Found 764 results
Open Access
Article
03 November 2025Sequential Thermal and Optical Upgrades for Passive Solar Stills: Toward Sustainable Desalination in Arid Climates
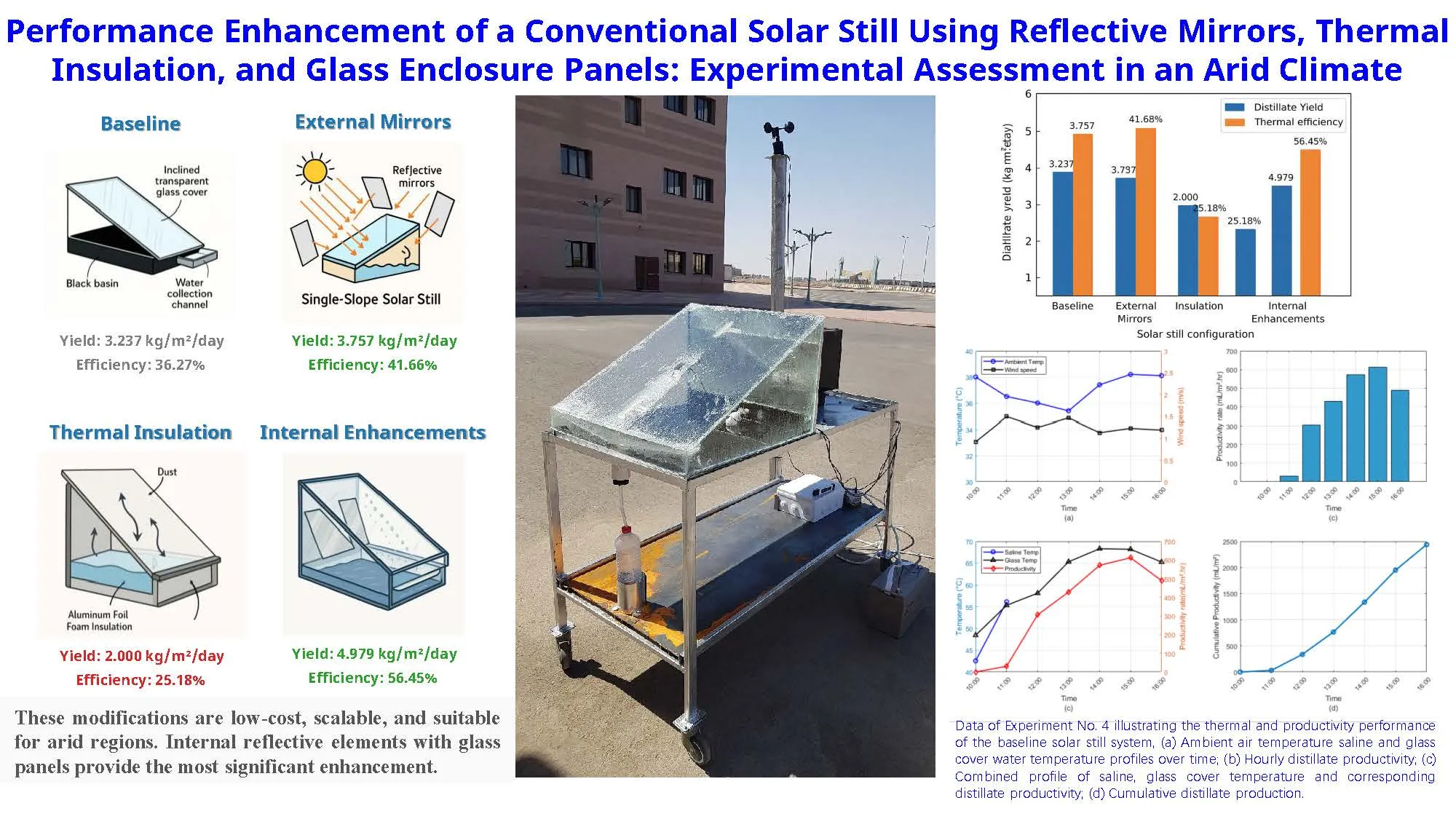
This study investigates the thermal performance and freshwater productivity of a passive single-slope solar still under four distinct configurations, aimed at enhancing distillation efficiency using low-cost modifications. The experiments were conducted in Tabuk, Saudi Arabia (28°23′50″ N, 36°34′44″ E), a region characterized by high solar irradiance ranging from 847 to 943 W/m2. The baseline system, constructed with a stainless-steel basin and inclined transparent glass cover, served as the control, achieving a cumulative distillate yield of 3.237 kg/m2/day and a thermal efficiency of 36.27%. Subsequent modifications included the addition of external reflective mirrors (Experiment 2), aluminum foil foam insulation (Experiment 3), and internal enhancements with side glass panels and internal aluminum mirrors (Experiment 4). Results demonstrated that the external mirror modification improved the distillate yield by 16% to 3.757 kg/m2/day, with a corresponding efficiency of 41.66%. However, insulation under dusty conditions led to a reduced yield of 2.000 kg/m2 and an efficiency of 25.18%, highlighting the critical influence of solar transmittance. The most notable improvement was recorded in the fourth configuration, which combined internal reflective elements and transparent side panels, resulting in a maximum yield of 4.979 kg/m2/day and thermal efficiency of 56.45%. These findings confirm that optical and thermal design enhancements can significantly augment the performance of passive solar stills, especially under high-irradiance, clear-sky conditions. The proposed modifications are low-cost, scalable, and suitable for implementation in remote and arid regions facing freshwater scarcity. This study offers valuable insights into the systematic optimization of solar distillation systems to improve sustainable water production.
Open Access
Communication
31 October 2025Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitors on PA Pressures in D-TGA after Atrial Switch Operations
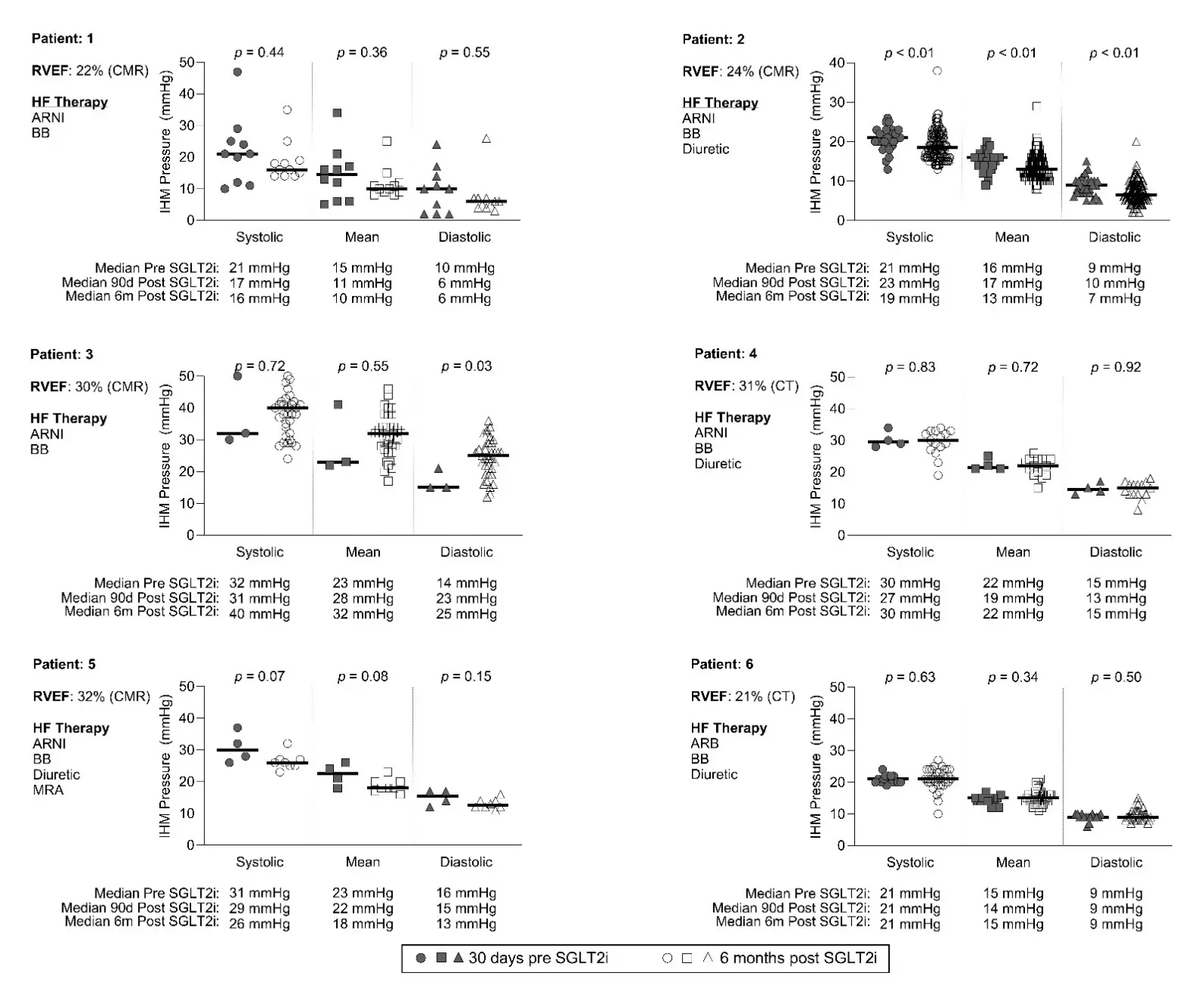
Heart failure (HF) is the leading cause of mortality in adults with congenital heart disease (ACHD), including patients with systemic right ventricles, such as those with dextro-transposition of the great arteries with an atrial switch (DTGA-AS). With more ACHD patients surviving well into adulthood, there is an increase in advanced heart failure (HF) and pulmonary hypertension (PH), many of whom are being treated with SGLT2-inhibitors (SGLT2-i). However, there is a paucity of data supporting SGLT2-i inhibitor use in the ACHD population and on how they may impact pulmonary artery pressures (PAP). This single center retrospective study aimed to evaluate the impact of SGLT2-i on (PAP) in patients with DTGA-AS. Six patients were studied, all male (mean age 41 [range 38–52] years), with a mean systemic right ventricular ejection fraction of 27% (range 22–32%), with an implanted hemodynamic CardioMEMs monitor data were recorded one month prior to medication start and six months afterwards. Half of the patients had normal PAP, and the addition of SGLT2i did not result in a significant change in PAP in all patients. However, half of the patients demonstrated a trend towards improvement. In conclusion, in this study with a small sample size of DTGA-AS patients, there was no significant reduction in PAP.
Open Access
Article
31 October 2025Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithms for Predicting Organic Photovoltaic Efficiency
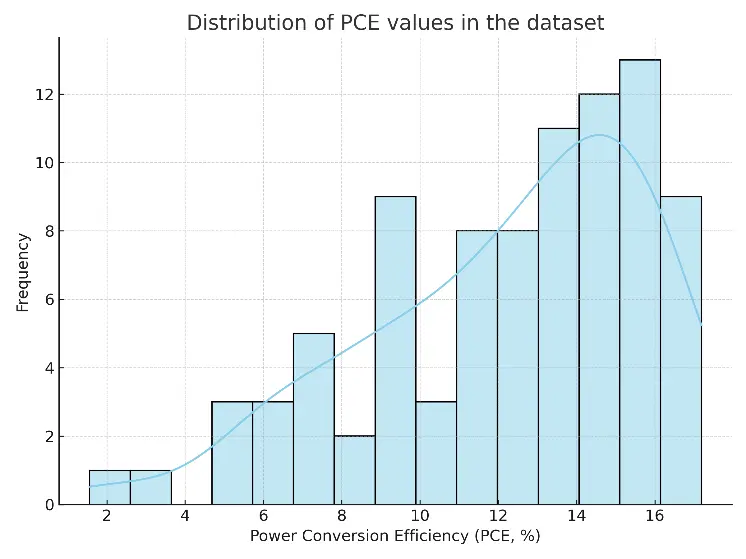
This study forecasts the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of organic solar cells using data from experiments with donors and non-fullerene acceptor materials. We built a dataset that includes both numerical and categorical features by using standard scaling and one-hot encoding. We developed and compared several machine learning (ML) models, including multilayer perceptron, random forest, XGBoost, multiple linear regression, and partial least squares. The modified XGBoost model performed best, achieving a root mean squared error (RMSE) of 0.564, a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.446, and a coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.980 on the test set. We also assessed the model’s ability to generalize and its reliability by examining learning curve trends, calibration curve analysis, and residual distribution. Plots of feature correlation and permutation importance showed that ionization potential and electron affinity were key predictors. The results demonstrate that with proper tuning, gradient boosting methods can provide highly accurate and easy-to-understand predictions of organic solar cell efficiency. This work establishes a repeatable machine learning process to quickly screen and thoughtfully design high-efficiency photovoltaic materials.
Open Access
Article
30 October 2025Postural Education Program for Indigenous Children in School: Case Study
To investigate whether a Postural Education Program (PEP) is capable of promoting changes in body knowledge and self-perception of posture among indigenous school-aged children. The study included 9 indigenous children with a mean age of 8 years, of whom 7 completed both the initial and final evaluations. The PEP consisted of four sessions, each lasting approximately two hours, which included an initial assessment, theoretical-practical classes on postural education, and a final assessment. Responses to the Self-bodpos questionnaire, collected at the beginning and end of the sessions, were tabulated using SPSS 22.0 and analyzed through descriptive statistics and the Wilcoxon test, with the significance level set at α ≤ 0.05. Verbal information collected from the focus group was analyzed using content analysis techniques. Among the 7 participants who completed both evaluations, 4 showed statistically significant differences in four of the seven items assessed by the Self-bodpos. In addition, positive outcomes were observed in the theoretical knowledge questionnaire and in the focus group discussions. The PEP was effective in promoting changes in body knowledge and self-perception of posture among indigenous school-aged children.

Open Access
Article
30 October 2025Smart Drone Neutralization: AI Driven RF Jamming and Modulation Detection with Software Defined Radio
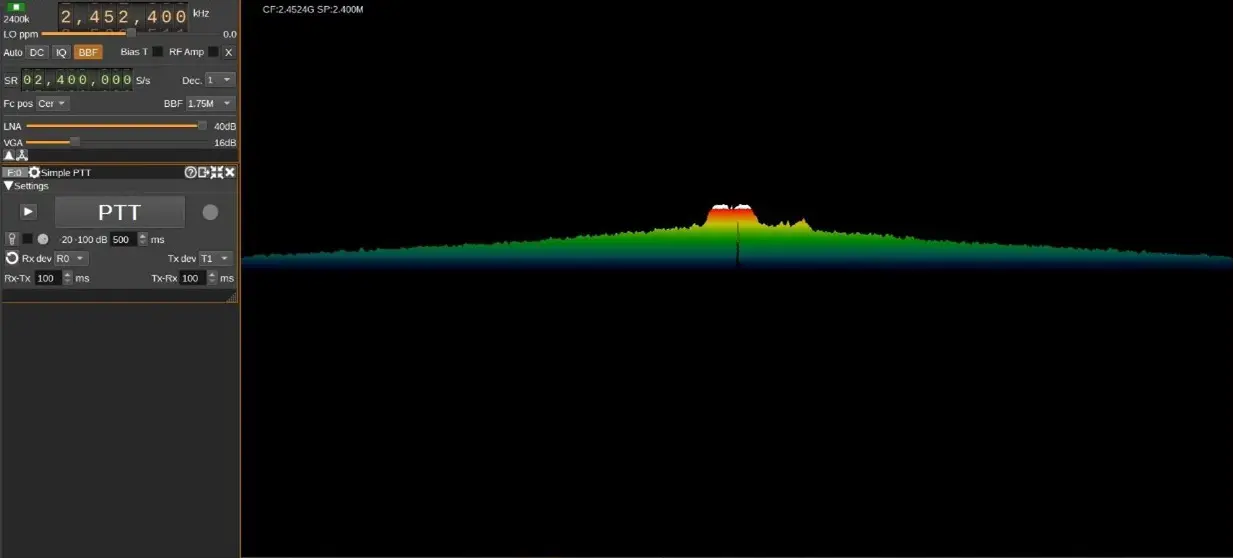
The increasing use of wireless technologies in many aspects of people’s lives has led to a congested electromagnetic spectrum, making it critical to manage the limited available spectrum as efficiently as possible. This is particularly important for military activities such as electronic warfare, where jamming is used to disrupt enemy communication, self-attacking drones, and surveillance drones. However, current detection methods used by armed personnel, such as optical sensors and Radio Detection and Ranging (RADAR), do not include Radio Frequency (RF) analysis, which is crucial for identifying the signals used to operate drones. To combat security vulnerabilities posed by the rogue or unidentified transmitters, RF transmitters should be detected not only by the available data content of broadcasts but also by the physical properties of the transmitters. This requires faster fingerprinting and identifying procedures that extend beyond the traditional hand-engineered methods. In this paper, RF data from the drones’ remote controller is identified and collected using Software Defined Radio (SDR), a radio that employs software to perform signal-processing tasks that were previously accomplished by hardware. A deep learning model is then provided to train and detect modulation strategies utilized in drone communication and a suitable jamming strategy. This paper overviews Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) neutralization, communication signals, and Deep Learning (DL) applications. It introduces an intelligent system for modulation detection and drone jamming using Software Defined Radio (SDR). DL approaches in these areas, alongside advancements in UAV neutralization techniques, present promising research opportunities. The primary objective is to integrate recent research themes in UAV neutralization, communication signals, and Machine Learning (ML) and DL applications, delivering a more efficient and effective solution for identifying and neutralizing drones. The proposed intelligent system for modulation detection and jamming of drones based on SDR, along with deep learning approaches, holds great potential for future research in this field.
Open Access
Article
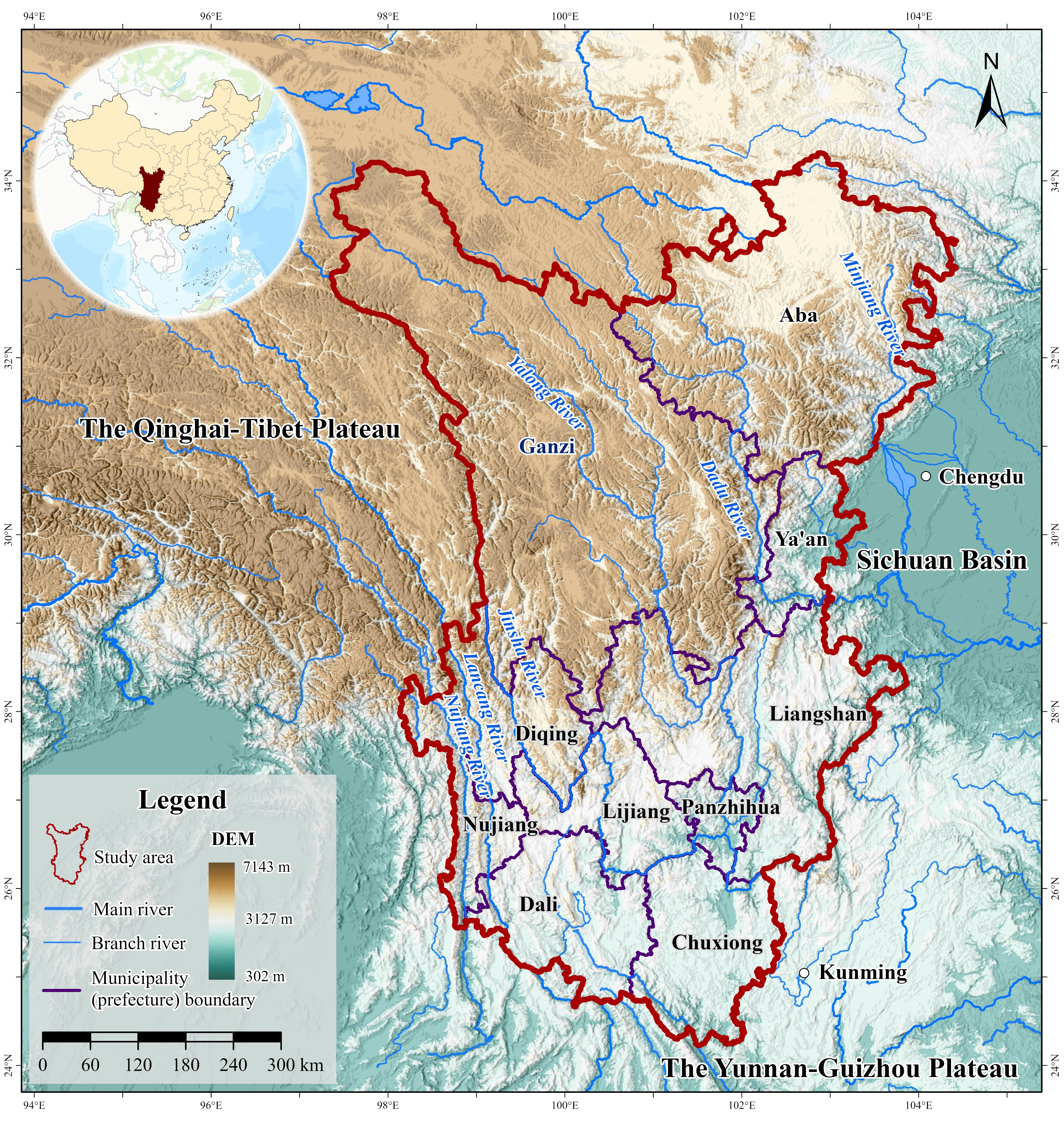
29 October 2025Solutions of Minimized Agrochemicals Input in the Post Zero-Growth Era: A State-of-the-Art Analysis of the Hengduan Mountains, China
How to further reduce the input of agrochemicals after zero-growth is an important challenge faced by mountainous areas. Up to now, the combined solution for minimized agrochemicals intervention in the post zero-growth era has not been systematically analyzed globally. Here, the Hengduan Mountain regions (HMR) in China, as a case, we estimated the turning points of agrochemicals input intensities using a quadratic equation, as well as integrating policy document analysis and literature review. Results show that the occurred timeline of fertilizer and pesticide use zero-growth in 10 municipalities (prefectures) in the HMR is relatively wide, with a distribution from 2009 to 2019, illustrating that all municipalities (prefectures) have been achieved national goals ahead of 2020 deadline. Thus, the incentive of a series of national-level policies focusing on chemical fertilizers and pesticides has proven effective in achieving the zero-growth target of agrochemicals input in the HMR. However, comparison with major mountainous countries like Germany, Italy, Portugal, Romania, Austria, and Spain etc., there are clearly many opportunities for enhancement in reducing fertilizer and pesticide uses. We present a practical route to minimize agrochemicals application in the HMR through crop rotation-based agro-biodiversity solutions, organic alternative-based soil health solutions, professionalization-based precision farming solutions, smallholder farmers’ awareness-based behavior intervention solutions, conservation reserve-based zoning solutions, etc.
Open Access
Article
29 October 2025Material Analysis of CNT’s as Conductive Additive for NMC Lithium-Ion Polymer Batteries Cathode Electrode
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are promising conductive additives for lithium-ion polymer (LiPo) batteries. The performance of lithium metal oxide cathodes is highly dependent on the properties of the conductive carbon additive. This study investigates the advantages of CNTs over conventional carbon black for this application. Material properties, including hardness, tensile strength, thermal conductivity, and electrical resistivity, were analyzed and compared using Ansys Granta (CES EduPack 2024 R2) software. The results demonstrate that CNTs are superior in tensile strength (110 MPa), hardness (50 HV), and thermal conductivity (210 W/m·°C). These properties enhance the mechanical integrity of the CNT-based cathode composite, leading to improved battery performance. Furthermore, the electrochemical behavior of CNT/LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 composite cathodes was investigated, focusing on the carbon precursor (methane vs. natural gas) and CNT diameter. At a current rate of 3 °C, multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) derived from methane delivered a specific capacity 20 mAh/g higher than those derived from natural gas. This indicates that methane-derived MWCNTs exhibit superior electrochemical performance, which is attributed to reduced polarization and a higher discharge potential. The study also revealed that MWCNTs with a smaller diameter (30–50 nm) performed better at high charge/discharge rates, owing to a higher number of primary particles per unit mass. This analysis aids in understanding material selection and its implications for battery design and lifecycle. The findings serve as a reference for future research exploring the use of CNTs in advanced battery materials.

Open Access
Review
29 October 2025Admixture of Amerindian, African and European Genes: Cuba, Mexico and Colombia as Study Cases
One hundred years after Columbus arrived in America in 1492, Amerindian population had fallen from 80 to 8 million in North and South America. The main causes were new microbes, slavery conditions and war. The people of San Basilio de Palenque (Colombia), close to Cartagena, in the Colombian Caribbean Coast, were established by runaway African slaves who built a refuge in San Basilio. The Spanish governors pressured the Spanish monarchs in Madrid to grant freedom to the Africans of San Basilio de Palenque, who became the first free Africans in the Americas. They speak the only Bantu-Spanish Creole and preserve African genetic traits according to HLA genes. Research also examined Cubans from Havana, showing that around 12% of the typical Amerindian HLA genes are present in Havana’s population. Cubans’ blood contains Amerindian genes in spite of that Amerindian physical traits do not exist now in the Cuban population. Amerindian HLA and other genes analyses and other cultural traits observed in Mexico—such as those of the Pacific Mayo/Yoreme and the Atlantic Huastecan/Teenek groups—suggest that the initial peopling of the American continent occurred much earlier than traditionally proposed, and that there was a bidirectional exchange of populations between the Pacific and Atlantic in relation to Europe (finding in America of European Paleolothic Solutrean traits) peoples may have occurred.

Open Access
Review
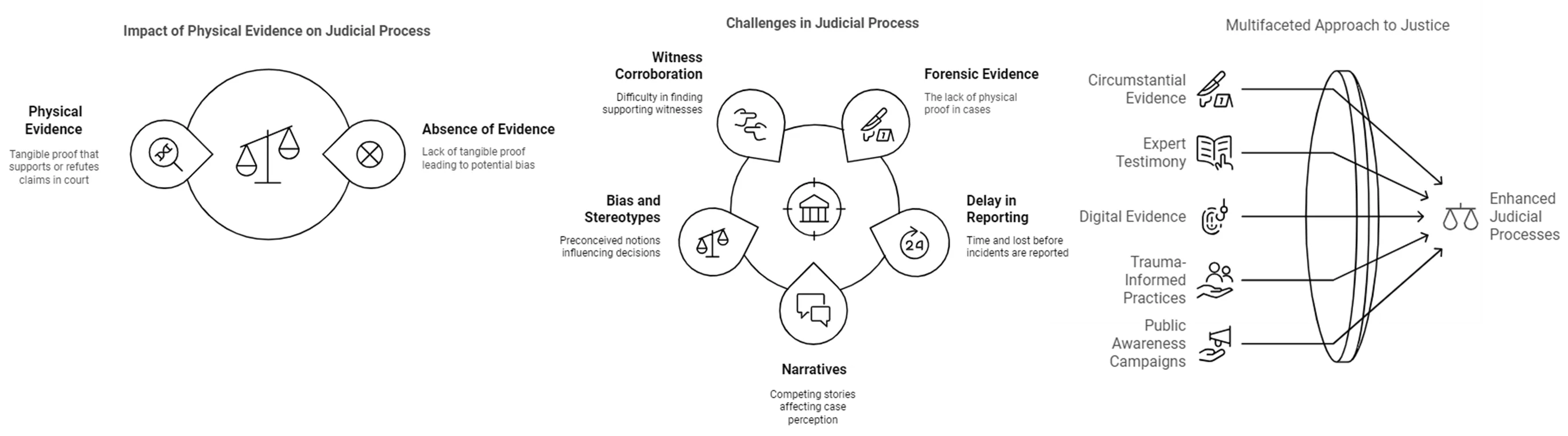
28 October 2025Prosecution of Cases Involving Sexual Crimes without Physical Evidence
Sexual crimes are rising at a concerning rate around the globe. The perpetrators are successfully acquitted of the charges, specifically in cases that lack physical evidence. Forensic evidence can associate a perpetrator with criminal activity. Occasionally, the victims of sexual misconduct do not show up right after the incident because of shame, bias, and stereotypes in society. This causes the loss of essential evidence necessary to prove the crime and the guilt of the perpetrator. Such incidents do not have any witnesses either. Therefore, it becomes hard for the jury to give a verdict in favor of the prosecution. This review article explores the factors, evidence, and initiatives that can help prosecute the victims of sexual crimes in the absence of physical evidence. A multifaceted approach comprised of scientific, psychological, and legal innovation can reduce bias, strengthen prosecution, and enhance legal outcomes, leading to improved conviction rates of sexual crimes.
Open Access
Article
28 October 2025The Role of Knowledge Transferred between Rural Inhabitants and Newcomers in the Development of Rural Areas
The purpose of this study is to find the answer to the question: What is the role of the transfer of knowledge between the permanent and new residents of the countryside. The results are based on qualitative inquiry, carried out in 18 Polish villages, situated in socially and historically diverse regions and outside of the metropolitan areas. Knowledge, which is transmitted in the contacts between the two groups considered, has a very clearly informative character. This concerns primarily the basic information pieces, meant to ensure satisfaction of the daily needs of the groups of inhabitants considered. Knowledge transfer is relatively little intensive and takes place during sporadic encounters, mainly in public spaces—a street, a central square, a shop. This, presumably, exerts an influence on the nature and quality of knowledge and information exchange. The permanent residents are, first of all, the source of current information and practical knowledge, concerning broadly conceived village life, answering the fundamental questions of what, where, and when. On the other hand, the newcomers, side by side with informative knowledge, provide also knowledge of advisory and non-material character. Knowledge and information provided by permanent rural residents serve the needs of daily life and the satisfaction of current necessities, while newcomers introduce new lifestyles and behaviors, leading to increased social activity in the countryside.
