use, from the earliest thermal degradation techniques to the emerging strategies. The conventional techniques for thermal degradation of discarded plastics frequently encounter difficulties due to the necessity for elevated temperatures, substantial energy consumption, and the generation of a heterogeneous product mixture. Significant advances have been made in the fields of catalytic solvolysis, hydrotreating, and oxidative cleavage for the recycling and upcycling of plastics under mild conditions. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the chemical treatment methods currently employed for plastics, with a particular focus on the principles and current developments, as well as the reaction mechanisms involved. Additionally, it offers a detailed introduction to various advanced catalytic technologies and the catalysts utilized. Finally, it presents prospective outlooks for different methods, based on their current development status and the gap between actual needs.