Found 469 results
Open Access
Review
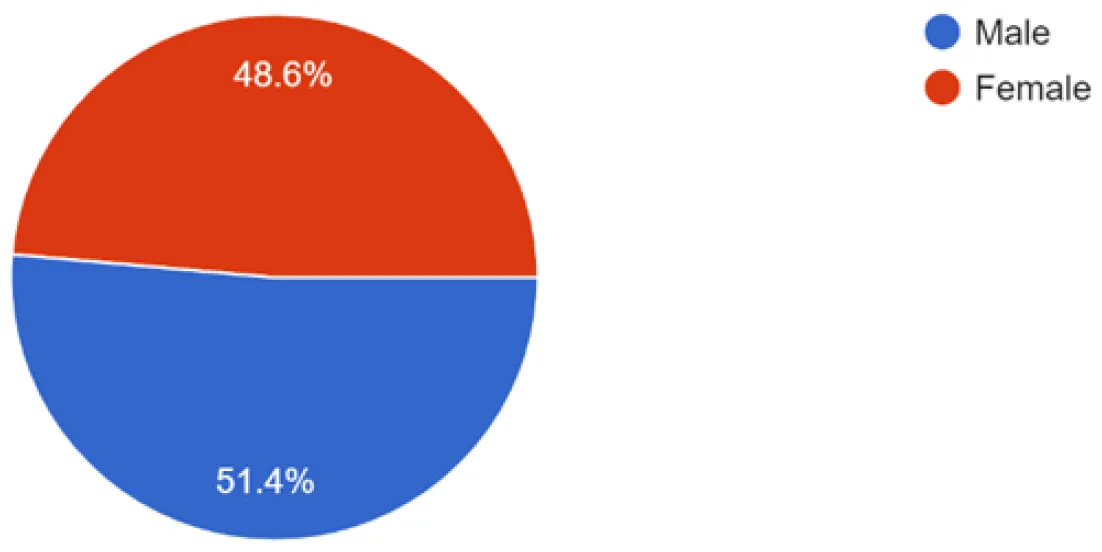
23 October 2024The Notch3 Pathway in Organ Fibrosis
Fibrosis occurs in many organs, including the lung, heart, skin, liver or kidney, and is characterized by progressive tissue scarring in response to repetitive or chronic non-resolving injury, ultimately leading to organ failure and death. It is, in fact, a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, being estimated to account for 45% of deaths in the world. Despite this fact, little progress has been made therapeutically, and fibrosis remains a major clinical and therapeutic challenge. Although significant advances in our understanding of cellular and molecular mechanisms driving tissue fibrosis have been made, the lack of an efficient treatment reflects the limited insight into the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the initiation and progression of the fibrotic process. Thus, there is an urgent need for better understanding of tissue fibrosis and repair mechanisms that later lead to the development of new therapeutic approaches to fight fibrosis. The Notch pathway is a highly conserved signaling pathway that has been linked to tissue fibrosis in many organs and promises to open new therapeutic opportunities. This manuscript reviews the relevance of Notch signaling in the development and progression of tissue fibrosis in several organs with a special focus on the Notch3 pathway due to the unique features of this receptor.
Open Access
Review
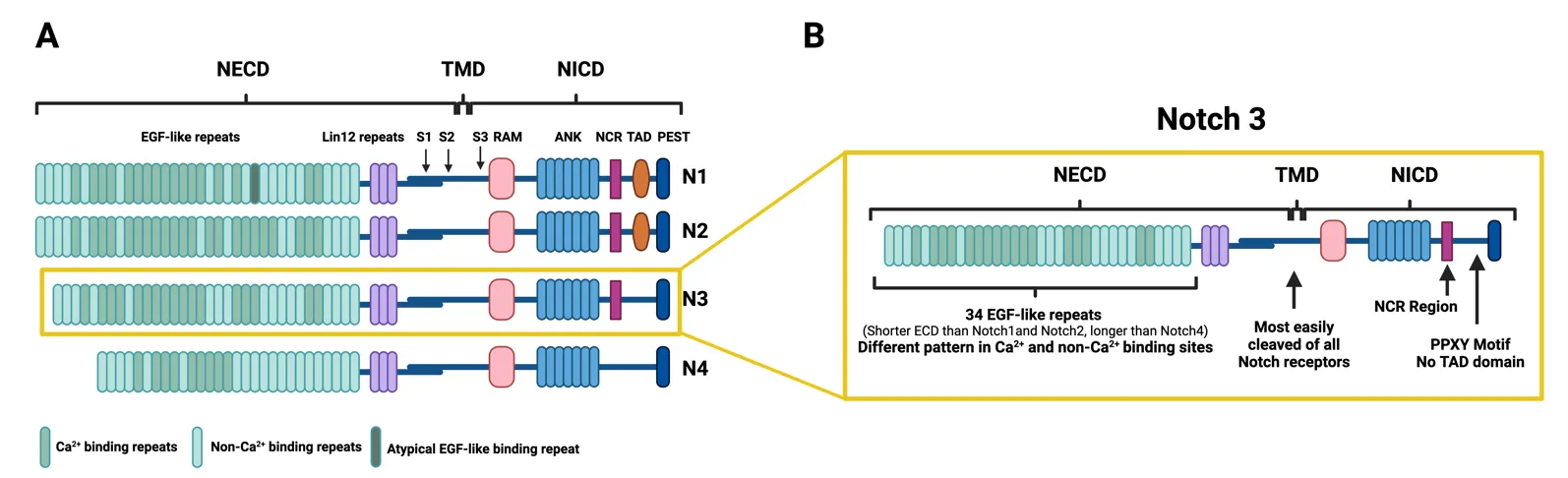
22 October 2024Engineering of Cu-Based Quaternary Sulfide Nanomaterials for Photocatalytic Applications
Semiconductor nanomaterials have been widely used as light-responsive photocatalysts for solar-to-fuel conversion over the past decade. However, the wide band gap of the most reported photocatalysts stems from light absorption in the visible region and results in low solar conversion efficiency. Therefore, it is necessary to develop new semiconductor nanomaterials with high absorption coefficients over the visible region as photocatalysts. The most promising candidates include Cu-based quaternary sulfide nanomaterials (CQSNs), such as Cu-II-III-S (e.g., CuZnInS, CuZnGaS), Cu-II-IV-S (e.g., Cu2ZnSnS4, Cu2ZnGeS4), and I-III-IV-S (e.g., CuInSnS4, Cu3GaSnS5). This review provides a comprehensive overview of the recent progress in developing CQSNs for various photocatalytic applications. Firstly, we present an overview of the synthesis of CQSNs with precise control over crystal phase, composition, size, and shape using solution-based methods. Then, the enhancement of photocatalytic performance was presented via the engineering of CQSNs, which included surface engineering, elemental doping, cocatalyst loading, vacancy engineering, and interface engineering. Subsequently, we further introduce the photocatalytic applications in the fields of photocatalytic and photoelectrochemical hydrogen conversion, CO2 reduction, organic synthesis, and pollutant degradation. Lastly, this review ends with views on the current challenges and opportunities of CQSNs in future studies.
Open Access
Article
18 October 2024Multi-Objective Distributed Real-Time Trajectory Planning for Gliding Aircraft Cluster
A new combat strategy that enables coordinated operations of gliding aircraft clusters for multi-target strikes imposes higher demands on the coordination, real-time responsiveness, and strike accuracy of gliding aircraft clusters. Due to the high speed and large inertia characteristics of gliding aircraft, traditional trajectory planning methods often face challenges such as long computation times and difficulty in responding to dynamic environments in real-time when dealing with large-scale gliding aircraft clusters. This paper proposes a distributed cooperative trajectory planning method for multi-target strikes by gliding aircraft clusters to address this issue. By introducing a multi-objective distributed real-time trajectory planning approach based on Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradients (MADDPG), the gliding aircraft execute distributed cooperative trajectory planning based on the trained model. Due to its robust real-time performance, the gliding aircraft do not need to recalculate trajectories for different initial positions of the cluster. Simulation results show that the average error between the gliding aircraft cluster and the target point is 2.1 km, with a minimum error of 0.06 km and a hit rate of 96.6%, verifying the significant advantages of this method in real-time planning capability and strike accuracy.

Open Access
Article
15 October 2024Stable Boundaries of Phragmites australis Marsh Development after Peat Mining in a Northern Japan Bog
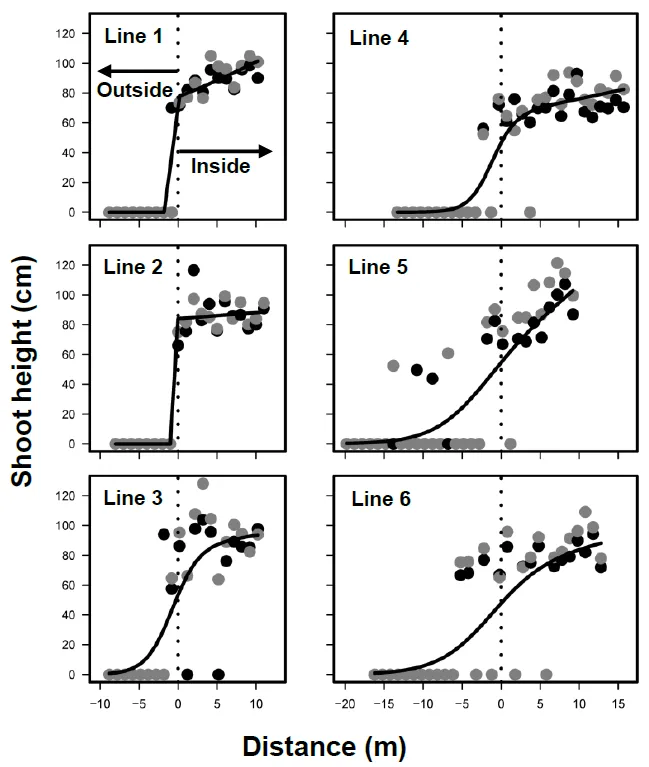
Since Phragmites australis often develop marshes soon after human disturbances, such as peat mining in bogs, the establishment patterns should be clarified for restoration purposes. The inside and outside boundaries of P. australis marshes were investigated following peat mining in Sarobetsu mire, northern Japan, in 2016 and 2017. The boundaries of marshes did not move during the two years, due mostly to the slow expansion of shoots. Various vegetation types developed outside of the marsh. P. australis coexisted with neither ericaceous nor carnivorous plants, which favor Sphagnum bogs. The succession in the marsh did not progress the original bogs. P. australis dispersed seeds mostly within the marshes, suggesting limited dispersal, and developed transient seed bank. Therefore, seed dispersal (sexual reproduction) and rhizomes (vegetative reproduction) contributed to population maintenance rather than population enlargement during the studied period. Peat moisture was higher in the marsh, whereas photosynthetic active radiation was lower. Water levels did not differ between inside and outside the marshes. Chemical properties in peat water were not different between inside and outside the marshes. Therefore, water chemistry and levels did not adequately explain the marsh development. These results suggest that, for wetland restoration, environmental manipulation is ineffective in reducing P. australis and unpredictable or stochastic events alter the dynamics of P. australis marshes.
Open Access
Review
14 October 2024Sex and Gender Differences in Liver Fibrosis: Pathomechanisms and Clinical Outcomes
The accumulation of extracellular matrix proteins is the hallmark of liver fibrosis associated with all chronic liver disease (CLD) types. Liver fibrosis results from repeated bouts of liver injury, which trigger the wound-healing response, ultimately disrupting the normal hepatic architecture. Over time, fibrosis can progress to cirrhosis, portal hypertension, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma, worsening patient outcomes. Biological modifiers, such as sex and socio-cultural constructs like gender, influence the development of liver fibrosis through various genetic, hormonal, immunological, metabolic, and lifestyle-related factors, including alcohol consumption, diet, sedentary behavior, and hormonal therapy. Moreover, liver fibrosis is significantly modulated by age, reproductive status, and the etiology of CLD. This review aims to summarize the most well-characterized pathomechanisms underlying sex and gender differences in hepatic fibrogenesis as well as liver-related complications (cirrhosis, portal hypertension, hepatic encephalopathy, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma) and extra-hepatic correlates of liver fibrosis (sarcopenia, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and dementia) across various types of CLD due to viral-related, autoimmune, drug-induced and metabolic etiologies. Understanding these disease modifiers and their mechanisms is crucial for developing innovative treatment strategies and precision medicine approaches in this field.

Open Access
Review
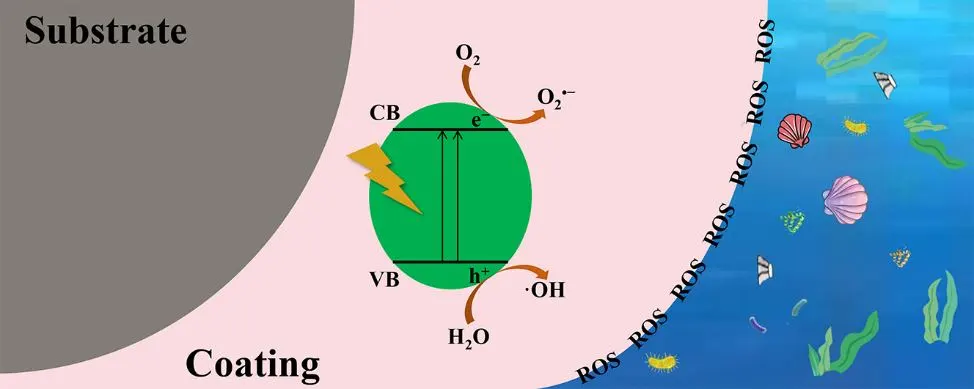
14 October 2024Photocatalytic Antifouling Coating: From Fundamentals to Applications
With the rapid development of shipping industry, marine vessels frequently suffer from biofouling caused by marine organisms, making the effective prevention of marine biofouling a critical issue. Traditional antifouling coatings, which utilize toxic and harmful substances, pose significant risks to marine ecosystems. Therefore, the development of environmentally sustainable antifouling coatings has become imperative. Photocatalytic antifouling coatings, as an eco-friendly alternative, present a promising solution to these economic, energy, and ecological challenges. This review compares the environmental benefits of photocatalytic antifouling coatings to traditional ones, highlighting the underlying mechanisms of marine biofouling. Additionally, it explores the preparation techniques employed in photocatalytic antifoulant, analyzing the advantages, disadvantages, and potential modifications for photocatalytic coatings. Based on these insights, the future development of photocatalytic antifouling coatings is discussed, aiming to provide valuable references for the exploration of more efficient, broad-spectrum, energy-saving, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective marine antifouling technologies.
Open Access
Article
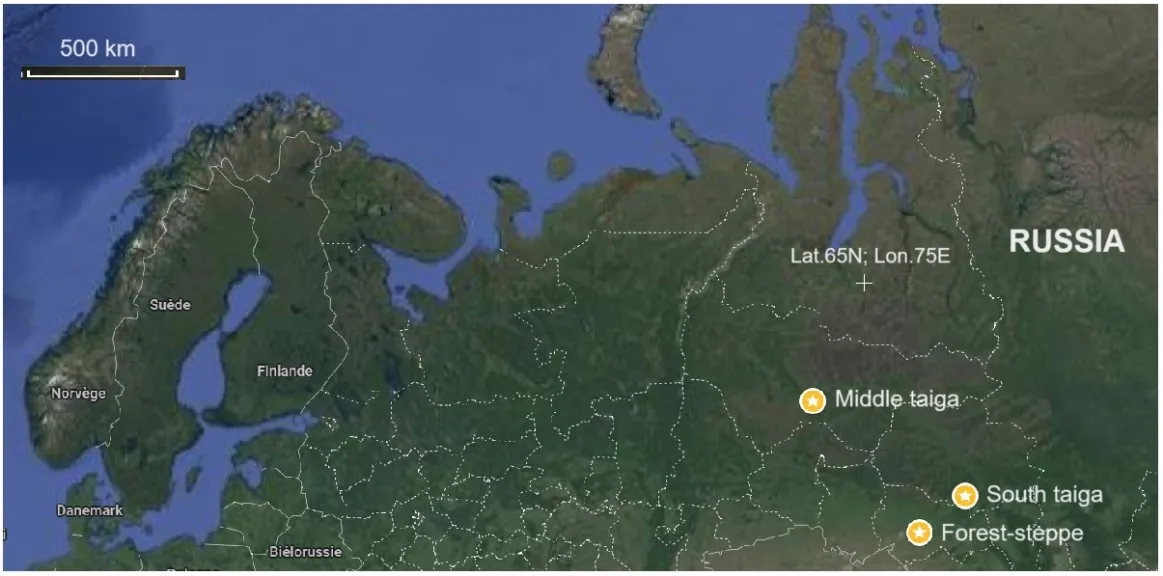
12 October 2024Production and Destruction of Plant Organic Matter in Bog Ecosystems in the South of Western Siberia
There are still many gaps in studies of the carbon cycle in northern ecosystems. It is challenging also in the context of climate change. This new study focuses on providing the state of the art data on the dynamics of plant organic matter, namely, the live plant biomass (phytomass), the dead biomass (mortmass), the Net Primary Production (NPP), as well as the rate of decomposition of plant organic matter of the major plant species, contributed to peat deposits. The study was conducted via direct in–situ measurements of different fractions of plant organic matter at a few test sites of oligotrophic pine–dwarf shrub–Sphagnum bogs at a wide geographic gradient (from the middle taiga to the forest-steppe regions in Western Siberia) based on an original methodology of measurements developed by the authors. In general, the five groups of plant species were distinguished in terms of productivity and decomposition rates. The study revealed a strong correlation between the net primary production (NPP) and the rate of decomposition of plant organic matter in pristine northern peatlands: an increase in productivity (NPPs) was basically leading to an increase in rates of decomposition in all plant materials collected in bog ecosystems. The study contributes to a global understanding of patterns and main drivers related to basic set of carbon cycle components in the northern wetland (peatland) ecosystems, their diversity and their spatial distribution.
Open Access
Perspective
10 October 2024Conceptual Design of Aerostat-Based Autonomous Docking and Battery Swapping System for Extended Airborne Operation
In response to the ever-growing global demand for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, efficient battery solutions have become vital. This paper proposes a design and concept of an Autonomous Mid Air Battery Swapping System for Vertical Take-Off and Landing Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. The proposed design integrates Aerial Mechatronics, Lighter than Air Systems, and Digital Modelling by leveraging the innovative concept of aerostats for battery swapping. This adaptive and effective technology paves the way for the next generation of autonomous Vertical Take-Off and Landing, ensuring a longer flight time and range. Modern-day technologies have empowered Unmanned Aerial Vehicles to operate autonomously and be remotely controlled, expanding their utility across diverse industries. The enhanced Vertical Take-Off and Landing capabilities include the ability to dock on an aerostat-mounted system, facilitating seamless battery swapping without human intervention and ensuring extended flight duration and operational flexibility. These advancements promise to broaden the applications of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles across various industries.

Open Access
Review
30 September 2024Ecological Civilizations—A Development Narrative for the Global South?
We explore possibilities for the ecological civilization imaginary of China to become a sustainable development narrative shared by a growing number of GS nations. We first highlight the influence GS countries had on the evolution of the concept of sustainable development. GS nations’ interest in retaining economic development options, including energy and materials needed for industrialization and economic expansion, will increasingly contradict global environmentalist narratives of the latter half of the 20th century. The adaptation of GS nations to previously untested energy and material futures will depend on experimentation and learning from initiatives primarily designed and implemented by GS governments at the national, provincial, and local levels. If China succeeds in demonstrating practical examples of ecological civilization construction, it will stimulate other GS countries to learn and adapt lessons to suit their own needs. Multi-country arrangements that China has created could serve as forums to refine the ecological civilization narrative as a development alternative to the dualist conservation vs development thinking and practice of the latter half of the 20th century.
Open Access
Article
30 September 2024Synthetic Biology in Nigeria: The Level of Awareness amongst Stakeholders
Synthetic biology, an emerging field at the intersection of biotechnology and engineering, has seen a global surge in application and awareness, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its safe potentials to drive the bio-economy. This study aimed to assess the awareness and perceptions of synthetic biology among Nigerian biosciences stakeholders, including researchers, academicians, policymakers and students. The study employed a purposive online survey targeting diverse bioscience individuals and groups across Nigeria’s six geopolitical zones. The study received 107 responses from balanced gender representation with majority within the age group of 31–45 years old. The findings revealed a significant knowledge gap, with only 27.1% of respondents familiar with synthetic biology and 23.4% entirely unaware of it. Most respondents associated synthetic biology with biotechnology or genetic engineering and identified its applications to be in agriculture, medicine, environmental sustainability and research. Despite recognizing its benefits, many expressed concerns about safety, ethics, and regulation; notably, 43.9% of the respondents had concerns about synthetic biology with primary focus on safety and ethical implications. As regards the regulation of synthetic biology, the study showed that 80.4% of the respondents supported the need for synthetic biology regulation with few of the respondents (16.8%) aware of existing agency mandated to regulate synthetic biology. The respondents provided valuable insights into the various ways synthetic biology can be advanced in Nigeria which include increased awareness and capacity building, engagement through social media platforms, integration into education curricula and increased funding and investment in the research. The overall sentiment towards synthetic biology was positive, with 81.3% supporting its practice and 76.6% recognizing its positive global impact. However, a significant portion of respondents remained undecided. This study concludes that there is substantial gap in the knowledge of synthetic biology among bioscience stakeholders in Nigeria and the need for a heightened advocacy including continuous conferences and symposiums for the Nigeria bioscience community on the global potentials, concerns and regulation of synthetic biology. This will foster the acceptance of safe and responsible synthetic biology in Nigeria, thereby contributing to the broader national bio-economy development.