Found 469 results
Open Access
Article
09 January 2025Advanced Materials: Nature of Strongly Correlated Quantum Spin Liquid in Sr3CuNb2O9
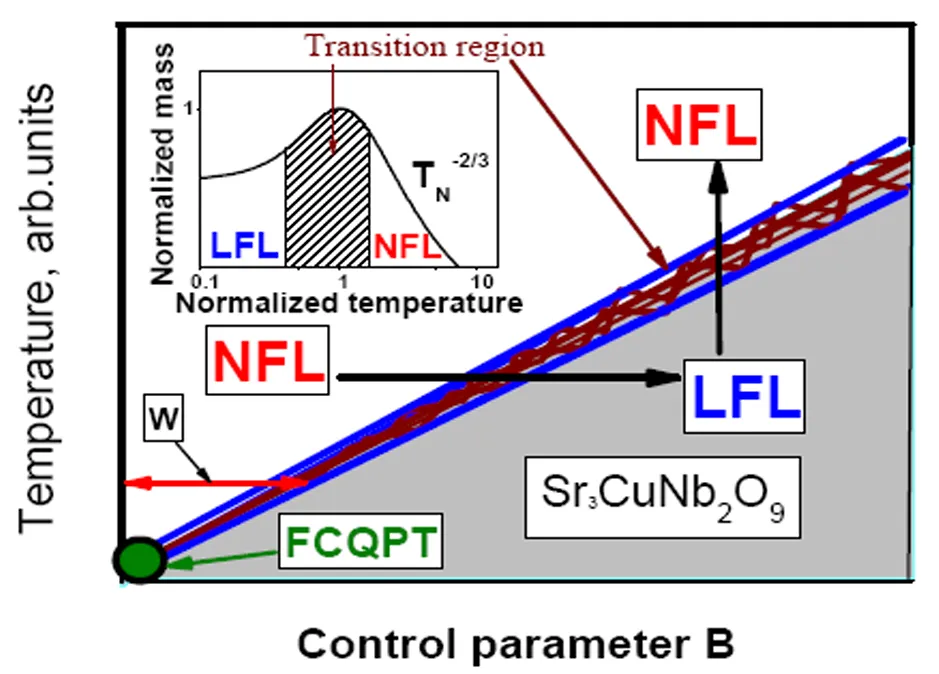
Quantum spin liquids of frustrated magnets are among the most attractive and basic systems in physics. Frustrated magnets exhibit exceptional properties as insulators and metals, making them advanced materials that represent materials for future technologies. Therefore, a reliable theory describing these materials is of great importance. The fermion condensation theory provides an analytical description of various frustrated quantum spin liquids capable of describing the thermodynamic and transport properties of magnets based on the idea of spinons, represented by chargeless fermions filling the Fermi sphere up to the Fermi momentum pF . We show that the low temperature thermodynamic of Sr3CuNb2O9 in magnetic fields is defined by strongly correlated quantum spin liquid. Our calculations of its thermodynamic properties agree well with recent experimental facts and allow us to reveal their scaling behavior, which is very similar to that observed both in heavy-fermion metals and in frustrated magnets or insulators. We demonstrate for the first time that Sr3CuNb2O9 belongs to the family of strongly correlated Fermi systems that form a new state of matter.
Open Access
Review
09 January 2025Recent Advancements in Alumina-Based High-Temperature Insulating Materials: Properties, Applications, and Future Perspectives
As a high-temperature thermal insulation material with excellent mechanical properties, alumina (Al2O3)-based materials hold significant potential for applications in aerospace, advanced manufacturing, automobiles, industrial furnaces, and other fields. However, the inherent brittleness of alumina poses a limitation to its wider application. Therefore, there is a pressing need to develop alumina-based materials that offer high toughness while retaining superior mechanical properties. This paper begins by exploring the structure of alumina, highlighting its thermal conductivity, insulation, and mechanical properties in high-temperature environments. It then reviews the classification and synthesis methods of alumina-based materials, along with the latest advances in design strategies. Notably, the rational design of alumina composition, structure, and morphology is emphasized as crucial for optimizing material performance, thereby supporting the industrial development and application of these materials in high-tech sectors. Finally, the paper discusses the challenges and evolution of alumina-based materials in real-world industrial applications and suggests potential directions for future development.
Open Access
Article
09 January 2025Sustainability Practices and Financial Performance: Evidence from BIST Electricity Index
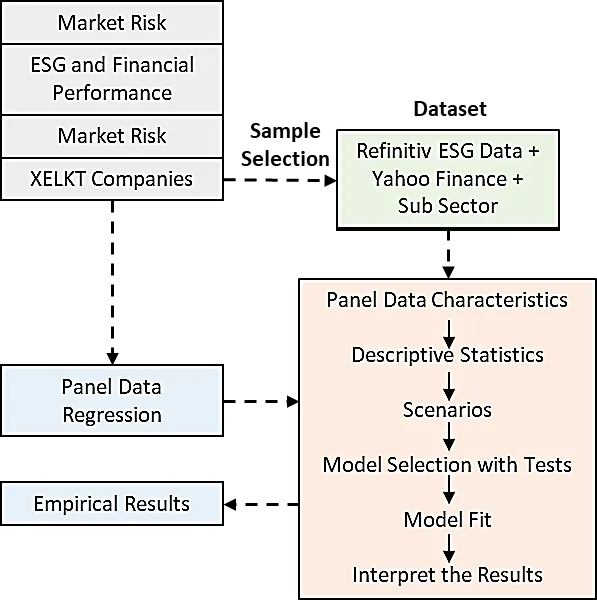
Amidst the backdrop of heightened market risks associated with transitioning to a lower-carbon economy, this study pioneers an examination of the correlation between sustainability and financial performance within Turkish energy market generator and retailer companies. In this study, the sustainability performance, exposure to market risks and effects on the financial performance of sub-sectors of companies listed in the BIST Electricity index were analyzed using panel data regression. The findings reveal a nuanced relationship between sustainability factors and financial performance, underscoring the imperative for electricity sector companies to prioritize sustainability initiatives not only for ethical reasons but also as a strategic imperative for long-term financial success and stakeholder value creation. Finally, the possibility of impending regulatory changes underscores the importance of early adoption of sustainability practices to mitigate potential financial liabilities and navigate future market risks effectively.
Open Access
Communication
08 January 2025Development of Eco-Friendly Composites Using Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and Diss Fibers (Ampelodesmos Mauritanicus)
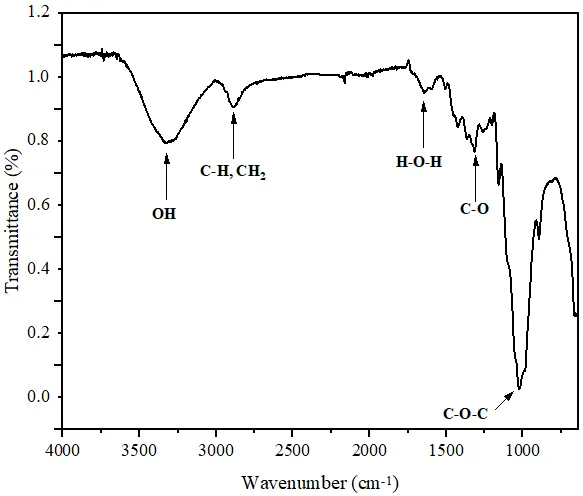
In response to the growing environmental threats and pollution linked to synthetic plastics, current scientific inquiry is prioritizing the advancement of biodegradable materials. In this context, this study investigates the possibility of developing fully biodegradable materials using plant fibers extracted from the Diss plant (Ampelodesmos mauritanicus) as reinforcement in poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV)-based biocomposites. The biocomposites were prepared by melt blending in the following weight ratio: PHBV/Diss fibers 80/20. The chemical structure of Diss fibers was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF). The impact of Diss fibers on the mechanical properties of biocomposites has also been investigated in comparison to neat PHBV. FTIR and XRF analyses identified cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin as the main components of Diss fibers. On the other hand, the results showed a significant enhancement of Young’s modulus (⁓21%) of PHBV/DF biocomposites in comparison to neat PHBV due to a better dispersion of the fibers in the matrix, as confirmed by atomic force microscopy (AFM) images.
Open Access
Article
07 January 2025Trace DNA Recovery: Insights from Dubai Police Casework
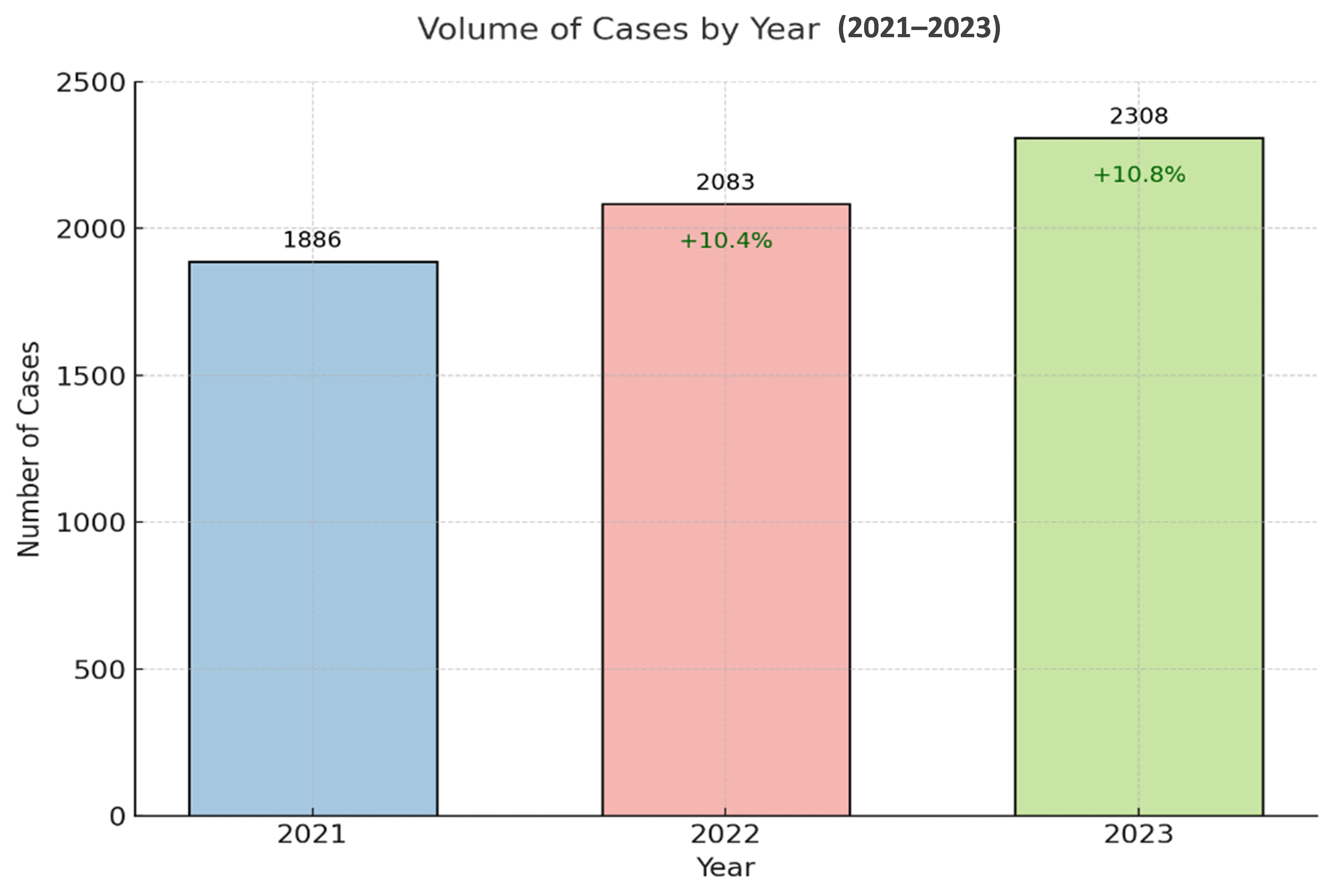
Trace DNA represents a critical form of forensic evidence, frequently recovered from a wide variety of touched or used items. Despite its evidentiary value, trace DNA analysis poses significant challenges due to the minute quantities of DNA involved, as well as the influence of factors such as surface type, collection methods, and environmental exposure. This study systematically examines the success rates and characteristics of trace DNA profiles recovered from six-item categories—tools, stolen items, wearable items, packaging materials, vehicles, and touched items—processed between 2021 and 2023 by the Biology and DNA Section of the Dubai Police Force. A total of 6277 cases were analyzed, encompassing a range of crimes, including homicide, suicide, missing persons, paternity disputes, and burglary. The results demonstrated an overall trace DNA success rate of 64%, with wearable items yielding the highest success rate at 76% and packaging materials yielding the lowest at 54%. Detailed analysis of positive DNA trace samples revealed significant variability in DNA profile types across item categories. Wearable items and touched items predominantly yielded full single (FS) DNA profiles, reflecting their reliability as sources of singular and high-quality DNA. Conversely, stolen items and packaging materials showed a greater prevalence of full mixed (FM) DNA profiles, highlighting their association with complex mixtures due to handling by multiple contributors. Tools and vehicles, meanwhile, exhibited higher rates of partial profiles, presenting unique challenges related to surface irregularities and environmental factors. This study emphasizes the importance of tailoring forensic strategies to item-specific characteristics, as well as the need for systematic mechanisms to categorize trace samples. Addressing operational challenges such as manual sorting and leveraging automation or AI-based systems can further streamline trace DNA analysis. The findings also underscore the importance of data sharing and standardization across forensic laboratories to enhance trace DNA recovery protocols and improve reliability in forensic investigations. Future research should focus on the effects of material properties, environmental exposure, and collection techniques on DNA retention, advancing the field of trace DNA profiling and its applications in forensic science.
Open Access
Article
06 January 2025A Bounded-Function-Based Scheme for Finite-Time Stabilization of a NWMR with Input Constraints
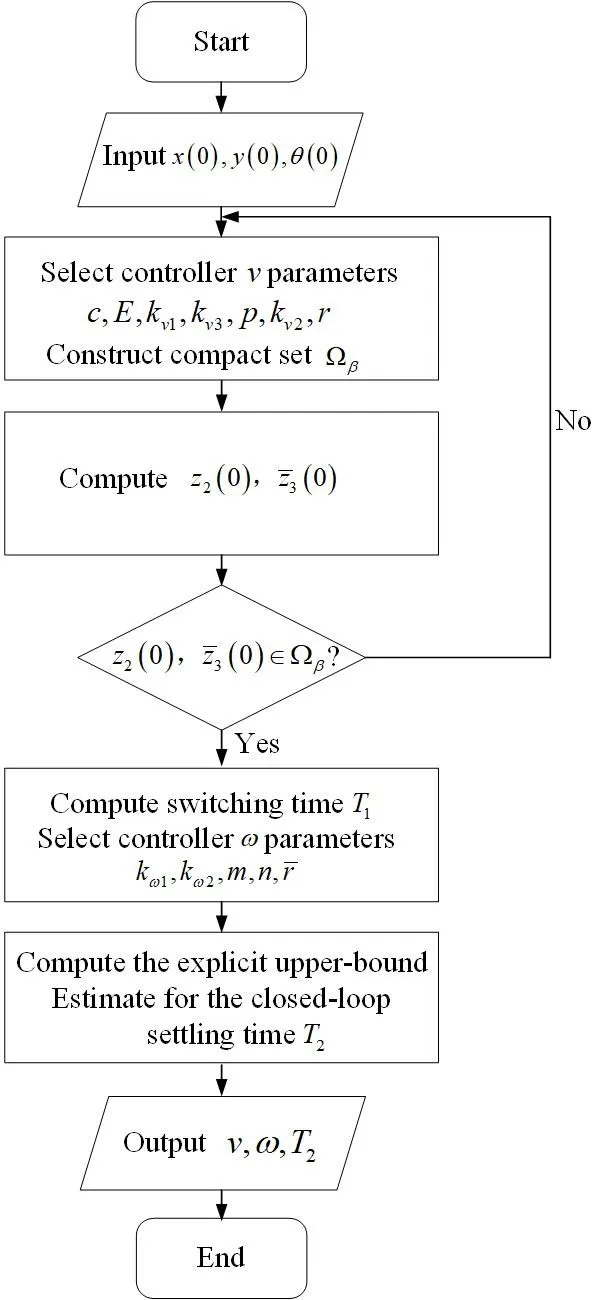
This paper addresses the finite-time stabilization problem for a nonholonomic wheeled mobile robot (NWMR) with input constraints. By utilizing the hyperbolic tangent function tanh(·), bounded finite-time stabilization controllers are developed. In addition, an explicit upper-bound estimate for the closed-loop settling time is given, and the level of input constraints is characterized by parameters that depend on the actuator’s capacity. A thorough finite-time stability analysis is carried out using appropriate Lyapunov functions. For a compact set contained in the domain of attraction, a guideline is presented to clarify how to construct it. Finally, simulation results show the effectiveness of the developed controllers.
Open Access
Commentary
03 January 2025Geographies of Peripheral Rural Areas—Some Comments
The dominance of positivist approaches has led to the development of center-periphery models, which establish a relatively naturalized relationship between urban core areas and residual rural areas. Recent approaches to planetary rural geographies provide an opportunity to re-situate this issue and address it within the context of the revitalization of many rural areas, not only in the global North but also in the global South. However, multiple competing realities continue to shape the dynamics of these spaces. In large areas of the global South, material challenges persist despite some promising trends, while in the global North, dynamics are largely influenced by post-industrial societies. Africa serves as a relevant example to illustrate the limitations and shortcomings of recent planetary approaches to rural geography development. As an alternative, smaller-scale approaches focusing on community participation and the living conditions of people are proposed.

Open Access
Review
30 December 2024
Fire-Retardant
Wastepaper Reinforced Waste Polyethylene Composite: A Review
The increase in fire
outbreaks recently and the need for eco-friendly and fire-resistant materials
have inspired a wave of studies, focusing on producing innovative composite
materials with effective fire-resistant properties. This review delves into the
world of fire-resistant wastepaper-reinforced waste polyethylene composites.
Using wastepaper as a strengthening factor in polyethylene matrices, combined
with fire-retardant additives like nanoparticles, introduces a hopeful path for
waste management and improved material properties. This work carefully
considers the combining approaches, physical and mechanical properties,
fire-resistant mechanisms, and environmental impacts of these composites. The
review underscores the possible and potential applications, difficulties, and
prospects of such environmentally friendly materials in various industries.
Understanding these composites’ blending, attributes, and conceivable
utilization is essential for advancing maintainable and fire-safe material innovation
in pursuing a greener future.
Open Access
Article
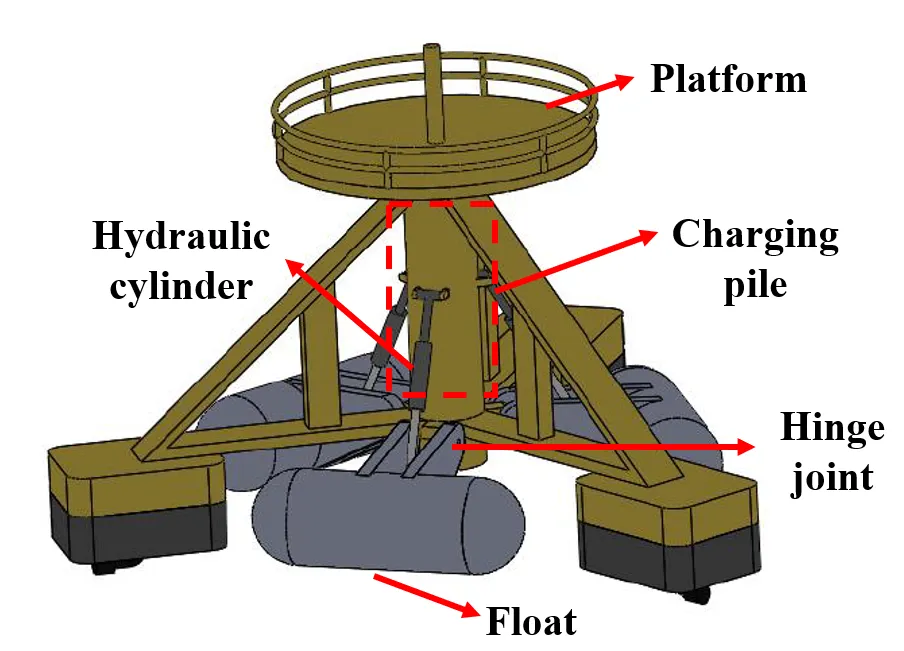
24 December 2024Hydrodynamic Performance of a Hybrid Floating Power Dock Combining Multi-Cantilever Type Buoys
This paper proposes a novel three-dimensional oscillating pendulum wave energy converter (WEC) that integrates an oscillating float dock station. The device captures wave energy by utilizing both the pitch and roll motions of its primary float and the pendular motion of a buoy. A time-domain analysis method is used to numerically evaluate the hydrodynamic behavior and energy conversion efficiency of the WEC. In ANSYS AQWA, a multi-cantilever WEC model is employed to address the fluid-solid coupling, calculating the device’s motion response and capturing the width ratio under various environmental conditions. Additionally, by modifying key geometric parameters including float radius, length, and cantilever angle, the study examines the rotation at the articulation point and the capture width ratio variation for different device configurations. Results indicate that the device achieves a maximum capture width ratio at a float radius of approximately 120 mm under T = 1.4 s, and a 130 mm for wave periods of 1.5 s and 1.6 s. The highest average capture width ratio is reached at a power take-off (PTO) damping coefficient of 400 N·s/m. The study further investigates the effect of cantilever angle and float length, aiding in the optimization of these geometric parameters.