Found 469 results
Open Access
Opinion
29 September 2025Modeling Cardiac Response to Transient Hemodynamic Changes: Beyond dp/dt Max and New Insights from IVCO and ES Point Analysis
Traditional indices such as dp/dt max remain widely used in assessing ventricular contractility, yet their load-dependence limits clinical precision, particularly during dynamic hemodynamic shifts. This letter to the Editor advocates for a more physiologically grounded approach using dual pressure catheters equipped with two high-fidelity sensors, one in the left ventricle (LV) and one in the aorta, to capture real-time pressure gradients and valve events with high temporal resolution. When combined with transient inferior vena cava occlusion (IVCO), this setup enables accurate identification of the true end-systolic (ES) point, typically marked by dp/dt min or the dicrotic notch on the aortic pressure waveform. This method allows for the construction of more physiologically valid end-systolic pressure-volume relationships (ESPVR). It introduces the novel peak pressure end-systolic pressure-volume relationship (PPESPVR) model, which links peak LV pressure to the ES point within a single cardiac cycle. The resulting volume intercept (Vint) and end-systolic fraction (ESF) offer new insights into myocardial performance under varying preload and afterload conditions, without requiring extensive hemodynamic manipulation. This dual-sensor approach not only enhances diagnostic accuracy but also opens the door to real-time, patient-specific contractility assessment in both research and clinical settings.
Open Access
Case Report
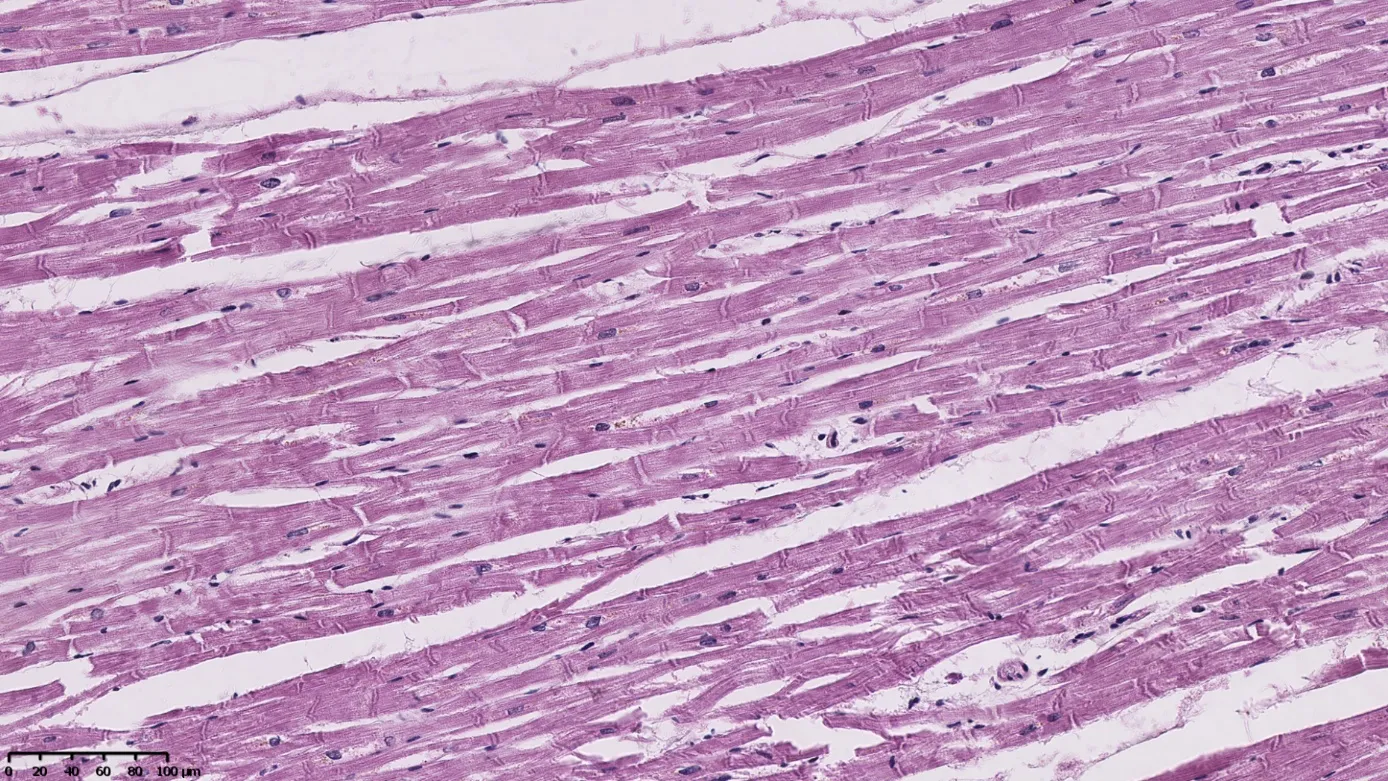
28 September 2025Usefulness of Histopathological Examinations in Assessing Cases of Fatal Poisoning with New Psychoactive Substances—Preliminary Studies
Investigating the cause and mechanism of death in cases of suspected fatal poisoning with new psychoactive substances (“legal highs”) is no different from classic post-mortem diagnostics in forensic medicine. There is no characteristic autopsy appearance in individuals poisoned with “legal highs”, therefore, in practice, biological material is most often reserved for complementary histopathological and toxicological examinations. This study aimed to assess the usefulness of microscopic examinations in assessing cases of fatal poisoning with new psychoactive substances. The authors’ analysis of the literature and the results of histopathological examinations of victims of “legal high” poisoning from their own practice at the Department of Forensic Medicine and Forensic Toxicology of the Silesian Medical University in Katowice revealed that the most common pathological or diagnostically questionable changes are observed in the heart, kidneys, and liver. In the heart, signs of early myocardial ischemia are often observed in the absence of atherosclerotic changes in the coronary vessels or changes such as muscle bridging along these vessels. Considering the relatively young age of the deceased, it is highly probable that the pathological changes observed are related to the use of “legal highs”, especially given their known cardiotoxicity. In the kidneys, signs of acute tubular necrosis (ATN) are most frequently seen. These signs are usually mild and overlap with autolytic changes, making their assessment difficult, especially since they may be periagonal (artifacts). Morphological changes in the liver typically represent focal hepatocyte degeneration. Only in one case did they demonstrate signs of active inflammation and developing fibrosis. The nature of the observed changes does not allow for a clear connection with the use of “legal highs”, as the same changes may be associated with metabolic disorders, obesity, alcohol abuse, or viral hepatitis. In summary, microscopic examination of internal organ samples collected during autopsies and post-mortem examinations of individuals who died from legal highs is only supportive, as there is no characteristic microscopic image that would allow for a definitive diagnosis. The extent of the patho-logical changes observed depends primarily on age and whether the poisoned individual was hospitalized. Infectious complications are often observed in cases of long-term stays in intensive care units (e.g., pneumonia associated with respirator therapy, signs of generalized infection).
Open Access
Article
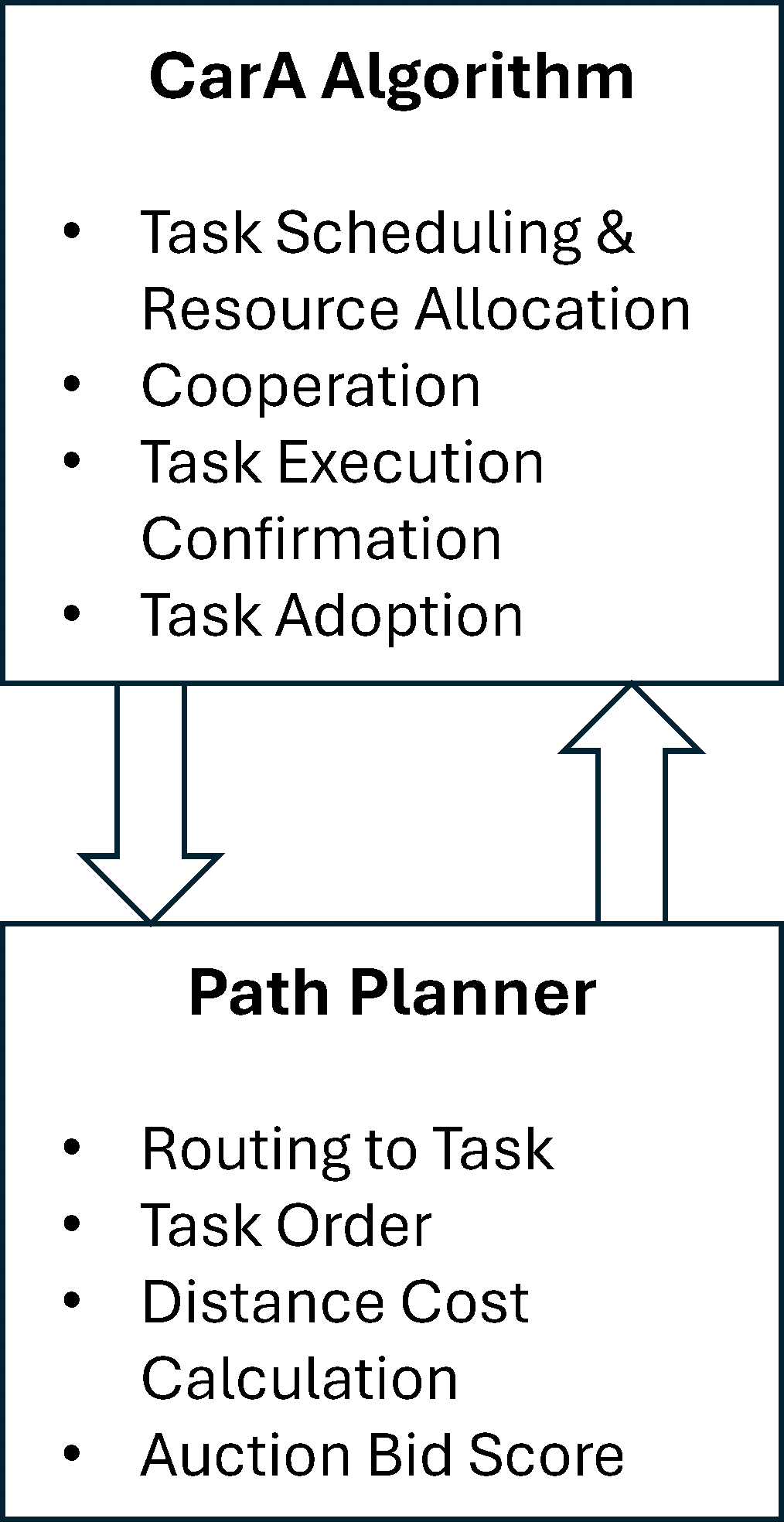
28 September 2025Integrated Consensus Framework for Task Assignment and Path Planning of a Degraded UAV Fleet
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) systems can fail during civil and military operations. This presents a significant challenge for human teleoperators (remote pilots) in determining task reallocation after member loss within the fleet. To alleviate the high cognitive load on teleoperators in critical situations, a decentralized strategy was developed to resolve the combined task assignment and vehicle routing problems. This Integrated Consensus Framework (ICF) not only solves the combined problem but also adds a unique ability to identify the loss of a vehicle and dynamically reroute agents to abandoned tasks to achieve a satisfactory solution. ICF is a two-tiered approach that combines a novel algorithm, the Caravan Auction (CarA) algorithm, with a path-planning strategy to identify when UAVs are lost and reallocate orphaned tasks. The CarA Algorithm consists of three phases: auction, consensus, and validation phases. An experiment using Monte Carlo simulations was conducted to determine the performance of ICF. Teleoperators assigned to complete multiple tasks with UAVs in dangerous environments can allow the proposed system to perform task assignments and reallocation while offering only supervisory control as needed. The results indicate this novel approach provides comparable performance to existing strategies, doing so with the addition of randomized UAV loss.
Open Access
Article
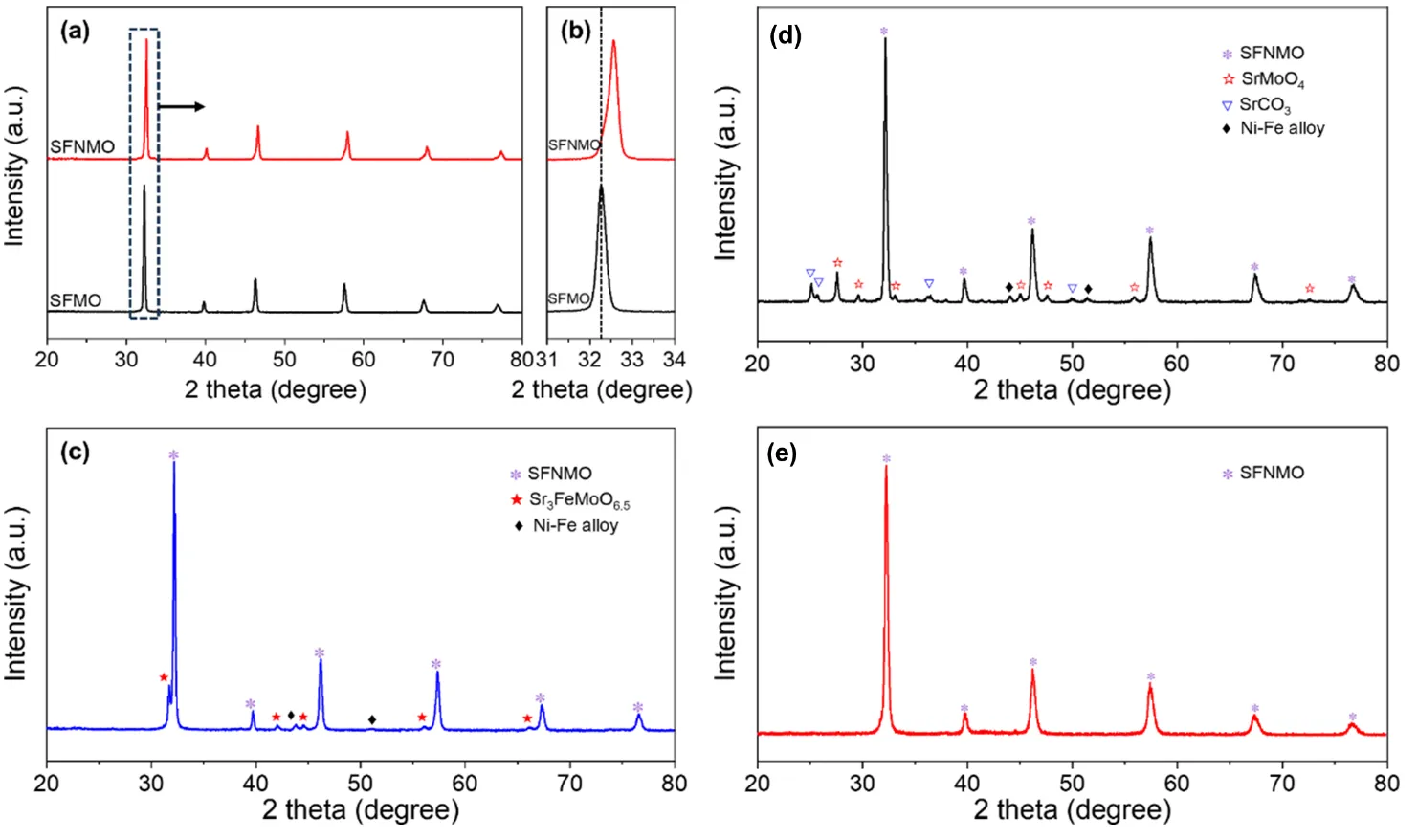
28 September 2025Enhancing the Performance of Sr2Fe1.3Ni0.2Mo0.5O6−δ as Methane-Fueled SOFC Anode via In-Situ Exsolution of Ni-Fe Nano-Catalyst
The Sr2Fe1.5Mo0.5O6−δ (SFMO) perovskite exhibits promising performance as a solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) anode for hydrogen fuel but demonstrates limited catalytic activity with hydrocarbon fuels. To address this limitation, a Sr2Fe1.3Ni0.2Mo0.5O6−δ (SFNMO) perovskite was developed via B-site Ni substitution, and its in-situ exsolution behavior and methane electrooxidation performance were systematically investigated. Combined XRD, SEM, and TEM-EDS analyses reveal the in-situ exsolution of Ni-rich Ni-Fe alloy nanoparticles from the SFNMO matrix under a hydrogen atmosphere. A symmetrical SOFC employing Gd0.1Ce0.9O2−δ (GDC) electrolyte and SFNMO electrodes achieved an initial maximum power density of 82 mW cm−2 in wet methane fuel at 800 °C, which represents an approximately 33% improvement over the symmetrical cell with SFMO electrode (61 mW cm−2). Remarkably, the cell maintained stable operation under constant current for 50 h in methane fuel, with the peak power density further increasing to 113 mW cm−2, demonstrating the excellent catalytic activity of the in-situ exsolved Ni-Fe nanoparticles for methane conversion.
Open Access
Commentary
28 September 2025From Crisis to Coordination: How AI Transformed Public Health Policies during COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic showed the shortcomings of traditional policy-making procedures and highlighted serious flaws in international public health institutions. Artificial intelligence (AI) became a transformative force in response to the crisis’s urgency, allowing for data-driven, flexible, and better-coordinated public health measures. This viewpoint article examines how AI improved communication, accelerated vaccine development and distribution, enhanced decision-making, and optimized healthcare delivery during the COVID-19 pandemic. These advancements collectively contributed to significant changes in public health policy. Real-time analysis of large, complex datasets, ranging from case numbers and mobility patterns to hospital capacities and disinformation trends, was made possible by AI technologies including machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP). Timely interventions like resource allocation, targeted lockdowns, and control of misinformation were made possible by this capability. AI also played a crucial role in forecasting infection trends, identifying vulnerable populations, and informing evidence-based decisions. AI-powered solutions further enhanced public involvement and cross-sector cooperation through chatbots and digital platforms delivering trustworthy health information. Additionally, AI-powered solutions enhanced public involvement and cross-sector cooperation, including the use of chatbots and digital platforms to provide trustworthy health information. AI sped up supply chain optimization and candidate screening in vaccine development, guaranteeing efficient, and quick delivery. However, ethical issues including bias, data privacy, and equity in healthcare access were also brought about by the integration of AI. This study emphasizes the need for open, inclusive, and morally sound AI governance by highlighting AI’s twin roles as a technological enabler and a tool for policy. The pandemic provides a fundamental lesson for countries preparing for future health emergencies: AI may be a key instrument in creating public health systems that are more robust, responsive, and equitable if it is applied properly.

Open Access
Article
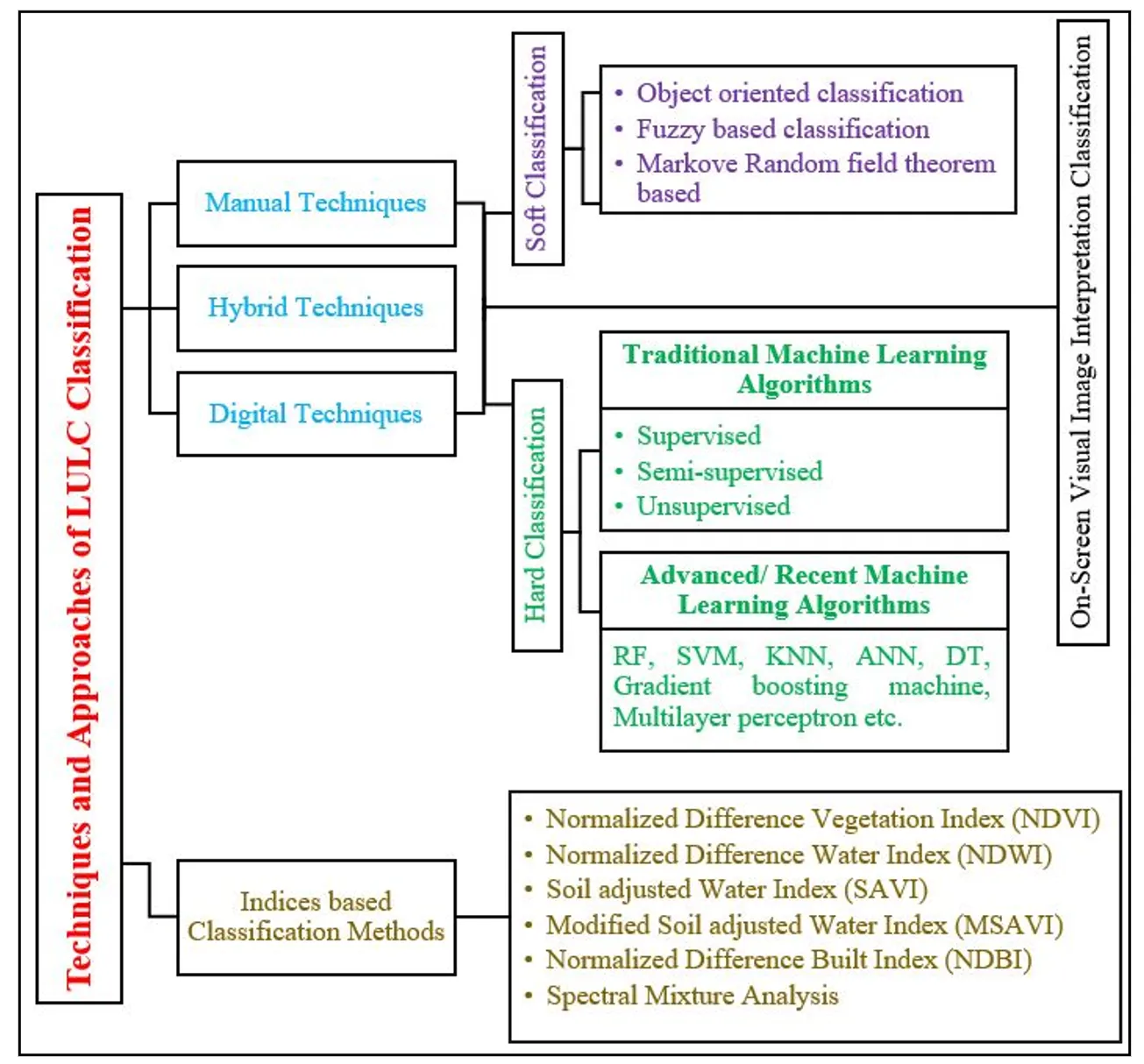
26 September 2025Land Use and Land Cover Assessment of Jalandhar, India: A Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning and Visual Interpretation
For the sustainable management of natural resources and to understand how the climate affects the landscape, accurate land use and land cover (LULC) classification is essential. Robust classification techniques and high-quality datasets are necessary for precise and effective LULC classification. The effectiveness of various combinations of satellite data and classification techniques must be carefully evaluated to help choose the optimal strategy for LULC classification, given the growing availability of satellite data, geospatial analysis tools, and classification techniques. This study focuses on the LULC classification of Jalandhar, Punjab, India, using machine learning (ML) algorithms and visual image interpretation. Sentinel-2 satellite data, with its high spatial and spectral resolution, has been utilized for feature extraction and classification. Python was employed for implementing various ML algorithms, including Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine (SVM), K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN), Gradient Boosting (GB), Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), and Decision Tree (DT), while ArcGIS was used to classify LULC using visual image interpretation and for maps preparation. Agriculture was the dominant class across all methods, with GB estimating 1774.26 sq.km, followed by plantation (268.13 sq.km) and built-up areas (171.76 sq.km). Waterbodies were mapped with high precision due to their distinct spectral features, with estimates ranging from 18.34 sq.km (GB) to 26.05 sq.km (Visual interpretation). Among all models, GB outperformed others with the highest overall accuracy (95.0%) and a kappa value of 0.94, followed by RF (94.2%), and SVM (93.8%). Visual interpretation achieved a comparative accuracy of 90.1%, though it showed limitations in distinguishing spectrally mixed classes like plantation and built-up. This study concludes that while Visual interpretation remains a useful and accessible method, especially for real-time interpretation, ML-based approaches, particularly GB and RF, offer superior accuracy and reliability. The study highlights the importance of visual interpretation for a better accurate LULC at a regional level; meanwhile, leveraging advancements in ML algorithms in a hybrid approach will enhance the accuracy in many-fold.
Open Access
Review
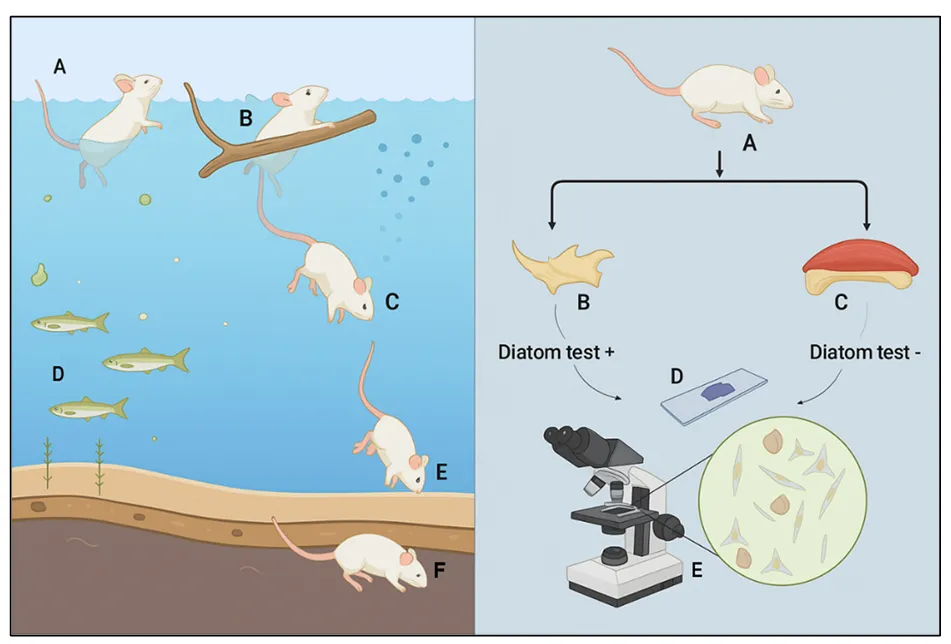
25 September 2025Forensic Diagnosis of Drowning in Animals: A Critical Review of Diagnostic Modalities and the Efficacy of the Diatom Test in Veterinary Medicine
Veterinary forensic pathology is an interdisciplinary field that critically investigates animal mortality under suspicious or unlawful circumstances. Among various causes of death, drowning remains one of the most diagnostically challenging conditions due to its pathophysiological complexity and the lack of pathognomonic post-mortem findings. Drowning in animals typically results from submersion or immersion in liquid, leading to asphyxial death with distinct physiological consequences depending on the medium, either freshwater or saltwater. The post-mortem diagnosis of drowning is complicated by factors such as environmental contamination, autolysis, and the difficulty in distinguishing ante-mortem from post-mortem immersion. While classical diagnostic indicators, such as pulmonary oedema and frothy exudate, are frequently non-specific, the diatom test remains widely utilised in forensic investigation. However, environmental confounders and inconsistent protocols limit the technique’s reliability. This review critically evaluates current diagnostic methodologies for drowning in animals, including macroscopic, microscopic, and ancillary techniques, with particular attention to the diatom test and emerging technologies. It proposes an integrated diagnostic approach to enhance diagnostic accuracy and support judicial and animal welfare outcomes.
Open Access
Correction
24 September 2025
Open Access
Article
23 September 2025Side Chain Piperidinium Functionalized AEMs with an Ethylene Oxide Spacer for Improving Ion Conductivity and Alkaline Stability
In this work, grafting alkaline stable piperidinium cations via ethylene oxide (EO) spacers onto an aryl ether-free poly(oxindole terphenylene) backbone was adopted as a strategy for designing self-aggregating side chain AEMs with optimized alkaline stability. Aryl ether-free poly(oxindole terphenylene) backbones were synthesized via superacid-catalyzed step-growth polycondensation and were subsequently functionalized with either piperidinium containing hydrophilic, dipolar EO or hydrophobic alkyl spacer, aiming to explore the effect of side chain-engineering on conductivity and alkaline stability of the resulting AEMs. The AEM membrane containing dipolar ethylene oxide spacer, despite its lower ion exchange capacity (IEC), exhibited a more pronounced microphase separated morphology as evidenced by TEM, and higher ionic conductivity (reaching up to 30.5 mS cm−1 at 80 °C) compared to the hydrophobic alkyl spacer-containing AEM membrane. This was attributed to its higher water uptake stemming from the EO hydrophilic nature and the formation of interconnected ion-conducting channels due to piperidinium–EO interactions. Additionally, the hydrophilic nature of the ethylene oxide groups endowed the membrane with enhanced alkaline stability, preserving its mechanical integrity and retaining 71.5% of its initial conductivity after 3 weeks of immersion in 2 M KOH at 80 °C. In contrast, the AEM with an alkyl spacer experienced severe degradation under the same conditions. These results suggest that incorporating flexible alkoxy-containing spacers onto an aryl ether-free backbone is a promising and simple route for fabricating mechanically and chemically robust AEMs with sufficient conductivity.

Open Access
Article
23 September 2025Promoting Sustainable Development through Community Education on Flood- and Storm-Resistant Architecture
Pakistan is experiencing climate-induced disasters such as floods and storms with an increased frequency and intensity every single year. This study aims to explore the integration of resilient architecture into environmental education as a pathway toward sustainable development and disaster risk reduction. The research examines current levels of understanding regarding flood- and storm-resistant building practices and identifies key barriers to their adoption in high-risk regions of Pakistan. The study used a mixed-methods approach by administering surveys. These surveys were administered to 500 community members in different cities of Sindh and Punjab. The study also incorporated two in-depth case studies: the Heritage Foundation’s low-cost housing initiative in Makli, Sindh, and the Aga Khan Agency for Habitat’s Safe Housing Program in Chitral, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. These cases provide valuable insights into effective, culturally appropriate, and scalable models of resilient construction in Pakistan. Findings of the present study reveal that public awareness of resilient architecture is below a satisfactory level, with common misconceptions. Challenges, including high costs, lack of technical knowledge, and minimal government support, were identified as significant obstacles. Despite these issues, communities showed strong interest in learning about safer building practices when exposed to practical examples and local success stories. The study recommends integrating resilient construction education into community outreach, school curricula, and builder training programs. It also advocates for greater government involvement, financial incentives, and replication of proven models to foster widespread adoption of resilient architecture for long-term sustainability.
