Found 301 results
Open Access
Article
13 March 2023Reduced Climate Impacts of Dairy Sludge Management by Introducing Hydrothermal Carbonization
Dairies which produce cheese and milk products can, however, produce large volumes of wastewater that require treatment, usually via activated sludge treatment. Disposal of the resulting activated sludge to land is viewed favorably as the sludge is rich in phosphorus (P) and nitrogen (N) and enables nutrient recycling. Nonetheless, sludge management can significantly influence the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to the atmosphere. This manuscript has modelled the GHG emissions arising from two sludge management strategies currently adopted by Danish dairies whereby: (i) sludge is stored and later applied to fields; or (ii) sludge is treated by anaerobic digestion (AD), stored, and the digestate will later be applied to fields. This is compared to (iii) an alternative sludge management strategy with treatment by Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC). HTC is a technologically simple sludge treatment that could lower the cost for dewatering dairy sludge, forming a biochar-like material known as hydrochar. The produced hydrochar can be applied to the land for the purpose of carbon sequestration, P and N recycling. Our calculations indicate that GHG balances of HTC sludge management can result in a net carbon sequestration of 63 kg CO2eq per ton sludge, as opposed to net emissions of 420 and 156 kg CO2eq per ton sludge for strategies (i) and (ii), therefore offering significant reductions GHG emissions for the dairy sector.
Open Access
Perspective
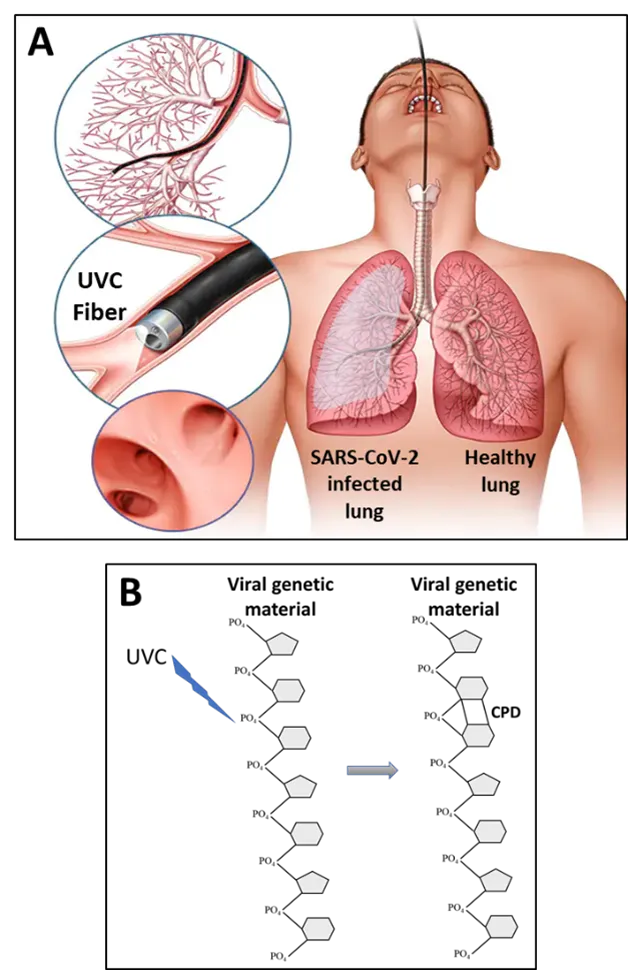
07 March 2023Pulsed Ultraviolet C as a Potential Treatment for COVID-19
Currently, low dose radiotherapy (LDRT) is being tested for treating life-threatening pneumonia in COVID-19 patients. Despite the debates over the clinical use of LDRT, some clinical trials have been completed, and most are still ongoing. Ultraviolet C (UVC) irradiation has been proven to be highly efficient in inactivating the coronaviruses, yet is considerably safer than LDRT. This makes UVC an excellent candidate for treating COVID-19 infection, especially in case of severe pneumonia as well as the post COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis. However, the major challenge in using UVC is its delivery to the lungs, the target organ of COVID-19, due to its low penetrability through biological tissues. We propose to overcome this challenge (i) by using pulsed UVC technologies which dramatically increase the penetrability of UVC through matter, and (ii) by integrating the pulsed UVC technologies into a laser bronchoscope, thus allowing UVC irradiation to reach deeper into the lungs. Although the exact characteristics of such a treatment should yet to be experimentally defined, this approach might be much safer and not less efficient than LDRT.
Open Access
Communication
03 March 2023Evaluating Different UAS Flight Methods for 3D Model Generation and Printing of a Tornado Destroyed Cultural Heritage: Caddo House in Texas
In recent years, the use of Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) to obtain imagery for photogrammetry has become commonplace. Using these data to develop 3D products has also grown significantly in both research and commercial applications. This study aims to find a relatively simple and low cost UAS flight method as a means to obtain data to produce a 3D model suitable for 3D printing. The study subject chosen to assess different flight methods was the Caddo House at Caddo Mounds State Historical Site located near Alto, Cherokee County, Texas, USA. To collect images for analysis, a DJI Phantom 4 Pro UAS was used with Pix4DCapture mission control app. Two main missions were carried out, one being a pre-defined double-grid flight, and the other being an orbital free-flight method. The findings of this study indicate that if the goal is to create a true-to-life 3D model of an object using UAS, the best method would be a curated orbital free-flight method. If there is time constraint and the subject is sufficiently large and not considerably irregular, a double-grid mission with sufficient forward and side overlap can produce desirable results, but with a slight loss of fine details. The 3D model developed from the curated orbital flight method was successfully printed with a customer grade FDM 3D printer.

Open Access
Article
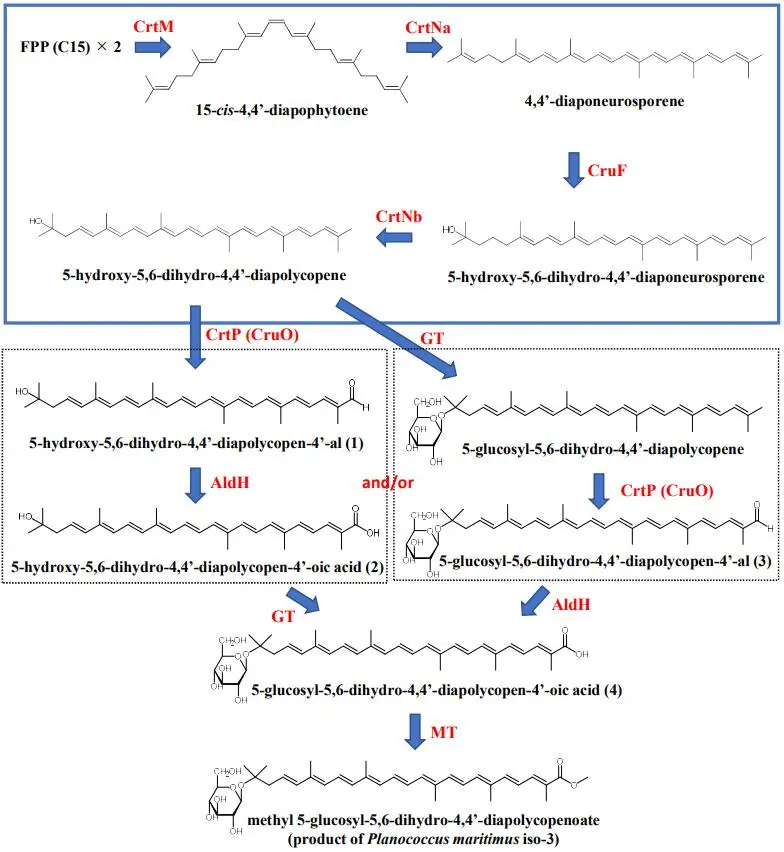
07 February 2023Production of Highly Modified C30-carotenoids with Singlet Oxygen-quenching Activities, 5-glucosyl-5,6-dihydro-4,4’-diapolycopen-4’-oic Acid, and Its Three Intermediates Using Genes from Planococcus maritimus Strain iso-3
Planococcus maritimus strain iso-3 was previously isolated from intertidal sediment in the North Sea and was found to produce a highly modified C30-carotenoid, methyl-5-glucosyl-5,6-dihydro-4,4’-diapolycopenoate, as the final product. In this study, we analyzed the function of the carotenoid terminal oxidase crtP (renamed cruO) and aldehyde dehydrogenase aldH genes in P. maritimus strain iso-3 and elucidated the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway for this strain at the gene level. We produced four novel C30-carotenoids with potent singlet oxygen-quenching activities, 5-glucosyl-5,6-dihydro-4,4’-diapolycopen-4’-oic acid and its three intermediates, which were obtained using E. coli cells carrying the cruO (and aldH) gene(s) in addition to the known P. maritimus carotenogenic genes.
Open Access
Article
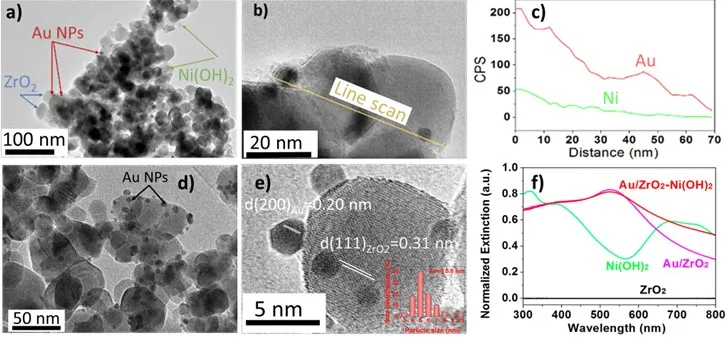
07 February 2023Plasmon Enhanced Nickel(II) Catalyst for Photocatalytic Lignin Model Cleavage
Photocatalytic-induced cleaving of the ether C–O bond in model lignin compounds was studied with a closely-coupled compo-site material consisting of Ni(OH)2 and gold nanoparticles (NPs) on a zirconia support (Au/ZrO2–Ni(OH)2). The three important ether bond types consisting of α-O-4, β-O-4, and 4-O-5 linkages can all be cleaved using this catalyst at reaction temperatures 40, 85 and 95 °C when under low-flux visible light irradiation. The Au NPs action as a light-harvesting antenna provided light-generated hot electrons that reduced Ni2+ to Ni0. The Ni0 was the active catalytic site where reductive cleavage of ether C–O bonds occurred while it was oxidized to Ni2+ to complete the catalysis cycle. The plasmonic antenna system with supported Ni(OH)2 exhibited better ability for the catalytic reductive ether cleavages under visible light irradiation compared to photocata-lysts of Au NPs and Ni2+ ions immobilized on alumina fibers.
Open Access
Article
30 January 2023Metal-Free Lewis Pair Catalysts for a One-Pot Terpolymerization of Propylene Oxide, ʟ-Lactide and CO2
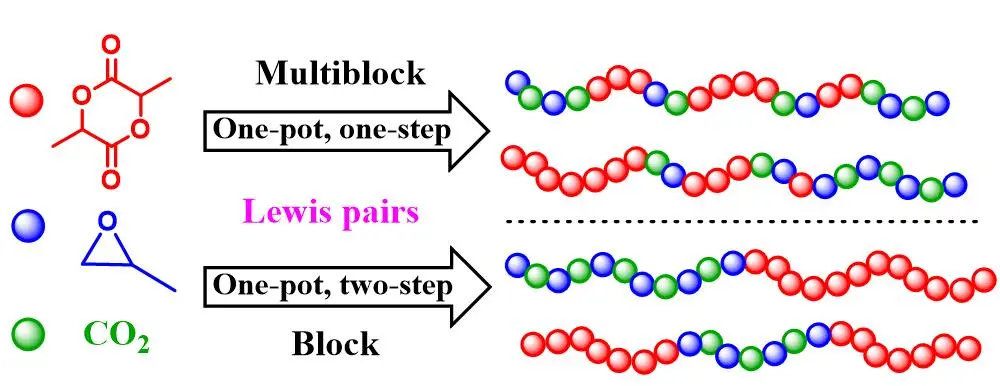
Multiblock and di-/tri-block copolymers are successfully synthesized for the first time via the metal-free terpolymerization of propylene oxide (PO), ʟ-lactide (LA) and CO2 in one-pot/one-step and one-pot/two-step protocols respectively. Firstly, triethyl borane (TEB) and bis(triphenylphosphine)iminium chloride (PPNCl) Lewis pair is employed in the ring-opening polymerization of LA, wherein the catalytic efficiency is significantly correlated to the TEB/PPNCl feed ratio. Next, a series of TEB/base pairs are selected to synthesize the PO/LA/CO2 terpolymer (PPCLA) in one-pot/one-step strategy. In PPCLA synthesis, LA exhibits the fastest reaction rate but severe transesterification is almost unavoidable, resulting in low molecular weight products. In order to prepare high-molecular-weight terpolymers, a one-pot/two-step methodology has to be applied. By this method, the copolymerization of PO/CO2 proceeds first to form poly(propylene carbonate) (PPC) macroinitiators, which triggers the polymerization of LA to polylactide (PLA), leading to PLA-PPC or PLA-PPC-PLA block copolymers. The synthesized PLA-PPC-PLA block copolymers display improved thermal stability compared with PPC.
Open Access
Article
28 January 2023Current Challenges to the Sustainable Development of Rural Communities in Russia's Central Chernozem Region
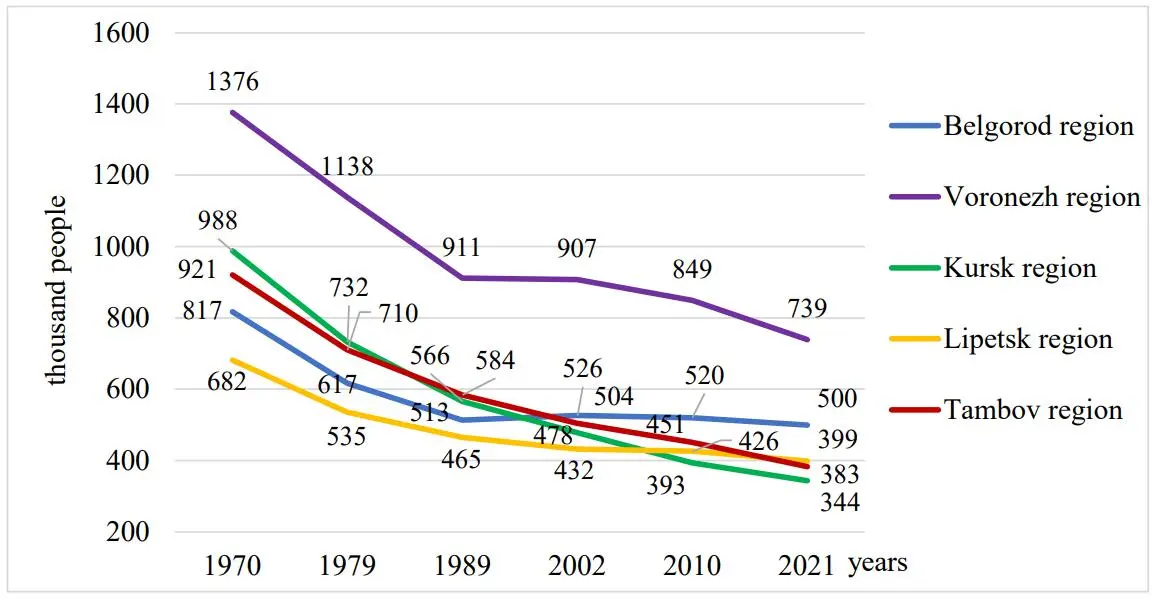
The rural community system in the Central Chernozem Economic Region in Russia is undergoing a radical transformation under the interrelated influence of fundamental factors that have rendered the development of many communities unsustainable. This paper analyses the role of urbanisation processes in population changes and transformation of rural community systems in the region; determines the level of horizontal mobility among the rural population, as well as its impact on settlement evolution; assesses the share of small and extremely small communities in settlement composition; and outlines these communities’ future development prospects. The authors believe that the socio-demographic “desertification” of peripheral municipalities can pose challenges to rural development: a shortage of labour resources, changes in population quality, and problems of innovation diffusion. The study recommends improving the comfort of the living environment and accelerating the technical re-equipment and automation of agricultural production.
Open Access
Article
22 December 2022Image Fusion Capability from Different Cameras for UAV in Cultural Heritage Applications
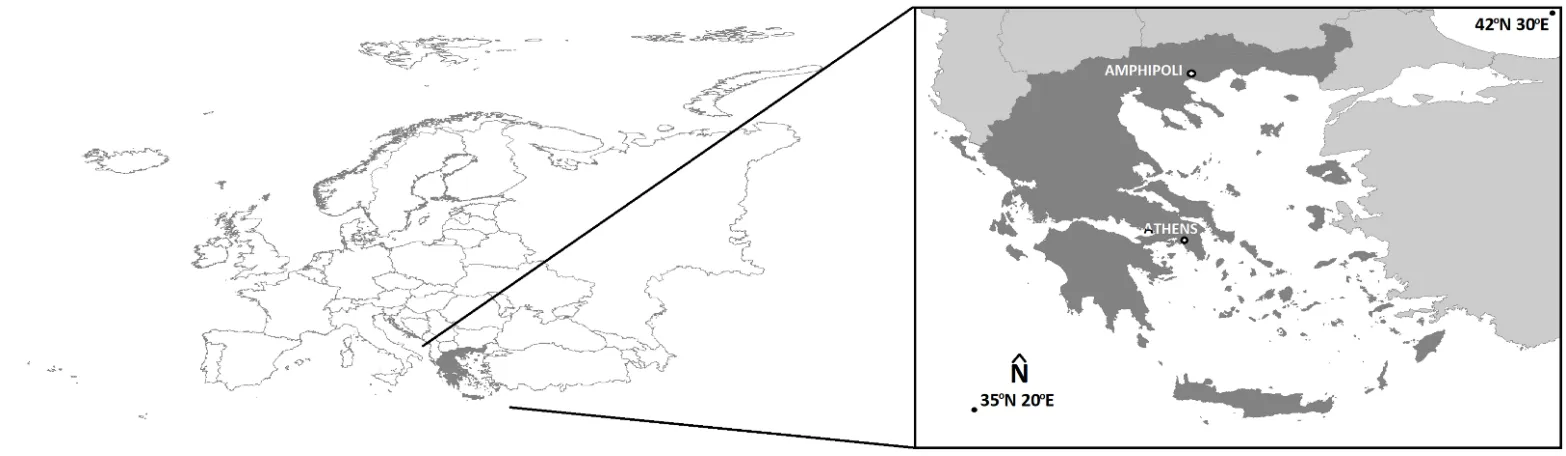
In this paper, image fusion is performed by utilizing images derived from different cameras for the unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). By producing the fused image, the spatial resolution of the multispectral (MS) image is improved on the one hand and the classification accuracy on the other hand. First, however, the horizontal and vertical accuracy of the generated products, orthophoto mosaics, and digital surface models, is determined using checkpoints that do not participate in the processing of the image blocks. Also, the changes of these accuracies with a 50% increase (or decrease) of the UAV's flight height are determined. The study area is the Early Christian Basilica C and the flanking Roman buildings, at the archaeological site of Amphipolis (Eastern Macedonia, Greece).
Open Access
Editorial
31 October 2022
Open Access
Editorial
25 October 2022