Found 21 results
Open Access
Article
06 March 2026Bioeconomy, Green Transition and Environmental Sustainability: The Roccamonfina Area in the Campania Region (Italy)
The paper aims to contribute to planning decisions, policies, strategies, and management of inland areas affected by a protected natural area in the Campania region (Italy). Inland and rural areas, often affected by depopulation and economic decline, can and must be a crucial resource in the ecological transition. At a time when urbanisation is expected to increase, the bioeconomy offers a way to repopulate rural areas, promoting a transition to a more sustainable and inclusive production model and making the best use of the resources already present in the area. A significant example of the circular bioeconomy in action is the Campania region, which has been designated as a hub for a series of European projects currently underway that aim to integrate innovation, sustainability, and social inclusion. In this context, the area chosen is Roccamonfina, a volcanic area that has been inactive for thousands of years, with forests at the top and very fertile foothills. The area, which is part of the province of Caserta, one of the five provinces of the Campania Region (Italy), is characterised by a sparse human presence and by abandonment, in which local communities alone are unable to create conditions for sustainable development. The methodological approach starts from an analysis of the territory and gives priority to landscape, environmental, socio-economic, productive, and cultural characteristics, using a SWOT analysis. This approach aims to define policy scenarios to promote conditions for sustainable development. The results achieved in the study are designed to be scalable to similar areas.
Open Access
Article
26 January 2026Investigating the Interplay of Springshed Phenomenon and Its Crucial Role in Fostering Sustainable Practices and Community Resilience: Reflection from the Indian Himalayan Regions
This study examines the critical role of springsheds in fostering resilient communities and sustainable practices in the Indian Himalayan regions, focusing on Kalimpong I (Kalimpong) and Bhurung (Sikkim). The research addresses the pressing environmental challenges, particularly resource depletion and water scarcity, that threaten these ecologically sensitive areas. By integrating physical, environmental, and socio-economic analyses, the study compares the spring water quality, utility, and mobility in the two springsheds. It also identifies obstacles residents face in accessing these water sources. Utilizing mixed methods, including field surveys, in-depth interviews, GIS-based mapping, and water quality analysis, the study reveals the indispensable role of springs in daily life, providing essential water for drinking, agriculture, and domestic use. The findings emphasize the need to integrate traditional knowledge with sustainable practices, such as rainwater harvesting and afforestation, to enhance community resilience. This research highlights the importance of community-driven approaches to environmental sustainability, offering valuable insights for similar ecological settings worldwide.

Open Access
Review
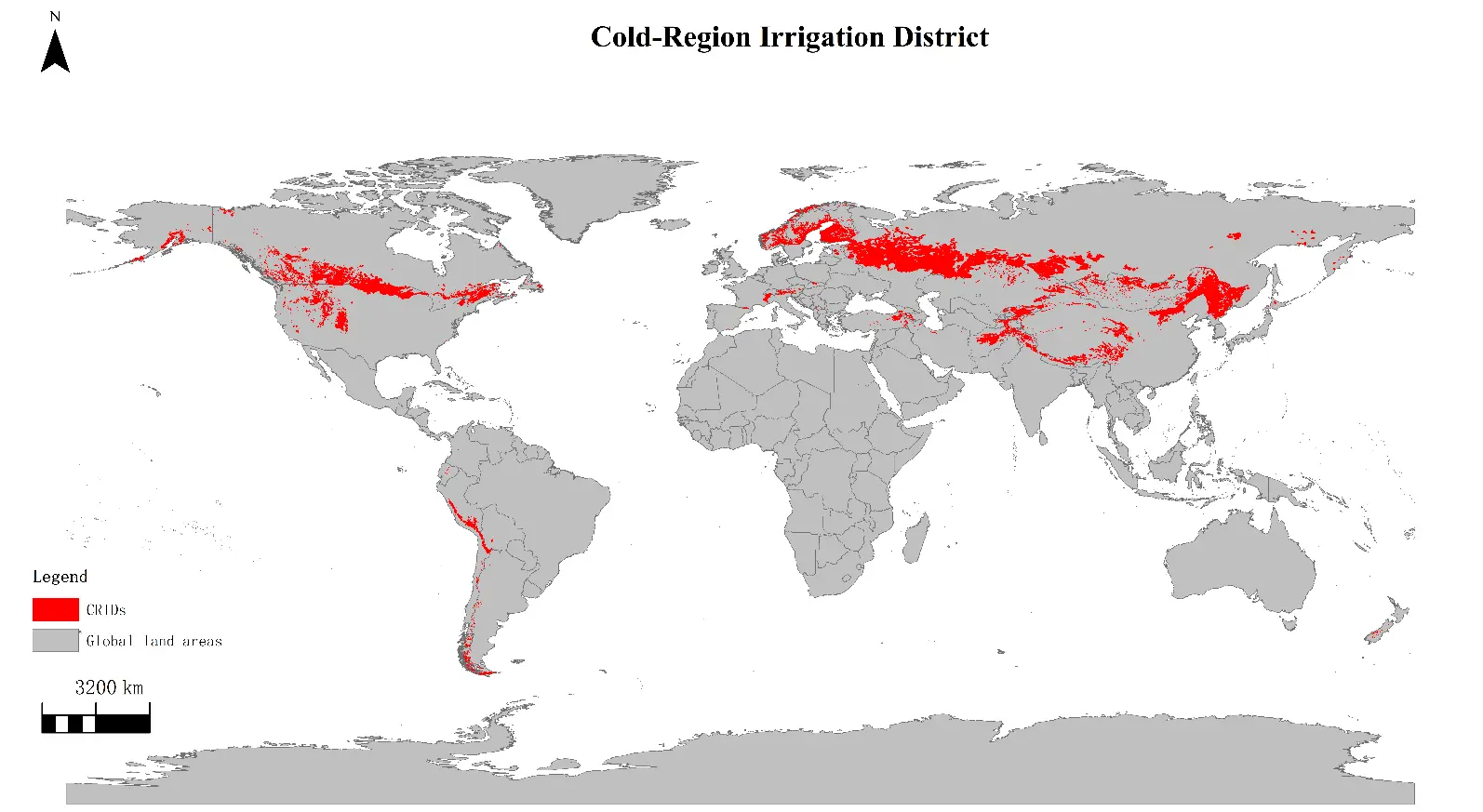
30 December 2025Advances in Hydrology of Irrigation Districts in Cold Regions
Given the extreme complexity of systems, the strategic importance of water resources, and the high ecological vulnerability in cold-region irrigation districts (CRIDs), research on the hydrological processes in these areas represents not only an interdisciplinary scientific endeavor, but also a critical practical challenge with direct implications for food security, water security, ecological safety, and sustainable regional development in high-altitude and high-latitude regions. The evolution of this field has progressed from early phenomenon identification to mechanistic analysis and, more recently, to multi-process and multi-scale simulation frameworks. This paper provides a systematic review of hydrological processes in CRIDs. It first examines fundamental components such as precipitation, evaporation, snowmelt, and groundwater recharge, highlighting their distinct behaviors under the combined influence of freeze–thaw cycles and irrigation practices, and further discusses the interactions and coupling mechanisms among these processes. Irrigation not only alters soil moisture distribution and freeze–thaw dynamics but also, together with freeze–thaw processes, shapes the transient hydrological dynamics characteristics of water and energy transfer, thereby influencing system stability and agricultural productivity. Hydrological modeling has advanced from simplified empirical approaches to mechanistic frameworks that integrate multiple processes and scales, yet challenges remain in the representation of nonlinear freeze–thaw, the integration of irrigation management, and cross-scale consistency. Moreover, cold-region irrigation districts exhibit heightened sensitivity to extreme events, such as rapid snowmelt, severe droughts or heavy rainfall. Future research should deepen the integration of freeze–thaw mechanisms with crop models, advance multi-scale coupled simulations, enhance long-term monitoring and scenario analysis, and systematically incorporate water–carbon balance and ecological effects into hydrological assessments. These efforts will support sustainable management and precision regulation of water resources in cold-region irrigation districts.
Open Access
Article
09 December 2025Defiant Doctorates: Reshaping the Social, Cultural and Intellectual Value of the Doctorate in Regional Universities
Universities are ranked and clustered into ‘like-minded’ institutions. Regional universities—as an adjective and noun or a compound noun—are defined via location, rather than academic standards, teaching innovation, research rigour, or the use of innovative technology. Through the ‘regional’ labelling, they are marked and separated as different from, and implicitly less than, urban and metropolitan institutions, which carry the excitement of urbanity, encompassing Virilian speed and prestigious alumni. This differentiation has consequences for grants, funding, academic staff attrition, and leadership. But what happens to PhD students at regional universities? Where is their voice? How are their views recognized, codified, and understood? Written between an experienced supervisor and a PhD student, this paper offers a different pathway through the regional graduate programme, offering a different lens to re-vision regional higher education, beyond cliches of partnerships and collaborations. As a theoretical and conceptual paper, it creates and holds space for PhD students in a revisioning of regional universities.
Open Access
Article
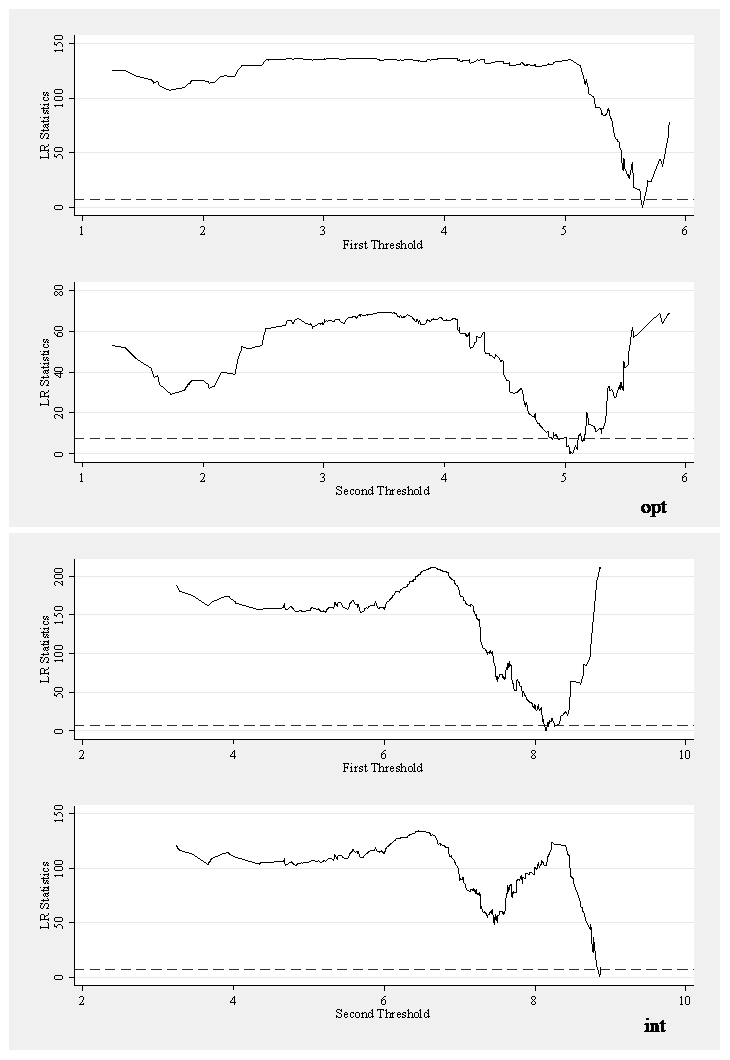
25 November 2025The Impact of Digital Infrastructure on Economic Resilience: Evidence from the Four Major Regions of China
Amid accelerating global structural changes and China’s transition to the digital-driven fourth industrial revolution, this paper examines the impact of digital infrastructure on economic resilience by clustering China’s 31 provinces into the four major economic regions during 2008–2022. Through the application of the Threshold Regression Model, Mediation Effect Model, and GTWR Model, the analysis reveals that digital infrastructure exhibits a threshold effect in enhancing economic resilience, with significant increasing marginal returns beyond specific scale thresholds. Regional heterogeneity is pronounced: the eastern region demonstrates amplified nonlinear benefits, while the northeast exhibits diminishing returns after crossing the threshold. Industrial diversification is an effective way for digital infrastructure to build resilience. The effects of industrial specialization, however, vary by region: it strengthens resilience in the east, weakens it in the central region, and shows no statistically significant impact in the western and northeastern regions. The findings provide empirical evidence for regionalized policymaking during technological paradigm shifts, highlighting the need to consider both digital infrastructure scale thresholds and industrial structure dynamics in economic resilience strategies.
Open Access
Article
24 November 2025Bridging the Urban-Rural Divide: How Urban Agriculture Enhances Food Security in High-Urbanized Regions in Guangdong, China
The COVID-19 pandemic starkly exposed vulnerabilities in global food supply chains, highlighting the critical need for resilient, localized alternatives to ensure urban food security. Urban agriculture (UA), which we define as all agricultural output occurring in cities with an urbanization rate exceeding 85%, emerges as a pivotal strategy to mitigate such risks by shortening supply chains, particularly for perishable goods like vegetables and fruits. This study investigates the underexplored role of UA in Guangdong Province, China—a region characterized by rapid urbanization, high population density, and economic dynamism- to assess its contribution to food self-sufficiency. Leveraging a novel classification framework, we categorize Guangdong’s 21 prefecture-level cities into two groups based on an 85% urbanization threshold (2017–2022), distinguishing high-degree urbanized cities (e.g., Shenzhen, Guangzhou) from others. Using panel data, we analyze spatial-temporal patterns in grain, vegetable, and fruit self-sufficiency through geospatial and statistical methods. Key findings reveal pronounced disparities: high-degree urbanized cities exhibit critically low grain self-sufficiency, relying heavily on external supplies, while non-urbanized regions achieve exceptional surpluses. Conversely, vegetables and fruits demonstrate a center-periphery gradient, with peri-urban zones bridging the gap between urban cores and rural surplus hubs. Despite incremental gains in UA productivity, urban yields lag behind non-urban areas for grains and vegetables, though fruit production shows convergence, underscoring UA’s niche potential. These results highlight the indispensability of non-urban regions in sustaining provincial food security while emphasizing UA’s role in fresher, faster urban supply chains. We propose actionable policies, including: (1) integrating farmland protection redlines with UA incentives (e.g., vertical farming subsidies, peri-urban logistics optimization); (2) scaling technology-driven UA (controlled-environment agriculture, digital platforms); and (3) reducing post-harvest losses through urban-centric infrastructure. Our findings advance the discourse on crisis-resilient food systems, offering a replicable framework for high-density regions globally.
Open Access
Article
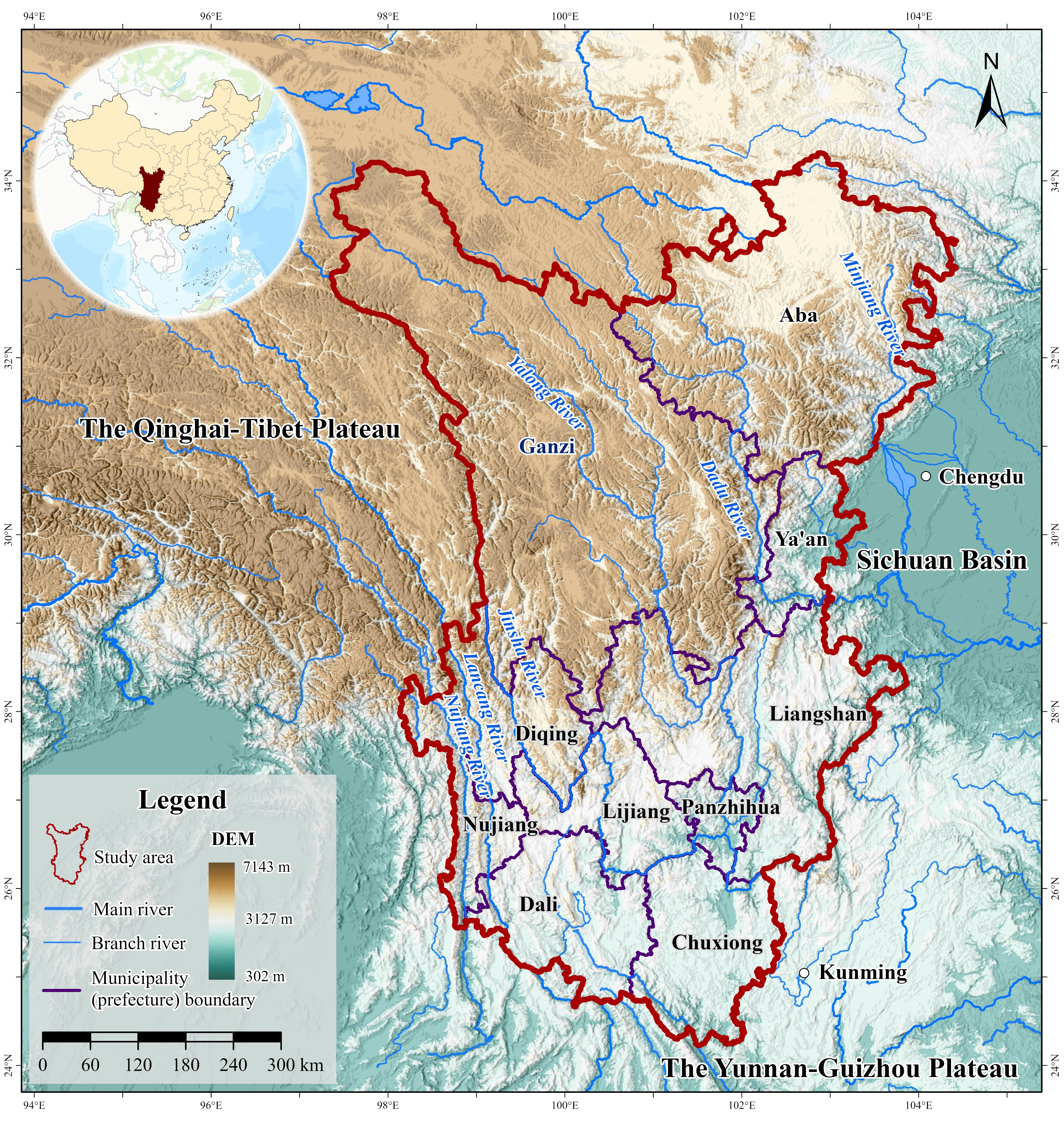
29 October 2025Solutions of Minimized Agrochemicals Input in the Post Zero-Growth Era: A State-of-the-Art Analysis of the Hengduan Mountains, China
How to further reduce the input of agrochemicals after zero-growth is an important challenge faced by mountainous areas. Up to now, the combined solution for minimized agrochemicals intervention in the post zero-growth era has not been systematically analyzed globally. Here, the Hengduan Mountain regions (HMR) in China, as a case, we estimated the turning points of agrochemicals input intensities using a quadratic equation, as well as integrating policy document analysis and literature review. Results show that the occurred timeline of fertilizer and pesticide use zero-growth in 10 municipalities (prefectures) in the HMR is relatively wide, with a distribution from 2009 to 2019, illustrating that all municipalities (prefectures) have been achieved national goals ahead of 2020 deadline. Thus, the incentive of a series of national-level policies focusing on chemical fertilizers and pesticides has proven effective in achieving the zero-growth target of agrochemicals input in the HMR. However, comparison with major mountainous countries like Germany, Italy, Portugal, Romania, Austria, and Spain etc., there are clearly many opportunities for enhancement in reducing fertilizer and pesticide uses. We present a practical route to minimize agrochemicals application in the HMR through crop rotation-based agro-biodiversity solutions, organic alternative-based soil health solutions, professionalization-based precision farming solutions, smallholder farmers’ awareness-based behavior intervention solutions, conservation reserve-based zoning solutions, etc.
Open Access
Article
08 September 2025Open Water in Winter: An Influential but Underestimated Ecosystem in Northern Boreal Mountain Regions
Patches of open water (polynyas) persist throughout six-month winters on many ice-covered lakes in boreal mountain ecoregions of northwestern North America. We explored their distribution, hydrological correlates, and the diversity of species using them from freeze-up to break-up. In headwater drainages, lakes with outflow polynyas were significantly larger than those without, but many small lakes also had polynyas. There was a consistent threshold in upstream catchment size below which outflow polynyas were absent and above which they persistently occurred in downstream lakes. Outflow polynyas depend on winter-long through-flow of water, likely maintained by the hydraulic head of higher elevation ground water in perched water tables in this region of very limited permafrost. Based on camera trapping, two species, the American dipper and river otter, used polynyas heavily throughout winter foraging. Polynyas likely provided crucial forage for at least 9 species of migratory waterfowl (Anatidae) to complete their spring migration or to prepare for reproduction on local lakes. Cameras recorded additional 5 bird and 11 mammal species, as foragers, scavengers, or incidentally. We report previously undocumented significance of these spatially-limited and seasonal polynya ecosystems in expanding the diversity of winter ecological opportunity for numerous species on small to medium-sized lakes.

Open Access
Communication
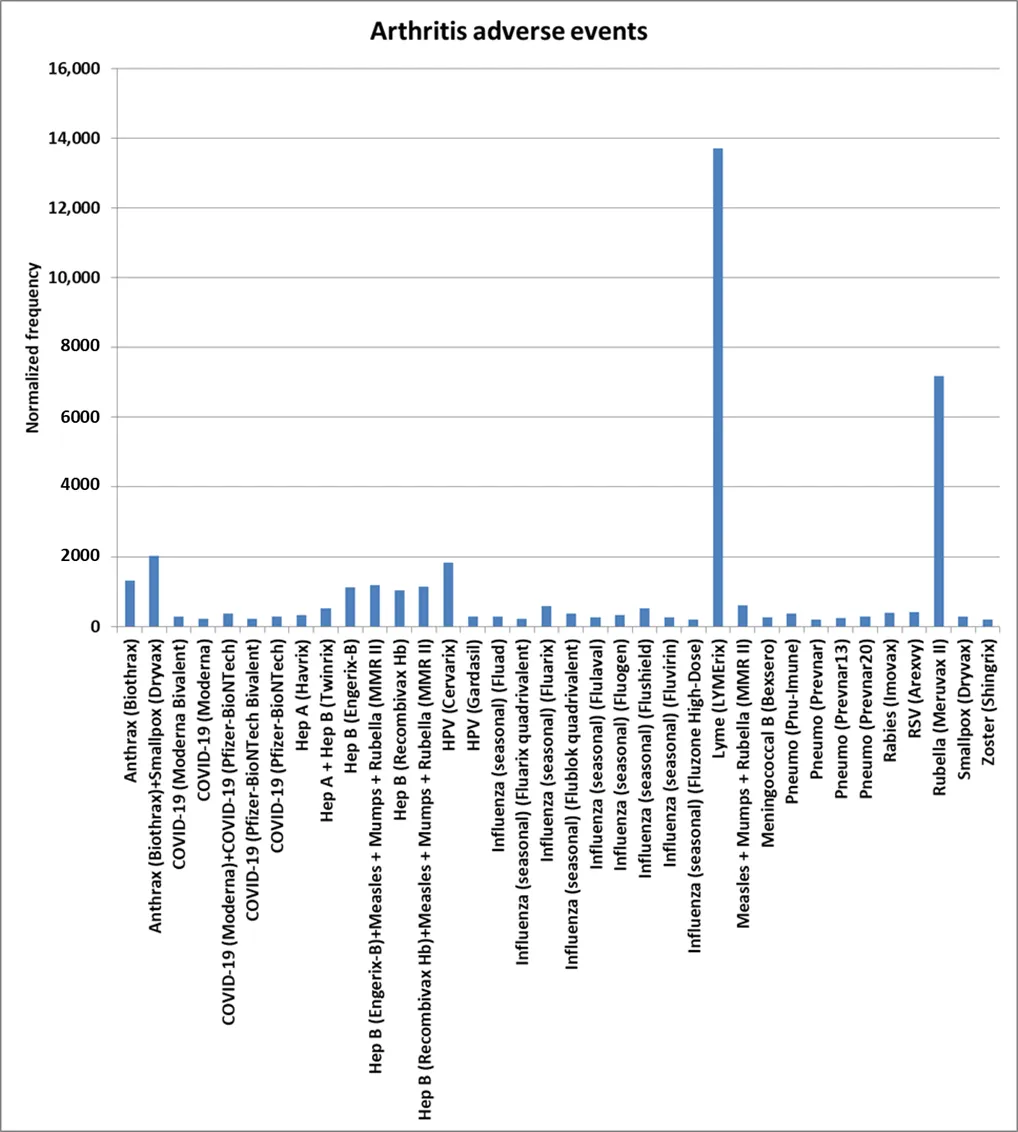
05 August 2025Autoimmune Adverse Events Following Immunization
Adverse events (AEs) following immunization can include autoimmune AEs for some vaccines and combinations. This study retrospectively examines autoimmune AEs to detect safety signals for vaccines and concomitantly administered vaccines in the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) database. This study focuses on which vaccines were administered or coadministered for retrospective analysis of analyzed autoimmune AEs. Observed results include multiple autoimmune AE safety signals: human papillomavirus (HPV) Cervarix, HPV Gardasil, hepatitis (Hep) A + Hep B (Twinrix), Lyme disease (LYMErix), coadministered COVID-19 Moderna + Pfizer-BioNTech, Hep B (Engerix-B), and others. Identified arthritis AE safety signals include Lyme disease (LYMErix), rubella (Meruvax II), HPV (Cervarix), Anthrax (Biothrax) + Smallpox (Dryvax), and more. Coadministered DTaP + HepB + IPV (Pediarix) + Hib (Pedvaxhib) + Pneumococcal (Prevnar13) + Rotavirus (Rotarix) may be exhibiting synergy AE rate for eczema AEs. Thirty five influenza vaccines were observed with Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) AE safety signals, plus additional safety signals for multiple other vaccines. influenza (H1N1 monovalent) (GSK) exhibits a very high rate for narcolepsy AEs.
Open Access
Article
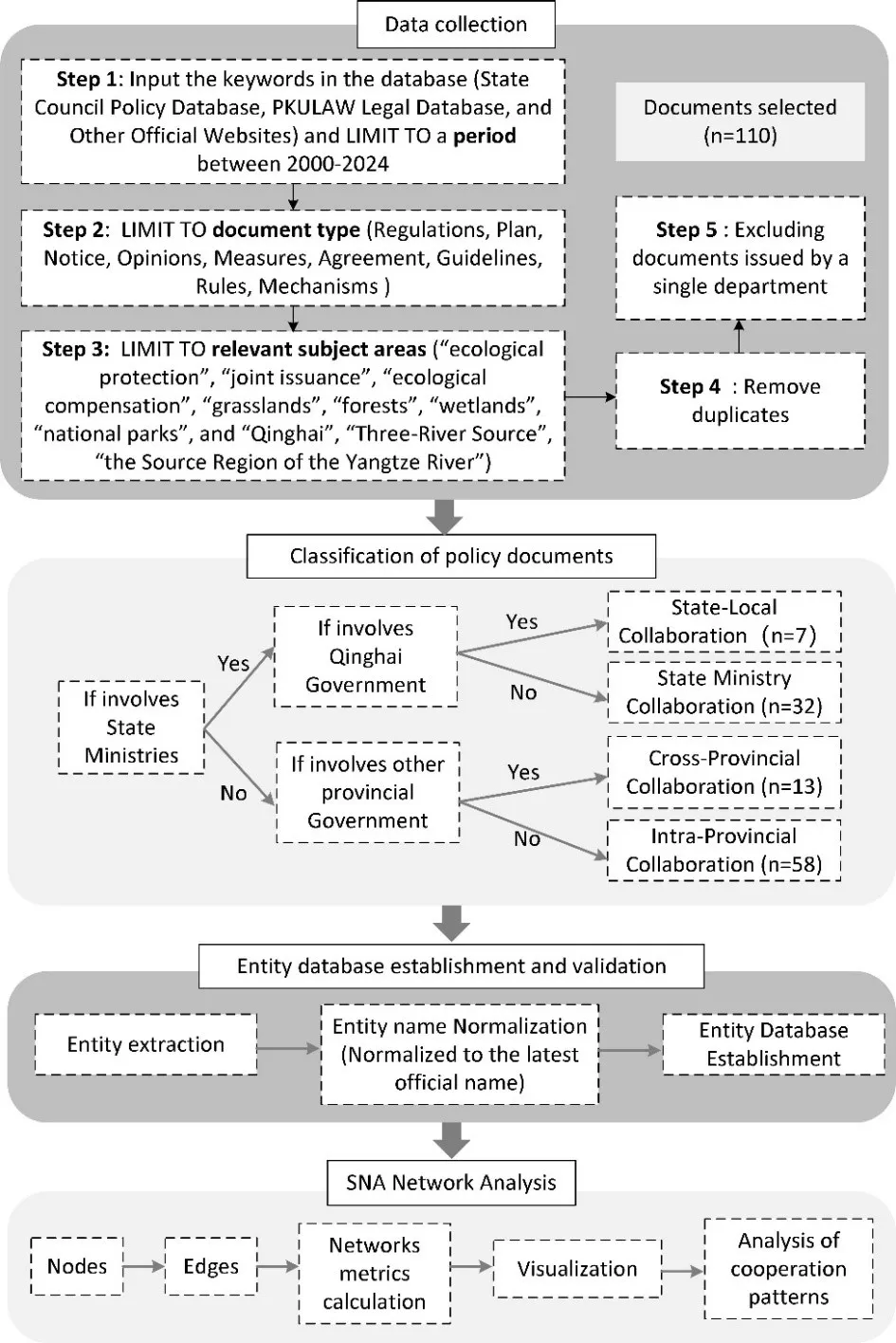
21 July 2025The Intergovernmental Networks of Ecological Protection Policies Issuing Entities in the Source Region of the Yangtze River: A Case Study of Qinghai Province
Ecological conservation and governance play key roles in constructing an ecological civilization society, while intergovernmental cooperation provides new perspectives for cross-regional ecological governance. We employed a social network analysis (SNA) method to examine 110 published ecological policies from 2000 to 2024 in the Source Region of the Yangtze River (SRYR). The study has three key findings. Firstly, intergovernmental collaborative policies on ecological protection showed an upward trend, with intra-provincial collaborations within Qinghai Province being the most frequent. Secondly, four collaboration models were demonstrated, namely: national ministries, national and provincial, cross-provincial and intra–provincial collaborations. National agencies and Qinghai provincial agencies collaboratively set objectives, which Qinghai operationalizes with incentive-constraint measures. Then, the targeted guidelines were launched by national and provincial authorities. Afterward, cross–provincial agreements and mechanisms facilitate joint actions. Thirdly, we revealed the hierarchical structures, including a national network, two central-local sub-networks, three-tier inter-provincial partnerships, and four regional sub-clusters. Core actors include national ministries that coordinate cross-departmental efforts. The Qinghai provincial government serves as a central-local hub. It maintains strong transboundary ties with Aba and Ganzi Prefectures of Sichuan Province. Provincial departments such as ecology and environment, forestry and grasslands, and finance lead intra-provincial collaborations. These findings offer new insights for integrating multi-level governance in ecological protection and ecological civilization construction.