Found 469 results
Open Access
Article
18 April 2024Biodegradable Composite Materials Based on Cassava Starch and Reinforced with Topinambur (Helianthus tuberosus) Aerial Part Fiber
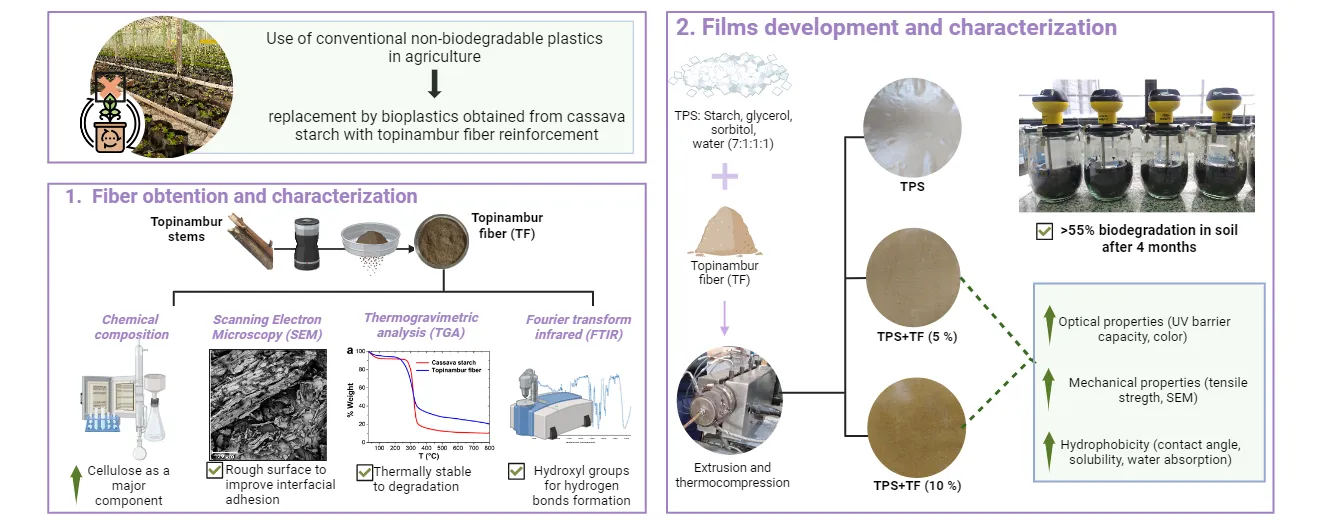
The cultivation of topinambur (Helianthus tuberosus) has aroused the interest of producers since it is a source of inulin and can be used for biofuel production. During tuber processing, the aerial part of the crop remains as a by-product with no practical application. This work aimed to characterize the fibers obtained from the aerial part of topinambur and to evaluate their reinforcing potential in cassava starch-based films. Starch-based films with topinambur fiber (0, 5, and 10%) were prepared by extrusion followed by thermocompression. Topinambur residue contains 88.6% of total fiber, 8.5% ash, and 0.68% lipid. Mechanical film properties evidenced the reinforcement action of topinambur fiber, 10% content was able to increase up to 70% the Young’s modulus. SEM micrographs evidenced the good fiber-matrix interaction. UV-visible capacity, opacity, and chromaticity parameters of TPS films increased with fiber content in the formulation. Fiber incorporation improved the hydrophobicity of the biocomposite materials by increasing the contact angle. Starch-based films biodegraded more than 55% after 110 days, showing a similar trend to that of microcrystalline cellulose. Thus, topinambur residue can be effectively used as a reinforcing agent for TPS materials, being an innovative and non-toxic additive within the circular economy premises.
Open Access
Article
17 April 2024Thermogravimetric Study of the Oxidation Behavior of the Cantor’s Alloy at 1000 °C and Beyond
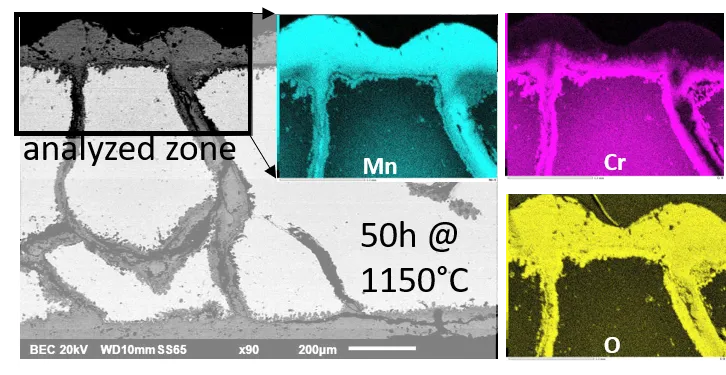
A polycrystalline Cantor alloy, equimolar in Co, Cr, Fe, Mn and Ni, was cast. It was subjected to oxidation in a thermo-balance in a flow of synthetic dry air, at 1000, 1050, 1100 and 1150 °C. The mass gain was globally parabolic but rather irregular. The parabolic constants, ranging from 55 to 700 × 10−12·g2·cm−4·s−1, are much higher than for a chromia-forming alloy. They obey an Arrhenius law with an activation energy equal to 270 kJ/mol. The external oxide scales formed are composed of an outer part made of manganese oxide and an inner part made of (Cr, Mn) oxide containing a thin internal layer of chromia. The Mn and Cr-depleted depths and the Mn and Cr masses lost by the alloy increase with the oxidation temperature. Cr-rich acicular particles precipitated in subsurface at 1100 °C and internal oxidation along the grain boundaries are present in the whole thickness of the sample oxidized at 1150 °C. Oxide spallation occurred during the cooling, at temperatures in the 200–350 °C range, only for the alloys oxidized at 1050 and 1100 °C. Not too thick scale (1000 °C) or deep internal oxidation (1150 °C) may be favorable for scale adherence.
Open Access
Review
15 April 2024Human Mobility in the Central and Eastern Mediterranean during Hellenistic and Roman Times: The Potential and Limitations of Bioarchaeological Research
This paper offers a review of bioarchaeological research on human mobility during the Hellenistic and Roman period in the Central and Eastern Mediterranean. This period was marked by significant connectivity amidst the establishment of major political entities. The paper begins with an overview of bioarchaeological methods used to study past mobility, including biodistance, isotopic and ancient DNA analyses. It then examines published studies that have utilized these methods to explore mobility during the Hellenistic and Roman periods. The paper concludes by critically assessing the current research limitations and proposing directions for future studies. These suggestions emphasize the importance of conducting additional research to investigate human mobility in neglected areas, as well as at different temporal and spatial scales. Integrating mobility data with other sources of evidence, such as historical accounts, paleoenvironmental data and osteobiographic information is another important future direction of research. Finally, relevant research should be more theoretically informed and its contemporary implications should be effectively communicated within and beyond the academic community. An enhancement of our understanding of the nature and impact of mobility is crucial in today’s society, where misconceptions linking immigration to the decline of the Roman Empire can perpetuate biases against contemporary mobility.
Open Access
Article
09 April 2024Anisotropic Superelastic and Shape Memory Effect of Nitinol Manufactured by Electron Beam Powder Bed Fusion
This study explores the impact of energy input and build orientation on the anisotropic mechanical and functional properties of Ti-rich Nitinol (NiTi) produced via electron beam powder bed fusion (PBF-EB), integrated with layerwise in-situ monitoring of the melted surface via backscatter electron detection (ELO). NiTi, a binary alloy of nickel and titanium, exhibits shape memory and superelasticity, making it widely used in biomedical applications and sustainable technologies. PBF-EB, particularly with ELO, is highlighted for its advantages in producing crack-free NiTi with tailored microstructures. The investigation reveals that energy input significantly influences microstructure phases, with higher energy promoting increased evaporation of Ni and enhancing Ti-rich Ti2Ni precipitates, allowing for tailored material properties. Build orientation also proves crucial, impacting mechanical responses and functional properties. The 0° orientation yields the hardest mechanical response with the highest ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and the highest strain recovery ratio while the 45° orientation shows improved ductility but lower UTS. The influencing factors towards the formation of the anisotropic material properties are explained and the potential of tailoring the NiTi properties for specific applications by controlling energy input and build orientation in the PBF-EB process are underlined. These insights offer valuable criteria for designing innovative NiTi parts.
Open Access
Review
02 April 2024Mapping the (in)Effective Enforcement of EU Environmental Law in Greece: Lessons from the EU and Domestic Courts
The effective implementation and enforcement of EU environmental law at national level constitutes a thorny issue with both legal and practical aspects. Greece is among the EU Member States which has historically faced difficulties in complying with the EU environmental acquis due to the poor functioning of the Greek administration, the limited manpower, expertise and resources (especially during the recent period of the economic crisis) for the competent authorities, the lack of political will, the low awareness of environmental problems. In this context, this paper aspires to unpack these enforcement challenges at the national level based on the case law of both the Greek Council of State and the Court of Justice of the European Union. Considering that waste management, nature protection, and water and air quality sectors are recognized as areas with the most significant deficiencies in implementation at the domestic level, the analysis will focus on these four key sectors. To this end, by reviewing the relevant EU and Greek jurisprudence, this paper aspires to identify the disparities between the formal requirements and the practical application of EU environmental regulations in Greece in light of the national political, economic, social, and cultural dynamics.

Open Access
Article
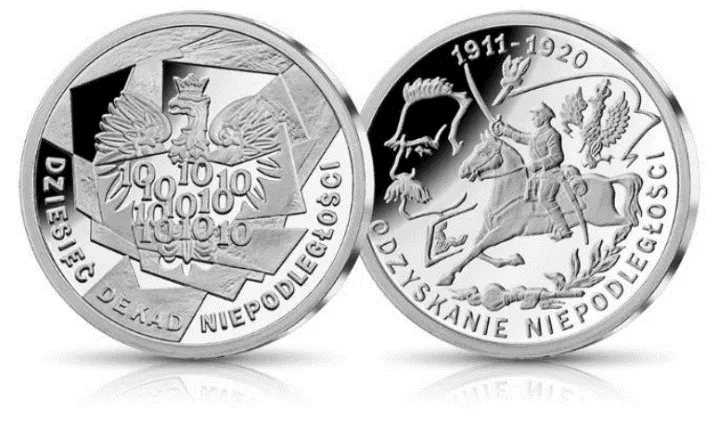
01 April 2024Fighting Arts on Today’s Coins, Medals and Badges: Popularity or Uniqueness
Background. Medallic art is used to promote the subject matter which is important for the issuer. Also fighting arts and martial traditions are used here as icons in the coins and medals. Problem. What is the purpose of occasional coins, medals or badges relative to their contents or symbolism, the metal used or the volume of the release? Does an issuer aim at promotion or rather at recognition and at maintaining the uniqueness? Material and Method. The study uses a regression method, comparative analysis and literature review. Approximately one hundred examples are discussed. Statistical analyses took into account N = 64 of contemporary coins (47) and medals (17), representing the relevant thematic groups. Pearson C coefficient was calculated for the factor of popularity FA and a number of variables. Results. It has been found that medals are issued in small volumes and are significantly varied in terms of the subject matter (uniqueness and originality). Some organisations seek to ensure the exceptional status of medal-type award which is granted based on strictly defined rules. Conclusions. Presentations of martial arts on coins, medals and badges make reference to the related symbolism or to the issuer’s national traditions. Large volume releases are mainly done for promotional purposes. On the other hand medals issued in small numbers are meant to be unique—they find their way to a select group of people deserving special recognition.

Open Access
Article
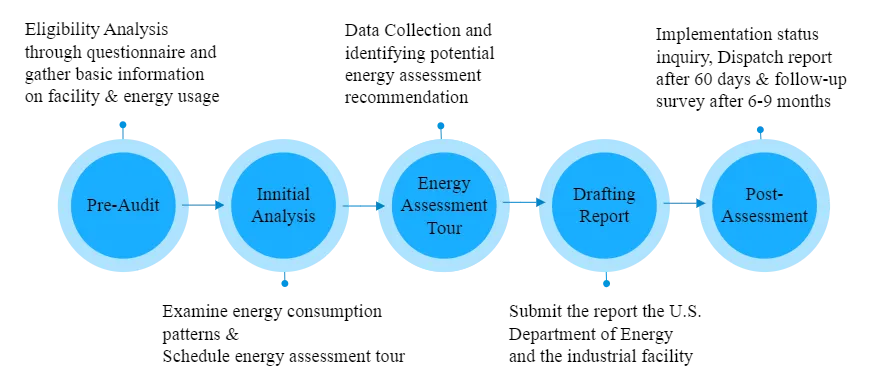
01 April 2024Cost Effectiveness of the Industrial Internet of Things Adoption in the U.S. Manufacturing SMEs
This research paper explores the financial adoption challenges of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) in industry. Previous studies have mainly concentrated on designing affordable IIoT devices, reducing operational costs, and creating conceptual frameworks to assess the financial impact of IIoT adoption. The objective of this paper is to investigate whether IIoT adoption’s financial benefits outweigh the initial costs in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The data from the Industrial Assessment Centers (IAC) database were analyzed, focusing on 62 U.S. manufacturing SMEs across 10 states and 25 Standard Industrial Classifications (SICs), evaluating projected IIoT implementation costs and anticipated cost savings. Results from the analyses reveal that statistically, the difference between implementation costs and savings is significant at a 95% confidence level. Practically, this indicates that SMEs, despite facing high initial costs, can expect these investments to be counterbalanced by substantial savings. From an engineering perspective, this finding raises awareness among SMEs that, beyond overcoming financial barriers, IIoT technologies serve as a strategic enhancement to operational efficiency and competitive positioning. This study acknowledges the limitations including reliance on estimated projections and a narrow industry focus. Future research should broaden the sample and explore the lifecycle costs of IIoT.
Open Access
Review
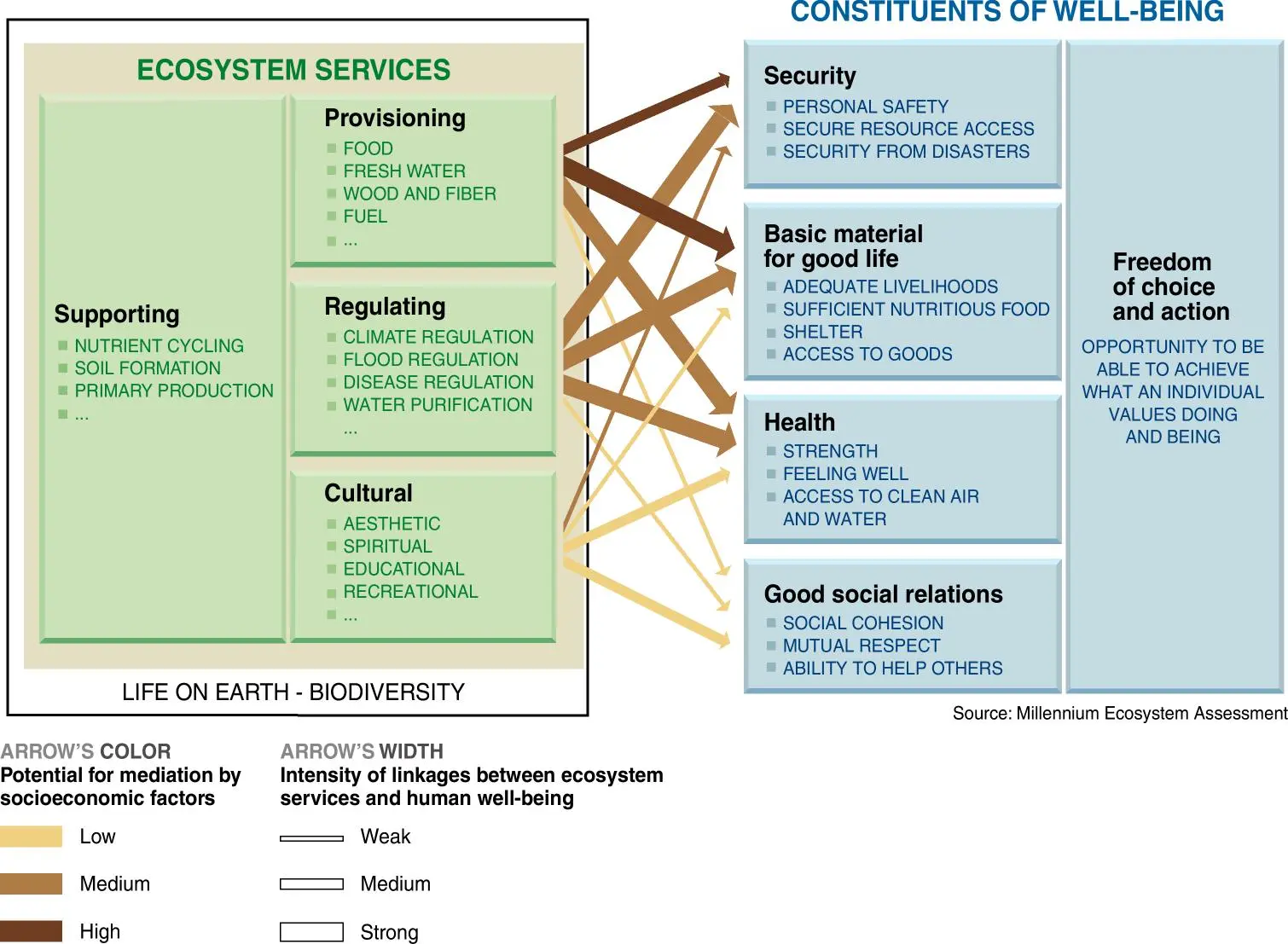
01 April 2024Desperately Seeking Sustainable Human Well-Being: A Review of Indicators, Concepts, and Methods
Evaluating progress in human development and well-being is imperative for policymakers to assess the impact of their policies. Traditional measurement methods focus mostly on economic growth and socio-economic objectives, often neglecting vital components of the natural environment, particularly the ecological determinants essential for the sustainability of human well-being. The tension between sustainability and development becomes apparent as the recognition of the dependence of human well-being on the natural environment and ecosystem services is crucial for safeguarding the environment for present and future generations. This highlights the necessity for indicators that capture the intricate relationship between human well-being and environmental changes while addressing the challenges posed by the tension between sustainable practices and traditional development models. This paper presents a literature review examining the domains, dimensions, and indicators related to the sustainability of human well-being regarding economic, social, and natural environments. Emphasizing the multidimensional nature, this paper highlights the drawbacks of relying solely on socioeconomic indicators for assessment. The review explores diverse concepts and methodologies proposed to evaluate the components and multidimensional factors influencing the sustainability of human well-being. Ultimately it offers a holistic understanding serving as a foundation for further research and policy development.
Open Access
Article
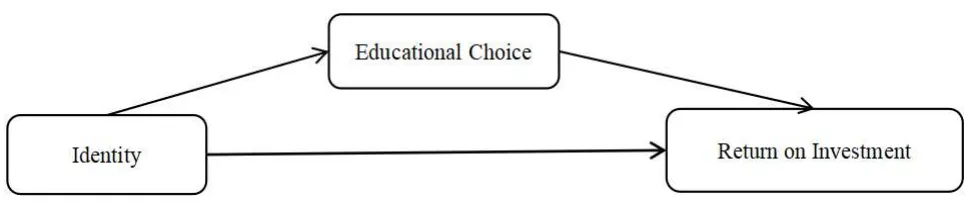
01 April 2024Identity, Secondary Vocational Education Options and Return on Investment: Evidence from Children of Rural Chinese Families
With the continuous improvement of living standards, the importance of educational choice becomes more and more prominent. Based on the data of China General Social Survey (CGSS), a simultaneous equation model of identity, secondary vocational education choice and investment return is constructed. On the basis of fully considering endogeneity and sample selection bias, this paper analyzes the influence of identity on secondary vocational education choice and investment return by means of instrumental variables and propensity score matching (PSM). It is found that class differentiation is the main factor affecting class identity. The more blurred class differentiation, the higher class identity. Class identity has a significant positive impact on identity. The higher class identity, the easier it is to form identity. Identity has a direct positive impact on personal investment return. The stronger the identity, the higher the investment return. At the same time, identity has a significant positive impact on the choice of secondary vocational education. The stronger the identity, the more inclined to choose secondary vocational education. Compared with individuals with junior high school education, individuals with secondary vocational education have a higher return on education investment. Therefore, identity can not only directly improve an individual’s return on investment, but also improve the possibility of an individual’s choice of secondary vocational education, thereby improving an individual’s return on education investment, and ultimately increasing an individual’s return on investment.
Open Access
Article
31 March 2024
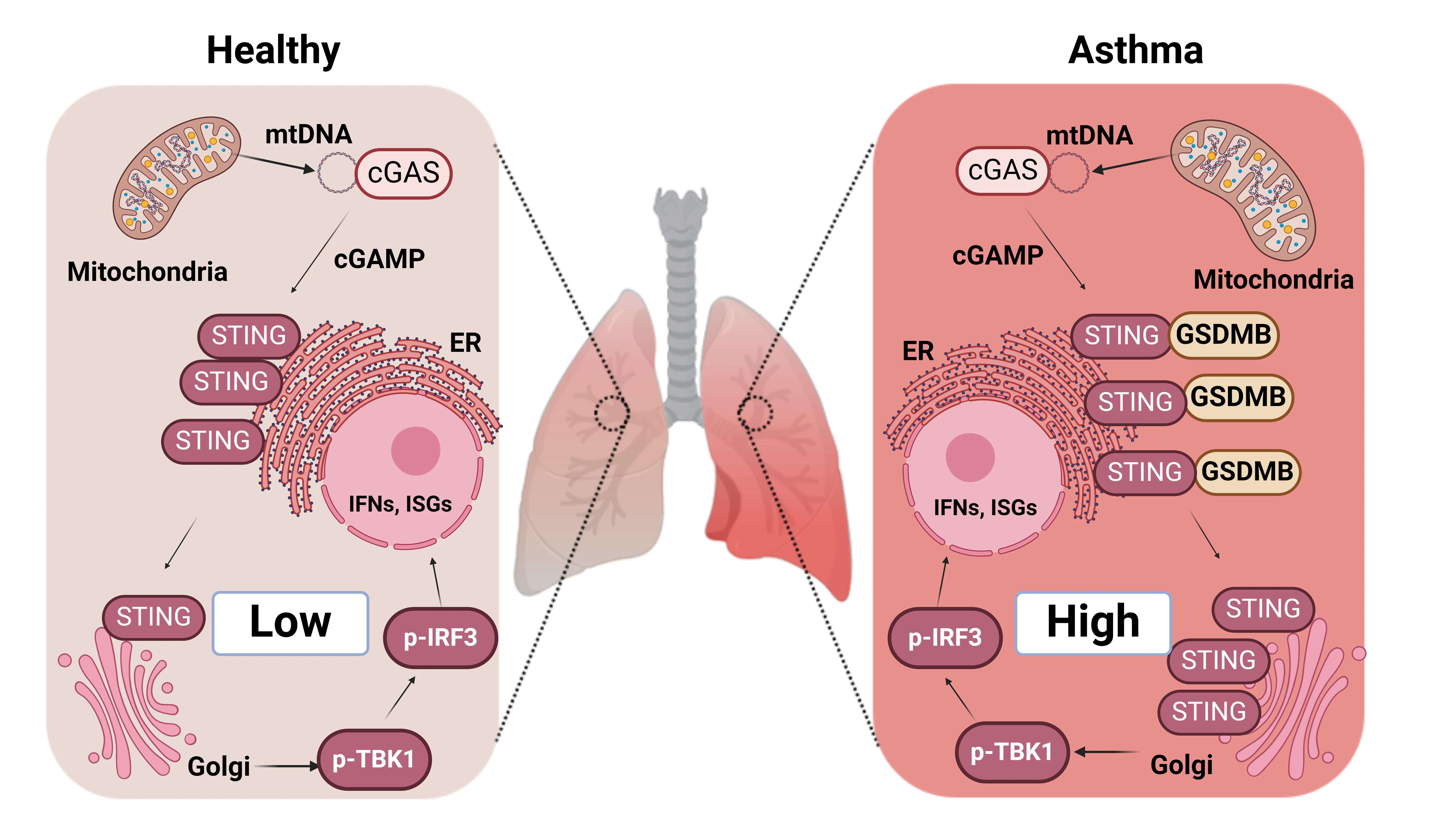
The Asthma Risk Gene, GSDMB, Promotes Mitochondrial DNA-induced ISGs Expression
Released mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in cells activates cGAS-STING pathway, which induces expression of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) and thereby promotes inflammation, as frequently seen in asthmatic airways. However, whether the genetic determinant, Gasdermin B (GSDMB), the most replicated asthma risk gene, regulates this pathway remains unknown. We set out to determine whether and how GSDMB regulates mtDNA-activated cGAS-STING pathway and subsequent ISGs induction in human airway epithelial cells. Using qPCR, ELISA, native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, co-immunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence assays, we evaluated the regulation of GSDMB on cGAS-STING pathway in both BEAS-2B cells and primary normal human bronchial epithelial cells (nHBEs). mtDNA was extracted in plasma samples from human asthmatics and the correlation between mtDNA levels and eosinophil counts was analyzed. GSDMB is significantly associated with RANTES expression in asthmatic nasal epithelial brushing samples from the Genes-environments and Admixture in Latino Americans (GALA) II study. Over-expression of GSDMB promotes DNA-induced IFN and ISGs expression in bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells and nHBEs. Conversely, knockout of GSDMB led to weakened induction of interferon (IFNs) and ISGs in BEAS-2B cells. Mechanistically, GSDMB interacts with the C-terminus of STING, promoting the translocalization of STING to Golgi, leading to the phosphorylation of IRF3 and induction of IFNs and ISGs. mtDNA copy number in serum from asthmatics was significantly correlated with blood eosinophil counts especially in male subjects. GSDMB promotes the activation of mtDNA and poly (dA:dT)-induced activation of cGAS-STING pathway in airway epithelial cells, leading to enhanced induction of ISGs.