Prebiotic and Probiotic Foods in MASLD: Microbiome-Mediated Therapeutic Strategies
Received: 06 October 2025 Revised: 27 October 2025 Accepted: 19 November 2025 Published: 26 November 2025
© 2025 The authors. This is an open access article under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
1. Introduction
Fermented foods have historically played a central role in culinary traditions worldwide. Initially developed as a method for long-term food preservation, these foods have undergone continuous refinement, acquiring distinctive flavors and textures through microbial fermentation processes [1]. Such characteristics have contributed to their widespread popularity and recognition across diverse cultural contexts. Based on their primary raw materials, fermented foods can be broadly classified into fermented dairy products, vegetables, grains, legumes, and beverages.
Studies on the spontaneous fermentation of foods using naturally occurring microbial consortiums from the food source, including probiotics and bioactive compounds they contain, combined with a deeper understanding of their role in regulating the gut microbiome, have led to advancements in certain fermented foods as functional foods with tangible health benefits [2]. Advances in synthetic biology have pushed the field of functional foods via engineering and modification of fermentation strains, such as lactic acid bacteria (LAB), Bacillus, and other probiotics, alongside improvements in fermentation processes, further enhancing the functional properties of these foods, thereby reinforcing their role in promoting health and supporting dietary interventions [3].
Naturally occurring microbes found on the surface of raw products often help in the spontaneous fermentation of these functional foods, imbuing these foods with health-benefiting properties. The main players that provide these health-benefiting properties are probiotics and prebiotics. Microbes are considered probiotics owing to the health-benefiting properties they confer to consumers by regulating intestinal flora, enhancing intestinal barrier function, and modulating immune responses [4]. Additionally, probiotics must survive the harsh environment of the gastrointestinal tract and do not naturally assimilate into the host microbiota [4]. Prebiotics, in contrast, are dietary compounds that resist digestion by the human host, typically in the form of indigestible fibers, which serve as substrates for probiotics in the gut, promoting their growth and activity and leading to the production of beneficial bioactive compounds [4]. The synergistic effect of probiotics and prebiotics, referred to as symbiotic, fosters a favorable intestinal environment increasingly recognized as crucial for metabolic health [4]. The emergence of engineered probiotics aims to deliver targeted health benefits beyond those provided by natural strains, offering new therapeutic functions and opening avenues for dietary and medical interventions.
Studies have linked the gut microbiome to the pathogenesis of various metabolic disorders, including metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and its progression to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) [5]. Numerous studies have linked MASLD incidences to changes in dietary patterns within communities, especially in East Asian communities adapting Western dietary habits [6]. Dietary intervention remains the cornerstone for managing MASLD progression, even with FDA-approved medications available [7,8]. Strategies such as modulating the intestinal environment and metabolism via probiotics, limiting carbohydrate intake, and increasing consumption of bioactive substances, including short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and polyphenols, are considered effective in mitigating MASLD risk [9]. Engineered probiotics and next-generation fermented foods may further strengthen the efficacy of dietary interventions.
This review provides a comprehensive overview of the impact of fermented foods on MASLD, emphasizing the health benefits conferred by probiotics and bioactive compounds. It discusses the nutritional composition, bioactive constituents, and the mechanisms through which probiotics influence liver metabolic processes and the intestinal microenvironment. Drawing upon this body of evidence, the review highlights current dietary strategies as practical approaches to improving liver health and metabolic outcomes, while offering a forward-looking perspective on the role of engineered probiotics and next-generation fermented foods in MASLD dietary management.
2. The Role of Fermented Foods in Preventing MASLD Pathogenesis
Currently, dietary habits, gut microbiome imbalance, and leaky gut are considered the predominant causes of MASLD, where MASLD patients manage the disease via lifestyle changes and dietary interventions [5,9]. Dietary habits that contribute to MASLD progression include overconsumption of calories, saturated fats, sodium, added sugars, and alcohol [5].
Historically, the dietary cultures are shaped by the available crops that grow readily in the region. The nutritional content of different foods varies, giving rise to different results in fermented foods and their attributed health-benefiting properties. Furthermore, the fermentation process itself can significantly alter the nutritional composition of fermented foods compared to the raw materials. For example, sauerkraut has a lower protein content than fermented soy products [10,11]. These fermentative bacteria use nutrients in the food to produce metabolites that improve the nutritional value or flavor profile of the food [2]. For instance, LAB fermentation of milk consumes basic sugars to produce lactic acid, calcium with better bioavailability, conjugated linoleic acids, and fat-soluble vitamins that are useful to the host body [12].
The fermentation of foods may play a pivotal role in reducing the risk of developing MASLD by altering the nutritional values of foods and providing consumers with better access to health-benefiting metabolites (Figure 1).
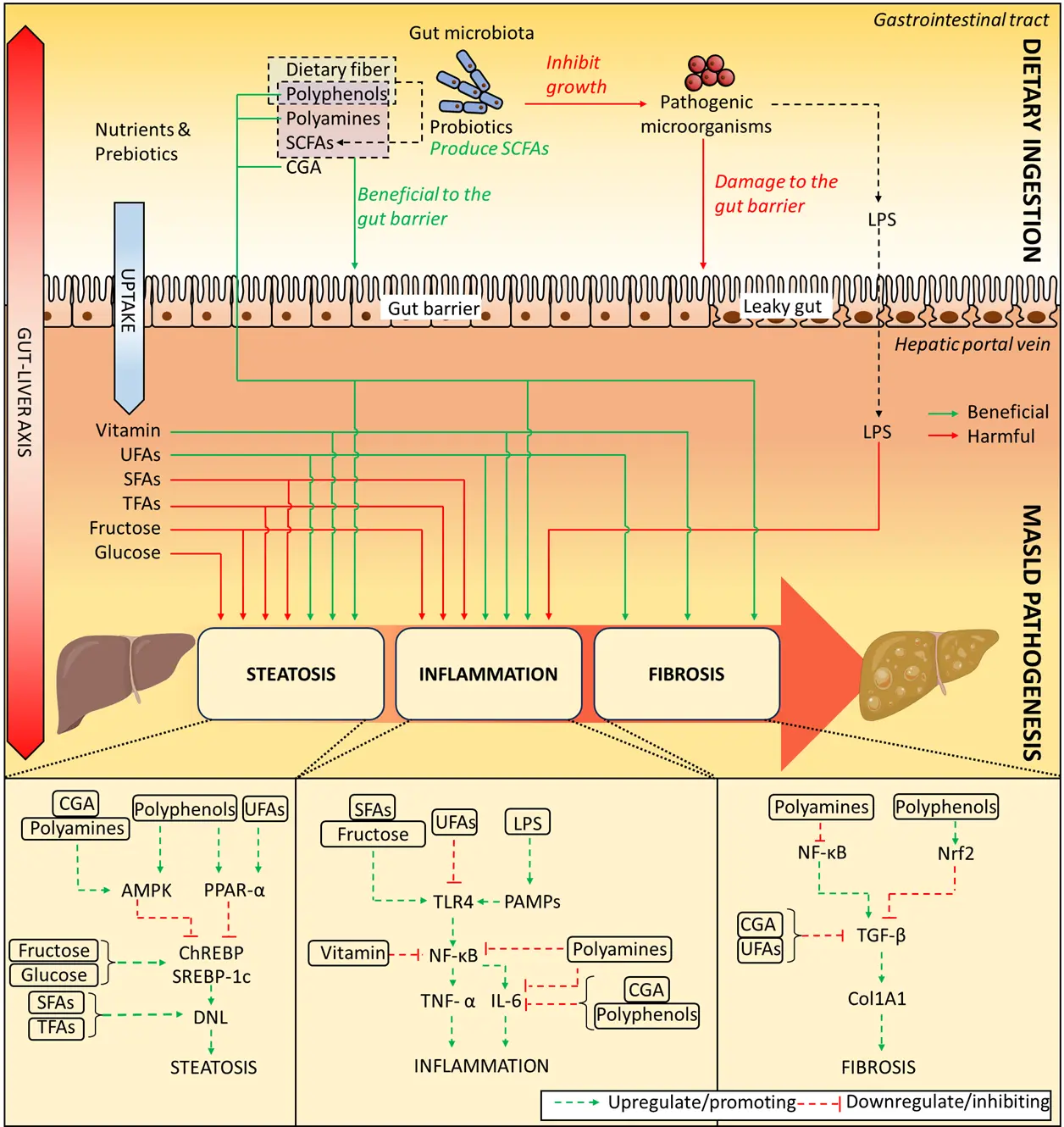
Figure 1. Regulatory role of fermented foods in the management of MASLD. Dietary intervention with fermented foods exerts regulatory effects on metabolic-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Rich in prebiotics and probiotics, fermented foods modulate the complex metabolic networks underlying hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis, thereby contributing to both the prevention and management of MASLD. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; CGA, chlorogenic acid; ChREBP, carbohydrate response element-binding protein; Col1A1, collagen type I alpha 1 chain; DNL, de novo lipogenesis; IL-6, Interleukin-6; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MASLD, Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappaB; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; PPAR-α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; SFAs, saturated fatty acids; SCFAs, short-chain fatty acids; SREBP-1c, Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c; TFA, trans fatty acids; TGF-β, Transforming growth factor-β; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; UFAs, unsaturated fatty acids.
2.1. Causes of MASLD: Disorders of Fat Metabolism and Inflammatory Pathways
MASLD is a metabolic disease caused by multiple cumulative disorders of liver lipid metabolism, liver inflammatory pathways, and complex crosstalk between multiple related pathways [13]. The liver is an important organ for lipid metabolism, where approximately 25% of the systemic fatty acids are sequestered in the liver [14]. De novo lipogenesis (DNL), which also takes place in adipose and hepatic tissues, is an important biological process that produces endogenous triglycerides (TG) from dietary substrates, where unregulated processes can lead to excessive fatty acid metabolic pressure [15]. Upon breaching the upper threshold of fat metabolic pressure, lipotoxicity occurs, resulting in a series of downstream reactions such as endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative stress, leading to cell apoptosis, inflammatory response, and exacerbated liver cell damage. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipotoxicity can also activate the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway, increase the level of inflammatory factors, and induce insulin resistance, further aggravating fat accumulation.
Perturbations in the gut-liver axis and impaired intestinal barrier function (i.e., leaky gut) can allow bacteria and their metabolites, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), to enter the hepatic portal vein, activating pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and releasing inflammatory mediators through the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MYD88) nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB) pathway [14,16]. PAMPs and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) can also activate the NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome pathway, which in turn enhances IL-1β and IL-18 levels through caspase-1, amplifying the immune response [17]. Overall, the inflammation in MASLD is the result of a multifactorial and multi-pathway interaction, including lipotoxicity-induced oxidative stress, gut-derived inflammatory stimulation, stress kinase activation, and the involvement of the NLRP3 inflammasome [18].
Notably, interventions with probiotics and prebiotics have been shown to ameliorate these deleterious processes. Probiotics can competitively inhibit colonization of pathogenic bacteria, upregulate the expression of tight junction proteins (including claudin, occludin, and zonula occludens-1), and enhance mucin secretion, thereby strengthening intestinal barrier integrity [19,20]. Prebiotics selectively stimulate the proliferation and metabolic activity of beneficial gut microbiota, leading to increased production of SCFAs such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate [21]. These SCFAs serve as an energy source for intestinal epithelial cells, modulate local immune responses, and, upon translocation to the liver via the portal circulation, regulate hepatic lipid metabolism and suppress inflammatory signaling [22]. Collectively, probiotics and prebiotics reduce the translocation of microbial products such as LPS, attenuate the activation of TLR4–MYD88–NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathways, and modulate gut–liver immune crosstalk, thereby exerting protective effects against the progression of MASLD [23].
2.2. Food Nutrients and the Regulatory Effects on MASLD
The nutritional content of fermented foods may regulate MASLD through two main approaches. First, their unique nutritional and bioactive components regulate liver fat metabolism and inflammatory responses. Second, consuming fermented foods can significantly improve consumers’ gut microbiome, which also plays a significant role in regulating MASLD [24]. This section will comprehensively elaborate on the nutritional and bioactive components of fermented foods along with relevant clinical or preclinical studies on MASLD patients (Table 1).
2.2.1. Fatty Acids
Fatty acids involved in lipid metabolism can be categorized into saturated fatty acids (SFAs), unsaturated fatty acids (UFAs), and trans fatty acids (TFAs). During the fermentation of dairy products, lipases secreted by LAB can hydrolyze lipids, releasing free fatty acids and thereby increasing the levels of both SFAs and UFAs. Certain LAB are also capable of synthesizing unsaturated fatty acids, such as conjugated linoleic acid, during fermentation [25,26]. Moreover, SFAs can be metabolized by probiotic bacteria into SCFAs, including acetate and butyrate. From a pathophysiological perspective, SFAs are known to promote the development of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) by serving as substrates for DNL and significantly contributing to hepatic triglyceride accumulation [27]. Working synergistically with SFAs, TFAs have a stimulatory effect on MASLD. In contrast, UFAs have been shown to alleviate MASLD [27].
Dietary SFAs are primarily palmitic acid and stearic acid. Palmitic acid is a substrate for DNL, which ultimately leads to TG accumulation and can contribute to the pathogenesis of MASLD [15]. Excessive intake of SFAs can lead to endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative stress, leading to hepatocyte apoptosis [28]. SFAs can also exacerbate insulin resistance. Notably, excessive intake of SFAs impairs the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, which are also thought to be involved in the regulation of MASLD [29]. In addition, SFAs can activate inflammatory pathways related to TLR4 signaling, beyond their effects on lipid metabolism [30,31]. TFAs exacerbate hepatic steatosis by increasing DNL, impairing beta-oxidation, and promoting inflammation; a diet high in TFAs induces features of steatohepatitis [32].
UFAs can be divided into monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), which can alleviate MASLD by regulating lipid metabolism and inflammatory responses [33]. Oleic acid is a MUFA that is abundant in olive oil, which can reduce the severity of MASLD and is a key component of the Mediterranean diet [34]. MUFAs affect signaling pathways by replacing SFAs in cell membranes, thereby improving insulin sensitivity and lipid profiles. PUFAs include omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids include eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which can inhibit sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c (SREBP-1c) by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) and suppress DNL [35]. In mouse models, omega-3 PUFAs can alleviate high fat diet (HFD)-induced steatosis by stimulating the proliferation and differentiation of preadipocytes [36]. PUFAs can also reduce inflammatory responses in MASLD. Linoleic acid, an omega-6 fatty acid, can inhibit inflammatory responses by inhibiting the JNK pathway and NF-κB. EPA and DHA mediate anti-inflammatory effects by activating GPR120 [37]. DHA also alleviates liver inflammation by inhibiting hepatic expression of CD14 and TLRs and consequently suppressing NF-κB [38,39]. In addition, DHA reduces the gene and protein expression of collagen type I alpha 1 chain (Col1A1) in hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) by attenuating transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling, thereby alleviating liver fibrosis [40]. Therefore, DHA has a better therapeutic effect than EPA. However, in clinical practice, the therapeutic effects of EPA and DHA are inconsistent [41,42,43,44,45].
2.2.2. Carbohydrates
Dietary carbohydrates can be categorized into sugars (monosaccharides, disaccharides, and oligosaccharides) and dietary fiber. During food fermentation, the composition and concentration of carbohydrates undergo substantial alterations, largely determined by the metabolic characteristics of the fermenting microorganisms. In most LAB–mediated fermentations, sugars are metabolized through glycolytic and heterofermentative pathways to yield lactic acid, ethanol, acetic acid, and, in some cases, carbon dioxide. The total dietary fiber content may decline during fermentation, primarily due to microbial enzymatic degradation. In legumes, for instance, soluble dietary fiber typically decreases, whereas the insoluble fraction remains relatively stable [46]. These fermentable fibers can be further utilized by probiotic microorganisms during fermentation process or within the gastrointestinal tract, leading to the production of SCFAs that exert beneficial effects on host metabolism and gut health. The monosaccharides fructose and glucose play a key role in the progression of MASLD [15]. Excessive intake of these sugars can lead to hepatic steatosis, insulin resistance, and systemic inflammation.
While both glucose and fructose can increase DNL levels, their mechanisms are different. Glucose stimulates hepatic DNL primarily by enhancing carbohydrate response element-binding protein (ChREBP) and SREBP-1c [47,48]. High blood glucose levels are associated with insulin resistance, which in turn maintains the sensitivity of the SREBP-1c pathway, leading to elevated SREBP-1c levels. DNL may produce diacylglycerol and ceramides, which promote insulin resistance, thereby creating a positive feedback loop and further exacerbating disease progression [49,50]. Fructose primarily activates ChREBP, but can also induce SREBP-1c activation in an insulin-dependent or -independent manner, or enhance DNL through the liver X receptor (LXR) and PGC-1β pathways involved in TG metabolism [51,52,53]. In addition, excess fructose is metabolized to acetate by gut microbes in the small intestine, which is then converted to acetyl-CoA by ACSS2 and enters the TG production pathway of DNL as a new, independent substrate [54]. Therefore, the lipogenic effect of fructose is considered to be stronger than that of glucose.
Various studies have been conducted to validate that excessive sugar intake exacerbates inflammatory responses. Murine models fed fructose showed TLR4 signaling activation, leading to inflammatory responses via increased expression of the inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and TNF-α [55,56]. Additionally, excessive fructose intake induces oxidative stress caused by both increased lipid metabolic pressure and the production of uric acid from fructose metabolism [57].
Dietary fiber, typically a non-digestible polysaccharide, is often added to foods as a prebiotic [58]. Gut microbes metabolize ingested dietary fiber to produce SCFAs that exert beneficial health effects [59]. Dietary fiber intake can improve hepatic fat metabolism, delay blood sugar absorption, reduce insulin spikes, inhibit lipogenesis, and promote lipolysis, which are beneficial for reducing fat accumulation in the liver [60]. Studies have shown that intake of total fiber, cereal fiber, fruit fiber, and plant fiber is negatively correlated with the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [61]. Dietary fiber can also improve intestinal barrier integrity and reduce the translocation of inflammatory factors [60].
2.2.3. Vitamins
Vitamins are essential micronutrients for human health, as humans cannot synthesize them or their precursors endogenously, and must acquire them through dietary intake. The alterations in vitamin content during fermentation are complex and depend on microbial activity and substrate composition. In general, fermentation enhances the levels of B vitamins and vitamin K, which are synthesized as metabolic byproducts of fermenting microorganisms. For instance, increased concentrations of B vitamins have been observed in yogurt, fermented soy products, and kimchi, while vitamin K levels rise notably in natto [62]. In contrast, vitamin C, a water-soluble and chemically unstable compound, tends to degrade easily, although it may remain relatively stable during the early stages of vegetable fermentation [63]. Overall, fermentation processes generally improve the bioavailability and nutritional value of vitamins [62].
In the context of liver health, accumulating evidence indicates a strong association between vitamin deficiencies and liver disease. There is a synergistic relationship between vitamins and liver function, reflected by the intricate interplay between vitamins and the liver–adipose axis [64]. It was found that liver impairment leads to poor vitamin uptake, while vitamin deficiencies were found to worsen hepatic pathology. Corresponding, intestinal absorption of vitamins A, D, K, and C is impaired in patients with disrupted bile secretion [65]. While there is evidence supporting the vitamins and liver–adipose axis, it remains poorly understood and is currently an emerging area of clinical investigation [66].
Vitamins regulate hepatic metabolism and influence the progression of liver disease primarily through their effects on lipid metabolism. These vitamins include:
-
-
Vitamins A and K play a complex, reciprocal role in MASLD regulation. Vitamin A prevents lipid accumulation in white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT) [67]. Its metabolite, retinoic acid, exerts therapeutic effects in NAFLD by enhancing fatty acid oxidation and activating RAR-mediated thermogenic pathways, although these effects are not always liver-specific [68]. Conversely, NAFLD progression increases circulating levels of the vitamin A transporter RBP4, leading to chronically elevated vitamin A and impaired mitochondrial lipid oxidation [69]. Vitamin K, as a fat-soluble nutrient, is prone to sequestration in excessive adipose tissue, resulting in deficiency [64]. Nonetheless, vitamin K may alleviate hepatic steatosis by modulating the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/SREBP1/PPARα signaling cascade through GAS6 activation [70].
-
-
B vitamins Evidence linking B-vitamins to NAFLD remains limited and occasionally inconsistent [66]. Niacin (vitamin B3), as a precursor of NAD and NADPH, modulates lipid metabolism, enhances hepatic redox balance, and reduces TG accumulation, although prolonged supplementation may impair insulin sensitivity [71]. Folate (vitamin B9) deficiency promotes hyperhomocysteinemia and hepatic lipid deposition, whereas supplementation may activate AMPK, thereby mitigating steatosis [72]. Vitamin B12 deficiency interferes with mitochondrial β-oxidation via disrupted methylmalonyl-CoA metabolism, correlating with increased fibrosis severity [73]. Similarly, vitamin B6 deficiency elevates homocysteine levels, inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress and SREBP-1c–driven lipogenesis [66]. Collectively, these findings highlight the potential metabolic and hepatoprotective roles of B-vitamins in NAFLD pathogenesis, though clinical evidence remains inconclusive.
-
-
Vitamin C reduces circulating and hepatic TG, enhances lipolysis, and decreases microsomal TG transfer protein (MTP) levels [74]. In addition, it promotes AMPK phosphorylation, inhibits nuclear translocation of LXR, and suppresses DNL [75].
-
-
Vitamin D plays a critical role in lipid homeostasis, and its deficiency promotes macrophage infiltration into WAT, thereby driving fibrosis and aggravating MASLD [76]. Supplementation with vitamin D has been shown to attenuate WAT-associated inflammation and hepatic steatosis [77,78].
-
-
Vitamin E exerts robust protective functions in MASLD. Specifically, α-tocopherol inhibits DNL through its antioxidant capacity and lipid solubility [79]. Various isoforms of vitamin E also demonstrate synergistic activity and may represent therapeutic targets for reducing lipid deposition and inflammation in both adipose tissue and liver, in part by suppressing NF-κB signaling and activating PPARα [80].
2.2.4. Polyphenols
Polyphenols constitute a structurally diverse class of plant-derived bioactive compounds with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic regulatory properties [81].
Polyphenols constitute a structurally diverse class of plant-derived bioactive compounds endowed with potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolic regulatory activities [81]. In food matrices, phenolic compounds are frequently present in conjugated or macromolecular-bound forms, such as complexes with glycosides, cellulose, starch, or proteins, which substantially limit their bioaccessibility and bioavailability. During fermentation, microorganisms not only engage in the metabolic transformation of substrates but also secrete a wide array of enzymes with specific catalytic functions, including tannase, esterase, phenolic acid decarboxylases, and glycosidase [82]. These enzymes effectively hydrolyze or depolymerize bound polyphenols, thereby releasing free phenolic acids, flavonoids, and other low-molecular-weight phenolics. Specifically, tannase catalyzes the depolymerization of complex high-molecular-weight tannins into simpler phenolic acids or catechin derivatives; esterase cleaves ester linkages between hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives and macromolecules such as proteins, lignin, or cellulose; phenolic acid decarboxylases mediates the redox transformation of hydroxycinnamic acids, modifying their structural and antioxidant properties and generating volatile phenolic compounds; while glycosidase hydrolyzes glycosidic bonds between polyphenols and sugars, thereby enhancing the bioactivity and bioavailability of flavonoids [82]. Collectively, these enzymatic transformations increase the solubility and intestinal absorption of phenolic compounds, thereby augmenting the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial potential of fermented foods and ultimately improving their nutritional and health-promoting properties.
In the field of MASLD research, curcumin, hesperidin, naringenin, genistein, catechin, and silymarin have demonstrated direct therapeutic potential against MASLD [83,84]. Specifically, curcumin reduces liver enzyme levels, TG, total cholesterol, and insulin resistance, while attenuating hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis through modulation of AMPK, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), TGF-β, and IL-6 signaling pathways [85]. Silymarin lowers liver enzyme levels and diminishes hepatic lipid accumulation via the FXR pathway [86]. Catechins, abundantly present in tea, effectively mitigate TG levels and insulin resistance, where green tea extract-derived catechins confer hepatoprotective effects through activation of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes, SIRT1, and AMPK [87,88,89]. Hesperidin enhances hepatic metabolic function via SIRT1/PGC1α activation, resulting in reductions in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) levels and attenuation of inflammatory markers [90,91]. Resveratrol alleviates lipid accumulation and inflammatory responses by upregulating SIRT1 and AMPK, although its efficacy varies across studies [92,93,94].
Additionally, polyphenols indirectly modulate MASLD pathogenesis by altering the gut microbiota. Silymarin changes microbial composition and reduces liver stiffness through FXR-mediated mechanisms [95,96]. Fermented black buckwheat exhibits decreased rutin content, increased total phenolics (quercetin and kaempferol), and elevates populations of Lactobacillus, Faecalibaculum, and Allobaculum in murine models [97]. Fu brick tea polyphenol extracts ameliorate intestinal oxidative stress and inflammation, reinforce intestinal barrier integrity, and promote gut microbial diversity, thereby enhancing Akkermansia muciniphila, Alloprevotella, Bacteroides, and Faecalibaculum [98]. While most of these studies did not directly assess overall hepatic health, these studies established that the interplay between MASLD and the gut-liver axis suggests that these microbial alterations contribute to hepatic benefits.
Despite their extensive bioactivities, polyphenols are characterized by limited oral bioavailability and a short biological half-life. Polyphenols with lower molecular weight or aglycone forms generally exhibit higher physiological activity. Probiotic fermentation enhances the bioactivity of polyphenols by converting high-molecular-weight compounds into smaller, more bioactive forms. Consequently, the polyphenol composition of fermented foods differs substantially from that of raw materials [82]. For instance, rutin and isoquercetin in fermented black buckwheat, jujubes, and sourdough bread are hydrolyzed to quercetin, whereas glycosyl glycosides (daidzin and genistin) in soybeans are reduced, with concomitant increases in aglycones (daidzein, glycitein, and genistein) [97,99,100]. These alterations in polyphenol composition confer functional advantages, as evidenced by the enhanced antioxidant activity and DNA-protective properties of fermented soy products [101].
2.2.5. Polyamines
Aliphatic polycations, commonly referred to as polyamines, play a critical role in the pathogenesis of MASLD by modulating cellular lipid accumulation, mitochondrial function, and fibrosis progression [102]. Polyamines can be synthesized endogenously through intrinsic metabolic pathways or acquired exogenously via the diet, with principal sources including whole grains, soy products, mushrooms, and fermented foods. During fermentation, polyamines undergo a series of dynamic transformations, encompassing microbial decarboxylation of amino acids—such as ornithine conversion to putrescine, lysine to cadaverine, and arginine to spermidine—followed by oxidative deamination and interconversion reactions [103]. These processes are tightly regulated by factors including the composition of the microbial community, fermentation duration, pH, and redox conditions, which collectively shape the polyamine profile of the final product [103]. Furthermore, commensal and probiotic gut microorganisms, including Fusobacterium and Bacteroides, are capable of synthesizing polyamines, with spermidine and putrescine concentrations in the intestinal lumen of healthy individuals typically ranging from 0.5 to 1 mM [104]. This evidence suggests that polyamines derived from both dietary intake and the gut microbiota contribute synergistically to the maintenance of host metabolic homeostasis.
Among them, spermidine has been the most extensively studied for its relation to MASLD. Preclinical studies indicate that spermidine ameliorates hepatic steatosis and inflammation in MASLD models by inducing autophagy and activating AMPK [105]. Dietary supplementation with spermidine reduces hepatic lipid accumulation, mitigates liver injury, and attenuates fibrosis by suppressing proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-1β [105]. Additionally, spermidine regulates lipid metabolism through activation of SIRT1 and inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), which contributes to improved hepatic insulin sensitivity and decreased oxidative stress [106]. Spermine has also been shown to confer hepatoprotective effects in preclinical models. Supplementation can attenuate acute liver injury by suppressing proinflammatory responses in liver-resident macrophages via an ATG5-dependent autophagy pathway [107]. In addition, spermine enhances liver barrier function, regulates amino acid transporter activity, and inhibits apoptosis, further supporting its protective role in hepatic homeostasis [108].
Direct clinical evidence regarding the effect of putrescine on MASLD progression is currently lacking. In animal models, putrescine supplementation has been shown to exert anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects by inhibiting NF-κB and IL-6 signaling pathways, thereby alleviating hepatic injury [109]. Conversely, other studies have reported that elevated endogenous putrescine levels and increased ornithine decarboxylase activity are positively correlated with MASLD severity, with higher putrescine concentrations leading to enhanced CK-18 release [109].
2.2.6. Caffeine and Chlorogenic Acid
Caffeine and chlorogenic acid (CGA), commonly present in coffee and tea, have been proposed to exert hepatoprotective effects in MASLD. Epidemiological evidence suggests an inverse association between caffeine and CGA intake and MASLD progression; however, findings are inconsistent, with some studies reporting contrasting results [110,111,112]. Some of these findings discovered that these compounds modulate hepatic lipid metabolism by suppressing DNL and enhancing fatty acid β-oxidation [113,114,115,116]. Despite accumulating evidence supporting a protective role of caffeine and CGA, the precise molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood.
Current research on the mechanisms of caffeine and CGA has revealed that caffeine reduces hepatic TG accumulation by inhibiting SREBP-1c and ChREBP while upregulating PPARα and CPT1 [113]. It also activates AMPK signaling, resulting in decreased hepatic lipid content and improved insulin sensitivity. CGA attenuates hepatic steatosis by suppressing lipogenesis and enhancing fatty acid β-oxidation, and activates AMPK signaling, inhibits SREBP-1c and LXRα, thus reducing hepatic TG levels [117]. Both caffeine and CGA mitigate inflammation and fibrotic pathways through modulation of IL-6/STAT3 signaling [118]. Furthermore, CGA has been shown to slow fibrosis via the TGF-β1/Smad7 pathway [119].
The reported variability in the effects of caffeine and CGA on MASLD may stem from differences in experimental models, dosage, treatment duration, age, and sex of subjects [120]. Accordingly, further studies are warranted to elucidate the parameters and limitations of using caffeine and CGA to regulate MASLD and MASH pathogenesis and progression.
2.2.7. Probiotics and Microorganisms
The role of microorganisms in food fermentation relies heavily on their interaction with other microbes and the nutritional composition of the foods. While most microbes would not survive gastrointestinal passage, the metabolic products from the fermentation process and probiotic microbes within the fermentation communities exert their influence on MASLD pathogenesis. Studies of intestinal microbiota indicate that some bacterial populations may have complex or even detrimental effects on MASLD progression.
Evidence indicates that gut microbiota composition changes progressively across MASLD and MASH stages [121]. At the phylum level, Bacteroidetes are consistently reduced, whereas Firmicutes and Proteobacteria are expanded [121]. At the family level, Enterobacteriaceae are enriched, while Rikenellaceae and Ruminococcaceae are depleted [121]. At the genus level, Escherichia, Dorea, and Peptoniphilus are increased, whereas Anaerosporobacter, Coprococcus, Eubacterium, Faecalibacterium, and Prevotella are reduced [121]. These shifts indicate a dysbiotic microbial community favoring pro-inflammatory and endotoxin-producing taxa [121,122].
Table 1. Impact of dietary nutrients and bioactive compounds on MASLD metabolism.
| Category | Effect on MASLD Metabolism | References |
|---|---|---|
| Fatty Acids | ||
| SFAs | DNL↑, insulin resistance↑, inflammation↑ | [28,29,30,31] |
| TFAs | DNL↑, beta-oxidation↓, inflammation↑; hepatic steatosis↑ | [32] |
| MUFAs | Insulin sensitivity↑, reduce the severity of MASLD | [33,34] |
| PUFAs | EPA: DNL↓, inflammation↓ | [35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] |
| DHA: DNL↓, inflammation↓, fibrosis↓ | ||
| Carbohydrates | ||
| Fructose | DNL↑, insulin resistance↑, inflammation↑ | [47,48,51,52,53] |
| Glucose | DNL↑, insulin resistance↑ | [47,48,49,50] |
| Dietary fiber | Lipogenesis↓, lipolysis↑, improve gut barrier | [58,59,60] |
| Vitamins | ||
| Vitamin A | Fatty acid oxidation↑, prevents lipid accumulation in adipose | [67,68,69] |
| Vitamin K | Hepatic steatosis↓ | [70] |
| Vitamin B | Modulates lipid metabolism, TG↓, hepatic steatosis↓ | [66,71,72,73] |
| Vitamin B12 deficiency: fibrosis↑; Vitamin B6 deficiency: Lipogenesis↑ | ||
| Vitamin C | TG↓, lipolysis↑, DNL↓. | [74,75] |
| Vitamin D | Deficiency: macrophage infiltration in WAT↑, fibrosis↑; | [76,77,78] |
| Supplementation: inflammation↓, hepatic steatosis↓ | ||
| Vitamin E | DNL↓, lipid deposition↓, inflammation↓, | [79,80] |
| Polyphenols | ||
| Curcumin | Hepatic steatosis↓, inflammation↓, fibrosis↓ | [85] |
| Silymarin | Lipid accumulation↓ | [86] |
| Catechins | TG↓, insulin resistance↓ | [87,88,89] |
| Hesperidin | Inflammation↓ | [90,91] |
| Resveratrol | Lipid accumulation↓, inflammation↓ | [92,93,94] |
| Polyamines | ||
| Spermidine | Lipid accumulation↓, Hepatic steatosis↓, inflammation↓, fibrosis↓ | [105,106] |
| Spermine | Inflammation↓ | [107,108] |
| Putrescine | Inflammation↓ | [109] |
| Others | ||
| Caffeine | TG↓, insulin sensitivity↑, inflammation↓, fibrosis↓. | [113,118] |
| CGA | Lipogenesis↓, fatty acid β-oxidation↑, inflammation↓, fibrosis↓ | [117,118,119] |
| Probiotics | Hepatic steatosis↓, inflammation↓, improve gut barrier | [121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134,135,136] |
A key functional consequence of these changes is the altered production of SCFAs, which are critical for maintaining intestinal epithelial integrity, stimulating mucus secretion, and preventing bacterial translocation [123]. Specifically, Bacteroides are primary producers of acetate, while Firmicutes predominantly generate butyrate [124]. Reduced butyrate availability is associated with impaired barrier function and enhanced inflammatory signaling along the gut-liver axis [125].
Given these insights, probiotic interventions have been explored to restore microbial balance and mitigate liver injury. In mouse models of hepatic steatosis, four-week probiotic administration significantly reduced liver fat accumulation [126]. Multiple strains, including Lactobacillus casei, L. rhamnosus, L. bulgaricus, Bifidobacterium longum, and Streptococcus thermophilus, have demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects in the liver [127]. Long-term supplementation with B. longum combined with fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) and lifestyle interventions significantly reduced TNF-α, C-reactive protein (CRP), AST, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), and serum endotoxin levels, while improving hepatic steatosis and the MASH activity index [128]. In other models, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii supplementation restored intestinal barrier integrity, and four-week supplementation with Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM® improved insulin sensitivity via reductions in LPS levels, modulation of TLR signaling, and cytokine regulation [129,130]. Experiments with MIYAIRI 588, a butyrate-producing probiotic, in NAFLD rat models also demonstrated reductions in hepatic TG accumulation, insulin resistance, serum endotoxin levels, and markers of liver inflammation [131].
Nonetheless, the clinical efficacy of probiotics remains controversial. While some trials suggest that combinations of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Streptococcus are most effective, other studies have failed to replicate these findings [127,132]. Variations in probiotic formulations, dosage, treatment duration, and patient populations contribute to inconsistent outcomes.
Overall, probiotic supplementation represents a promising adjunctive therapy for MASLD/MASH, yet well-designed randomized controlled trials are required to determine optimal strains, combinations, and treatment regimens. Engineered probiotics have the potential to enhance the viability and therapeutic potential of beneficial strains. Next-generation fermented foods can more effectively control microbial composition, thereby improving their impact on MASLD management.
2.2.8. Engineered Probiotics
Probiotics, including Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, have been shown to improve liver function parameters, attenuate hepatic steatosis, and modulate glucose, insulin, and lipid profiles in MASLD [133]. Engineered strains have emerged as novel therapeutic strategies beyond conventional probiotics.
Preclinical studies demonstrate that IL-22, an IL-10 cytokine family member, delivered via engineered Lactobacillus reuteri, induces localized expression of the antimicrobial protein regenerating islet-derived 3-gamma (Reg3γ), effectively reducing bacterial translocation and mitigating ethanol-induced liver injury, steatosis, and inflammation [134].
Similarly, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) delivered through engineered Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 or Lactobacillus gasseri enhances insulin secretion, decreases body weight, improves lipid profiles, and ameliorates liver biochemistry and histopathology [135,136]. These findings underscore the therapeutic potential of both conventional and engineered probiotics in MASLD.
2.3. The Impact of Fermented Foods on MASLD
Fermented foods confer multiple benefits for liver health. Firstly, microbial fermentation substantially increases the levels of bioactive metabolites within these foods. Secondly, certain nutrients such as fructose and glucose, which may be detrimental in MASLD, can serve as metabolic substrates for microbial growth and are converted into beneficial bioactive compounds, including PUFAs. Additionally, the fermentation process often breaks down large molecules into smaller, more bioavailable forms, such as polyphenols [82]. Enhanced bioavailability of polyphenols following microbial fermentation contributes to their health-promoting effects. Moreover, consumption of fermented foods frequently modulates the intestinal microbiome, and probiotics, such as LAB, are commonly incorporated into these products.
2.3.1. Fermented Dairy Products
Fermented dairy products—including yogurt, kefir, and cheese—are widely consumed, available in diverse forms, and have been extensively investigated as potential interventions for the management of MASLD [137,138,139]. Notably, kefir, a fermented dairy beverage containing diverse probiotics and yeasts, has been shown to reduce hepatic lipid accumulation, lower serum ALT levels, and attenuate inflammatory responses in preclinical MASLD models [140]. Another study further suggested that regular consumption of fermented dairy products improves insulin resistance and lipid profiles, thereby exerting protective effects [139]. The underlying mechanisms include bioactive peptides and SCFAs generated during LAB fermentation [141].
2.3.2. Fermented Legume Products
Fermented soy products are regarded as having numerous health benefits [142]. Fermentation enhances the bioavailability of key bioactive compounds, such as SCFAs, polyphenols, and antioxidant peptides, thereby improving their physiological effects [143,144]. Common fermented soy products, including natto, miso, and tempeh, have demonstrated benefits in the prevention and management of MASLD [145,146,147]. Evidence from animal studies indicates that miso and natto can attenuate hepatic steatosis and inflammation, primarily through modulation of the gut microbiota [147]. Although large-scale randomized controlled trials remain limited, current findings suggest that fermented soy products represent a promising dietary strategy for MASLD management [142].
2.3.3. Fermented Plant-Based Beverages
Fermented beverages constitute another important category of fermented foods. While many fermented beverages traditionally contain alcohol, such as beer and red wine, a wide range of non-alcoholic alternatives—including fermented juices and teas—are also widely consumed. Although research in this area remains limited, existing studies indicate that fermented juices may exert protective effects against liver disease [148,149].
The effects of alcoholic fermented beverages, such as wine and beer, on MASLD remain inconclusive. Because excessive alcohol intake is a well-established cause of alcoholic liver disease, most studies investigating this topic are confined to moderate consumption levels (≤30 g/day for men and ≤20 g/day for women) [150]. Beer contains a variety of bioactive compounds, including polyphenols such as xanthohumol, isoxanthohumol, and phenolic acids, as well as bitter and α-acid derivatives derived from hops (humulones, lupulones, and isohumulones) [151]. Wine, in contrast, is particularly rich in polyphenolic constituents, comprising stilbenes (e.g., resveratrol), phenolic acids, and flavonoids (including flavan-3-ols, anthocyanins, and quercetin) [151]. These compounds have been reported to exert antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid metabolism–modulating effects. Nevertheless, it remains uncertain whether such bioactive components can counteract the hepatotoxic effects of alcohol itself [151]. Overall, the influence of alcohol consumption on MASLD is still controversial: the available evidence is limited, and findings across studies are inconsistent with respect to the significance and direction of this association [152].
Among non-alcoholic beverages, kombucha, a fermented tea that has gained global popularity, is notable for its abundance of polyphenols, organic acids, and water-soluble vitamins, as well as its documented antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties [153]. Evidence from murine models demonstrates that kombucha supplementation reduces hepatic steatosis, lowers TG levels, and decreases markers of liver injury [154]. Moreover, kombucha has been shown to modulate the gut microbiota, thereby potentially alleviating inflammatory stress along the gut-liver axis [155]. Collectively, these findings suggest that kombucha represents a promising adjunct to dietary interventions for the management of MASLD.
3. Applications and Technologies of Engineered Fermentative Bacteria
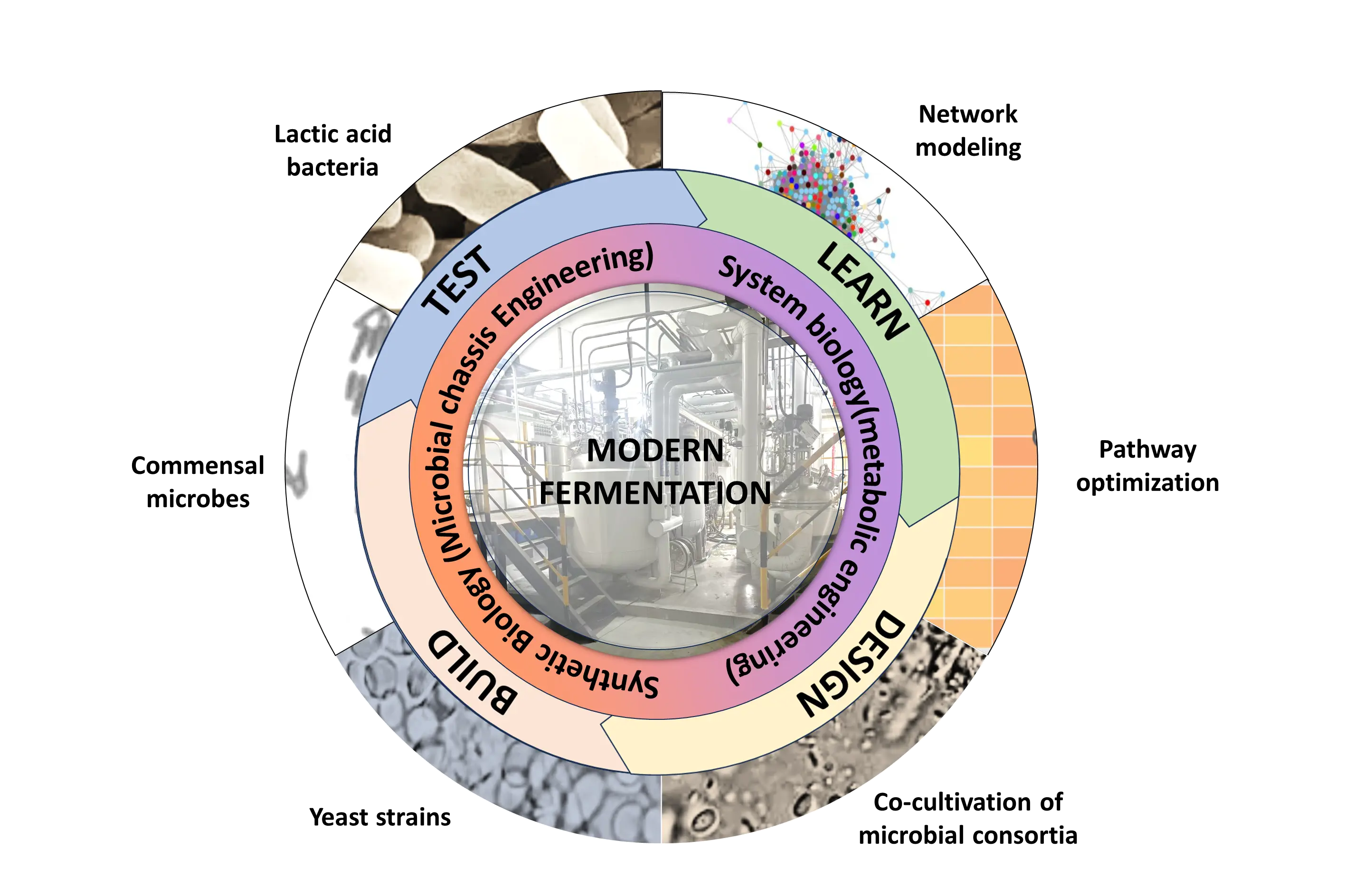
With the advancement of the modern food industry, fermentation technology has evolved significantly. Progress spans from the selection and breeding of fermentative strains to their modification through genetic techniques and metabolic engineering; from naturally occurring multi-strain fermentations to single-strain fermentations for controlled quality; and to co-culture fermentations designed to enhance flavor and nutritional value [156]. The development of food fermentation is closely intertwined with advances in modern biotechnology, with contemporary fermentation emphasizing not only flavor and texture but also functionality and process controllability [157]. Figure 2 highlights the principal technological innovations that drive contemporary advances in fermentation.
3.1. Comparison of Traditional and Modern Fermentation
Traditional fermentation relies on natural bacterial flora or empirically selected strains, often resulting in substantial batch-to-batch variability and low process stability [158]. In contrast, modern fermentation typically employs standardized or engineered strains, allowing controlled fermentation through single-strain or co-culture approaches. The application of metabolically engineered strains of LAB, Bacillus, and yeast can increase yields of target metabolites, reduce undesirable byproducts, and inhibit the growth of harmful microorganisms [159,160].
Traditional methods of improving the fermentation process involve isolating strains that have undergone directed evolution over many iterations of fermentation [161]. This process can be observed in historically documented instances of starter cultures that have been maintained by selective brewers and fermentation experts, where certain starter cultures used in fermentation confer improved flavor profiles, color, aroma, and health-benefiting properties. This selection process represents the domestication of strains that have been conditioned to use a particular nutrient source over many generations of fermentation, allowing the microbial community to enhance their selected characteristics. These selected characteristics are often the result of genetic enhancements within the microbe, selected by evolutionary pressure to gain an advantage over other microbial counterparts. An overall comparative overview of the distinguishing features of traditional versus modern fermentation is presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Comparison between traditional and modern fermentation.
|
Feature |
Traditional Fermentation |
Modern Fermentation |
|---|---|---|
|
Strain type |
Natural microbial communities or empirically selected strains |
Standardized or engineered strains (e.g., LAB, Bacillus, yeast) |
|
Process control |
Difficult to control, dependent on natural selection/experience |
Highly controllable, employing single strains or co-culture methods |
|
Process stability |
Low, often leading to large batch-to-batch variability |
High, with predictable and standardized outcomes |
|
Product optimization |
Directed evolution through multiple fermentation cycles (time-consuming) |
Genetic technologies and metabolic engineering (rapid and efficient) |
|
Main advantages |
Development of unique flavors, colors, and textures |
Increased yield of target metabolites, reduced undesirable byproducts, and inhibition of harmful microorganisms |
|
Technical basis |
Accumulated empirical knowledge, strain domestication |
Modern biotechnologies (e.g., CRISPR, metabolic engineering, synthetic biology) |
3.2. Applications of Engineered Bacteria in Fermentation
Engineered strains are increasingly used to produce a variety of bioactive compounds to address unmet nutritional needs. PUFAs, for example, are natural products that are difficult to synthesize chemically [162]. Researchers have developed microbial production platforms, using prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms with polyketide synthase (PKS) pathways, to synthesize DHA and EPA. Marine bacteria such as Colwellia psychrerythraea, Moritella marina, and Shewanella pneumatophori serve as microbial hosts for PKS-mediated PUFA biosynthesis [163,164,165,166]. The selection of these microbial chassis for engineering stems from the native ability of the microbe to generate sufficient CoA precursors needed to power the PKS catalysis. Biosynthesized DHA and EPA are now utilized as functional food additives [167].
LAB and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens are mature biological platforms suitable for engineering as fermentation strains [168]. CRISPR-based genetic toolkits enable rapid gene knockout and integration of functional genes in B. amyloliquefaciens, thereby enhancing its utility in food applications [169]. For instance, metabolic engineering has increased γ-poly glutamic acid (γ-PGA) production in fermented corn [170]. B. amyloliquefaciens also exhibits probiotic properties; feeding B. amyloliquefaciens strain SC06 to mice on a high-fat diet reduced fat accumulation, improved insulin sensitivity, and attenuated liver inflammation, along with decreased levels of inflammatory markers such as IL-6 and TNF-α [171]. Engineered LAB fermentation in dairy products has been used to enhance conjugated linoleic acid production, contributing to the mitigation of MASLD progression [172].
Similarly, CRISPR-based genetic engineering has been used extensively to remove competing pathways within microbial cells to enhance the production of targeted therapeutics and value-added chemicals within fermented foods [173]. Other approaches leverage the use of engineered microbes to ferment ingested unfermented foods within the gastrointestinal tract of the host, allowing the preservation of sensitive metabolites that would not otherwise survive the gastrointestinal passage [174].
3.3. Systems Biology and Synthetic Biology in Fermentation
Modern fermentation has progressed from traditional methods using natural strains to highly efficient systems that integrate molecular biology, metabolic engineering, and synthetic biology. Synthetic biology enables precise design and reconstruction of microbial genomes, metabolic pathways, and regulatory networks, rendering fermentation processes more controllable, high-yielding, and functional. LAB and B. amyloliquefaciens serve as primary “biological chassis” in food fermentation, with gene editing technologies such as CRISPR-Cas facilitating insertion, deletion, or regulation of target genes to enhance production of PUFAs, polyphenols, SCFAs, and antioxidant peptides [175,176]. For example, by using CRISPR/Cas to reconstruct the expression architecture of the PUFA synthesis gene cluster in Yarrowia lipolytica, the researchers significantly increased the production of DHA, proving that precise engineering of the PUFA metabolic pathway can indeed increase the output of functional lipids [177].
Metabolic pathway optimization is central to modern fermentation. By using in silico prediction and modeling to regulate key enzymatic activities, substrate flux, and byproduct formation, engineered strains can achieve a dynamic balance between product yield and cell growth [178]. Modular design and controllable co-culture strategies allow different strains to specialize in distinct functional modules, achieving metabolic division of labor and enhancing production efficiency [179]. For example, in the co-culture system of Aspergillus oryzae and Lactobacillus plantarum, the former is mainly responsible for the hydrolysis of starch to release fermentable substrates, while the latter uses these substrates to ferment and produce organic acids and increase the content of protein and amino acids [180]. The protein content and amino acid improvement effect of the co-culture output are significantly better than those of single-strain fermentation.
Synthetic microbial consortia (SMCs) have recently emerged as a rapidly expanding research frontier in microbial biotechnology. By leveraging metabolic modeling, co-culture engineering, and multi-omics–guided strain selection, these systems enable the rational design and optimization of microbial communities, thereby achieving more precise control over interspecies interactions and metabolic fluxes in fermentation processes [181]. Such approaches enhance the efficiency, stability, and functionality of fermentation systems, ultimately improving the flavor complexity, nutritional quality, and bioactive compound profiles of fermented foods [182]. For example, OuYang et al. developed an SMC comprising Lactobacillus plantarum NF2 and Acetobacter pasteurianus NF171 to optimize citrus vinegar fermentation [183]. This defined consortium markedly increased the production of ethyl acetate, a key contributor to desirable aroma, while simultaneously promoting the accumulation of several phenolic acids (such as chlorogenic and ferulic acids) and flavonoids (including rutinarin and nobiletin) [183]. These findings highlight the potential of SMC-based strategies to tailor microbial metabolism for enhanced sensory and functional attributes in fermented food products.
In the field of probiotics, the application of defined microbial consortia represents an emerging paradigm shift that departs from the conventional single-strain approach, which often produces inconsistent or limited physiological outcomes [184]. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species, for instance, are well recognized for their capacity to generate SCFAs that contribute to gut and metabolic health [185]. Building upon this concept, Ye et al. developed a synthetic microbial consortium composed of seven well-characterized gut commensals—Alistipes putredinis, Barnesiella intestinihominis, Coprococcus catus, Dorea longicatena, Agathobacter rectalis (formerly Eubacterium rectale), Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, and Roseburia hominis—and fermented it with a prebiotic mix [186]. In elderly participants, the intervention markedly enhanced the relative abundance of beneficial taxa and stimulated SCFAs production, indicating improved microbial metabolic activity [186]. Collectively, these findings underscore the therapeutic and nutritional potential of synthetic microbial consortia as a next-generation probiotic strategy capable of targeted modulation of the gut ecosystem and host metabolism.
The pursuit of improved nutrient utilization systems is a key goal in fermentation science, specifically, aiming to mitigate excessive microbial catabolism of beneficial nutrients. Limiting microbial consumption during fermentation is crucial for maximizing nutrient content and maintaining the sensory properties of the final fermented product [187,188]. Precision fermentation uses precise genetic perturbations to reprogram microbial metabolic pathways, thereby conferring desirable nutrients and flavors to food [189]. This advanced bioprocess utilizes genetically engineered microbial hosts (such as yeast or fungi) as cell factories to synthesize single, specific target molecules (such as proteins, enzymes, or lipids) [189]. Engineered strains incorporate biosensing capabilities, enabling them to respond to nutrient gradients and other environmental cues by inhibiting or inducing cellular functions, thereby ensuring efficient, high-purity production of the desired compound [189]. For instance, Sathivel et al. demonstrated how harnessing quorum sensing in microbial consortia could impart distinctive sensory properties to red wine [190].
The integration of systems biology and machine learning has further improved strain design and fermentation process optimization. By analyzing genomic, transcriptomic, and metabolomic data, researchers can predict metabolic bottlenecks, regulatory networks, and inter-strain interactions, providing guidance for the application of engineered strains in functional fermented foods [158]. For instance, Josephs-Spaulding et al. applied transcriptomics combined with machine learning to reconstruct the regulatory network of Limosilactobacillus reuteri, identifying key modules of riboflavin and fatty acid metabolism, which guide metabolic optimization for functional food applications [191]. Peerapat et al. applied machine learning to the design-build-test-learn cycle, demonstrating that machine learning has great potential to accelerate and optimize metabolic engineering processes [192]. Overall, modern synthetic biology-based fermentation not only increases the concentration of health-promoting ingredients in fermented foods but also offers new strategies for supporting liver health and managing metabolic diseases, such as MASLD, while maintaining food safety, stability, and sensory quality.
4. Challenges and Outlook
Despite the availability of pharmacological treatments for MASLD, dietary interventions and healthy lifestyle modifications remain the primary strategies for mitigating disease progression [9]. In recent years, the Mediterranean diet has been recognized as an effective reference for dietary intervention in MASLD. However, due to regional dietary habits and limitations in food accessibility, the Mediterranean diet is not universally applicable, as individuals differ in their biochemical, genetic, and microbiome makeup. In contrast, fermented foods offer distinct advantages for MASLD management. They provide functional nutrients, including polyphenols, SCFAs, PUFAs, and antioxidant peptides, which have demonstrated potential therapeutic effects in preclinical and some clinical studies by improving hepatic lipid metabolism and reducing oxidative stress and inflammation. Moreover, the fermentation process imparts unique flavors such as sour, aromatic, and umami, enhancing sensory appeal, acceptability, and adherence to dietary regimens. Fermented foods with local characteristics are found globally, many of which exhibit potential therapeutic benefits for MASLD. Compared with single functional supplements, functional fermented foods can address chronic metabolic disorders without requiring significant dietary changes, making them widely applicable and feasible for MASLD prevention and treatment.
Fermented foods not only provide functional nutrients but also offer a distinctive sensory experience. Nevertheless, the strong flavors of certain fermented foods can limit their widespread adoption. For instance, natto, a traditional Japanese fermented soy product, possesses a sticky texture and a characteristic ammoniacal odor, often described as “unpleasant” or “like rotten garbage”. Although it is rich in beneficial nutrients, including probiotics, dietary fiber, protein, and vitamin K2, its intense flavor has impeded global acceptance [142]. To overcome this limitation, researchers are exploring the use of engineered LAB to enhance flavor profiles. Co-cultivation with specific LAB strains can modulate volatile compound production, reduce the release of undesirable odors, and improve overall sensory quality [193]. Additionally, substituting traditional soybeans with alternative fermented substrates such as red lentils, green peas, or chickpeas in natto production has been shown to reduce off-flavors while maintaining or enhancing nutritional content [194]. These flavor modification strategies increase the acceptability of fermented foods and expand dietary options for MASLD patients. By integrating functional nutrients with improved sensory properties, fermented foods are poised to become a vital component of MASLD intervention.
Modern biotechnology, including gene editing, holds promise for increasing the yield of functional products and optimizing metabolic pathways in engineered fermentation strains. Nonetheless, these approaches face significant limitations, particularly for commonly used fermentation bacteria such as LAB and B. amyloliquefaciens. Regulatory constraints and safety considerations are the primary limiting factors. Because fermented foods are intended for human consumption, transgenic strains generated through conventional gene editing are generally classified as genetically modified organisms (GMOs). In Europe, the United States, and numerous other countries, GMO food approvals are stringent, and consumer acceptance is low, restricting the commercial application of engineered strains [195]. Even strains demonstrating excellent metabolic performance in laboratory settings may encounter legal and market barriers that hinder practical implementation.
To address these challenges, several complementary strategies can be pursued. From the standpoint of regulation and societal acceptance, the establishment of clearer classification frameworks for gene-edited microorganisms and the development of more comprehensive risk assessment systems would facilitate the safe and responsible integration of new technologies into the food industry. Concurrently, enhancing public awareness and understanding of the potential benefits and associated risks of these technologies is essential for improving societal acceptance, a process that is inherently gradual and often contentious. The adoption of novel biotechnological tools in domains closely related to human health and nutrition is therefore expected to follow a prolonged and carefully regulated trajectory.
At present, however, several technical strategies may enable the attainment of desired functional improvements without contravening existing regulatory frameworks. First, non-GMO approaches such as laboratory-directed evolution and random mutagenesis can be employed to enhance strain performance while avoiding the introduction of exogenous DNA, thereby circumventing transgenic regulatory constraints. Second, the development and application of SMC present considerable potential in this context. Without the need for gene-editing interventions, such consortia can leverage quorum-sensing mechanisms and the inherent metabolic capabilities of distinct strains to enhance the production of target compounds in fermented foods or to introduce novel functional and sensory attributes. For instance, as noted previously, OuYang et al. demonstrated that this strategy could be applied to enrich citrus vinegar with additional flavor and bioactive constituents [183]. Future research exploring the utilization of synthetic microbial communities in fermented food production, either to confer specific health-promoting properties or to design next-generation probiotic formulations, represents a highly promising and forward-looking direction for the field.
Engineering efficiency and strain characteristics further constrain the use of traditional gene editing. LAB, despite their widespread use in food fermentation, often exhibit low transformation efficiency and limited genetic tool availability. Gene knockout or overexpression may impair growth or fermentation performance. While Bacillus subtilis demonstrates robust environmental resistance and high product potential, gene editing may affect spore formation or disrupt metabolic balance, compromising industrial fermentation stability. Traditional gene editing primarily targets single genes, making comprehensive metabolic network optimization challenging. Fermentation bacteria possess complex metabolic pathways in which the synthesis of multiple products is interdependent and substrate-competitive. Consequently, single-gene modifications rarely achieve global metabolic optimization and may lead to byproduct formation or impaired cell growth. Additional challenges arise in industrial-scale production: strains optimized under laboratory conditions may experience metabolic drift or trait instability in large-scale fermentation, affecting product consistency and functionality. In multi-strain co-culture systems, engineered strains may fail to compete effectively with native strains, reducing overall fermentation efficiency and target metabolite yield.
To achieve safe, efficient, and acceptable production of functional fermented foods, modern fermentation technologies must integrate metabolic engineering, synthetic biology, modular design, co-culture strategies, and computational simulation optimization. Such approaches aim to balance strain functionality with sensory quality, thereby enhancing the potential of fermented foods in MASLD intervention and the broader health food market.
Statement of the Use of Generative AI and AI-Assisted Technologies in the Writing Process
During the preparation of this manuscript, the author(s) used Grammarly in order to improve grammar, refine wording, and enhance the overall clarity of the text. After using this tool/service, the author(s) reviewed and edited the content as needed and take(s) full responsibility for the content of the published article.
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely express their sincere gratitude to Xinyi Chen and Xiaofang Huang for their assistance in proofreading the document and laboratory management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.C. and C.L.H.; Investigation, B.C., Y.L., J.H.-E.C. and J.C.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, B.C.; Figure Preparation, J.X., B.C. and C.L.H.; Writing—Review & Editing, B.C., J.-P.T. and C.L.H.; Supervision, C.L.H.; Funding Acquisition, C.L.H.
Ethics Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The statement is required for all original articles which informs readers about the accessibility of research data linked to a paper and outlines the terms under which the data can be obtained.
Funding
This review and all its investigative work was funded by Chinese Academy of Sciences Hundred Talents Program grant number E444111001 (awarded to C.L.H).
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Tamang JP, Cotter PD, Endo A, Han NS, Kort R, Liu SQ, et al. Fermented foods in a global age: East meets west. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 184–217. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12520. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee A, Breselge S, Dimidi E, Marco ML, Cotter PD. Fermented foods and gastrointestinal health: Underlying mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 248–266. doi:10.1038/s41575-023-00869-x. [Google Scholar]
- Mirsalami SM, Mirsalami M. Advances in genetically engineered microorganisms: Transforming food production through precision fermentation and synthetic biology. Future Foods 2025, 11, 100601. doi:10.1016/j.fufo.2025.100601. [Google Scholar]
- Salminen S, Collado MC, Endo A, Hill C, Lebeer S, Quigley EMM, et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. doi:10.1038/s41575-021-00440-6. [Google Scholar]
- Benede-Ubieto R, Cubero FJ, Nevzorova YA. Breaking the barriers: The role of gut homeostasis in Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2331460. doi:10.1080/19490976.2024.2331460. [Google Scholar]
- Loomba R, Sanyal AJ. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 686–690. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2013.171. [Google Scholar]
- Petta S, Targher G, Romeo S, Pajvani UB, Zheng M-H, Aghemo A, et al. The first MASH drug therapy on the horizon: Current perspectives of resmetirom. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2024, 44, 1526–1536. doi:10.1111/liv.15930. [Google Scholar]
- Beygi M, Ahi S, Zolghadri S, Stanek A. Management of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease/Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: From Medication Therapy to Nutritional Interventions. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2220. doi:10.3390/nu16142220. [Google Scholar]
- Simancas-Racines D, Annunziata G, Verde L, Fascì-Spurio F, Reytor-Gonzàlez C, Muscogiuri G, et al. Nutritional Strategies for Battling Obesity-Linked Liver Disease: The Role of Medical Nutritional Therapy in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) Management. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2025, 14, 7. doi:10.1007/s13679-024-00597-6. [Google Scholar]
- Karačić A, Zonjić J, Stefanov E, Radolović K, Starčević A, Renko I, et al. Short-term supplementation of sauerkraut induces favorable changes in the gut microbiota of active athletes: A proof-of-concept study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4421. doi:10.3390/nu16244421. [Google Scholar]
- Miao X, Niu H, Sun M, Dong X, Hua M, Su Y, et al. A comparative study on the nutritional composition, protein structure and effects on gut microbiota of 5 fermented soybean products (FSPs). Food Res. Int. 2024, 183, 114199. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114199. [Google Scholar]
- Shiby VK, Mishra HN. Fermented milks and milk products as functional foods—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 482–496. doi:10.1080/10408398.2010.547398. [Google Scholar]
- Masoodi M, Gastaldelli A, Hyötyläinen T, Arretxe E, Alonso C, Gaggini M, et al. Metabolomics and lipidomics in NAFLD: Biomarkers and non-invasive diagnostic tests. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 835–856. doi:10.1038/s41575-021-00502-9. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg GR, Valvano CM, De Nardo W, Watt MJ. Integrative metabolism in MASLD and MASH: Pathophysiology and emerging mechanisms. J. Hepatol. 2025, 83, 584–595. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2025.02.033. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z, Zhang X, Pan Q, Zhang L, Chai J. In-depth analysis of de novo lipogenesis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Mechanism and pharmacological interventions. Liver Res. 2023, 7, 285–295. doi:10.1016/j.livres.2023.11.003. [Google Scholar]
- Vallianou NG, Kounatidis D, Psallida S, Vythoulkas-Biotis N, Adamou A, Zachariadou T, et al. NAFLD/MASLD and the gut-liver axis: From pathogenesis to treatment options. Metabolites 2024, 14, 366. doi:10.3390/metabo14070366. [Google Scholar]
- Taru V, Szabo G, Mehal W, Reiberger T. Inflammasomes in chronic liver disease: Hepatic injury, fibrosis progression and systemic inflammation. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 895–910. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2024.06.016. [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y, Park Y, Rho H, Yao T, Gao B, Hwang S. Inflammation in MASLD progression and cancer. JHEP Rep. 2025, 7, 101414. doi:10.1016/j.jhepr.2025.101414. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y, Zhang Z, Tang P, Wu Y, Zhang A, Li D, et al. Probiotics fortify intestinal barrier function: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1143548. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1143548. [Google Scholar]
- Rose EC, Odle J, Blikslager AT, Ziegler AL. Probiotics, prebiotics and epithelial tight junctions: A promising approach to modulate intestinal barrier function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6729. doi:10.3390/ijms22136729. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S, Zhao J, Xie F, He H, Johnston LJ, Dai X, et al. Dietary fiber-derived short-chain fatty acids: A potential therapeutic target to alleviate obesity-related nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13316. doi:10.1111/obr.13316. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang D, Jian Y-P, Zhang Y-N, Li Y, Gu L-T, Sun H-H, et al. Short-chain fatty acids in diseases. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 212. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01219-9. [Google Scholar]
- Yan M, Man S, Sun B, Ma L, Guo L, Huang L, et al. Gut liver brain axis in diseases: The implications for therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 443. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01673-4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu J, Li C, Yang Y, Li J, Sun X, Zhang Y, et al. Special correlation between diet and MASLD: Positive or negative? Cell Biosci. 2025, 15, 44. doi:10.1186/s13578-025-01382-1. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira CP, Álvares TS, Gomes LS, Torres AG, Paschoalin VMF, Conte-Junior CA. Kefir grains change fatty acid profile of milk during fermentation and storage. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139910. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0139910. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav H, Jain S, Sinha PR. Production of free fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid in probiotic dahi containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus casei during fermentation and storage. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 1006–1010. doi:10.1016/j.idairyj.2006.12.003. [Google Scholar]
- Hodson L, Gunn PJ. The regulation of hepatic fatty acid synthesis and partitioning: The effect of nutritional state. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 689–700. doi:10.1038/s41574-019-0256-9. [Google Scholar]
- Iturbe-Rey S, Maccali C, Arrese M, Aspichueta P, Oliveira CP, Castro RE, et al. Lipotoxicity-driven metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). Atherosclerosis 2025, 400, 119053. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2024.119053. [Google Scholar]
- Law HG, Khan MA, Zhang W, Bang H, Rood J, Most M, et al. Reducing saturated fat intake lowers LDL-C but increases Lp(a) levels in African Americans: The GET-READI feeding trial. J. Lipid Res. 2023, 64, 100420. doi:10.1016/j.jlr.2023.100420. [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Lu Z, Ru JH, Lopes-Virella MF, Lyons TJ, Huang Y. Saturated fatty acid combined with lipopolysaccharide stimulates a strong inflammatory response in hepatocytes in vivo and in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E745–E757. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00015.2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zou Y, Tian L, Pei L, Hao J, Chen T, Qi J, et al. SFAs facilitates ceramide’s de novo synthesis via TLR4 and intensifies hepatocyte lipotoxicity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 147, 114020. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114020. [Google Scholar]
- Oteng A-B, Kersten S. Mechanisms of action of trans fatty acids. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 697–708. doi:10.1093/advances/nmz125. [Google Scholar]
- Spooner MH, Jump DB. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Mechanisms and Clinical Use. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2023, 43, 199–223. doi:10.1146/annurev-nutr-061021-030223. [Google Scholar]
- George ES, Forsyth A, Itsiopoulos C, Nicoll AJ, Ryan M, Sood S, et al. Practical dietary recommendations for the prevention and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in adults. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 30–40. doi:10.1093/advances/nmx007. [Google Scholar]
- Bae J-S, Oh A-R, Cha J-Y. Regulation of cholesterol metabolism in liver: Link to NAFLD and impact of n-3 PUFAs. J. Lifestyle Med. 2013, 3, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kim JK, Lee KS, Lee DK, Lee SY, Chang HY, Choi J, et al. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid and ursodeoxycholic acid have an additive effect in attenuating diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Exp. Mol. Med. 2014, 46, e127. doi:10.1038/emm.2014.90. [Google Scholar]
- Oh DY, Talukdar S, Bae EJ, Imamura T, Morinaga H, Fan W, et al. GPR120 is an omega-3 fatty acid receptor mediating potent anti-inflammatory and insulin-sensitizing effects. Cell 2010, 142, 687–698. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.041. [Google Scholar]
- Enguita M, Razquin N, Pamplona R, Quiroga J, Prieto J, Fortes P. The cirrhotic liver is depleted of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), a key modulator of NF-κB and TGFβ pathways in hepatic stellate cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 14. doi:10.1038/s41419-018-1243-0. [Google Scholar]
- Tan W, Mao L, Yu S, Huang J, Xie Q, Hu M, et al. DHA and EPA improve liver IR in HFD-induced IR mice through modulating the gut microbiotas-LPS-liver axis. J. Funct. Foods 2024, 112, 105917. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2023.105917. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K, Chang Y, Shi Z, Han X, Han Y, Yao Q, et al. ω-3 PUFAs ameliorate liver fibrosis and inhibit hepatic stellate cells proliferation and activation by promoting YAP/TAZ degradation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30029. doi:10.1038/srep30029. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira MA, Oliveira CP, Alves VAF, Stefano JT, dos Reis Rodrigues LS, Torrinhas RS, et al. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in treating non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 578–586. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2015.05.001. [Google Scholar]
- Scorletti E, Bhatia L, McCormick KG, Clough GF, Nash K, Calder PC, et al. Design and rationale of the WELCOME trial: A randomised, placebo controlled study to test the efficacy of purified long chain omega-3 fatty treatment in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2014, 37, 301–311. doi:10.1016/j.cct.2014.02.002. [Google Scholar]
- Musazadeh V, Dehghan P, Khoshbaten M. Efficacy of omega-3-rich camelina sativa on the metabolic and clinical markers in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, controlled trial. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 34, 537. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000002297. [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal AJ, Abdelmalek MF, Suzuki A, Cummings OW, Chojkier M. No significant effects of ethyl-eicosapentanoic acid on histologic features of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in a phase 2 trial. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 377–384.e1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2014.04.046. [Google Scholar]
- Nobili V, Carpino G, Alisi A, Vito RD, Franchitto A, Alpini G, et al. Role of Docosahexaenoic Acid Treatment in Improving Liver Histology in Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88005. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0088005. [Google Scholar]
- Martín-Cabrejas MA, Sanfiz B, Vidal A, Mollá E, Esteban R, López-Andréu FJ. Effect of fermentation and autoclaving on dietary fiber fractions and antinutritional factors of beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 261–266. doi:10.1021/jf034980t. [Google Scholar]
- Foufelle F, Ferré P. New perspectives in the regulation of hepatic glycolytic and lipogenic genes by insulin and glucose: A role for the transcription factor sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c. Biochem. J. 2002, 366, 377–391. doi:10.1042/bj20020430. [Google Scholar]
- Ferré P, Foufelle F. SREBP-1c transcription factor and lipid homeostasis: Clinical perspective. Horm. Res. 2007, 68, 72–82. doi:10.1159/000100426. [Google Scholar]
- Choi CS, Savage DB, Kulkarni A, Yu XX, Liu Z-X, Morino K, et al. Suppression of diacylglycerol acyltransferase-2 (DGAT2), but not DGAT1, with antisense oligonucleotides reverses diet-induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 22678–22688. doi:10.1074/jbc.M704213200. [Google Scholar]
- Xia JY, Holland WL, Kusminski CM, Sun K, Sharma AX, Pearson MJ, et al. Targeted induction of ceramide degradation leads to improved systemic metabolism and reduced hepatic steatosis. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 266–278. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2015.06.007. [Google Scholar]
- Herman MA, Peroni OD, Villoria J, Schön MR, Abumrad NA, Blüher M, et al. A novel ChREBP isoform in adipose tissue regulates systemic glucose metabolism. Nature 2012, 484, 333–338. doi:10.1038/nature10986. [Google Scholar]
- Bindesbøll C, Fan Q, Nørgaard RC, MacPherson L, Ruan H-B, Wu J, et al. Liver X receptor regulates hepatic nuclear O-GlcNAc signaling and carbohydrate responsive element-binding protein activity. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 771–785. doi:10.1194/jlr.M049130. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y, Yonemitsu S, Erion DM, Iwasaki T, Stark R, Weismann D, et al. The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1 β in the pathogenesis of fructose-induced insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 252–264. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2009.01.011. [Google Scholar]
- Jang C, Hui S, Lu W, Cowan AJ, Morscher RJ, Lee G, et al. The small intestine converts dietary fructose into glucose and organic acids. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 351–361.e3. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2017.12.016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu J, Zhuang Z, Bian D, Ma X, Xun Y, Yang W, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 signalling in the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by high-fat and high-fructose diet in mice. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 41, 482–488. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.12241. [Google Scholar]
- Todoric J, Di Caro G, Reibe S, Henstridge DC, Green CR, Vrbanac A, et al. Fructose stimulated de novo lipogenesis is promoted by inflammation. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 1034–1045. doi:10.1038/s42255-020-0261-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hannou SA, Haslam DE, McKeown NM, Herman MA. Fructose metabolism and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 545–555. doi:10.1172/JCI96702. [Google Scholar]
- Sarita B, Samadhan D, Hassan M, Kovaleva E. A comprehensive review of probiotics and human health-current prospective and applications. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1487641. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2024.1487641. [Google Scholar]
- Mann ER, Lam YK, Uhlig HH. Short-chain fatty acids: Linking diet, the microbiome and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 577–595. doi:10.1038/s41577-024-01014-8. [Google Scholar]
- Perazza F, Leoni L, Selvatici B, Girolami F, Bonalumi A, Beretta A, et al. Dietary Strategies to Modulate Gut Microbiota in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Nutrients 2025, 17, 1906. doi:10.3390/nu17111906. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y, Yang H, Zhang Y, Rao S, Mo Y, Zhang H, et al. Dietary fiber intake and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: The mediating role of obesity. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1038435. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.1038435. [Google Scholar]
- Keyvan E, Adesemoye E, Champomier-Vergès M-C, Chanséaume-Bussiere E, Mardon J, Nikolovska Nedelkoska D, et al. Vitamins formed by microorganisms in fermented foods: Effects on human vitamin status—A systematic narrative review. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1653666. doi:10.3389/fnut.2025.1653666. [Google Scholar]
- Vaitkeviciene N, Jariene E, Kulaitiene J, Lasinskas M, Blinstrubiene A, Hallmann E. Effect of solid-state fermentation on vitamin C, photosynthetic pigments and sugars in willow herb (Chamerion angustifolium (L.) Holub) leaves. Plants 2022, 11, 3300. doi:10.3390/plants11233300. [Google Scholar]
- Tattoli I, Mathew AR, Verrienti A, Pallotta L, Severi C, Andreola F, et al. The Interplay between Liver and Adipose Tissue in the Onset of Liver Diseases: Exploring the Role of Vitamin Deficiency. Cells 2024, 13, 1631. doi:10.3390/cells13191631. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann AF. The Continuing Importance of Bile Acids in Liver and Intestinal Disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 2647–2658. doi:10.1001/archinte.159.22.2647. [Google Scholar]
- Abe RAM, Masroor A, Khorochkov A, Prieto J, Singh KB, Nnadozie MC, et al. The Role of Vitamins in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2021, 13, e16855. doi:10.7759/cureus.16855. [Google Scholar]
- Wang B, Du M. Increasing adipocyte number and reducing adipocyte size: The role of retinoids in adipose tissue development and metabolism. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 10608–10625. doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2227258. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu S, Zhang J, Zhu D, Jiang X, Wei L, Wang W, et al. Adipose tissue plays a major role in retinoic acid-mediated metabolic homoeostasis. Adipocyte 2022, 11, 47–55. doi:10.1080/21623945.2021.2015864. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao M, Zhong H, Lin H, Liu C, Yan Y, Ke Y, et al. Higher serum vitamin a is associated with a worsened progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults: A prospective study. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 970–977. doi:10.1039/D1FO03119H. [Google Scholar]
- Bordoloi J, Ozah D, Bora T, Kalita J, Manna P. Gamma-glutamyl carboxylated Gas6 mediates the beneficial effect of vitamin K on lowering hyperlipidemia via regulating the AMPK/SREBP1/PPARα signaling cascade of lipid metabolism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 70, 174–184. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.05.006. [Google Scholar]
- Pickett-Blakely O, Young K, Carr RM. Micronutrients in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 451–462. doi:10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.07.004. [Google Scholar]
- Raza S, Tewari A, Rajak S, Sinha RA. Vitamins and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A molecular insight. Liver Res. 2021, 5, 62–71. doi:10.1016/j.livres.2021.03.004. [Google Scholar]
- Li J, Cordero P, Nguyen V, Oben JA. The role of vitamins in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Integr. Med. Insights 2016, 11, IMI.S31451. doi:10.4137/IMI.S31451. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain MM, Rava P, Walsh M, Rana M, Iqbal J. Multiple functions of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 9, 14. doi:10.1186/1743-7075-9-14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang D, Yin Z, Han L, Zhang M, Li H, Yang X, et al. Ascorbic acid inhibits transcriptional activities of LXRα to ameliorate lipid metabolism disorder. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 88, 104901. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2021.104901. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente-Postigo M, Tinahones A, El Bekay R, Malagón MM, Tinahones FJ. The role of autophagy in white adipose tissue function: Implications for metabolic health. Metabolites 2020, 10, 179. doi:10.3390/metabo10050179. [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on adipose tissue inflammation and NF-κB/AMPK activation in obese mice fed a high-fat diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10915. doi:10.3390/ijms231810915. [Google Scholar]
- Marziou A, Philouze C, Couturier C, Astier J, Obert P, Landrier J-F, et al. Vitamin D Supplementation Improves Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Reduces Hepatic Steatosis in Obese C57BL/6J Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 342. doi:10.3390/nu12020342. [Google Scholar]
- Podszun MC, Alawad AS, Lingala S, Morris N, Huang WCA, Yang S, et al. Vitamin E treatment in NAFLD patients demonstrates that oxidative stress drives steatosis through upregulation of de-novo lipogenesis. Redox Biol. 2020, 37, 101710. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101710. [Google Scholar]
- Juretić N, Sepúlveda R, D’Espessailles A, Vera DB, Cadagan C, de Miguel M, et al. Dietary alpha- and gamma-tocopherol (1:5 ratio) supplementation attenuates adipose tissue expansion, hepatic steatosis, and expression of inflammatory markers in a high-fat-diet–fed murine model. Nutrition 2021, 85, 111139. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2021.111139. [Google Scholar]
- Yang K, Chen J, Zhang T, Yuan X, Ge A, Wang S, et al. Efficacy and safety of dietary polyphenol supplementation in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 949746. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.949746. [Google Scholar]
- Yang F, Chen C, Ni D, Yang Y, Tian J, Li Y, et al. Effects of Fermentation on Bioactivity and the Composition of Polyphenols Contained in Polyphenol-Rich Foods: A Review. Foods 2023, 12, 3315. doi:10.3390/foods12173315. [Google Scholar]
- Flores-Peña R, Monroy-Ramirez HC, Caloca-Camarena F, Arceo-Orozco S, Salto-Sevilla JA, Galicia-Moreno M, et al. Naringin and naringenin in liver health: A review of molecular and epigenetic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 979. doi:10.3390/antiox14080979. [Google Scholar]
- Huang Q, An Z, Xin X, Gou X, Tian X, Hu Y, et al. The Effectiveness of Curcumin, Resveratrol, and Silymarin on MASLD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 10010–10029. doi:10.1002/fsn3.4595. [Google Scholar]
- Karatayli E, Sadiq SC, Schattenberg JM, Grabbe S, Biersack B, Kaps L. Curcumin and its derivatives in hepatology: Therapeutic potential and advances in nanoparticle formulations. Cancers 2025, 17, 484. doi:10.3390/cancers17030484. [Google Scholar]
- Yi M, Manzoor M, Yang M, Zhang H, Wang L, Zhao L, et al. Silymarin targets the FXR protein through microbial metabolite 7-keto-deoxycholic acid to treat MASLD in obese mice. Phytomedicine 2024, 133, 155947. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155947. [Google Scholar]
- Bae U-J, Park J, Park IW, Chae BM, Oh M-R, Jung S-J, et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate-rich green tea extract ameliorates fatty liver and weight gain in mice fed a high fat diet by activating the sirtuin 1 and AMP activating protein kinase pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 617–632. doi:10.1142/S0192415X18500325. [Google Scholar]
- Santamarina AB, Oliveira JL, Silva FP, Carnier J, Mennitti LV, Santana AA, et al. Green tea extract rich in epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents fatty liver by AMPK activation via LKB1 in mice fed a high-fat diet. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141227. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0141227. [Google Scholar]
- Santamarina AB, Carvalho-Silva M, Gomes LM, Okuda MH, Santana AA, Streck EL, et al. Decaffeinated green tea extract rich in epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents fatty liver disease by increased activities of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes in diet-induced obesity mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1348–1356. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.07.002. [Google Scholar]
- Cheraghpour M, Imani H, Ommi S, Alavian SM, Karimi-Shahrbabak E, Hedayati M, et al. Hesperidin improves hepatic steatosis, hepatic enzymes, and metabolic and inflammatory parameters in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2118–2125. doi:10.1002/ptr.6406. [Google Scholar]
- Chen S, Lu H, Yin G, Zhang X, Meng D, Yu W, et al. Hesperitin prevents non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by modulating mitochondrial dynamics and mitophagy via the AMPKα-Drp1/PINK1-parkin signaling pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2025, 1870, 159570. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2024.159570. [Google Scholar]
- Cicero AFG, Colletti A, Bellentani S. Nutraceutical approach to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): The available clinical evidence. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1153. doi:10.3390/nu10091153. [Google Scholar]
- Ranneh Y, Bedir AS, Abu-Elsaoud AM, Al Raish S. Polyphenol intervention ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An updated comprehensive systematic review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4150. doi:10.3390/nu16234150. [Google Scholar]
- Heebøll S, Kreuzfeldt M, Hamilton-Dutoit S, Kjær Poulsen M, Stødkilde-Jørgensen H, Møller HJ, et al. Placebo-controlled, randomised clinical trial: High-dose resveratrol treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 456–464. doi:10.3109/00365521.2015.1107620. [Google Scholar]
- Jin Y, Wang X, Chen K, Chen Y, Zhou L, Zeng Y, et al. Silymarin decreases liver stiffness associated with gut microbiota in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lipids Health Dis. 2024, 23, 239. doi:10.1186/s12944-024-02220-y. [Google Scholar]
- Wah Kheong C, Nik Mustapha NR, Mahadeva S. A randomized trial of silymarin for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2017, 15, 1940–1949.e8. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2017.04.016. [Google Scholar]
- Ren Y, Wu S, Xia Y, Huang J, Ye J, Xuan Z, et al. Probiotic-fermented black tartary buckwheat alleviates hyperlipidemia and gut microbiota dysbiosis in rats fed with a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 6045–6057. doi:10.1039/D1FO00892G. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou F, Li Y-L, Zhang X, Wang K-B, Huang J-A, Liu Z-H, et al. Polyphenols from fu brick tea reduce obesity via modulation of gut microbiota and gut microbiota-related intestinal oxidative stress and barrier function. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 14530–14543. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.1c04553. [Google Scholar]
- Ren W, Ma Y, Liu D, Liang P, Du J, Yang S, et al. Chemical composition analysis, antioxidant activity, and target cell-based screening of the potential active components in jujube and its fermented product. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 664–685. doi:10.1111/1750-3841.16022. [Google Scholar]
- Lukšič L, Bonafaccia G, Timoracka M, Vollmannova A, Trček J, Nyambe TK, et al. Rutin and quercetin transformation during preparation of buckwheat sourdough bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 69, 71–76. doi:10.1016/j.jcs.2016.02.011. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao Y, Fan J, Chen Y, Rui X, Zhang Q, Dong M. Enhanced total phenolic and isoflavone aglycone content, antioxidant activity and DNA damage protection of soybeans processed by solid state fermentation with rhizopus oligosporus RT-3. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 29741–29756. doi:10.1039/C6RA00074F. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz Y. Postbiotics as antiinflammatory and immune-modulating bioactive compounds in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, e2400754. doi:10.1002/mnfr.202400754. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri F, Montanari C, Gardini F, Tabanelli G. Biogenic amine production by lactic acid bacteria: A review. Foods 2019, 8, 17. doi:10.3390/foods8010017. [Google Scholar]
- Tofalo R, Cocchi S, Suzzi G. Polyamines and gut microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 16. doi:10.3389/fnut.2019.00016. [Google Scholar]
- Gao M, Zhao W, Li C, Xie X, Li M, Bi Y, et al. Spermidine ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through regulating lipid metabolism via AMPK. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 505, 93–98. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.078. [Google Scholar]
- Choksomngam Y, Pattanakuhar S, Chattipakorn N, Chattipakorn SC. The metabolic role of spermidine in obesity: Evidence from cells to community. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 15, 315–326. doi:10.1016/j.orcp.2021.06.009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou S, Gu J, Liu R, Wei S, Wang Q, Shen H, et al. Spermine alleviates acute liver injury by inhibiting liver-resident macrophage pro-inflammatory response through ATG5-dependent autophagy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 948. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.00948. [Google Scholar]
- Liu G, Zheng J, Cao W, Wu X, Jia G, Zhao H, et al. Effects of spermine on liver barrier function, amino acid transporters, immune status, and apoptosis in piglets. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 11054–11062. doi:10.1039/C8RA05421E. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez-Sánchez MÁ, Martínez-Sánchez MA, Sierra-Cruz M, Lambertos A, Rico-Chazarra S, Oliva-Bolarín A, et al. Increased hepatic putrescine levels as a new potential factor related to the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. J. Pathol. 2024, 264, 101–111. doi:10.1002/path.6330. [Google Scholar]
- Sakata R, Nakamura T, Torimura T, Ueno T, Sata M. Green tea with high-density catechins improves liver function and fat infiltration in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients: A double-blind placebo-controlled study. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 989–994. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2013.1503. [Google Scholar]
- Izadi F, Farrokhzad A, Tamizifar B, Tarrahi MJ, Entezari MH. Effect of sour tea supplementation on liver enzymes, lipid profile, blood pressure, and antioxidant status in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 477–485. doi:10.1002/ptr.6826. [Google Scholar]
- Pezeshki A, Safi S, Feizi A, Askari G, Karami F. The effect of green tea extract supplementation on liver enzymes in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 7, 28. doi:10.4103/2008-7802.173051. [Google Scholar]
- Xin X, Chen C, Xu X, Lv S, Sun Q, An Z, et al. Caffeine ameliorates metabolic-associated steatohepatitis by rescuing hepatic Dusp9. Redox Biol. 2025, 80, 103499. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2025.103499. [Google Scholar]
- Velázquez AM, Roglans N, Bentanachs R, Gené M, Sala-Vila A, Lázaro I, et al. Effects of a Low Dose of Caffeine Alone or as Part of a Green Coffee Extract, in a Rat Dietary Model of Lean Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Inflammation. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3240. doi:10.3390/nu12113240. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi R, Kobayashi M, Matsuda Y, Ojika M, Shigeoka S, Yamamoto Y, et al. Coffee and caffeine ameliorate hyperglycemia, fatty liver, and inflammatory adipocytokine expression in spontaneously diabetic KK-ay mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5597–5603. doi:10.1021/jf904062c. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S-J, Li Y-F, Wang G-E, Tan R-R, Tsoi B, Mao G-W, et al. Caffeine ameliorates high energy diet-induced hepatic steatosis: Sirtuin 3 acts as a bridge in the lipid metabolism pathway. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2578–2587. doi:10.1039/C5FO00247H. [Google Scholar]
- Xu M, Yang L, Zhu Y, Liao M, Chu L, Li X, et al. Collaborative effects of chlorogenic acid and caffeine on lipid metabolism via the AMPKα-LXRα/SREBP-1c pathway in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7489–7497. doi:10.1039/C9FO00502A. [Google Scholar]
- Lou L, Zhou J, Liu Y, Wei Y, Zhao J, Deng J, et al. Chlorogenic acid induces apoptosis to inhibit inflammatory proliferation of IL-6-induced fibroblast-like synoviocytes through modulating the activation of JAK/STAT and NF-κB signaling pathways. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 11, 2054–2060. doi:10.3892/etm.2016.3136. [Google Scholar]
- Yang F, Luo L, Zhu Z-D, Zhou X, Wang Y, Xue J, et al. Chlorogenic acid inhibits liver fibrosis by blocking the miR-21-regulated TGF-β1/Smad7 signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 929. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00929. [Google Scholar]
- Dungubat E, Fujikura K, Kuroda M, Fukusato T, Takahashi Y. Food Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds for Managing Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2211. doi:10.3390/nu17132211. [Google Scholar]
- Aron-Wisnewsky J, Vigliotti C, Witjes J, Le P, Holleboom AG, Verheij J, et al. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: Disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 279–297. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-0269-9. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed H, Díaz LA, Gil-Gómez A, Burton J, Bajaj JS, Romero-Gomez M, et al. Microbiome-centered therapies for the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2025, 31, S94–S111. doi:10.3350/cmh.2024.0811. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl K, Moodley P, Dhanda A. The effect of increasing intestinal short-chain fatty acid concentration on gut permeability and liver injury in the context of liver disease: A systematic review. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 1498–1506. doi:10.1111/jgh.15899. [Google Scholar]
- den Besten G, van Eunen K, Groen AK, Venema K, Reijngoud D-J, Bakker BM. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. doi:10.1194/jlr.R036012. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira CM, Vieira AT, Vinolo MAR, Oliveira FA, Curi R, Martins FDS. The central role of the gut microbiota in chronic inflammatory diseases. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 689492. doi:10.1155/2014/689492. [Google Scholar]
- Li Z, Yang S, Lin H, Huang J, Watkins PA, Moser AB, et al. Probiotics and antibodies to TNF inhibit inflammatory activity and improve nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2003, 37, 343–350. doi:10.1053/jhep.2003.50048. [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y, Yang L, Wu J, Hu J, Wan M, Bie J, et al. Optimal probiotic combinations for treating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2024, 43, 1224–1239. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2024.04.004. [Google Scholar]
- Malaguarnera M, Vacante M, Antic T, Giordano M, Chisari G, Acquaviva R, et al. Bifidobacterium longum with fructo-oligosaccharides in patients with non alcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 545–553. doi:10.1007/s10620-011-1887-4. [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen AS, Larsen N, Pedersen-Skovsgaard T, Berg RMG, Møller K, Svendsen KD, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM on insulin sensitivity and the systemic inflammatory response in human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 1831–1838. doi:10.1017/S0007114510002874. [Google Scholar]
- Everard A, Cani PD. Diabetes, obesity and gut microbiota. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, 73–83. doi:10.1016/j.bpg.2013.03.007. [Google Scholar]
- Endo H, Niioka M, Kobayashi N, Tanaka M, Watanabe T. Butyrate-producing probiotics reduce nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression in rats: New insight into the probiotics for the gut-liver axis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63388. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063388. [Google Scholar]
- Silva-Sperb AS, Moraes HA, Barcelos STA, de Moura BC, Longo L, Michalczuk MT, et al. Probiotic supplementation for 24 weeks in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: The PROBILIVER randomized clinical trial. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1362694. doi:10.3389/fnut.2024.1362694. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpton SR, Maraj B, Harding-Theobald E, Vittinghoff E, Terrault NA. Gut microbiome–targeted therapies in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 139–149. doi:10.1093/ajcn/nqz042. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrikx T, Duan Y, Wang Y, Oh J-H, Alexander LM, Huang W, et al. Bacteria engineered to produce IL-22 in intestine induce expression of REG3G to reduce ethanol-induced liver disease in mice. Gut 2019, 68, 1504–1515. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2018-317232. [Google Scholar]
- Duan FF, Liu JH, March JC. Engineered commensal bacteria reprogram intestinal cells into glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cells for the treatment of diabetes. Diabetes 2015, 64, 1794–1803. doi:10.2337/db14-0635. [Google Scholar]
- Ma J, Li C, Wang J, Gu J. Genetically engineered escherichia coli nissle 1917 secreting GLP-1 analog exhibits potential antiobesity effect in high-fat diet-induced obesity mice. Obesity 2020, 28, 315–322. doi:10.1002/oby.22700. [Google Scholar]
- Ding C, Weng S. Unraveling the association between cheese consumption and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Insights from a two-sample mendelian randomization analysis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70213. doi:10.1002/fsn3.70213. [Google Scholar]
- Sandby K, Magkos F, Chabanova E, Petersen ET, Krarup T, Bertram HC, et al. The effect of dairy products on liver fat and metabolic risk markers in males with abdominal obesity—A four-arm randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 534–542. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2023.12.018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen H-L, Tung Y-T, Tsai C-L, Lai C-W, Lai Z-L, Tsai H-C, et al. Kefir improves fatty liver syndrome by inhibiting the lipogenesis pathway in leptin-deficient ob/ob knockout mice. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 1172–1179. doi:10.1038/ijo.2013.236. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi F, Razmjooei N, Mohsenpour MA, Nejati MA, Eftekhari MH, Hejazi N. The effects of kefir drink on liver aminotransferases and metabolic indicators in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Nutr. 2025, 11, 3. doi:10.1186/s40795-024-00989-w. [Google Scholar]
- Gao Y, Liu Y, Ma T, Liang Q, Sun J, Wu X, et al. Fermented Dairy Products as Precision Modulators of Gut Microbiota and Host Health: Mechanistic Insights, Clinical Evidence, and Future Directions. Foods 2025, 14, 1946. doi:10.3390/foods14111946. [Google Scholar]
- do Prado FG, Pagnoncelli MGB, de Melo Pereira GV, Karp SG, Soccol CR. Fermented Soy Products and Their Potential Health Benefits: A Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1606. doi:10.3390/microorganisms10081606. [Google Scholar]
- Tan ST, Tan SS, Tan CX. Soy protein, bioactive peptides, and isoflavones: A review of their safety and health benefits. PharmaNutrition 2023, 25, 100352. doi:10.1016/j.phanu.2023.100352. [Google Scholar]
- Adebo JA, Njobeh PB, Gbashi S, Oyedeji AB, Ogundele OM, Oyeyinka SA, et al. Fermentation of cereals and legumes: Impact on nutritional constituents and nutrient bioavailability. Fermentation 2022, 8, 63. doi:10.3390/fermentation8020063. [Google Scholar]
- Kanno R, Koshizuka T, Miyazaki N, Kobayashi T, Ishioka K, Ozaki C, et al. Protection of Fatty Liver by the Intake of Fermented Soybean Paste, Miso, and Its Pre-Fermented Mixture. Foods 2021, 10, 291. doi:10.3390/foods10020291. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Yusof H, Ali NM, Yeap SK, Ho WY, Beh BK, Koh SP, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of fermented soybean (nutrient enriched soybean tempeh) against alcohol-induced liver damage in mice. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 274274. doi:10.1155/2013/274274. [Google Scholar]
- Wang P, Gao X, Li Y, Wang S, Yu J, Wei Y. Bacillus natto regulates gut microbiota and adipose tissue accumulation in a high-fat diet mouse model of obesity. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 68, 103923. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2020.103923. [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Liang J, Han M, Wang X, Ren Y, Wang Y, et al. Sequentially fermented dealcoholized apple juice intervenes fatty liver induced by high-fat diets via modulation of intestinal flora and gene pathways. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111180. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111180. [Google Scholar]
- Guo M, Mao B, Ahmed Sadiq F, Hao Y, Cui S, Yi M, et al. Effects of noni fruit and fermented noni juice against acute alcohol induced liver injury in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 70, 103995. doi:10.1016/j.jff.2020.103995. [Google Scholar]
- Choi JH, Sohn W, Cho YK. The effect of moderate alcohol drinking in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 662–669. doi:10.3350/cmh.2020.0163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y, Hua J, Huang Z. Effects of beer, wine, and baijiu consumption on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Potential implications of the flavor compounds in the alcoholic beverages. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1022977. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.1022977. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J, Chen Z, Gu Y, Liang Y, Yao Z. Effects of alcohol consumption on the prevalence and incidence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0330105. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0330105. [Google Scholar]
- Onsun B, Toprak K, Sanlier N. Kombucha tea: A functional beverage and all its aspects. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2025, 14, 69. doi:10.1007/s13668-025-00658-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hyun J, Lee Y, Wang S, Kim J, Kim J, Cha J, et al. Kombucha tea prevents obese mice from developing hepatic steatosis and liver damage. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 861–866. doi:10.1007/s10068-016-0142-3. [Google Scholar]
- Jung Y, Kim I, Mannaa M, Kim J, Wang S, Park I, et al. Effect of kombucha on gut-microbiota in mouse having non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 261–267. doi:10.1007/s10068-018-0433-y. [Google Scholar]
- Graham A, Ledesma-Amaro R. The microbial food revolution. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2231. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-37891-1. [Google Scholar]
- Yang H, Hao L, Jin Y, Huang J, Zhou R, Wu C. Functional roles and engineering strategies to improve the industrial functionalities of lactic acid bacteria during food fermentation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 74, 108397. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2024.108397. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez Rojas AA, Swidah R, Schindler D. Microbes of traditional fermentation processes as synthetic biology chassis to tackle future food challenges. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 982975. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.982975. [Google Scholar]
- Xing Z, Fu X, Huang H, Xu Y, Wei L, Shan C, et al. Recent advances in lactobacillus plantarum fermentation in modifying fruit-based products: Flavor property, bioactivity, and practical production applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2025, 24, e70160. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.70160. [Google Scholar]
- Chu Y, Li M, Jin J, Dong X, Xu K, Jin L, et al. Advances in the Application of the Non-Conventional Yeast Pichia kudriavzevii in Food and Biotechnology Industries. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 170. doi:10.3390/jof9020170. [Google Scholar]
- Yao Z, Xie T, Deng H, Xiao S, Yang T. Directed Evolution of Microbial Communities in Fermented Foods: Strategies, Mechanisms, and Challenges. Foods 2025, 14, 216. doi:10.3390/foods14020216. [Google Scholar]
- Metz JG, Roessler P, Facciotti D, Levering C, Dittrich F, Lassner M, et al. Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids by polyketide synthases in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Science 2001, 293, 290–293. doi:10.1126/science.1059593. [Google Scholar]
- Methé BA, Nelson KE, Deming JW, Momen B, Melamud E, Zhang X, et al. The psychrophilic lifestyle as revealed by the genome sequence of colwellia psychrerythraea 34H through genomic and proteomic analyses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10913–10918. doi:10.1073/pnas.0504766102. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M, Ueno A, Kawasaki K, Yumoto I, Ohgiya S, Hoshino T, et al. Isolation of clustered genes that are notably homologous to the eicosapentaenoic acid biosynthesis gene cluster from the docosahexaenoic acid-producing bacterium vibrio marinus strain MP-1. Biotechnol. Lett. 1999, 21, 939–945. doi:10.1023/A:1005601606929. [Google Scholar]
- Allen EE, Bartlett DH. Structure and regulation of the omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid synthase genes from the deep-sea bacterium photobacterium profundum strain SS9The GenBank accession numbers for the sequences reported in this paper are AF409100 and AF467805. Microbiology 2002, 148, 1903–1913. doi:10.1099/00221287-148-6-1903. [Google Scholar]
- Yazawa K. Production of eicosapentaenoic acid from marine bacteria. Lipids 1996, 31, S297–S300. doi:10.1007/BF02637095. [Google Scholar]
- Shah AM, Yang W, Mohamed H, Zhang Y, Song Y. Microbes: A hidden treasure of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 827837. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.827837. [Google Scholar]
- Abedin M, Chourasia R, Phukon L, Sarkar P, Ray R, Singh S, et al. Lactic acid bacteria in the functional food industry: Biotechnological properties and potential applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 10730–10748. doi:10.1080/10408398.2023.2227896. [Google Scholar]
- Xin Q, Chen Y, Chen Q, Wang B, Pan L. Development and application of a fast and efficient CRISPR-based genetic toolkit in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LB1ba02. Microb. Cell Factories 2022, 21, 99. doi:10.1186/s12934-022-01832-2. [Google Scholar]
- Gao W, He Y, Zhang F, Zhao F, Huang C, Zhang Y, et al. Metabolic engineering of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LL3 for enhanced poly-γ-glutamic acid synthesis. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 932–945. doi:10.1111/1751-7915.13446. [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Wu Y, Wang B, Xu H, Mei X, Xu X, et al. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SC06 protects mice against high-fat diet-induced obesity and liver injury via regulating host metabolism and gut microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1161. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2019.01161. [Google Scholar]
- Sosa-Castañeda J, Hernández-Mendoza A, Astiazarán-García H, Garcia HS, Estrada-Montoya MC, González-Córdova AF, et al. Screening of lactobacillus strains for their ability to produce conjugated linoleic acid in milk and to adhere to the intestinal tract. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 6651–6659. doi:10.3168/jds.2014-8515. [Google Scholar]
- Haryani Y, Abdul Halid N, Goh SG, Nor-Khaizura MAR, Md Hatta MA, Sabri S, et al. Efficient metabolic pathway modification in various strains of lactic acid bacteria using CRISPR/Cas9 system for elevated synthesis of antimicrobial compounds. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 395, 53–63. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2024.09.002. [Google Scholar]
- Liu F, Song Z, Zhang T, Tong X, Chen MY, Gao D, et al. Characterization of the Therapeutic Properties and Flavor Profile of Coffee via Monoculture Fermentation with Endophytic Microbial Isolates. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 1039–1049. doi:10.1021/acsfoodscitech.2c00108. [Google Scholar]
- Hamese S, Mugwanda K, Takundwa M, Prinsloo E, Thimiri Govinda Raj DB. Recent advances in genome annotation and synthetic biology for the development of microbial chassis. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2023, 21, 156. doi:10.1186/s43141-023-00598-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zalila-Kolsi I, Ben-Mahmoud A, Al-Barazie R. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens: Harnessing its potential for industrial, medical, and agricultural applications—A comprehensive review. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2215. doi:10.3390/microorganisms11092215. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich D, Jovanovic-Gasovic S, Cao P, Kohlstedt M, Wittmann C. Refactoring the architecture of a polyketide gene cluster enhances docosahexaenoic acid production in yarrowia lipolytica through improved expression and genetic stability. Microb. Cell Factories 2023, 22, 199. doi:10.1186/s12934-023-02209-9. [Google Scholar]
- Kim GB, Kim WJ, Kim HU, Lee SY. Machine learning applications in systems metabolic engineering. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 64, 1–9. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2019.08.010. [Google Scholar]
- de-Bashan LE, Bashan Y, Moreno M, Lebsky VK, Bustillos JJ. Increased pigment and lipid content, lipid variety, and cell and population size of the microalgae Chlorella spp. when co-immobilized in alginate beads with the microalgae-growth-promoting bacterium Azospirillum brasilense. Can. J. Microbiol. 2002, 48, 514–521. doi:10.1139/w02-051. [Google Scholar]
- Kryachko Y, Arasaratnam L, House JD, Ai Y, Nickerson MT, Korber DR, et al. Microbial protein production during fermentation of starch-rich legume flours using Aspergillus oryzae and Lactobacillus plantarum starter cultures. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2025, 139, 288–295. doi:10.1016/j.jbiosc.2024.12.015. [Google Scholar]
- Xin Y, Qiao M. Towards microbial consortia in fermented foods for metabolic engineering and synthetic biology. Food Res. Int. 2025, 201, 115677. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2025.115677. [Google Scholar]
- Nikoloudaki O, Aheto F, Di Cagno R, Gobbetti M. Synthetic microbial communities: A gateway to understanding resistance, resilience, and functionality in spontaneously fermented food microbiomes. Food Res. Int. 2024, 192, 114780. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114780. [Google Scholar]
- OuYang Y, Zou S, Liu P, Xie L, Xiao Y, Wang Y, et al. Synthetic microbial consortium enhances acetoin production and functional quality of citrus vinegar via metabolic and process optimization. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1664794. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2025.1664794. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Castellanos JF, Biclot A, Vrancken G, Huys GR, Raes J. Design of synthetic microbial consortia for gut microbiota modulation. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 49, 52–59. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2019.07.005. [Google Scholar]
- Mkilima T. Engineering artificial microbial consortia for personalized gut microbiome modulation and disease treatment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2025, 1548, 29–55. doi:10.1111/nyas.15352. [Google Scholar]
- Ye H, Meehan D, Timmons S, O’Toole PW. Effects of Prebiotics and a Synthetic Microbiome Consortium on the Composition and Metabolites of the Elderly Gut Microbiota In Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 11720–11729. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.5c00364. [Google Scholar]
- Jovanovic S, Dietrich D, Becker J, Kohlstedt M, Wittmann C. Microbial production of polyunsaturated fatty acids—High-value ingredients for aquafeed, superfoods, and pharmaceuticals. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2021, 69, 199–211. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2021.01.009. [Google Scholar]
- Gong Y, Wan X, Jiang M, Hu C, Hu H, Huang F. Metabolic engineering of microorganisms to produce omega-3 very long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 56, 19–35. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2014.07.001. [Google Scholar]
- Hilgendorf K, Wang Y, Miller MJ, Jin Y-S. Precision fermentation for improving the quality, flavor, safety, and sustainability of foods. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2024, 86, 103084. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2024.103084. [Google Scholar]
- Thivijan S, Undugoda LJS, Nugara RN, Manage PM, Thambulugala KM, Kannangara SD, et al. Quorum sensing capability of wine microbial consortium involved in spontaneous fermentation of regional wine production. Stud. Fungi 2023, 8, 20. doi:10.48130/SIF-2023-0020. [Google Scholar]
- Josephs-Spaulding J, Rajput A, Hefner Y, Szubin R, Balasubramanian A, Li G, et al. Reconstructing the transcriptional regulatory network of probiotic L. reuteri is enabled by transcriptomics and machine learning. mSystems 2024, 9, e01257-23. doi:10.1128/msystems.01257-23. [Google Scholar]
- Khamwachirapithak P, Sae-Tang K, Mhuantong W, Tanapongpipat S, Zhao X-Q, Liu C-G, et al. Optimizing ethanol production in saccharomyces cerevisiae at ambient and elevated temperatures through machine learning-guided combinatorial promoter modifications. ACS Synth. Biol. 2023, 12, 2897–2908. doi:10.1021/acssynbio.3c00199. [Google Scholar]
- Ren X, Wang X, Lin X, Zhang S, Ji C. Improving natto quality through co-fermentation of functionally complementary bacillus and lactiplantibacillus species. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104960. doi:10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104960. [Google Scholar]
- Rocchi R, Zwinkels J, Kooijman M, Garre A, Smid EJ. Development of novel natto using legumes produced in europe. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26849. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26849. [Google Scholar]
- Rozas P, Kessi-Pérez EI, Martínez C. Genetically modified organisms: Adapting regulatory frameworks for evolving genome editing technologies. Biol. Res. 2022, 55, 31. doi:10.1186/s40659-022-00399-x. [Google Scholar]