Found 7 results
Open Access
Communication
08 January 2025Development of Eco-Friendly Composites Using Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and Diss Fibers (Ampelodesmos Mauritanicus)
In response to the growing environmental threats and pollution linked to synthetic plastics, current scientific inquiry is prioritizing the advancement of biodegradable materials. In this context, this study investigates the possibility of developing fully biodegradable materials using plant fibers extracted from the Diss plant (Ampelodesmos mauritanicus) as reinforcement in poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV)-based biocomposites. The biocomposites were prepared by melt blending in the following weight ratio: PHBV/Diss fibers 80/20. The chemical structure of Diss fibers was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF). The impact of Diss fibers on the mechanical properties of biocomposites has also been investigated in comparison to neat PHBV. FTIR and XRF analyses identified cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin as the main components of Diss fibers. On the other hand, the results showed a significant enhancement of Young’s modulus (⁓21%) of PHBV/DF biocomposites in comparison to neat PHBV due to a better dispersion of the fibers in the matrix, as confirmed by atomic force microscopy (AFM) images.
Open Access
Review
09 December 2024Synthesize and Applications of Biodegradable Plastics as a Solution for Environmental Pollution Due to Non-Biodegradable Plastics, a Review
Biodegradable plastics are a potential sustainable alternative to conventional petrochemical-based non-degradable plastics. Due to their lightweight, flexibility, durability, versatile applications, chemical inertness, electrical and heat insulation, and conductivity, plastics have become an essential material for many industries, with annual production currently exceeding 450 million tons. However, these materials are non-biodegradable, leading to detrimental consequences such as the formation of microplastics from improper disposal and the generation of toxic gases, including furans, dioxins, mercury, and polychlorinated biphenyls, from burning plastic waste. This results in environmental pollution, affecting land, water bodies, and the atmosphere. In response, studies where the focus has been on creating bio-degradable polymers such as polylactic acid, polyhydroxy alkanoates, Polycaprolactone, Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate), and Polybutylene succinate, which were extracted from renewable resources or chemically modified as biodegradable polymers. Biodegradable polymers exhibit a wide range of properties and can now be modified to be used in various applications suitable for substituting some conventional plastic products. Thus, the article highlights the critical issue of environmental pollution caused by non-biodegradable plastics and provides a comprehensive overview of the synthesis processes, properties, novel applications, and challenges associated with the use of biodegradable plastics.
Open Access
Article
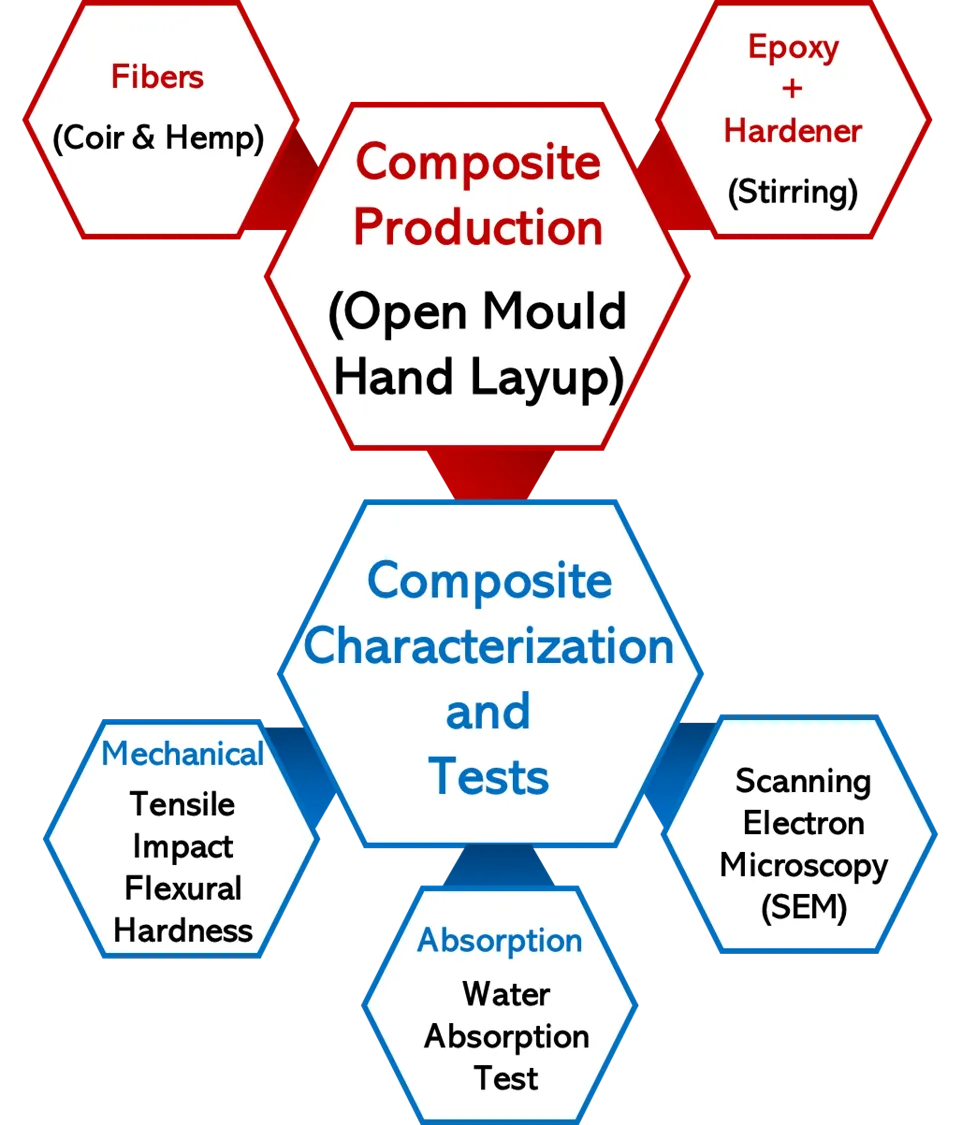
01 November 2024Alkaline Modified Coir and Unmodified Hemp Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Based Composite for Automotive Application
The growing demand for sustainable materials in the automotive industry has prompted research into natural fiber-reinforced composites. To reduce carbon footprints and enhance product sustainability, the sectors increasingly focus on renewable and biodegradable materials. Composites made from natural fibers, such as coir and hemp, offer a promising solution for creating lightweight, high-performance components with a reduced environmental impact.In this study, an experimental investigation was conducted to examine the impact of single and hybrid and treated and untreated fibers, on the properties of epoxy-based composites. Untreated hemp fiber with treated Coir fiber was used for the research. The composites were fabricated through the open mould hand lay-up technique. Samples were prepared by randomly dispersing the fibers in the epoxy matrix before pouring them into the respective moulds prepared according to ASTM standards. Tensile, impact, and hardness tests were conducted on the cured samples to determine their mechanical properties, while a scanning electron microscope was used to evaluate the fractured surface. Water absorption tendencies were also determined. The results showed that the sample denoted as 5CF wt.% had the best property combination with tensile strength (32.4 MPa), tensile modulus (11.9 GPa), flexural strength (167.0 MPa), and impact strength (46.8 kJ/mm2). It was discovered that hemp fiber-based composites were not enhanced properly due to lack of fiber surface modifications. Though optimum results were obtained from treated coir fiber-based single/distinct composite, untreated hemp fiber was discovered to aid some flexural modulus and hardness properties in the hybrid composite based on the best results obtained in its distinct-based composite. Therefore, untreated hemp fiber can be used in hybrid form with treated coir fiber where one of the fibers is scarce or when fiber surface medication is difficult to achieve. Thus, the results showed that 5CH-based composites are the most suitable composition for automotive components development where high-mechanical properties are essential.
Open Access
Article
12 August 2024Comparative Study: Biodegradable Chelating Agents vs. Aqua Regia for Extraction of Indispensable Elements from Pyrite Ore of Bagrot, Gilgit Baltistan
This study investigates the optimization of metal extraction from Bagrot pyrite ore, with a focus on gold recovery. Initial characterization using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) provided a comprehensive elemental profile of the ore. Fire assaying was employed to establish a baseline gold concentration. Systematic leaching experiments were conducted, varying parameters such as reaction time, temperature, and stirring speed, and the results were analyzed using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). Among the chelating agents tested Ethylenediamine N-N′ disuccinic acid (EDDS), Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) only limited efficacy in gold extraction was observed. In contrast, ammonium thiosulfate demonstrated substantial potential for effective gold recovery. Mercaptobenzothiazole (MBT) and N,N-Dimethylglycine (DMG) were determined to be ineffective for metal leaching under the tested conditions. This research highlights the critical role of reagent selection and parameter optimization in enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of gold extraction processes, positioning ammonium thiosulfate as a promising alternative to traditional cyanide-based methods.

Open Access
Article
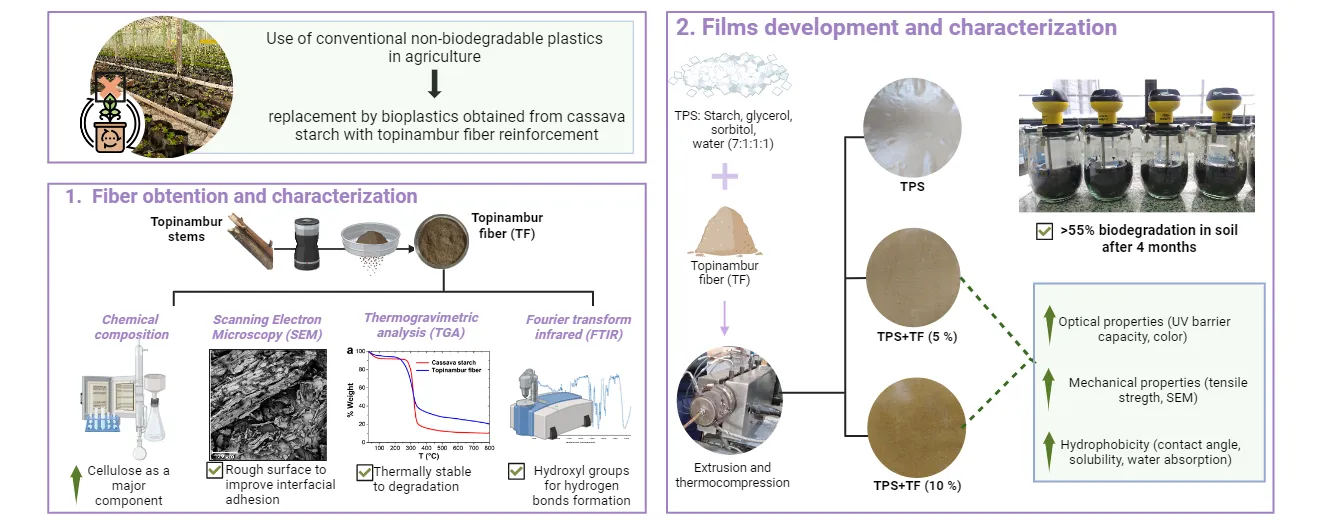
18 April 2024Biodegradable Composite Materials Based on Cassava Starch and Reinforced with Topinambur (Helianthus tuberosus) Aerial Part Fiber
The cultivation of topinambur (Helianthus tuberosus) has aroused the interest of producers since it is a source of inulin and can be used for biofuel production. During tuber processing, the aerial part of the crop remains as a by-product with no practical application. This work aimed to characterize the fibers obtained from the aerial part of topinambur and to evaluate their reinforcing potential in cassava starch-based films. Starch-based films with topinambur fiber (0, 5, and 10%) were prepared by extrusion followed by thermocompression. Topinambur residue contains 88.6% of total fiber, 8.5% ash, and 0.68% lipid. Mechanical film properties evidenced the reinforcement action of topinambur fiber, 10% content was able to increase up to 70% the Young’s modulus. SEM micrographs evidenced the good fiber-matrix interaction. UV-visible capacity, opacity, and chromaticity parameters of TPS films increased with fiber content in the formulation. Fiber incorporation improved the hydrophobicity of the biocomposite materials by increasing the contact angle. Starch-based films biodegraded more than 55% after 110 days, showing a similar trend to that of microcrystalline cellulose. Thus, topinambur residue can be effectively used as a reinforcing agent for TPS materials, being an innovative and non-toxic additive within the circular economy premises.
Open Access
Review
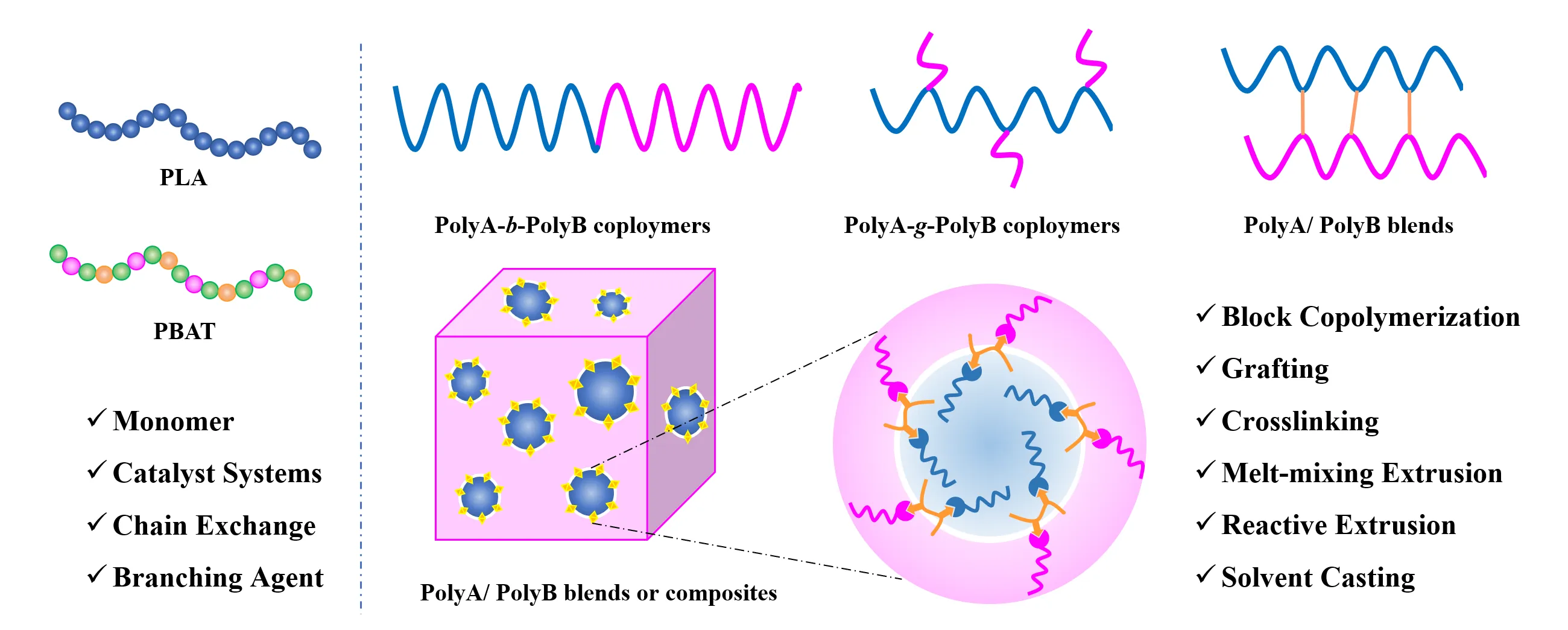
12 April 2023Recent Progress in Modification and Preparations of the Promising Biodegradable Plastics: Polylactide and Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)
The acquisition of high-performance biodegradable plastics is of great significance in addressing the problem of environmental pollution of plastics. Polylactide (PLA) and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) are the most promising biodegradable polymers and have excellent functional properties. However, low elongation at break and impact strength of PLA and low tensile modulus and flexural strength of PBAT hinder their application. A large number of studies focus on improving the performance of PLA and PBAT and broadening their applications. In terms of polymer modification, this paper summarized recent progresses in both chemical and physical modification methods for PLA and PBAT, respectively. The properties of PLA can be improved by co-polymerization, grafting, cross-linking and blending. The properties of PBAT can be improved mainly through blending with other degradable polymers, natural macromolecules and inorganic materials. This review can provide the reference and ideas for the modification of biomass-based biodegradable plastics like PLA and fossil-based biodegradable plastics like PBAT.
Open Access
Article
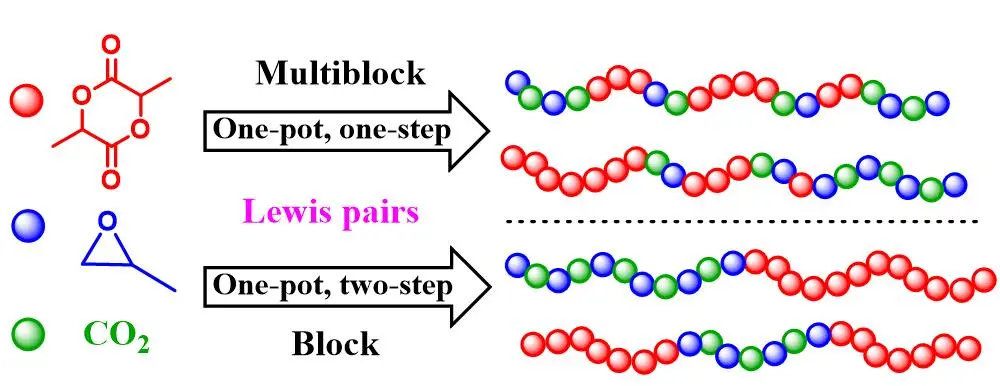
30 January 2023Metal-Free Lewis Pair Catalysts for a One-Pot Terpolymerization of Propylene Oxide, ʟ-Lactide and CO2
Multiblock and di-/tri-block copolymers are successfully synthesized for the first time via the metal-free terpolymerization of propylene oxide (PO), ʟ-lactide (LA) and CO2 in one-pot/one-step and one-pot/two-step protocols respectively. Firstly, triethyl borane (TEB) and bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride (PPNCl) Lewis pair is employed in the ring-opening polymerization of LA, wherein the catalytic efficiency is significantly correlated to the TEB/PPNCl feed ratio. Next, a series of TEB/base pairs are selected to synthesize the PO/LA/CO2 terpolymer (PPCLA) in one-pot/one-step strategy. In PPCLA synthesis, LA exhibits the fastest reaction rate but severe transesterification is almost unavoidable, resulting in low molecular weight products. In order to prepare high-molecular-weight terpolymers, a one-pot/two-step methodology has to be applied. By this method, the copolymerization of PO/CO2 proceeds first to form poly(propylene carbonate) (PPC) macroinitiators, which triggers the polymerization of LA to polylactide (PLA), leading to PLA-PPC or PLA-PPC-PLA block copolymers. The synthesized PLA-PPC-PLA block copolymers display improved thermal stability compared with PPC.