Found 27 results
Open Access
Article
16 January 2026Operation Management Optimization of Hydropower Stations Based on Big Data Technology: A Case Study of X Hydropower Station Group
In the operation management of hydropower stations, uneven scheduling often leads to issues such as resource wastage and unequal energy distribution; big data technology offers a new approach for optimizing the scheduling of hydropower stations in the information era. Taking the X Hydropower Station Group as a case study, this paper explores data acquisition, cleaning, clustering analysis, and the formulation of seasonal scheduling strategies to enhance the efficient utilization of hydropower resources and ensure the stable operation of the power grid. K-means clustering analysis is applied to explore typical output curves of cascaded hydropower stations, revealing the relationships between water levels, inflow rates, and load rates. Furthermore, a grey prediction model is developed to forecast future load rates, providing robust data support for short-term operational scheduling plans. The research not only improves monitoring and decision-support capabilities but also enhances the adaptability and response speed to seasonal changes, ensuring the stability and reliability of the power supply.
Open Access
Article
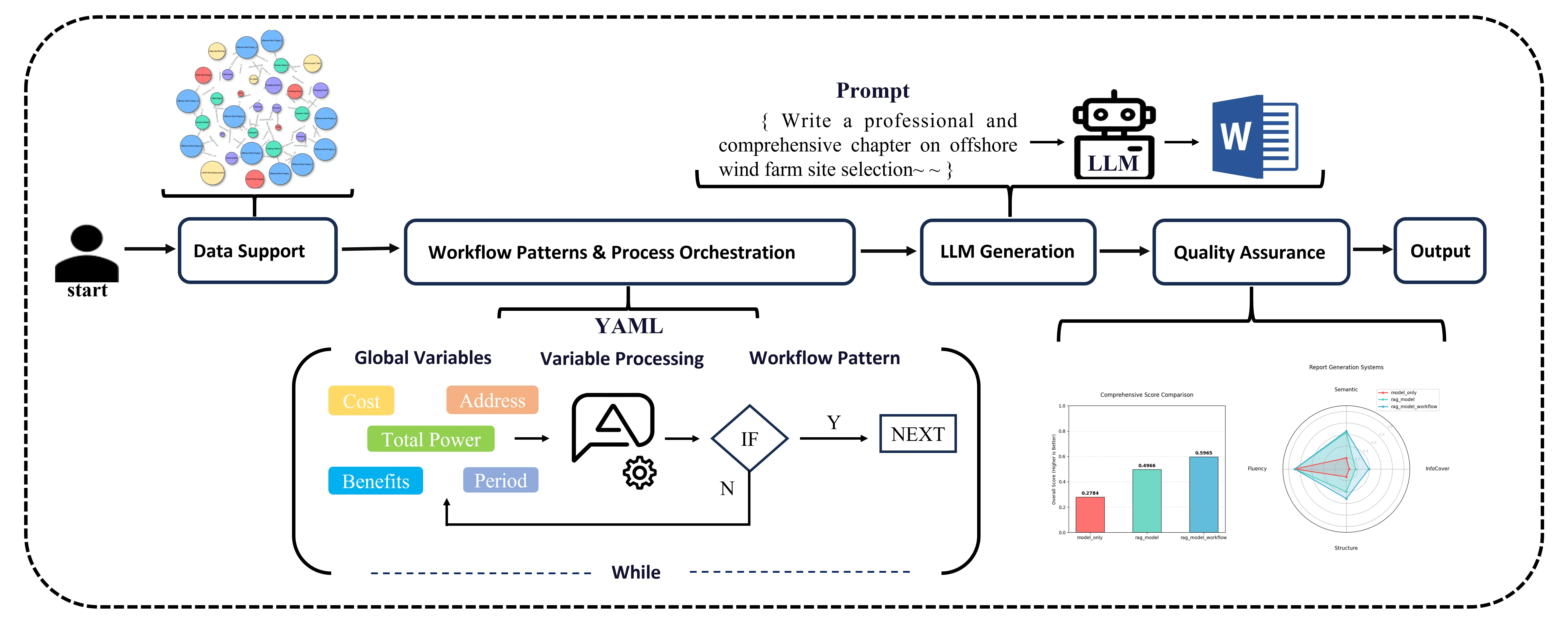
08 January 2026A Large-Scale Language Model Based System for Automated Generation of Offshore Wind Power Feasibility Study Reports
Driven by global energy transition goals, the large-scale development of offshore wind power imposes rigid requirements for professionalism, standardization, and timeliness on feasibility study reports (FSR). Traditional manual compilation and existing automated methods fail to meet these requirements due to interdisciplinary complexity, poor process controllability, and insufficient domain adaptation. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a configurable and interpretable offshore wind FSR generation system built on a three-tier framework that encompasses “data support, process orchestration, and quality assurance”. The system integrates a YAML-based workflow architecture, multi-level prompt engineering, and a comprehensive evaluation system. Notably, the introduced “Cyclic Aggregation Mode” enables the iterative generation and logical summarization of multi-subproject data, effectively distinguishing this system from traditional linear text generation models. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed “Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) + Large-scale Language Model (LLM) + Workflow” system outperforms baseline models with key metrics including semantic consistency (0.6592), information coverage (0.3908), structural compliance (0.5123), and an overall score (0.5965). Ablation studies validate the independent contributions of the RAG and Workflow components, thereby establishing the “RAG + LLM + Workflow” paradigm for intelligent professional document generation. This work addresses core challenges related to controllability, accuracy, and interpretability in high-stakes decision-making scenarios while providing a reusable technical pathway for the automated feasibility demonstration of offshore wind power projects.
Open Access
Article
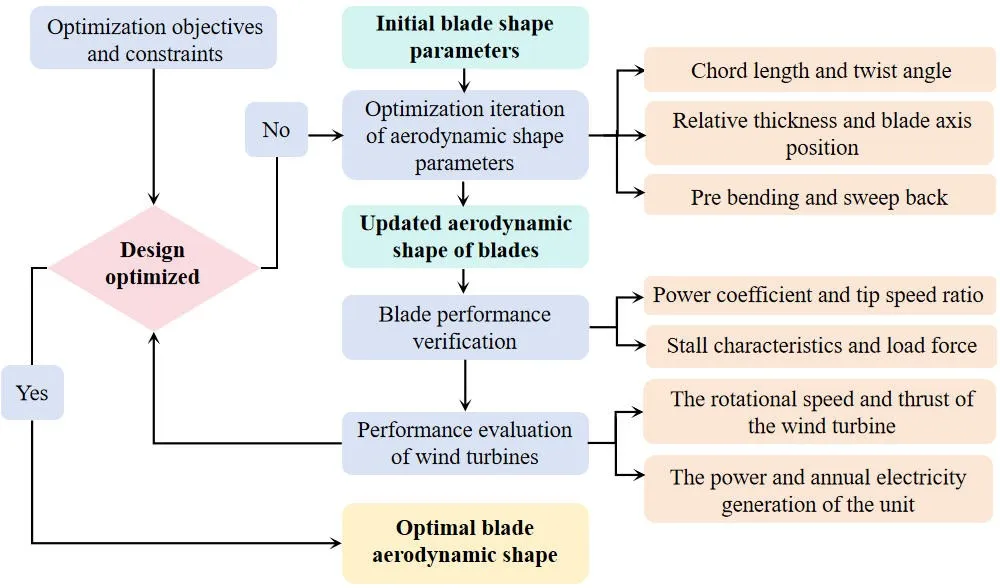
06 November 2025Application of Blades Aerodynamic Optimization Design Platform Based on the Performance of Offshore Wind Turbines
Optimizing aerodynamic performance with low loads is a core objective in high-power wind turbine blade design. This study develops a blade aerodynamic optimization design platform based on the performance of a wind turbine. By applying automated design principles, the platform rapidly iterates to obtain blade profiles that meet turbine development requirements, significantly improving design efficiency and reliability. Key findings include That Optimizing chord length and relative thickness distributions substantially contribute to enhancing power generation while reducing load levels. Relative thickness and twist angle distributions are critical parameters influencing stall characteristics during blade operation. Superior aerodynamic performance notably increases annual rated power generation hours but simultaneously elevates blade thrust and root loads. Among the evaluated designs meeting turbine specifications, the #436 blade achieves a maximum power coefficient of 0.4679 while maintaining low ultimate and fatigue loads. Furthermore, when paired with the wind turbine, its rated wind speed reaches 10.9 m/s, and its annual rated power generation hours under various inflow wind speed conditions all meet the turbine system’s development requirements. Consequently, the #436 blade demonstrates exceptional system compatibility, making the 8.5 MW turbine equipped with this blade highly competitive in the market.
Open Access
Article
31 October 2025Performance Evaluation of Machine Learning Algorithms for Predicting Organic Photovoltaic Efficiency
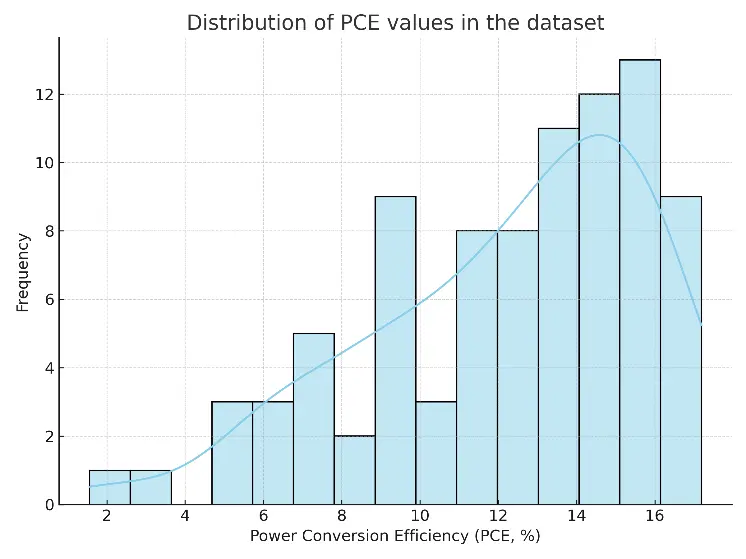
This study forecasts the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of organic solar cells using data from experiments with donors and non-fullerene acceptor materials. We built a dataset that includes both numerical and categorical features by using standard scaling and one-hot encoding. We developed and compared several machine learning (ML) models, including multilayer perceptron, random forest, XGBoost, multiple linear regression, and partial least squares. The modified XGBoost model performed best, achieving a root mean squared error (RMSE) of 0.564, a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.446, and a coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.980 on the test set. We also assessed the model’s ability to generalize and its reliability by examining learning curve trends, calibration curve analysis, and residual distribution. Plots of feature correlation and permutation importance showed that ionization potential and electron affinity were key predictors. The results demonstrate that with proper tuning, gradient boosting methods can provide highly accurate and easy-to-understand predictions of organic solar cell efficiency. This work establishes a repeatable machine learning process to quickly screen and thoughtfully design high-efficiency photovoltaic materials.
Open Access
Review
23 October 2025Unpacking the Transformative Power of the Rights of Nature: Rethinking Self, Society, and Nature in Environmental Governance in Tanzania
This study examines the transformative potential of integrating the Rights of Nature (RoN) into Tanzania’s environmental governance framework to address persistent ecological degradation, legal marginalization of local communities, and systemic governance gaps. Despite global progress in adopting the Rights of Nature (RoN), where ecosystems are granted legal personhood and communities serve as guardians Tanzania’s legal and institutional frameworks remain predominantly anthropocentric, lacking provisions that recognize nature’s intrinsic value. The primary objective of the study was to critically evaluate the extent to which Tanzania’s current governance systems reflect or exclude RoN principles and to propose transformative pathways grounded in justice, inclusivity, and local knowledge. The study analyzed international legal instruments, Tanzanian statutes, scholarly literature, and case studies using a doctrinal and thematic review methodology. Findings reveal that, despite Tanzania’s comprehensive environmental legislation, such as the Environmental Management Act (2004), key provisions fail to ensure procedural justice and exclude communities from meaningful participation, particularly under Strategic Environmental Assessment regulations. Conversely, local and Indigenous communities such as the Maasai, Chagga, and Zaramo have long practiced ecological stewardship grounded in relational worldviews, echoing RoN values. However, these systems are neither legally recognized nor institutionalized. The study concludes that a shift towards rights-based and transformative governance is necessary to address environmental injustice and ecological decline. It recommends revising legal frameworks to grant ecosystem rights, mandating participatory governance, and embedding Indigenous and local knowledge into environmental policy. Such reforms will not only enhance ecological integrity and local empowerment but also contribute to achieving Tanzania’s commitments under Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 13, 15, and 16.

Open Access
Article
19 September 2025Cutting Power Model for Material Identification during Helical Milling of Aerospace Stacks
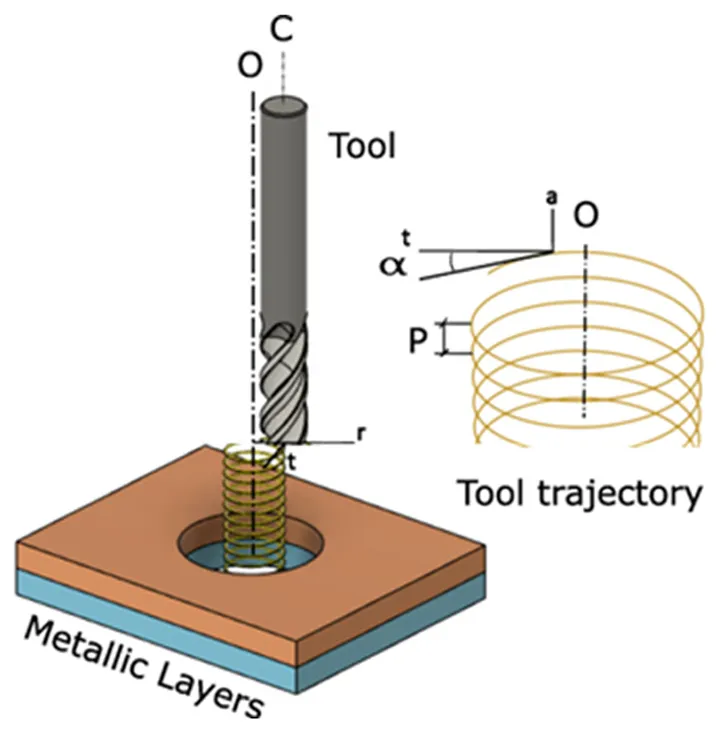
Smart factories increasingly rely on real-time data to optimize manufacturing, yet machining operations, particularly in aerospace stack drilling, still face challenges such as low productivity and accelerated tool wear. While advanced CNC machines already capture rich process data, its full potential for real-time decision-making remains underexplored. This work introduces a novel approach that leverages machine learning (ML) to identify material layers and optimize cutting conditions during drilling (helical milling) of aluminum–titanium stacks. Unlike prior methods that require additional sensors or complex instrumentation, our approach uniquely utilizes only spindle power signals from the CNC machine. Data maps consisting of cutting coefficients are used to train ML models to reliably predict material transitions across multiple layers under a range of cutting conditions. The results demonstrate appropriate material identification in comparison to experiments, enabling significant improvements in the hole-making of aerospace stacks. This study contributes a scalable, sensor-free, and non-intrusive framework for smart machining, establishing a practical pathway for process optimization in aerospace manufacturing without disrupting existing shop-floor setups.
Open Access
Article
08 September 2025Large Language Model for Secure Operation of Power Systems
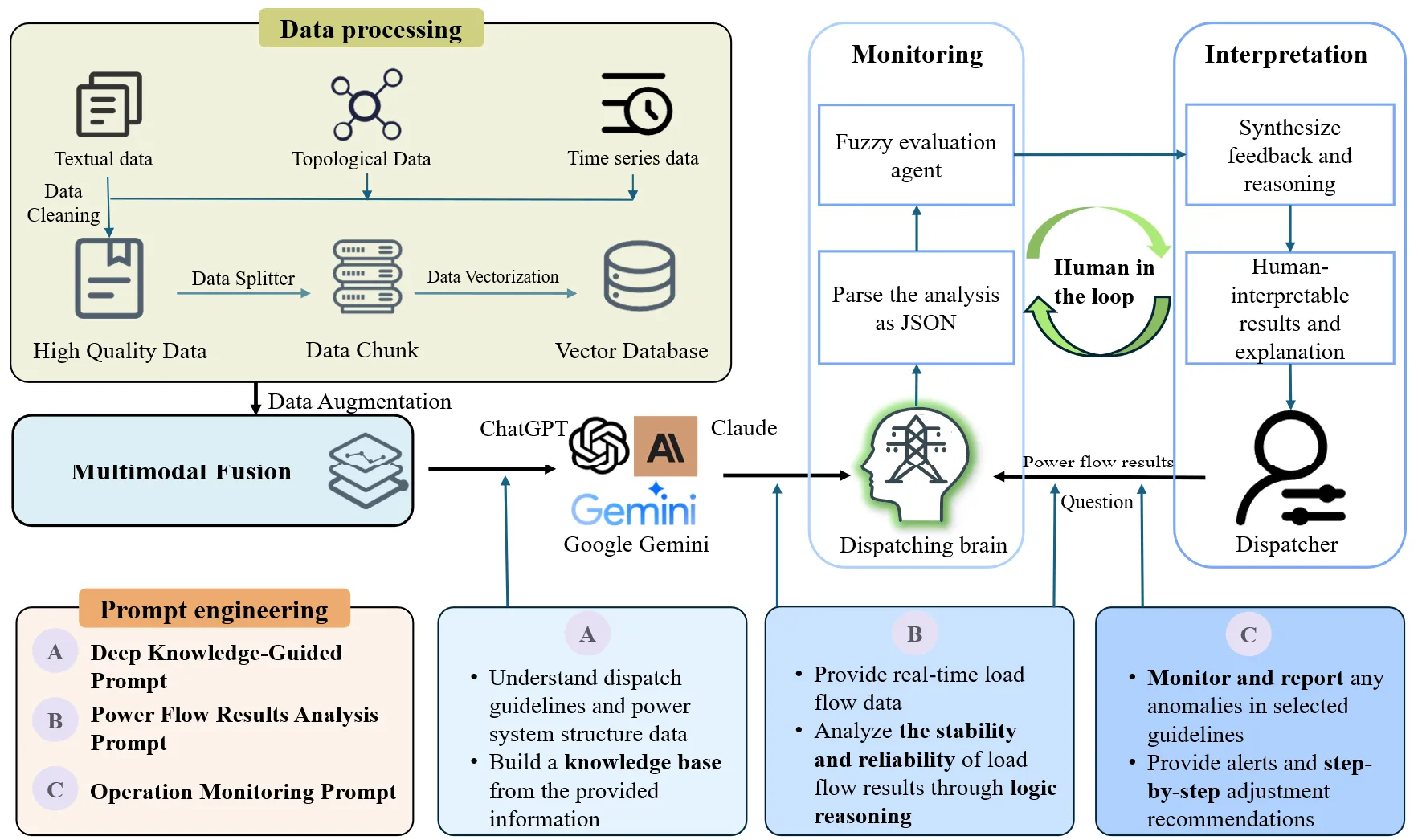
The integration of large-scale renewable energy, multi-criteria operational constraints, and complex grid topologies has intensified the challenges faced by the security monitoring process within power system dispatch. Dispatch guidelines, typically expressed in natural language, are difficult for conventional algorithms to interpret and apply in real time, while general-purpose Large Language Models (LLMs) lack domain-specific knowledge, risking inaccurate or unsafe recommendations. This study proposes an LLM-based monitoring framework that integrates domain-specific prompt engineering with fuzzy evaluation to address these limitations. The framework interprets dispatch guidelines, analyzes real-time power flow data, and converts semantic assessments into quantitative safety scores, enabling closed-loop decision-making. Validation on the IEEE 14-bus system demonstrates that the optimized LLM outperforms a general LLM in accuracy, logical consistency, and stability under complex multi-standard scenarios, while reducing reliance on manual intervention. The results highlight the framework’s potential to enhance monitoring efficiency and ensure intelligent, secure power system operation.
Open Access
Article
26 August 2025Hybrid Encoder–Decoder Model for Ultra-Short-Term Prediction of Wind Farm Power
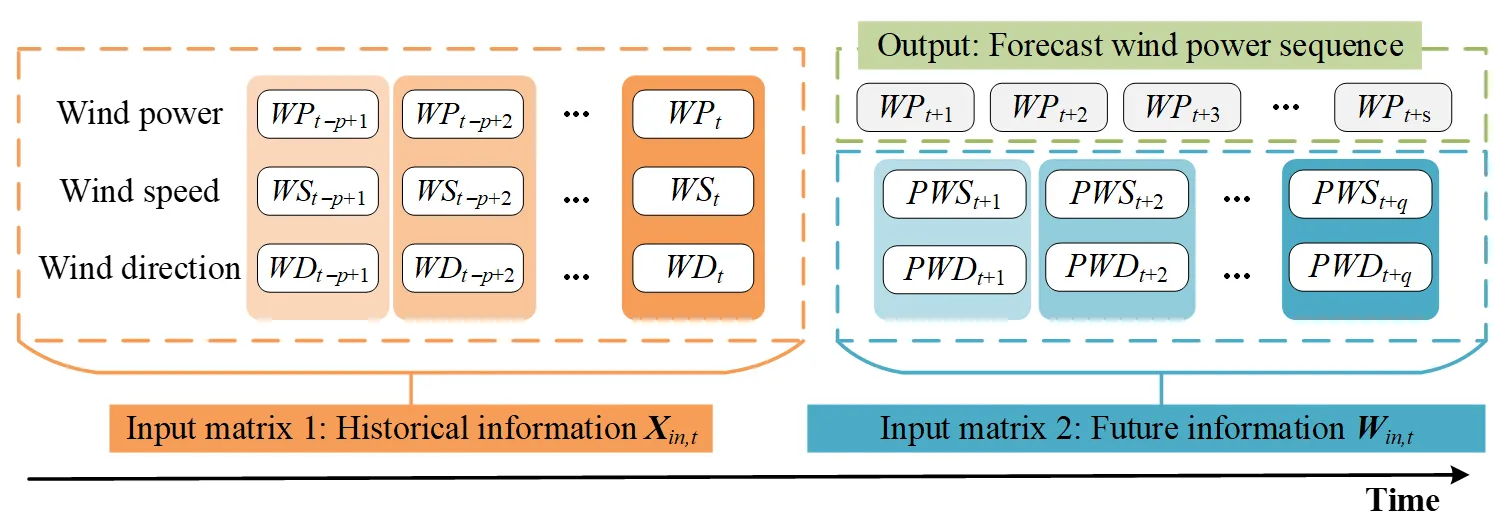
The ability to ensure safe and economic operation of power grids is challenging because of the large-scale integration of wind power as a result of its intermittent and fluctuating nature. Accurate wind power prediction is critical to overcome these concerns. This study proposed a novel hybrid encoder–decoder model by combining bidirectional gated recurrent unit, multi-head attention mechanism, and ensemble technique for multi-step ultra-short-term power prediction of wind farms. The bidirectional gated recurrent unit accurately details the complex temporal dependency of input sequence information in the encoder and outputs the encoded vector. To focus on features that contribute more to the output, two types of multi-head attention mechanism, including self-attention and cross-attention, were used in the decoder to decode the encoded vector and obtain the forecast wind power sequence. Furthermore, an ensemble technique was used to integrate forecast results from various individual predictors, which reduced the uncertainty of individual prediction results and improved predictive accuracy. The input data included historical information from the wind farm and future information from numerical weather prediction. The forecast model was validated using actual data, and results showed that it achieved superior accuracy and stability compared with other existing models in four multi-step prediction scenarios (1-, 2-, 3-, and 4-h prediction).
Open Access
Article
19 August 2025Inventory of Ant Fauna in the Influence Area of a Small Hydropower Plant in the State of Paraná, Brazil
The construction of hydroelectric dams for power generation causes environmental alterations and ecosystem restructuring in directly and indirectly affected areas. This study aimed to survey the ant fauna in the indirect area of influence of a small hydroelectric plant located in Mangueirinha, Paraná State, Brazil. Seven sampling campaigns were conducted, two before and five during the project’s implementation, using pitfall traps as the sampling method. A total of 72 ant species were recorded, belonging to 26 genera and six subfamilies. Species richness and abundance did not differ significantly between the pre-implementation and implementation phases. The Chao1 estimator indicated that actual species richness may be approximately 7.6% higher than observed. These findings contribute to understanding ant biodiversity in areas subject to land-use change in Paraná State. The results highlight the value of using insect species richness and abundance, particularly of bioindicator groups such as ants, for environmental impact monitoring.

Open Access
Article
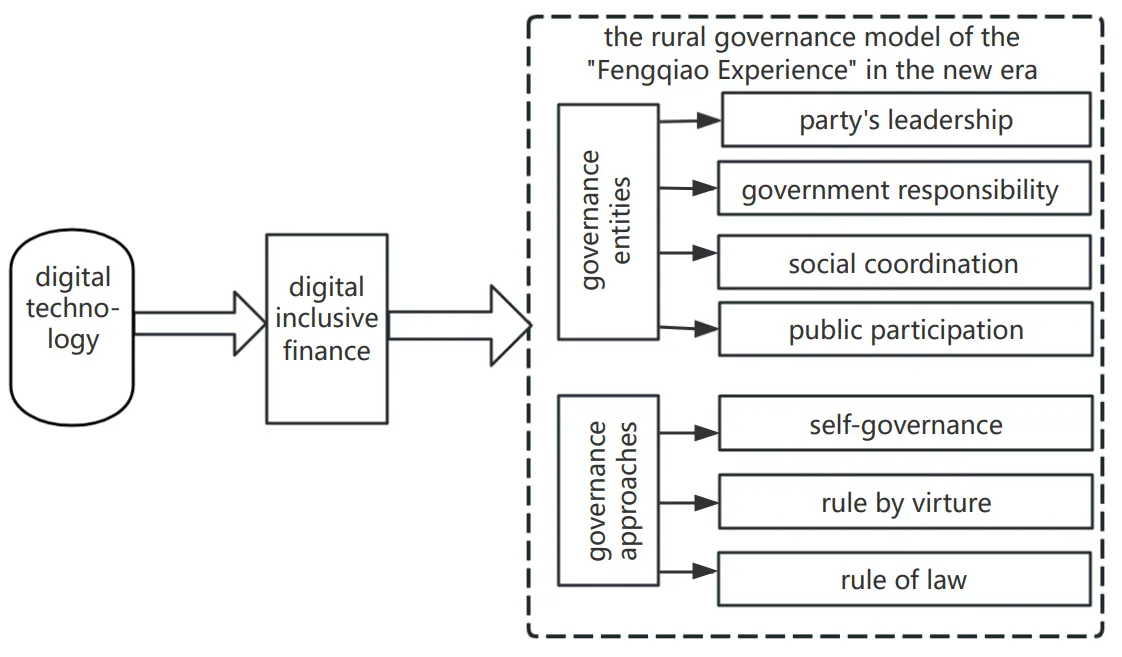
15 July 2025Exploring the Sustainable Path of Rural Governance: An Empirical Study on Digital Technology Empowering the “Fengqiao Experience” Model in the New Era
Understanding digital technology and digital inclusive finance in rural governance is key to exploring the sustainable development path of rural governance in China. This study constructs a multidimensional index evaluation system for the “Fengqiao Experience” rural governance model in the new era, measures the model’s rural governance level in 30 provinces in China (2011–2022), and empirically assesses digital technology’s impact on rural governance and its mechanism. The results are as follows: (1) During the sample survey period, the rural governance level of digital technology and “Fengqiao Experience” in 30 provinces in China has improved year by year. (2) Benchmark returns to reality and digital technology significantly promotes the improvement of rural governance levels, which remains valid after using GLS, replacing core explanatory variables, excluding the impact of the epidemic, and excluding municipalities directly under the central government. (3) Digital inclusive finance plays an intermediary role in the digital technology process, enabling rural governance. (4) Digital technology’s impact on rural governance has significant spatial spillover characteristics. Such technology helps improve the level of rural governance both locally and in surrounding areas. This study contributes to the understanding of the mechanism, effect, and regional differences of digital technology-enabled rural governance.