Found 469 results
Open Access
Article
23 June 2025A Structured Framework for Formalized and Quantitative Handwriting Examination
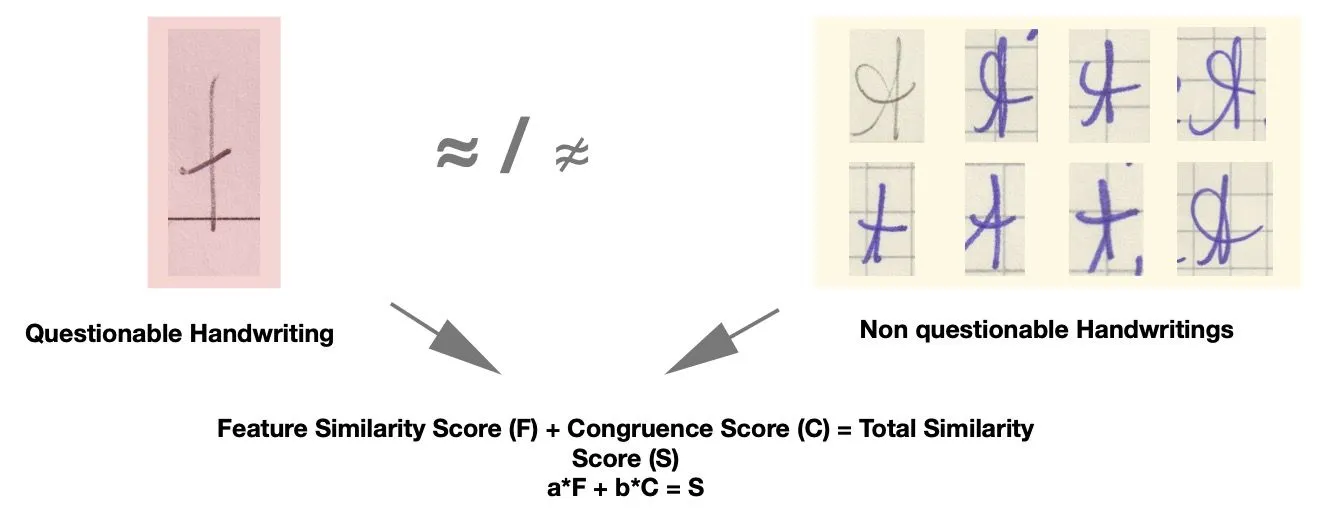
The demand for a formalized and transparent approach to handwriting assessment has long been recognized within forensic and legal contexts. A structured methodology not only reduces interpretative subjectivity but also enables quantifiable measurement and ensures greater consistency in evaluations. This article presents a practical framework that models the degree of similarity between handwriting samples—texts and signatures—through a two-stage process: feature-based evaluation and congruence analysis. Both stages produce quantitative markers that are integrated into a unified similarity score, forming the foundation for more complex comparisons involving multiple questions and known texts. The proposed procedure, which is the major result of the paper, is not merely theoretical; it has been applied in real forensic casework, yielding preliminary statistical outcomes. In particular, it demonstrates the discriminative power of different handwriting features. The paper also discusses future directions for development, with a focus on the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance specific components of the assessment process.
Open Access
Article
23 June 2025A Systematic Review of Clean Cooking and to Whom Does the Clean Cooking Agenda Belong? Empirical Evidence from East African Community
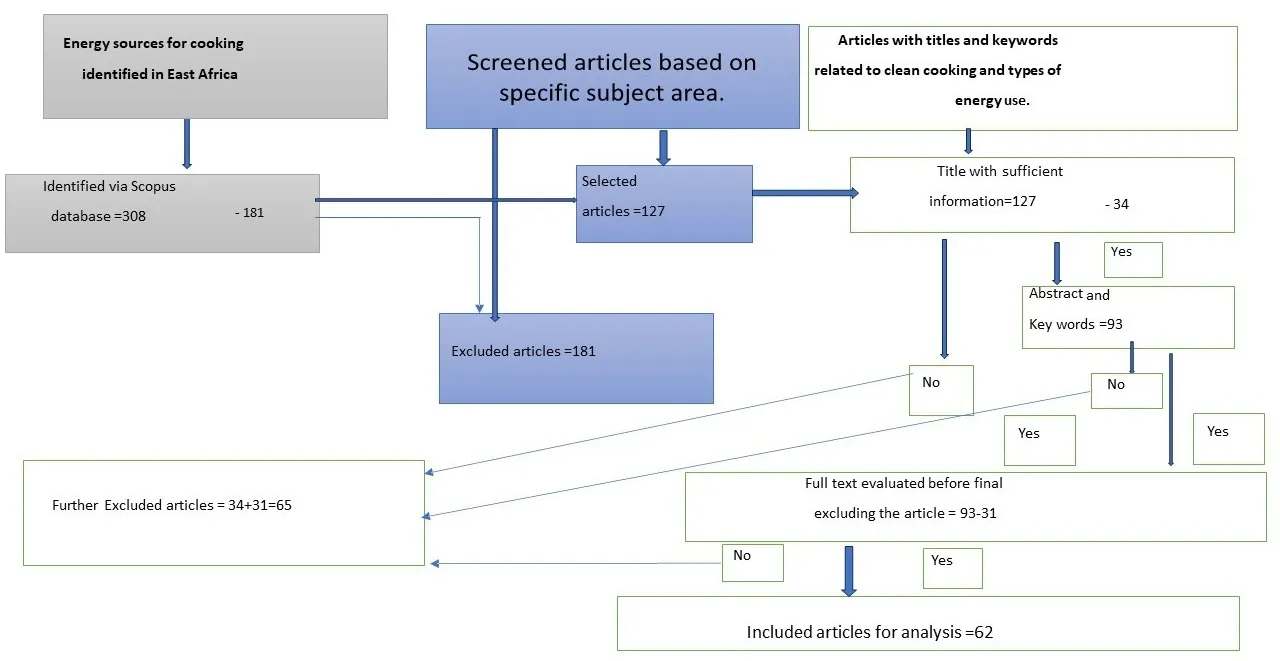
Today, about three billion people, including those in Tanzania, still cook using traditional methods and solid fuels. This practice, which primarily affects women and children who cook in many developing nations, contributes to serious health risks and forest degradation. Every year, household air pollution is responsible for over 34.4 million preventable deaths worldwide, with about 346,600 of those deaths occurring in East African Community and the Nile Basin. Even though switching to clean cooking technologies is a global health priority, adoption is still low in the East African community, and little is known about the factors influencing this change. To determine the factors driving East Africa’s energy transition to clean cooking, this study conducts a systematic review and looks at the history of the research agenda. A total of 308 articles were found using the Scopus database; 62 of these were chosen for analysis based on important search terms such as solar, biogas, firewood, charcoal, LPG, and electric stoves. Even though traditional fuels continue to be the most commonly used in the regions, the empirical analysis showed a focus on clean cooking technologies like electricity, improved cookstoves, and LPG. The clean cooking agenda appears to be primarily externally driven by European and USA researchers, which may have an impact on local adoption and relevance. It is noteworthy that authors from outside the region constituted 63.6 percent of publications on clean cooking in the East African Community.
Open Access
Article
20 June 2025Optimization of Powder Distribution and Feeding Efficiency Using an Annular Powder-Feeding Nozzle: A Numerical and Experimental Study
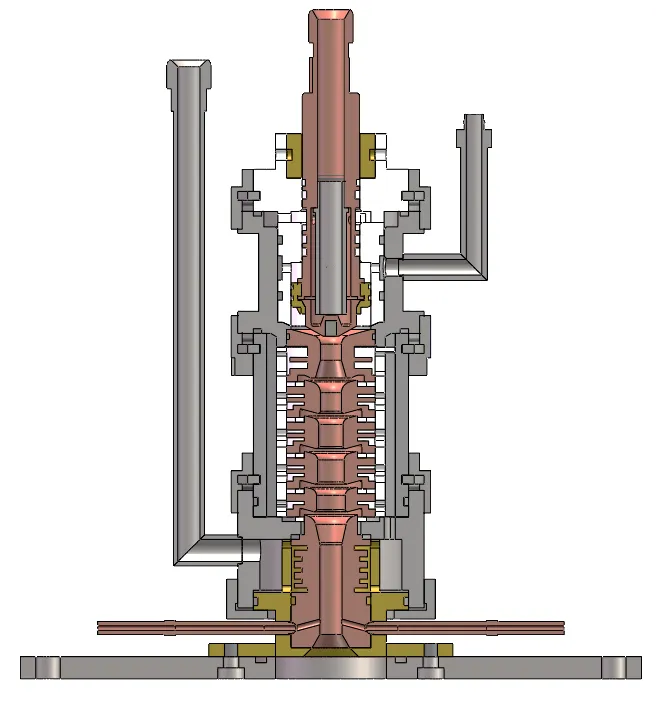
The quality of spherical powders required in plasma spheroidization is particularly important to advanced manufacturing, such as additive manufacturing and thermal spray coatings. Traditional powder feeding systems, such as radial and coaxial nozzles, often suffer from suboptimal powder distribution, low powder capture efficiency, and poor control of particle trajectories. These issues deteriorate spheroidization quality and material efficiency. We propose here an innovative annular powder-feeding plasma torch for these challenges and to optimize the powder-feeding dynamics. The novel nozzle consists of a tangential powder feeding mechanism and a concentric conical structure that provides uniform powder distribution and minimizes plasma jet interference. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations and Discrete Phase Modeling (DPM), combined with a literature review, are used to study such as throat size and convergent-divergent profiles of nozzles for gas-powder interactions. Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) powder was used for the experimental validation of the annular nozzle; the annular nozzle was found to outperform traditional nozzles in this application with a powder capture efficiency of 75%, a deposition efficiency of 92%, and a spheroidization efficiency of 85%; 85% of the particles had a circularity index >0.9. These results indicate that powder distribution uniformity, deposition efficiency, as well as spheroidization quality are greatly improved than those from conventional plasma spheroidization systems, demonstrating the potential for better process performance for plasma spheroidization. These findings demonstrate the relevance of the optimized annular nozzle in the field of high-value material manufacturing as it yields increased coating quality and minimized material wastage.
Open Access
Review
18 June 2025Coupling Electrocatalysis and Biotransformation for CO2-Based Biomanufacturing
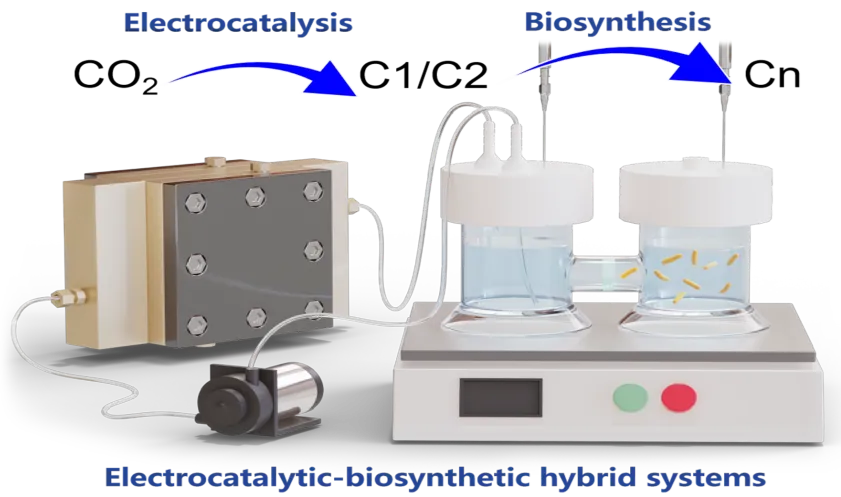
Transformation of CO2 into high-value, long-chain carbon compounds is a long-term goal for CO2 conversion and utilization. Electrocatalytic CO2 reduction can achieve C1/C2 products with a high formation rate, while biosynthesis can utilize these C1/C2 species as substrates for carbon chain elongation. Coupling these two processes offers a promising avenue for efficient CO2 fixation via synergizing the advantages of both sides. However, it is still challenging to realize its widespread application because of the poor compatibility between different modules. This review summarizes and discusses current developments in electrocatalytic-biosynthetic hybrid systems for CO2 upcycling. First, the recent advances of individual modules are introduced, including conversion pathways, representative electrocatalysts and typical reactors for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction process and microbial synthesis and in vitro multi-enzyme cascade catalysis for low-carbon bio-conversion process. Then, key factors that influence system coupling are discussed via analyzing the features of single modules and their cross-interference effects. Finally, several construction strategies are proposed based on different integration scenarios, offering guidance for the design and optimization of these hybrid systems.
Open Access
Article
18 June 2025CO2 Emissions Comparisons on Cementous Sustainable Flooring Options: Modeling and Evaluation
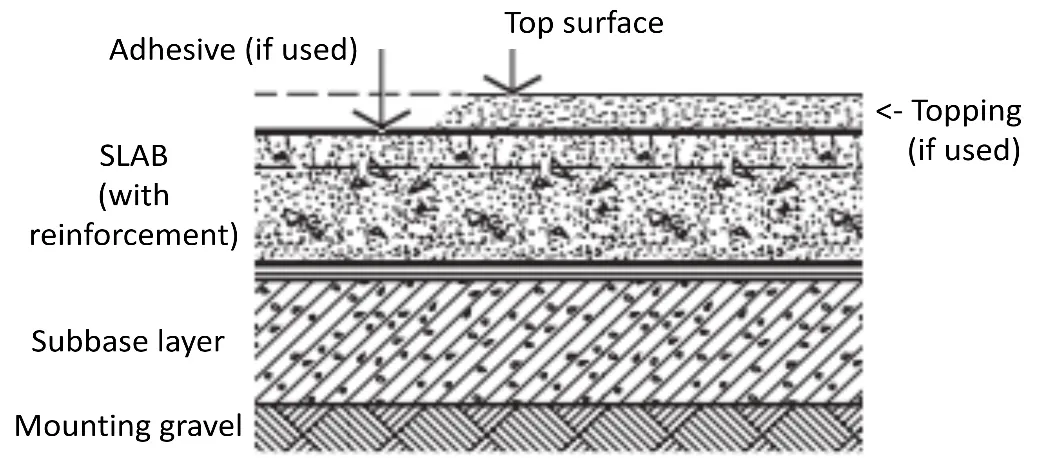
CO2 and greenhouse gas emissions have become a major environmental issue worldwide, and emissions have spiked faster than most could ever imagine. The issues have made it crucial to find financially feasible and long-term, use-efficient solutions that fulfill industrial needs. As society so much depends on the current industry outputs, we need to reduce emissions coming from those industrial facilities and premises where people shop and buy services and assets on a daily basis. These emissions need to be reduced on a global scale, and here, concrete as a building material comes into play as one of the most used materials, especially on industrial floors. A typical solution is a sturdy base slab with a use case-specific coating on it. The base slab is expected to last the whole life of the building, whereas the coating might be considered consumable and refurbished/fixed as a maintenance job many times before the building itself is demolished. In heavy use cases, the maintenance cycle might be fast, which reduces the usable time of the building and generates downtimes for business. The coating decisions have a major impact on the building’s lifetime emissions, which is the key focus of this study, too. Bad decisions can introduce unnecessary microplastics and nano dust particles to work environments and also generate restructuring needs of the operational activities. In the worst case, operations have to be shut down. Luckily, there are options, and emissions can be reduced in many ways. By using long-term and durable cementitious mix-based dry shake coatings, one can reduce top coating-based emissions, and by decreasing the amount of used reinforcement components in the base slab, an extra positive impact can be achieved. With a base slab, also more environmentally friendly low-carbon cement formulations can be considered, like fly ash or GGBS (ground granulated blast furnace slag) based formulas, which we discuss in detail and analyses traditional options compared to modern CEM3a and CEM3b versions. For the top coating, emissions are generated in the construction and maintenance phases. To find different options with cross implications on lifetime emissions, our study analyzes CO2 emissions sources for several concrete mixes, which are then paired with floor-top coatings based on Cementous mix or epoxy coating. We have pinpointed the potential for reducing the building’s floor-based lifetime CO2 emissions. The analysis is based on the impacts of the base slab and floor coating selection combinations. As a de facto comparison element, we used a 100 percent virgin Portland cement-based mix. The Portland cement was compared to CEM3a and CEM3b mixes. On the top surface of the floor, traditional epoxy base floor coating was compared to a modern dry shake-based option. In the analysis, the dry-shake-based floor showed major benefits. Emissions were drastically reduced, fewer maintenance downtimes were needed, and the general life expectancy was a lot longer for the dry shake option.
Open Access
Article
18 June 2025Orthoptera Colonising the Urban Landscape and Urban Lawns: A Case of a Middle-Russian City
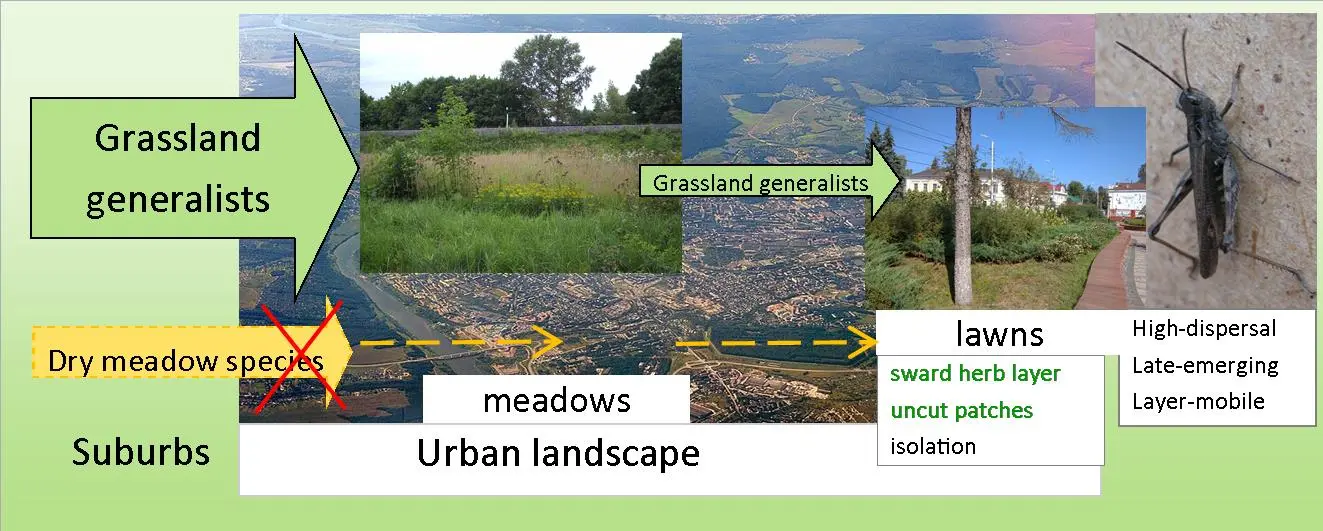
Orthoptera are often surveyed in research on urban environments, but results are ambiguous in different regions and cities. We studied the insects in a city located in the centre of the East-European plain, at the junction of the Continental and Boreal biogeoregions. We distinguished suburbs and the urban landscape and meadows and lawns within the urban landscape. To find orthopterans in grassland habitats, we used sweepnet, acoustic and visual observations, and pitfall traps. Urban habitats are colonised by 20 species of Orthoptera from 29 species observed in the suburbs. Only five species are as frequent in urban habitats as in suburban ones. The urban environment negatively affects both forest species, all three species of dry meadows and only one of ten grassland generalists. On lawns, we found 11 species. Total abundance and species numbers were lower in lawns than in meadows. Only three late-emerging and high-dispersing species were quite frequent in lawns. The occurrence of Conocephalus fuscus in lawns was positively influenced by the presence of uncut patches, Chorthippus dorsatus—by the density of the herb layer. Ch. mollis, which is native to dry meadows, preferred unshaded lawns. Chorthippus biguttulus is a single species inhabiting lawns of almost every quality.
Open Access
Review
13 June 2025Advances in Sintering Technologies for SiC Ceramics: Mechanisms, Challenges, and Industrial Applications
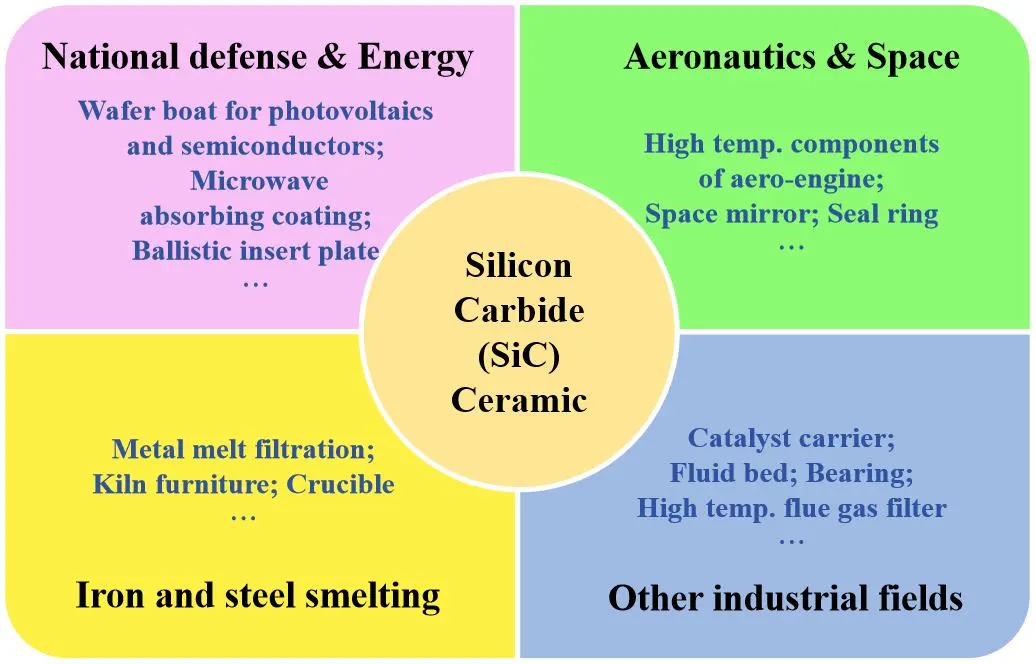
Silicon carbide (SiC) ceramics have become critical materials for high-temperature engineering applications because of their exceptional mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and chemical stability. In order to meet the diverse needs of industrial applications, various sintering methods have been developed. These include traditional methods such as pressureless sintering, reaction-bonded sintering, hot pressing, and recrystallization, as well as advanced technologies like spark plasma sintering, oscillatory pressure sintering, and flash sintering. This review provides a systematic analysis of both traditional and advanced sintering techniques for SiC ceramics. It highlights their mechanisms, critical process parameters, and impacts on the final material properties. Key challenges, including high sintering temperatures, additive selection, microstructural control, and scalability, are examined. Strategies for balancing cost-efficiency with performance are also discussed. In addition, recent advancements in SiC-based composite materials for applications ranging from aerospace components to catalytic filtration systems are presented. Finally, future research directions are proposed. These focus on precise additive engineering, microstructure tailoring, and innovative sintering methodologies to speed up the transition of high-performance SiC ceramics from laboratory prototypes to large-scale industrial implementation.
Open Access
Article
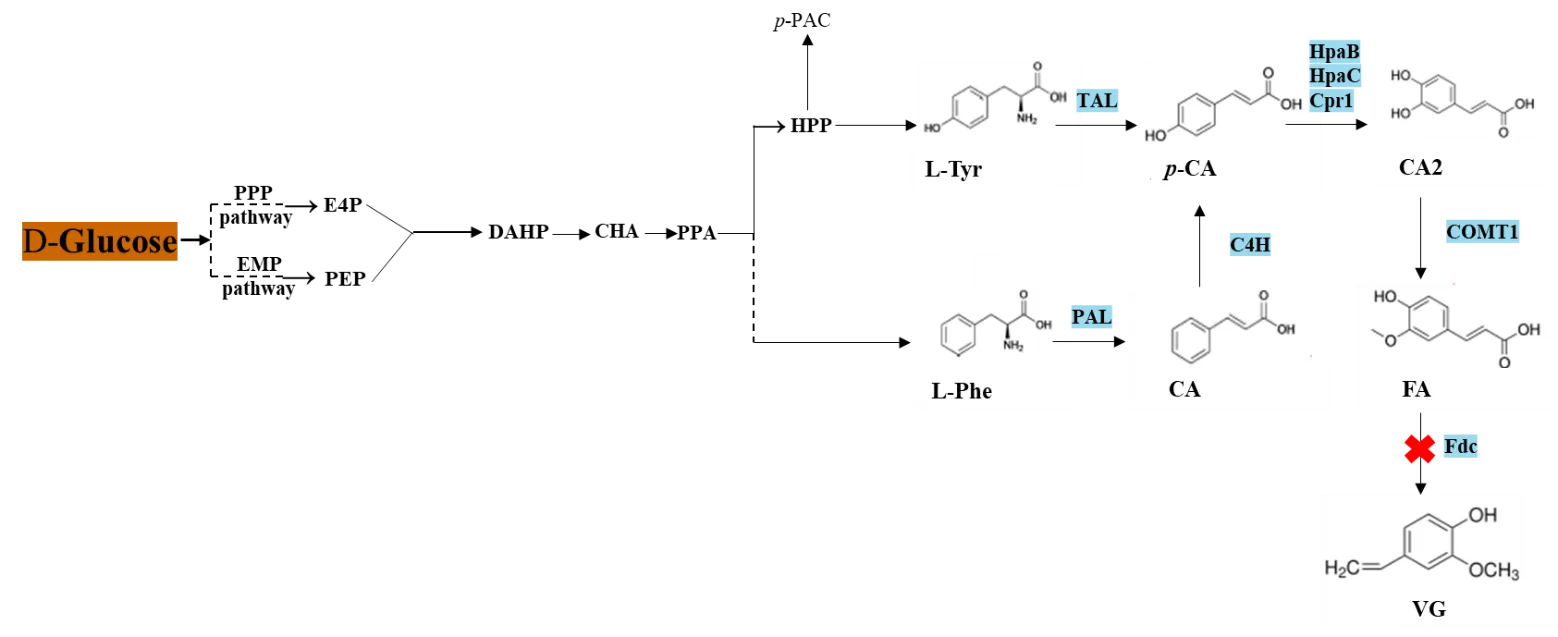
13 June 2025Development of a Tailored Culture Medium for Improved De Novo Biosynthesis of Ferulic Acid in Fed-Batch Biphasic Fermentation with Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Ferulic acid (FA) is a natural phenolic compound with diverse biological properties, widely used in the food and cosmetic industries. Its production from fermentation is a promising strategy because its extraction from biomass is costly. To enable cost-effective microbial production, medium optimization is mandatory. In this study, we focused on applying a fed-batch biphasic strategy for the production of ferulic acid (FA) from d-glucose. FA production was first assessed in a classically defined medium, 2X Yeast Nitrogen Base (YNB) without amino acids, and complex Yeast Peptone Dextrose (YEPD) medium. Finally, as FA has deleterious antimicrobial properties, continuous extraction from the broth using fed-batch biphasic fermentation was implemented. Our results showed that YEPD medium resulted in the production of 207 mg·L−1 of FA in a medium composed of 30 g·L−1 d-glucose, 10 g·L−1 yeast extract, 1 g·L−1 (NH4)2SO4, 10 g·L−1 peptone, 4 g·L−1 KH2PO4 and 2 g·L−1 K2HPO4. Fed-batch biphasic fermentation system resulted in almost a two-fold increase in FA production compared to batch one (312.6 mg·L−1 and 176.7 mg·L−1, respectively) showing the importance of fed-batch biphasic fermentation and medium detoxification.
Open Access
Opinion
11 June 2025Reflections on Photocatalysis Progress Since the Inspiration of Prof. David Ollis in 1992
Why has photocatalysis not gained the wide-ranging commercial applications in environmental purification of air and water that seemed promising 30+ years ago since the first international conference on TiO2 photocatalytic purification and treatment of water in 1992? The primary reason lies in its low intrinsic efficiency. The progress of R&D to enhance this efficiency has been slow, possibly due to an incomplete understanding of the underlying mechanisms of photocatalysis. There is also the possibility that certain factors, with effects comparable to those of the band gap, significantly influence photocatalytic performance but remain underexplored. Additionally, challenges such as mass transfer limitations and surface contamination hinder the industrial application of photocatalysts. It may be time for scientists to reconsider and address the limitations and practical application scenarios of photocatalysis.

Open Access
Article
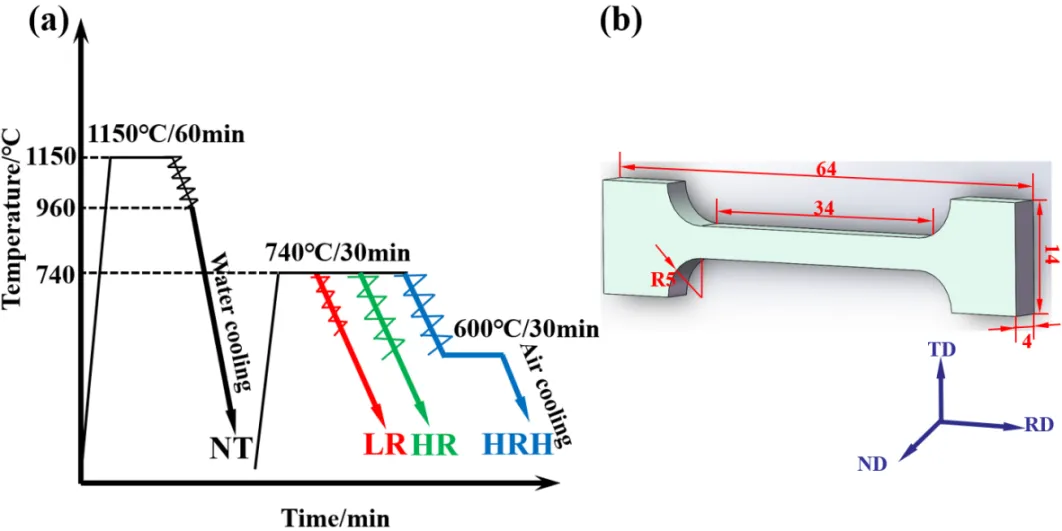
11 June 2025Effect of Post Rolling Strategies on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Martensitic Heat-Resistant Steel
Four different rolling strategies were applied to comparatively study the post-rolling process on the microstructure and high-temperature mechanical properties of a high-boron P92 martensitic heat-resistant steel. Both the characteristics of martensitic lath structures and the evolution of precipitation and texture states are illustrated. Their influence on mechanical properties was also discussed based on the recrystallization state, dislocation density, precipitation state, and also the activation tendency of slipping systems of the dominated texture component. Results revealed that the post-rolling process can significantly improve the plasticity of quenched P92 steel while leading to the reduction of strength simultaneously. However, a high reduction and post isothermal holding sample (HRH) shows the best high-temperature mechanical performance with a balanced tensile strength of 352 MPa and elongation of 33.6%. It is the enhanced precipitation strengthening, recrystallization refinement, and lower Schmid values of main texture components that contribute to the mechanical property improvement of the HRH sample.