Found 40 results
Open Access
Article
16 January 2024The Interplay between Experimental Data and Uncertainty Analysis in Quantifying CO2 Trapping during Geological Carbon Storage
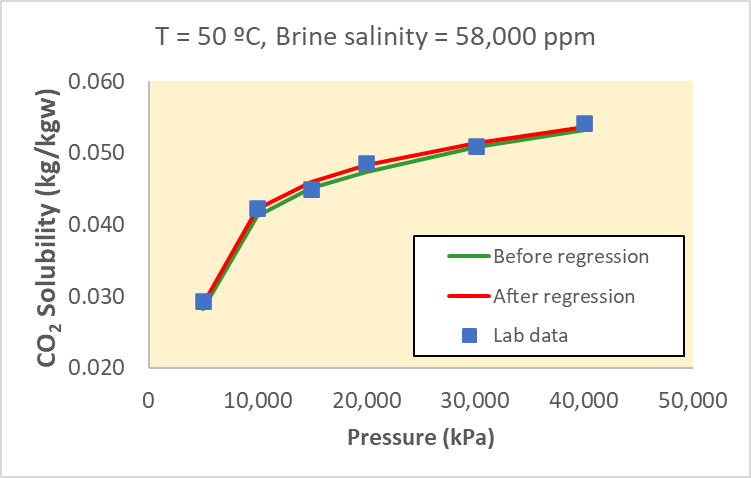
Numerical simulation is a widely used tool for studying CO2 storage in porous media. It enables the representation of trapping mechanisms and CO2 retention capacity. The complexity of the involved physicochemical phenomena necessitates multiphase flow, accurate fluid and rock property representation, and their interactions. These include CO2 solubility, diffusion, relative permeabilities, capillary pressure hysteresis, and mineralization, all crucial in CO2 trapping during carbon storage simulations. Experimental data is essential to ensure accurate quantification. However, due to the extensive data required, modeling under uncertainty is often needed to assess parameter impacts on CO2 trapping and its interaction with geological properties like porosity and permeability. This work proposes a framework combining laboratory data and stochastic parameter distribution to map uncertainty in CO2 retention over time. Published data representing solubility, residual trapping, and mineral trapping are used to calibrate prediction models. Geological property variations, like porosity and permeability, are coupled to quantify uncertainty. Results from a saline sandstone aquifer model demonstrate significant variation in CO2 trapping, ranging from 17% (P10 estimate) to 56% (P90), emphasizing the importance of considering uncertainty in CO2 storage projects. Quadratic response surfaces and Monte Carlo simulations accurately capture this uncertainty, resulting in calibrated models with an R-squared coefficient above 80%. In summary, this work provides a practical and comprehensive framework for studying CO2 retention in porous media, addressing uncertainty through stochastic parameter distributions, and highlighting its importance in CO2 storage projects.
Open Access
Article
05 January 2024Benzene Bridged Carbon Nitride for Efficient Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution
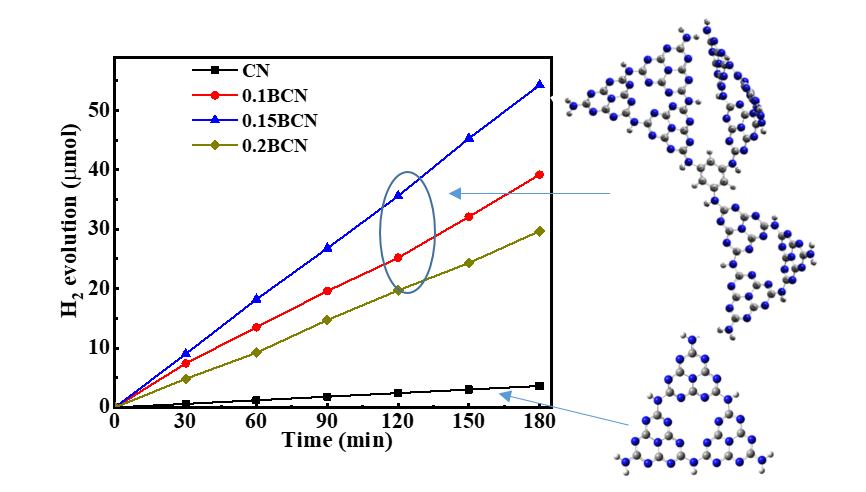
Turing the electronic structure by inserting certain functional groups in graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4, CN for short) skeleton through molecular doping is an effective way to improve its photocatalytic performance. Herein, we prepare a benzene bridged carbon nitride (BCN) by calcining urea and 1,3,5-tribromobenzene at elevated temperature. The introduction of benzene ring in g-C3N4 layers improves the separation efficiency and lifetime of photogenerated carriers, inhibits the recombination rate of electron/hole pairs, thus the performance of photocatalytic hydrogen evolution improves. The optimal hydrogen evolution rate of 1.5BCN reaches 1800 µmol/h·g, which is nine times that of the pure g-C3N4. DFT calculation proved the benzene bridged CN increased the distance of charge transfer (DCT) and the push-pull electronic effect of intramolecular electrons. This work may provide a pathway for preparing molecular doped g-C3N4 with improved photocatalytic performance.
Open Access
Article
07 October 2023Comprehensive Evaluation of Sustainable Treatment Technology of Oily Sludge Based on AHP-FCE
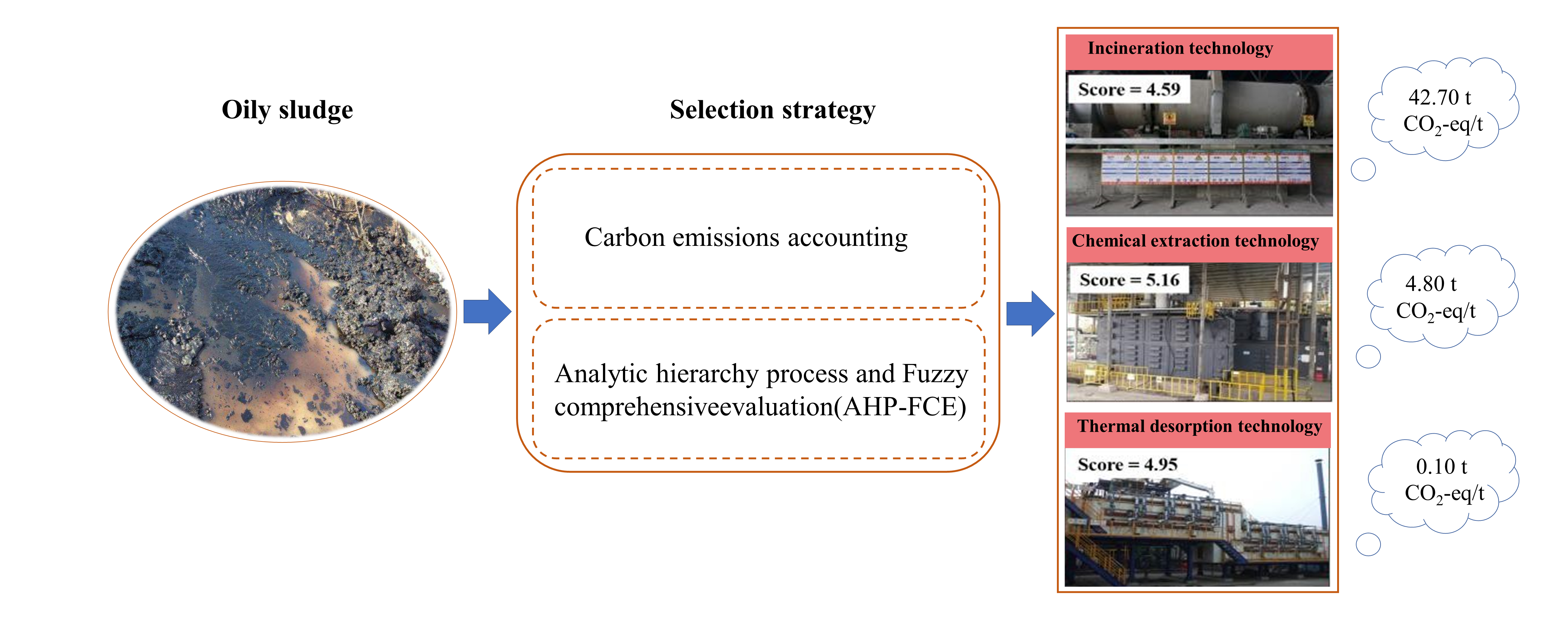
Oil is an unsustainable energy since it is non-renewable. However, oil may not be completely replaced in a short time, so the environmental problems caused by the oil development still require our attention. The oily sludge is a kind of hazardous waste produced during the oil development. To reduce the environmental impact caused by oily sludge, low-carbon and sustainable treatment technologies need to be selected. The incineration, chemical extraction and thermal desorption are common technologies for treatment of oily sludge. We calculated the carbon emissions of these technologies. Then the index evaluation system of oily sludge treatment technology was established with the environmental, economic, social, and technical factors. And the weight of evaluation index was determined by the analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Through the investigation of industry experts, we evaluated the treatment technologies by the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method (FCE). The results showed that the carbon emissions of incineration are 42.70 t CO2-eq/t which is the highest. Meanwhile, it is 4.80 t CO2-eq/t and 0.10 t CO2-eq/t for chemical extraction and thermal desorption, respectively. The comprehensive scores of incineration, chemical extraction and thermal desorption were 4.59, 5.16 and 4.95, respectively. Therefore, the chemical extraction technology is an optimal treatment technology for oily sludge with the relatively low carbon emission and the highest comprehensive technical score. At the same time, the thermal desorption technology has strong application potential with the lowest carbon emissions. This result provides a reference for achieving clean and sustainable energy development processes.
Open Access
Article
08 September 2023Synthesis and Characterization of Cyclic Carbonate End-Functional Linear and Star Polyesters via Ring-Opening Polymerization
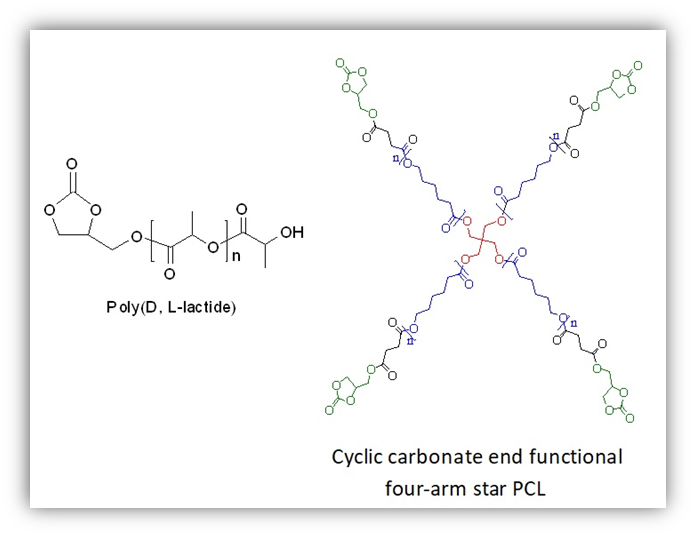
Well-defined α-(cyclic carbonate), ω-hydroxyl heterotelechelic poly (D,L-lactide)s (PDLLAs) were prepared with good end-group fidelity by ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of D,L-lactide catalyzed by organo catalyst namely, N,N′ dimethyl amino pyridine (DMAP) in conjunction with a renewable, functional bio-based initiator namely glycerol 1,2-carbonate (GC) in bulk at 135 °C with 82% yield. In the case of GC/DMAP catalyzed polymerizations, the HO-PDLLA-COOH series was not observed in MALDI TOF mass analysis unlike as obtained due to transesterification reactions when catalyzed by GC/Sn(Oct)2. Also, cyclic carbonate end-functional 4-arm star poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) was prepared via coupling of GC with (PCL-COOH)4 at room temperature in the presence of N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) and DMAP. Quantitative conversion of hydroxyl functionality in (PCL-OH)4 to carboxylic acid and then to cyclic carbonate functionality was achieved with 90% yield for low molecular weight 4-arm star PCL confirmed by NMR, FT-IR, and MALDI TOF mass spectroscopy.
Open Access
Review
01 September 2023In Vitro BioTransformation (ivBT): Definitions, Opportunities, and Challenges
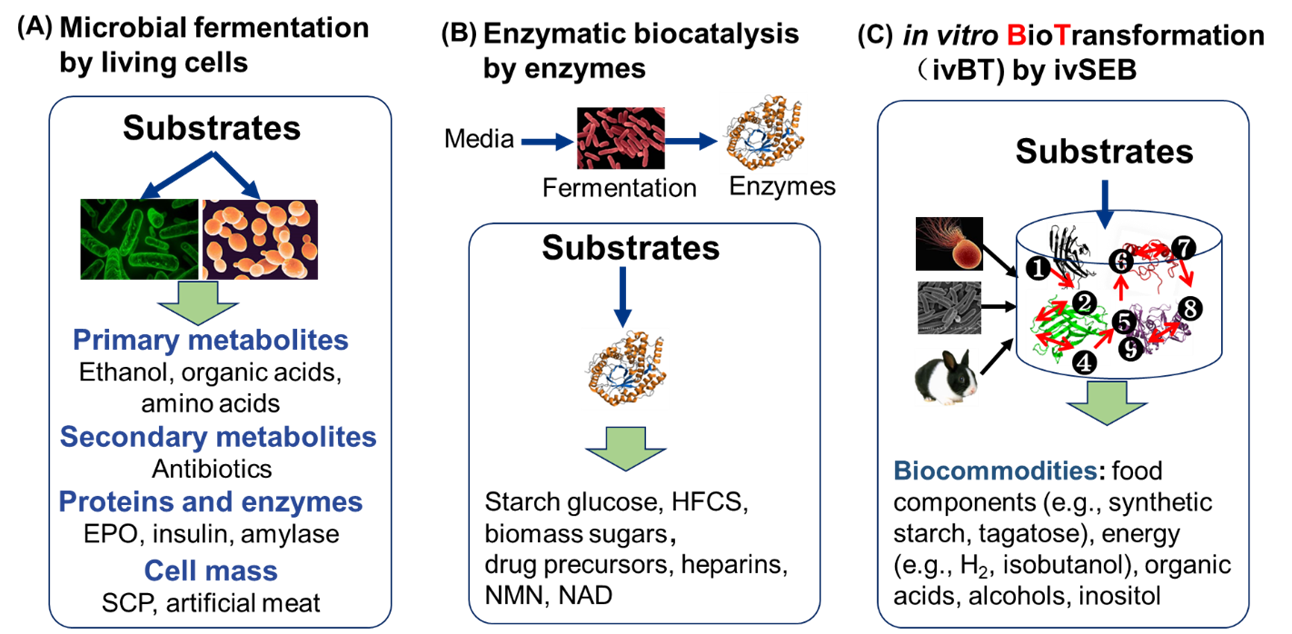
Great needs always motivate the birth and development of new disciplines and tools. Here we propose in vitro BioTransformation (ivBT) as a new biomanufacturing platform, between the two dominant platforms—microbial fermentation and enzymatic biocatalysis. ivBT mediated by in vitro synthetic enzymatic biosystems (ivSEBs) is an emerging biomanufacturing platform for the production of biocommodities (i.e., low-value and bulk biochemicals). ivSEB is the in vitro reconstruction of artificial (non-natural) enzymatic pathways with numerous natural enzymes, artificial enzymes, and/or (biomimetic or natural) coenzymes without living cell’s constraints, such as cell duplication, basic metabolisms, complicated regulation, bioenergetics, and so on. The two great needs (i.e., food security and the carbon-neutral renewable energy system) have motivated the birth and development of ivBT. Food security could be addressed by making artificial food from nonfood lignocellulose and artificial photosynthesis for starch synthesis from CO2. The carbon-neutral renewable energy system could be addressed by the construction of the electricity-hydrogen-carbohydrate cycle, where starch could be a high density of hydrogen carrier (up to 14.8% H2 wt/wt) and an electricity storage compound (greater than 3000 Wh/kg). Also, ivBT can make a number of biocommodities, such as inositol, healthy sweeteners (e.g., D-allulose, D-tagatose, D-mannose), advanced biofuels, polymer precursors, organic acids, and so on. The industrial biomanufacturing of the first several biocommodities (e.g., myo-inositol, D-tagatose, D-mannose, and cellulosic starch) would wipe off any prejudice and doubt on ivBT. Huge potential markets of biocommodities with more than tens of trillions of Chinese Yuan would motivate scientists and engineers to address the remaining technical challenges and develop new tools within the next decade.
Open Access
Article
08 May 2023A High-efficiency Cathode Using Co3O4 and Carbon Paper by Electrodeposition for Rechargeable Lithium-oxygen Batteries
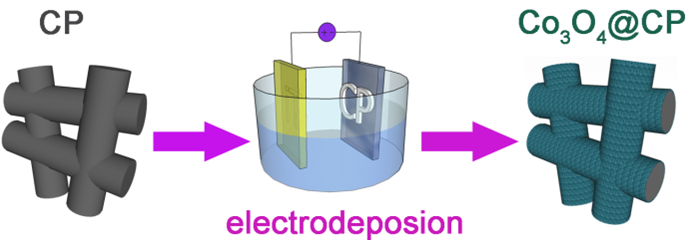
The conductivity, microstructure, low cost, eco-friendliness, simple and controllable preparation are key points of the preparation and application of cathode materials for lithium-oxygen batteries. Considering the above-mentioned important factors comprehensively, the Co3O4@CP electrode with a three-dimensional structure was prepared by directly growing Co3O4 on the surface of carbon paper (CP) using a simple and controllable electrodeposition method. The obtained Co3O4 depositing layer has a nanosheet microstructure and can provide abundant catalytic active sites for the oxygen evolution and reduction reactions. The network architecture of electronic transmission is constructed by CP in the cathode, promoting the efficiency of the electrode reaction. It’s worth noting that the binder-free and conductive additive-free cathode is beneficial to reduce side reactions. The lithium-oxygen battery assembled with the obtained Co3O4@CP electrode showed satisfactory electrochemical performance. The cell assembled with the obtained Co3O4@CP electrode provided a discharge specific capacity of 10954.7 mA·h·g−1 at a current density of 200 mA·g−1, and the voltage profiles of the cell were good under 100 mA·g−1 at a limited capacity of 500 mA·h g−1 based on the mass of Co3O4. Therefore, the Co3O4@CP composite material is a promising candidate with good application prospects as a cathode material for lithium-oxygen batteries.
Open Access
Article
21 March 2023Waterborne Polyurethane Dispersion Synthesized from CO2 Based Poly (Ethylene Carbonate) Diol with High Performance
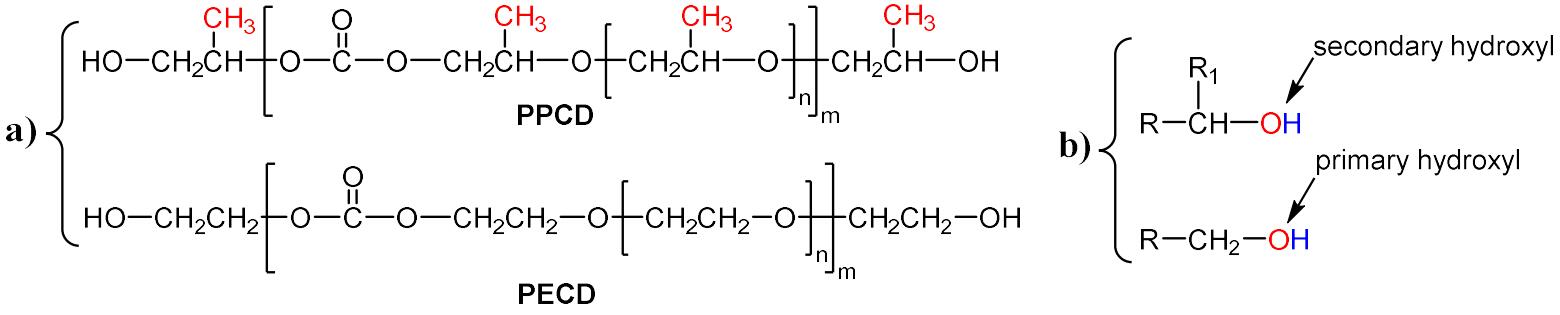
CO2-based aliphatic polycarbonates (APCs) are not widely commercialized due to the poor performance and high cost, compared to the traditional synthetic materials. In this paper, poly(ethylene carbonate) diol (PECD) was synthesized from CO2 and ethylene oxide (EO), and the comprehensive properties were characterized. Furthermore, the preparation and properties of waterborne polyurethane dispersion (WPU) derived from PECD were studied. The result showed that PECD had high reactivity, narrow molecular weight distribution index and excellent thermal stability. The obtained WPU exhibited superior tensile performance, adhesion properties and surface hardness. Due to the low cost of EO and CO2, PECD is expected to be widely used in the preparation of polyurethanes.
Open Access
Article
13 March 2023Reduced Climate Impacts of Dairy Sludge Management by Introducing Hydrothermal Carbonization
Dairies which produce cheese and milk products can, however, produce large volumes of wastewater that require treatment, usually via activated sludge treatment. Disposal of the resulting activated sludge to land is viewed favorably as the sludge is rich in phosphorus (P) and nitrogen (N) and enables nutrient recycling. Nonetheless, sludge management can significantly influence the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to the atmosphere. This manuscript has modelled the GHG emissions arising from two sludge management strategies currently adopted by Danish dairies whereby: (i) sludge is stored and later applied to fields; or (ii) sludge is treated by anaerobic digestion (AD), stored, and the digestate will later be applied to fields. This is compared to (iii) an alternative sludge management strategy with treatment by Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC). HTC is a technologically simple sludge treatment that could lower the cost for dewatering dairy sludge, forming a biochar-like material known as hydrochar. The produced hydrochar can be applied to the land for the purpose of carbon sequestration, P and N recycling. Our calculations indicate that GHG balances of HTC sludge management can result in a net carbon sequestration of 63 kg CO2eq per ton sludge, as opposed to net emissions of 420 and 156 kg CO2eq per ton sludge for strategies (i) and (ii), therefore offering significant reductions GHG emissions for the dairy sector.
Open Access
Article
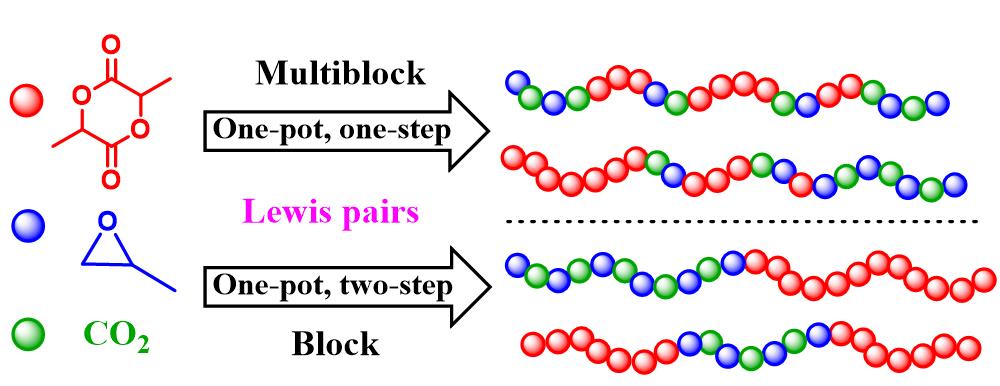
30 January 2023Metal-Free Lewis Pair Catalysts for a One-Pot Terpolymerization of Propylene Oxide, ʟ-Lactide and CO2
Multiblock and di-/tri-block copolymers are successfully synthesized for the first time via the metal-free terpolymerization of propylene oxide (PO), ʟ-lactide (LA) and CO2 in one-pot/one-step and one-pot/two-step protocols respectively. Firstly, triethyl borane (TEB) and bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride (PPNCl) Lewis pair is employed in the ring-opening polymerization of LA, wherein the catalytic efficiency is significantly correlated to the TEB/PPNCl feed ratio. Next, a series of TEB/base pairs are selected to synthesize the PO/LA/CO2 terpolymer (PPCLA) in one-pot/one-step strategy. In PPCLA synthesis, LA exhibits the fastest reaction rate but severe transesterification is almost unavoidable, resulting in low molecular weight products. In order to prepare high-molecular-weight terpolymers, a one-pot/two-step methodology has to be applied. By this method, the copolymerization of PO/CO2 proceeds first to form poly(propylene carbonate) (PPC) macroinitiators, which triggers the polymerization of LA to polylactide (PLA), leading to PLA-PPC or PLA-PPC-PLA block copolymers. The synthesized PLA-PPC-PLA block copolymers display improved thermal stability compared with PPC.
Open Access
Perspective
29 January 2023Carbon Neutrality and Life Cycle Thinking
Climate change is one of the most critical sustainability challenges facing the humanity. International communities have joined forces to mitigate climate change impact and aim to achieve carbon neutrality in the coming decades. To achieve this ambitious goal, life cycle thinking can play critical roles. Specifically, life cycle thinking helps evaluate the true climate impacts to avoid shifting emissions across processes in a product life cycle. It can also help inform consumers with carbon footprint information to make climate-conscious choices. Finally, it can help identify key processes dominating the carbon footprint of a product so that future improvement can set priorities. High quality data is required for accurate and timely carbon footprint accounting and critical challenges exist to obtain and share such data.
