Found 301 results
Open Access
Article
17 December 2024Upcycling of Waste Poly(ethylene terephthalate) into 2,4-Pyridine Dicarboxylic Acid by a Tandem Chemo-Microbial Process
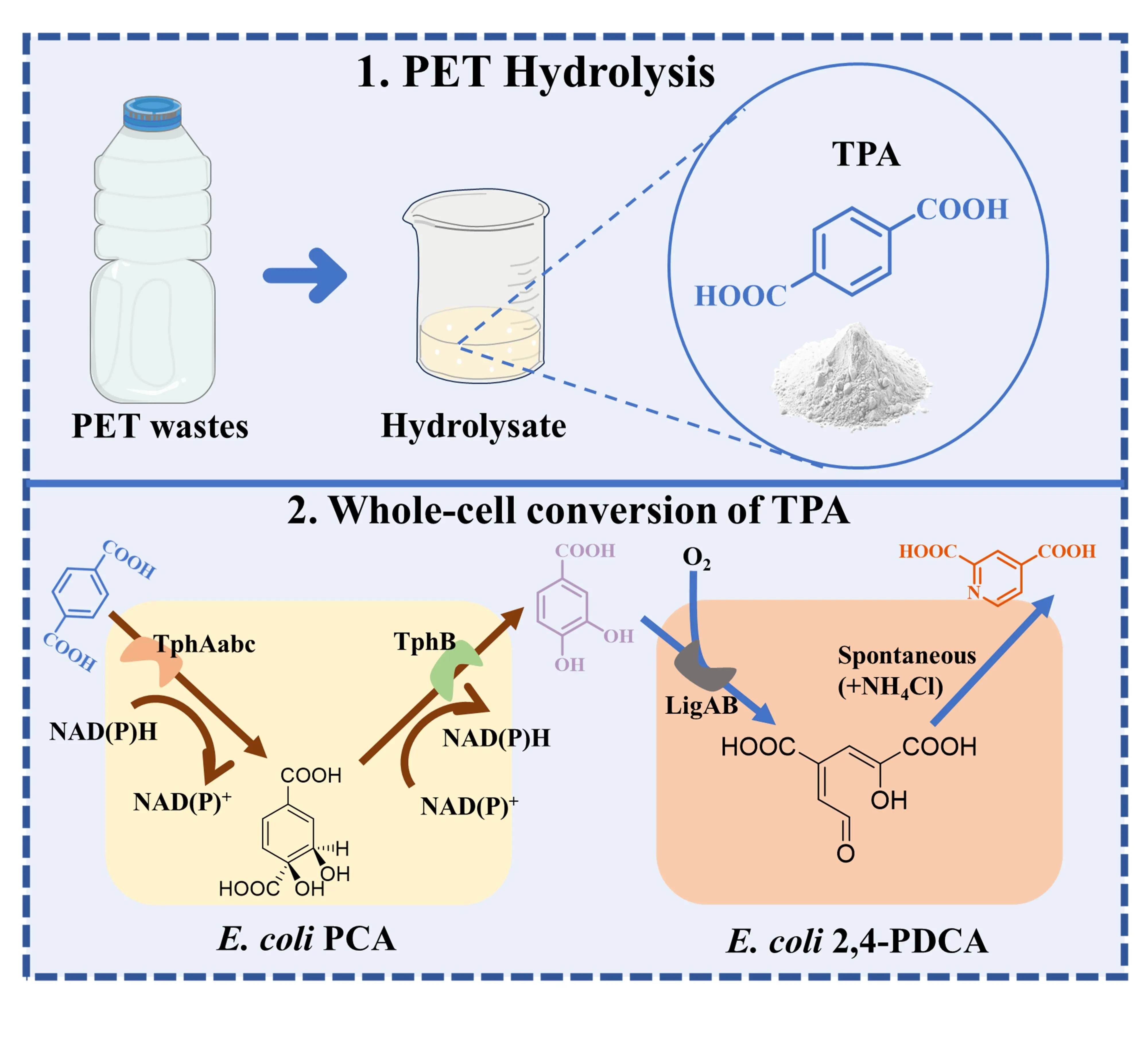
This study presents a chemo-microbial cascade process for the upcycling of waste poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) into valuable compound 2,4-pyridine dicarboxylic acid (2,4-PDCA). Initially, waste PET undergoes efficient hydrolysis to terephthalic acid (TPA) with a high yield of 92.36%, catalyzed by p-toluenesulfonic acid (PTSA). The acid catalyst exhibits excellent reusability, maintaining activity over five cycles. Subsequently, a one-pot, two-step whole-cell conversion system utilizing genetically modified Escherichia coli strains (E. coli PCA and E. coli 2,4-PDCA) converts the generated TPA into 2,4-PDCA. By integrating the PET hydrolysis module with the 2,4-PDCA biosynthesis module, the study achieves an impressive overall efficiency of 94.01% in converting challenging PET waste into valuable 2,4-PDCA. Our research presents a rational design strategy for PET upcycling and 2,4-PDCA synthesis methods. This research provides a systematic approach to PET upcycling, demonstrating its feasibility and potential for industrial application.
Open Access
Article
16 December 2024Price and Output Response of Major Food Grains of Nadia District of West Bengal
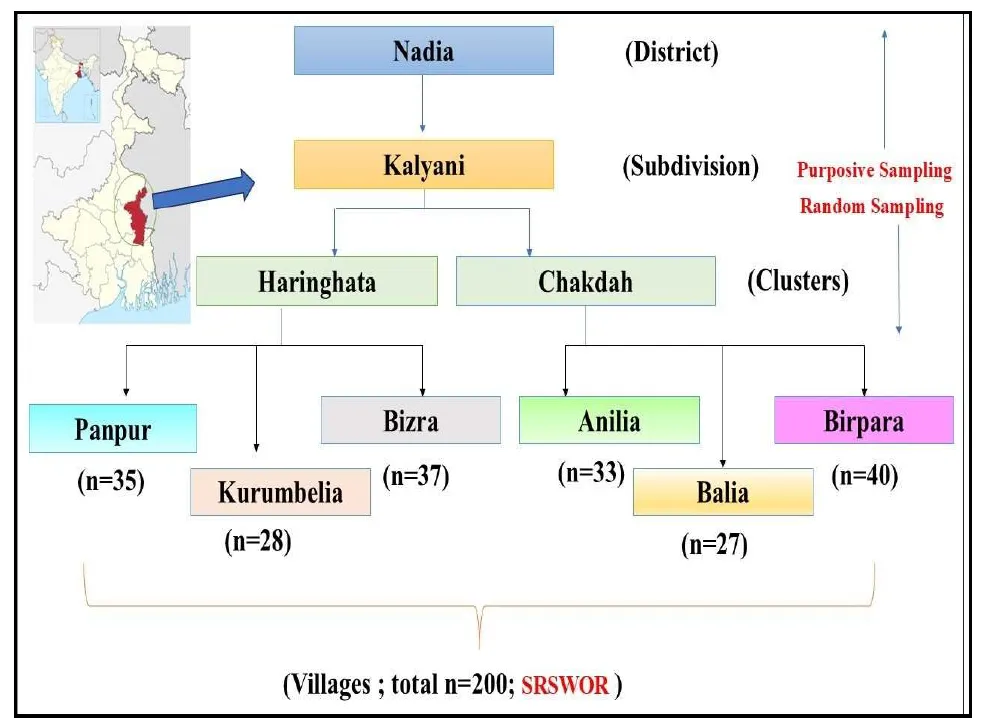
The price and output response of food crops is a critical area in agricultural economics as this interaction refers to how the quantity of food grains supplied responds to changes in market prices. This research investigates the surplus ratios and price elasticities for rice, lentil, and gram in the Nadia district of West Bengal. Two hundred farmers were interviewed in different villages of the district and information was collected regarding socio-economics, marketed surplus and, selling price, etc. Further, elasticity and a modified version of the Raj Krishna model have been employed. The findings reveal that for rice, the ratios of gross, net marketed, and marketable surplus are 69.59%, 55.46%, and 16.27%, respectively. The gross marketed surplus ratio decreases with a reduction in farm size, while net marketed and marketable surpluses increase as farm size expands. For lentils, the gross and net marketed surplus ratios are recorded at 66.64% and 65.57%, with an average marketable surplus of 35.30%. Marginal gram farmers have a gross marketed surplus ratio of 80.33%, slightly lower than the overall average of 81.12%, whereas larger farms exceed this average, with ratios of 82.19% and 83.18%. Output elasticities for rice are positive and exceed unity for both marginal and large farms, at 1.03 and 1.45, respectively, though slightly below unity at 0.85 for small farms. The average elasticity for rice across all farm sizes is 1.12. Lentil output elasticities are also positive and greater than unity for marginal and large farms (1.00 and 1.07, respectively) but fall below unity at 0.78 for medium farms, with an overall average of 0.91. The output elasticities for gram remain consistently positive and above unity across all farm sizes, averaging 1.09.
Open Access
Article
16 December 2024Exploring the Values of Sustainability and the Cost of Going Green: A Case of Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method (BREEAM)
Despite the expansion of BREEAM and the benefits of adopting sustainable building practices, there are concerns that the cost of going green may outweigh the benefits. Whilst previous studies have not provided adequate clarity in this regard, there is consensus among scholars that BREEAM provides indirect benefits that can be considered as added value. This paper aims to investigate the potential cost implication and benefits of sustainable building practices from the lens of the Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method (BREEAM) in the UK. Adopting survey research strategy, questionnaires, and interviews with 34 construction industry professionals in Southeast England were conducted to investigate their perceptions of BREEAM, the extra value it contributes to projects, and the possible limitations hindering its wider adoption. Findings show that while there is an upfront investment associated with achieving BREEAM certification, the benefits of such certification include added values such as improved environmental performance, increased market appeal, improved indoor air quality, reduced carbon emissions, and lower operational costs. This study validates the need to encourage wider adoption of sustainable building practices and promote the use of the BREEAM methodology in the UK. This research provides a foundation for future research and development in this area, with the goal of reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainable development.

Open Access
Article
12 December 2024Adsorption of Bisphenol A and 2,6-Dichlorophenol in Water Using Magnetic Phosphogypsum Composite Materials
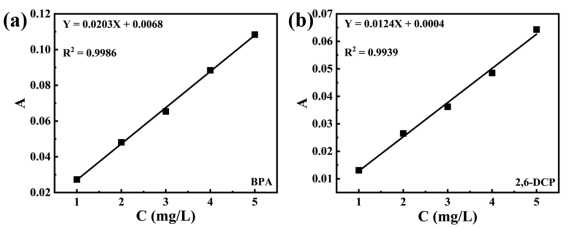
Phenolic pollutants in water bodies pose a huge threat to human health and environmental safety. In this paper, a hydrophobicity-enhanced magnetic C-SiO2/MPG composite was prepared by a two-step method to remove bisphenol A (BPA)and 2,6-dichlorophenol (2,6-DCP), typical phenolic trace pollutants in livestock wastewater and natural water bodies. The results of pH gradient experiments showed that C-SiO2/MPG showed a stable removal effect on BPA in the pH range of 2–11. The adsorption of 2,6-DCP by C-SiO2/MPG peaked at pH = 2, while the adsorption of 2,6-DCP by C-SiO2/MPG was severely inhibited under alkaline conditions. The PSO kinetic model and the Langmuir isotherm model can better describe the adsorption process of BPA and 2,6-DCP on C-SiO2/MPG, indicating that the monolayer chemical adsorption has a rate-controlling step. With the Langmuir equation fitting, the maximum adsorption capacity of C-SiO2/MPG for BPA and 2,6-DCP at 298 K was calculated to be 561.79 mg/g and 531.91 mg/g, respectively. The results of adsorption thermodynamics indicated that the adsorption of BPA and 2,6-DCP on C-SiO2/MPG was spontaneous, accompanied by a process of entropy decrease. C-SiO2/MPG showed good environmental resistance and repeated use stability for BPA and 2,6-DCP in electrolyte ion interference, actual water samples and cycle experiments. Mechanism analysis showed that the adsorption of BPA and 2,6-DCP on C-SiO2/MPG was mainly controlled by hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions. This study designed an efficient adsorbent for phenolic pollutants that can be used in actual wastewater and broadened the resource utilization of industrial waste phosphogypsm.
Open Access
Article
10 December 2024Sailing the X.0 Wave Theory: Navigating the Future of Civilization
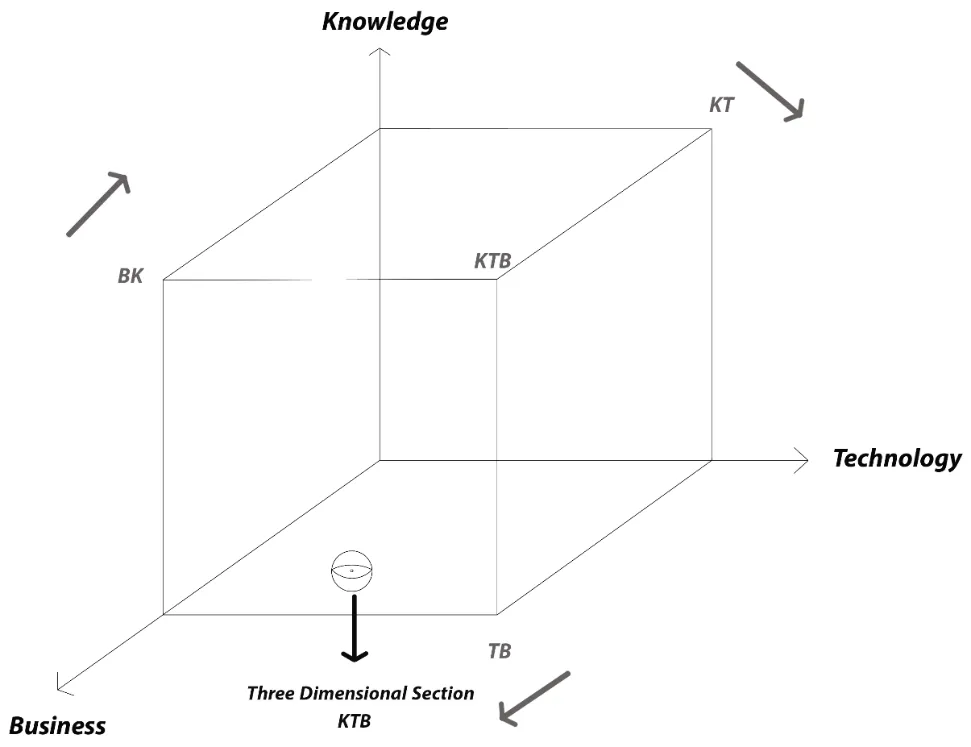
This paper delves into the X.0 Wave/Tomorrow Age Theory, a comprehensive framework conceived, invented, introduced, and developed by Prof. Dr. Hamid Mattiello between 2010 and 2017, to analyze the evolution of human civilization through distinct epochs of knowledge, technology, and business (KTB). The theory segments history into transformative waves, from the first development (X.0 ≤ 1.0) and Agricultural Age (X.0 = 1.0) and the X.0 Wave/Tomorrow Age Theory (2.1 ≤ X.0 ≤ 2.2) spanning the 17th Century to 1870, to the current Age of Artificial Intelligence (X.0 = 4.0). It also projects into the anticipated Human Age (X.0 = 5.0) and Transhuman Age (X.0 = 6.0) and beyond (6.0 ≤ X.0). Each wave represents a revolutionary phase characterized by significant advancements that shape societies, industries, and technologies. The X.0 Wave Theory integrates these historical phases with the Seven Pillars of Sustainability (7PS) to evaluate their societal impacts. The paper explores how these waves influence future developments by examining historical roots, emerging technological paradigms, and socio-economic dynamics. It examines how advancements in AI, biotechnology, and virtual reality are reshaping industries and global business practices, while also addressing the ethical and sustainability considerations essential for navigating these changes. By forecasting future trends, confronting current challenges, and preparing for potential crises, the X.0 Wave Theory offers a robust framework for understanding and adapting to the rapid pace of technological evolution. This paper provides deep insights into how these transformative waves shape our past, present, and future, offering valuable perspectives for navigating the complexities of an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
Open Access
Article
06 December 2024Population Dynamics and Stock Assessment of the Spottail Mantis Shrimp Squilla mantis (Linnaeus, 1758) in the North Aegean Sea, Greece
In Greek waters, the spottail mantis shrimp Squilla mantis (Linnaeus, 1758) presents significant ecological and low to moderate economic value. This study investigates the population dynamics and stock assessment of the species in the north Aegean Sea. A total of 856 individuals were collected using commercial bottom trawls between April 2021 and April 2023. Key population parameters such as size distribution, sex ratio, growth, size at maturity and spawning seasonality were assessed. Results indicate a relatively stable population with a slight male dominance and peak spawning activity occurring in late spring to early summer. Growth parameters were estimated using the von Bertalanffy growth model, revealing moderate growth rates and a maximum length slightly higher than previously recorded for this species in other Mediterranean regions. Stock assessment, conducted through yield-per-recruit analysis, suggests that the current exploitation levels are approaching sustainable limits. However, potential overfishing risks necessitate continuous monitoring and the implementation of adaptive management strategies. This study underscores the importance of integrative approaches combining biological and fisheries data to ensure the sustainable management of S. mantis populations in the Aegean Sea.
Open Access
Meeting Report
04 December 2024Progress and Gaps in Respiratory Disease Research and Treatment: Highlights of the IRM 2024 in Shanghai
Respiratory diseases pose a major public health challenge globally, necessitating collaborative efforts between basic researchers and clinicians for effective solutions. China, which is heavily impacted by a broad spectrum of respiratory disorders, has made notable strides in both research and clinical management of these diseases. The International Respiratory Medicine (IRM) meeting was organized with the primary goal of facilitating the exchange of recent research developments and promoting collaboration between Chinese and American scientists in both basic and clinical research fields. This article summarizes key insights from IRM2024, held in Shanghai, where a wide range of topics were discussed, including lung tissue development, disease mechanisms, and innovative therapeutic strategies. By integrating perspectives from basic, translational, and clinical research, IRM2024 highlighted recent advancements, addressed persistent challenges, and explored future directions in respiratory science and clinical practice. The insights gained from IRM2024 are poised to be pivotal in shaping future research and therapeutic approaches, further reinforcing the global commitment to enhancing respiratory health and improving patient outcomes.
Open Access
Review
02 December 2024The Interplay of Heart Failure and Lung Disease: Clinical Correlations, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Implications
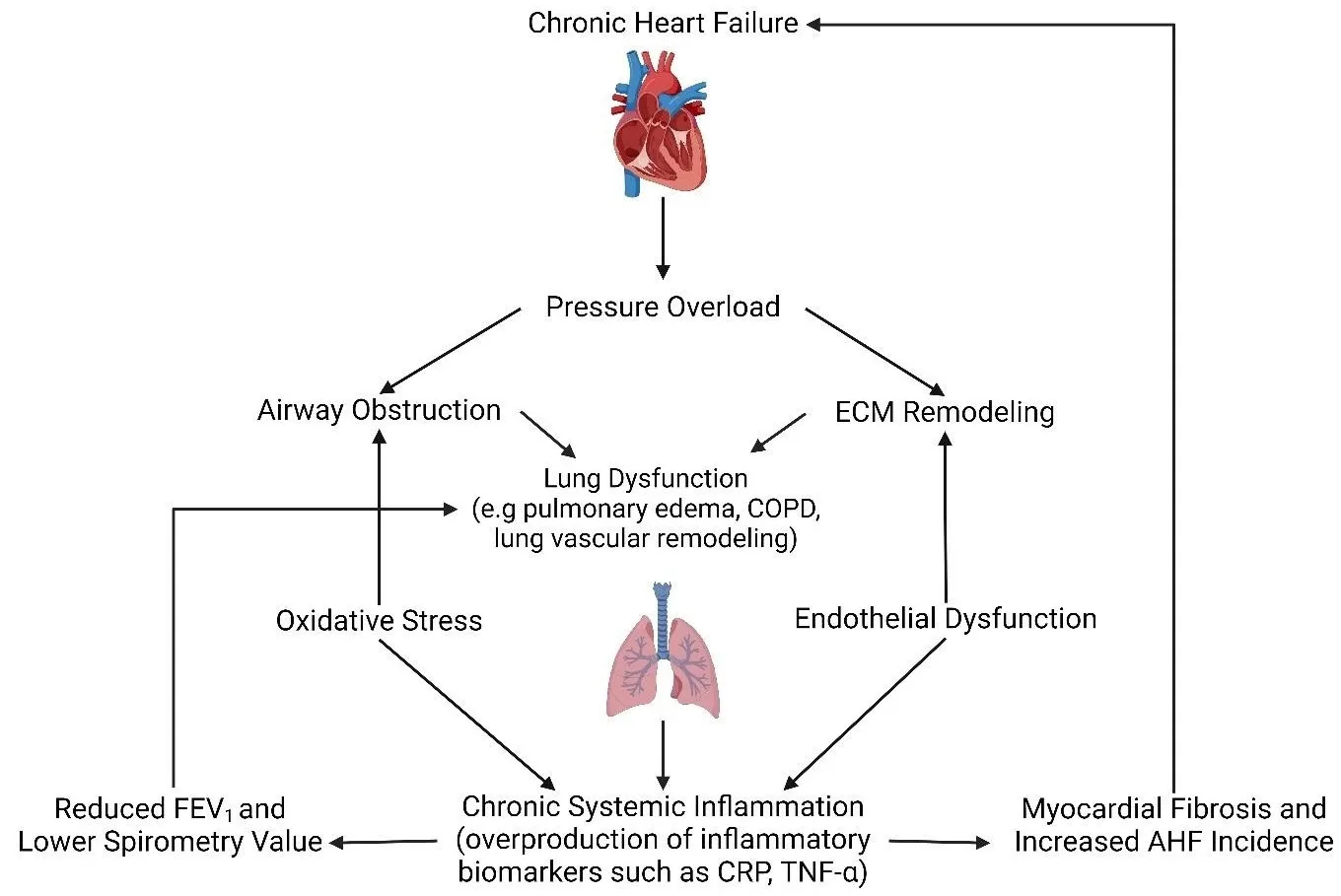
Heart failure (HF) is a common clinical syndrome marked by reduced cardiac output, elevated intracardiac pressures, and heart dysfunction. Chronic HF (CHF) is a syndrome characterized by a lack of blood flow and impaired pumping ability to the heart over time, while acute HF (AHF) arises suddenly due to incidents like myocardial infarction or cardiac arrest. HF has a significant impact on pulmonary health and function, leading to conditions such as pulmonary edema and restrictive lung patterns. Clinical evidence highlights the bidirectional relationship between HF and lung dysfunction. Declining lung function serves as a predictor for HF progression and severity, while HF contributes to worsening lung health. Animal models that induce HF through surgical methods further demonstrate the connection between heart and lung pathology. The main mechanisms linking HF and lung dysfunction are pressure overload and chronic systemic inflammation, with changes in the extracellular matrix (ECM) also playing a role. Additionally, environmental factors like air pollution exacerbate lung inflammation, increasing the risk of both HF and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) incidence. Combined treatment approaches involving pharmaceutical drugs such as statins, Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, and Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) may benefit by reducing inflammation. This review will explore the complex interplay between HF and lung function, emphasizing their interconnected pathophysiology and potential integrated treatment strategies.
Open Access
Article
27 November 2024Photocatalytic CO2 Fixation into Formate under Visible Light by the Photo-Enzyme Hybrid of Gold Nanocapsules and Formate Dehydrogenase
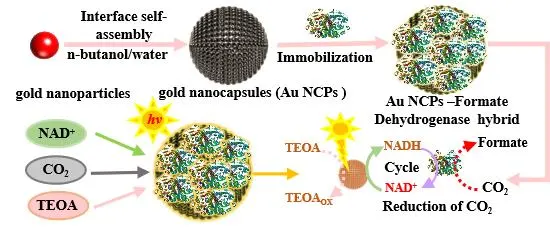
The photo-enzyme hybrid system presents a promising approach for the selective conversion of CO2 into valuable chemicals. However, its high dependence on the expensive coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced form (NADH), coupled with the need for external electron mediators and highly active photocatalysts, limits its widespread application. Here, we developed a gold nanocapsule—formate dehydrogenase (FDH) hybrid system for in situ NADH regeneration to facilitate the light-driven conversion of CO2 to formate. The results demonstrated that gold nanocapsules (Au NCPs), in conjunction with triethanolamine (TEOA), protected 83.67% of NADH from photodegradation. Under light-driven conditions with TEOA as the electron donor and without external electron mediators, the Au NCPs catalyzed in situ NADH regeneration, achieving a regeneration yield of 22.65%. This process aided FDH in reducing CO2 to formate, resulting in a production rate of 67.40 µmol/L/h. This research provides valuable insights for developing photo-enzyme hybrid systems that efficiently convert CO2 without the need for external electron mediators.
Open Access
Article
26 November 2024Identification of Cutting Workpiece Surface Defects Based on an Improved Single Shot Multibox Detector
In the mechanical cutting process, the surface defects of the workpiece are an important indicator of cutting quality and also reflect the condition of both the machine tool and the cutting tool. Effective detection of defects on the surface of the workpiece plays an important role in adjusting the processing conditions promptly, reducing losses, improving the utilization rate of the workpiece, and maintaining the normal operation of the equipment. To address the challenge of detecting surface defects on workpieces, an inspection method based on an improved Single Shot Multibox Detector (SSD) model is proposed. The method simplifies the detection model and reduces the computation by proposing a DH-MobileNet network instead of a VGG16 network in the SSD structure. The inverse residual structure is also used for position prediction, and null convolution is used instead of a down-sampling operation to avoid information loss. A scanning electron microscope was used to obtain the surface image of the workpiece. A dataset of workpiece surface defects was constructed and expanded, then used to train and test the model for detecting three common types of high-frequency defects: peel-off, chip adhesion, and scratches. The effect was compared with YOLO, Faster R-CNN, and the original SSD model. The detection results show that the method can detect the defects on the surface of the workpiece more accurately and quickly, which provides a new idea for defect detection in real industrial scenarios.
