Found 46 results
Open Access
Review
18 September 2025Programmable Multiplex Genome Editing: Innovations in CRISPR Effectors, crRNA Engineering, and Delivery Strategies
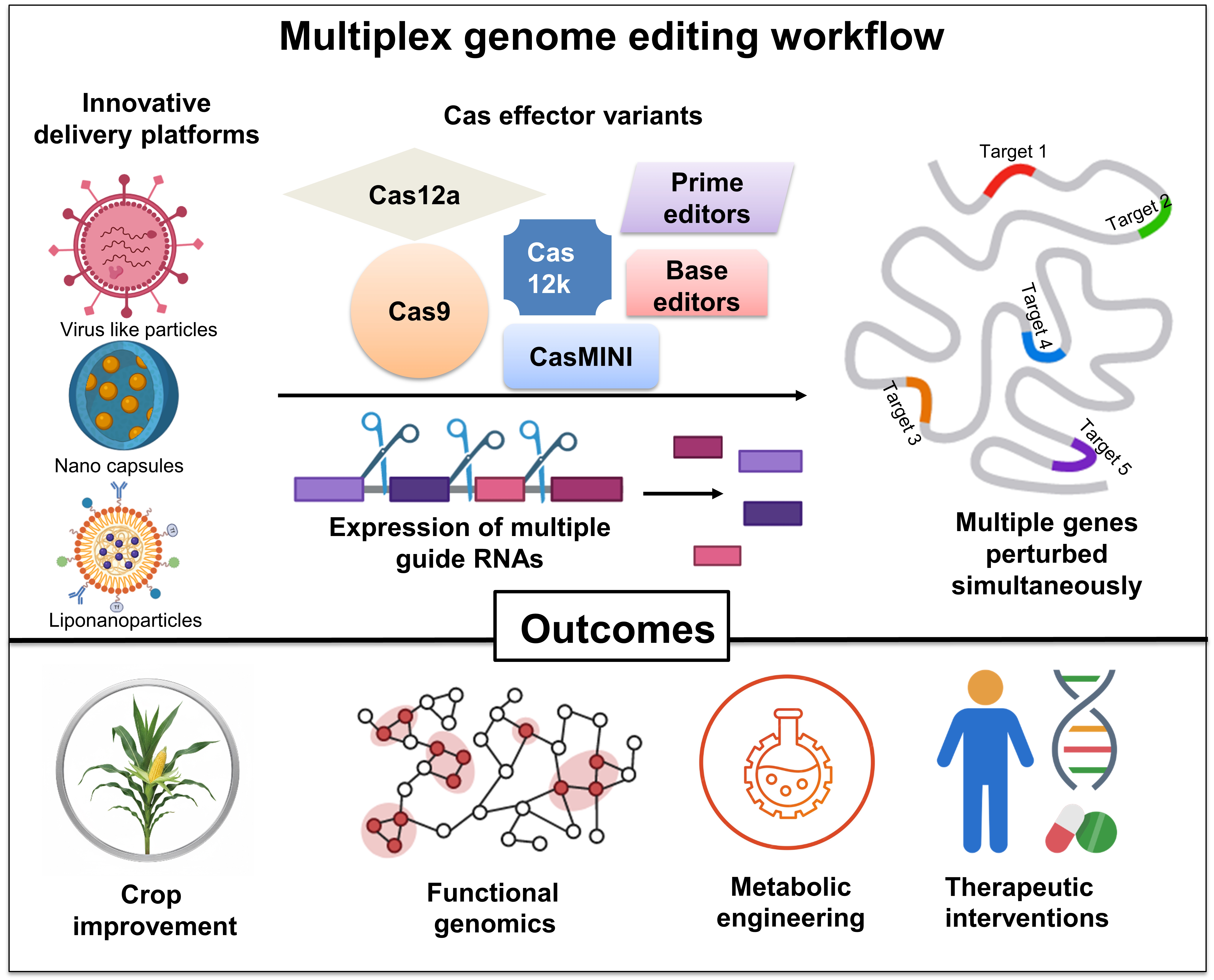
The discovery of CRISPR based technologies has transformed genome engineering and synthetic biology. With advancements in the ability to do multiplex genome editing, it is now emerging as an ideal approach for trait stacking to improve crops, functional genomics, and complex metabolic engineering in various biological systems. This review discusses engineering and optimization of the latest CRISPR effectors for scalable and precise multiplex editing, ranging from well-known systems like Cas9 and Cas12 variants, to newer, smaller variants such as CasMINI, Cas12j2, and Cas12k. We highlight how the emergence of base editors and prime editors enabled efficient editing across multiple loci without double strand breaks. We also elaborate on the expression and processing strategies of crRNA arrays, which are central to any multiplexing approach. These include tRNA-based and ribozyme-mediated methods, synthetic modular designs, and AI-optimized guide RNAs tailored to diverse systems. Additionally, we assess next-generation delivery platforms such as lipid nanoparticles, virus-like particles, and metal-organic frameworks that overcome conventional barriers in in vivo applications. This review provides a critical take on technological advances enabling precise, high-throughput, and programmable multiplex genome editing across biological systems, setting the foundation for future innovations in synthetic biology, crop improvement, and therapeutic intervention in multigene diseases.
Open Access
Article
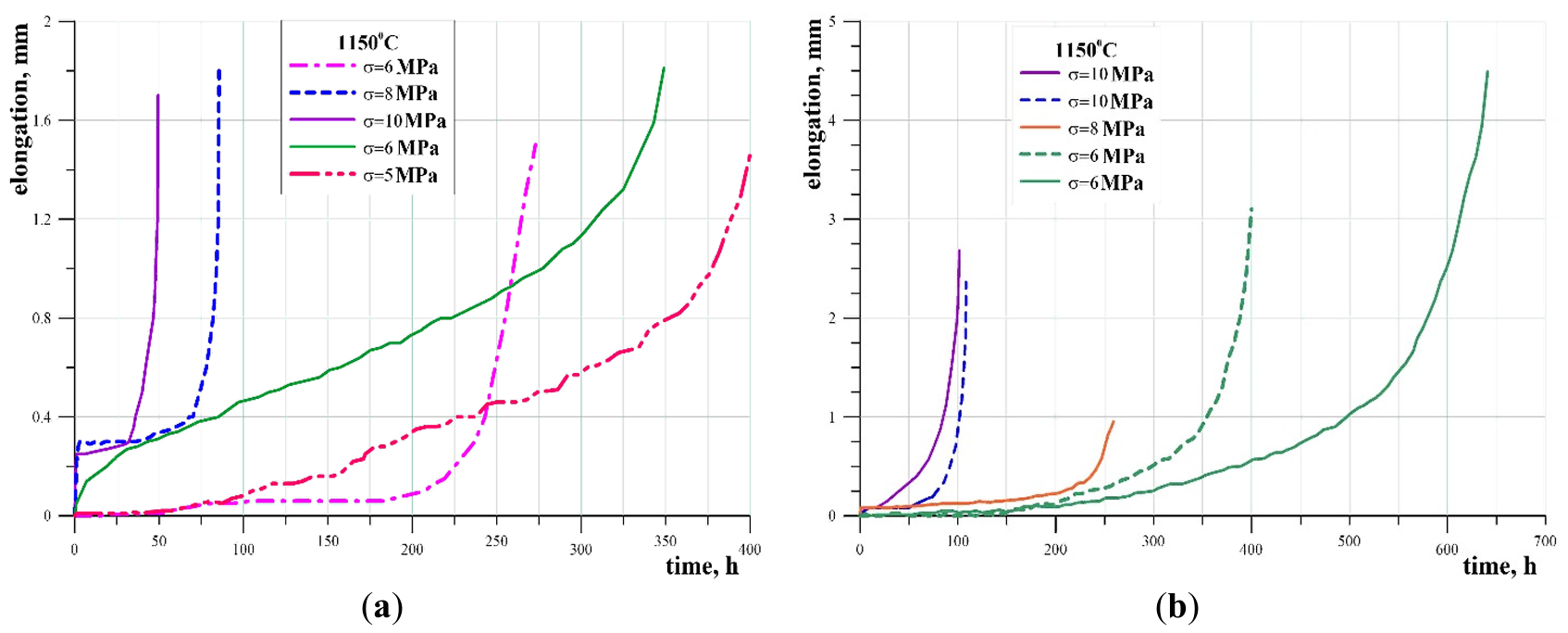
15 September 2025Heat Resistance of Centrifugally Cast Tubes Made of 32%Cr-43%Ni Refractory Alloy and Its Welded Joints at Temperatures up to 1150 °C
The results of microstructura l analysis, short-term and long-term strength tests of modified sparingly alloyed refractory alloy of 32%Cr-43%Ni and its welded joints are presented. A quantitative analysis of the dispersed phases in the initial state and after long-term strength tests has been carried out. It is shown that the network of carbide-intermetallic precipitates persists after long-term strength tests at a temperature of 1150 °C. This ensures the ability of the developed alloy and its welded joints to withstand high-temperature creep for a long time. It has been established that after long-term strength tests at a temperature of 1150 °C, niobium carbide particles present in the base metal and weld metal are almost completely transformed into an intermetallic phase based on Cr-Ni-Si-Nb-N. The penetration of atmospheric nitrogen into the metal stimulates this process.
Open Access
Article
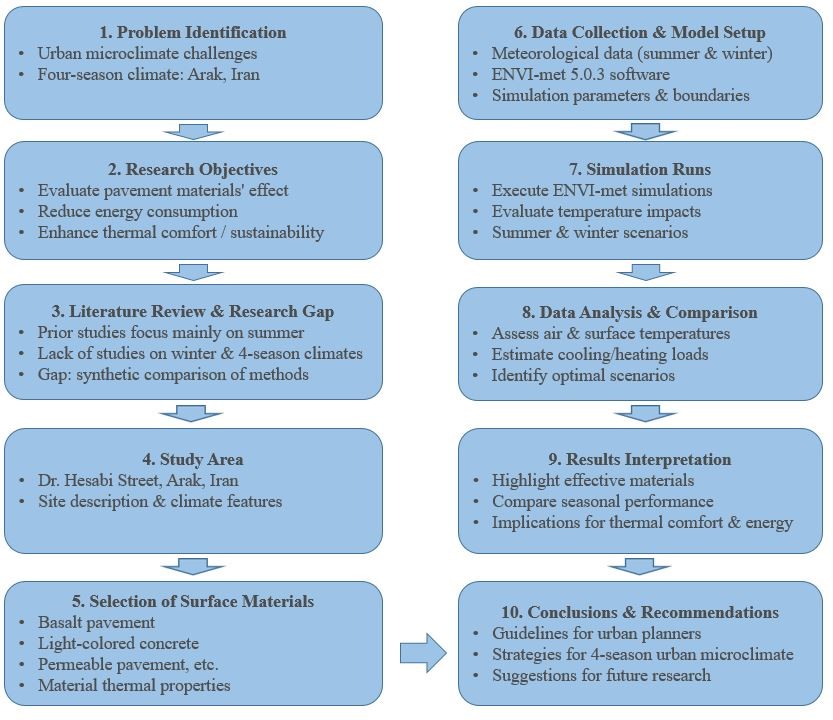
28 August 2025The Thermal Impact of Various Pavement Materials on Outdoor Temperature in a Temperate Four-Season Climate: A Case Study of Arak City, Iran
Urban heat and oasis effects significantly alter urban microclimates due to anthropogenic heat emissions and the thermal properties of urban surfaces. This study aims to quantitatively assess the thermal effects of different pavement types on outdoor temperatures across seasonal extremes in a temperate four-season climate. Conducted in Arak city, Iran, on 22 July and 22 January 2023, this research investigates both warm and cold seasons to provide a comprehensive understanding of pavement influence on urban microclimates throughout the year. Using the ENVI-met 5.0.3 modeling software, an environmental meteorology tool for simulating urban microclimates, the thermal performance of commonly used asphalt pavement was compared with alternative materials such as basalt and light-colored concrete on Dr. Hesabi Street. Simulation results reveal that basalt and light-colored concrete pavements reduce summer cooling loads by up to 3.49 degrees Celsius (°C), enhancing pedestrian thermal comfort, but simultaneously increase winter heating demands by 1.04 °C. This balance presents an optimal scenario to minimize adverse climate effects across seasons. The findings offer valuable insights for sustainable urban planning, promoting resilient city design strategies that mitigate heat and oasis effects in diverse climates. This study contributes actionable recommendations for urban planners seeking to balance thermal performance in temperate climates with seasonal variability.
Open Access
Article
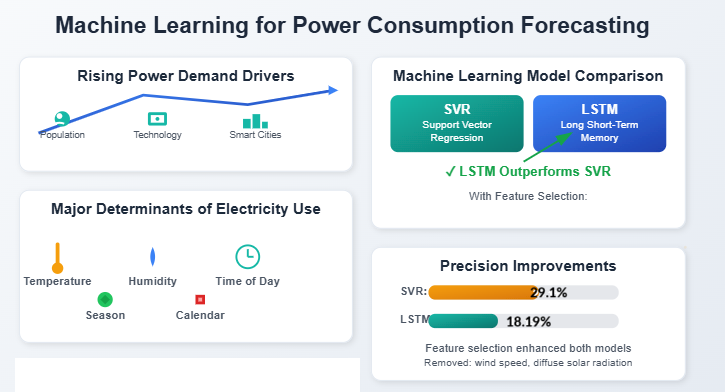
25 August 2025Feature Selection Technique Using Multiple Linear Regression for Accurate Electricity Demand Forecasting
The rising power demand, driven by population growth, technological innovations, and the advent of smart cities, necessitates precise forecasting to ensure efficient energy distribution and align supply with demand. This paper presents a novel methodology for predicting short-term power consumption through machine learning approaches, specifically employing multiple linear regression for feature selection. In this study, two models are implemented and compared: Support Vector Regression (SVR) and Long-Short-Term Memory (LSTM). Exploratory data analysis was used to discover the relationships and associations between variables. It reveals that temperature, humidity, time of day, and season are major determinants of electricity use. The results indicate that the LSTM model surpasses Support Vector Regression (SVR) in terms of accuracy and precision. By incorporating multiple linear regression (MLR) for feature selection, the performance of both models improved, with precision gains of 29.1% for SVR and 18.19% for LSTM. Removing extraneous elements, such as wind speed and diffuse solar radiation, enhanced the models’ efficiency and interpretability, allowing for a focus on the most significant factors. The study’s findings underscore the need to optimize feature selection to enhance forecast accuracy and streamline models. This method provides critical insights for enhancing energy management strategies and facilitating sustainable power distribution in light of rising global energy demand.
Open Access
Article
19 August 2025Inventory of Ant Fauna in the Influence Area of a Small Hydropower Plant in the State of Paraná, Brazil
The construction of hydroelectric dams for power generation causes environmental alterations and ecosystem restructuring in directly and indirectly affected areas. This study aimed to survey the ant fauna in the indirect area of influence of a small hydroelectric plant located in Mangueirinha, Paraná State, Brazil. Seven sampling campaigns were conducted, two before and five during the project’s implementation, using pitfall traps as the sampling method. A total of 72 ant species were recorded, belonging to 26 genera and six subfamilies. Species richness and abundance did not differ significantly between the pre-implementation and implementation phases. The Chao1 estimator indicated that actual species richness may be approximately 7.6% higher than observed. These findings contribute to understanding ant biodiversity in areas subject to land-use change in Paraná State. The results highlight the value of using insect species richness and abundance, particularly of bioindicator groups such as ants, for environmental impact monitoring.

Open Access
Article
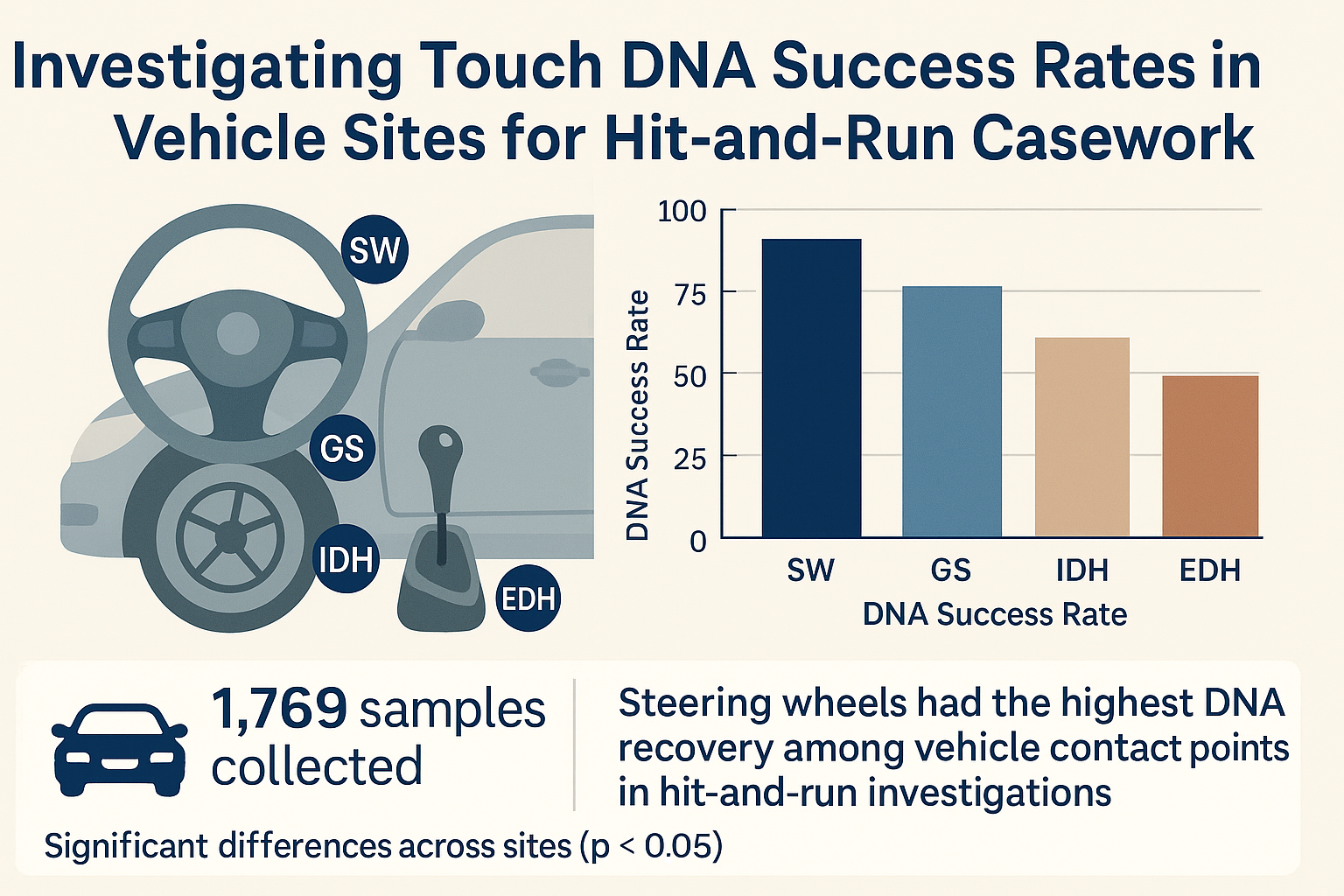
28 July 2025Investigating Touch DNA Success Rates in Vehicle Sites for Hit-and-Run Casework
This study evaluated the effectiveness of Touch DNA recovery from four key vehicle contact points—steering wheel (SW), gear shift (GS), interior door handle (IDH), and exterior door handle (EDH)—in the context of hit-and-run forensic casework. 1769 samples were collected from 359 vehicles processed between 2020 and 2023. Statistically significant differences were observed in the quantity and quality of DNA recovered across these sites (p < 0.05). The steering wheel yielded the highest DNA success rates, followed by the gear shift, whereas the exterior and interior door handles demonstrated substantially lower recovery efficiency. These findings underscore the critical role of strategic sampling site selection in maximizing evidentiary outcomes. The results support prioritizing the steering wheel and gear shift as primary targets for DNA collection in vehicle-based investigations. The study highlights the practical utility of Touch DNA in linking individuals to vehicular crimes and calls for further research into alternative sampling techniques and contamination control measures to optimize forensic DNA recovery protocols in real-world hit-and-run scenarios.
Open Access
Article
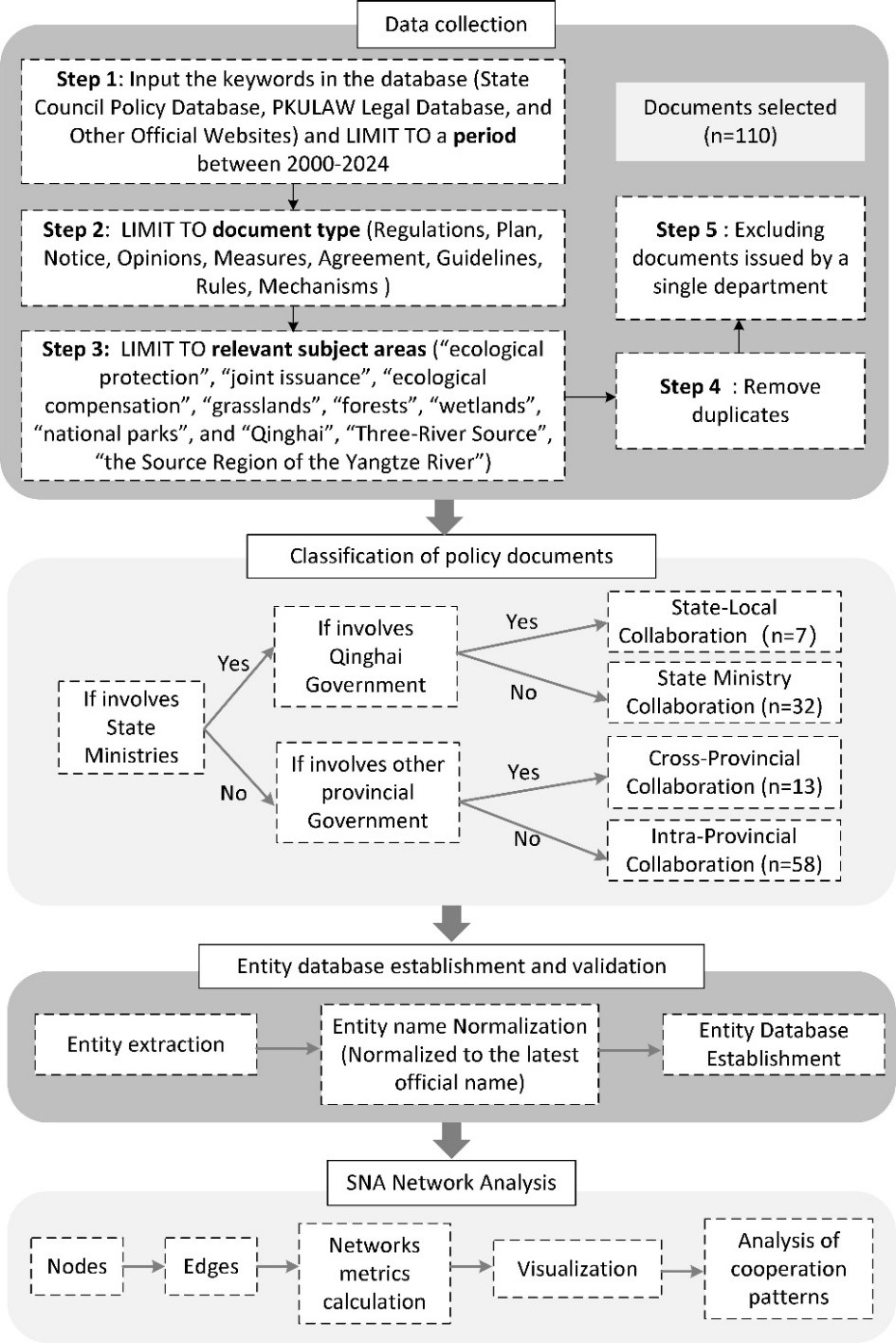
21 July 2025The Intergovernmental Networks of Ecological Protection Policies Issuing Entities in the Source Region of the Yangtze River: A Case Study of Qinghai Province
Ecological conservation and governance play key roles in constructing an ecological civilization society, while intergovernmental cooperation provides new perspectives for cross-regional ecological governance. We employed a social network analysis (SNA) method to examine 110 published ecological policies from 2000 to 2024 in the Source Region of the Yangtze River (SRYR). The study has three key findings. Firstly, intergovernmental collaborative policies on ecological protection showed an upward trend, with intra-provincial collaborations within Qinghai Province being the most frequent. Secondly, four collaboration models were demonstrated, namely: national ministries, national and provincial, cross-provincial and intra–provincial collaborations. National agencies and Qinghai provincial agencies collaboratively set objectives, which Qinghai operationalizes with incentive-constraint measures. Then, the targeted guidelines were launched by national and provincial authorities. Afterward, cross–provincial agreements and mechanisms facilitate joint actions. Thirdly, we revealed the hierarchical structures, including a national network, two central-local sub-networks, three-tier inter-provincial partnerships, and four regional sub-clusters. Core actors include national ministries that coordinate cross-departmental efforts. The Qinghai provincial government serves as a central-local hub. It maintains strong transboundary ties with Aba and Ganzi Prefectures of Sichuan Province. Provincial departments such as ecology and environment, forestry and grasslands, and finance lead intra-provincial collaborations. These findings offer new insights for integrating multi-level governance in ecological protection and ecological civilization construction.
Open Access
Article
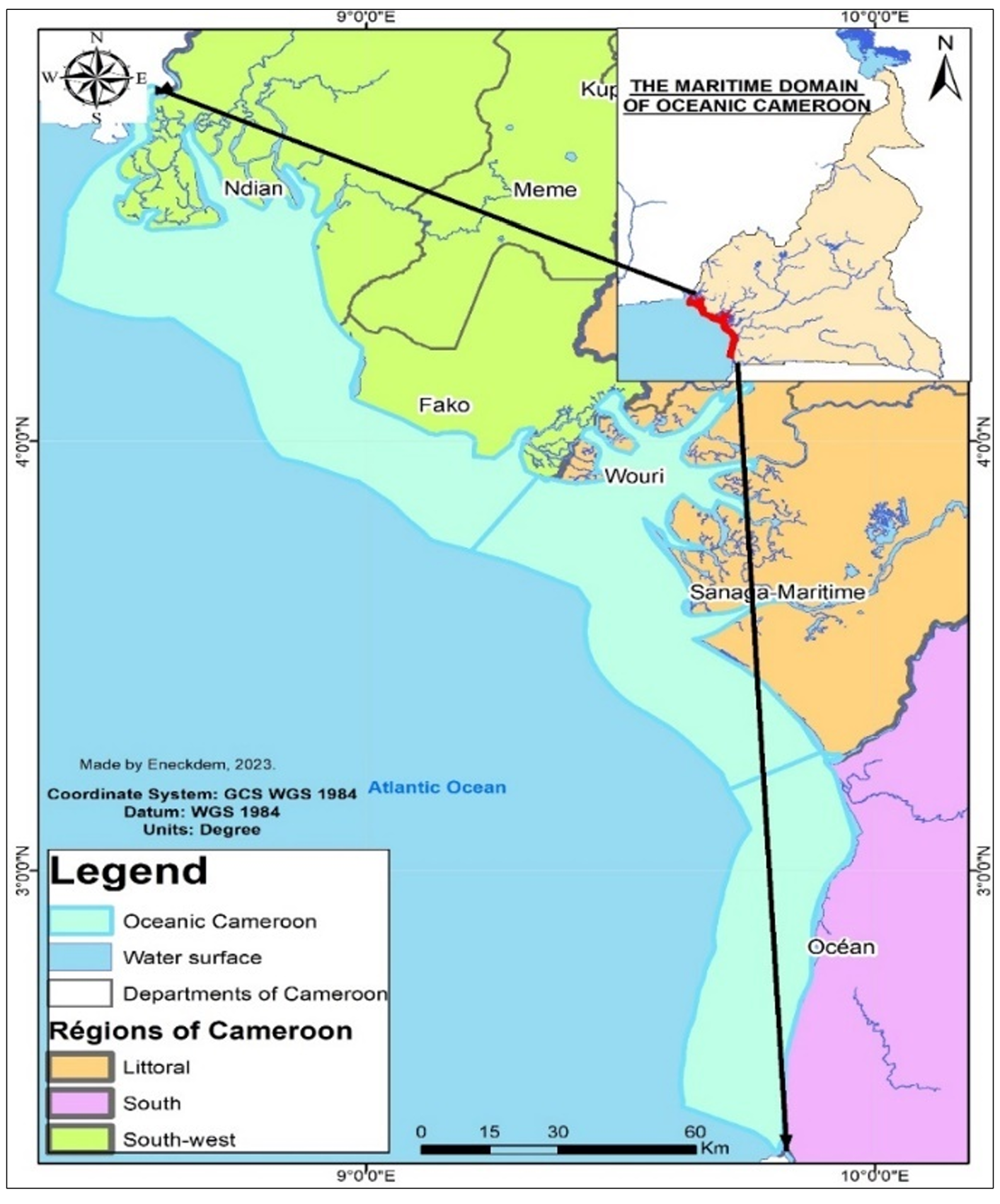
26 June 2025Assessment and Spatialization of the Potential of Marine Renewable Energies in the Gulf of Guinea: Case of the Cameroonian Coast
This study explores, through mathematical simulation and Geographic Information Systems, the electricity production potential of Marine Renewable Energies (MRE) on the Cameroonian coast. The study uses data from the National Institute of Cartography and, in the absence of in situ oceanographic observation, data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and those of Copernicus Marine Services, to determine and identify, after calculations on Excel and spatial representation on ArcGIS 10.2.2, areas with high MRE potential. The analyses carried out show that the Cameroonian coastline is full of significant potential for the development of MRE. Indeed, with a potential of approximately 6 kW at sea and approximately 1 kW on the coast, current energy constitutes a capitalizable opportunity. Concerning wave energy, the average production potential of the Cameroonian marine area is approximately 3.37 kW/m. However, it is much higher on the Kribi coast (between 4 and 7 kW/m). Furthermore, significant potential for tidal energy can be identified in the Wouri estuary, as well as in other sectors such as marine thermal energy and osmotic energy, although this requires further analysis to be better understood. These results would help promote research on these energies in Cameroon.
Open Access
Article
25 June 2025Time Is Lung: Inpatient Transbronchial Lung Cryobiopsy Decreases Wait Time to Treatment Initiation for Newly Diagnosed Interstitial Lung Disease
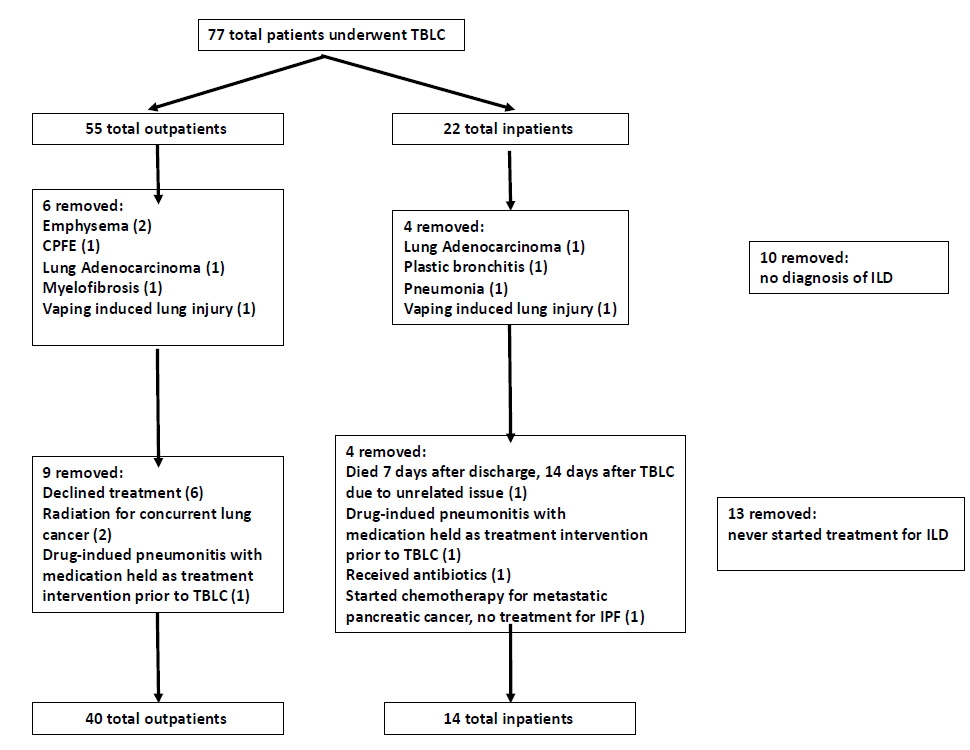
Although performing lung biopsies on hospitalized patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) has risk, initial studies have shown transbronchial lung cryobiopsy (TBLC) may be safely performed in this patient group. Data evaluating the value of this intervention in establishing a diagnosis and impacting management is lacking. We present a comparison of TBLC for inpatients and outpatients and provide data on the impact on medical therapy initiation and wait times from consultation to biopsy and treatment. Demographic data, pulmonary function values, chest imaging patterns, procedural information, diagnosis, and medical therapy changes, defined as medication initiation, adjustment, or cessation guided by TBLC results, were recorded from enrolled patients with newly identified ILD. Changes in medical therapy were the primary outcome. Time from consultation to biopsy and treatment was the secondary outcome. Fifty-four (54) patients (40 outpatient, 14 inpatient) were included. Inpatients underwent biopsy 2.5 ± 4.4 days after consultation compared to 15.5 ± 16.1 days for outpatients (p < 0.001). Medical therapy changes occurred 10.3 ± 7.9 days after biopsy for inpatients compared to 34.6 ± 37.0 days for outpatients (p < 0.001). There were no significant differences in medical therapy changes between the groups (p = 0.45). Our initial study suggests that performing TBLC on inpatients with newly identified ILD decreases wait times to treatment initiation and diagnosis. Efforts to understand the impact of a decreased wait time on ILD prognosis, including the development of progressive disease or fibrosis, symptom evolution, and quality of life, require further evaluation.
Open Access
Article
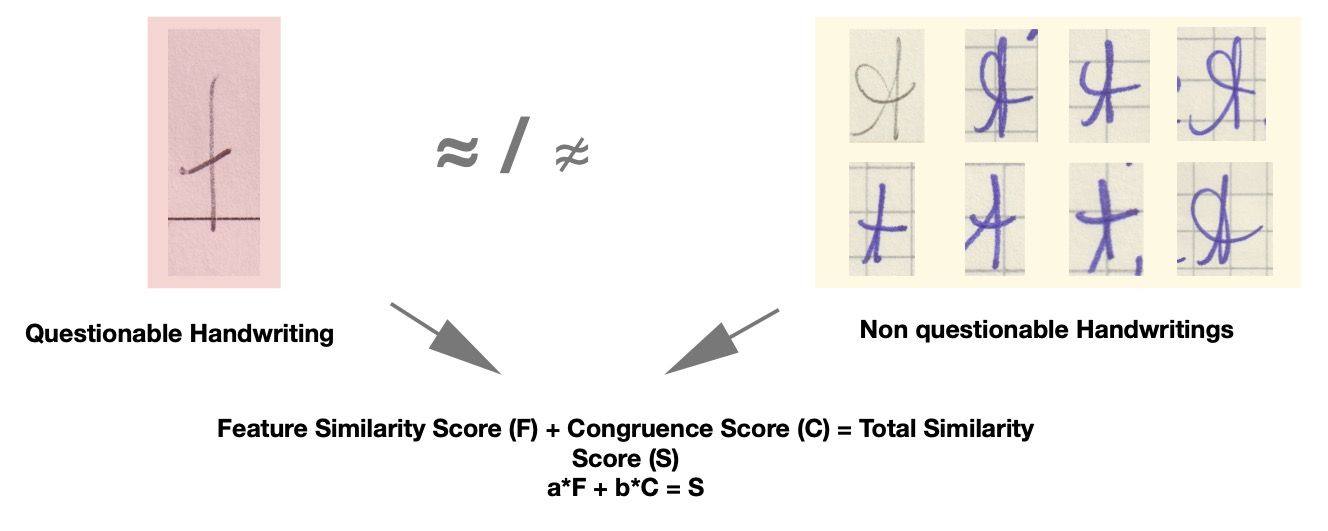
23 June 2025A Structured Framework for Formalized and Quantitative Handwriting Examination
The demand for a formalized and transparent approach to handwriting assessment has long been recognized within forensic and legal contexts. A structured methodology not only reduces interpretative subjectivity but also enables quantifiable measurement and ensures greater consistency in evaluations. This article presents a practical framework that models the degree of similarity between handwriting samples—texts and signatures—through a two-stage process: feature-based evaluation and congruence analysis. Both stages produce quantitative markers that are integrated into a unified similarity score, forming the foundation for more complex comparisons involving multiple questions and known texts. The proposed procedure, which is the major result of the paper, is not merely theoretical; it has been applied in real forensic casework, yielding preliminary statistical outcomes. In particular, it demonstrates the discriminative power of different handwriting features. The paper also discusses future directions for development, with a focus on the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance specific components of the assessment process.