Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitors on PA Pressures in D-TGA after Atrial Switch Operations
Received: 28 August 2025 Revised: 22 October 2025 Accepted: 24 October 2025 Published: 31 October 2025
© 2025 The authors. This is an open access article under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
1. Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is the leading cause of death for adults with congenital heart disease in the form of dextro-transposition of the great arteries (D-TGA) who have undergone an atrial switch procedure (Mustard or Senning: DTGA-AS) [1]. Unfortunately, guideline directed HF therapy has not been shown to have a significant impact on outcomes in patients with DTGA-AS [2], though sacubitril-valsartan has shown some improvement in systolic function and functional class [3].
Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) are the latest addition to HF medical therapy for patients with acquired HF, as evidence shows reduced cardiovascular death and hospitalization for HF with reduced ejection fraction and preserved ejection fraction HF [4,5,6,7], and growing evidence for their use in patients with congenital heart disease [8]. The mechanism for SGLT2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) for improving HF outcomes has been relatively unknown. A key feature in the clinical physiology of HF is inadequate cardiac output, resulting in congestion and secondary pulmonary hypertension [9]. The ability of SGLT2i to improve higher pulmonary artery pressures has been reported in those without congenital heart disease, with one trial showing a small but significant reduction in pulmonary artery pressures (PAP) by implanted hemodynamic monitoring (IHM) after SGLT2i initiation [10,11].
Though SGLT2i have been safely utilized and have shown some improvement in systemic ventricular function and functional class in patients with DTGA-AS [12], no study has evaluated the hemodynamic impact of SGLT2i in patients with DTGA-AS. To this extent, we conducted a retrospective review of patients with D-TGA-AS with IHM (CardioMEMSTM HF system; Abbott, Abbott Park, IL, USA) to evaluate the impact of SGLT2i initiation on PAP.
2. Methods
This was a single center retrospective observational study. Inclusion criteria included ambulatory adults with DTGA-AS and without ventricular assist devices, who had previously received a CardioMEMSTM device, and received either Dapagliflozin or Empagliflozin at the discretion of the treating physician. No significant changes in diuretics or other medications occurred during the study period. Patients enrolled were queried from an internal database of institutional patients who had a CardioMEMSTM and were stored on the password protected CardioMEMSTM platform (hf.g1.merlin.net, accessed on 2 June 2025). Hemodynamic information was obtained from the medical record and the online CardioMEMSTM platform and measured at baseline (1 month before SGLT2i initiation), 90 days after therapy initiation, and 6 months after therapy initiation. Hemodynamic recordings were not included if they were marked as suspicious or erroneous at the time of entry. PAP is reported as the median. Statistical analysis was performed using the Mann-Whitney test to evaluate PAP data before and 6 months after SGLT2i therapy (significance was established if the p value < 0.05). Analysis was performed using Prism 10 for Windows 64-bit (Version10.2.1 (509) GraphPad Software, Boston, MA, USA; www.graphpad.com, accessed on 2 June 2025). This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at both The Ohio State University and Nationwide Children’s Hospital.
3. Results
We identified 6 total patients who fit the inclusion criteria; all male (mean age 41 [range 38–52] years), with a mean systemic right ventricular ejection fraction of 27% (range 22–32%). Three patients met the hemodynamic definition of pulmonary hypertension, with mean PAP > 20 mmHg. Five patients were already prescribed sacubitril-valsartan, and 1 was on an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (Figure 1). The mean number of recordings per patient was 10.2 prior to starting an SGLT2i (range 3–24), and 39.7 after initiation (range 7–140). The IHM PAP recordings and comparisons are shown in Figure 1. One patient (#2) had a significant decrease in all PAPs after SGLT2i, who notably sent IHM transmissions daily. There were 2 patients (#1, #5) with PAP values that trended towards improvement but were not statistically significant, 2 patients (#4, #6) had no change. One patient had increased PAP over this time period (#3), though notably this was during a time of decompensated HF, superimposed on notable pulmonary venous baffle dystrophic calcification. Patients #1 and #3 had SGLT2i added after hospital admission for HF exacerbations.
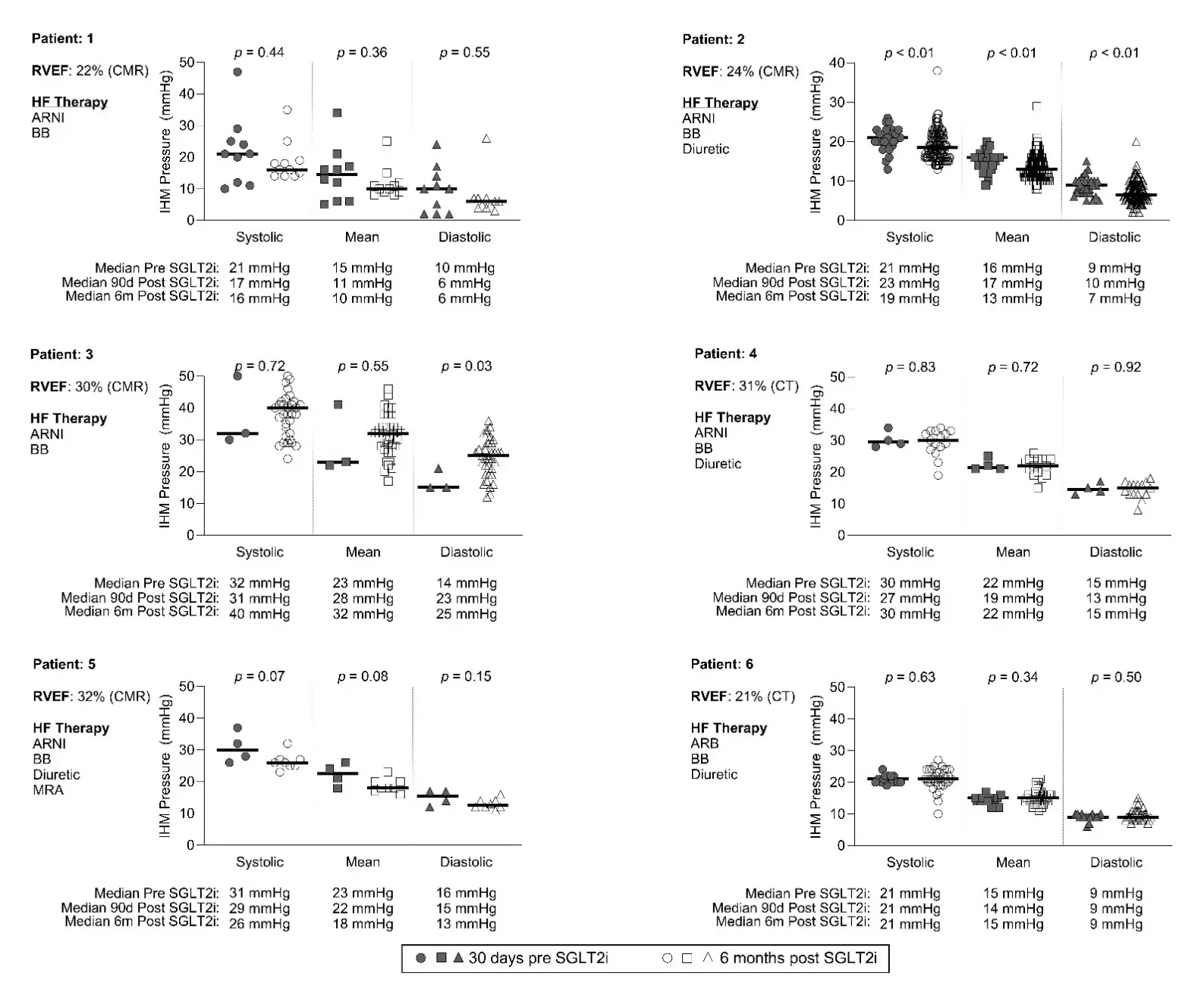
Figure 1. Change in PAP by implanted hemodynamic monitor before and after treatment with SGLT2i. CT = computed tomography; CMR = cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; RVEF = right ventricular ejection fraction; HF = heart failure; ARNI = angiotensin-neprolysin inhibitor; BB = beta blocker, SLGT2i = Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor.
4. Discussion
In this small single-center study of adults with DTGA-AS and systemic ventricular systolic dysfunction, where 50% of patients had normal PAP and most (5/6) were already on an angiotensin-neprolysin inhibitor (ARNI), the addition of SGLT2i did not result in a significant change in PAP in all patients.
It is well described that there is an increase in PAP in acquired heart failure due to the physiology of systolic and diastolic left ventricle dysfunction [13]. While the mechanism of SGLT2i in HF is not fully understood, the proposed benefits in heart failure physiology have been direct impacts on myocardial remodeling, attenuation of vascular dysfunction, and improvements in volume status [14,15,16,17]. In acquired heart disease, smaller scale research studies have shown that SGLT2i lowers PAP and decreases the incidence of elevated right ventricle systolic pressure and exercise-induced pulmonary hypertension [10,18].
In patients with DTGA-AS, PH is a well-known late-onset complication [19]. Large cohort studies report a prevalence of PH as high as 50–55% in patients with systemic right ventricles, which was associated with worse transplant-free survival [20,21]. Therefore, interventions to treat PH, or help sustain normal PAP in this patient population may help improve long term outcomes.
There was ultimately a small but significant PAP reduction in 1 patient with a large number of IHM transmissions in this study. We posit that in this small patient sample size, the relatively small number of IHM transmissions for most patients, as well as the one patient with increased PAP (#3), may have skewed the outcome assessment. For instance, there was a large difference between transmissions submitted in defined timeframes prior to and after the initiation of the SGLT2i (a mean of 10.2 recordings per patient prior to starting an SGLT2i and 39.7 after initiation). Furthermore, one patient (#3) had increased PAP with normal systemic right ventricular end diastolic pressures and an elevated wedge pressure, which is likely related to pulmonary venous baffle calcifications, a concept previously reported [22]. Thus, any improvement in ventricular filling pressures is not reflected in PAP change, as opposed to other patients with concordant wedge and systemic ventricular pressures during cardiac catheterization.
In addition to a small patient cohort and IHM transmission per patient sample size, further limitations include the single center, retrospective nature and lack of a placebo group. One notable strength, however, is that most patients were already taking sacubitril-valsartan, ensuring that any change is likely attributable solely to the SGLT2i.
5. Conclusions
To our knowledge, this is the first report of the hemodynamic impact of SGLT2i on PAP by IHM in patients with DTGA-AS. Though a significant decrease was not seen in all patients in short-term follow up after SGLT2i, sustained “normal” PAP is also noteworthy in this population of patients at risk for PH. Larger studies with prolonged follow up may assist in revealing if certain subsets of patients with DTG-AS and systemic ventricular dysfunction, especially those with significant post capillary pulmonary hypertension, may have a hemodynamic benefit from an SGLT2i.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L. and W.H.M.V; Methodology, M.L. and W.H.M.V; Software, W.H.M.V; Validation, M.L., W.H.M.V; Formal Analysis, M.L. and W.H.M.V; Investigation, M.L. and W.H.M.V; Resources, M.L. and W.H.M.V Data Curation, M.L. and W.H.M.V; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, M.L.; Writing—M.L. and W.H.M.V; Visualization, M.L. and W.H.M.V Supervision, W.H.M.V; Project Administration, M.L.; Funding Acquisition, W.H.M.V.
Ethics Statement
This study was approved with waivered consent by The Ohio State University Biomedical Institutional Review Board (ID: 2022H0297).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective fashion of the study.
Data Availability Statement
Accessibility of research data is available upon request.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Broberg CS, van Dissel AC, Minnier J, Aboulhosn J, Kauling RM, Ginde S, et al. Long-Term Outcomes After Atrial Switch Operation for Transposition of the Great Arteries. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 951–963. [Google Scholar]
-
Zaragoza-Macias E, Zaidi AN, Dendukuri N, Marelli A. Medical Therapy for Systemic Right Ventricles: A Systematic Review (Part 1) for the 2018 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Adults With Congenital Heart Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 1564–1578. [Google Scholar]
-
Fusco F, Scognamiglio G, Merola A, Iannuzzi A, Palma M, Grimaldi N, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Sacubitril/Valsartan in Patients with a Failing Systemic Right Ventricle: A Prospective Single-Center Study. Circ. Heart Fail. 2023, 16, e009848. [Google Scholar]
-
McMurray JJ, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Køber L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar]
-
Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Pocock SJ, Carson P, et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar]
-
Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Ferreira JP, Bocchi E, Böhm M, et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar]
-
Solomon SD, McMurray JJ, Claggett B, de Boer RA, DeMets D, Hernandez AF, et al. Dapagliflozin in Heart Failure with Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar]
-
Marshall WH, Wright L. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Adult and Pediatric Congenital Heart Disease: Review of Emerging Data and Future Directions. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2024, 19, 419–433. [Google Scholar]
-
Rosenkranz S, Gibbs JS, Wachter R, De Marco T, Vonk-Noordegraaf A, Vachiery JL. Left ventricular heart failure and pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 942–954. [Google Scholar]
-
Nassif ME, Qintar M, Windsor SL, Jermyn R, Shavelle DM, Tang F, et al. Empagliflozin Effects on Pulmonary Artery Pressure in Patients with Heart Failure: Results from the EMBRACE-HF Trial. Circulation 2021, 143, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar]
-
Kirschbaum K, Vasa-Nicotera M, Zeiher AM, Cremer S. SGLT2 inhibitor therapy and pulmonary artery pressure in patients with chronic heart failure-further evidence for improved hemodynamics by continuous pressure monitoring. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2022, 111, 469–472. [Google Scholar]
-
Marshall WH, Daniels CJ. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Patients With Systemic Right Ventricles: Incrementally Building the Evidence Base. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2025, 14, e043096. [Google Scholar]
-
Guazzi M, Naeije R. Pulmonary Hypertension in Heart Failure: Pathophysiology, Pathobiology, and Emerging Clinical Perspectives. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 1718–1734. [Google Scholar]
-
Alshnbari AS, Millar SA, O’Sullivan SE, Idris I. Effect of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors on Endothelial Function: A Systematic Review of Preclinical Studies. Diabetes Ther. 2020, 11, 1947–1963. [Google Scholar]
-
Lee MM, Brooksbank KJ, Wetherall K, Mangion K, Roditi G, Campbell RT, et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Left Ventricular Volumes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, or Prediabetes, and Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (SUGAR-DM-HF). Circulation 2021, 143, 516–525. [Google Scholar]
-
Omar M, Jensen J, Frederiksen PH, Kistorp C, Videbæk L, Poulsen MK, et al. Effect of Empagliflozin on Hemodynamics in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2740–2751. [Google Scholar]
-
Durante W, Behnammanesh G, Peyton KJ. Effects of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors on Vascular Cell Function and Arterial Remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8786. [Google Scholar]
-
Kayano H, Koba S, Hirano T, Matsui T, Fukuoka H, Tsuijita H, et al. Dapagliflozin Influences Ventricular Hemodynamics and Exercise-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Type 2 Diabetes Patients—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Circ. J. 2020, 84, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar]
-
Ebenroth ES, Hurwitz RA, Cordes TM. Late onset of pulmonary hypertension after successful Mustard surgery for d-transposition of the great arteries. Am. J. Cardiol. 2000, 85, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
-
Van De Bruaene A, Toh N, Hickey EJ, Benson L, Horlick E, Granton JT, et al. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with a subaortic right ventricle: Prevalence, impact and management. Heart 2019, 105, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar]
-
Chaix MA, Dore A, Mercier LA, Mongeon FP, Marcotte F, Ibrahim R, et al. Late Onset Postcapillary Pulmonary Hypertension in Patients with Transposition of the Great Arteries and Mustard or Senning Baffles. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e006481. [Google Scholar]
-
Cowgill JA, Moran AM. Stiff “Left Atrial” syndrome post-mustard procedure. J. Cardiol. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 6, 69–73. [Google Scholar]