Found 26 results
Open Access
Article
28 February 2026Unveiling the Dynamics: How Does the Digital Economy Influence the Development of New-Type Urbanization in China
Digital economy is a vital driving engine for new-type urbanization and continues to promote the regional economy. In this study, it adopts the entropy weight method is adopted to measure the digital economy and new-type urbanization in 31 provinces in China from 2011 to 2021, and conducts an in-depth analysis on the relationship between them. The conclusions are: Digital economy has a significant role in promoting new-type urbanization and is regionally heterogeneous, especially the impact in eastern region; Moreover, through the mediating mechanisms analysis, it indicates that industrial structure and innovation level are important paths to promote new-type urbanization. Along with the increase of R&D intensity, the promotion effect shows a non-linear characteristic of “increasing marginal effect”. In light of this, the following countermeasures are put forward to strengthen digital economy’s impetus for new-type urbanization: promote the gradient development of digital technologies and innovate digital economy application scenarios to fuel new-type urbanization; establish a novel digital-industrial integration model and capitalize on the fundamental role of industrial transformation in new-type urbanization; and refine the innovation system and fully realize the marginal incremental effect of R&D intensity once it crosses the threshold.

Open Access
Article
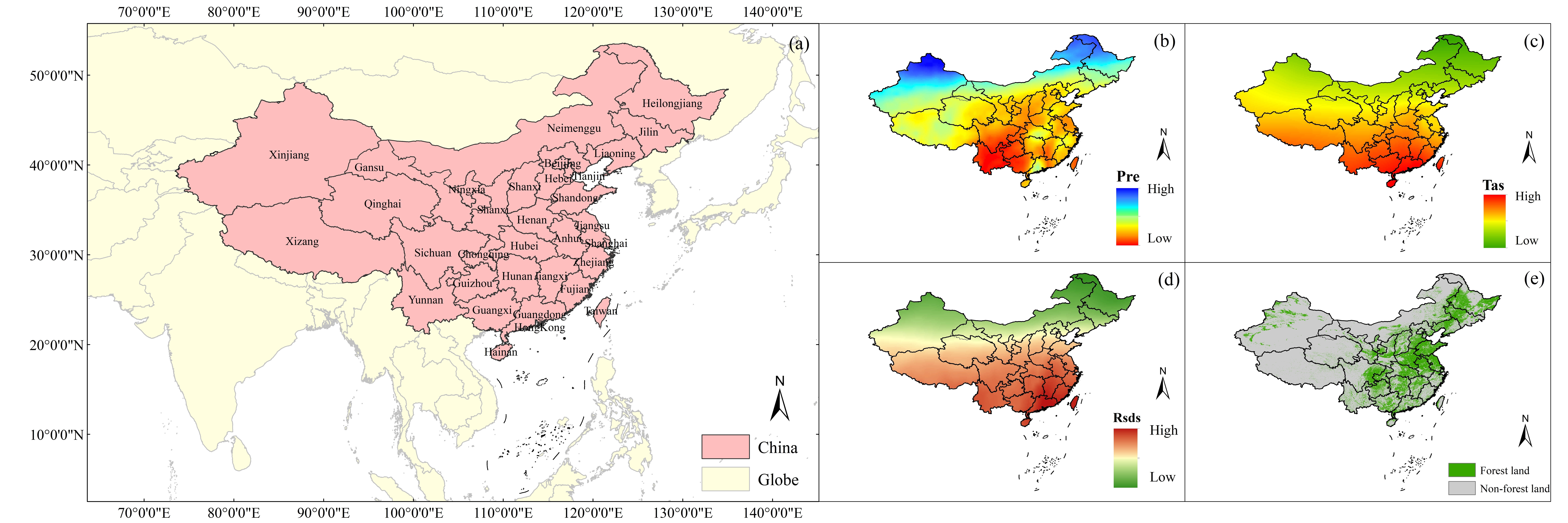
30 January 2026Forecasting Forest Product Yields in China Based on a Random Forest Model: Interaction Between Climate Change and Socio-Economic Factors
This study presents a comprehensive projection of China’s forest product yield dynamics (encompassing commodity timber and logs) through 2100, employing an innovative integration of machine learning and economic modeling. We developed a hybrid analytical framework combining random forest algorithms with Cobb-Douglas production functions to assess multi-dimensional drivers, including climatic variables, socio-economic indicators, and demographic trends. Our multi-model validation demonstrated strong predictive performance (R2 are 0.86 and 0.92), particularly in quantifying climate-production interactions, with sensitivity analysis identifying surface downward shortwave radiation (RSDS), population density (POP), and mean annual temperature (MAT) as dominant predictors explaining 68% of yield variance. Future yields exhibited significant spatial and temporal variations under different SSP scenarios, especially under SSP126, where yields were more stable, and under SSP245 and SSP370, where yields showed a moderate increasing trend. The SSP585 shows higher fluctuations and a decreasing trend in yields due to climate change. Geospatial modeling uncovered critical regional disparities, suggesting potential production migration from traditional southern bases to north-eastern/northwestern frontiers under climate stress. The southern subtropical belt emerged as particularly vulnerable to thermal extremes and precipitation variability, while northern regions demonstrated greater climate resilience but require substantial silvicultural adaptation. These results provide a scientific basis for developing more precise forest management policies and sustainable development strategies to help meet the challenges posed by future demand for forest products and climate change.
Open Access
Article
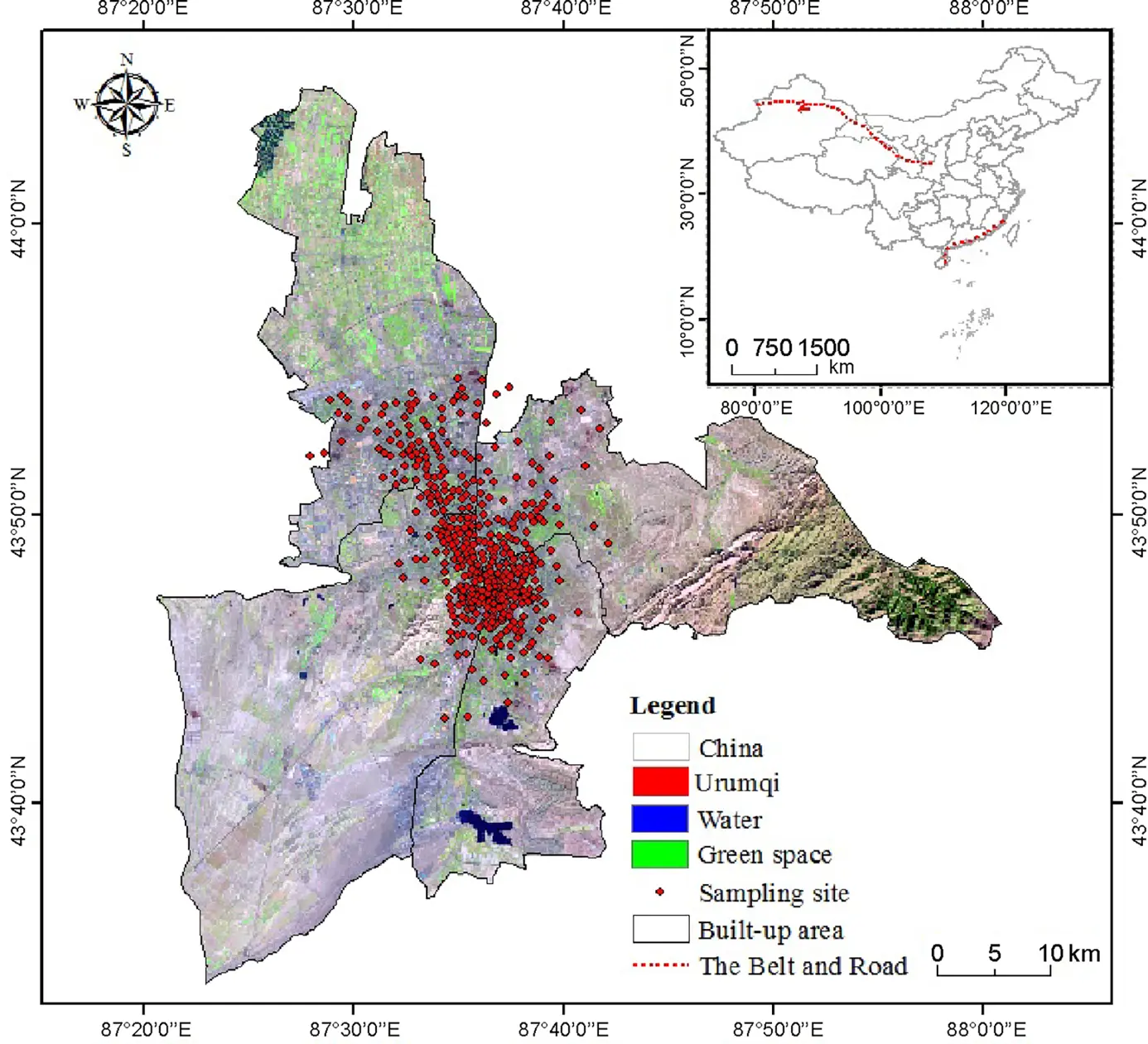
08 December 2025Public Participation in Ecological Civilization Construction in Urumqi: A Case Study of a Rapidly Expanding Arid Metropolis in Northwestern China
Public participation in ecological civilization construction is a critical pathway for advancing ecological urban design. This study examines residents’ perceptions, satisfaction, and participation in the construction of ecological civilization in Urumqi, northwestern China. Drawing on 1012 questionnaires, this empirical study investigates factors influencing public participation in the construction of ecological civilization. The findings indicate that residents exhibited a strong subjective awareness of public participation in ecological civilization construction (mean score = 4.66), yet ecological cognition (2.75) and participation confidence (2.97) were relatively weak and require further improvement. Satisfaction levels were relatively higher for green status (2.51) and information transparency (2.41), whereas overall satisfaction remained modest, with water resources (1.81) and waste management (1.99) emerging as key concerns. Residents demonstrated a moderate willingness to contribute financially and primarily engaged in low-cost, habitual ecological practices. Significant differences were observed across socio-demographic variables (p < 0.05). Uncivil behaviors and natural pressures were observed as visible obstacles. Strong government leadership, active public engagement, and effective media communication contribute to advancing ecological civilization construction. These results provide valuable insights for promoting ecological civilization construction in northwestern China.
Open Access
Article
25 November 2025Self-Determination of Adolescents with Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities in China: Evidence from Students and Teachers
Self-determination is closely associated with individuals’ autonomy and independence and is crucial for people with intellectual and developmental disabilities. This study investigated the self-determination of adolescents with intellectual and developmental disabilities in China. Using the AIR Self-Determination Scale, data were collected from 116 students and 29 corresponding special education teachers. Findings indicated that the adolescent with intellectual and developmental disabilities had a moderate level of self-determination. However, teachers consistently rated students’ self-determination lower than students’ self-rating. Students’ self-evaluations of their self-determination were significantly influenced by geographic location, age, and disability severity, and teacher evaluations were affected by students’ age and disability severity, as well as teachers’ teaching experience and subject area. The study revealed that teachers face notable challenges in their conceptual understanding and pedagogical implementation of self-determination instruction. Based on these findings, recommendations are proposed across four domains: parents, teachers, schools, and broader society.

Open Access
Article
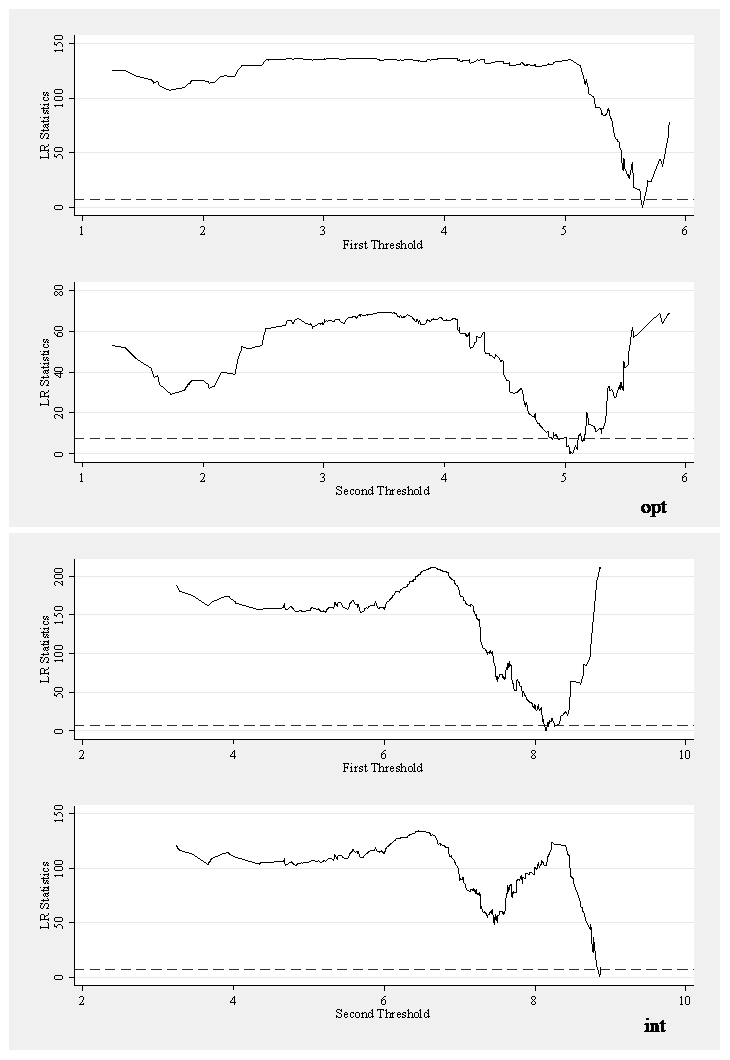
25 November 2025The Impact of Digital Infrastructure on Economic Resilience: Evidence from the Four Major Regions of China
Amid accelerating global structural changes and China’s transition to the digital-driven fourth industrial revolution, this paper examines the impact of digital infrastructure on economic resilience by clustering China’s 31 provinces into the four major economic regions during 2008–2022. Through the application of the Threshold Regression Model, Mediation Effect Model, and GTWR Model, the analysis reveals that digital infrastructure exhibits a threshold effect in enhancing economic resilience, with significant increasing marginal returns beyond specific scale thresholds. Regional heterogeneity is pronounced: the eastern region demonstrates amplified nonlinear benefits, while the northeast exhibits diminishing returns after crossing the threshold. Industrial diversification is an effective way for digital infrastructure to build resilience. The effects of industrial specialization, however, vary by region: it strengthens resilience in the east, weakens it in the central region, and shows no statistically significant impact in the western and northeastern regions. The findings provide empirical evidence for regionalized policymaking during technological paradigm shifts, highlighting the need to consider both digital infrastructure scale thresholds and industrial structure dynamics in economic resilience strategies.
Open Access
Article
24 November 2025Bridging the Urban-Rural Divide: How Urban Agriculture Enhances Food Security in High-Urbanized Regions in Guangdong, China
The COVID-19 pandemic starkly exposed vulnerabilities in global food supply chains, highlighting the critical need for resilient, localized alternatives to ensure urban food security. Urban agriculture (UA), which we define as all agricultural output occurring in cities with an urbanization rate exceeding 85%, emerges as a pivotal strategy to mitigate such risks by shortening supply chains, particularly for perishable goods like vegetables and fruits. This study investigates the underexplored role of UA in Guangdong Province, China—a region characterized by rapid urbanization, high population density, and economic dynamism- to assess its contribution to food self-sufficiency. Leveraging a novel classification framework, we categorize Guangdong’s 21 prefecture-level cities into two groups based on an 85% urbanization threshold (2017–2022), distinguishing high-degree urbanized cities (e.g., Shenzhen, Guangzhou) from others. Using panel data, we analyze spatial-temporal patterns in grain, vegetable, and fruit self-sufficiency through geospatial and statistical methods. Key findings reveal pronounced disparities: high-degree urbanized cities exhibit critically low grain self-sufficiency, relying heavily on external supplies, while non-urbanized regions achieve exceptional surpluses. Conversely, vegetables and fruits demonstrate a center-periphery gradient, with peri-urban zones bridging the gap between urban cores and rural surplus hubs. Despite incremental gains in UA productivity, urban yields lag behind non-urban areas for grains and vegetables, though fruit production shows convergence, underscoring UA’s niche potential. These results highlight the indispensability of non-urban regions in sustaining provincial food security while emphasizing UA’s role in fresher, faster urban supply chains. We propose actionable policies, including: (1) integrating farmland protection redlines with UA incentives (e.g., vertical farming subsidies, peri-urban logistics optimization); (2) scaling technology-driven UA (controlled-environment agriculture, digital platforms); and (3) reducing post-harvest losses through urban-centric infrastructure. Our findings advance the discourse on crisis-resilient food systems, offering a replicable framework for high-density regions globally.
Open Access
Article
17 November 2025The Reconstruction of China’s Land-Based Marine Pollution Governance under the Concept of “Rights of Nature”
Under the concept of “Rights of Nature”, the governance of land-based marine pollution in China faces unprecedented opportunities and challenges. Traditional governance paradigms are predominantly anthropocentric, treating the ocean as a resource to be utilized. From this perspective, governance measures for the prevention and control of land-based marine pollution primarily rely on administrative management and end-of-pipe treatments. Within this context, “Rights of Nature” provide a new pathway for marine ecological protection. However, promoting a shift in land-based marine pollution governance from the traditional anthropocentric view to an eco-centrism under the “Rights of Nature” concept is by no means an instantaneous process, and it must proceed gradually and systematically. Currently, China’s institutional framework for preventing and controlling land-based marine pollution remains dominated by the anthropocentric paradigm. Furthermore, it encounters multiple difficulties across many key areas, including the legal system, law enforcement mechanisms, relief mechanisms, and public participation. Issues such as poor coordination within the legal framework, fragmented law enforcement, lagging legislation related to ecological restoration, and insufficient public participation significantly constrain the effectiveness of land-based marine pollution governance. Given the fundamental differences between anthropocentrism and “Rights of Nature”, directly introducing this concept would likely have a substantial impact on China’s existing legal framework. Therefore, at the current stage, China could first incorporate the proposition from the “Rights of Nature” concept that nature possesses “intrinsic value independent of human use or perception”. This involves weakening the perception of the ocean as a mere appendage to human activities, recognizing and respecting the unique value of the ocean as a living entity and ecosystem at a conceptual level, and gradually forming a set of nature-friendly governance paradigms for land-based marine pollution that respect the intrinsic value of nature. This approach can ultimately drive transformative practices in China’s land-based marine pollution governance.

Open Access
Article
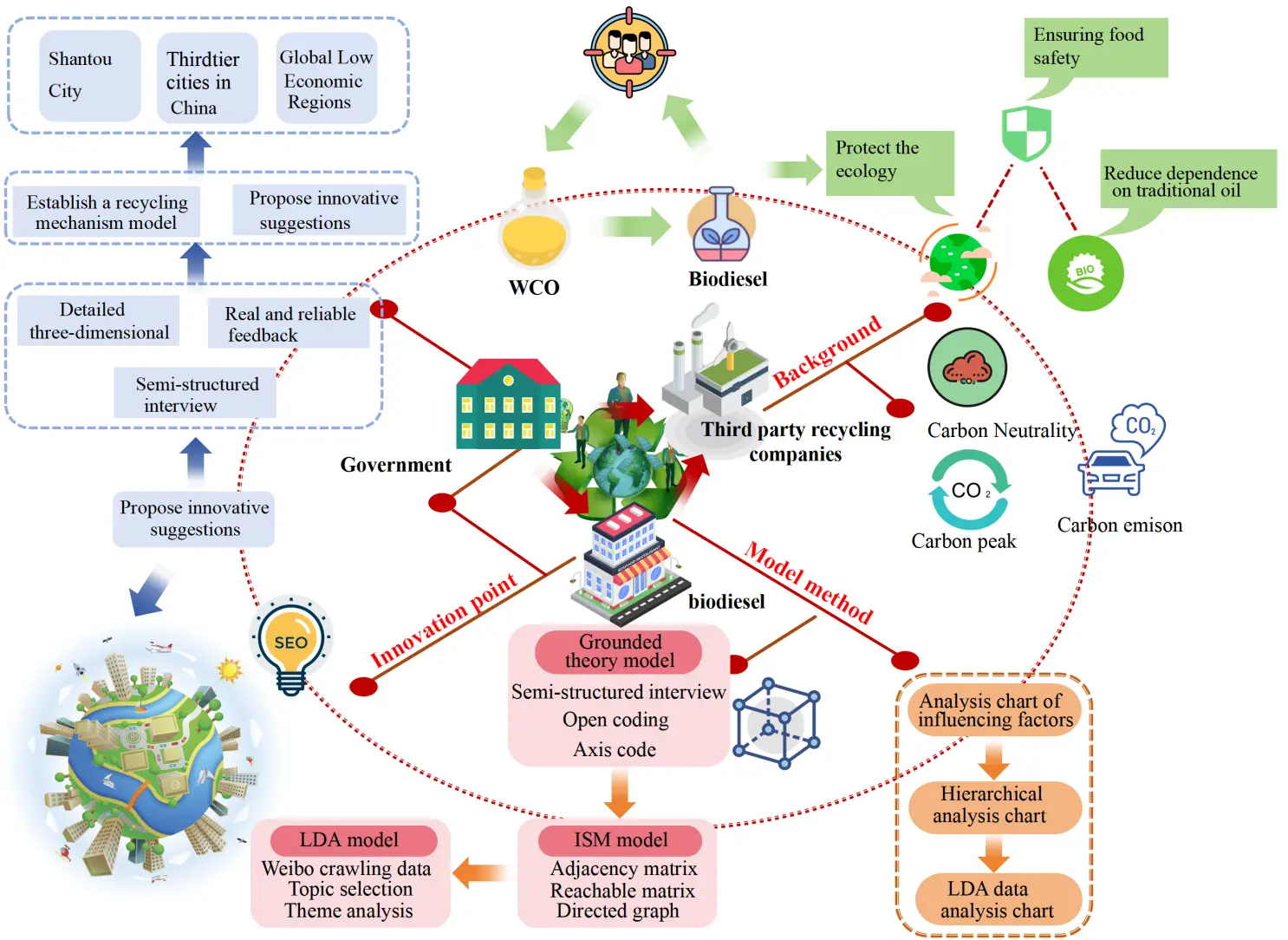
06 November 2025Sustainable Recycling Mechanisms for Waste Cooking Oil in China’s Third-Tier Cities: Evidence from Restaurant Practices
The conversion of waste cooking oil (WCO) into biodiesel is a key strategy for advancing energy sustainability, particularly within China’s rapidly expanding restaurant industry. In third-tier cities such as Shantou, Guangdong Province, WCO collection faces unique challenges. Through in-depth interviews with 20 restaurant operators, this study identifies multiple barriers to effective WCO management, including an aging population, underdeveloped local economies, limited technological infrastructure, and unequal access to educational opportunities, all of which hinder the adoption of advanced filtration systems and broader environmental sustainability initiatives. Moreover, the non-standardized operations of third-party WCO collection services, coupled with space constraints in small restaurant kitchens, further exacerbate inefficiencies in recovery processes. To address these challenges, this study develops a comprehensive framework for WCO collection that is adaptable to regions with similar socio-economic conditions. Integrating grounded theory, Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM), and Latent Dirichlet Allocation, the framework fills critical gaps in existing research. The analysis reveals that government financial incentives occupy the foundational layer of the ISM hierarchy and serve as a key driver of recycling behavior among restaurant operators; educational attainment enhances awareness and compliance but is moderated by structural constraints; and trust in third-party recyclers exerts a relatively limited influence. Correspondingly, H1 receives qualitative support, H2 is partially supported, and H3 gains only limited support. Building on these findings, the study proposes a multi-stakeholder governance framework that includes a “community-school-family” education system, an intelligent third-party management platform, and a government-led industrial chain to promote the formation of a closed-loop circular economy. The results demonstrate that the proposed framework not only offers actionable policy recommendations but also facilitates the adoption of sustainable practices and deepens the understanding of socio-economic and operational factors affecting WCO management, thereby providing strong support for energy and environmental sustainability.
Open Access
Article
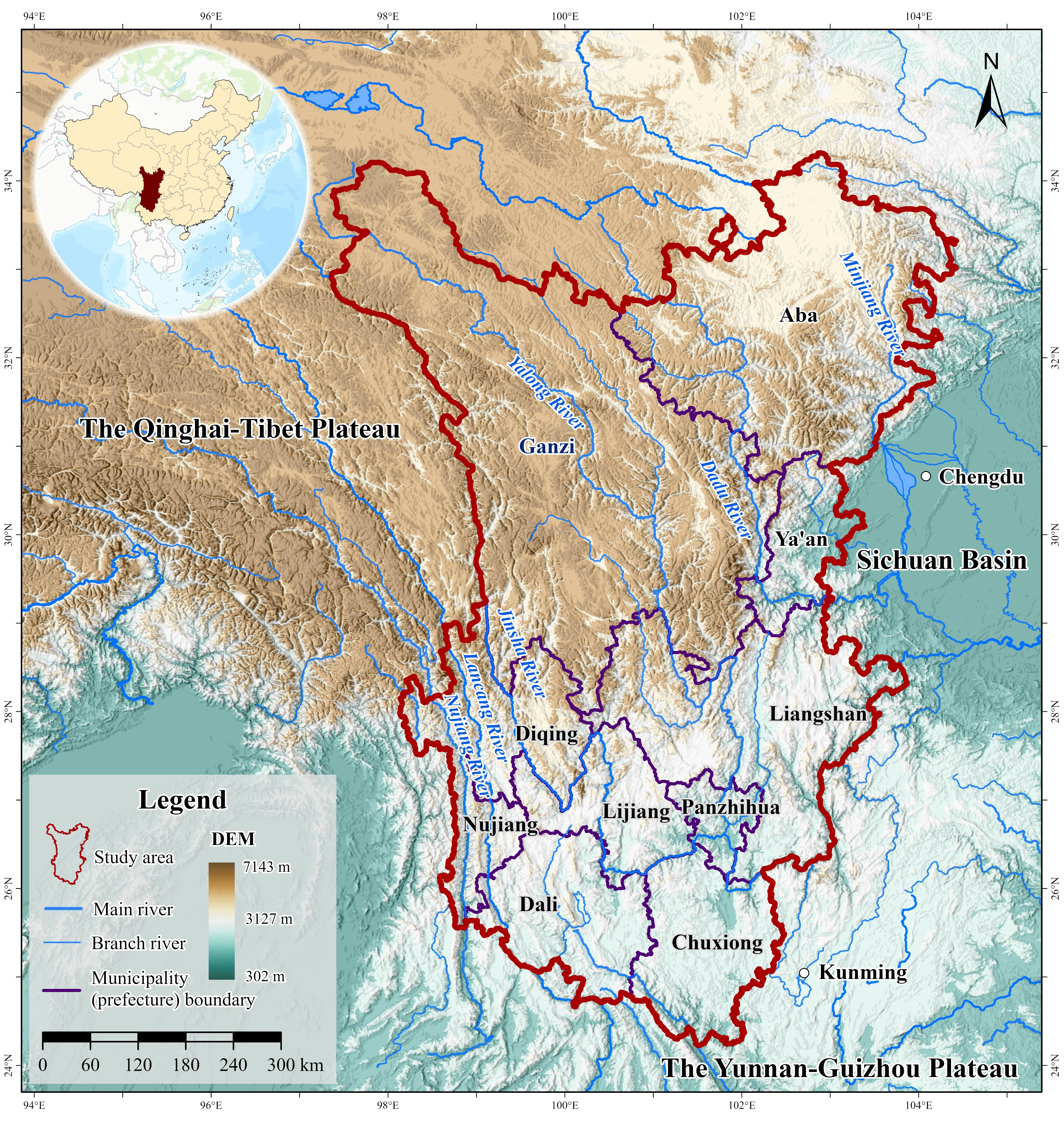
29 October 2025Solutions of Minimized Agrochemicals Input in the Post Zero-Growth Era: A State-of-the-Art Analysis of the Hengduan Mountains, China
How to further reduce the input of agrochemicals after zero-growth is an important challenge faced by mountainous areas. Up to now, the combined solution for minimized agrochemicals intervention in the post zero-growth era has not been systematically analyzed globally. Here, the Hengduan Mountain regions (HMR) in China, as a case, we estimated the turning points of agrochemicals input intensities using a quadratic equation, as well as integrating policy document analysis and literature review. Results show that the occurred timeline of fertilizer and pesticide use zero-growth in 10 municipalities (prefectures) in the HMR is relatively wide, with a distribution from 2009 to 2019, illustrating that all municipalities (prefectures) have been achieved national goals ahead of 2020 deadline. Thus, the incentive of a series of national-level policies focusing on chemical fertilizers and pesticides has proven effective in achieving the zero-growth target of agrochemicals input in the HMR. However, comparison with major mountainous countries like Germany, Italy, Portugal, Romania, Austria, and Spain etc., there are clearly many opportunities for enhancement in reducing fertilizer and pesticide uses. We present a practical route to minimize agrochemicals application in the HMR through crop rotation-based agro-biodiversity solutions, organic alternative-based soil health solutions, professionalization-based precision farming solutions, smallholder farmers’ awareness-based behavior intervention solutions, conservation reserve-based zoning solutions, etc.
Open Access
Article
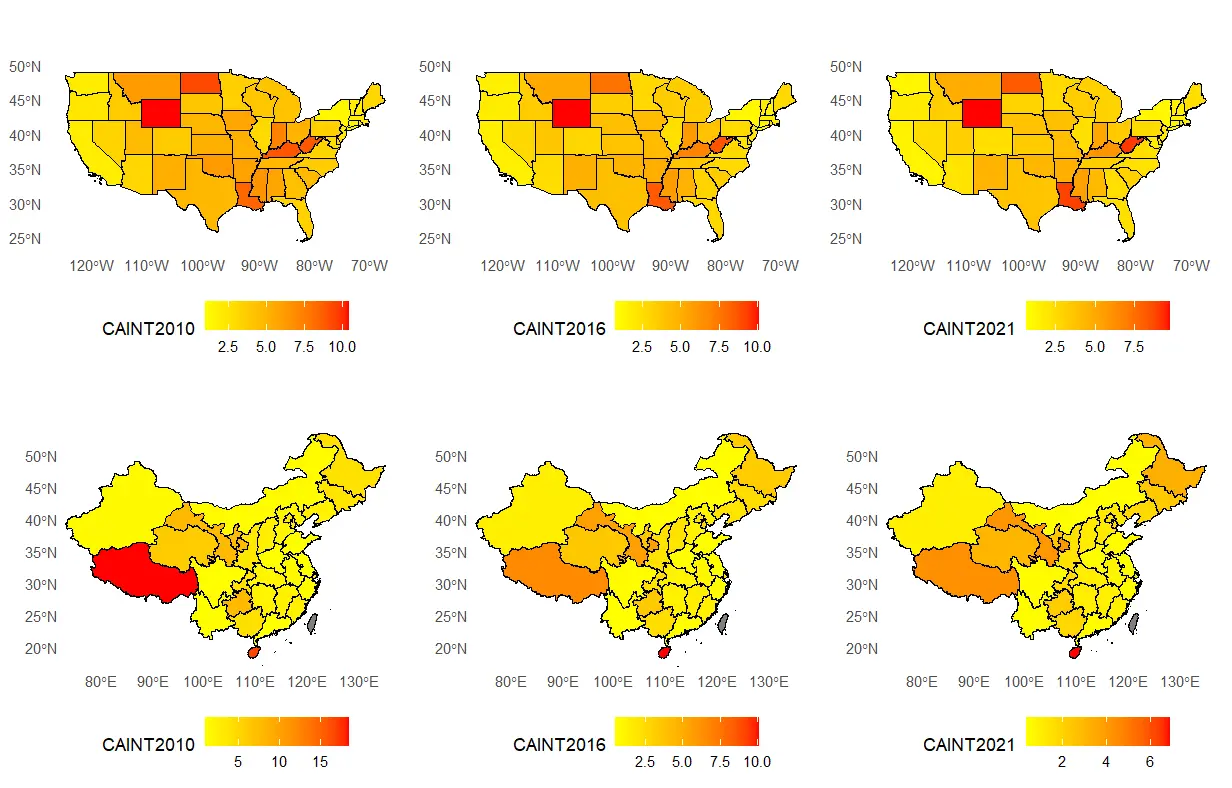
17 October 2025Bioenergy Technology and Carbon Intensity in U.S. and China: Threshold Roles of Capital Accumulation, Education and Inequality
Bioenergy technology holds significant promise for reducing carbon intensity and fostering sustainable development, yet its impact remains unclear. This article employs both a panel threshold model and a random forest model, analyzing data from the primary administrative regions in the United States and China to explore the threshold effects and regional heterogeneity of bioenergy technology on carbon intensity, where the bioenergy technology is measured using patent data. In the United States, the impact of bioenergy technology on carbon intensity initially shows a positive effect, which later turns negative as per capita capital stock increases. The technology’s inhibitory effect strengthens with higher levels of education but becomes insignificant as the Gini coefficient rises. In China, increasing per capita capital stock shifts the impact of bioenergy technology from negative to insignificant, while higher education levels enhance its inhibitory effect. The Gini coefficient, however, does not significantly affect the impact of technology. Additionally, these threshold effects exhibit notable regional variations. The study provides cross-country evidence of how institutional and structural conditions shape the carbon mitigation effects of bioenergy technology, offering practical insights for policies that combine trade facilitation, education, and inequality reduction with low-carbon energy transitions.