Found 15 results
Article
06 May 2024Assessing Energy Emissions and Environmental Impact of Wool Processing: A Case Study of an Indian Textile Mill
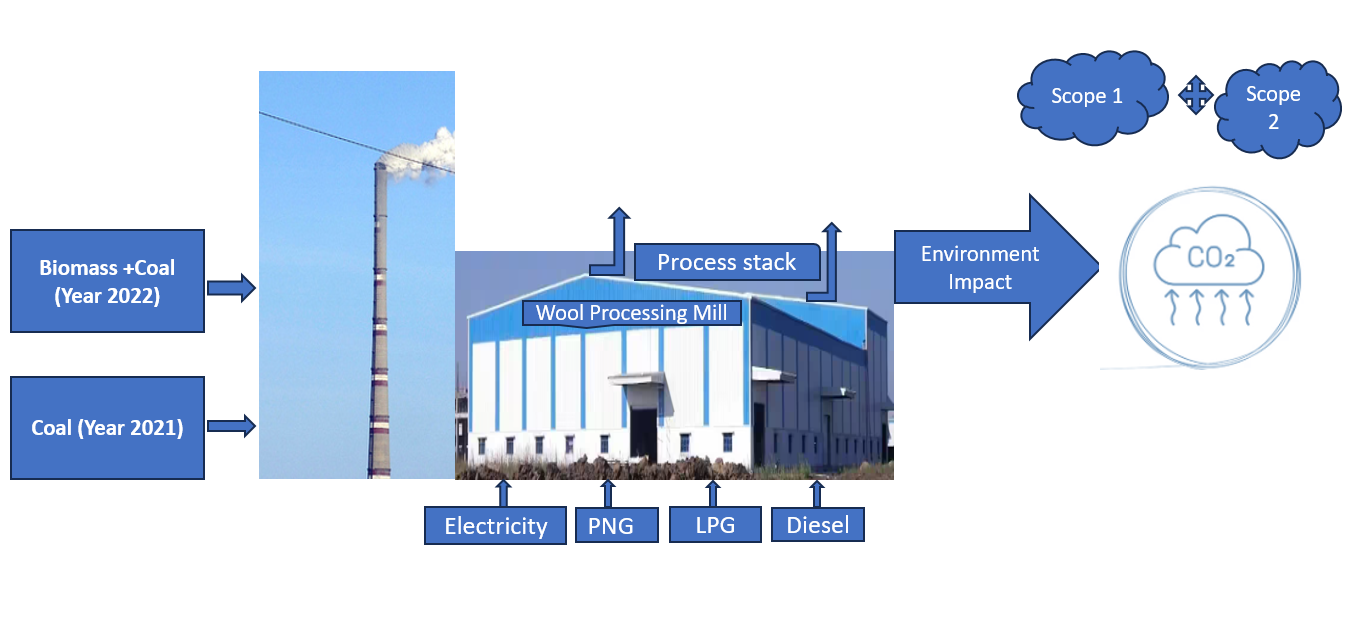
The objective of this study is to investigate and analyze the effect of varying sources of energy inputs and their impact on carbon emissions during wool fiber processing. The method involved industrial visits to the textile wool processing mill and interaction with the manufacturing as well as commercial sourcing teams to gather relevant data. The results and outcome of this analysis indicate that wool wet processing is responsible for a significant carbon emission of about 0.031 tCO2e/unit of production. Coal as a source of energy has the highest carbon emission 0.066 tCO2e/product, while the use of biomass and Pressurized Natural Gas (PNG) had significantly lower CO2 emissions. Further, this study evaluated the scope 1 and scope 2 category emissions produced at the wool processing stage which accounted for 56303.2 tCO2e and 1817.10 tCO2e respectively.
Commentary
25 April 2024Monitoring Complexity in Clean Energy Systems Applications
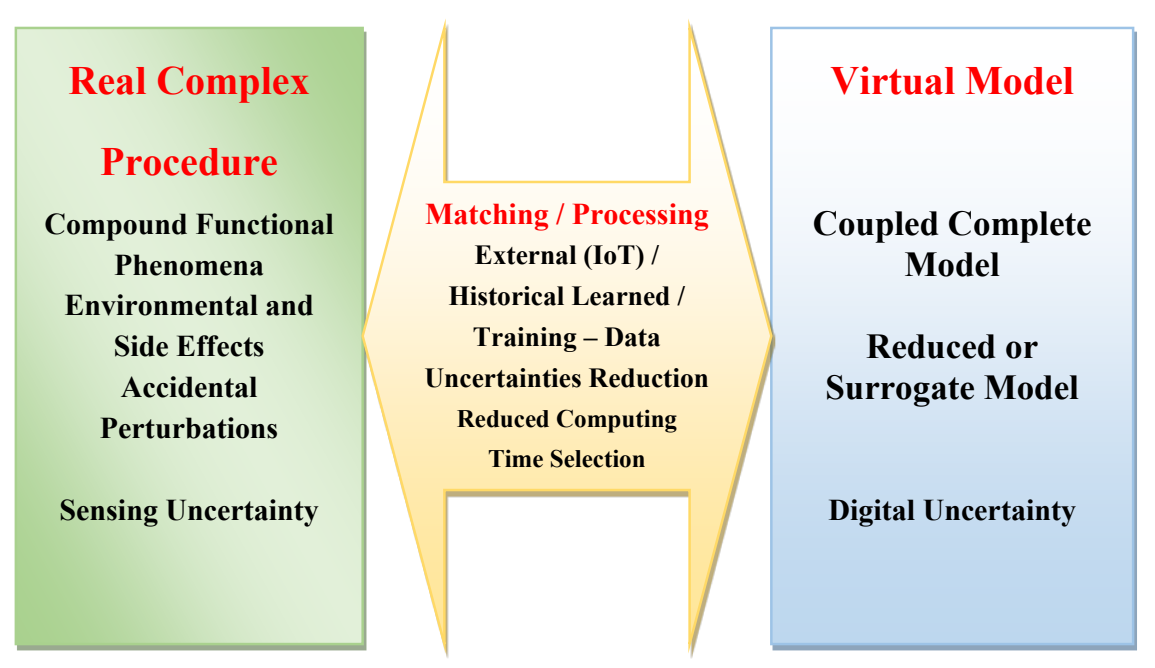
Clean energy applications often involve systems with technological process monitoring. This supervision aims to optimize operation, in particular efficiency, performance and compatibility with dedicated criteria. Most of these energy systems involve complex procedures. A complex procedure is an arrangement of compound processes interacting in interdependent behaviors. The supervision of these complex procedures focuses on the interaction of compound processes, their digital coupling and the handling of uncertainties in their detection and digital tools. Real-virtual pairs, such as digital twins, could carry out such surveillance. This commentary aims to analyze and illustrate such supervision in clean electromagnetic energy systems based on a review of the literature. The notion of complexity and the interactions of the compound processes involved are first addressed and detailed. The modeling of these interactions is presented through the mathematical coupling of the electromagnetic equations with other equations of the phenomena involved. These phenomena are linked to the functional or environmental behaviors of the systems. Compound process monitoring in complex procedures is then analyzed taking into account threats, unsolicited external events and uncertainties related to the sensing and digital tools involved. This contribution illustrated several points relating to, the relationship between the complexities of a real energy procedure and its coupled virtual model, the dependence of the model reduction strategy on each specific application and the reduction of uncertainties through the matching of real-virtual pairs. The different analyses are supported by literature references permitting more information when necessary.
Article
01 April 2024Cost Effectiveness of the Industrial Internet of Things Adoption in the U.S. Manufacturing SMEs
This research paper explores the financial adoption challenges of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) in industry. Previous studies have mainly concentrated on designing affordable IIoT devices, reducing operational costs, and creating conceptual frameworks to assess the financial impact of IIoT adoption. The objective of this paper is to investigate whether IIoT adoption’s financial benefits outweigh the initial costs in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The data from the Industrial Assessment Centers (IAC) database were analyzed, focusing on 62 U.S. manufacturing SMEs across 10 states and 25 Standard Industrial Classifications (SICs), evaluating projected IIoT implementation costs and anticipated cost savings. Results from the analyses reveal that statistically, the difference between implementation costs and savings is significant at a 95% confidence level. Practically, this indicates that SMEs, despite facing high initial costs, can expect these investments to be counterbalanced by substantial savings. From an engineering perspective, this finding raises awareness among SMEs that, beyond overcoming financial barriers, IIoT technologies serve as a strategic enhancement to operational efficiency and competitive positioning. This study acknowledges the limitations including reliance on estimated projections and a narrow industry focus. Future research should broaden the sample and explore the lifecycle costs of IIoT.
Article
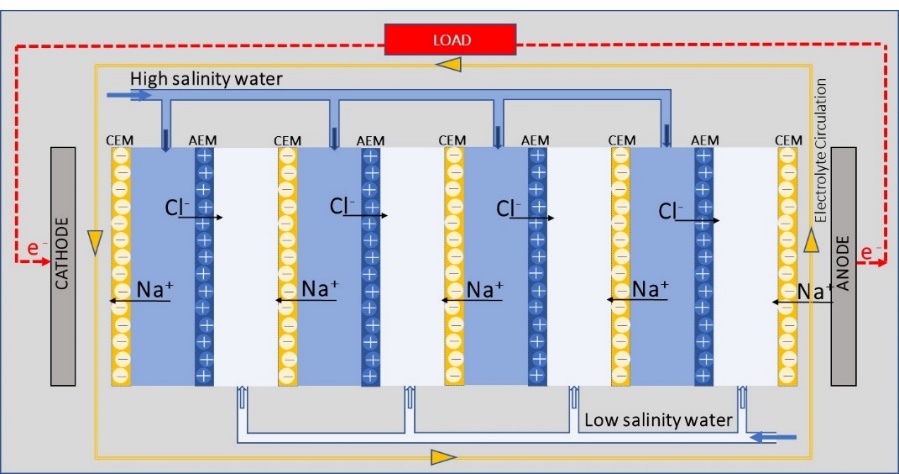
13 March 2024The Potential of Salinity Gradient Energy Using Reverse Electrodialysis to Generate Electricity for Seawater Desalination Plants, an example from Western Australia
Seawater desalination plays a vital role in addressing the increasing global demand for freshwater. However, the energy-intensive nature of desalination processes and the generation of brine by-products pose environmental challenges. In Western Australia (WA), approximately 48% of freshwater is supplied by two seawater desalination plants employing the energy-intensive seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) method. These plants are powered by a combination of renewable and conventional energy sources. Typically, the most efficient approach for desalination plants involves a blend of renewable energy sources. Salinity gradient energy (SGE) harnessed through the reverse electrodialysis (RED) system, which derives energy from mixing waters with varying salinities, has emerged as a potential solution. RED utilizes ion-exchange membranes to convert the chemical potential difference between two solutions into electric power. The net specific energy of SGE, calculated based on the Gibbs free energy associated with mixing seawater and wastewater, is estimated at approximately 0.14 kWh per cubic metre of brine for SWRO desalination plants. The combined SGE potential of WA’s two desalination facilities theoretically amounts to approximately 87.4 MWh of energy. However, due to the inherent limitations of the RED system’s current energy efficiency, only about 2.5% of the desalination plant’s energy requirements can be met through this technique. This paper addresses a significant gap in the literature by analyzing the technical and economic constraints of utilizing salinity gradient energy (SGE) through the reverse electrodialysis (RED) system for seawater desalination plants. This marks the first examination of its kind, shedding light on both the technical feasibility and economic challenges of SGE-RED application in this context. The scientific contribution lies in its innovative approach, integrating technical and economic perspectives to provide an understanding of SGE-RED technology’s potential drawbacks and opportunities. By identifying and tackling these challenges, this paper aims to pave the way for optimizing SGE-RED systems for practical implementation in seawater desalination plants.
Case Report
26 February 2024‘Greening’ an Oil Exporting Country: A Hydrogen and Helium Closed-cycle Gas Turbines Case Study
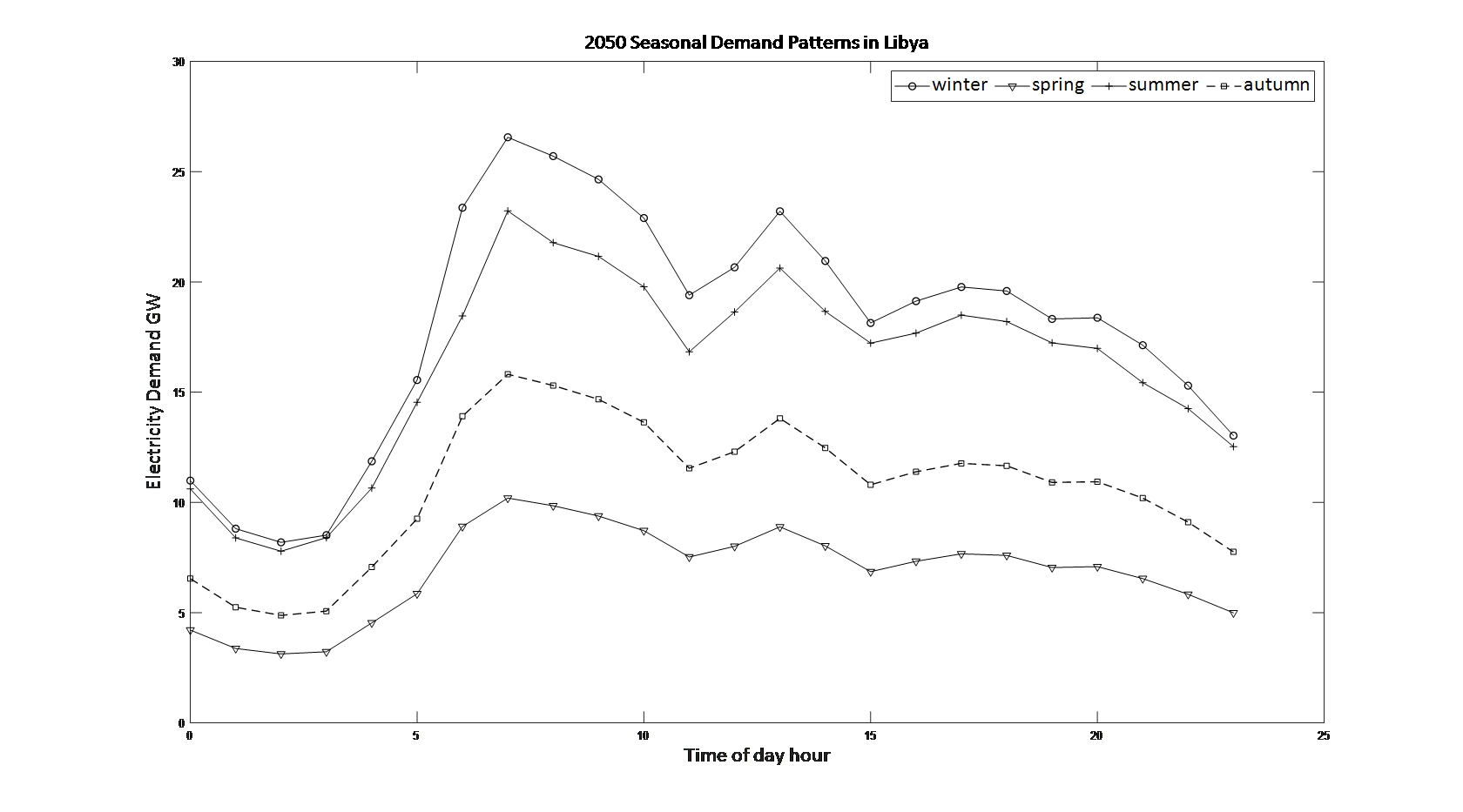
Holistic decarbonisation requires collaborative efforts and substantial investments across diverse economic sectors. This study introduces an innovative national approach, blending technological insights and philosophical considerations to shape decarbonization policies and practices. Libya is the case study. The proposed framework involves submersible power stations with continuous-duty helium closed-cycle gas turbines to supply electricity demand and hydrogen. Extensive national data is analysed, incorporating factors such as sectoral consumption, sea temperature, and port locations. An analytical model is developed, providing a valuable foundation for realistic decarbonization scenarios. The model aims to maintain the benefits of current energy consumption, assuming a 2% growth rate, while assessing changes in a fully green economy. The results offer qualitative and quantitative insights on hydrogen use and an expected rise in electricity demand. Two scenarios are examined: self-sufficiency and replacing oil exports with hydrogen exports. This study provides a quantitative perspective on decarbonization, focusing on a submersible helium closed cycle gas turbine concept resistant to natural disasters and proliferation. Findings underscore the substantial changes and investments needed for this transition, identifying primary needs of 27 GW or 129 GW for self-sufficiency and exports, respectively. This foundational analysis marks the start of research, investment, and political agendas toward decarbonization.
Article
20 February 2024Wind Influence on the Electrical Energy Production of Solar Plants
Solar energy, as a clean source of energy, plays a relevant role in this much desired (r)evolution. When talking about photovoltaics, despite the multiple studies on parameters that affect the panels operation, concrete knowledge on this matter is still in an incipient stage and precise data remains dispersed, given the mutability of outer factors beyond technology-related properties, hence the difficulties associated with exploration. Wind is one of them. Wind loads can affect the temperature of photovoltaics, whose efficiency is reduced when higher temperatures are reached. The viability of wind as natural cooling mechanism for solar plants and its influence on their electrical energy production is studied in this research work. Some appropriate results were achieved: depending on the module temperature prediction model used and on the photovoltaic technology in question, solar panels are foreseen to be up to approximately 3% more productive for average wind speeds and up to almost 7% more productive for higher speeds. Taking into consideration that wind speed values were collected in the close vicinity of the modules, these results can be proven to be even higher. That being said, this article contributes with accurate insights about wind influence on electrical energy production of solar plants.
Article
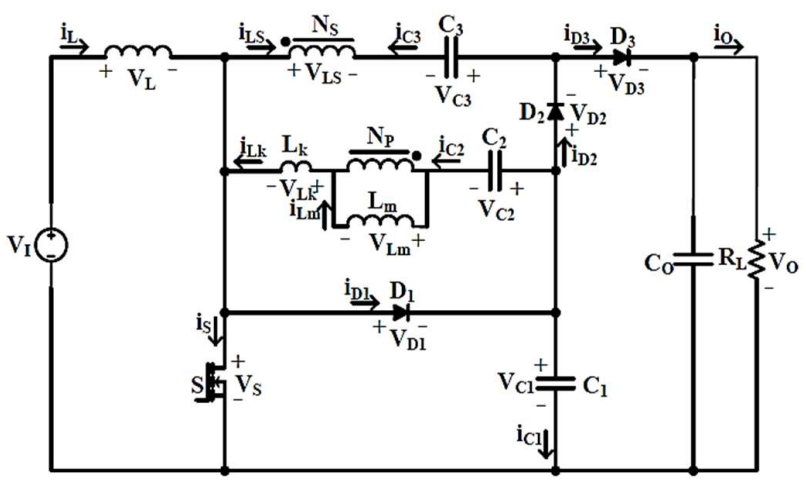
29 January 2024A Novel High Step-up DC-DC Converter Using State Space Modelling Technique for Battery Storage Applications
This paper focuses a novel non-isolated coupled inductor based DC-DC converter with excessive VG (voltage gain) is analyzed with a state-space modeling technique. It builds up of using three diodes, three capacitors, an inductor and CI (coupled inductor). The main switch S is turn on due to body diode and voltage stress is reduced at the switch S by using diode D1 and Capacitor C1. This paper focuses on design modelling, mathematical calculations and operation principle of DC-DC converter is discussed with state-space modelling technique. The performance has been presented for two different voltages for EV applications i.e., 12 V, 48 V as input voltages with an high step-up outputs of 66 V and 831.7 V respectively. The converter stability is studied and determined the bode plot along with simulation performance results which are carried out using MATLAB R2022B.
Article
29 January 2024The “Global Change Data Base” GCDB Facilitates a Transition to Clean Energy and Sustainability
This article presents the opportunities for constructing a global data base picturing underlying trends that drive global climate change. Energy-related CO2 emissions currently represent the key impact on climate change and thus become here the object of deep, long-term and historiographic analysis. In order to embrace all involved domains of technology, energy economy, fuel shares, economic efficacity, economic structure and population, a “Global Change Data Base” (GCDB) is suggested, based on earlier worldwide accepted data repositories. Such a GCDB works through regressions and statistical analysis of time series of data (on extensive magnitudes such as energy demand, population or Gross Domestic Product, GDP) as well as generation of derived data such as quotients of the former, yielding intensive magnitudes that describe systems and their structural properties. Moreover, the GCDB sets out to compute the first and second time derivatives of said magnitudes (and their percentual shares) which indicate new long-term developments already at very early phases. The invitation to participate in this foresight endeavour is extended to all readers. First preliminary GCDB results quantitatively portray the evolutionary structural global dynamics of economic growth, sectoral economic shifts, the shifts within energy carriers in various economic sectors, the ongoing improvements of energy intensity and energy efficiency in many economic sectors, and the structural changes within agricultural production and consumption systems.

Article
23 January 2024Analysis of a σ54 Transcription Factor L420P Mutation in Context of Increased Organic Nitrogen Tolerance of Photofermentative Hydrogen Production in Cereibacter sphaeroides Strain 2.4.1 Substrain H2
Photofermentative hydrogen production with non-sulfur purple bacteria like Cereibacter sphaeroides (formerly Rhodobacter sphaeroides) is a promising and sustainable process to convert organic waste into the energy carrier hydrogen gas. However, this conversion is inhibited by elevated organic nitrogen concentrations in the substrate, which limits its applicability to nitrogen-poor organic waste. We present genomic and transcriptomic insights into a substrain of Cereibacter sphaeroides strain 2.4.1 that shows unexpected high levels of photofermentative hydrogen evolution when fed with glutamate. Genome sequencing revealed 222 single nucleotide variances (SNVs) between the reference genome of C. sphaeroides strain 2.4.1 and the analyzed substrain H2. These affect 61 protein coding genes. A leucine-proline exchange is present in the σ54 factor (rpoN2 gene), a global hydrogen and nitrogen metabolism regulator. We propose a model how this mutation alters DNA-binding properties that explain the unexpected organic nitrogen tolerance of hydrogen production. Transcriptomic analyses under varying glutamate concentrations support this finding. Thus, we present the first thorough genomic and transcriptomic analysis of a Cereibacter strain that shows promising metabolic characteristics for biotechnological hydrogen gas production from organic waste. These results suggest a potential target for strain optimization. Possibly, our key finding can be transferred to other hydrogen producing microorganisms.
Article
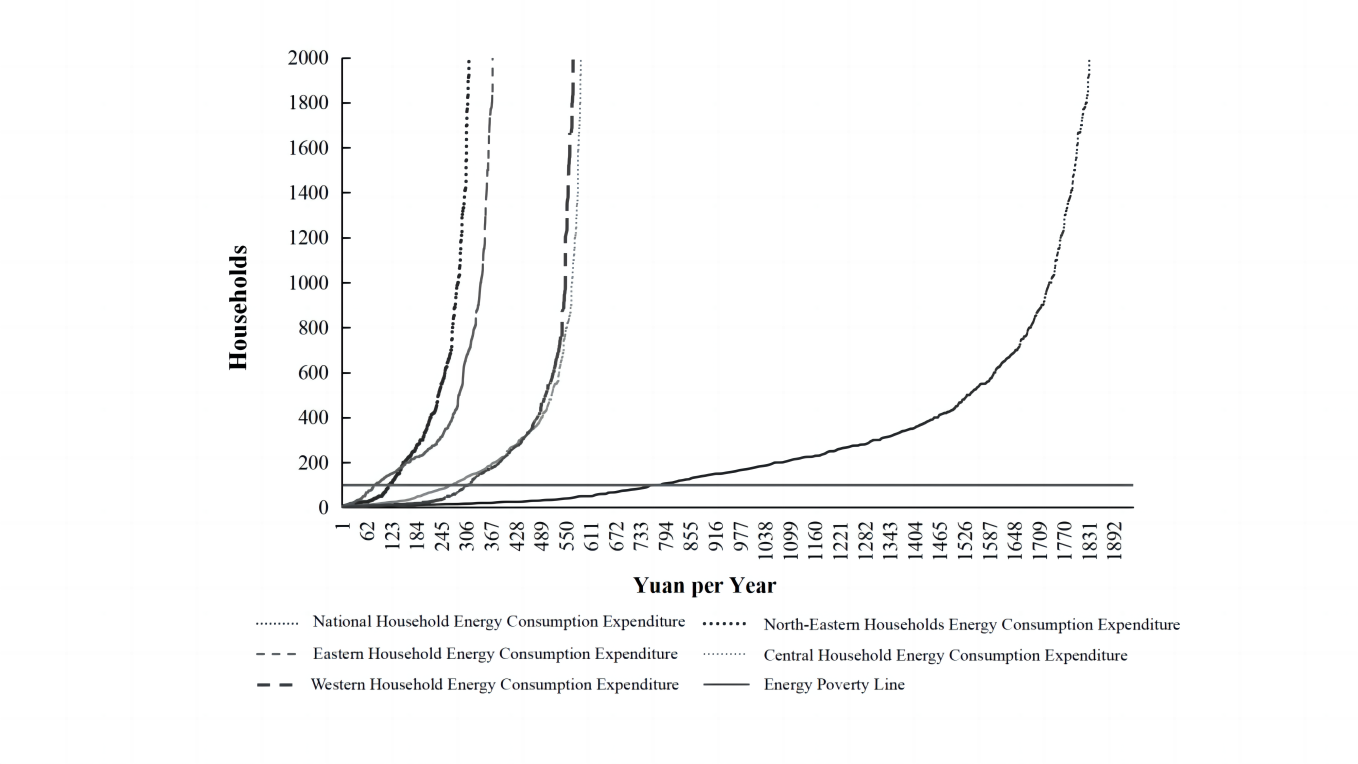
18 December 2023Measurement of Energy Poverty and Influencing Factors of Rural Households in China
Despite being the world’s largest developing country, China faces significant disparities between urban and rural areas, which exacerbates energy poverty in rural regions. This issue of energy poverty is a global concern, as millions of people lack access to modern energy necessary for a decent quality of life. This research aims to analyze the levels and structures of energy consumption in rural Chinese households, using data from the Chinese General Social Survey (CGSS) conducted in 2015 and 2018. The research employs the poverty line threshold and Theil index methods to comprehensively assess energy poverty in diverse regions. It also examines the economic, social, and familial factors influencing rural energy poverty. The findings reveal a transition in rural energy consumption towards cleaner sources, but energy poverty remains a significant issue. Factors such as energy prices and household size have a positive impact on energy poverty, while per capita income, education level, and social factors exert a negative influence.