Found 301 results
Open Access
Article
17 March 2025A Strategy for Resisting the Vested Interests Driving the Collapse of the Biosphere and Civilisation
The biosphere and civilisation are facing existential and other major threats: climate change, biodiversity loss, nuclear war, social inequality/injustice, loss of human rights, and autocracy. These threats are driven by politically powerful vested interests supported by an economic system based on the exploitation of the environment and most people for the benefit of a wealthy minority. This article proposes a strategy to resist and weaken state capture, i.e., the influence of the vested interests driving the principal threats, while simultaneously facilitating the transition to a sustainable society. Despite the achievements of diverse community-based non-government organisations (CNGOs) campaigning on specific issues, scientists are now warning of the potential collapse of civilisation. As the threats are linked together in several ways, I propose a strategy to address them together to yield multiple benefits, supplementing campaigns on individual issues. A broad social movement—comprising an alliance between CNGOs devoted to the environment, social justice, human rights, and peace—could exert sufficient political power to expose and defeat the methods of state capture. Simultaneously, the movement could gain widespread community support by campaigning for a well-being economy, including universal basic services and a job guarantee, thus facilitating the transition to an ecologically sustainable, more socially just, and more peaceful civilisation.

Open Access
Article
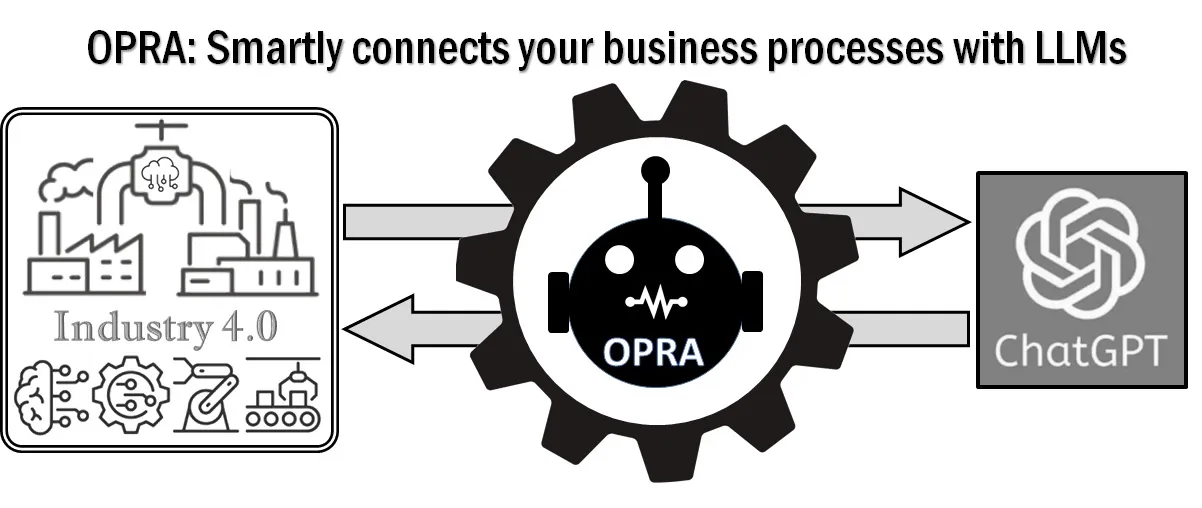
14 March 2025A Conceptual Design of Industrial Asset Maintenance System by Autonomous Agents Enhanced with ChatGPT
This article introduces OPRA (Observation-Prompt-Response-Action) and its multi-agent extension, COPRA (Collaborative OPRA), as frameworks offering alternatives to traditional agent architectures in intelligent manufacturing systems. Designed for adaptive decision-making in dynamic environments, OPRA enables agents to request external knowledge—such as insights from large language models—to bridge gaps in understanding and guide optimal actions in real-time. When predefined rules or operational guidelines are absent, especially in contexts marked by uncertainty, complexity, or novelty, the OPRA framework empowers agents to query external knowledge systems (e.g., ChatGPT), supporting decisions that traditional algorithms or static rules cannot adequately address. COPRA extends this approach to multi-agent scenarios, where agents collaboratively share insights from prompt-driven responses to achieve coordinated, efficient actions. These frameworks offer enhanced flexibility and responsiveness, which are critical for complex, partially observable manufacturing tasks. By integrating real-time knowledge, they reduce the need for extensive training data and improve operational resilience, making them a promising approach to sustainable manufacturing. Our study highlights the added value OPRA provides over traditional agent architectures, particularly in its ability to adapt on-the-fly through knowledge-driven prompts and reduce complexity by relying on external expertise. Motivational scenarios are discussed to demonstrate OPRA’s potential in critical areas such as predictive maintenance.
Open Access
Article
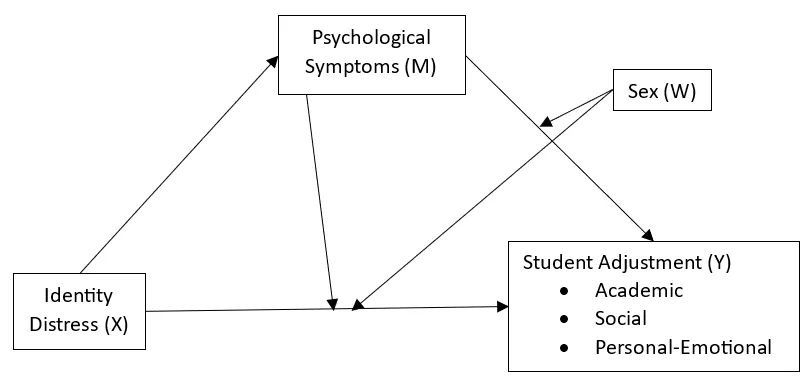
12 March 2025Cultural and Sex Differences in Emerging Adults: Identity Uncertainty, Psychological Symptoms and Adjustment at University
From the perspective of emerging adulthood, we investigated the role of culture and sex in associations between uncertainty and distress in identity development, psychological symptoms, and functioning at university among students in Canada, Spain, and Ecuador. The countries were categorized as individualistic or collectivistic according to Hofstede’s cultural dimensions. Participants included 661 students (median = 18 years, 76.6% female) in Canada (51.6%), Spain (16.2%), and Ecuador (32.2%). They completed the Identity Distress Scale, College Assessment of Psychological Problems Scale, and Student Adjustment to College Questionnaire with online surveys. Spanish students reported the greatest identity distress. Elevated academic adjustment was found for Ecuadorian students, who along with Spanish students exceeded those in Canada on social adjustment. Psychological symptoms mediated linkages between identity distress and academic and social adjustment for Canadian and Spanish women. Conversely, mediation was supported for the personal-emotional functioning of all students. Unexpected differences were found between males and females for identity distress and psychological difficulties among students in the individualistic countries. The findings underscore the need for the attention of researchers and counselors to potential variations in culture, sex, and other relevant personal and contextual factors and how they influence the identity development and well-being of university students worldwide.
Open Access
Article
12 March 2025Influence of Soil Damping and Aerodynamic Damping on the Dynamic Response of Monopile Wind Turbines under Earthquake and Wind Loads
Vibration damping is essential for predicting the responses of wind turbines, and contributions mainly come from structural, soil, and aerodynamic damping. In engineering design, it is difficult to precisely account for the individual contributions of each damping source. As a result, a simplified approach is commonly used, where a total damping factor is applied that combines the effects of structural, soil, aerodynamic, and other damping sources. However, the accuracy of this simplified approach in predicting the dynamic response of turbines has not been thoroughly evaluated. This study primarily focuses on the applicability of vibration-damping simplification methods, particularly in analyzing the dynamic response of turbines under earthquake and wind loads.

Open Access
Article
10 March 2025Leveraging Drone Technology for Precision Agriculture: A Comprehensive Case Study in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia
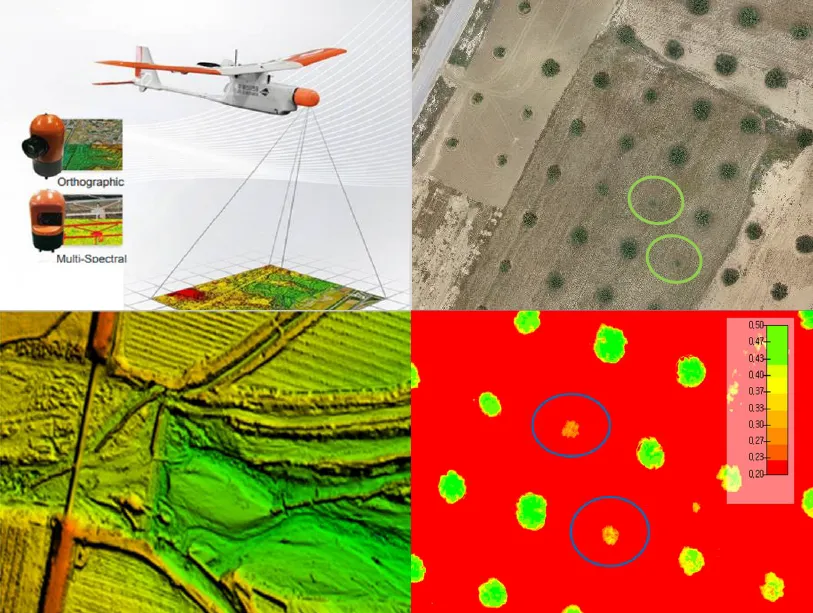
The integration of drone technology in precision agriculture offers promising solutions for enhancing crop monitoring, optimizing resource management, and improving sustainability. This study investigates the application of UAV-based remote sensing in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia, focusing on olive tree cultivation in a semi-arid environment. REMO-M professional drones equipped with RGB and multispectral sensors were deployed to collect high-resolution imagery, enabling advanced geospatial analysis. A comprehensive methodology was implemented, including precise flight planning, image processing, GIS-based mapping, and NDVI assessments to evaluate vegetation health. The results demonstrate the significant contribution of UAV imagery in generating accurate land use classifications, detecting plant health variations, and optimizing water resource distribution. NDVI analysis revealed clear distinctions in vegetation vigor, highlighting areas affected by water stress and nutrient deficiencies. Compared to traditional monitoring methods, drone-based assessments provided high spatial resolution and real-time data, facilitating early detection of agronomic issues. These findings underscore the pivotal role of UAV technology in advancing precision agriculture, particularly in semi-arid regions where climate variability poses challenges to sustainable farming. The study provides a replicable framework for integrating drone-based monitoring into agricultural decision-making, offering strategies to improve productivity, water efficiency, and environmental resilience. The research contributes to the growing body of knowledge on agricultural technology adoption in Tunisia and similar contexts, supporting data-driven approaches to climate-smart agriculture.

Open Access
Review
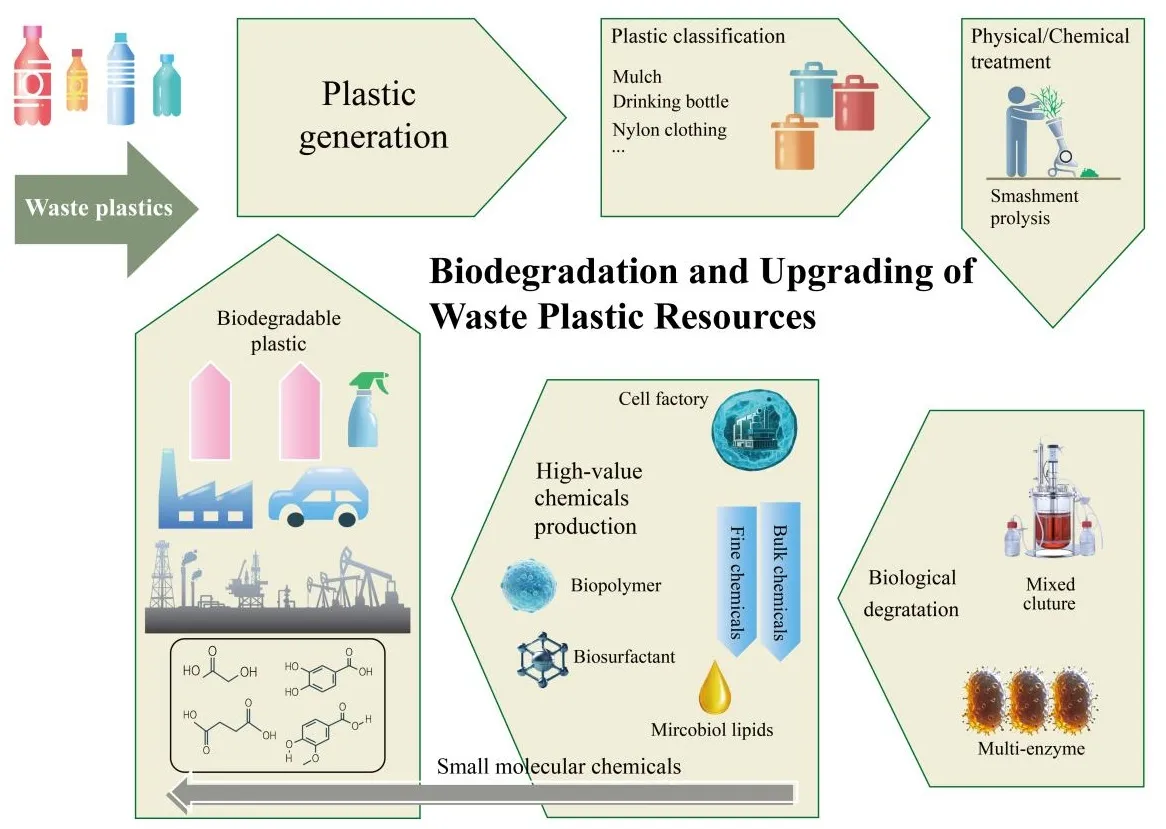
28 February 2025Synthetic Biology Boosts the Biological Depolymerization and Upcycling of Waste Plastic Resources
The high molecular weight, hydrophobicity, and strong chemical bonds of petroleum-based synthetic plastics make them highly resistant to both abiotic and microbial degradation. This resistance plays a significant role in the growing problem of “white pollution” where the accumulation of plastic waste has become a major environmental issue worldwide. Currently, plastic waste management relies largely on landfill disposal and incineration, with only about 20% of plastic waste being recycled. However, both methods create secondary environmental risks, such as contamination of groundwater, soil, air, and oceans. Therefore, developing a sustainable and efficient approach for recycling and reusing plastic waste is essential for tackling plastic pollution and promoting a circular plastic economy. One promising solution involves utilizing microorganisms and enzymes to break down plastics into oligomers or monomers, which can then be transformed into valuable chemicals. This method provides a more environmentally friendly and milder alternative to conventional waste management techniques. This review explores recent progress in biodepolymerization and biotransformation processes for plastic waste, including the identification of plastic-degrading microorganisms and enzymes, the creation of microbial consortia and enzyme mixtures, an investigation into the mechanisms of plastic depolymerization, and the conversion of degradation products into useful materials such as chemicals, energy, and other resources. Despite these advancements, several challenges remain, such as the limited availability of effective degradation enzymes, low degradation efficiency, and difficulties in utilizing the breakdown products. However, emerging technologies in synthetic biology, such as high-throughput screening, evolutionary metabolic engineering, and bioinformatics to study catalytic mechanisms of degradation enzymes, offer promising solutions to address these issues. By improving enzyme design, optimizing microbial consortia interactions, and developing efficient metabolic pathways for plastic degradation products, these innovations could greatly enhance plastic biodegradation. These advancements hold the potential to provide environmentally sustainable, economically feasible, and technically viable solutions for promoting a circular plastic economy, particularly in countries like China.
Open Access
Article
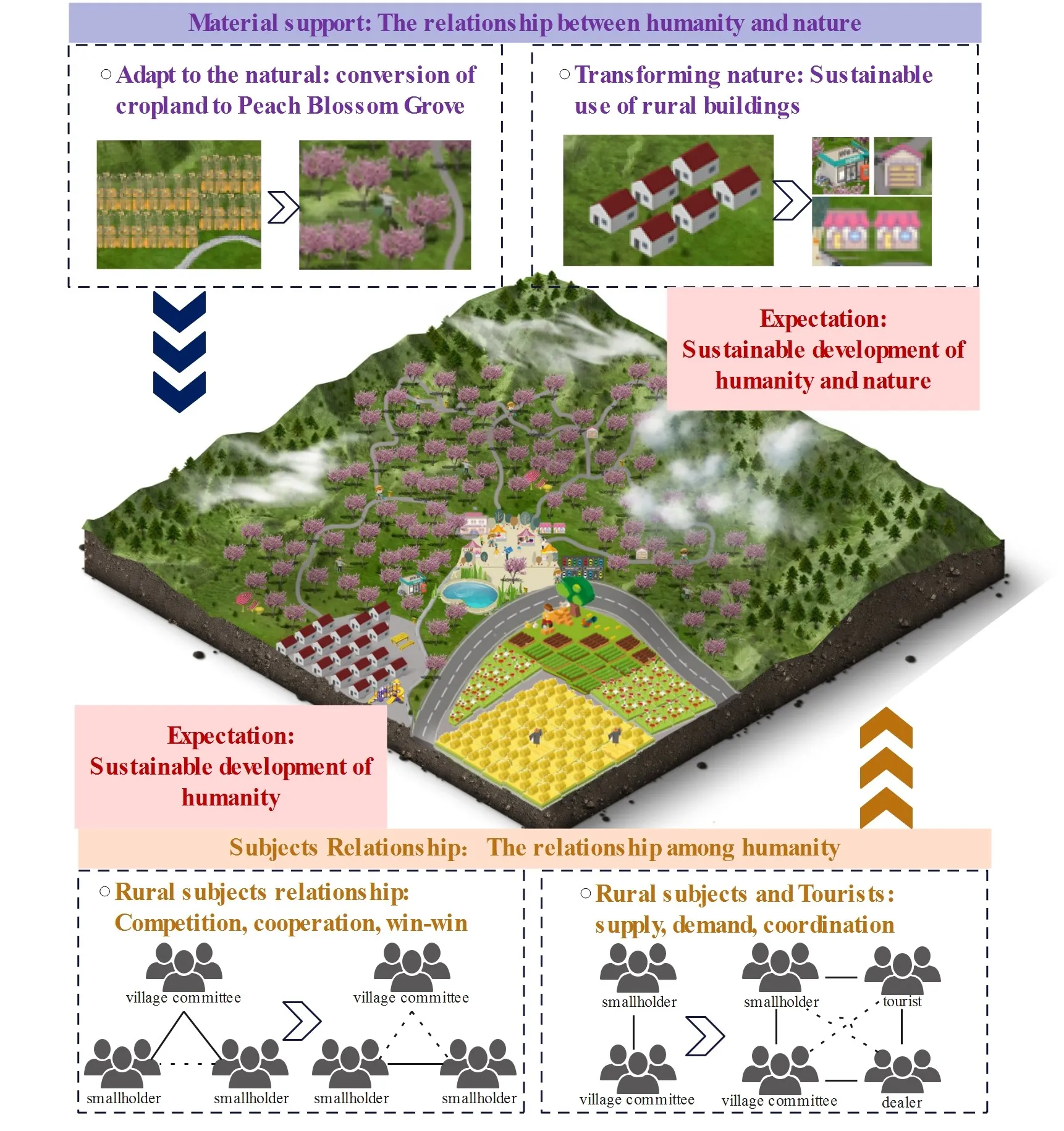
27 February 2025Deciphering How Promoting Flower-Viewing Economy for Construction of Harmonious-Villages in Mountainous and Hilly Areas
Sustainable development in mountainous and hilly regions is a critical component of global sustainability efforts. These regions are facing numerous challenges, including ecological fragility, labor migration, and resource scarcity and imbalance. Addressing these issues is imperative for sustainable development; this study identifies two primary conditions necessary for sustainable development in mountainous regions: achieving human and nature’s sustainable development, which provides reliable material support and social support for achieving the same in the mountainous and hilly regions. The flower-viewing economy, derived from transforming China’s mountain agriculture, is an efficient new format for mountainous and hilly regions. To verify these primary conditions, this study constructed a flower-viewing economy from three dimensions: material support, subject relationship, and expectation, using the peach blossom festival in Tingzi Village, Taihe Town of Chongqing City, as an example. Here, we explained that a sustainable development model focused on benefiting farmers is an endogenous, farmer-centered pathway to sustainable development, highly relevant to promoting sustainable development in developing countries’ mountain villages.
Open Access
Article
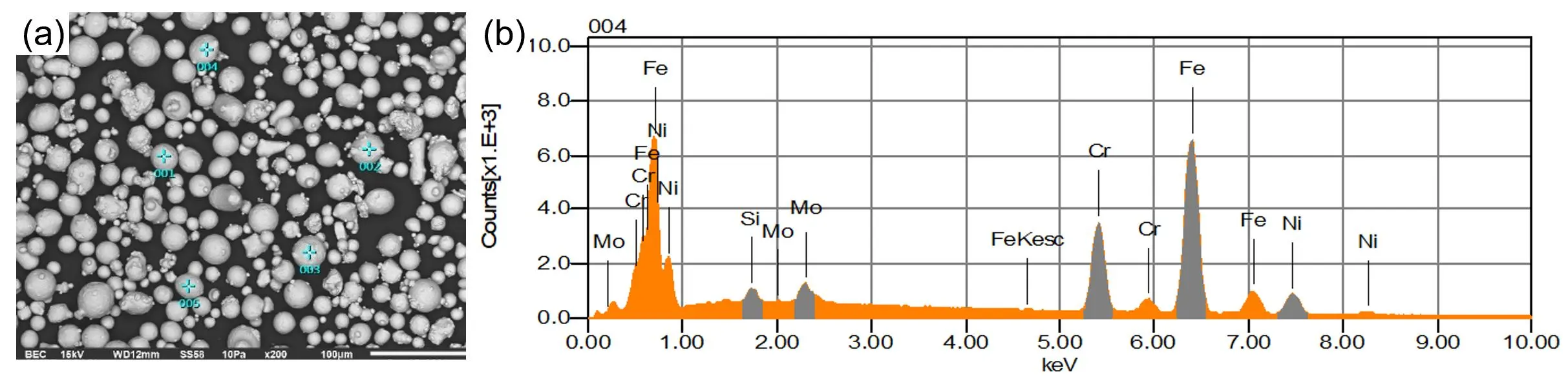
26 February 2025Life Cycle Assessment of Tensile Specimens of Stainless Steel Obtained by Additive Manufacturing versus Conventional Manufacturing
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of additive manufacturing (AM) evaluates the environmental impacts associated with each stage of the process, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. Unlike conventional manufacturing, AM offers significant advantages, such as reduced material waste, optimized designs for lightweight structures, and localized production, which can decrease transportation emissions. However, its environmental benefits are context-dependent, as energy-intensive processes like laser powder bed fusion or high reliance on specific materials can offset these gains. LCA provides a comprehensive framework to assess these trade-offs, guiding sustainable decision-making by identifying hotspots in energy use, material efficiency, and recyclability, ultimately driving innovation towards greener AM practices. This research conducted a cradle-to-gate study of a cylindrical dog-bone tensile specimen. The life-cycle inventory data were obtained from Ecoinvent for conventional manufacturing, while data from the literature review and our research were employed for laser-based powder bed fusion. The results obtained show that the additive manufacturing process is more environmentally friendly. Although the environmental impact is minor, this process consumes a large amount of energy, mainly due to the atomization process and the high laser power. Regarding the mechanical response, AM reduced the ductility but increased the yield strength and achieved the same fracture strength.
Open Access
Article
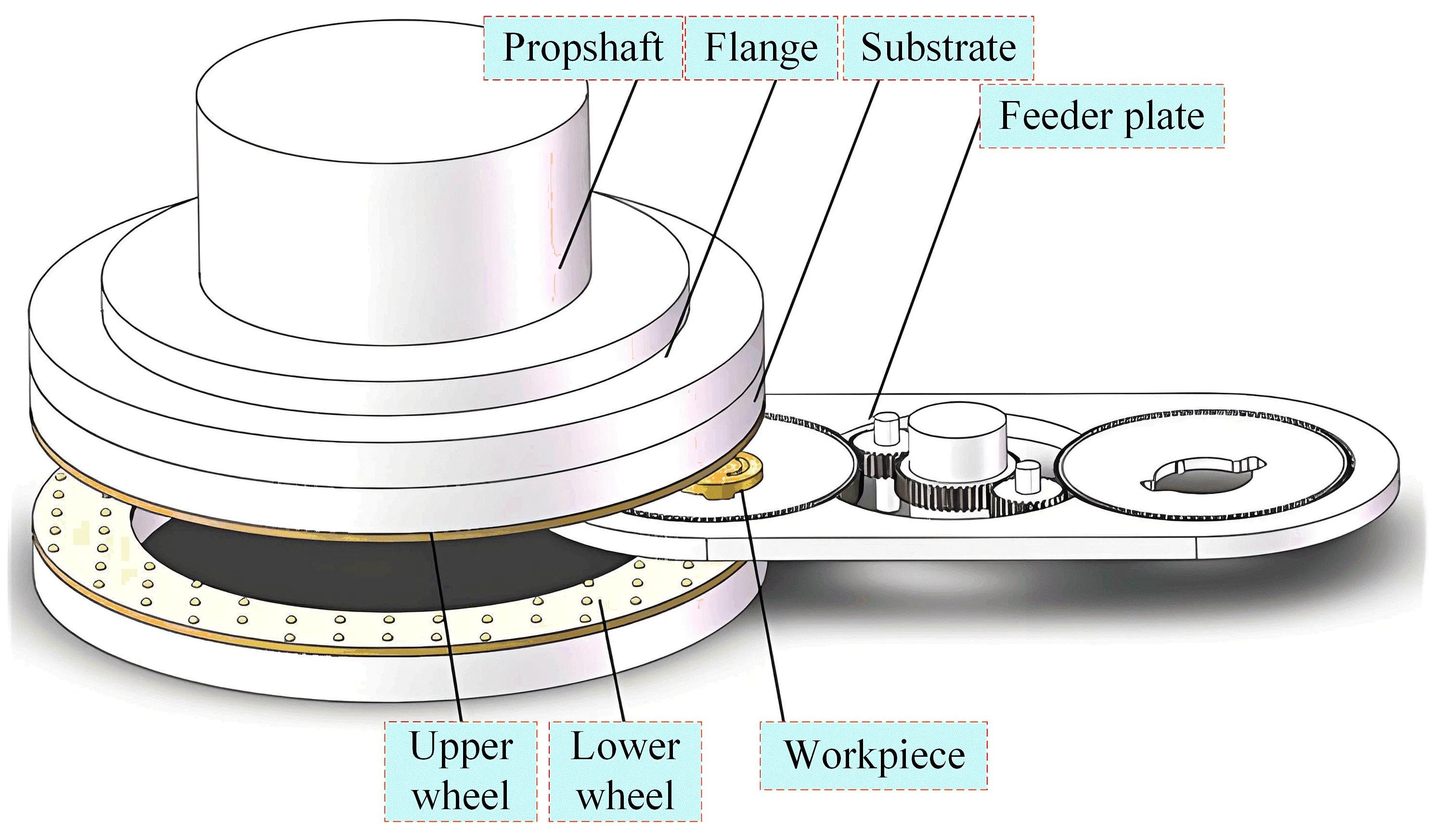
25 February 2025Thermal Characterization Study of Double End Face Grinding Powder Metallurgy Stainless Steel 316L
Double end face grinding machining is a highly efficient surface grinding technique. And grinding temperature is an important factor affecting the surface quality of workpieces. However, it is difficult to monitor the surface temperature of the workpiece in real time because of the covered contact between the grinding wheel and the upper and lower surfaces of the workpiece during the machining process. This paper aims to conduct a mechanistic analysis and experimental investigation of the machining process to address this challenge. Initially, the paper conducts an analysis of the kinematic mechanism, modal analysis, and the grinding force mechanism specific to the double end face grinding process. Afterwards, the mechanisms leading to the generation of grinding heat and the associated heat transfer mechanisms are explored in depth. The paper then proceeds to solve the instantaneous temperature field during double end face grinding by the finite element method (FEM). Furthermore, the micro and macro profile heights of the machined workpiece surfaces are measured and analyzed. The results show that the machined workpiece surface shows a high center and low edge. This is due to the fact that the temperature at the edge of the workpiece is higher than the center during machining, resulting in more material removal. Through these investigations, the study is able to determine the optimal process parameters for the machining process. This in turn improves machining efficiency and product conformity. And these findings not only guide practical production processes but also provide a foundation for future theoretical research in this area.