Found 469 results
Open Access
Article
18 November 2024Developing a Climate Litigation Framework: China’s Contribution to International Environmental Law
Although “climate litigation” is not an indigenous term in China, localizing it is essential to support the development of an independent environmental legal knowledge system in China. Rooted in China’s judicial tradition, which emphasizes substantive rationality, traditional legal theories have primarily focused on environmental law. However, the contemporary practices in the rule of law have created an unclear trajectory for climate litigation. Research in this area has long been trapped in a paradigm that relies on lawsuits for ecological environmental damage compensation and environmental public interest litigation, leading to a significant disconnect between theoretical framworks and practical application. With the advancement of the "dual carbon" strategic goals—carbon peaking and carbon neutrality—it has become imperative to redefine the concept of climate litigation within the Chinese context. We need to establish a theoretical framework that aligns with the “dual carbon” objectives while providing theoretical and institutional support for climate litigation, ultimately contributing to the international discourse on climate justice. Additionally, Hong Kong’s proactive climate governance and robust ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices provide valuable insights for developing comprehensive climate litigation mechanisms. Based on this analysis, we propose concrete plans for building a climate litigation system in China, establishing a preventive relief system and a multi-source legal framework at the substantive level and developing climate judicial mechanisms for mitigation and adaptation at the procedural level.

Open Access
Article
15 November 2024Long-Term Change in Human Impact and Environmental Perceptions: A 40-Year Case Study of an Environment-Focused Non-Governmental Organization
Non-governmental environmental organizations are diverse in scope, goals and doctrine, ranging from natural history societies to green parties. It was from the 1960s that they became widespread worldwide. To characterize a French NGO and assess the changing trends in its objectives over time, we have qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed the journal it has published without interruption for 40 years: 140 issues, 4500 pages, and almost 250 keywords. The initial scope of the NGO was focused on ‘humans and nature’: we do not protect the environment against humans but with humans, i.e., at the same time as humans, which is the very definition of sustainable development, with its three-fold focus: nature, economy and social justice. The primary issues included recognizing water as a shared resource for all people, promoting sustainable agriculture and transportation (such as railways), advancing peace efforts, and protecting nature. This approach emphasizes a rigorous, evolving scientific perspective that goes beyond a focus on a few charismatic species (‘deluxe biodiversity’), embracing biodiversity in its entirety. Over time, the discourse has kept track of the shifting priorities of most Green parties: less and less focused on nature (e.g., forests, ecosystems) and more and more on social issues (e.g., health, housing, transport). However, it differs in not focusing on the idées fixes of the Greens (e.g., rejection of civil nuclear power, GMOs).

Open Access
Article
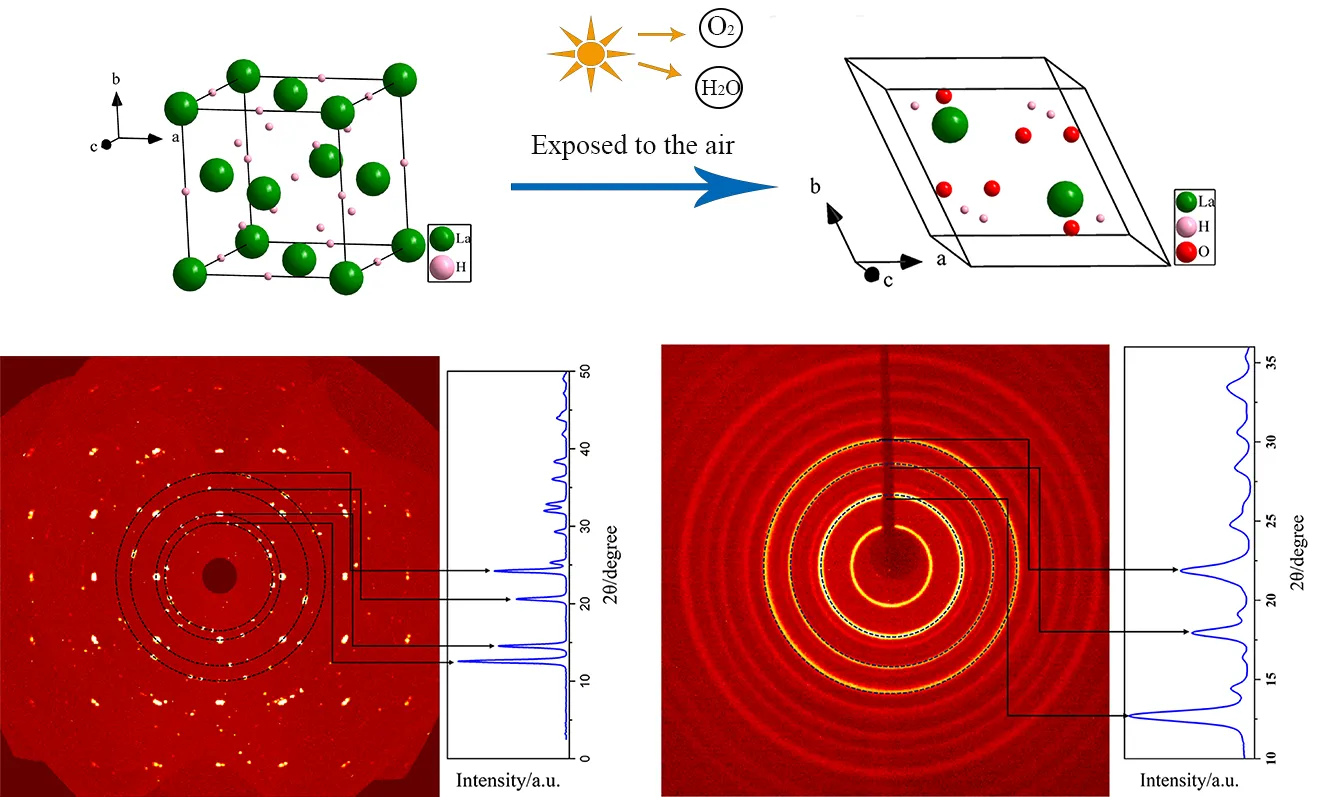
14 November 2024The Discovering of Rapid Formation La(OH)3 from LaH3
It was found that the single crystal of LaH3 specimen with $${Fm\overline{3}m}$$ (No.225) will decompose into powders within 24 h, which is later characterized to be La(OH)3 by single crystal X-ray diffraction (SXRD) measurements. The discovery motivates the examination of three possible transition paths by comparing formation enthalpy with first-principles calculations and employing a custom- designed hydrogen detection setup. Furthermore, the most suitable adsorption position of O2 molecules on the (111) surfaces has been investigated by comparing the adsorption enthalpy from different candidate positions by utilizing first-principles calculations, implying the pivotal role of O2 molecules played in the rapid formation of La(OH)3 along the optimal transition path.
Open Access
Article
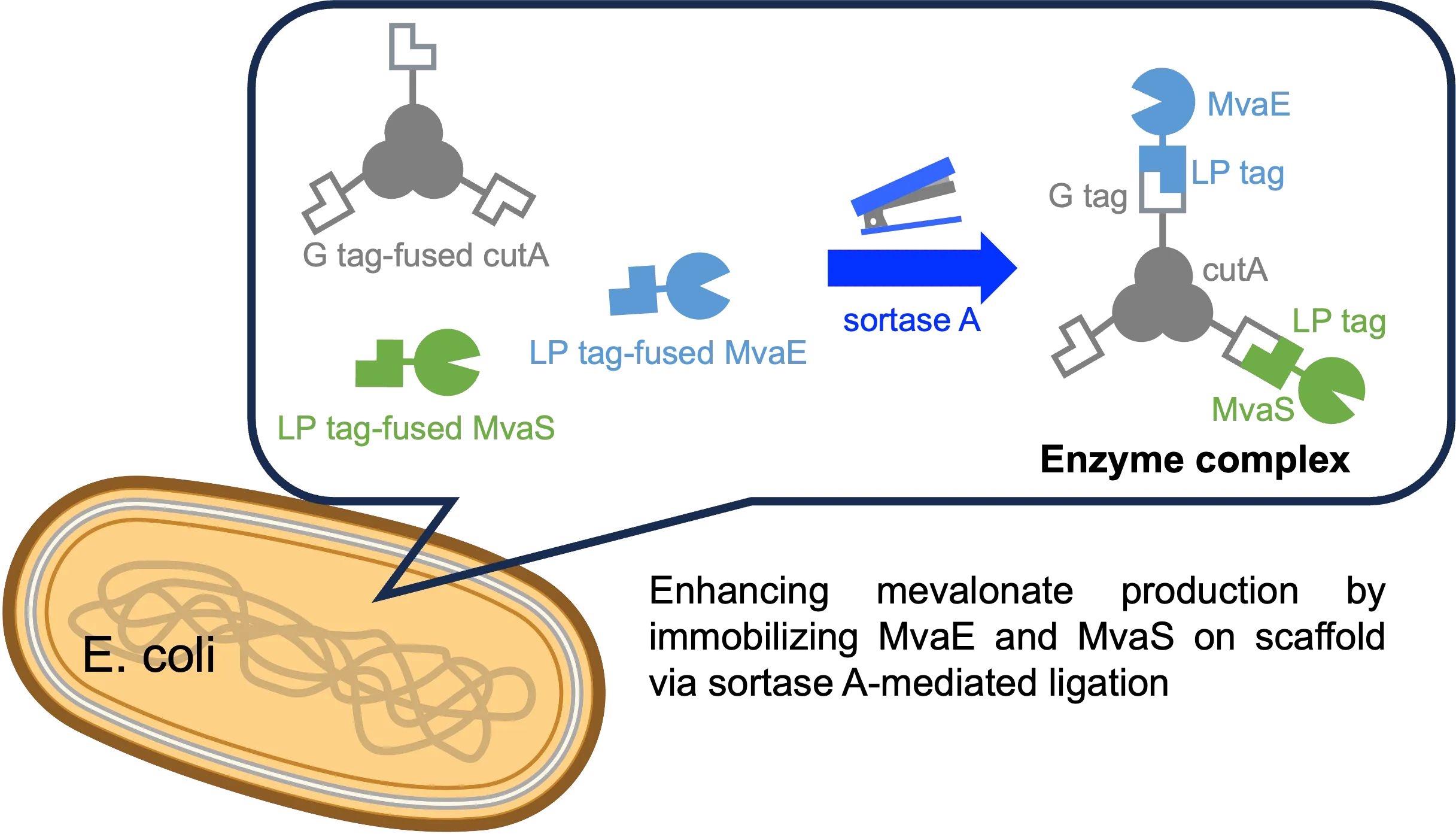
14 November 2024Sortase A-Mediated Enzyme Assembly on Multimeric Protein for Improving Mevalonate Production
Microorganisms have been extensively studied for their production of valuable chemicals. However, conventional gene fusion approaches often lack versatility and can result in enzyme inactivation. This study explored an alternative strategy for inducing metabolic channeling through sortase A-mediated ligation of metabolic enzymes. Sortase A recognizes specific amino acid sequences and selectively conjugates proteins at these sites. We focused on mevalonate production as a proof-of-concept to enhance the yield by assembling metabolic enzymes on a protein scaffold using sortase A. Although metabolic enzyme complexes were successfully formed using streptavidin as a scaffold, production did not improve. The use of CutA as a scaffold led to a 1.32-fold increase in production compared with that of the strain without the scaffold, demonstrating the efficacy of CutA in mevalonate production. These findings suggest that using sortase A to assemble metabolic enzymes onto a scaffold can effectively enhance microbial bioproduction.
Open Access
Article
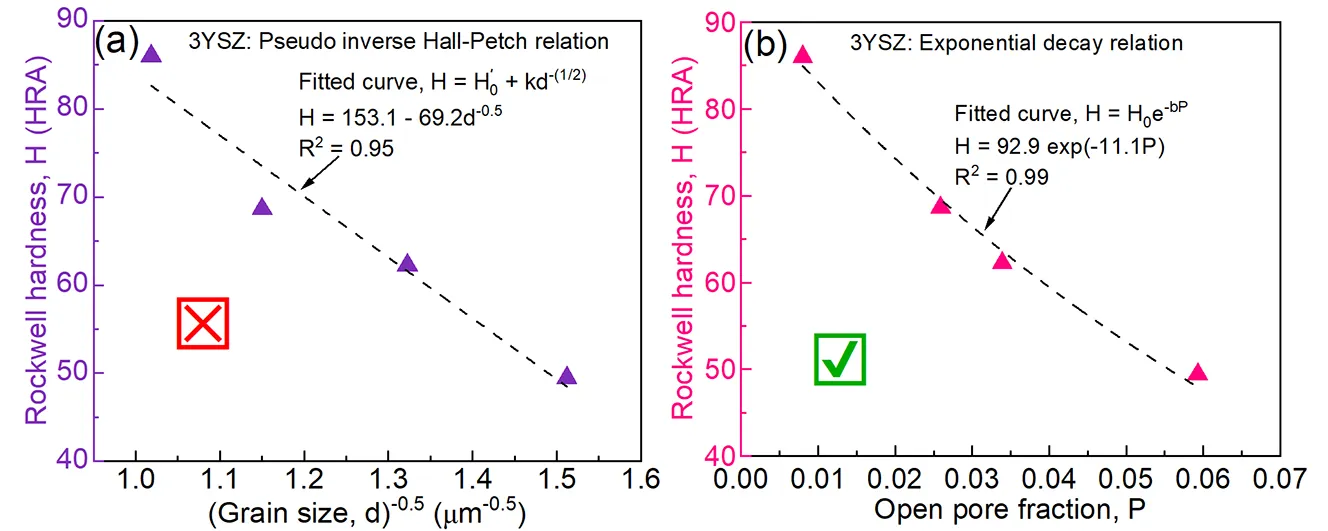
14 November 2024Hardness-Porosity-Grain Size Interrelationship in Conventionally Sintered 3 mol% Yttria Stabilized Zirconia
Considerable research has been done in the past on expensive, <50 nm particle size 3 mol% yttria-stabilized zirconia (3YSZ) using advanced sintering techniques. However, insights are still needed to reveal which factors among grain size and porosity, when both are changing simultaneously, more strongly control the hardness of conventionally sintered, relatively coarse, 250 nm 3YSZ powder, which can be used to make large industrial engineering ceramic parts at a lower cost. This investigation showed that elevating the sintering temperature from 1500 °C to 1650 °C increased the Rockwell hardness from 49.4 HRA to 86.0 HRA, which was concomitant with an increase in grain size and bulk density. A pseudo-inverse Hall-Petch relationship between hardness and grain size was observed given by H (in HRA) = 153.1 − 69.2/$$\small\sqrt{(\mathrm{grain}\,\mathrm{size})}$$ with a somewhat low R2 of 0.95, which was mainly due to the porosity being an additional important variable. Compared to grain size, the impact of open pore fraction (P) on hardness was stronger, inferred from a higher R2 of 0.99 while fitting the data into the well-known exponential decay equation, H = 92.9 exp(−11.1P). Finally, it was observed that the 3YSZ conventionally sintered at 1650 °C for 2 h had 0.8% open porosity, 6.08 g/cm3 bulk density, 960 nm grain size and consisted of only tetragonal ZrO2.
Open Access
Review
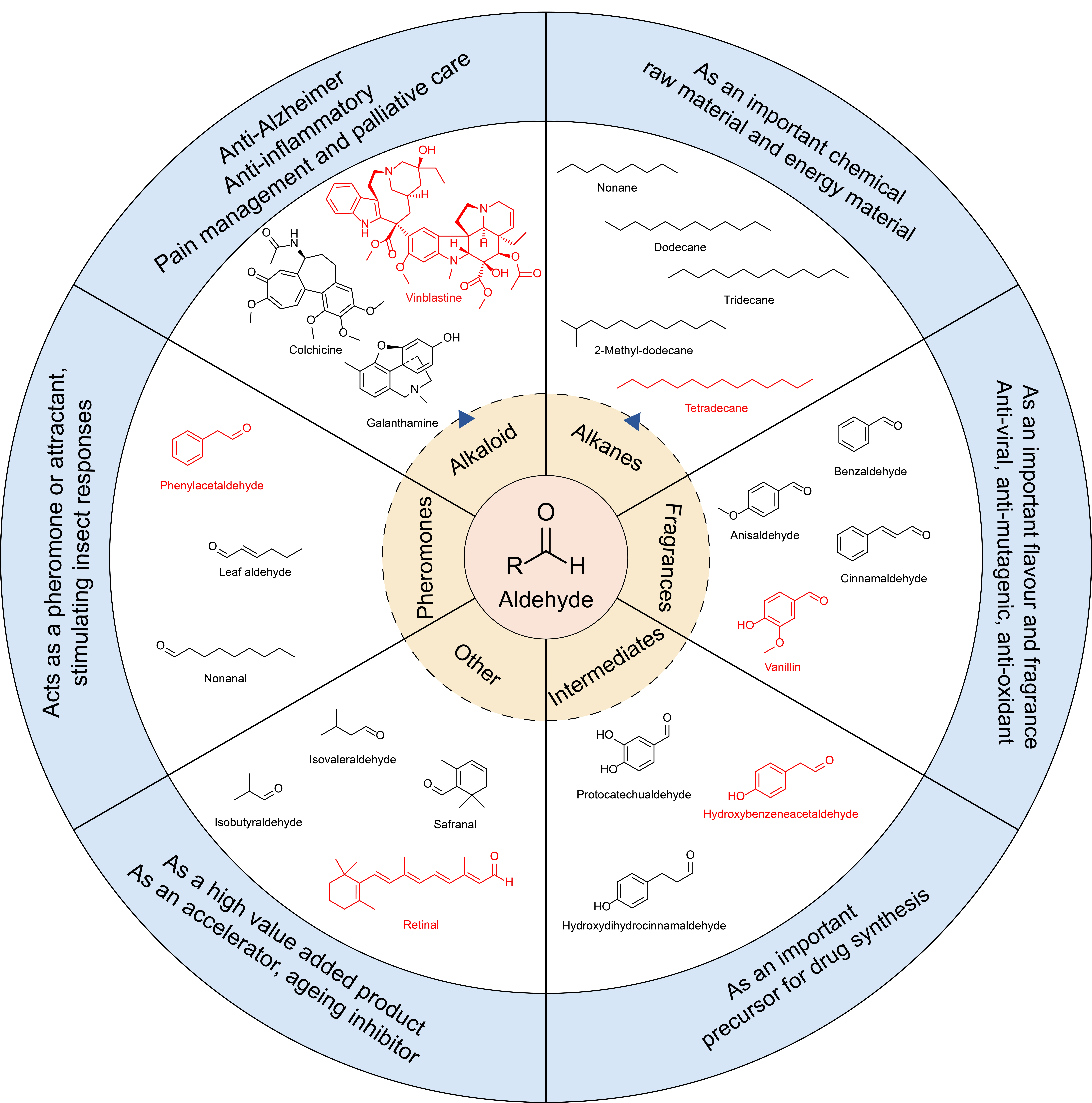
13 November 2024Recent Advances in Developing Aldehyde-Accumulating Microbes and Future Perspective of Biosynthetic Applications
Aldehydes are a class of compounds that contain carbonyl groups in their side chains and are widely used in industries such as fragrances, flavoring compounds, and pharmaceutical intermediates. In recent years, there has been a substantial rise in the application of microbial synthesis to generate aldehyde compounds and their derivatives. This review will conduct an in-depth analysis of the literature related to the manipulation of microorganisms for aldehyde accumulation and the subsequent generation of aldehyde-derived products using metabolic engineering and synthetic biology principles. Furthermore, the review further highlights the prospects and future potential of employing these aldehyde-accumulating microorganisms to synthesize a diverse range of value-added chemicals.
Open Access
Article
11 November 2024Rural Local Government Institutional Sustainability Programs and Plans in Cascadia: A Comparative Analysis
This research provides a comparative analysis of institutional sustainability programs in small and rural communities across British Columbia, Oregon, and Washington. The study reveals significant regional differences in the adoption of sustainability initiatives, with Oregon consistently leading in the implementation of various programs such as grant writing, conflict resolution, and e-government. The analysis identifies key factors influencing program adoption, including population growth, economic stability, and remoteness. Communities experiencing significant population growth and financial stability are more likely to adopt multiple sustainability programs, while remoteness and economic challenges, such as inflation, act as barriers. The study underscores the importance of regional context and local conditions in shaping the sustainability efforts of rural communities.

Open Access
Article
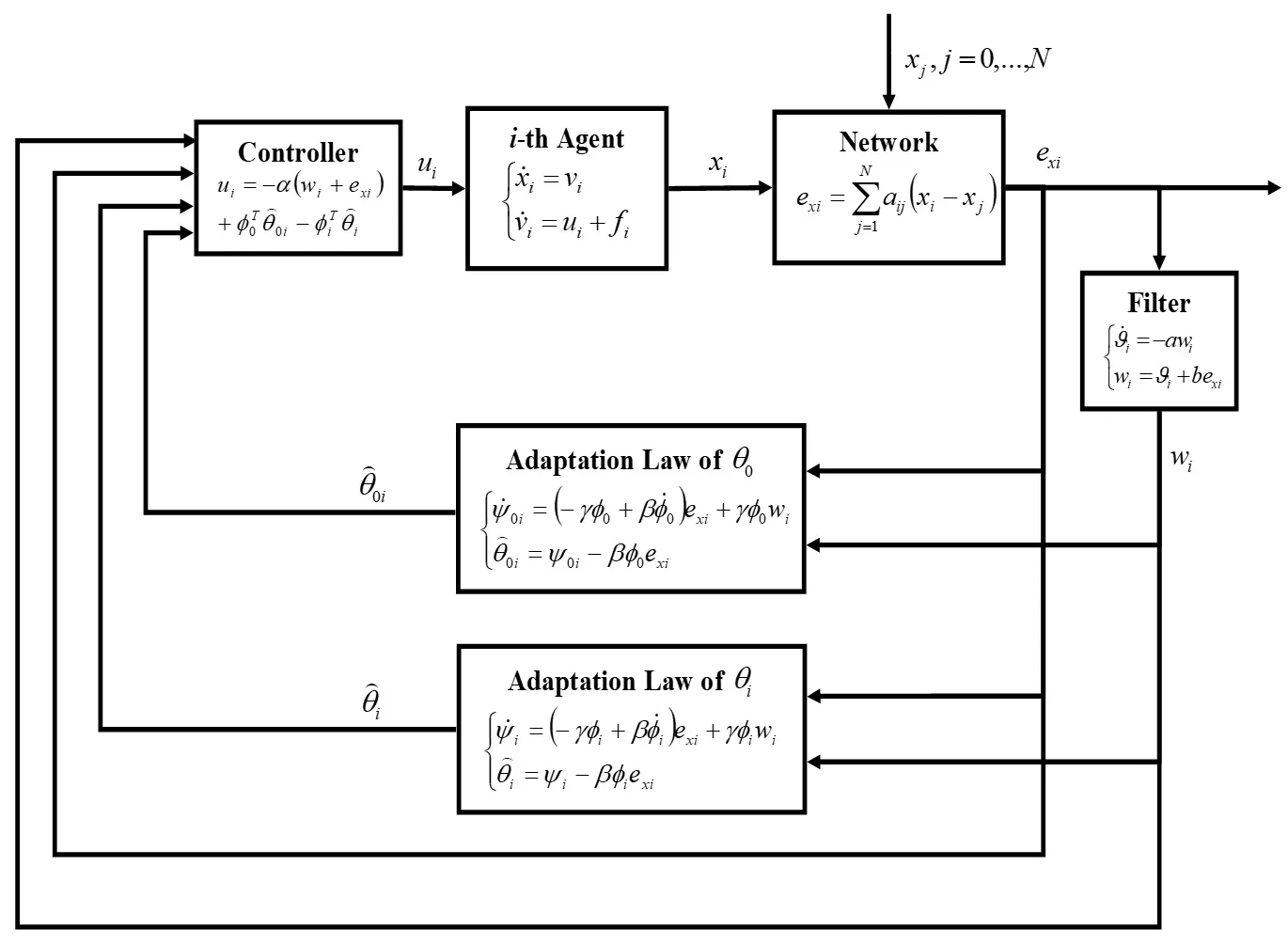
07 November 2024Fully- and Partially- Distributed Adaptive Consensus of Second-Order Multi-Agent Systems Using Only Relative Position Measurements
In this paper, the distributed leader-follower consensus of a group of agents with second-order dynamics under the undirected graph communication topology is studied. The main objective of this study is to solve a major practical multi-agent problem in which the acceleration of the leader is not communicated to each follower. In contrast, the follower agents include some unknown dynamics in their intrinsic structure. By assuming a linear regression structure for leader acceleration and agent’s unknown dynamics, Lyapunov-based adaptive control algorithms are devised to control the network of agents in the presence of the communication loss and modeling uncertainties. The presented study describes two multi-agent control strategies called fully-distributed adaptive control (FDAC) and partially-distributed adaptive control (PDAC) systems in the first method, the followers do not have any a priori information about the communication graph, while in the second method, some information about the eigenvalues of the communication graph is available. The mathematical manipulations required to prove the stability of the FDAC and PDAC methods are presented. Finally, illustrative simulations are conducted to render the proposed algorithms’ merits and efficiencies.
Open Access
Article
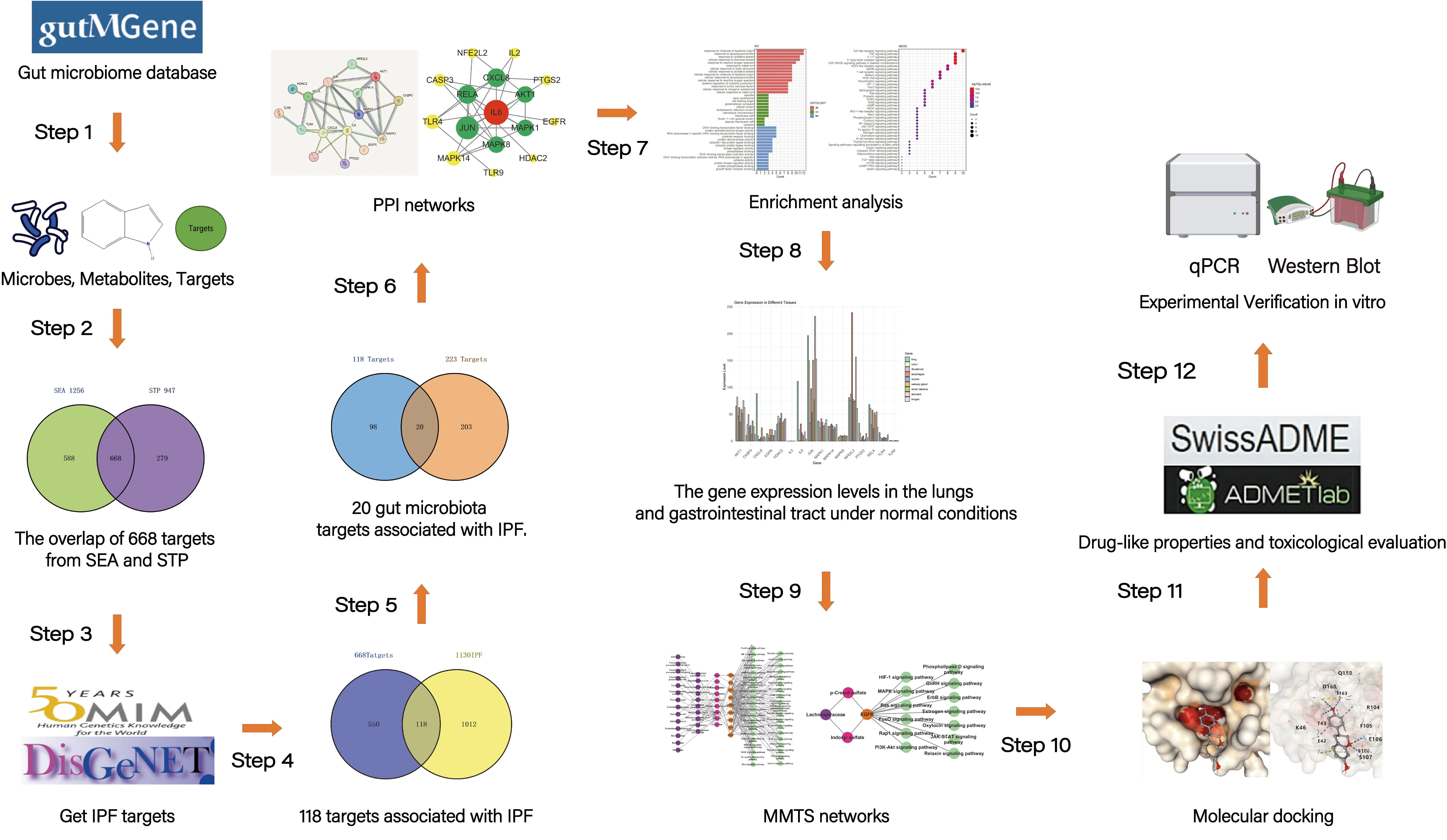
04 November 2024Exploring the Potential Relationship between Gut Microbiome Metabolites and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis via Network Pharmacology Study
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic, progressive fibrotic lung disease with a poor prognosis. Previous research has revealed that the gut microbiota is associated with human health and immunity, and it interacts with the lung through the “gut-lung axis”. This study explores the potential relationship between Gut Microbiome Metabolites and Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis via Network Pharmacology Study. The metabolites from gut microbiota were retrieved from the gutMGene database, and gene targets for these metabolites were obtained from previous studies. Gene targets of IPF were obtained from public databases (DisGeNET, OMIM). Subsequently, following the identification of shared targets, IL6 was determined as the core target through protein-protein interaction analysis. Then, a microbiota-metabolite-target-signaling pathway network (MMTS) was constructed using Cytoscape 3.10, and targets with low expression in the lungs and intestines were deleted. The MMTS network revealed that three short-chain fatty acids—acetate, butyrate, propionate, and a flavonoid compound called equol—are IL6-related metabolites. Then, we performed a molecular docking test (MDT) using CB-Dock2 to validate the affinity between core targets and metabolites. MDT confirmed that equol produced by the conversion of isoflavones from Lactobacillus paracasei JS1 was more stable in binding to IL6 than the other three short-chain fatty acids, thereby affecting multiple signaling pathways and influencing the progression of IPF. Finally, we validated this hypothesis through in vitro cell culture experiments, further confirming the effect of Equol.
Open Access
Article
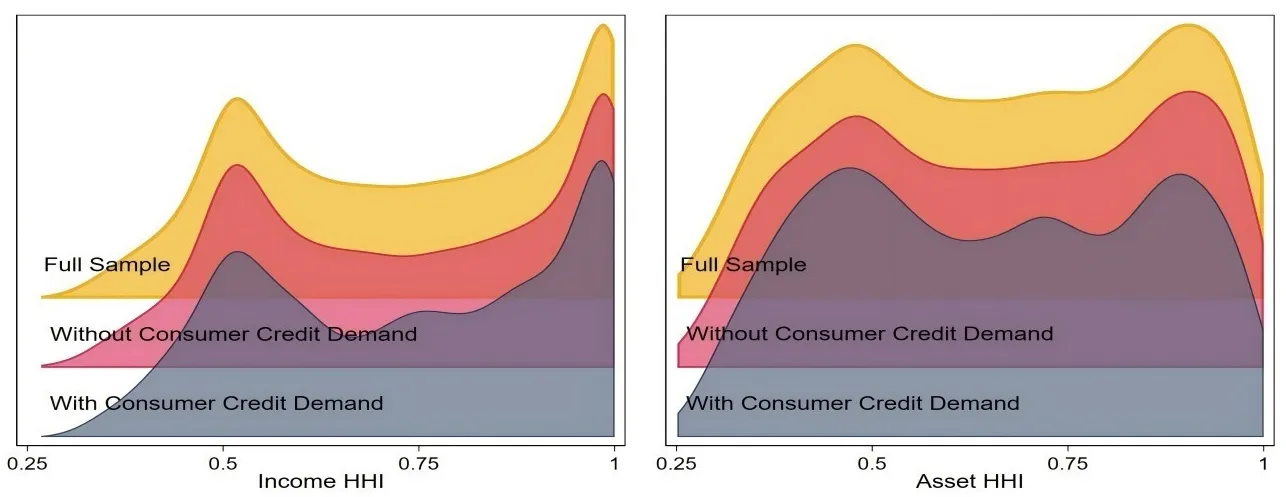
04 November 2024Understanding Rural Consumer Credit Demand: Insights from China’s Household Income and Asset Structures
China’s ongoing supply-side structural reforms and the government’s strategic focus on rural revitalization catalyze a significant transformation in rural landscapes. The steady rise in rural residents’ incomes and assets, along with gradual improvements in household quality of life, is unlocking significant potential for growth and upgrades in the rural consumer market.This evolution necessitates a more diversified and sophisticated approach to financial services that is more inclusive and widespread. Despite the challenges, such as an aging population and imperfect credit systems that have limited the quality and precision of rural financial services, the analysis of household income and asset structures is vital for understanding consumption patterns and enhancing the economic vitality of rural households. Our study, based on the 2019 China Household Finance Survey data of 11,386 households and employing the Heckman two-stage model, finds that the proportions of income components and financial assets, moving in opposite directions, significantly influence the amount of consumer credit demanded, while other asset types, such as real estate, show no significant effect. The examination of income and asset diversity through the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) demonstrates varying impacts of income and asset structures on credit demand, depending on the concentration levels of income and assets. Additionally, our analysis of heterogeneity based on the age of the household head and geographic region highlights the diverse influences on the amount of consumer credit demand, underscoring the importance of tailoring financial products and policies to meet the specific needs of rural households. These findings shed light on these dynamics and inform financial service innovations that align with the needs of rural consumers, thereby supporting the broader objectives of rural economic development and the achievement of China’s rural revitalization strategies.