Found 10 results
Article
10 March 2025Leveraging Drone Technology for Precision Agriculture: A Comprehensive Case Study in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia
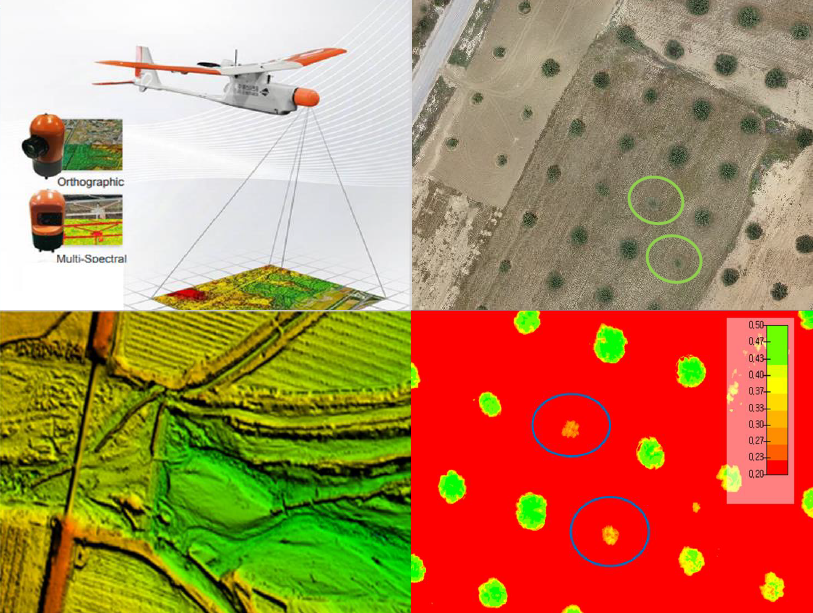
The integration of drone technology in precision agriculture offers promising solutions for enhancing crop monitoring, optimizing resource management, and improving sustainability. This study investigates the application of UAV-based remote sensing in Sidi Bouzid, Tunisia, focusing on olive tree cultivation in a semi-arid environment. REMO-M professional drones equipped with RGB and multispectral sensors were deployed to collect high-resolution imagery, enabling advanced geospatial analysis. A comprehensive methodology was implemented, including precise flight planning, image processing, GIS-based mapping, and NDVI assessments to evaluate vegetation health. The results demonstrate the significant contribution of UAV imagery in generating accurate land use classifications, detecting plant health variations, and optimizing water resource distribution. NDVI analysis revealed clear distinctions in vegetation vigor, highlighting areas affected by water stress and nutrient deficiencies. Compared to traditional monitoring methods, drone-based assessments provided high spatial resolution and real-time data, facilitating early detection of agronomic issues. These findings underscore the pivotal role of UAV technology in advancing precision agriculture, particularly in semi-arid regions where climate variability poses challenges to sustainable farming. The study provides a replicable framework for integrating drone-based monitoring into agricultural decision-making, offering strategies to improve productivity, water efficiency, and environmental resilience. The research contributes to the growing body of knowledge on agricultural technology adoption in Tunisia and similar contexts, supporting data-driven approaches to climate-smart agriculture.

Article
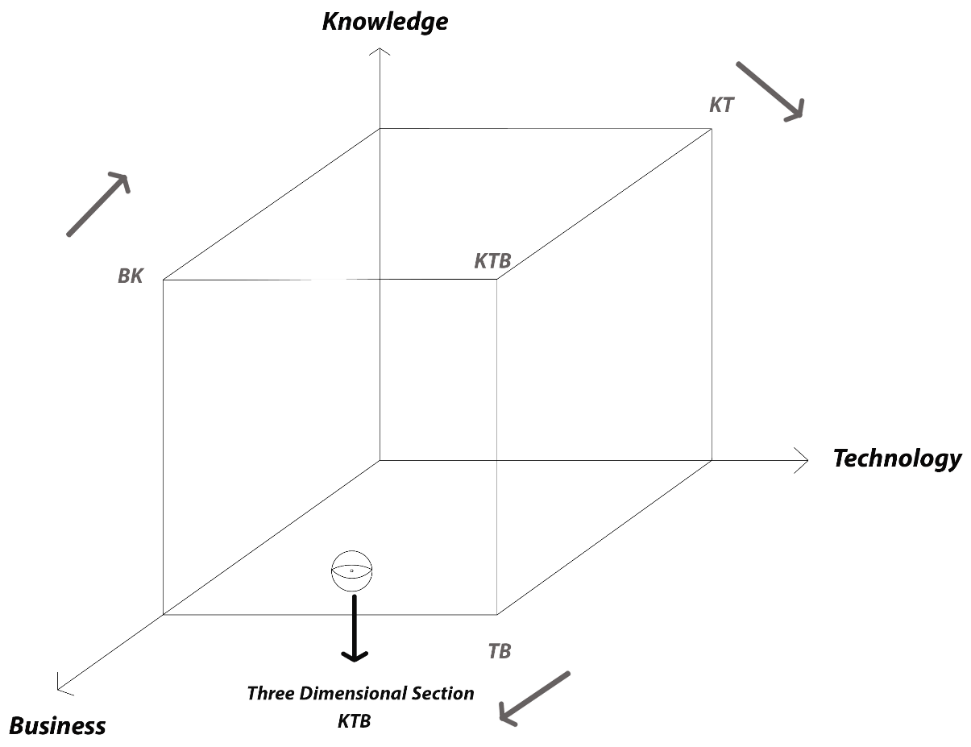
10 December 2024Sailing the X.0 Wave Theory: Navigating the Future of Civilization
This paper delves into the X.0 Wave/Tomorrow Age Theory, a comprehensive framework conceived, invented, introduced, and developed by Prof. Dr. Hamid Mattiello between 2010 and 2017, to analyze the evolution of human civilization through distinct epochs of knowledge, technology, and business (KTB). The theory segments history into transformative waves, from the first development (X.0 ≤ 1.0) and Agricultural Age (X.0 = 1.0) and the X.0 Wave/Tomorrow Age Theory (2.1 ≤ X.0 ≤ 2.2) spanning the 17th Century to 1870, to the current Age of Artificial Intelligence (X.0 = 4.0). It also projects into the anticipated Human Age (X.0 = 5.0) and Transhuman Age (X.0 = 6.0) and beyond (6.0 ≤ X.0). Each wave represents a revolutionary phase characterized by significant advancements that shape societies, industries, and technologies. The X.0 Wave Theory integrates these historical phases with the Seven Pillars of Sustainability (7PS) to evaluate their societal impacts. The paper explores how these waves influence future developments by examining historical roots, emerging technological paradigms, and socio-economic dynamics. It examines how advancements in AI, biotechnology, and virtual reality are reshaping industries and global business practices, while also addressing the ethical and sustainability considerations essential for navigating these changes. By forecasting future trends, confronting current challenges, and preparing for potential crises, the X.0 Wave Theory offers a robust framework for understanding and adapting to the rapid pace of technological evolution. This paper provides deep insights into how these transformative waves shape our past, present, and future, offering valuable perspectives for navigating the complexities of an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
Review
15 November 2024Intelligent Manufacturing Factory: A Bibliometric Analysis of Global Research Hotspots and Progress
Intelligent factories provide flexible and adaptive production processes, offering significant competitive advantages to manufacturers and are widely studied in industrial production. Information technology is recognized as a key factor influencing the production efficiency and intelligence of Intelligent factories. However, current research has primarily focused on the operational processes of intelligent factories, with limited analysis of information technology. To address this gap, this paper conducts a bibliometric analysis of information technology in intelligent factories, along with a review of its development and applications. Firstly, the data collection and visualization methods of bibliometrics are introduced. Secondly, bibliometric analyses are performed using platforms such as VOSviewer and Scimago to investigate co-authorship, co-citation, and contributions from countries and institutions in the field of information technology for intelligent factories. Finally, a framework for information technology in intelligent factories is established, summarizing its development in terms of information acquisition, transmission, processing, management, and control. This paper aims to assist scholars in understanding the development trends of intelligent factory technology and enhancing the informatization level of intelligent factories.
Article
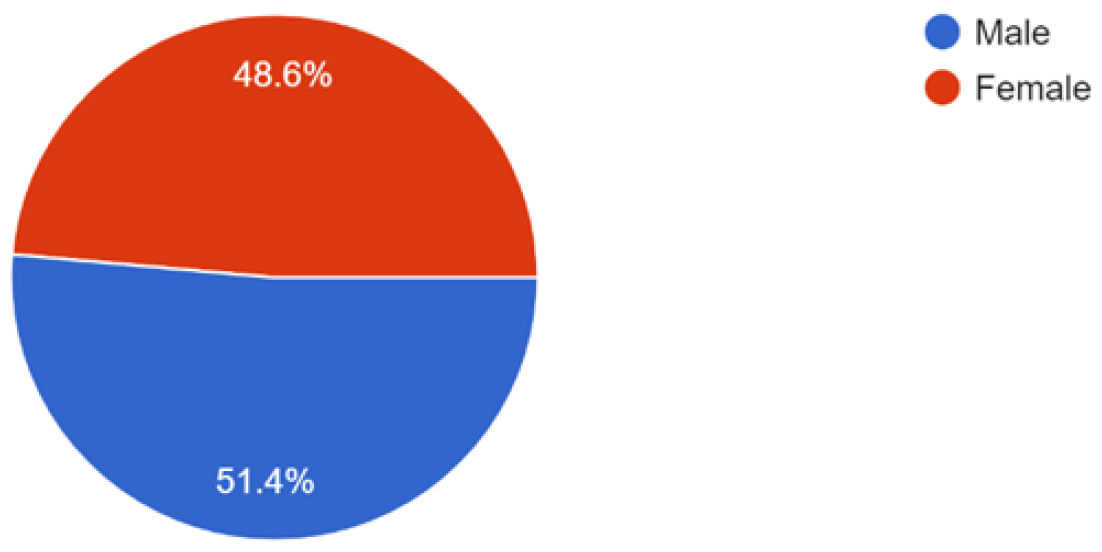
30 September 2024Synthetic Biology in Nigeria: The Level of Awareness amongst Stakeholders
Synthetic biology, an emerging field at the intersection of biotechnology and engineering, has seen a global surge in application and awareness, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its safe potentials to drive the bio-economy. This study aimed to assess the awareness and perceptions of synthetic biology among Nigerian biosciences stakeholders, including researchers, academicians, policymakers and students. The study employed a purposive online survey targeting diverse bioscience individuals and groups across Nigeria’s six geopolitical zones. The study received 107 responses from balanced gender representation with majority within the age group of 31–45 years old. The findings revealed a significant knowledge gap, with only 27.1% of respondents familiar with synthetic biology and 23.4% entirely unaware of it. Most respondents associated synthetic biology with biotechnology or genetic engineering and identified its applications to be in agriculture, medicine, environmental sustainability and research. Despite recognizing its benefits, many expressed concerns about safety, ethics, and regulation; notably, 43.9% of the respondents had concerns about synthetic biology with primary focus on safety and ethical implications. As regards the regulation of synthetic biology, the study showed that 80.4% of the respondents supported the need for synthetic biology regulation with few of the respondents (16.8%) aware of existing agency mandated to regulate synthetic biology. The respondents provided valuable insights into the various ways synthetic biology can be advanced in Nigeria which include increased awareness and capacity building, engagement through social media platforms, integration into education curricula and increased funding and investment in the research. The overall sentiment towards synthetic biology was positive, with 81.3% supporting its practice and 76.6% recognizing its positive global impact. However, a significant portion of respondents remained undecided. This study concludes that there is substantial gap in the knowledge of synthetic biology among bioscience stakeholders in Nigeria and the need for a heightened advocacy including continuous conferences and symposiums for the Nigeria bioscience community on the global potentials, concerns and regulation of synthetic biology. This will foster the acceptance of safe and responsible synthetic biology in Nigeria, thereby contributing to the broader national bio-economy development.
Editorial
19 June 2024
Review
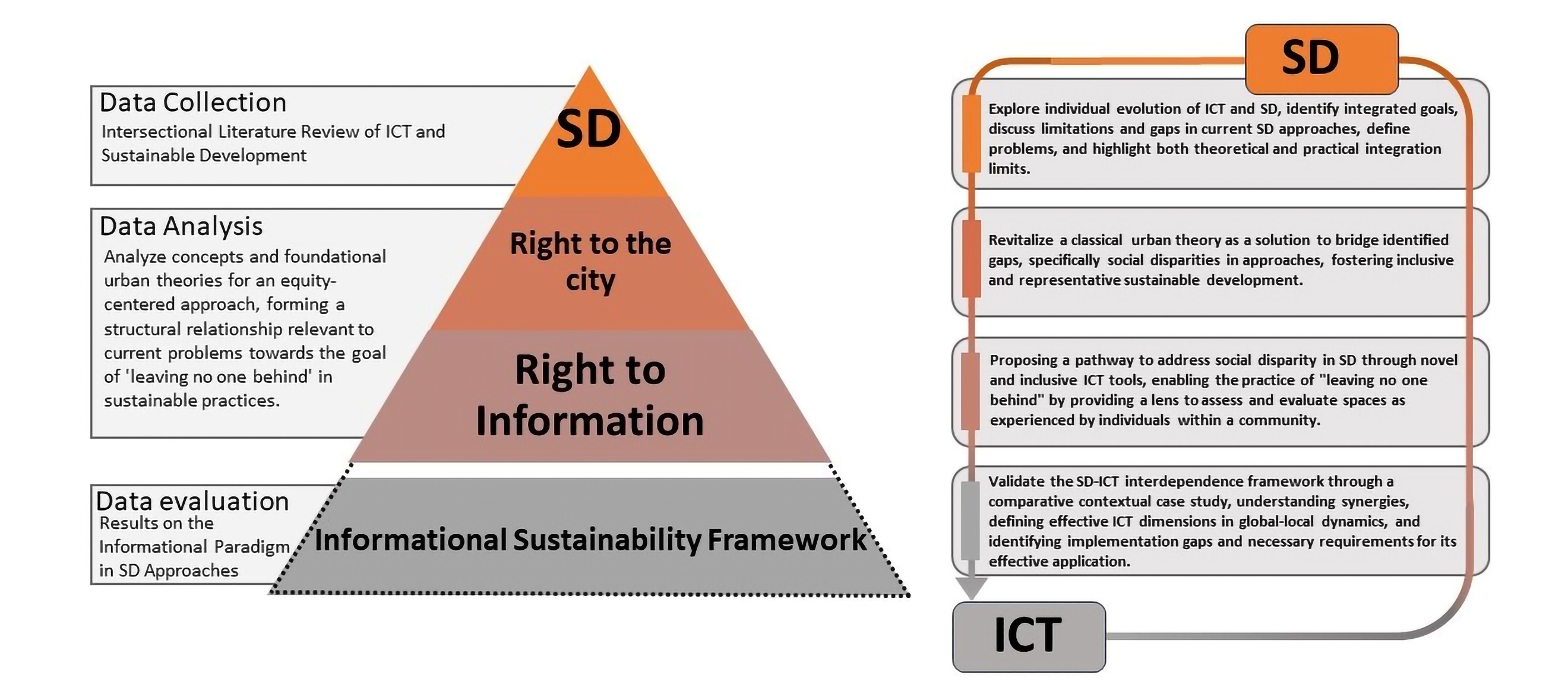
29 February 2024Conceptualizing an Informational Paradigm in the Pursuit of Sustainable Cities and Communities
This study seeks to conceptualize ‘Informational Sustainability’ by examining the dynamic relationship between Sustainable Development and the Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) Revolution through the exploration of two prominent urban theories—Lefebvre’s ‘Right to the City’ and Castells’ ‘Rise of the Network Society’—to underscore the importance of knowledge integration in the development of informed, sustainable communities. Conducting a cross-country comparison between developed and developing nations, the study underscores the critical role of informational transformation in enabling resource efficiency, knowledge sharing, innovation, and informed decision-making—key for achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), while also highlighting potential risks associated with resisting ICT adoption, including hindered growth, increased inequalities, and reduced social engagement and environmental stewardship. The core focus of this conceptual framework is to validate the precursor role of ICT in building sustainable cities and communities by identifying synergies in Sustainable Development, defining dimensions for effective ICT application within the dynamic interplay of global and local levels, and identifying implementation gaps and necessary presumptions for its effective use.
Review
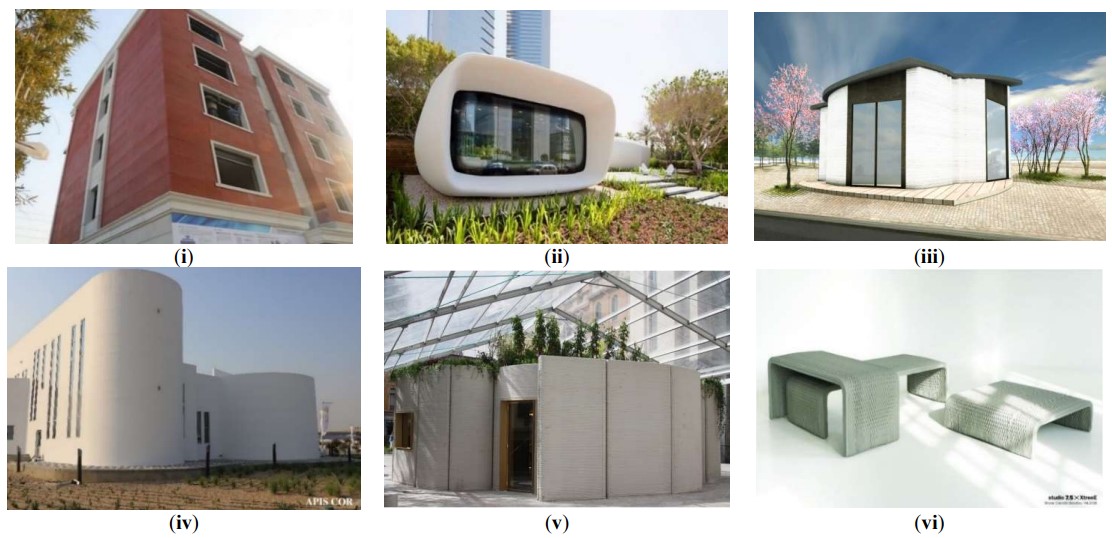
13 February 20243D Printing Technology for Rapid Response to Climate Change: Challenges and Emergency Needs
Providing rapid, efficient, inexpensive, and resilient solutions is an eminent and urgent need for emergency relief conditions, mainly and increasingly driven by the impacts of climate change. Under such disastrous circumstances, the current practice involves preparation, dispatching and managing significant amounts of materials, resources, manpower, and transportation of basic needs, which can be hindered remarkably by infrastructure damage and massive loss of lives. However, an emerging technology known as 3D printing (3DP) can play a significant role and rapidly bring unlimited innovative solutions in such conditions with much lesser resources to meet the necessities of large populations affected. Considering the recent progress of 3DP technology and applications in different industrial and consumer sectors, this study aims to provide an analysis of the status and current progress of 3DP technology in various fields to understand and present its potential for readiness and response to disasters, emergency and relief need driven by climate change. Secondly, this study also presents a sustainability assessment of 3DP technology for such cases to evaluate economic, environmental, and social impacts. Finally, policies and strategies are suggested to adapt 3DP technology in different sectors to prepare for large-scale emergencies.
Article
29 January 2024The “Global Change Data Base” GCDB Facilitates a Transition to Clean Energy and Sustainability
This article presents the opportunities for constructing a global data base picturing underlying trends that drive global climate change. Energy-related CO2 emissions currently represent the key impact on climate change and thus become here the object of deep, long-term and historiographic analysis. In order to embrace all involved domains of technology, energy economy, fuel shares, economic efficacity, economic structure and population, a “Global Change Data Base” (GCDB) is suggested, based on earlier worldwide accepted data repositories. Such a GCDB works through regressions and statistical analysis of time series of data (on extensive magnitudes such as energy demand, population or Gross Domestic Product, GDP) as well as generation of derived data such as quotients of the former, yielding intensive magnitudes that describe systems and their structural properties. Moreover, the GCDB sets out to compute the first and second time derivatives of said magnitudes (and their percentual shares) which indicate new long-term developments already at very early phases. The invitation to participate in this foresight endeavour is extended to all readers. First preliminary GCDB results quantitatively portray the evolutionary structural global dynamics of economic growth, sectoral economic shifts, the shifts within energy carriers in various economic sectors, the ongoing improvements of energy intensity and energy efficiency in many economic sectors, and the structural changes within agricultural production and consumption systems.

Article
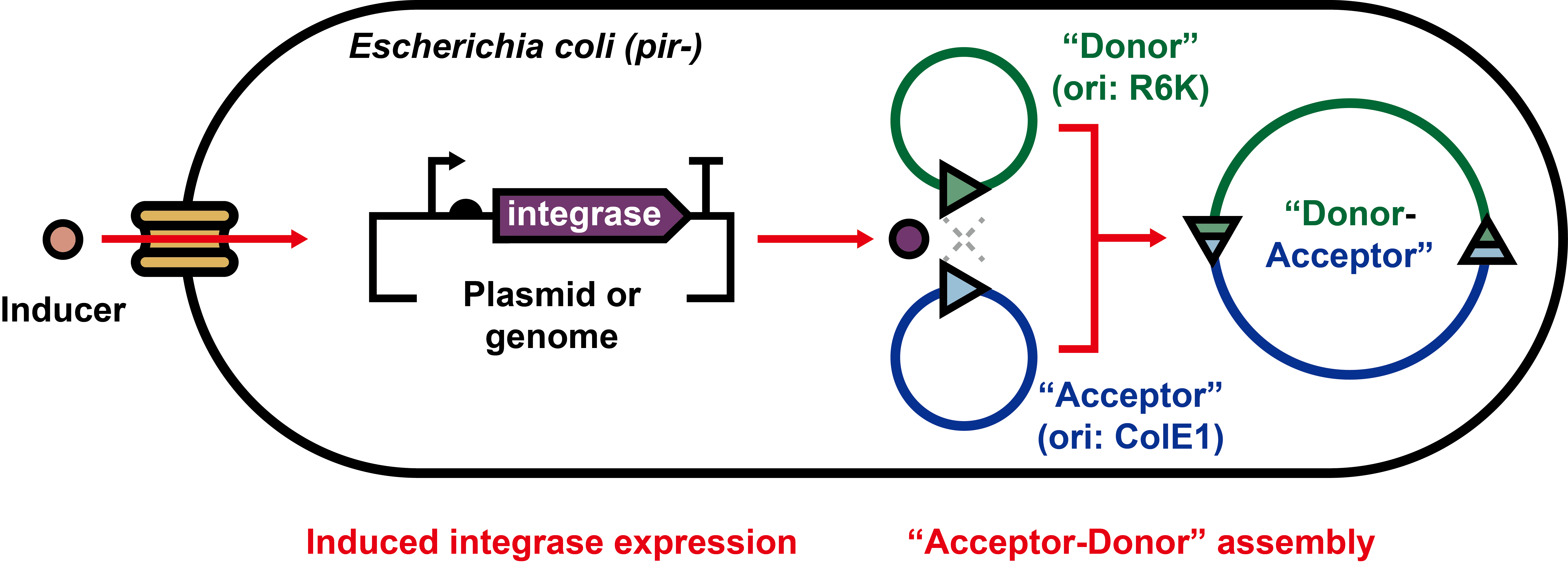
20 December 2023Serine Integrase-based Recombination Enables Direct Plasmid Assembly In Vivo
Serine integrases are emerging as one of the powerful tools for synthetic biology. They have been widely developed across genome engineering, biological part construction, genetic circuit design, and in vitro DNA assembly. However, the strategy of in vivo DNA assembly by serine integrases has not yet been reported. To address this opportunity, here we developed a serine integrase-based in vivo DNA (plasmid) assembly approach. First, we demonstrated that the engineered “Acceptor” plasmids could be assembled with diverse “Donor” plasmids by serine integrases (Bxb1 and phiC31) in Escherichia coli (E. coli). Then, by programming the “Donor” plasmids and the host E. coli cells, we established an assembly cascade procedure and finally constructed plasmids that could constitutively express three different fluorescent proteins. Moreover, we used this approach to assemble different chromoprotein genes and generated colored E. coli cells. We anticipate that this approach will enrich the serine integrase-based biotechnology toolbox, and accelerate multiple plasmid assembly for synthetic biology with broad applications.
Article
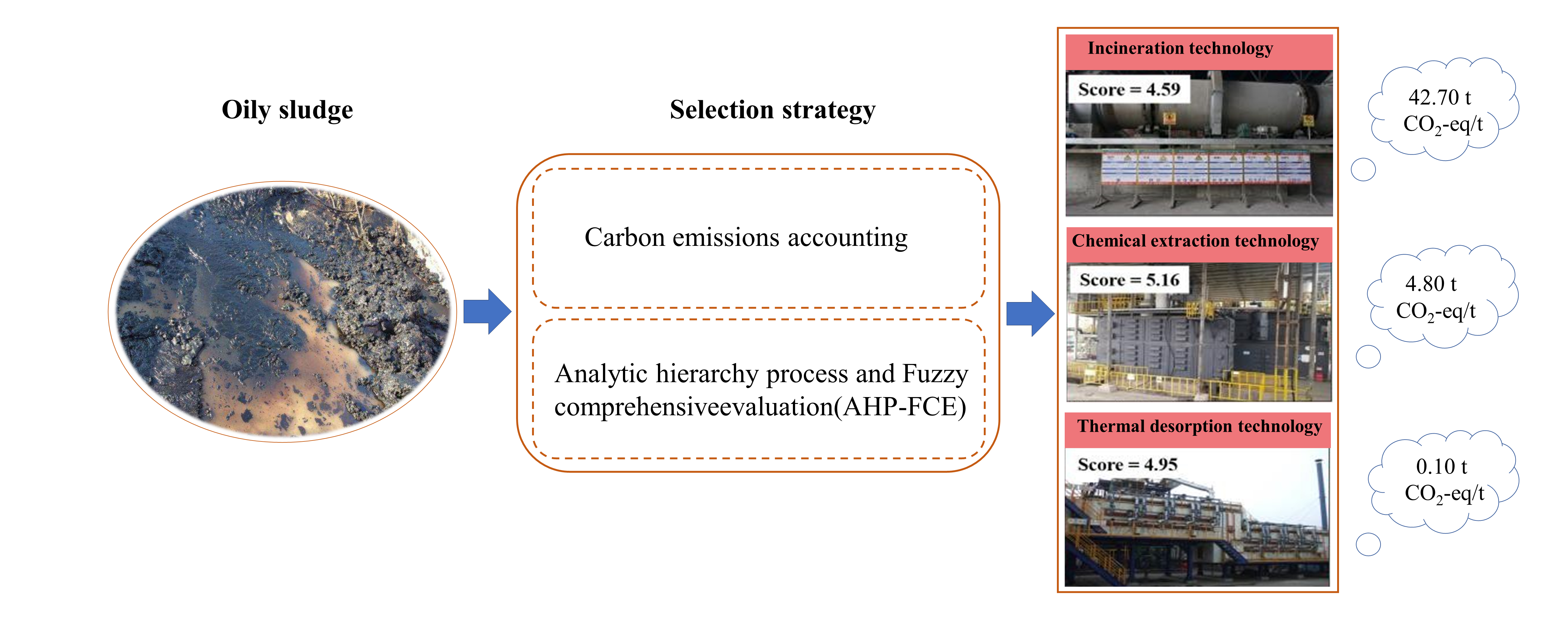
07 October 2023Comprehensive Evaluation of Sustainable Treatment Technology of Oily Sludge Based on AHP-FCE
Oil is an unsustainable energy since it is non-renewable. However, oil may not be completely replaced in a short time, so the environmental problems caused by the oil development still require our attention. The oily sludge is a kind of hazardous waste produced during the oil development. To reduce the environmental impact caused by oily sludge, low-carbon and sustainable treatment technologies need to be selected. The incineration, chemical extraction and thermal desorption are common technologies for treatment of oily sludge. We calculated the carbon emissions of these technologies. Then the index evaluation system of oily sludge treatment technology was established with the environmental, economic, social, and technical factors. And the weight of evaluation index was determined by the analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Through the investigation of industry experts, we evaluated the treatment technologies by the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method (FCE). The results showed that the carbon emissions of incineration are 42.70 t CO2-eq/t which is the highest. Meanwhile, it is 4.80 t CO2-eq/t and 0.10 t CO2-eq/t for chemical extraction and thermal desorption, respectively. The comprehensive scores of incineration, chemical extraction and thermal desorption were 4.59, 5.16 and 4.95, respectively. Therefore, the chemical extraction technology is an optimal treatment technology for oily sludge with the relatively low carbon emission and the highest comprehensive technical score. At the same time, the thermal desorption technology has strong application potential with the lowest carbon emissions. This result provides a reference for achieving clean and sustainable energy development processes.