Found 5 results
Review
14 April 2025Advancements in Flexible Ceramic Fibers for High-Temperature Applications: A Comprehensive Review
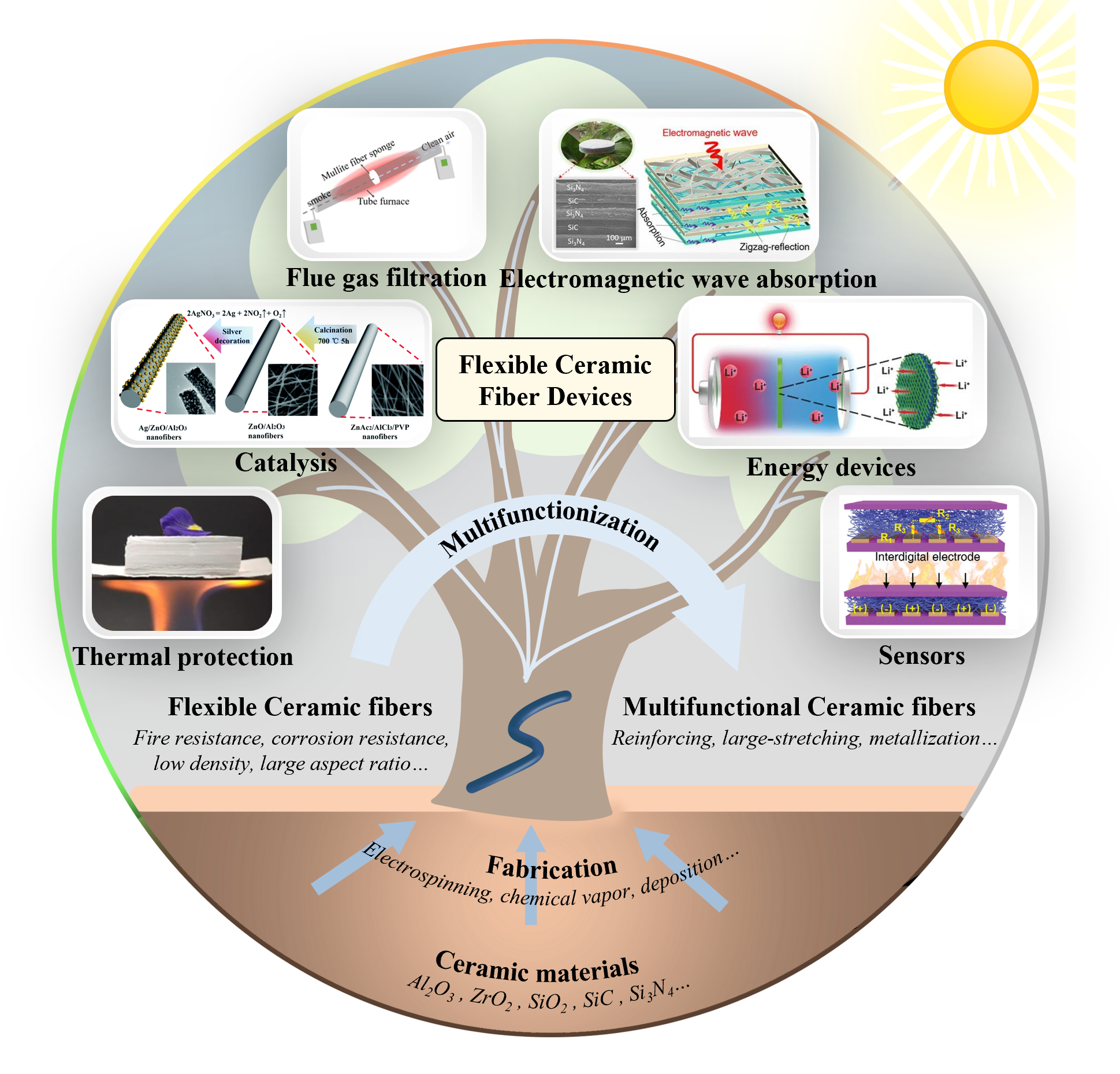
Flexible ceramic fibers (FCFs) have emerged as a highly promising material for high-temperature applications, effectively combining the excellent thermal stability of ceramic materials with the robust mechanical properties of flexible fibers. This review provides a comprehensive overview of recent advances in multifunctional FCF devices, focusing on innovative methods across material selection, structural design, and fabrication techniques to enhance their functional properties. These improvements, i.e., mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and oxidation resistance, make FCFs particularly suitable for a wide range of applications, including energy storage, sensing, and high-temperature filtration. Notably, advancements in fabrication techniques have enabled the creation of novel FCF devices for thermal insulation and high-temperature sensing, such as stretchable ceramic membranes and printable ceramic fiber papers. The review concludes by discussing the future potential of FCFs, especially in multifunctional applications in high-temperature environments, where they can serve as essential components of advanced technologies. This work highlights the versatility and potential of FCFs as a transformative material for next-generation high-temperature applications.
Communication
08 January 2025Development of Eco-Friendly Composites Using Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and Diss Fibers (Ampelodesmos Mauritanicus)
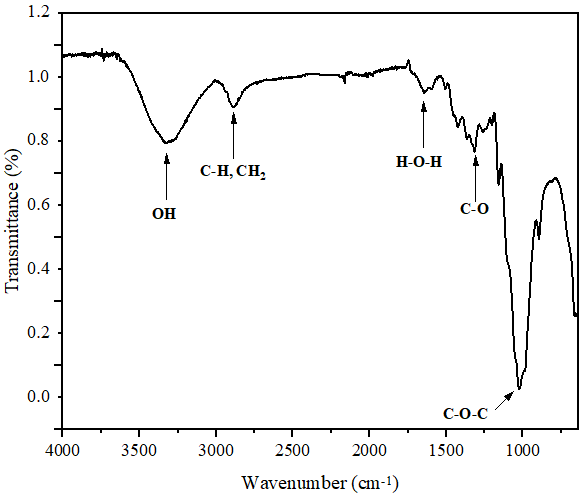
In response to the growing environmental threats and pollution linked to synthetic plastics, current scientific inquiry is prioritizing the advancement of biodegradable materials. In this context, this study investigates the possibility of developing fully biodegradable materials using plant fibers extracted from the Diss plant (Ampelodesmos mauritanicus) as reinforcement in poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV)-based biocomposites. The biocomposites were prepared by melt blending in the following weight ratio: PHBV/Diss fibers 80/20. The chemical structure of Diss fibers was characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF). The impact of Diss fibers on the mechanical properties of biocomposites has also been investigated in comparison to neat PHBV. FTIR and XRF analyses identified cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin as the main components of Diss fibers. On the other hand, the results showed a significant enhancement of Young’s modulus (⁓21%) of PHBV/DF biocomposites in comparison to neat PHBV due to a better dispersion of the fibers in the matrix, as confirmed by atomic force microscopy (AFM) images.
Article
11 October 2023Fibrous SiC-based Mesoporous Solids for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants under Artificial Light
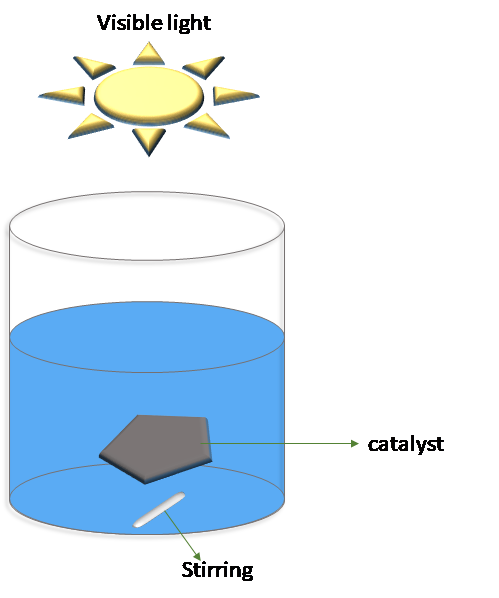
SiC-based mesoporous solids with fibrous nanostructure were prepared by impregnation of a polycarbosilane precursor on annealed polyacrylonitrile (PAN) fibers and subsequent pyrolysis. The obtained material exhibits a mesoporous structure and has a specific surface area of ~20 m2/g. It has a semiconducting electronic character with a bandgap of 2.65 eV, i.e., in the visible range. Adsorption tests of methylene blue were performed on the material under dark conditions, which showed an adsorption amount of 78 wt%. The photocatalytic activity of the material was then evaluated for the degradation of the dye under artificial daylight irradiation over a period of 7 h. A degradation of 94 wt% was achieved. Regeneration and reuse of the material was also tested and resulted in 97 wt% degradation after reuse, indicating potential interest of the material as a contactor in environmental remediation devices.
Review
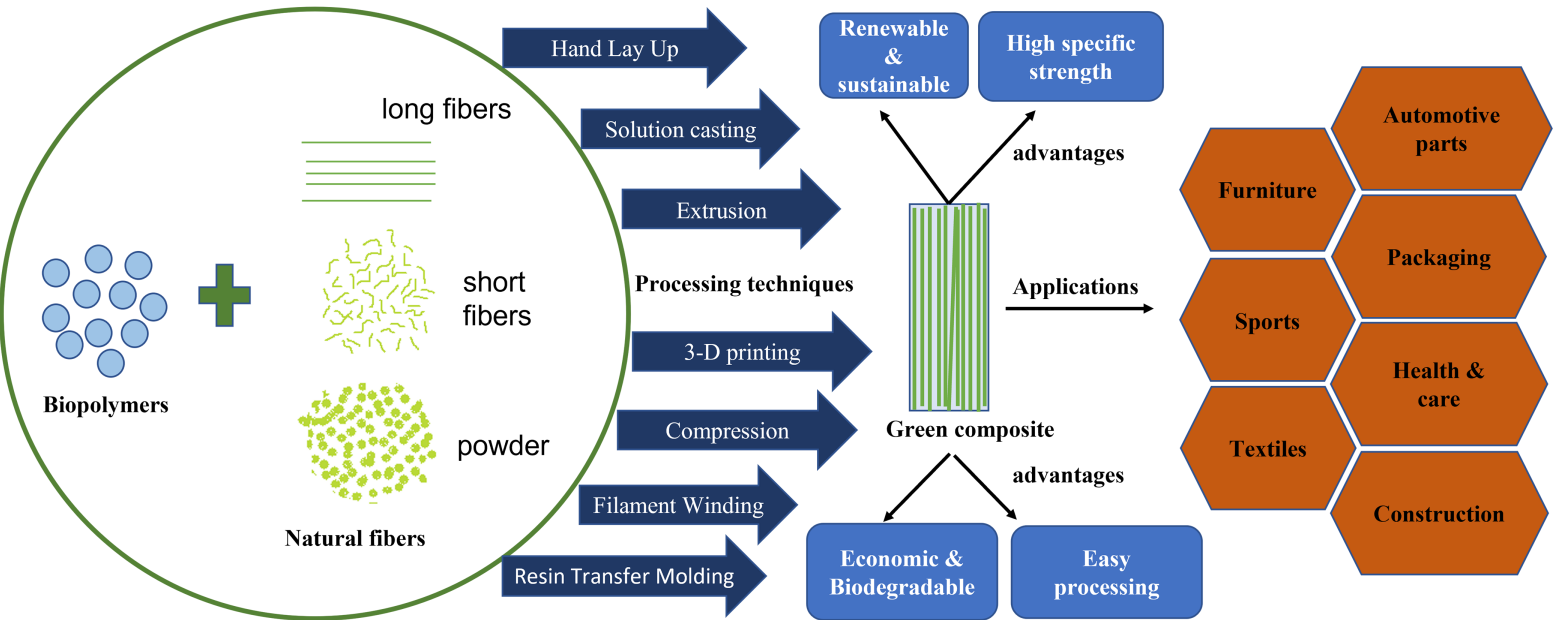
15 August 2023Green Composites Using Naturally Occurring Fibers: A Comprehensive Review
Depletion of non-renewable resources and health hazards of petroleum-based polymers and plastics has enforced the development of eco-friendly materials. The use of conventional plastics has to be minimized and can be replaced with environmentally friendly and sustainable bio-based polymers or biopolymers due to extensive environmental impact. A major share of petroleum-based polymers is used for polymeric composites with research focus on green composites and biocomposites containing renewable/bioderived matrix polymer and fillers from naturally occurring fibers. Biocomposites hold great promise to replace petroleum-based polymer composites owing to their lower cost, non-toxicity, abundance of raw material, renewability, and high specific strength. All these merits of biocomposites have led to an increment in the development of new biocomposites with enhanced properties, wide applicability and ever demanding criteria. The recently published review studies detailed the raw materials used, fabrication techniques, characterization, and applications including biodegradation and rheological studies performed in recent years. This review covers all the important properties of biocomposites along with detailed description of synthesis, properties, characterizations and applicability of these green composites in several areas. The review also focuses on their raw materials, types, recent biocomposites, processing techniques, characterizations, applications, and current challenges with future aspects.
Perspective
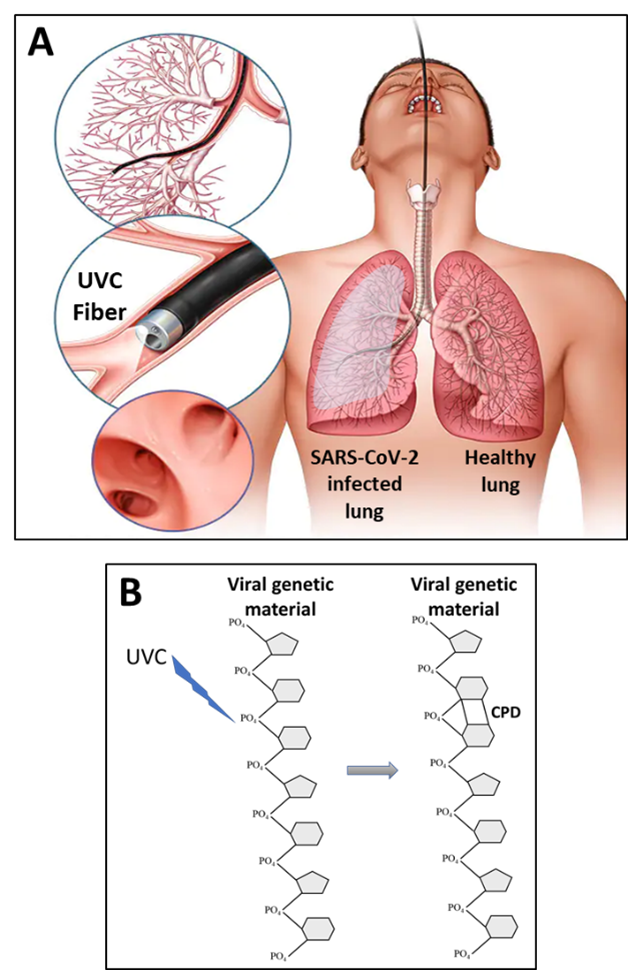
07 March 2023Pulsed Ultraviolet C as a Potential Treatment for COVID-19
Currently, low dose radiotherapy (LDRT) is being tested for treating life-threatening pneumonia in COVID-19 patients. Despite the debates over the clinical use of LDRT, some clinical trials have been completed, and most are still ongoing. Ultraviolet C (UVC) irradiation has been proven to be highly efficient in inactivating the coronaviruses, yet is considerably safer than LDRT. This makes UVC an excellent candidate for treating COVID-19 infection, especially in case of severe pneumonia as well as the post COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis. However, the major challenge in using UVC is its delivery to the lungs, the target organ of COVID-19, due to its low penetrability through biological tissues. We propose to overcome this challenge (i) by using pulsed UVC technologies which dramatically increase the penetrability of UVC through matter, and (ii) by integrating the pulsed UVC technologies into a laser bronchoscope, thus allowing UVC irradiation to reach deeper into the lungs. Although the exact characteristics of such a treatment should yet to be experimentally defined, this approach might be much safer and not less efficient than LDRT.