Found 301 results
Open Access
Review
14 January 2025A Review of Phosphorous in Fluvial Floodplains: Source or Sink?
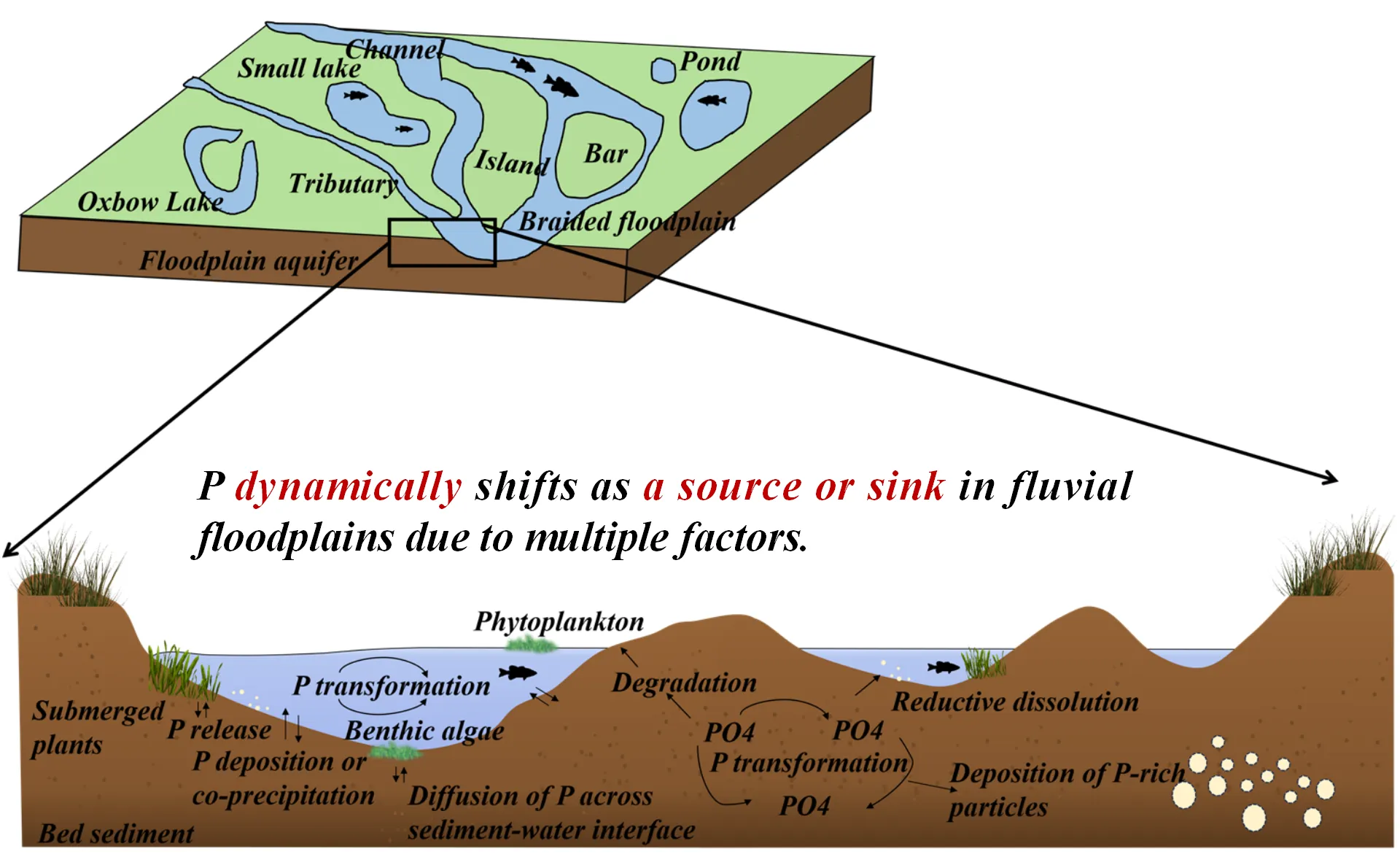
Fluvial floodplains are water-land transitional zones, playing an important role in hydrological and ecological systems. To date, the phosphorus migration and transformation in floodplain sediments remain elusive, which poses a large effect on river nutrient levels and primary productivity. This review summarized the sedimentary characteristics of floodplains and analyzed the spatial differences and temporal variations in phosphorus distribution. We further analyzed their potential change in floodplains under various conditions, determining the sedimentation and mineralization process of phosphorus. Meanwhile, phosphorus in the sediment will experience dynamic fluctuation as a source or sink of fluvial floodplains based on varying factors, including hydrological conditions, climate variations, biological activity, and pedological characteristics. In particular, the productivity and community population in floodplains, like vegetation and fishes, will be primarily associated with the periodic changes in phosphorus through food chain. Lastly, this review provided corresponding perspectives on improving the phosphorus administration in river floodplains based on existing problems. In total, it is anticipated that it will enhance the understanding of phosphorus resources or sink in the fluvial floodplains, contributing to the stability of aquatic ecosystems.
Open Access
Review
09 January 2025Recent Advancements in Alumina-Based High-Temperature Insulating Materials: Properties, Applications, and Future Perspectives
As a high-temperature thermal insulation material with excellent mechanical properties, alumina (Al2O3)-based materials hold significant potential for applications in aerospace, advanced manufacturing, automobiles, industrial furnaces, and other fields. However, the inherent brittleness of alumina poses a limitation to its wider application. Therefore, there is a pressing need to develop alumina-based materials that offer high toughness while retaining superior mechanical properties. This paper begins by exploring the structure of alumina, highlighting its thermal conductivity, insulation, and mechanical properties in high-temperature environments. It then reviews the classification and synthesis methods of alumina-based materials, along with the latest advances in design strategies. Notably, the rational design of alumina composition, structure, and morphology is emphasized as crucial for optimizing material performance, thereby supporting the industrial development and application of these materials in high-tech sectors. Finally, the paper discusses the challenges and evolution of alumina-based materials in real-world industrial applications and suggests potential directions for future development.
Open Access
Article
09 January 2025Sustainability Practices and Financial Performance: Evidence from BIST Electricity Index
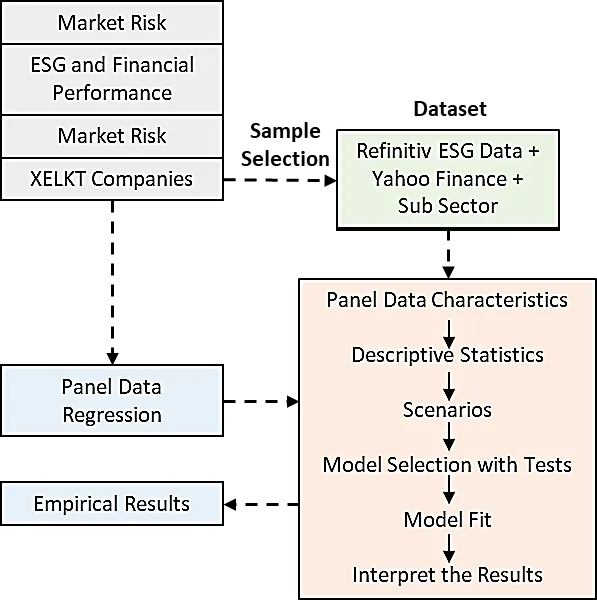
Amidst the backdrop of heightened market risks associated with transitioning to a lower-carbon economy, this study pioneers an examination of the correlation between sustainability and financial performance within Turkish energy market generator and retailer companies. In this study, the sustainability performance, exposure to market risks and effects on the financial performance of sub-sectors of companies listed in the BIST Electricity index were analyzed using panel data regression. The findings reveal a nuanced relationship between sustainability factors and financial performance, underscoring the imperative for electricity sector companies to prioritize sustainability initiatives not only for ethical reasons but also as a strategic imperative for long-term financial success and stakeholder value creation. Finally, the possibility of impending regulatory changes underscores the importance of early adoption of sustainability practices to mitigate potential financial liabilities and navigate future market risks effectively.
Open Access
Communication
08 January 2025Development of Eco-Friendly Composites Using Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and Diss Fibers (Ampelodesmos Mauritanicus)
In response to the growing environmental threats and pollution linked to synthetic plastics, current scientific inquiry is prioritizing the advancement of biodegradable materials. In this context, this study investigates the possibility of developing fully biodegradable materials using plant fibers extracted from the Diss plant (Ampelodesmos mauritanicus) as reinforcement in poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV)-based biocomposites. The biocomposites were prepared by melt blending in the following weight ratio: PHBV/Diss fibers 80/20. The chemical structure of Diss fibers was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF). The impact of Diss fibers on the mechanical properties of biocomposites has also been investigated in comparison to neat PHBV. FTIR and XRF analyses identified cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin as the main components of Diss fibers. On the other hand, the results showed a significant enhancement of Young’s modulus (⁓21%) of PHBV/DF biocomposites in comparison to neat PHBV due to a better dispersion of the fibers in the matrix, as confirmed by atomic force microscopy (AFM) images.
Open Access
Article
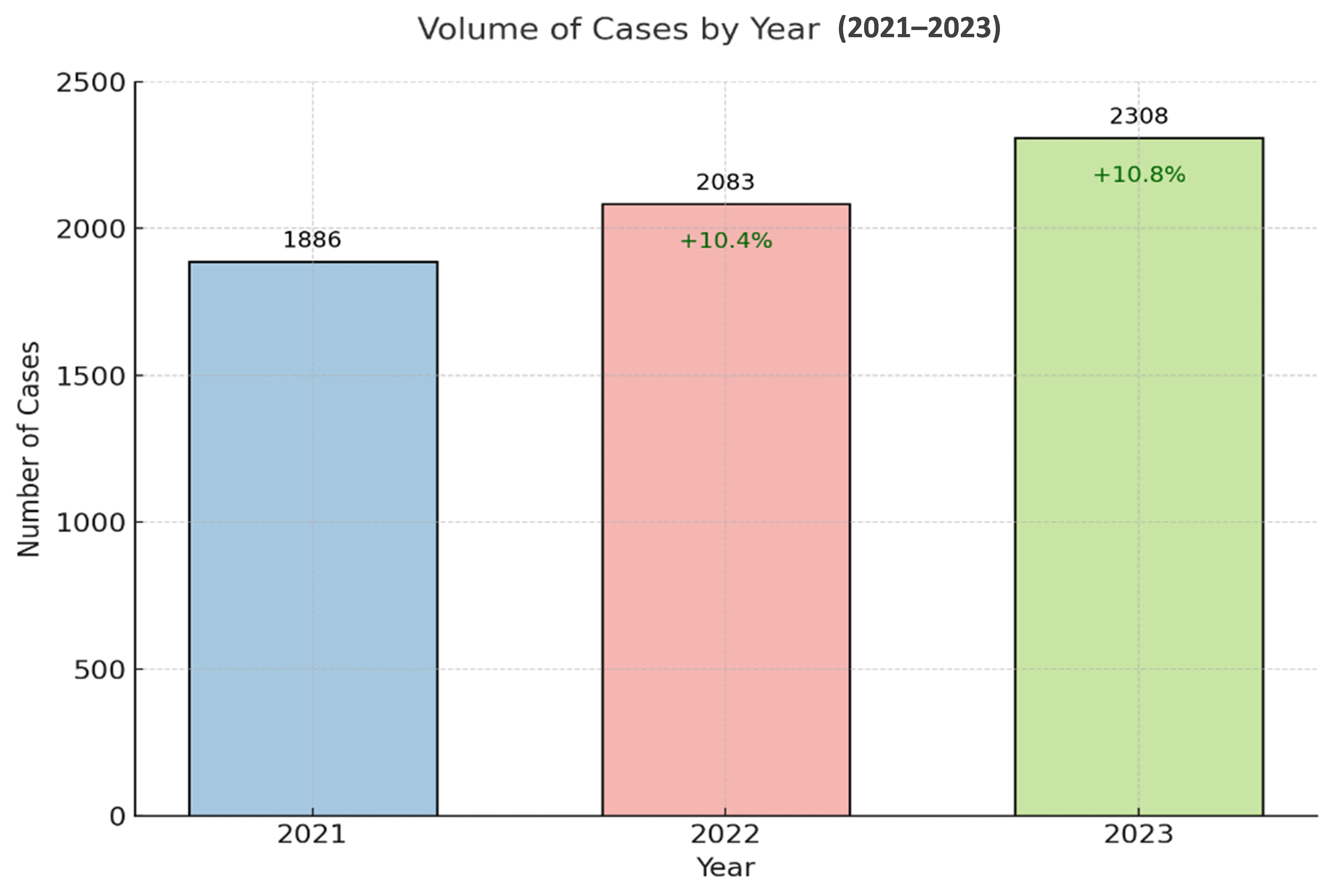
07 January 2025Trace DNA Recovery: Insights from Dubai Police Casework
Trace DNA represents a critical form of forensic evidence, frequently recovered from a wide variety of touched or used items. Despite its evidentiary value, trace DNA analysis poses significant challenges due to the minute quantities of DNA involved, as well as the influence of factors such as surface type, collection methods, and environmental exposure. This study systematically examines the success rates and characteristics of trace DNA profiles recovered from six-item categories—tools, stolen items, wearable items, packaging materials, vehicles, and touched items—processed between 2021 and 2023 by the Biology and DNA Section of the Dubai Police Force. A total of 6277 cases were analyzed, encompassing a range of crimes, including homicide, suicide, missing persons, paternity disputes, and burglary. The results demonstrated an overall trace DNA success rate of 64%, with wearable items yielding the highest success rate at 76% and packaging materials yielding the lowest at 54%. Detailed analysis of positive DNA trace samples revealed significant variability in DNA profile types across item categories. Wearable items and touched items predominantly yielded full single (FS) DNA profiles, reflecting their reliability as sources of singular and high-quality DNA. Conversely, stolen items and packaging materials showed a greater prevalence of full mixed (FM) DNA profiles, highlighting their association with complex mixtures due to handling by multiple contributors. Tools and vehicles, meanwhile, exhibited higher rates of partial profiles, presenting unique challenges related to surface irregularities and environmental factors. This study emphasizes the importance of tailoring forensic strategies to item-specific characteristics, as well as the need for systematic mechanisms to categorize trace samples. Addressing operational challenges such as manual sorting and leveraging automation or AI-based systems can further streamline trace DNA analysis. The findings also underscore the importance of data sharing and standardization across forensic laboratories to enhance trace DNA recovery protocols and improve reliability in forensic investigations. Future research should focus on the effects of material properties, environmental exposure, and collection techniques on DNA retention, advancing the field of trace DNA profiling and its applications in forensic science.
Open Access
Article
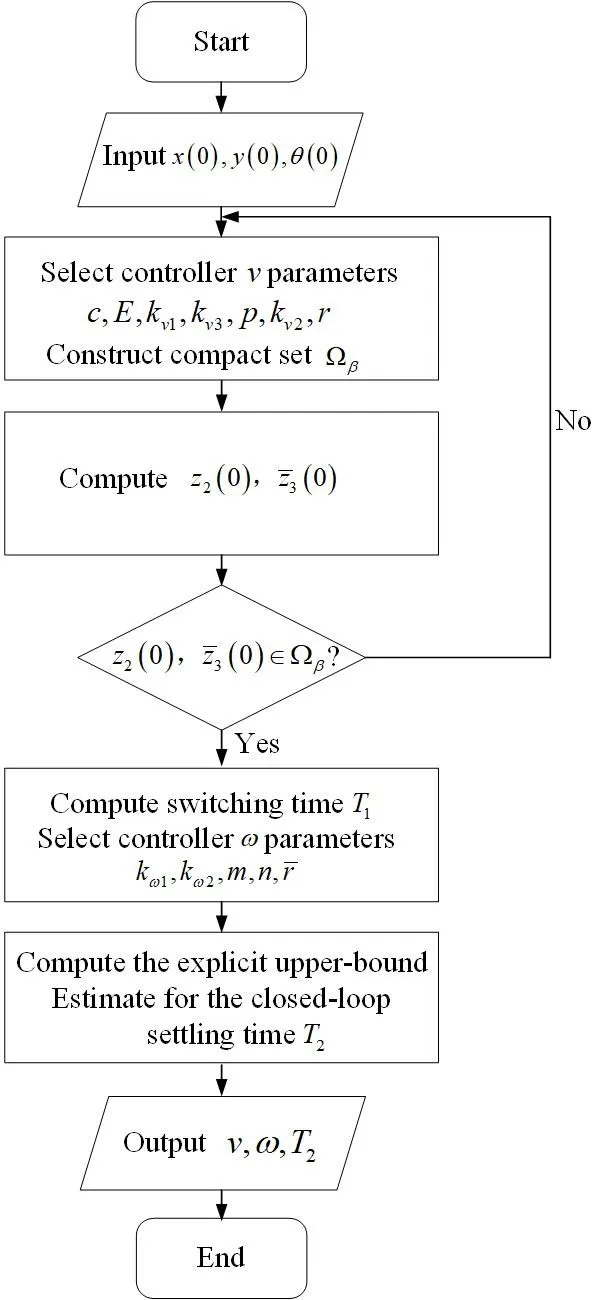
06 January 2025A Bounded-Function-Based Scheme for Finite-Time Stabilization of a NWMR with Input Constraints
This paper addresses the finite-time stabilization problem for a nonholonomic wheeled mobile robot (NWMR) with input constraints. By utilizing the hyperbolic tangent function tanh(·), bounded finite-time stabilization controllers are developed. In addition, an explicit upper-bound estimate for the closed-loop settling time is given, and the level of input constraints is characterized by parameters that depend on the actuator’s capacity. A thorough finite-time stability analysis is carried out using appropriate Lyapunov functions. For a compact set contained in the domain of attraction, a guideline is presented to clarify how to construct it. Finally, simulation results show the effectiveness of the developed controllers.
Open Access
Review
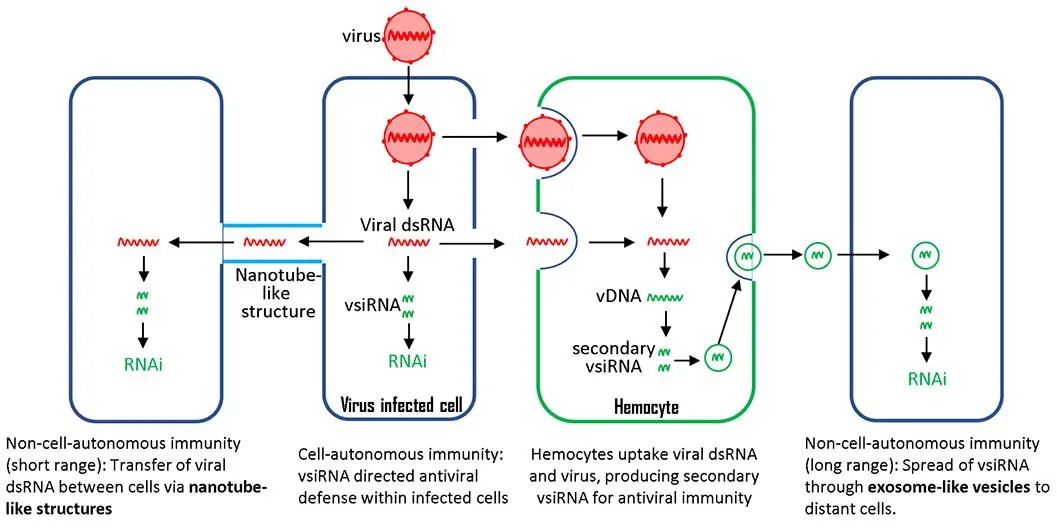
02 January 2025Cell-Autonomous and Non-Cell-Autonomous Antiviral Immunity via siRNA-Directed RNAi in Drosophila melanogaster
In Drosophila melanogaster, the siRNA-directed RNAi pathway provides crucial antiviral defenses. Cell-autonomously, Dicer-2 (Dcr-2) recognizes and cleaves viral dsRNA into siRNAs, which are incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). Argonaute 2 (Ago2) then targets and cleaves viral RNA, preventing replication. Non-cell-autonomously, infected hemocytes secrete exosomes containing viral siRNAs, spreading antiviral signals to other cells. Additionally, tunneling nanotubes can transfer RNAi components between neighboring cells, further enhancing systemic immunity. These findings highlight the sophisticated antiviral strategies in Drosophila, offering insights for broader antiviral research.
Open Access
Article
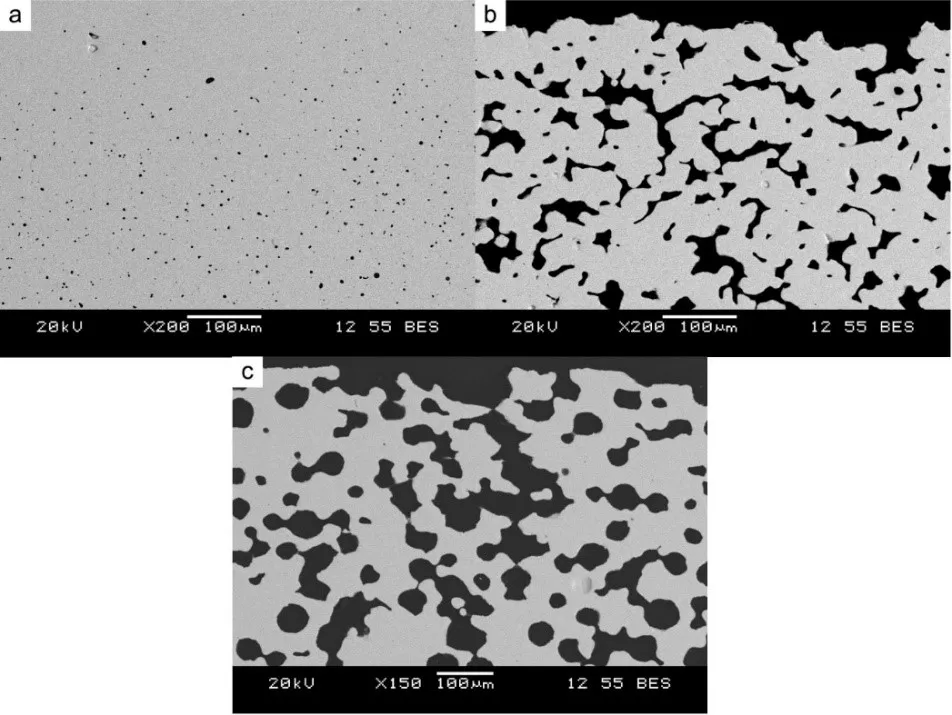
31 December 2024Porous 430L Stainless Steel as a Support Layer for Planar
Solid Oxide Cells: Effect of Porosity on Mechanical Properties
Porous 430L stainless steel
components fabricated via tape casting underwent mechanical testing for
potential in-vehicle application as mechanical supports of solid oxide cells.
Tests included three-point bending up to 5% strain to assess flexural strength,
yield strength, Young’s modulus, indentation hardness, and microstructural
characterization. This study aimed to establish the relationship between pore
former size and volume fraction and the resulting yield strength. It also
compared sintered material without pore former, focusing on the influence of a
wide range of porosity of up to 46.5%. The materials exhibited an inverse
relationship for Young’s modulus, hardness and yield strength as a function of
porosity. The lowest flexural yield strength obtained was approximately 120 MPa
at the highest porosity of 46.5%, meeting the requirement of 59 MPa for the
bipolar plates of existing proton-exchange membrane fuel cells.
Open Access
Perspective
31 December 2024
Offshore Renewable Energy Advance
Offshore renewable energy generation has become an important means to address the energy crisis and climate change, which has gained widespread attention in recent years. This article presents classic domestic and international cases that introduce the development and industrial transformation of generation technologies for offshore wind, offshore photovoltaics, ocean wave energy, tidal energy and temperature difference energy. Offshore power generation projects face challenges in design, safety, long-term operation and economic feasibility. Offshore renewable energy generation is gradually moving towards industrialization, and is expected to become a key component of global energy supply in the future with technological advancements and policy support, providing strong support for tackling climate change and achieving sustainable development goals.

Open Access
Article
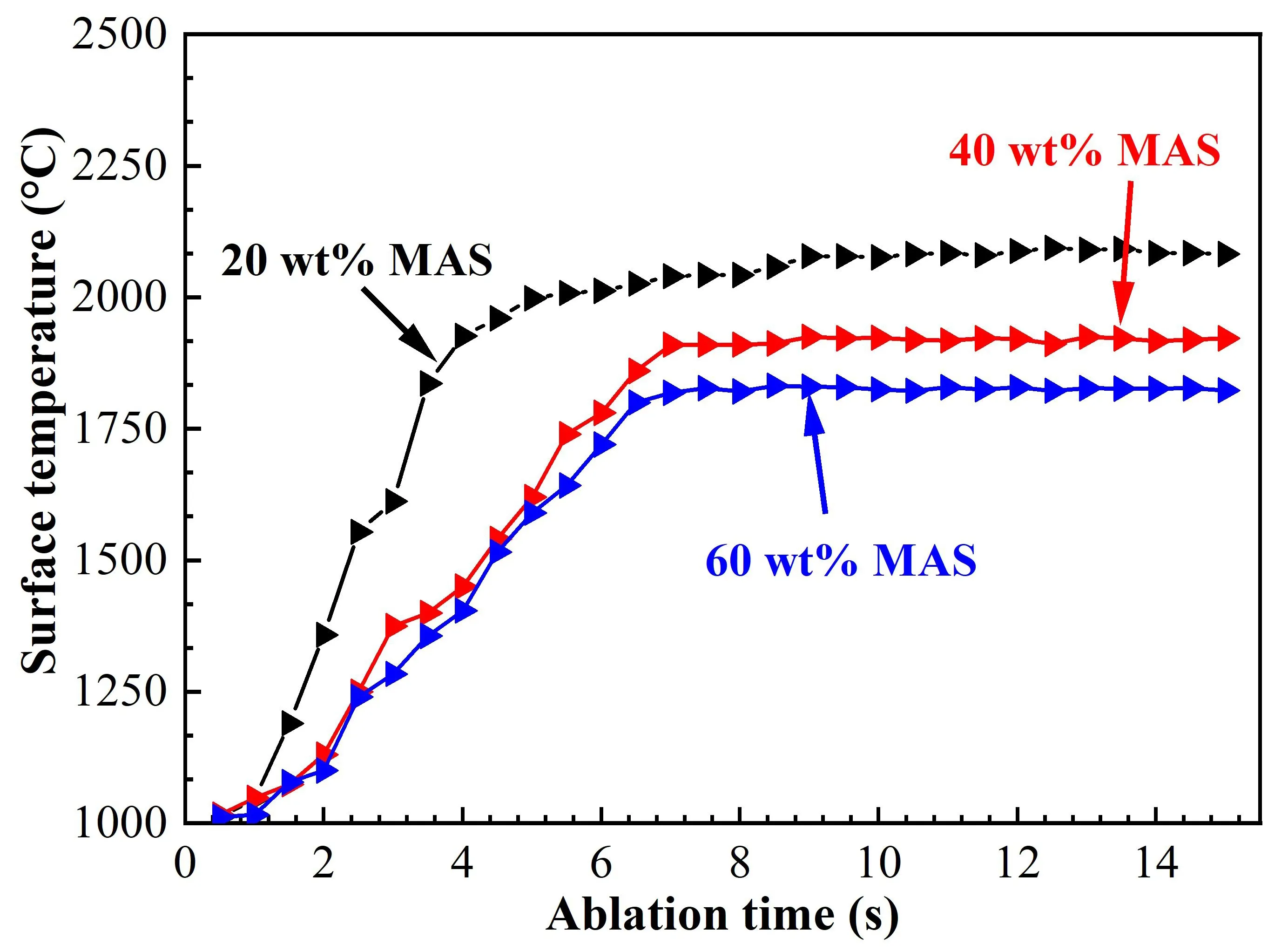
27 December 2024Effect of Magnesium Aluminum Silicate Addition on the Ablation Resistance of BN Matrix Ceramics
Ablation resistance is a critical factor in evaluating the performance of BN-based ceramic composites under extreme service conditions. This study investigates the ablation behavior and underlying mechanisms of BN-MAS wave-transparent ceramic composites with varying magnesium aluminum silicate (MAS) content through oxyacetylene torch tests. The results reveal that increasing the MAS content reduces the mass ablation rate from 0.0298 g/s to 0.0176 g/s and the linear ablation rate from 0.149 mm/s to 0.112 mm/s. The incorporation of MAS into h-BN ceramics significantly lowers the surface ablation temperature, primarily due to the evaporation of B2O3 (g) and MAS ceramics. Cross-sectional analysis of the ablated composites indicates the presence of micro- and macro-spallation in the ablation center. The primary ablation products are magnesium-aluminum borosilicate glass and mullite. Key ablation mechanisms include the oxidation of h-BN under flame exposure, the erosion of viscous oxidation products, and the physical degradation of the matrix caused by the high-velocity gas flow.