Found 469 results
Open Access
Article
19 May 2025Research on Thermal Fault Detection and Location of Photovoltaic Connectors Based on Multiple Model Estimator
Offshore photovoltaic (PV) systems encounter challenges due to high humidity and salt spray environments. The PV connectors on the DC input side of inverters are particularly susceptible to increased contact resistance and local overheating caused by environmental corrosion. This paper introduces a novel thermal fault location method utilizing a multiple model estimator (MME). The approach develops a lumped thermal model and an abnormal overheating disturbance model for the PV connectors. By combining a Kalman filter with a probability fusion algorithm, the method effectively detects thermal faults. Simulation and experimental results demonstrate that this approach can accurately locate faults while requiring only a minimal number of thermal sensors, thereby enhancing the reliability of offshore PV systems.

Open Access
Article
19 May 2025Database of Ecological Indicators of Freshwater Algae and Cyanobacteria
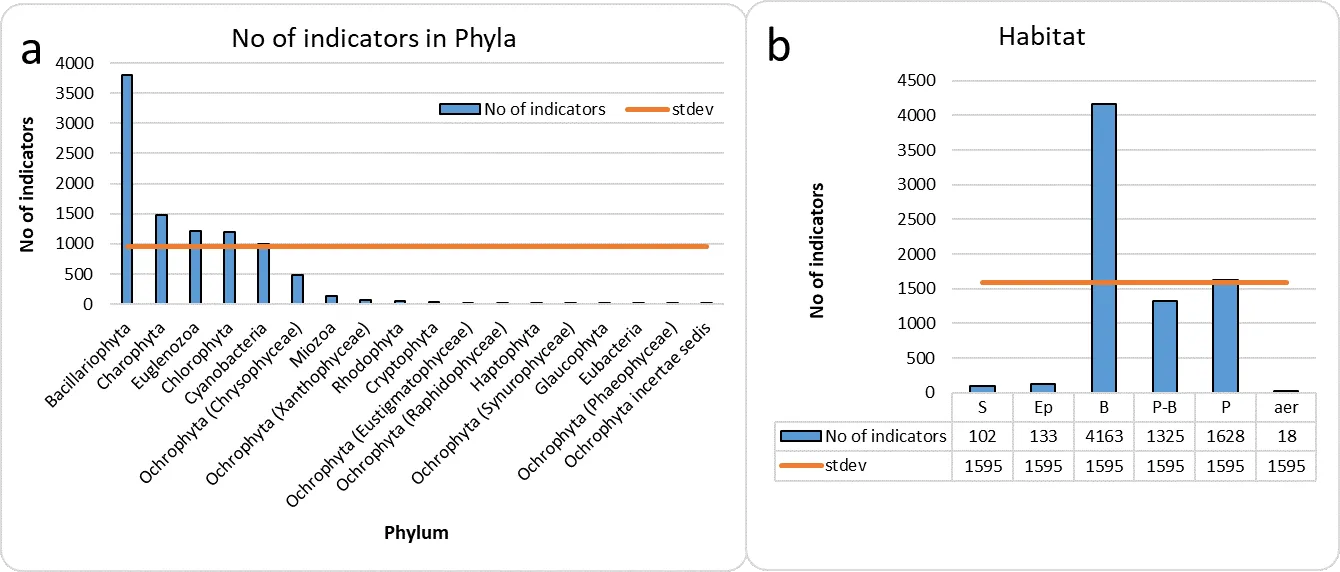
Accumulation of ecological data on species of algae and cyanobacteria represents 9531 taxa-indicators from 18 taxonomic phyla. The most represented among the indicators is the taxonomic group of diatoms. The indicators are grouped into twelve ecological groups, which can be indicators of nine environmental parameters. The environmental characteristics for each of the indicator systems and the relationship between some of them are given. Individual abbreviations of ecological indicator groups that have been established as a result of long-term use are given. References are given to examples of the application of analysis of specific water bodies using bioindication methods, and prospects for use in monitoring and assessing water quality are shown. A specific example of using the database is given. The table of indicator taxa contains cumulative ecological data and is easy to use. This table is a living tool that can be supplemented and transformed when new information about indicator species comes.
Open Access
Article
19 May 2025Quorum Sensing Systems Engineering for Enhanced iso-Butylamine Production in Escherichia coli
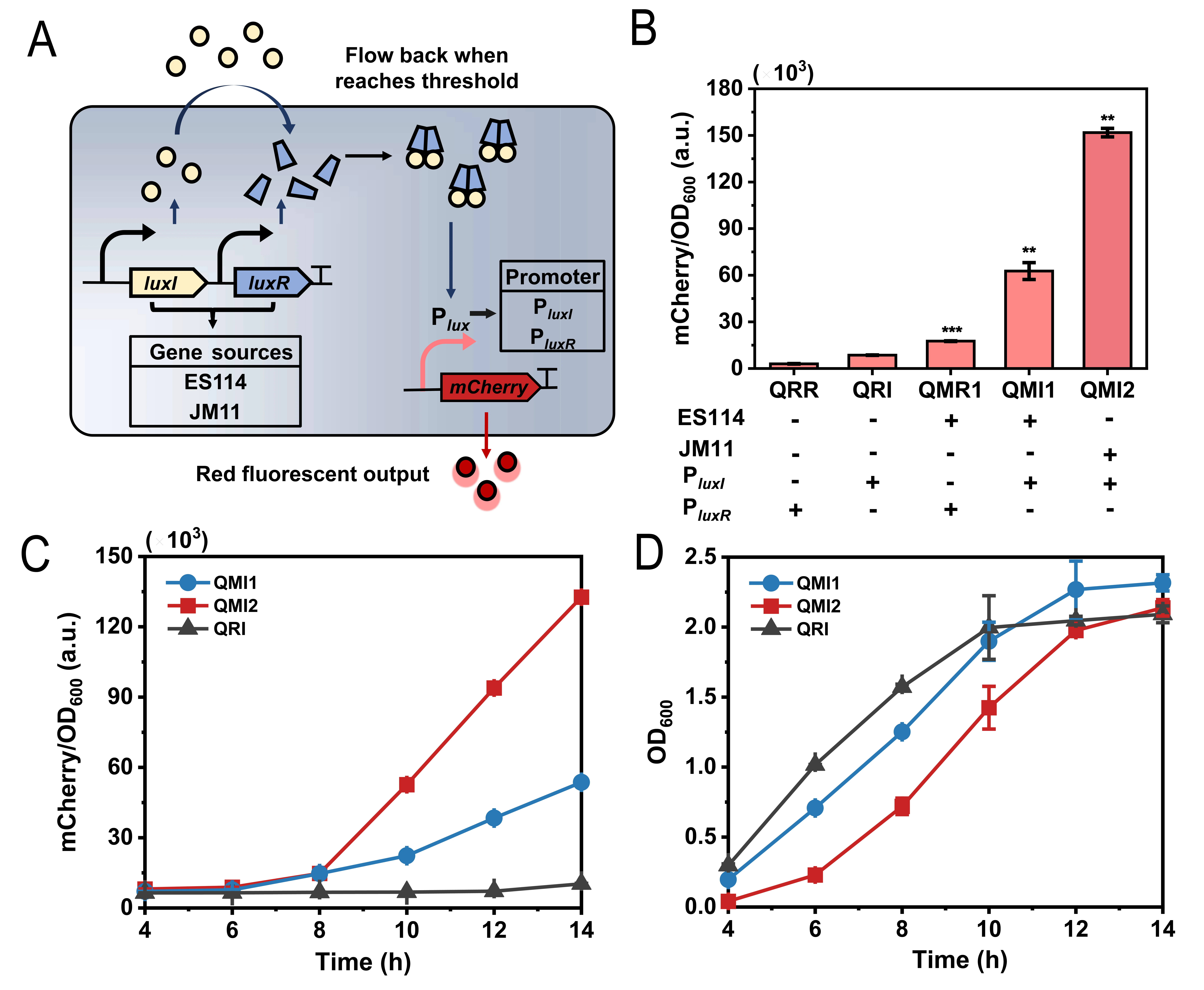
Quorum sensing (QS), characterized by pathway-independence and autonomous control, has been applied in bio-manufacturing, while the lack of versatile and functional regulatory components limits its broader applications. To address this issue, a series of efficient QS systems with diverse properties were established in Escherichia coli. Firstly, combinatorial optimization, including element selection and promoter replacement, led to an improvement of 8.82- and 3.03-fold in output range and response threshold, respectively. Then, a library of LuxR mutants was constructed for screening novel variants with decreased sensitivity to acyl-homoserine lactone through the high-throughput screening technique. Notably, the optimal variant V36E/H89L/P97L exhibited a decrease of 266-fold in the sensitivity. As a proof-of-concept, iso-butylamine biosynthesis was tested by re-directing pyruvate catabolism using QS circuits, and in particular, a total of 15.4 g/L iso-butylamine was generated in strain IB21 during the fed-batch culture, marking a 2.96-fold increase over the static control. Finally, the generated bioproduct reached 44.23 g/L in a bioreactor, representing the highest reported titer so far. In summary, this study not only enriches the genetic toolbox of QS systems, but also facilitates industrial applications in value-added chemical production.
Open Access
Review
19 May 2025Ecological Degradation and Restoration Process in the Source Region of Yangtze River: A Review Using the DPSIR Framework
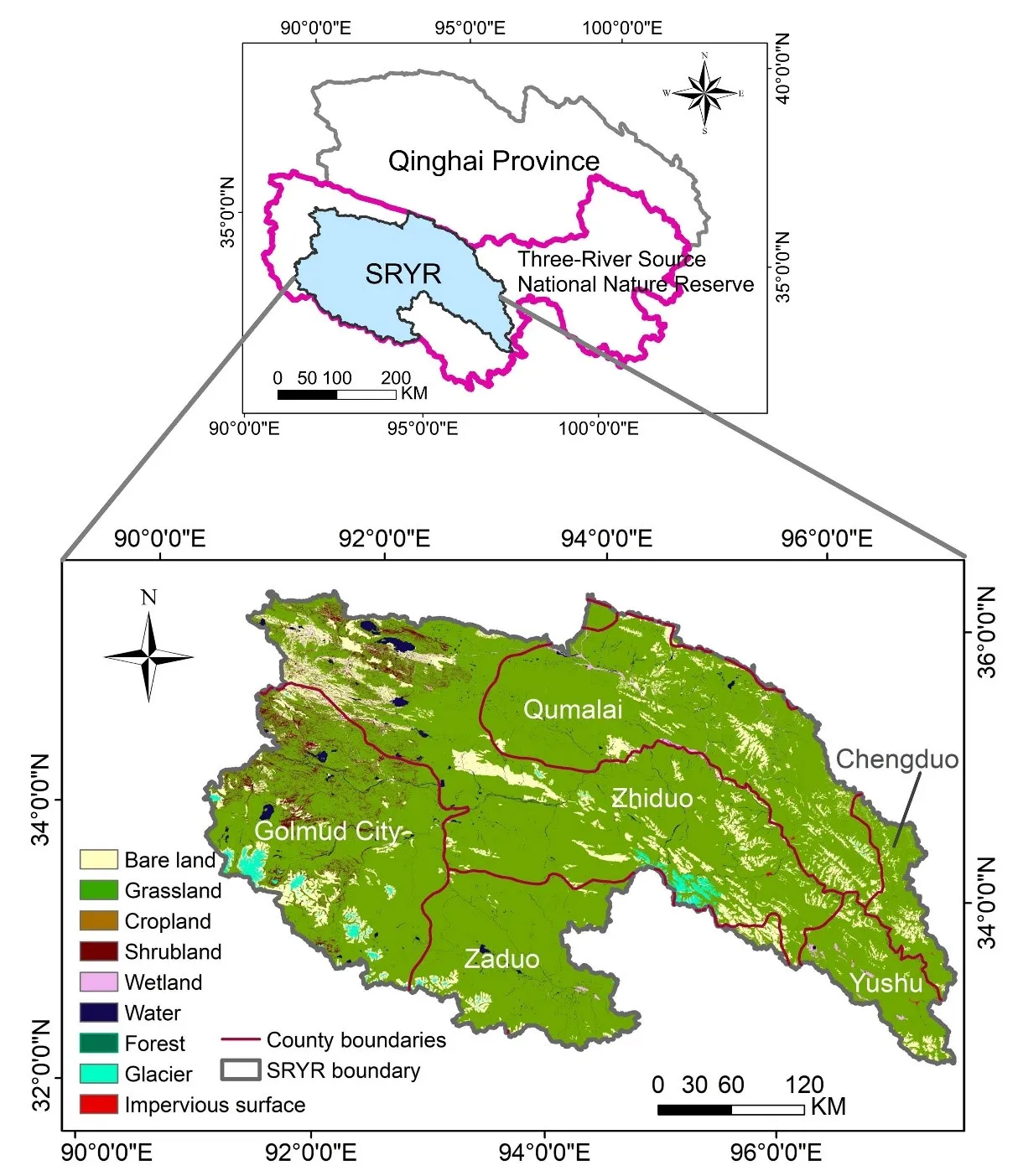
By the end of the 20th century, the Source Region of the Yangtze River (SRYR) suffered severe ecological degradation driven by the combined effects of climate change and human disturbances. To counteract ecological degradation, the Chinese government implemented multiple ecological protection and restoration measures. Based on a literature review, this study analyzed the entire process of ecological degradation and restoration in the SRYR using the DPSIR (Drivers-Pressures-States-Impacts-Responses) framework. It revealed that climate warming and grazing expansion were the main drivers. Under the dual pressures of natural and anthropogenic disturbances, grasslands experienced severe degradation, accompanied by significant losses of soil nutrients. The decline in grassland quality weakened ecosystem service functions and reduced the livelihood levels of herders. After implementing the ecological protection and restoration projects in China, the ecosystem had been effectively restored. Herders’ income levels had been improved. However, a mismatch persisted between ecological compensation standards and livestock reduction costs for herders. Future efforts should focus on the innovation of the institution and ecological restoration techniques. This study offers critical insights into ecological protection and restoration strategies, providing practical references for decision-makers to accelerate the realization of China’s ecological civilization objectives.
Open Access
Article
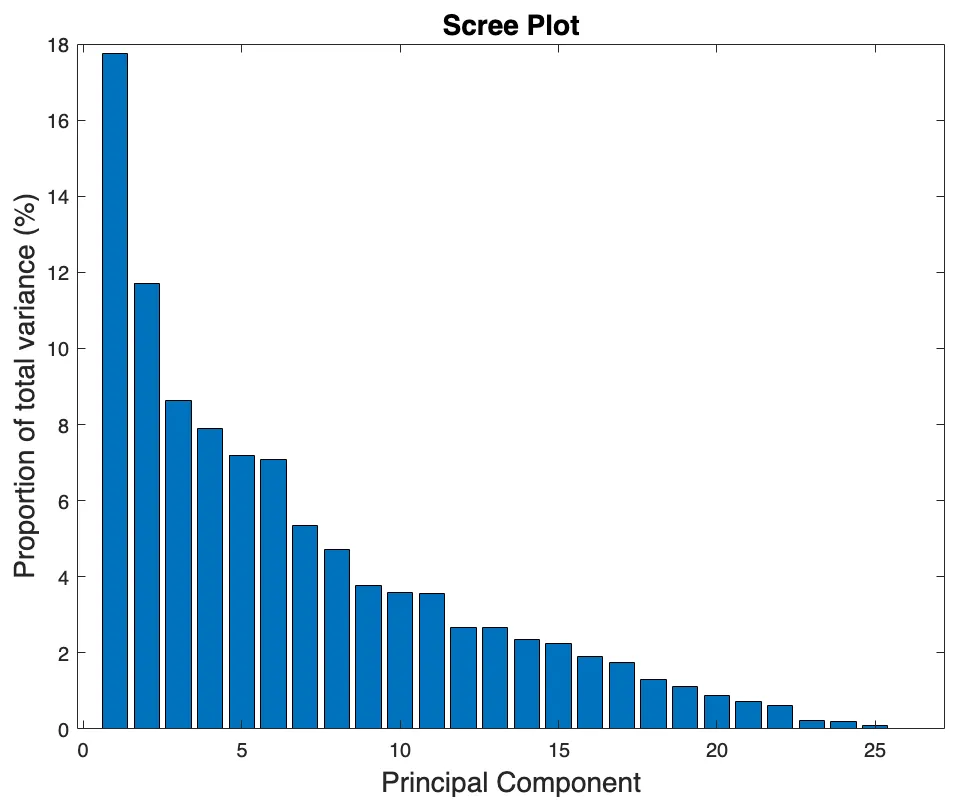
16 May 2025Application of Principal Component Analysis to Heterogenous Fontan Registry Data Identifies Independent Contributing Factors to Decline
Single ventricle disease is a serious and deadly illness, and advances in clinical management of individuals with Fontan circulation over the past two decades have yet to yield acceptable survival. Patients remain at risk of developing a diverse assortment of Fontan-associated comorbidities that ultimately require a heart transplant. Our goal in this observational cohort study was to determine if application of principal component analysis (PCA) to heterogeneous data collected from a sizable Fontan cohort (n = 140) would predict functional decline. The data, broadly comprised of blood biomarkers, lymphatic biomarkers, measures of cardiac and vascular function, and exercise (VO2max), were collected at a single site over 11 years; 16 events occurred over that time that we consider here as a single composite outcome measure. The standardized data was transformed via PCA, and principal components (PCs) characterizing >5% of total variance were thematically labeled based on their constituents and tested for association with the composite outcome. We found that the 6th PC (PC6), which represents 7.1% of the total variance, is superior to ejection fraction (EF) as a measure of proportional hazard, is greatly influenced by blood serum biomarkers and superior vena cava flow, and displays the greatest accuracy (according to area under the curve analysis) for classifying Fontan patients. In bivariate hazard analysis, we determined that models combining lymphatic dysfunction (PC6) and systolic function (EF or PC5) were most accurate, with the former having the highest c-statistic, and the latter having the greatest AIC. Our findings support our hypothesis that improved prognostication in a Fontan population should utilize a multifactorial model.
Open Access
Perspective
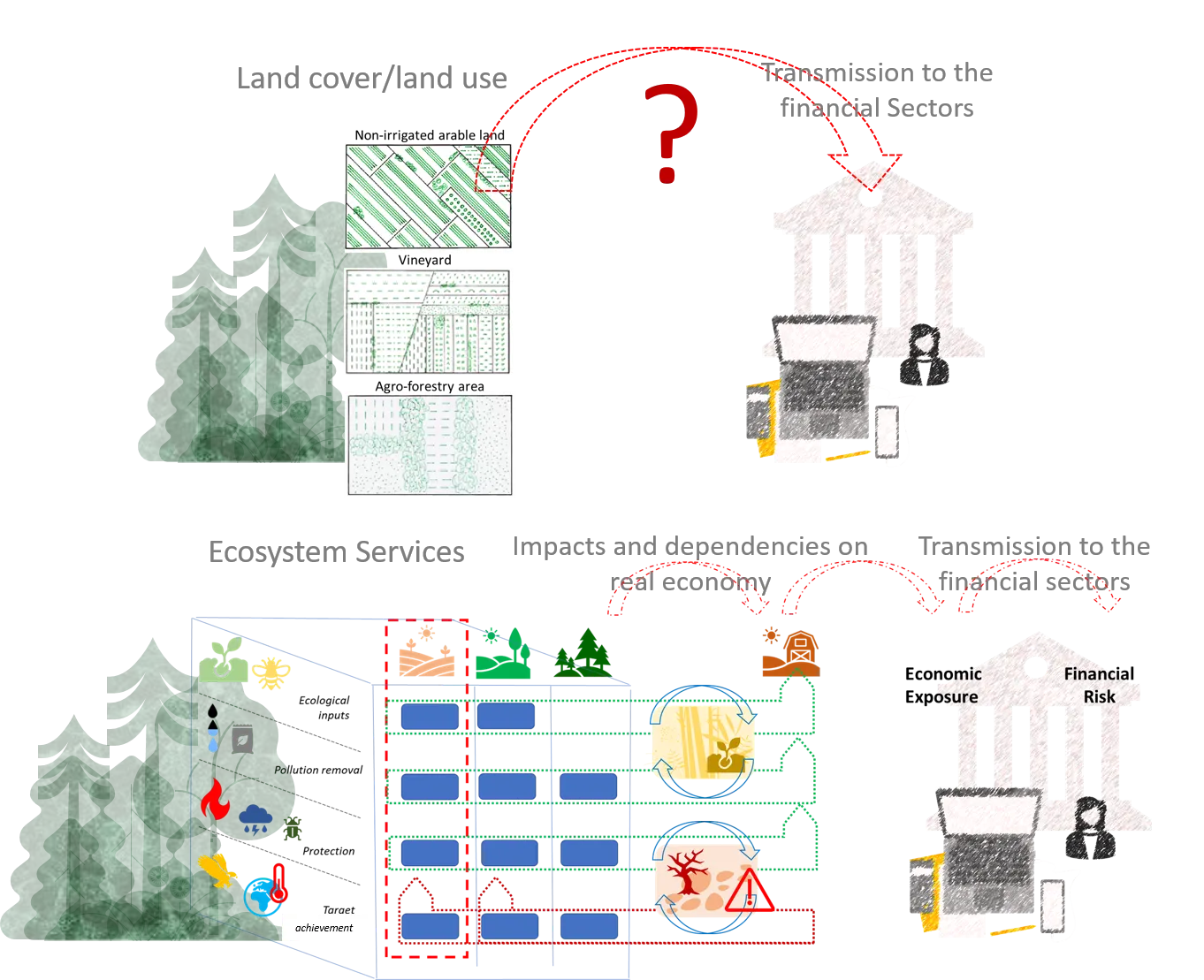
16 May 2025From “Land” to “Ecosystems”—Paving the Way for Ecosystem Services in Sustainable Finance
Although biodiversity loss is acknowledged as one of the main drivers of financial risk, there is still no clear understanding of how impacts and dependencies on biodiversity affect the financial sector. In fact, nature degradation does not manifest itself as a systemic risk because it does not threaten the very nature of the financial system. There are transmission channels between nature and finance that need to be investigated: the many intermediate cause-and-effect relationships should be identified and assessed. Such a process involves multiple disciplinary domains, ranging from ecology and economics to finance. An Ecosystem Services-based approach may represent a comprehensive framework to (i) reconcile coherently different environmental issues such as climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution and sustainable use of resources, and (ii) connect ecosystems and socio-economic systems. Not only can ecosystem services be assessed, but also ecosystem vulnerabilities which are at the origin of nature-related financial risks. Adopting an ecosystem services-based perspective can be the first step toward building ecologically meaningful and economically useful transmission channels for financial risks.
Open Access
Article
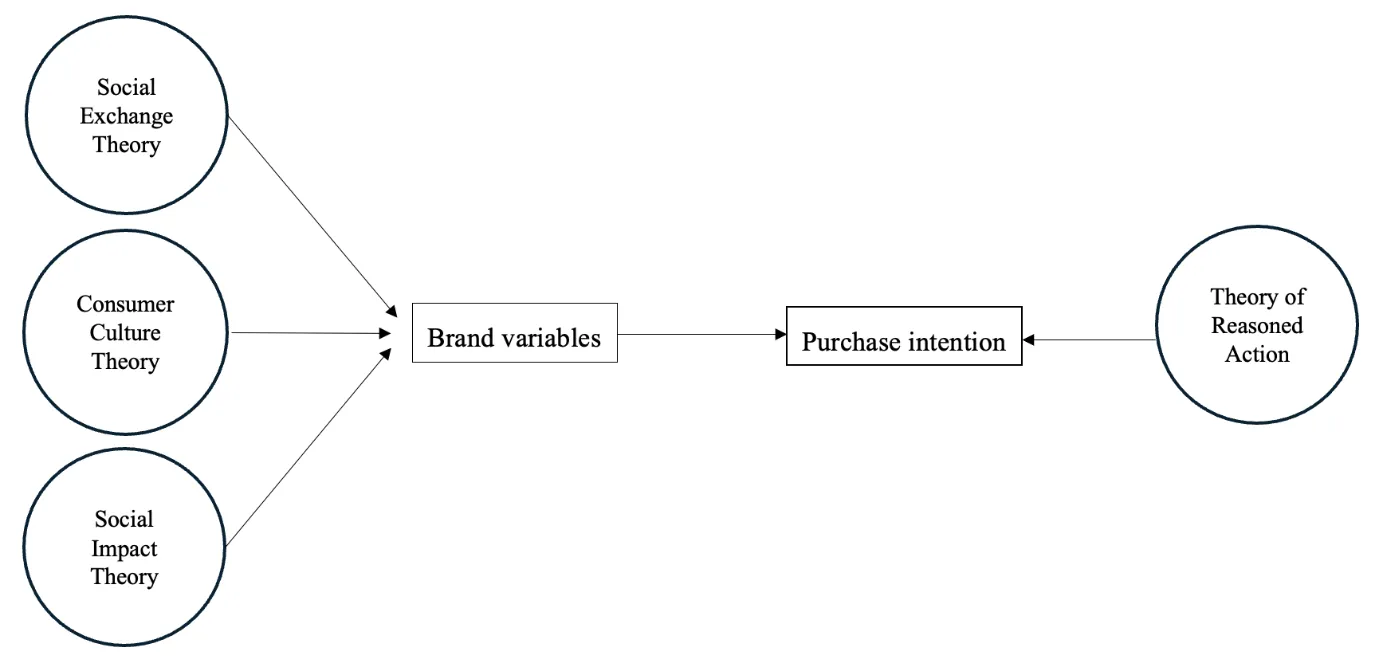
14 May 2025The Digital Generation: Branding and Consumer Behavior in Tech Adoption
This research investigates how different branding aspects influence Generation Z’s intention to purchase newly launched technological products designed for the agricultural sector. Given Gen Z’s strong digital engagement and preference for authenticity, sustainability, and innovation, branding plays a pivotal role in shaping their buying decisions. The study aims to assess the impact of key branding elements—such as brand experience, knowledge, image, trust, and loyalty—on the purchase intention of newly launched technological products with applications in agriculture management and informatics. As agricultural practices increasingly integrate smart farming technologies, data-driven decision-making, and precision agriculture, branding becomes crucial in ensuring the adoption of these innovations. Agricultural informatics—encompassing IoT-based monitoring systems, AI-driven analytics, and automated farm management solutions—relies on user trust and engagement for successful market penetration. Gen Z, a tech-savvy and socially conscious demographic, is particularly responsive to brands that emphasize efficiency, sustainability, and transparency in agricultural innovations. A quantitative research approach was adopted, utilizing a structured questionnaire administered to 302 Generation Z participants. Statistical analyses, including correlation and multiple regression, were conducted to examine the relationships between branding factors and purchasing behavior. The results indicate that online brand experience, brand knowledge, and brand image are the most significant predictors of purchase intention, highlighting the critical role of digital interactions, educational branding, and the perceived value of technology in optimizing agricultural processes. Although brand trust and loyalty influence consumer behavior, their impact is less significant than that of experience and knowledge. Although brand awareness and engagement correlate with purchase intention, they do not independently drive purchasing decisions. The study concludes that companies should prioritize enhancing digital brand experiences, providing transparent information, and reinforcing brand imagery to drive product adoption among Generation Z, particularly in the agricultural sector. As this generation continues to shape market trends, agricultural informatics, and smart farming technologies, businesses must craft branding strategies that align with Gen Z’s digital habits, values, and expectations. Future research should explore the long-term impact of branding on agricultural technology adoption and investigate the role of emerging technologies such as blockchain, AI, and big data in strengthening brand engagement and loyalty within the agricultural sector.
Open Access
Review
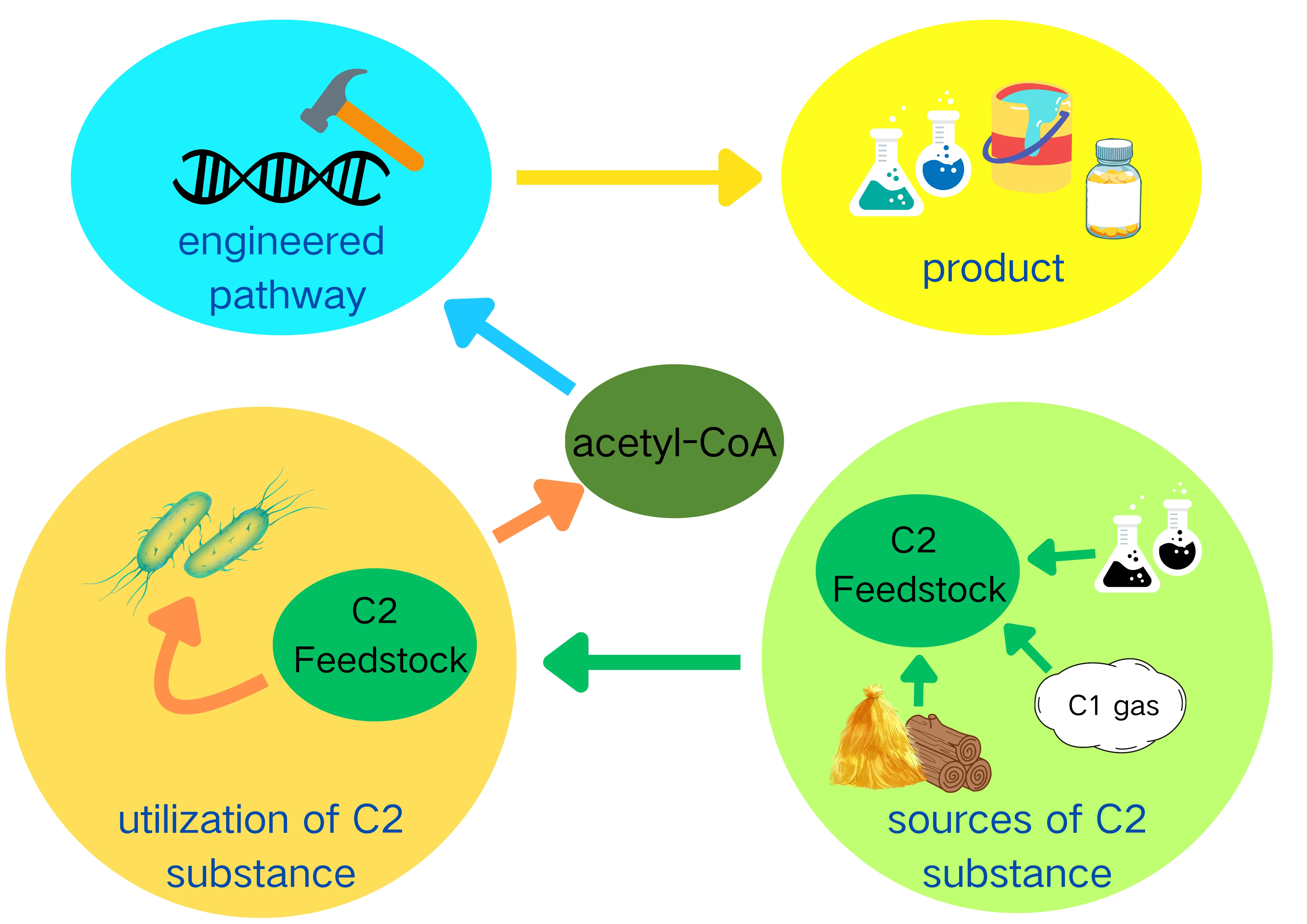
14 May 2025Current Status of Biological Production Using C2 Feedstocks
C2 feedstocks have emerged as promising carbon sources for the biological production of various value-added chemicals. Compared to the traditional C6/C5 sugars-contained/constituted feedstocks, C2 feedstocks have diverse and abundant sources, including non-food biomass, industrial by-products, and C1 gases. This diversification not only eliminates competition with human food demands but also aligns with environmental sustainability goals. Moreover, the metabolic route for C2 compounds to enter central carbon metabolism is more direct, which minimizes the carbon loss and enhances the efficiency of bio-based production processes. This review extensively analyzes three prominent C2 chemicals: ethylene glycol, ethanol, and acetate. After introducing the sources of those compounds, it details the metabolic pathways through which they are converted into acetyl-CoA in vivo. Several chemicals produced from these C2 feedstocks in fermentation are also exemplified. Furthermore, different perspectives are proposed to promote the efficient utilization of C2 feedstocks.
Open Access
Article
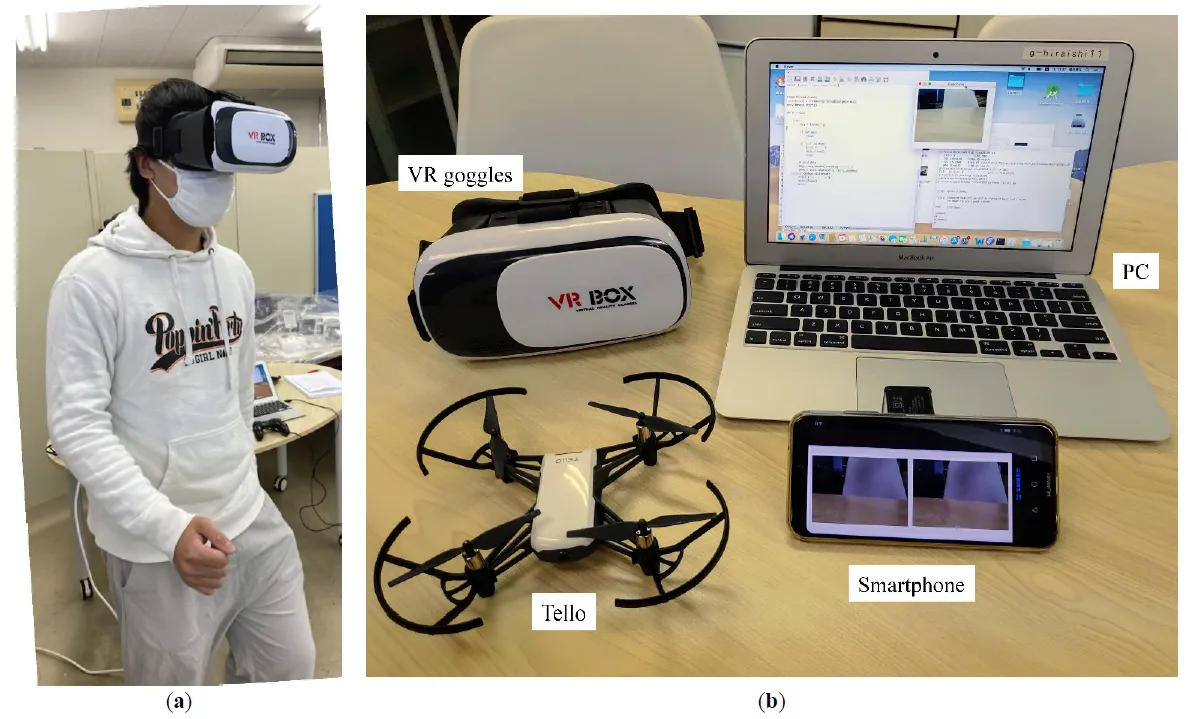
12 May 2025Drone Operation with Human Natural Movement
This study proposes a method for operating drones using natural human movements. The operator simply wears virtual reality (VR) goggles. An image from the drone camera was displayed on the goggles. When the operator changes the direction of his or her face, the drone changes the direction to match that of the operator. When the operator moves their head up or down, the drone rises or falls accordingly. When the operator walks in place, rather than walking, the drone moves forward. This allows the operator to control the drone as if they were walking in the air. Each of these movements was detected by the values of the acceleration and magnetic field sensors of the smartphone mounted on the VR goggles. A machine learning method was adopted to distinguish between walking and non-walking movements. Compared with operation via conventional remote control, it was observed that the remote controller performed better than the proposed approach in the early stages. However, when the participants familiarized themselves with the natural operation, these differences became relatively small. This study combined drones, VR, and machine learning. VR provides drone pilots with a sense of realism and immersion, whereas machine learning enables the use of natural movements.
Open Access
Article
09 May 2025Modeling and Assessing Economical Feasibilities for Waste to Energy Conversion/Incineration Process in Context of Municipal Solid Waste
At the time of the study, most of the municipal waste, including solid municipal waste, in the city of St. Petersburg and in the connected larger Leningrad region is processed by landfilling. This sort of waste processing in open landfills causes environmental damage, uncontrollable landfill fires, bad and dangerous odors, nearby rivers/streams, groundwater pollution, CH4 and CO2 emissions, to mention a few. Additionally, landfilling is a waste of energy and material resources present in the content dumped into landfills. In this context, Waste-to-Energy (WtE) incineration is a process that we use to recover the energy the materials have back to usable form, which we use in the form of heat and electricity. Even though a lot of resources and energy are available in the (municipal solid) waste, it does not mean that recovering it would always make sense. Our study analyses and estimates the profitability of a WtE incineration plant(s) in the city of St. Petersburg and the connected Leningrad region. With the available data and following analysis, we have concluded that the WtE incineration is economically feasible in this specific region and city areas, given that the implementations follow more traditional (economically less expensive and easier) technical and process model solutions. As a note of results stability, it needs to be pointed out that the changes in estimates of gate fees, cost of electricity and heat, and so on do impact the economic feasibility a lot, and larger scale changes in the assumed revenues would have a high impact on the outcome of repeatability of the results.