Open Access
Review
22 April 2025Counterfeit Drug Investigations: Techniques, Challenges, and the Role of Abductive Reasoning
Variable types of investigations exist regarding counterfeit drug detection, disruption, and regulation. Counterfeit drugs are spurious drugs, falsely labelled, falsified, substandard, unregistered/unlicensed, and infringe trademarks. Counterfeit drugs can mimic both legitimate and illegitimate drugs and are often distributed in virtual environments, such as illicit online pharmacies, the surface web, and the dark web. Counterfeit drug operators and operations are the typically corrupt and/or criminal individuals, groups, and techniques by which counterfeit drugs are produced and distributed. The manufacture and distribution of counterfeit drugs are ever-changing, which results in the need for investigative techniques that are equally adaptable and collaborative. Counterfeit drug investigations can be defined according to four categories: medical investigations in hospitals and through autopsies, chemical and non-chemical drug investigations in forensic toxicology laboratories, various track-and-trace technologies used in pharmaceutical industry investigations, and national and global coordinated investigations. Due to the diverse counterfeit drug investigations present, the logic and practice of abduction are highlighted as a primary part of the investigative element to counter ongoing efforts by offenders to evade detection. Abductive rationalities are prioritized in that they are contrary to an increasing reliance on technoscientific modes of data production alone. Rather, abductive reasoning plays a central role in counterfeit drug investigations at the levels of instigating and directing investigations, as well as interpreting and responding to evidential findings.
Open Access
Article
18 June 2025Forensic Value of Exif Data: An Analytical Evaluation of Metadata Integrity across Image Transfer Methods
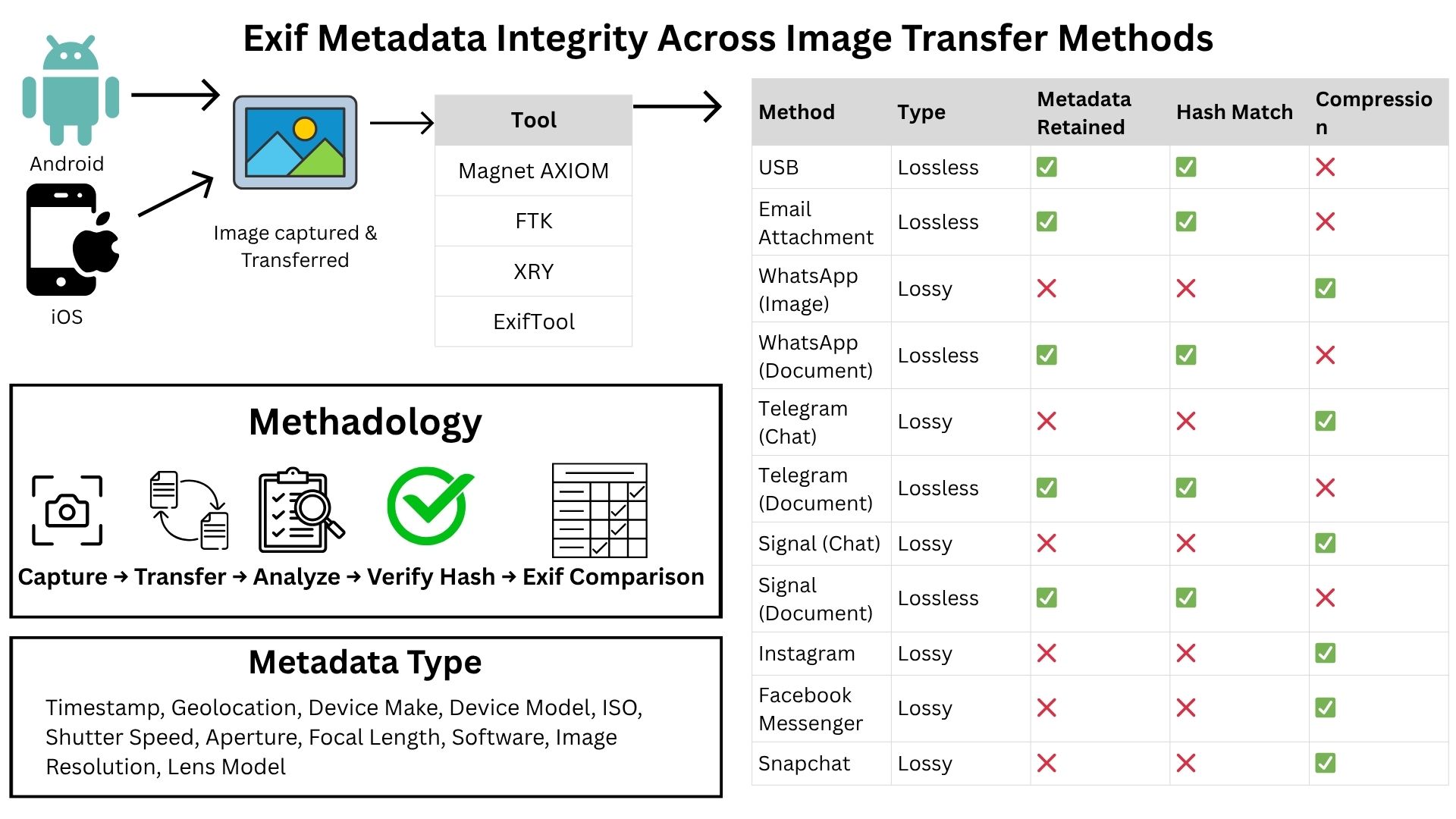
Exif metadata contained in digital photographs is an important forensic resource, offering authentic information like timestamps, geolocation, and device identifiers. The research assesses the integrity of Exif information on various methods of image transmission, such as USB, email, and messaging platforms like WhatsApp, Telegram, Signal, Instagram, Facebook Messenger, and Snapchat. With the controlled image dataset of Android, iOS phones, and the Flickr Creative Commons collection, we examined metadata preservation using forensic software (Magnet AXIOM, FTK, XRY, ExifTool). Document-based modes and direct transfers (USB, email) maintained all Exif fields and file hashes, providing forensic integrity. Chat/image-based transfers, fueled by compression, effectively remove metadata, changing the file integrity. These results emphasize the necessity of platform-aware evidence handling in order to preserve metadata integrity during digital forensic examinations.
Open Access
Article
23 June 2025A Structured Framework for Formalized and Quantitative Handwriting Examination
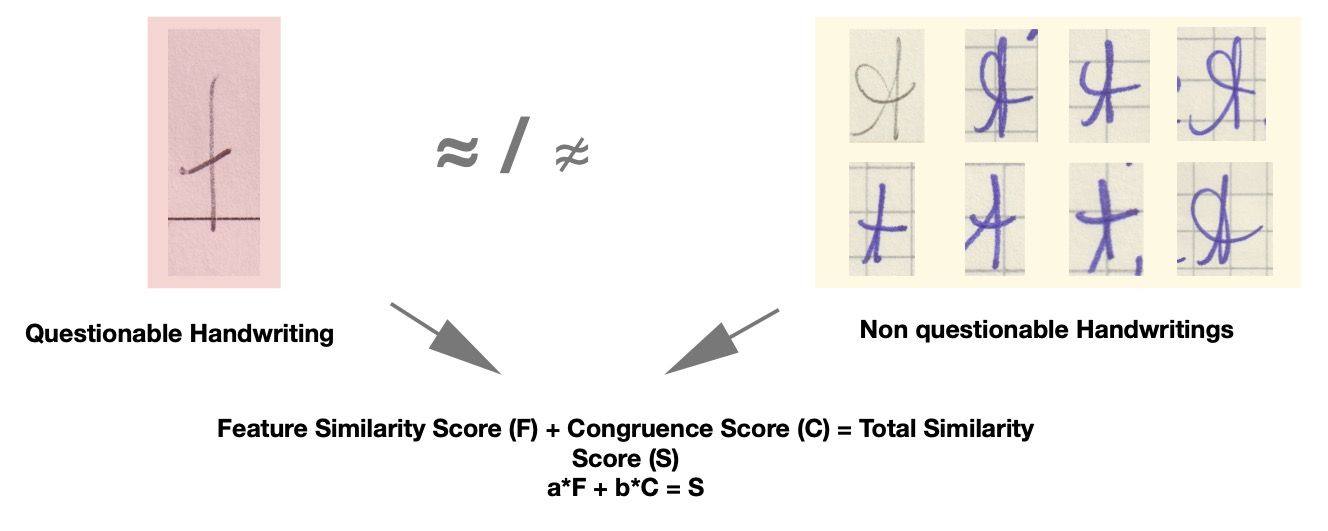
The demand for a formalized and transparent approach to handwriting assessment has long been recognized within forensic and legal contexts. A structured methodology not only reduces interpretative subjectivity but also enables quantifiable measurement and ensures greater consistency in evaluations. This article presents a practical framework that models the degree of similarity between handwriting samples—texts and signatures—through a two-stage process: feature-based evaluation and congruence analysis. Both stages produce quantitative markers that are integrated into a unified similarity score, forming the foundation for more complex comparisons involving multiple questions and known texts. The proposed procedure, which is the major result of the paper, is not merely theoretical; it has been applied in real forensic casework, yielding preliminary statistical outcomes. In particular, it demonstrates the discriminative power of different handwriting features. The paper also discusses future directions for development, with a focus on the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance specific components of the assessment process.
Open Access
Article
28 July 2025Investigating Touch DNA Success Rates in Vehicle Sites for Hit-and-Run Casework
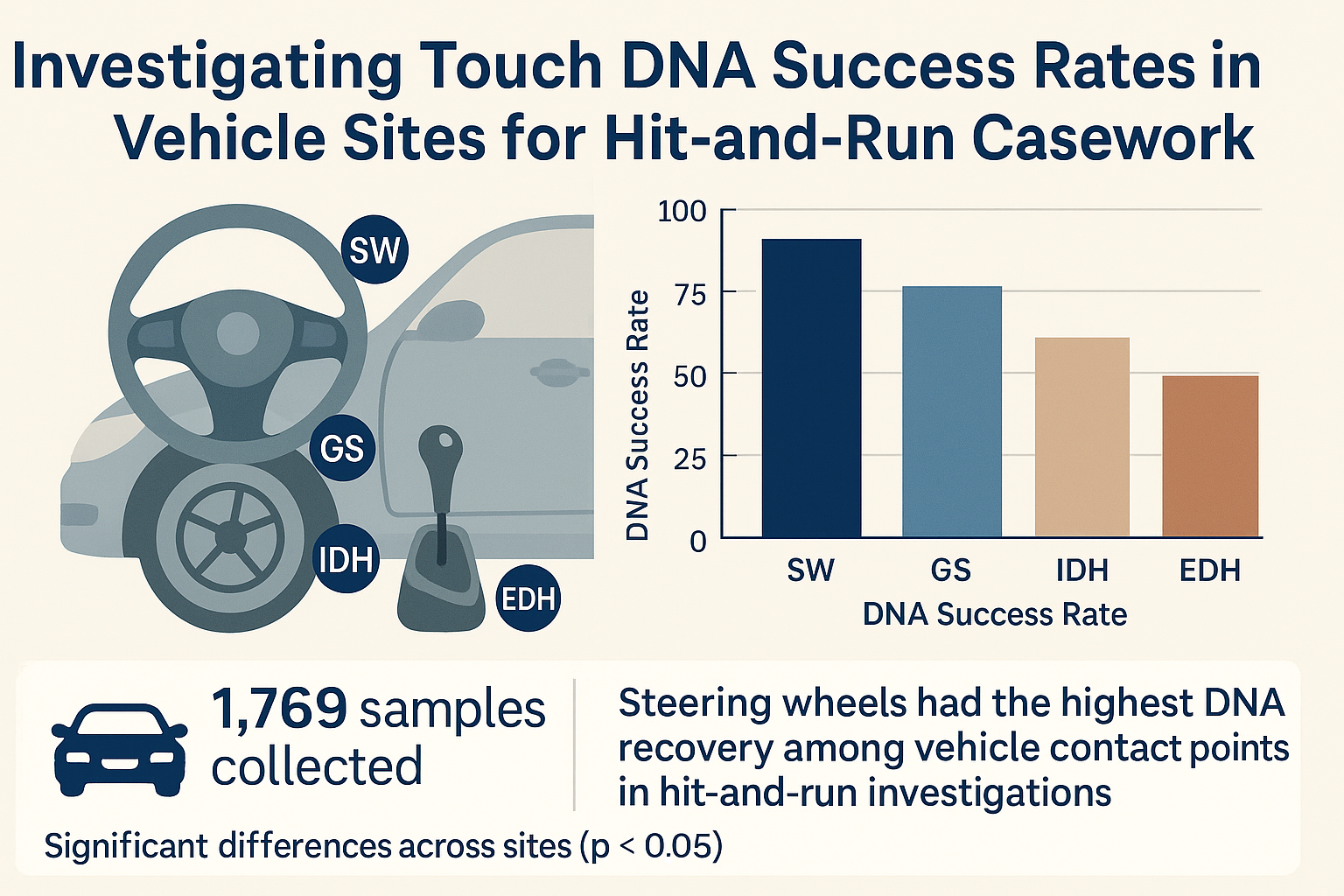
This study evaluated the effectiveness of Touch DNA recovery from four key vehicle contact points—steering wheel (SW), gear shift (GS), interior door handle (IDH), and exterior door handle (EDH)—in the context of hit-and-run forensic casework. 1769 samples were collected from 359 vehicles processed between 2020 and 2023. Statistically significant differences were observed in the quantity and quality of DNA recovered across these sites (p < 0.05). The steering wheel yielded the highest DNA success rates, followed by the gear shift, whereas the exterior and interior door handles demonstrated substantially lower recovery efficiency. These findings underscore the critical role of strategic sampling site selection in maximizing evidentiary outcomes. The results support prioritizing the steering wheel and gear shift as primary targets for DNA collection in vehicle-based investigations. The study highlights the practical utility of Touch DNA in linking individuals to vehicular crimes and calls for further research into alternative sampling techniques and contamination control measures to optimize forensic DNA recovery protocols in real-world hit-and-run scenarios.
Open Access
Article
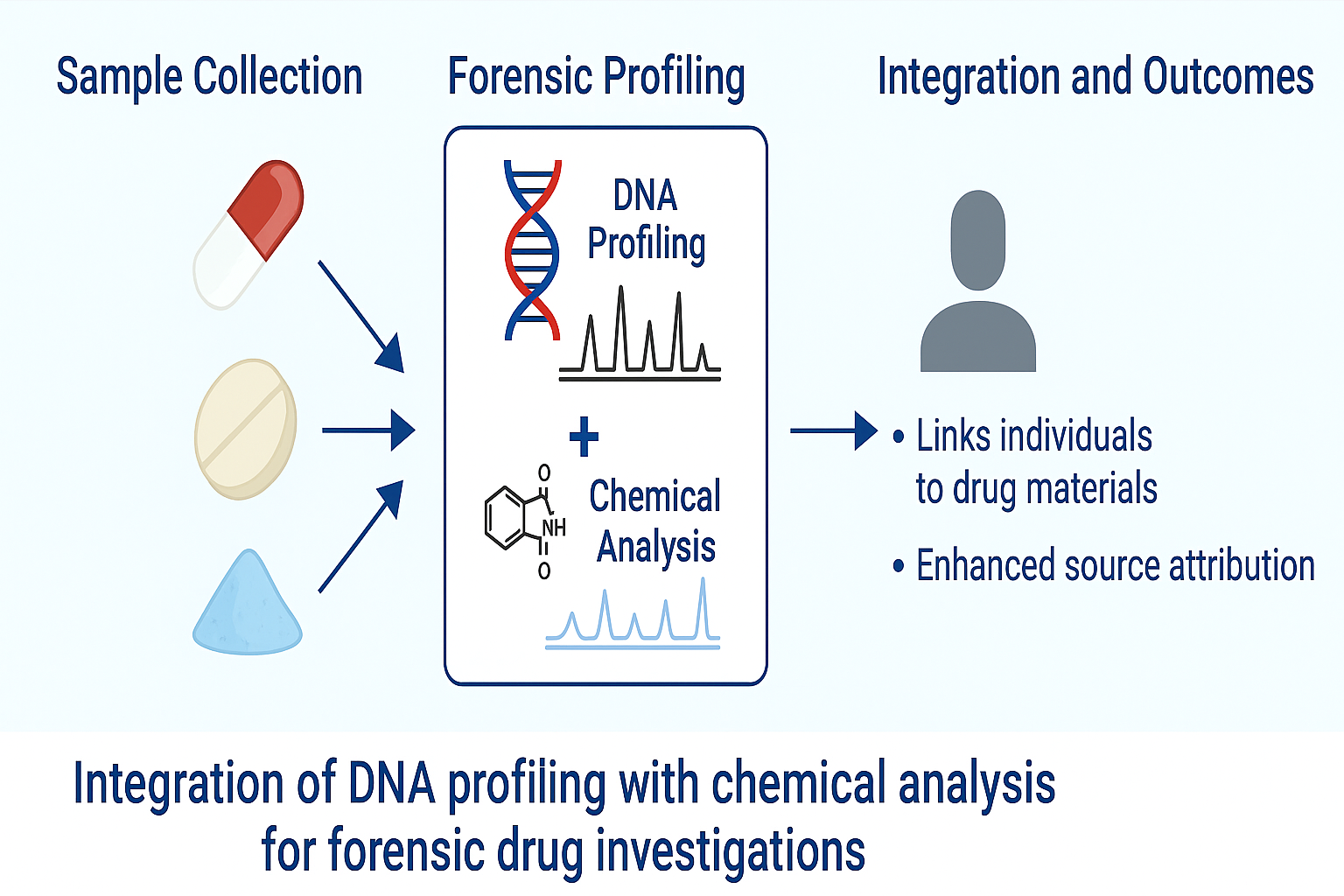
15 August 2025Integrating DNA and Chemical Profiling to Trace Illicit Drug Manufacture and Distribution
Illicit drug materials represent a valuable but underutilized source of forensic intelligence. While chemical profiling is routinely used to trace drug composition and origin, the recovery of trace DNA offers the potential to link these substances directly to individuals involved in their manufacture and distribution. This study evaluates the forensic utility of integrating DNA profiling with chemical analysis to improve source attribution across different drug formulations. Pharmaceutical-grade simulants in the form of capsules, tablets, and powders were handled by volunteers under controlled deposition scenarios. DNA was recovered using moistened cotton swabs, extracted via automated silica-based workflows, and analyzed using STR profiling. In parallel, chemical fingerprints were generated through GC-MS and LC-MS, with sample classification based on retention time and mass spectral data. Capsules yielded the highest DNA recovery (median: 310 pg), followed by tablets (230 pg) and powders (18 pg), with single-source STR profiles obtained in over 85% of capsule and tablet cases. Chemical profiling achieved 85% accuracy for capsules, 78% for tablets, and 65% for powders. When integrated, the combined approach significantly outperformed individual methods, achieving classification accuracies of 97% for capsules, 85% for tablets, and 72% for powders (p < 0.01). These findings demonstrate the enhanced evidentiary value of dual profiling, particularly in cases involving degraded or limited DNA. The proposed framework supports a more comprehensive forensic strategy, enabling biological and chemical linkage of drug materials to persons of interest and manufacturing sources. This integrative approach offers critical advantages for law enforcement and prosecution in disrupting drug trafficking networks.
Open Access
Article
18 August 2025From Police Academy Training to Criminal Investigation: Strengthening Forensic Science in Policing
Forensic science is a critical element of policing. In the past three decades, it has become one of the most important investigative tools in criminal investigations. The importance of forensic science is operationalized by linking suspects to crime scenes, exoneration of the wrongly convicted, novel forensic technologies in cold case clearances, and many other aspects. Although modern policing is equipped with forensic resources, it faces some challenges, including investigative flaws that are heavily impacted by the neglect and misuse of forensic science. With the development of forensic science, it is necessary to take advantage of technology in investigations to the maximum extent. From police academy training to criminal investigation, there are many procedures in the process that require forensic and related professionalism. In this respect, the need to strengthen forensic education, training, and practice to improve policing is urgent. This article addresses the current situation and problems of forensic science in general procedures and proposes strategies for improving forensic science in policing.
Open Access
Article
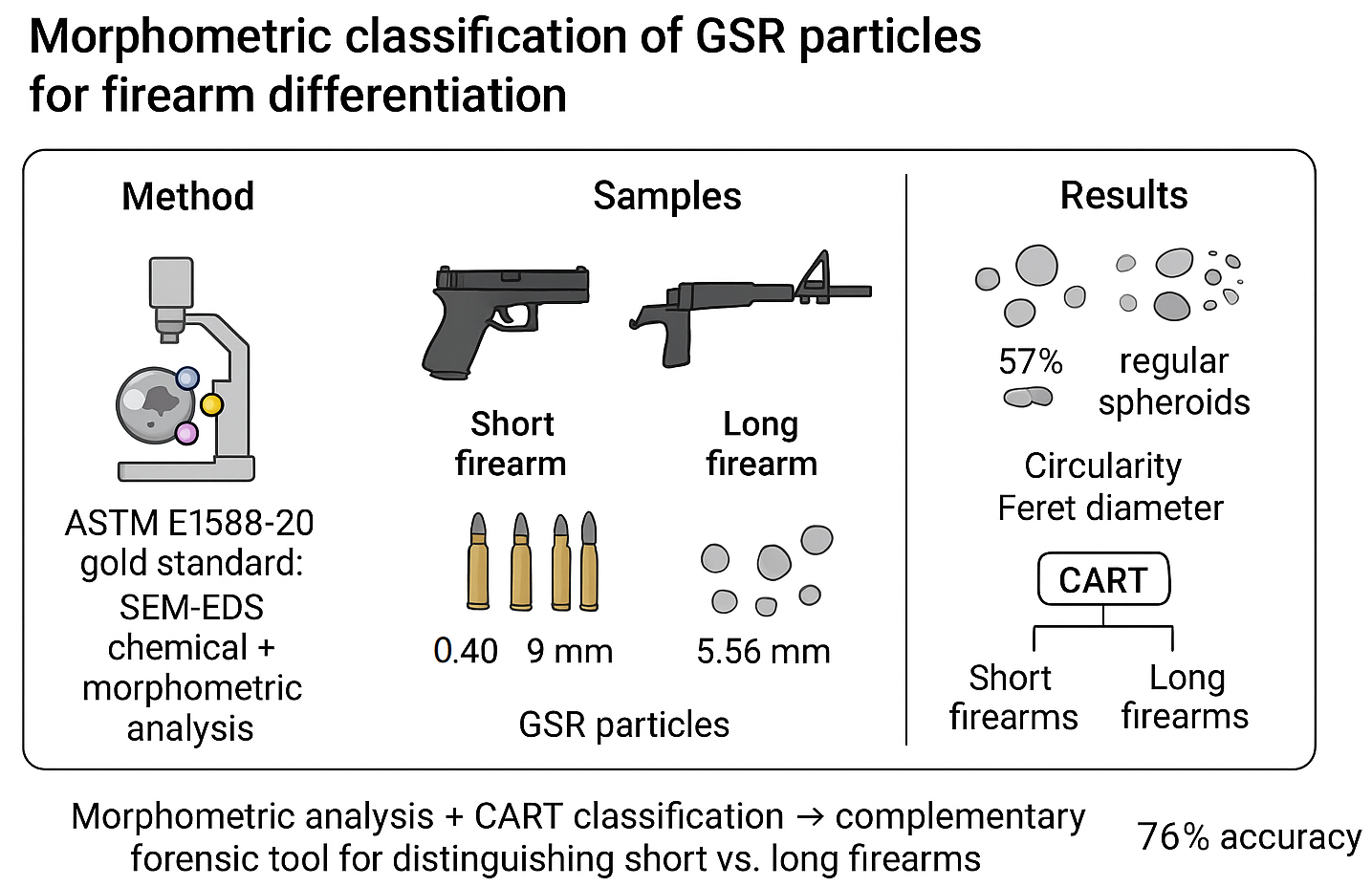
27 August 2025Statistical Analysis of GSR Particles Morphometry Using the CART Method
According to ASTM E1588-20, gunshot residue (GSR) particles can be unequivocally identified through chemical and morphometric analysis using scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), the gold standard technique for GSR detection. Recent studies have reported the presence of characteristic GSR particles—containing lead (Pb), barium (Ba), and antimony (Sb)—on vehicle occupants exposed to airbag deployment, underscoring the need for complementary analytical approaches. While elemental composition remains the primary criterion for GSR identification, morphometric analysis enhances the ability to differentiate GSR from other environmental particles. Furthermore, detailed characterization of GSR particle morphology may assist in determining the type of firearm used in a shooting incident. This study systematically analyzed characteristic GSR particles originating from four Brazilian-manufactured ammunition, establishing an initial framework for differentiating between two classes of firearms (short and long) based on morphometric features using the Classification and Regression Tree (CART) method. CART is well-suited for scenarios where interpretability and ease of implementation are priorities. Two short firearms—Taurus G2C pistol (0.40 caliber) and Glock G23 pistol (9 mm caliber) and two long firearms—Colt M16A2 rifle (5.56 mm caliber) and IMBEL FAL rifle (7.62 mm caliber) were tested: Ammunition types included CBC 0.40 S&W CSCV 160 gr, CBC 9 mm copper bullet (batch BNC10), CBC 5.56 mm AXO46 (batch A0142946), and CBC 7.62 × 51 mm Common. Morphometric analysis revealed distinct variations in characteristic GSR particle profiles across different ammunition calibers. A new four-category classification system for characteristic GSR particles was developed, with 57% identified as regular spheroids. Using CART analysis, a statistical model achieved 76% accuracy in distinguishing between short and long firearms based on morphometric parameters, particularly circularity and Feret diameter. Further research with expanded datasets and alternative predictive methods is recommended to enhance model performance and generalizability. These findings reinforce the potential of morphometric classification as a complementary tool in forensic ballistics.
Open Access
Review
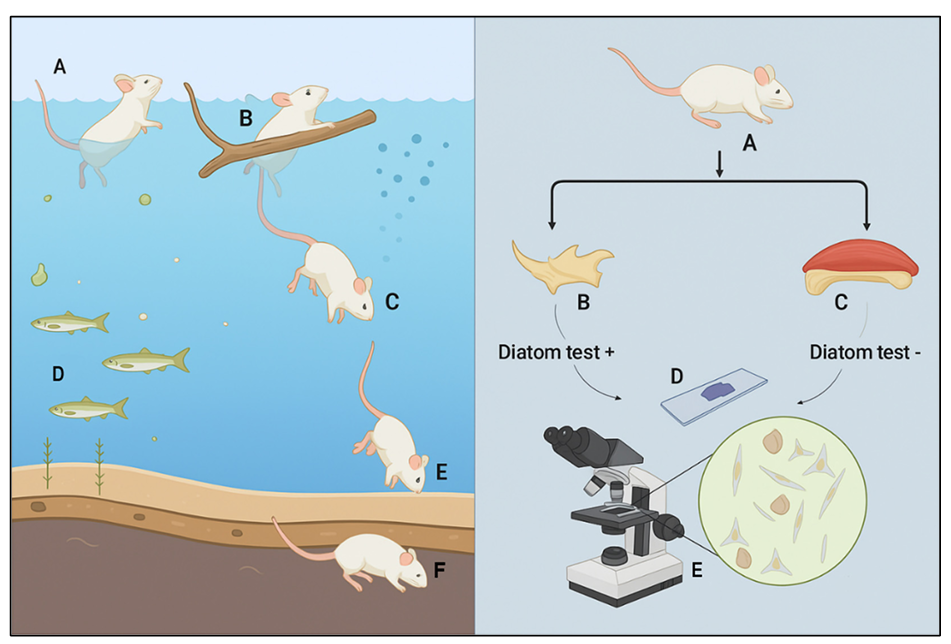
25 September 2025Forensic Diagnosis of Drowning in Animals: A Critical Review of Diagnostic Modalities and the Efficacy of the Diatom Test in Veterinary Medicine
Veterinary forensic pathology is an interdisciplinary field that critically investigates animal mortality under suspicious or unlawful circumstances. Among various causes of death, drowning remains one of the most diagnostically challenging conditions due to its pathophysiological complexity and the lack of pathognomonic post-mortem findings. Drowning in animals typically results from submersion or immersion in liquid, leading to asphyxial death with distinct physiological consequences depending on the medium, either freshwater or saltwater. The post-mortem diagnosis of drowning is complicated by factors such as environmental contamination, autolysis, and the difficulty in distinguishing ante-mortem from post-mortem immersion. While classical diagnostic indicators, such as pulmonary oedema and frothy exudate, are frequently non-specific, the diatom test remains widely utilised in forensic investigation. However, environmental confounders and inconsistent protocols limit the technique’s reliability. This review critically evaluates current diagnostic methodologies for drowning in animals, including macroscopic, microscopic, and ancillary techniques, with particular attention to the diatom test and emerging technologies. It proposes an integrated diagnostic approach to enhance diagnostic accuracy and support judicial and animal welfare outcomes.
Open Access
Case Report
28 September 2025Usefulness of Histopathological Examinations in Assessing Cases of Fatal Poisoning with New Psychoactive Substances—Preliminary Studies
Investigating the cause and mechanism of death in cases of suspected fatal poisoning with new psychoactive substances (“legal highs”) is no different from classic post-mortem diagnostics in forensic medicine. There is no characteristic autopsy appearance in individuals poisoned with “legal highs”, therefore, in practice, biological material is most often reserved for complementary histopathological and toxicological examinations. This study aimed to assess the usefulness of microscopic examinations in assessing cases of fatal poisoning with new psychoactive substances. The authors’ analysis of the literature and the results of histopathological examinations of victims of “legal high” poisoning from their own practice at the Department of Forensic Medicine and Forensic Toxicology of the Silesian Medical University in Katowice revealed that the most common pathological or diagnostically questionable changes are observed in the heart, kidneys, and liver. In the heart, signs of early myocardial ischemia are often observed in the absence of atherosclerotic changes in the coronary vessels or changes such as muscle bridging along these vessels. Considering the relatively young age of the deceased, it is highly probable that the pathological changes observed are related to the use of “legal highs”, especially given their known cardiotoxicity. In the kidneys, signs of acute tubular necrosis (ATN) are most frequently seen. These signs are usually mild and overlap with autolytic changes, making their assessment difficult, especially since they may be periagonal (artifacts). Morphological changes in the liver typically represent focal hepatocyte degeneration. Only in one case did they demonstrate signs of active inflammation and developing fibrosis. The nature of the observed changes does not allow for a clear connection with the use of “legal highs”, as the same changes may be associated with metabolic disorders, obesity, alcohol abuse, or viral hepatitis. In summary, microscopic examination of internal organ samples collected during autopsies and post-mortem examinations of individuals who died from legal highs is only supportive, as there is no characteristic microscopic image that would allow for a definitive diagnosis. The extent of the patho-logical changes observed depends primarily on age and whether the poisoned individual was hospitalized. Infectious complications are often observed in cases of long-term stays in intensive care units (e.g., pneumonia associated with respirator therapy, signs of generalized infection).
Open Access
Review
28 October 2025Prosecution of Cases Involving Sexual Crimes without Physical Evidence
Sexual crimes are rising at a concerning rate around the globe. The perpetrators are successfully acquitted of the charges, specifically in cases that lack physical evidence. Forensic evidence can associate a perpetrator with criminal activity. Occasionally, the victims of sexual misconduct do not show up right after the incident because of shame, bias, and stereotypes in society. This causes the loss of essential evidence necessary to prove the crime and the guilt of the perpetrator. Such incidents do not have any witnesses either. Therefore, it becomes hard for the jury to give a verdict in favor of the prosecution. This review article explores the factors, evidence, and initiatives that can help prosecute the victims of sexual crimes in the absence of physical evidence. A multifaceted approach comprised of scientific, psychological, and legal innovation can reduce bias, strengthen prosecution, and enhance legal outcomes, leading to improved conviction rates of sexual crimes.