Found 469 results
Open Access
Article
29 October 2025Material Analysis of CNT’s as Conductive Additive for NMC Lithium-Ion Polymer Batteries Cathode Electrode
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are promising conductive additives for lithium-ion polymer (LiPo) batteries. The performance of lithium metal oxide cathodes is highly dependent on the properties of the conductive carbon additive. This study investigates the advantages of CNTs over conventional carbon black for this application. Material properties, including hardness, tensile strength, thermal conductivity, and electrical resistivity, were analyzed and compared using Ansys Granta (CES EduPack 2024 R2) software. The results demonstrate that CNTs are superior in tensile strength (110 MPa), hardness (50 HV), and thermal conductivity (210 W/m·°C). These properties enhance the mechanical integrity of the CNT-based cathode composite, leading to improved battery performance. Furthermore, the electrochemical behavior of CNT/LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 composite cathodes was investigated, focusing on the carbon precursor (methane vs. natural gas) and CNT diameter. At a current rate of 3 °C, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) derived from methane delivered a specific capacity 20 mAh/g higher than those derived from natural gas. This indicates that methane-derived MWCNTs exhibit superior electrochemical performance, which is attributed to reduced polarization and a higher discharge potential. The study also revealed that MWCNTs with a smaller diameter (30–50 nm) performed better at high charge/discharge rates, owing to a higher number of primary particles per unit mass. This analysis aids in understanding material selection and its implications for battery design and lifecycle. The findings serve as a reference for future research exploring the use of CNTs in advanced battery materials.

Open Access
Review
29 October 2025Admixture of Amerindian, African and European Genes: Cuba, Mexico and Colombia as Study Cases
One hundred years after Columbus arrived in America in 1492, Amerindian population had fallen from 80 to 8 million in North and South America. The main causes were new microbes, slavery conditions and war. The people of San Basilio de Palenque (Colombia), close to Cartagena, in the Colombian Caribbean Coast, were established by runaway African slaves who built a refuge in San Basilio. The Spanish governors pressured the Spanish monarchs in Madrid to grant freedom to the Africans of San Basilio de Palenque, who became the first free Africans in the Americas. They speak the only Bantu-Spanish Creole and preserve African genetic traits according to HLA genes. Research also examined Cubans from Havana, showing that around 12% of the typical Amerindian HLA genes are present in Havana’s population. Cubans’ blood contains Amerindian genes in spite of that Amerindian physical traits do not exist now in the Cuban population. Amerindian HLA and other genes analyses and other cultural traits observed in Mexico—such as those of the Pacific Mayo/Yoreme and the Atlantic Huastecan/Teenek groups—suggest that the initial peopling of the American continent occurred much earlier than traditionally proposed, and that there was a bidirectional exchange of populations between the Pacific and Atlantic in relation to Europe (finding in America of European Paleolothic Solutrean traits) peoples may have occurred.

Open Access
Article
28 October 2025The Role of Knowledge Transferred between Rural Inhabitants and Newcomers in the Development of Rural Areas
The purpose of this study is to find the answer to the question: What is the role of the transfer of knowledge between the permanent and new residents of the countryside. The results are based on qualitative inquiry, carried out in 18 Polish villages, situated in socially and historically diverse regions and outside of the metropolitan areas. Knowledge, which is transmitted in the contacts between the two groups considered, has a very clearly informative character. This concerns primarily the basic information pieces, meant to ensure satisfaction of the daily needs of the groups of inhabitants considered. Knowledge transfer is relatively little intensive and takes place during sporadic encounters, mainly in public spaces—a street, a central square, a shop. This, presumably, exerts an influence on the nature and quality of knowledge and information exchange. The permanent residents are, first of all, the source of current information and practical knowledge, concerning broadly conceived village life, answering the fundamental questions of what, where, and when. On the other hand, the newcomers, side by side with informative knowledge, provide also knowledge of advisory and non-material character. Knowledge and information provided by permanent rural residents serve the needs of daily life and the satisfaction of current necessities, while newcomers introduce new lifestyles and behaviors, leading to increased social activity in the countryside.

Open Access
Review
28 October 2025Digital Transformation and Circular Economy Integration: Pathways for Sustainable Business Innovation
The accelerating pace of digital transformation has reshaped how industries pursue sustainability, offering innovative ways to integrate environmental responsibility into business strategy. This study examines how digital technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, the Internet of Things, and big data analytics enable the adoption of circular economy principles in sustainable business innovation. Using a systematic literature review of 85 studies published between 2015 and 2025, the research identifies key mechanisms through which digital transformation enhances resource efficiency, extends product lifecycles, and promotes transparent supply chains. The findings show that digitalization strengthens competitiveness and sustainability but presents challenges such as high implementation costs, unequal access to digital infrastructure, and the environmental footprint of information and communication technology systems. The study concludes that aligning digital adoption with organizational culture, governance structures, and supportive policy frameworks is essential for realizing circular economy strategies at scale and achieving resilient, low carbon, and sustainable business models.

Open Access
Article
27 October 2025Interacting Multiple Model Adaptive Robust Kalman Filter for Position Estimation for Swarm Drones under Hybrid Noise Conditions
This study evaluates the Interacting Multiple Model Adaptive Robust Kalman Filter (IMM-ARKF) for accurate position estimation in a leader-follower swarm of nine drones, consisting of one leader and eight followers following distinct trajectories. The evaluation is conducted under hybrid noise conditions combining Gaussian and Student’s t-distributions at 10%, 30%, and 50% ratios. The IMM-ARKF, which relies solely on its adaptive robust filtering mechanism, is compared with standard Interacting Multiple Model Kalman Filter (IMM-KF) and Extended Kalman Filter (IMM-EKF) methods. Simulations show that IMM-ARKF provides better accuracy, reducing root mean square error (RMSE) by up to 43.9% compared to IMM-EKF and 34.9% compared to IMM-KF across different noise conditions, due to its ability to adapt to hybrid noise. However, this improved performance comes with a computational cost, increasing processing time by up to 148% compared to IMM-EKF and 92.1% compared to IMM-KF, reflecting the complexity of its adaptive approach. These results demonstrate the effectiveness of IMM-ARKF in enhancing navigation accuracy and robustness for multi-drone systems in challenging environments.

Open Access
Article
24 October 2025N-TiO2 Photonic and Quantum Photocatalytic Efficiency Determined by Monte Carlo Simulation
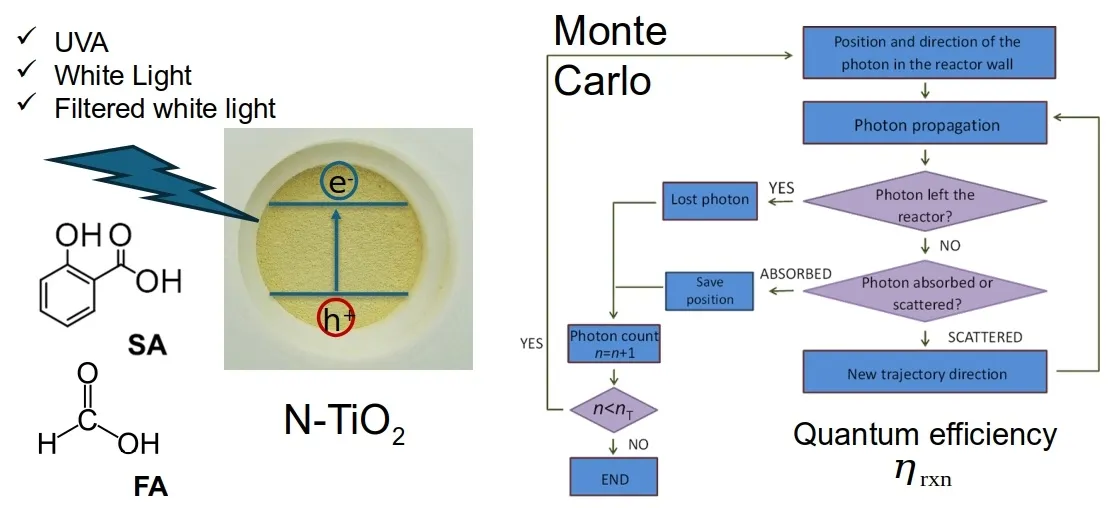
Nitrogen-modified titanium dioxide (N-TiO2) is proposed as an alternative to improve solar light absorption in photocatalytic applications. Due to its high chemical stability and low toxicity, various synthesis methods have been developed, yielding materials with different properties. Evaluating its performance compared to other photocatalysts requires calculating the quantum efficiency, which involves appropriate mathematical models to interpret experimental data. This study used a Monte Carlo approach to determine the local volumetric rate of photon absorption (LVRPA). TiO2 and N-TiO2 were synthesized via the sol-gel method using urea as the nitrogen source, and commercial TiO2 P-25 was used as a reference. Formic acid and salicylic acid were chosen as model pollutants due to their differing adsorption behavior on TiO2. Three light sources were used: UVA, white, and blue light. Nitrogen doping increased quantum efficiency for formic acid degradation under UVA from 2.4 to 3.5 (46% increase) and salicylic acid from 1.0 to 2.1 (110% increase). P-25 showed the highest efficiencies under UVA, with 6.2 for formic acid and 5.2 for salicylic acid. Under white light, salicylic acid degradation efficiency doubled from 0.4 to 0.8 after nitrogen doping. No activity was observed for formic acid with undoped TiO2 under white light, but N-TiO2 achieved 1.1. Under blue light, no activity was detected for formic acid, while salicylic acid degradation showed efficiencies of 0.3 (N-TiO2) and 0.2 (P-25). Quantum efficiency was highest under UVA, indicating that nitrogen doping improves visible light response but does not surpass UVA performance.
Open Access
Review
23 October 2025Adaptive Time Management: A Life-History Framework Integrating Mental Time Travel, Mortality Awareness, and Anticipatory Decision-Making
Adaptive time management is a newly developed life-history framework that integrates humans’ capacity for mental time travel with mortality awareness as a strategic process for time and resource allocation. Rather than triggering terror management, we conceptualize mortality awareness as an adaptive cue that recalibrates subjective time perception and episodic future thinking. This framework maps three key life-history factors (resource scarcity, unpredictability, and harshness) onto corresponding decision premises: perceived remaining time, death’s uncertainty, and life’s inevitability. We review evidence suggesting that: (1) constricted horizons accelerate delay discounting and favor immediate, fast strategies; (2) unpredictability of death (temporal variation of death) evokes emotions and prompt strategic present-oriented choices that secure survival under high-risk conditions; (3) inevitability of death (life’s finitude) fosters slow strategies through resource bet-hedging mental travel that allows time measure and management; and (4) episodic end-of-life thinking elicits anticipatory emotions that adaptively regulate self-control and cognitive reappraisal. We also introduce preliminary findings on “life-history intertemporal meditation” as a potential intervention for adaptive regulation. Finally, we discuss adaptive time management in applications in death education and mental health. Together, this framework highlights how harnessing life-history mental time travel and mortality awareness can promote adaptive decision-making and emotional resilience across the lifespan.

Open Access
Article
23 October 2025New Model of Multicomponent Raw Materials and Its Use in Intensifying Hydrotreating Process of Diesel Fuel
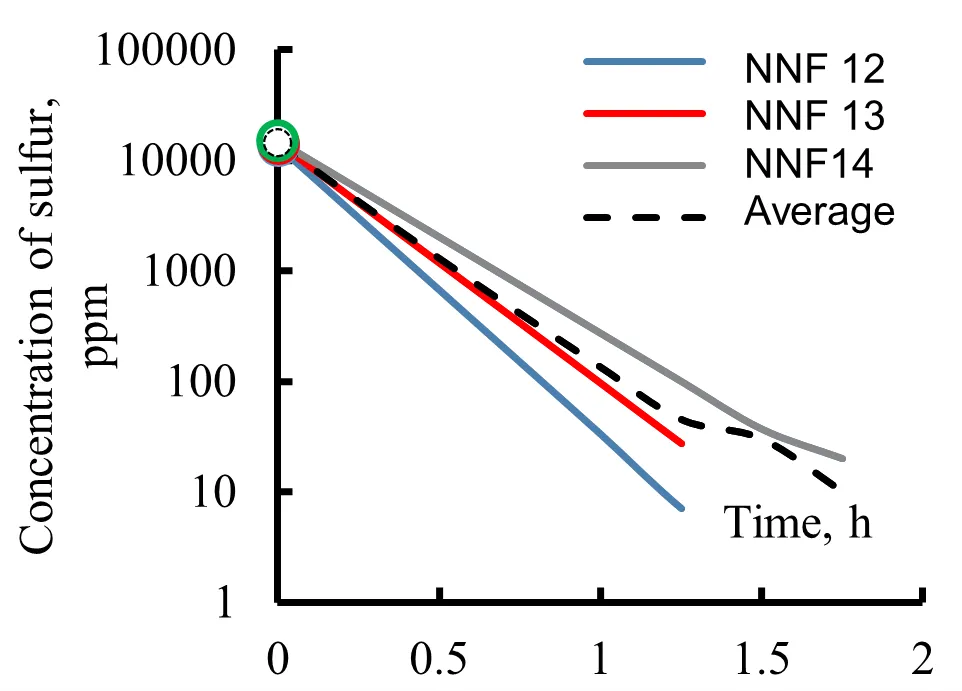
Hydrotreating of diesel fuel aims to reduce the sulfur content in the fuel to 10 ppm to meet environmental standards. However, this deep purification of diesel requires the use of expensive catalysts at hydrotreating plants with giant reactors with a capacity of 200–600 cubic meters. Such large volumes of reactors are associated with classical kinetic methods for chemical reactions, where the feedstock is in the reactor until the required conversion depth is reached. All known mathematical models for diesel hydrotreatment have a common drawback: they rely on approximations about the composition of multicomponent raw materials containing dozens of different organic sulfur compounds that react differently in hydrogenation reactions. This raw material is often presented in a mathematical model as a combination of two to six pseudo-components or lumps combining organosulfur impurities from one or more homologous groups. This theoretical basis allows us to simulate the current state of hydrotreating technology, but does not develop and promote it. We propose a new approach to mathematical modelling of diesel fuel hydrotreating, in which the structure of the mathematical model considers the composition of raw material as a set of 10–20 narrow fractions. The set of hydrogenated organosulfuric impurities within each fraction is treated as a single pseudocomponent. This allows us to integrate the system of differential equations of the model and adapt the rate constant to the concentration of hydrogenated organosulfur impurities at any given time during the process. The developed model has also allowed us to propose a new technology, hydrotreatment: separating the feedstock into two or three wide fractions, combining the corresponding narrow fractions, and then subjecting them to individual hydrogenation processes. As a new approach, this differential hydrotreatment technique will reduce the catalyst load in the hydrotreatment unit by approximately 50%, while maintaining efficiency of processing, or double efficiency while maintaining a similar catalyst load using traditional technology.
Open Access
Review
22 October 2025Beyond Genetics: Exploring Aspects of Non-Biological Kinship in Prehistoric Times
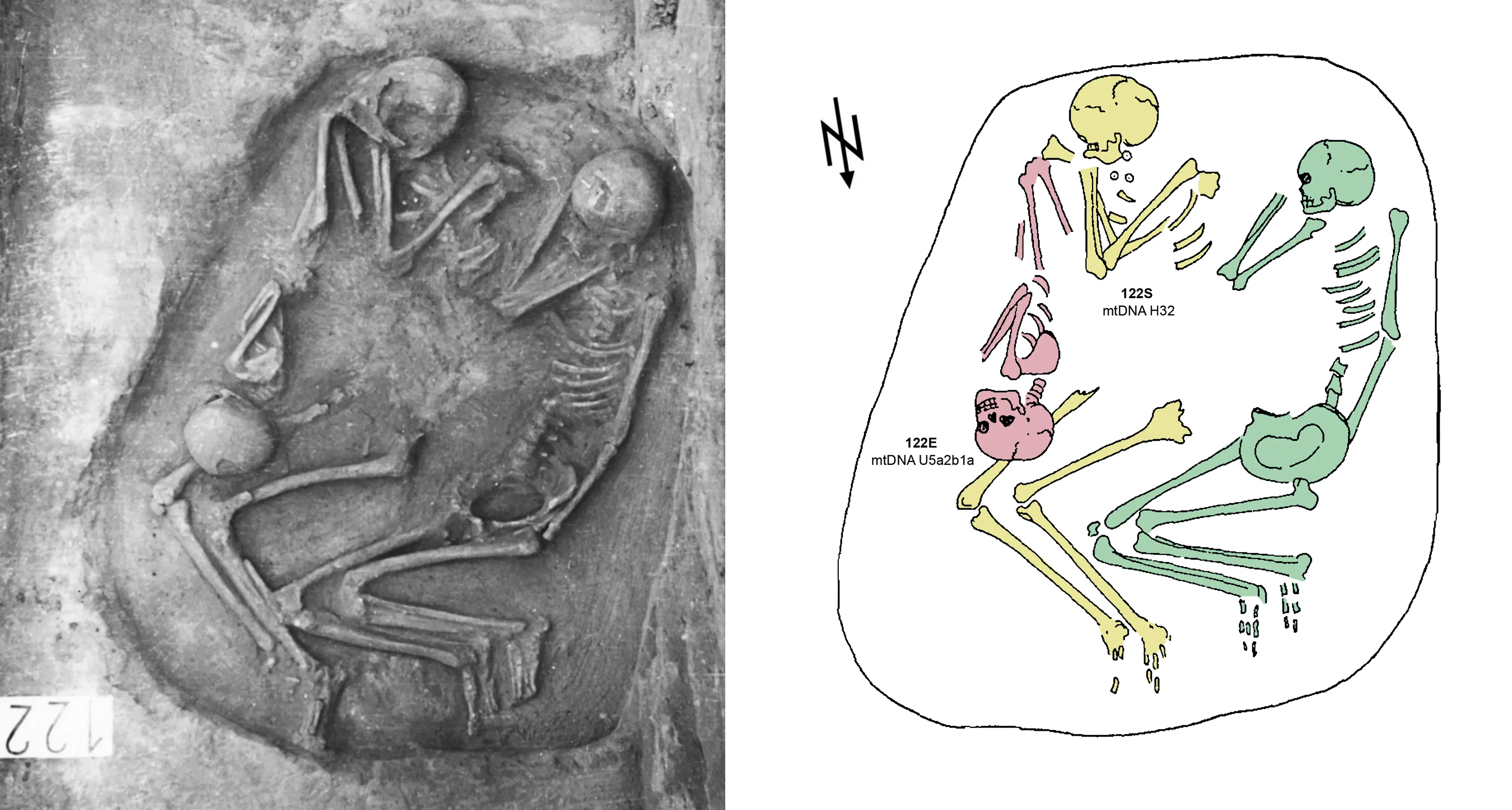
This article explores alternative ways of conceptualizing kinship in prehistoric contexts beyond the confines of genetic reductionism. While ancient DNA research has revitalized interest in the archaeology of kinship, it often privileges patrilineal or matrilineal models and risks obscuring forms of relatedness not grounded in biological ties. Drawing on comparative anthropological models and archaeological case studies, the paper highlights the complexity of kinship as manifested in practices of adoption, fosterage, commensality, co-residence, and non-biological affiliation within (non)nuclear households. By integrating socio-cultural, economic, and material dimensions, it demonstrates the diverse methodological and theoretical approaches necessary to move beyond descent-centered reconstructions. The discussion advocates for an interdisciplinary framework that challenges reductionist assumptions and opens new avenues for understanding relatedness in the deep past. Finally, the article emphasizes the village as a unit of analysis within a multi-scalar approach. It presents future directions and archaeological correlates of adoption, child circulation, and fosterage derived from archaeological, genetic, and ethnographic evidence.
Open Access
Article
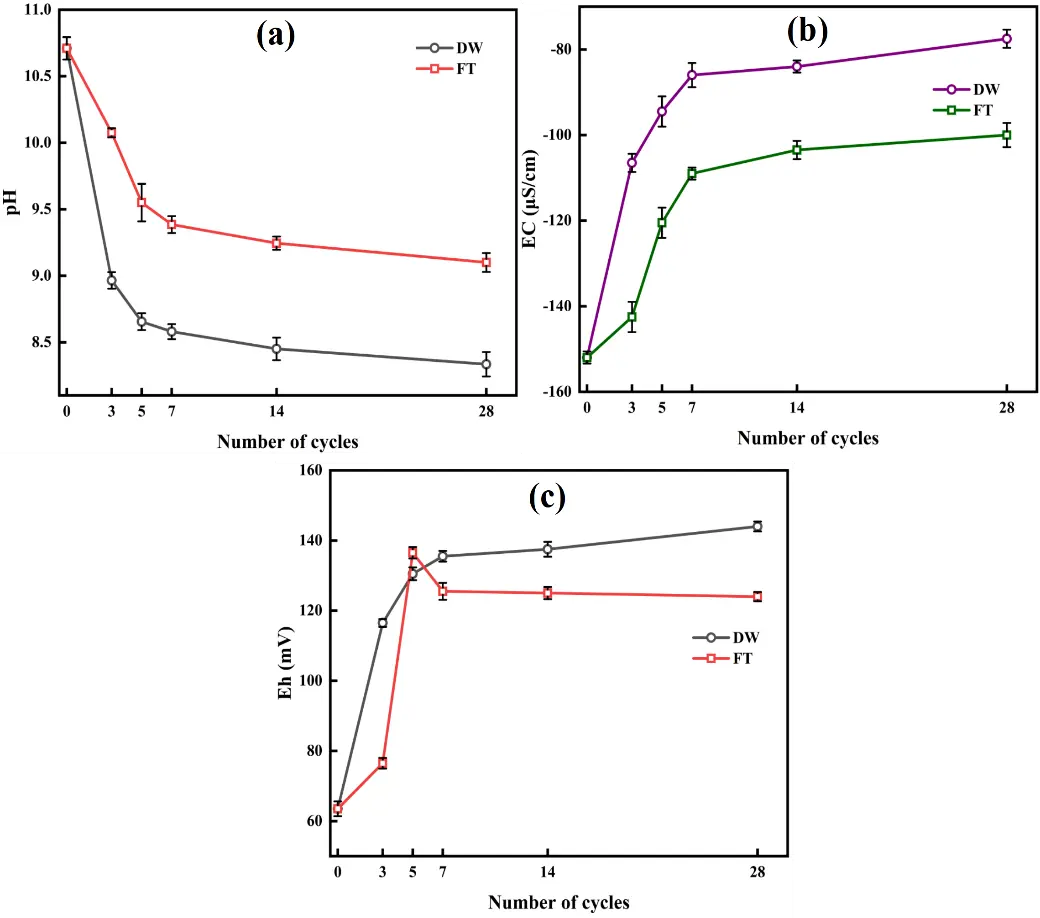
20 October 2025Divergent Aging Mechanisms of Calcium Arsenic Residue under Dry-Wet and Freeze-Thaw Cycles: Toxic Metal Mobility, Multiscale Physicochemical Characterization, and Escalated Ecological Risks
This study investigates the long-term mobility and ecological risks of As, Zn, and Cd in calcium arsenic residue (CAR) under simulated dry-wet (DW) and freeze-thaw (FT) cycles. Accelerated aging experiments, combined with multiscale characterization (XRD, XPS, SEM, FTIR), revealed distinct transformation mechanisms. DW cycles promoted carbonate-driven dissolution, As(III) oxidation to As(V) (resulting in an 18.4% increase in As(V) as shown by XPS), and sulfide oxidation (with reductions of 47.7% in ZnS and 15.08% in CdS). These processes increased the acid-soluble metal fractions (F1: As by 11.3%, Zn by 6.0%, and Cd by 8.7%) and metal release rates (52.39% for As, 42.63% for Zn, and 68.55% for Cd under DW conditions). In contrast, FT cycles induced mechanical fracturing and ice-mediated stabilization, which limited ion migration, partially amorphized ZnO, and promoted the precipitation of Cd(OH)2. Ecological risk assessments indicated rising risks, with integrated potential ecological risk indices (IPER) reaching 11,187.85 under DW conditions and 10,668.29 under FT conditions, with arsenic contributing over 80%. The Risk Assessment Code (RAC) reclassified all metals into moderate-risk categories (As: 11.9–19.7%, Zn: 9.4–15.2%, Cd: 12.1–18.6%). Weibull modeling (α = 6.98–10.98, R2 > 0.96) described the nonlinear kinetics, showing that cadmium aged the fastest (λ: Cd > As > Zn), with delayed but persistent risks under FT conditions. These results underscore the importance of developing climate-resilient stabilization strategies. The integrated framework combining mineral evolution, kinetics, and risk forecasting offers significant insights for managing legacy CAR pollution under changing climate conditions.