Found 469 results
Open Access
Article
28 November 2024Correlations of System Degradation, Losses and Significant Parameters for 49 MW Large Scale Solar Plant with Real Site Data Validations
A smooth transition towards a clean and sustainable environment will heavily rely on the continuous increase of renewable energy (RE) integration. Malaysian authorities have set targets to increase the RE capacity to 31% by the end of 2025 and achieve 40% by 2035, specifically through the power generation plan. Solar PV systems have been widely used, from industries to residential homes, because Malaysia receives a high irradiation potential of up to 5000 Wh/year. The increase in the potential of solar PV usage has allowed solar companies to provide this system regardless of its complexity and system size. However, a drop in efficiency due to system parameters within the photovoltaic (PV) system is evident over time. This study aims to analyze the relationship between solar PV system parameters and their energy performance, particularly in a tropical climate region, for a large-scale solar (LSS) plant. This project was undertaken with two objectives: First, it is to develop an optimum solar PV system by adhering to and implementing GCPV standards in Malaysia. Stage 1 will primarily focus on managing and manipulating various PV system parameters to ensure the optimum energy yield received from the plant. The system parameters analyzed are tilt angle, module technology and its effect on different temperatures, the effect of the optimizer, sizing and thermal loss. Stage 2 will then incorporate the industry data of the LSS plant by creating a Pearson’s Correlation model on how energy yield is correlated against real time system parameter values obtained. An optimum tilt angle of 10°, monocrystalline module and inclusion of optimizer increases the overall energy production from 88,986 MWh/year to 89,782 MWh/year and performance ratio (PR) from 78.9% to 79.8%. The outcome of this study demonstrates the significant parameters of the PV system to maximize the energy output to the grid. This will further support the government’s plan to reduce GHG emissions by 45% through the use of renewable energy, with the aim of producing up to 2.5 GW from LSS systems by 2030.
Open Access
Article
28 November 2024A Review of the Energy Policy in Greece in the Last 50 Years and Its Implications for Prosperity
This paper elucidates the development of electricity production and distribution in Greece from the 1950s to date, in correlation with national and European energy policy. During this period, Greece experienced a multifaceted energy transition, including both the transition of ownership of energy generation companies from public to private and a transition from an energy mix in which coal (lignite) served as a major and inexpensive resource to a mix in which wind power, solar power and natural gas gained a primary role, but with high costs for energy generation. The correlation between electrical energy consumption and economic growth is explored in this context, revealing an increase in consumption before the 2009 recession and a decline thereafter. The study investigates the correlation between escalating electricity prices and legislative dependencies that mandated the purchase of wind- and solar-generated electricity at exorbitant rates, the closure of cost-effective lignite units, and the reliance on natural gas—a commodity susceptible to geopolitical shifts. It also shows that, given the structure of the Greek energy mix, the increase in the share of wind and solar energy in the mix is directly related to the increase in the price of electricity. Highlighting the importance of energy costs for prosperity, this paper underscores, through the detailed review of the Greek energy “landscape”, that the major determinants of electricity prices are both the accessibility to natural resources but also their proper and judicious management.

Open Access
Article
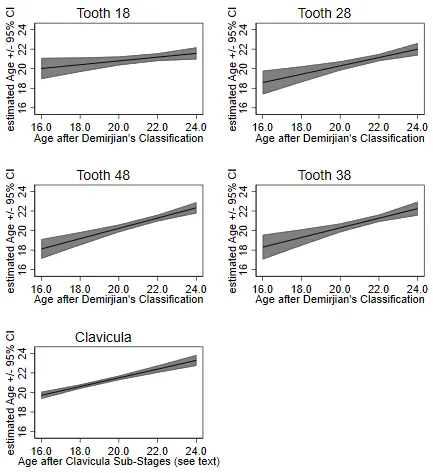
28 November 2024Forensic Dental Age Estimation: Reliability Rating Compared to Clavicula
This study aimed to investigate the age determination in forensic expert opinions at the Institute of Forensic Medicine (Mainz) over the last ten years and to determine the reliability rate of wisdom teeth in comparison to the clavicle. A total of 112 expert opinions were prepared between 2011 and 2021, following the guidelines established by the Working Group for Forensic Age Diagnostics (AGFAD). Five indicators were studied: clavicle development coded according to Wittschieber et al. using computed tomography and wisdom tooth development 18, 28, 38 and 48 coded according to Demirjian’s staging method in a dental panoramic radiograph. Following an ordinary least square regression analysis performed separately for each of the five indicators, it was possible to investigate whether the addition of more than one of the indicators would lead to a more predictive value for the age determination. The combination of the clavicle and tooth 48 showed the best value. Adding tooth 38, which showed the second-best prediction in the bivariate analyses, led to an increase of the explained variance of 11% to a total of 58% explained variance (p < 0.001). The addition of further wisdom teeth did not show any relevant effect. For the clinical performance of dental age diagnostics, the teeth of the mandible, in combination with the clavicle, should be primarily used.
Open Access
Article
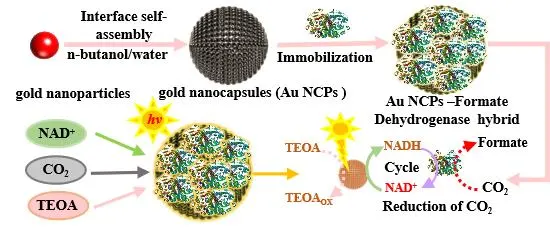
27 November 2024Photocatalytic CO2 Fixation into Formate under Visible Light by the Photo-Enzyme Hybrid of Gold Nanocapsules and Formate Dehydrogenase
The photo-enzyme hybrid system presents a promising approach for the selective conversion of CO2 into valuable chemicals. However, its high dependence on the expensive coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced form (NADH), coupled with the need for external electron mediators and highly active photocatalysts, limits its widespread application. Here, we developed a gold nanocapsule—formate dehydrogenase (FDH) hybrid system for in situ NADH regeneration to facilitate the light-driven conversion of CO2 to formate. The results demonstrated that gold nanocapsules (Au NCPs), in conjunction with triethanolamine (TEOA), protected 83.67% of NADH from photodegradation. Under light-driven conditions with TEOA as the electron donor and without external electron mediators, the Au NCPs catalyzed in situ NADH regeneration, achieving a regeneration yield of 22.65%. This process aided FDH in reducing CO2 to formate, resulting in a production rate of 67.40 µmol/L/h. This research provides valuable insights for developing photo-enzyme hybrid systems that efficiently convert CO2 without the need for external electron mediators.
Open Access
Article
25 November 2024Partial Duration Series of Wet and Dry Years Can Improve Flood Estimates in the Context of a Nonstationary Climate and Anthropogenic Disturbances
Accurately estimating flood levels is essential for effective infrastructure design, reservoir management, and flood risk mapping. Traditional methods for predicting these levels often rely on annual maximum flood (AMF) data, which may not always fit well to statistical models. To improve these estimates, we tested an approach that considers floods in relation to annual climate conditions—specifically, average, wet, and dry years—using daily streamflow data. We examined how well the Log Pearson Type III (LP3) distribution, a commonly used statistical model in flood frequency analysis, estimates flood levels when applied to these customized datasets instead of standard AMF data. Our study included over 70 years of data from 2028 basins across the United States, with drainage areas ranging from small (4.0 km2) to large (50,362 km2). We found that in some regions, LP3 better estimated frequent floods (recurrence interval of 2 to 25 years) when applied to AMF data. However, for less frequent, larger floods (recurrence interval of 50 to 200 years), the LP3 model worked better when applied to datasets representing wet or dry years. This approach could lead to more reliable flood predictions, which would benefit infrastructure planning and flood preparedness efforts.
Open Access
Commentary
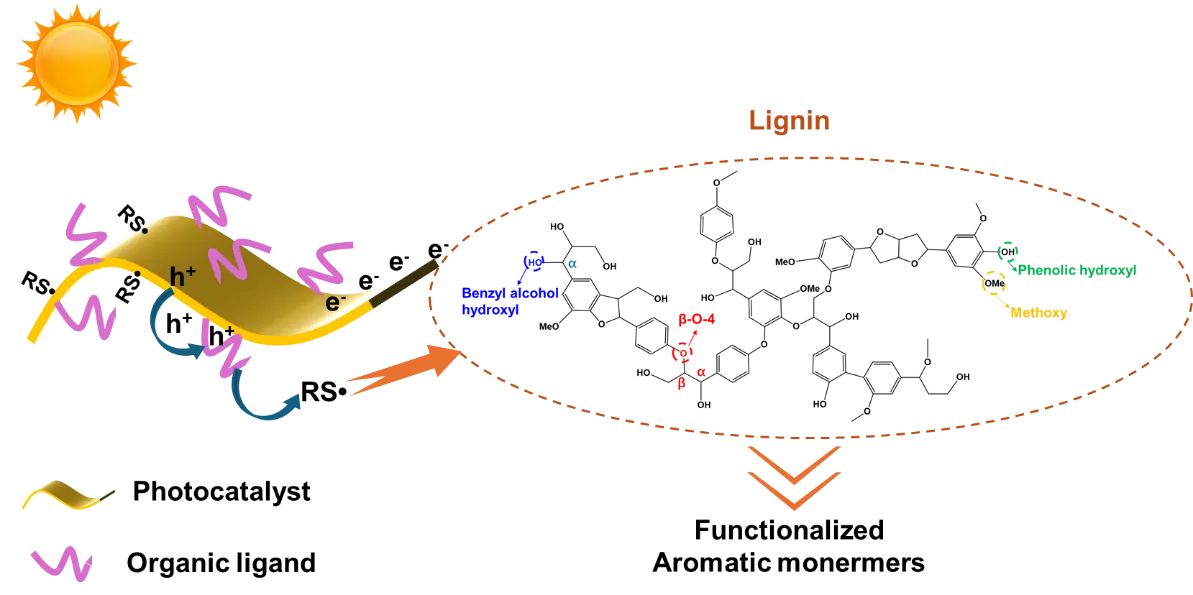
25 November 2024A Novel Mechanism for Photogenerated Thiyl Radical Cleavage of β-O-4 Bonds in Natural Lignin to Generate Functionalized Aromatic Compounds
The high-value conversion of native lignin into functionalized aromatic compounds under visible light holds significant promise yet presents considerable challenges. In a recent study published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition, Li and colleagues developed ultrathin ZnIn2S4 microribbons using mercaptoalkanoic acid ligands, enhancing the depolymerization efficiency of lignin under visible light. This approach provides a new mechanism for converting lignin into aromatic compounds by cleaving β-O-4 bonds in natural lignin under mild conditions.
Open Access
Review
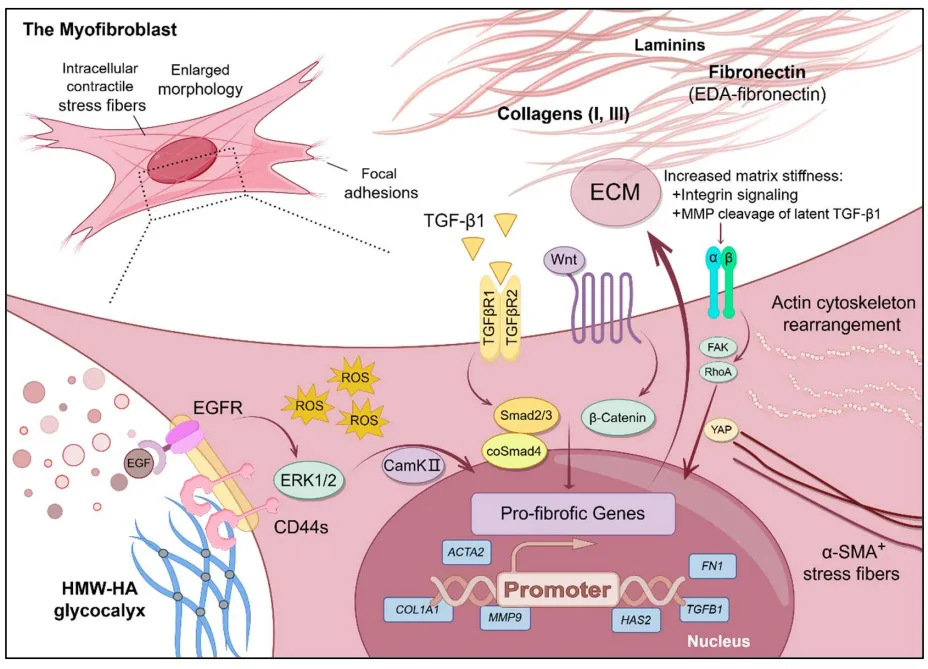
22 November 2024Dermal Fibrosis and the Current Scope of Hydrogel Strategies for Scarless Wound Healing
Dermal fibrosis poses a significant challenge in wound healing, affecting both the appearance and functionality of the scarred skin tissue. Beyond aesthetic implications, fibrosis can lead to pruritus, chronic pain, loss of mechanical flexibility, and impeded restoration of skin appendages, blood vessels, and nerves. Therefore, scar prevention remains a priority in wound management, and hydrogels, with their hydrophilic three-dimensional network and extracellular matrix-mimicking properties, have emerged as promising biomaterials for achieving scarless wound regeneration. In this review, we explore advancements in various hydrogel strategies designed to regulate myofibroblast differentiation, control the wound microenvironment, and mitigate dermal fibrosis. We provide an overview of dermal fibrosis, the scar-forming cells involved, and the various types of dermal scars. We then summarise advancements made in antifibrotic hydrogel formulations, emphasizing their practical applications in scarless skin wound healing. By reviewing the current research landscape and highlighting key hydrogel-based biomaterial strategies employed in this field, we aim to offer insights into design principles and underlying mechanisms of action. We intend for this review to serve as a valuable resource for researchers and clinicians interested in entering this field or exploring the potential of hydrogels to promote scarless wound healing.
Open Access
Article
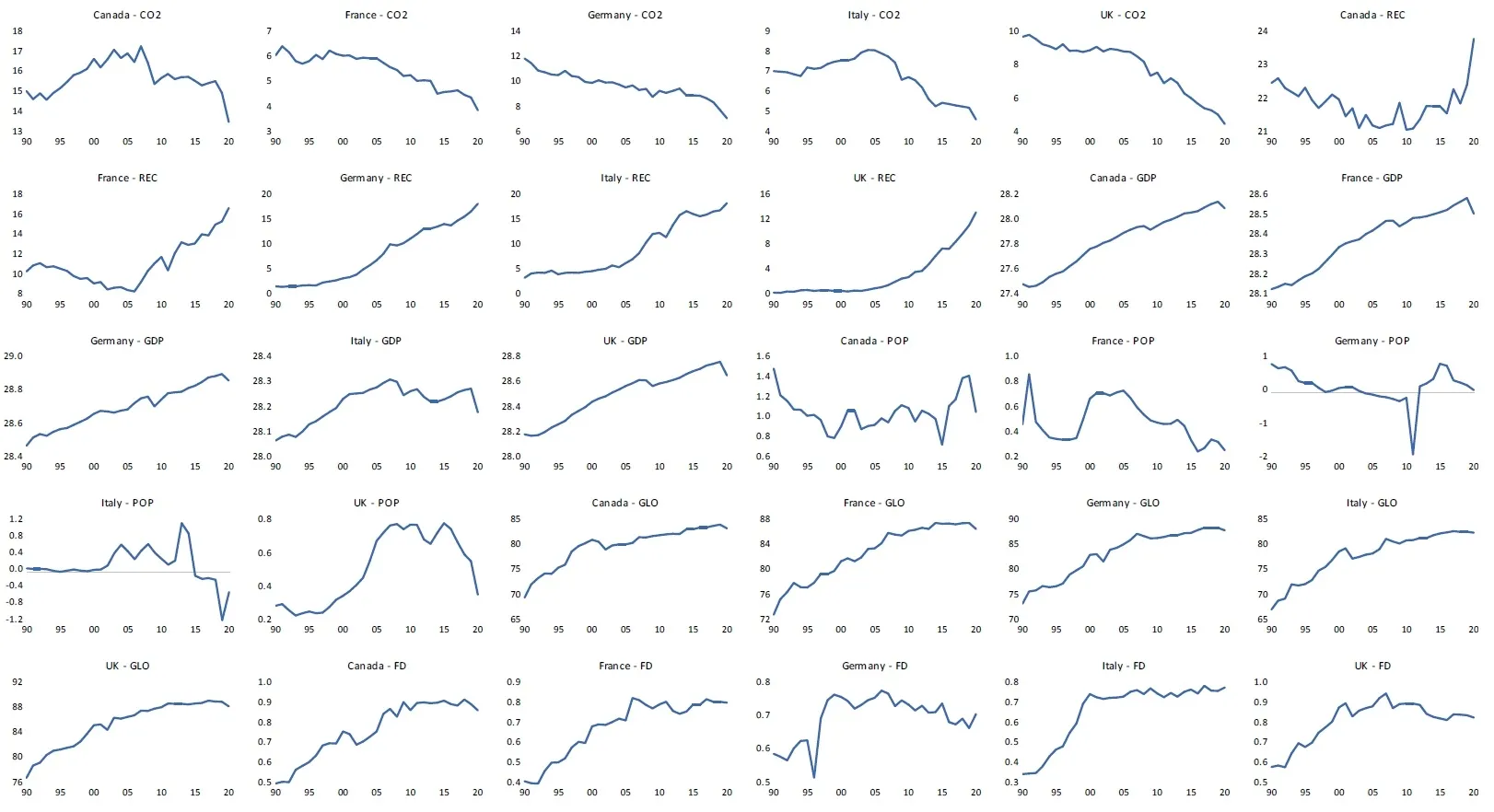
21 November 2024The Impact of Renewable Energy Consumption, Economic Growth, Globalization, and Financial Development on Carbon Dioxide Emissions: Evidence from Selected G7 Economies
The aggregate upsurge in carbon dioxide emissions (CO2) witnessed through environmental degradation and global climate change is a call for great concern. This, therefore, calls for the enactment, utilization and implementation of provisions and policies geared towards curbing this global economic bad without impeding global economic growth rates. This study ascertains the extent to which renewable energy consumption (REC), economic growth (GDP), population growth (POP), globalization (GLO), and financial development (FD) affect carbon dioxide emissions (CO2) in selected G7 economies (France, Germany, Canada, Italy, and the United Kingdom) from 1990–2020. The Dynamic Fixed Effect Autoregressive Distributive Lag (DFE-ARDL) and the Pooled Mean Group ARDL (PMG-ARDL) methods were employed for analysis. The empirical findings for DFE-ARDL showed that REC, GDP, and POP have an adverse association with CO2 in the long-term. However, in the short-term, REC and FD improve the environment, while GDP and POP drive CO2. It is observed that the result for REC in the short and long-run is consistent. The PMG-ARDL results revealed that REC and GLO negatively affect CO2 in the long-run, and in the short-run, GDP spurs CO2, while FD reduces it. The result summary of both methods employed demonstrates that REC, GLO, and FD benefit the environment. At the same time, GDP and POP harm the environment in the short-run but reduce CO2 in the long-run. Conclusively, the research recommends increasing the utilization of renewable energy and policies that enable economic growth and CO2 to move in the opposite direction.
Open Access
Article
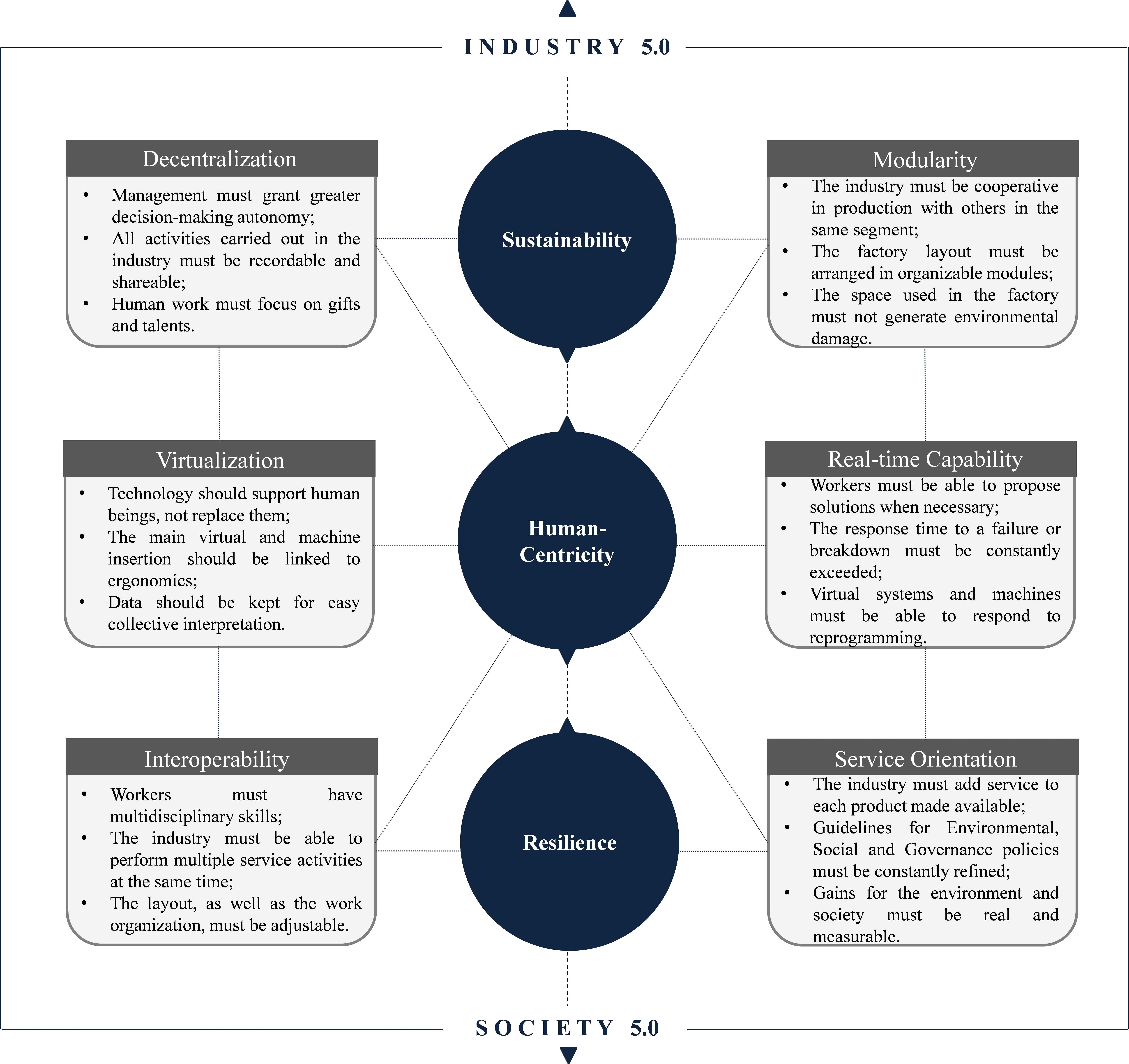
20 November 2024Contextualization of Industry 4.0 Design Principles for the Imminent Industry 5.0 Scenario
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, known as Industry 4.0 (I4.0), has introduced a completely disruptive pace compared to the rhythm of the three previous industrial revolutions. With a wide range of technologies, design principles, and a high potential to replace the human workforce, this industry presents aspects that urgently require greater attention. With a purpose close to meeting this need, Industry 5.0 (I5.0) emerges, a milestone not yet registered with historical facts but with great hopes for positive changes. While I4.0 maintains design principles for its complete activity, I5.0 has a supporting tripod for its operation. As I5.0 is still perceived as an evolutionary character of I4.0, it is expected that for the time being, it will use these same design principles for its activity and may later include new principles. Based on this context, this article seeks to contextualize, in a descriptive way, the functioning of design principles 4.0 for the imminent industrial context 5.0. The article uses a conceptual approach based on previously published literature on the subject of design principles in I4.0. Although the characteristics of I5.0 are not yet fully known, it is assumed that it has a more refined character than I4.0, so that points that presented a positive, significant, and already consolidated result are maintained for the new model. The distinctive feature of this article is its presentation of a textual analysis that breaks down the potential contributions of design principles in relation to the three core values of Industry 5.0: Sustainability, Human-Centricity, and Resilience.
Open Access
Article
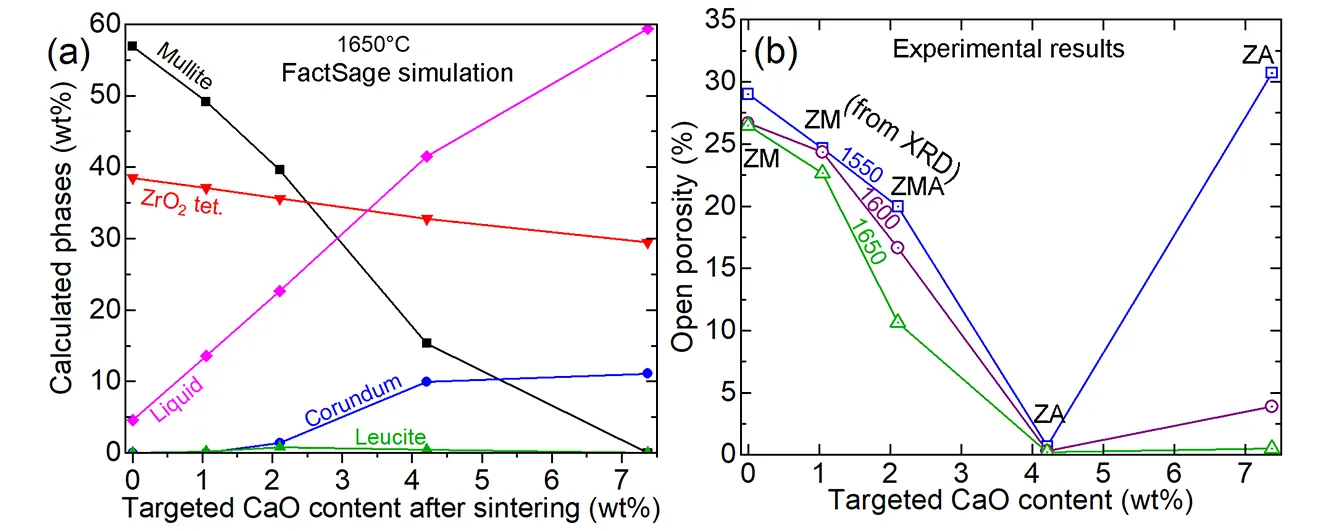
19 November 2024Calcite as a Mineralizer and Stabilizer for Low-Cost Zirconia-Mullite-Alumina Composites Synthesized from Siliceous Clay, Alumina and Zirconia
Fused zirconia-mullite (ZM) and zirconia-alumina (ZA) are expensive aggregates used in refractory formulations to enhance thermal shock tolerance and corrosion resistance, respectively. A cost-effective alternative approach was explored in this work to produce 37.4 wt% ZrO2 containing ZM utilizing conventional reaction sintering of siliceous clay, calcined alumina and monoclinic ZrO2. A series of chemical reactions ensued from 1200 °C, forming low quartz and cristobalite from the clay, in situ ZrSiO4, monoclinic ZrO2, α-Al2O3 and traces of leucite. 1600 °C was required to fully form mullite and monoclinic ZrO2 but it had 26.5% porosity even after firing at 1650 °C for 2 h. It consisted of small equiaxed primary mullite grains secondary mullite rods, and scattered and clustered, round ZrO2 grains. With 1.05% CaO addition, tetragonal ZrO2 formed, but 22.7% porosity remained despite the presence of 13.5% liquid phase having a low viscosity (0.6 Pa.s, from FactSage). With 2.11% CaO, porosity reduced to 10.7% but mullite partly dissolved, forming α-Al2O3 (ZMA aggregate). The added CaO mostly remained in the intergranular glassy phase rather than inside the ZrO2 grains but increased the thickness of the secondary mullite and the ZrO2 grains. Mullite was completely lost with 4.21% CaO doping but favorably formed cubic ZrO2 containing up to 0.26 at% Ca, interlinked α-Al2O3 rods and attained a low porosity of 0.2%. This ZA aggregate is limited to 1550 °C application temperature as excess liquid phase drained out beyond that. 7.37% CaO addition was detrimental as it formed an excessive anorthite-like liquid phase that percolated out at 1550 °C with 5.6% weight loss. Thus, in ZM-based calcium aluminate cement bonded refractory castables, the final CaO content should be restricted to below 2.1% to avoid partial dissolution of mullite.